Bio 30 Nervous System
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
What is the nervous system?
elaborate system that:
receives sensory input
processes, integrates and stores info
triggers response
Homeostasis
The tendency of the body to maintain stable internal conditions at an equilibrium
Ex. body temp, blood pH, blood pressure
Neuron
functional unit of the nervous system
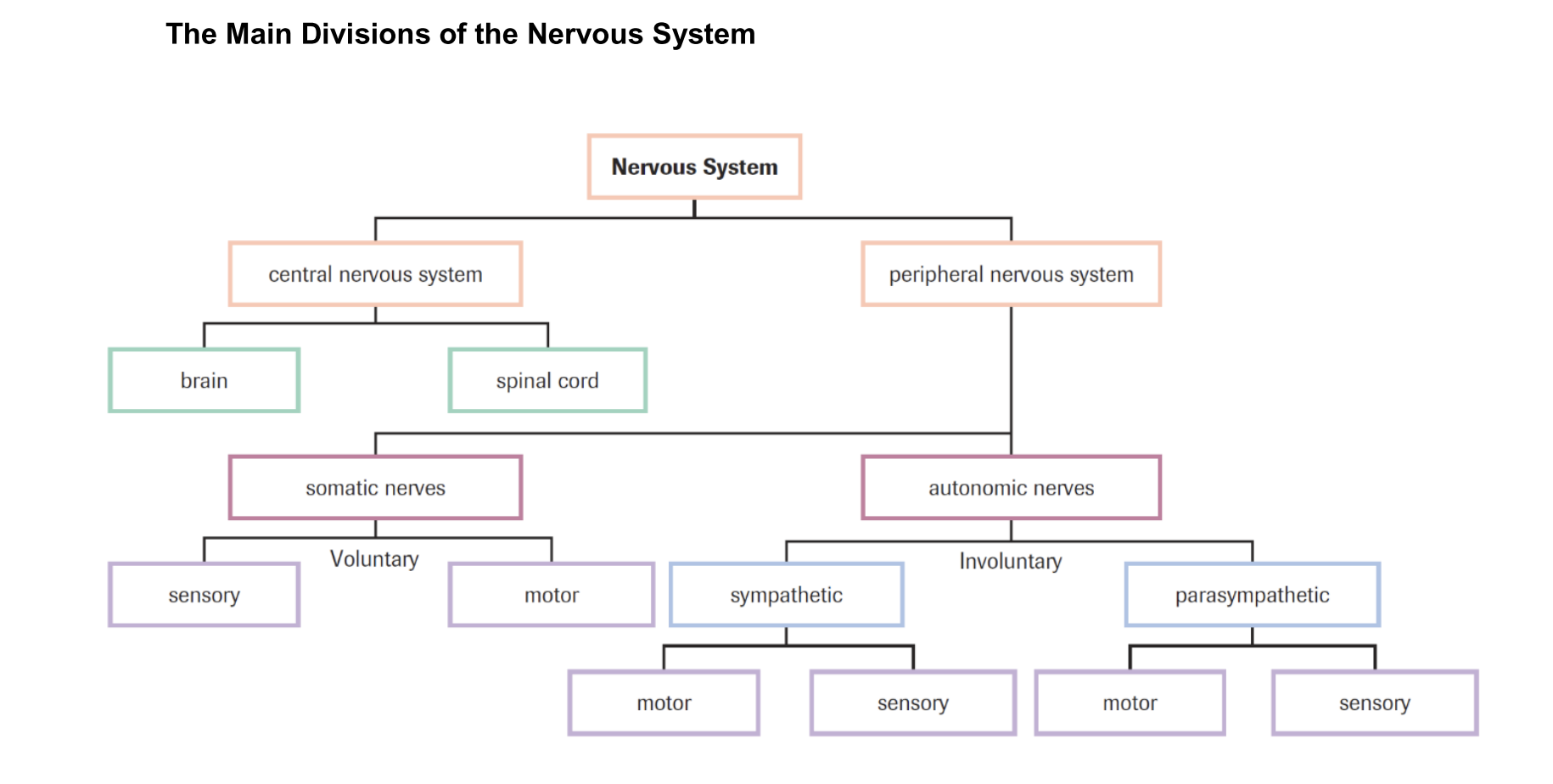
What are the 2 subdivisions of the nervous system?
CNS, PNS
CNS (Central nervous sytem)
composed of brain and spinal cord
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
composed of numerous nerves that extend from spinal cord
Somatic Nerves
Voluntary
bring sensory info to CNS about external environment
Autonomic nerves
involuntary
bring sensory info to CNS about internal environment
What is the autonomatic nervous system divided into?
Sympathetic: responds to stresses
Parasympathetic: regular functions like digestion, opposite of Symp bc/ bring body back to normal
Summarize the Nervous System
What 3 layer protective membrane surrounds the Brain
meninges
order from farthest to closest of meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
cerebrospinal fluid
circulates between innermost and middle meninges
acts as shock absorber
can be extracted via lumbar puncture
Function of the brain
control centre
receives, processes, integrates, and stores info
higher cognitive functions
regulates involuntary and voluntary functions
3 main sections of the brain
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
parts of the forebrain
Cerebrum, cerebral cortex, olfactory bulbs, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary
4 lobes of cerebrum and function
frontal: judgment behaviour and impulse control, decision making, complex motor movements
temporal: auditory processing
parietal: sensory processing of touch, taste
occipital: visual processing
cerebral cortex
surface of cerebrum
sulci
grooves of cerebral cortex
geri
bumps of cerebral cortex
motor homunculus
diagrammatic representation of body part size as proportional to area of cortex controlling it
Right hemisphere
visual patterns and spatial awareness
Left Hemisphere
verbal skills and analytical thought
Corpus Callosum
bundle of nerves that serve as connection between 2 hemispheres
thalamus
conducts sensory info to appropriate lobe
hypothalamus
plays role in regulating internal equilibrium
olfactory lobes
receives and interpret info about smell
Midbrain
Tectum
Tegmentum
Relays sensory signals to appropriate lobes
Hindbrain
includes cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata
cerebellum
regulates balance, posture and coordination
limb movements, balance, and muscle tone
pons
bridge for cerebellum and medulla oblongata
medulla oblongata
connected to spinal cord
mian region for autonomic nerve control
controls involuntary vital functions required for homeostasis
Spinal cord
conducts sensory nerve messages to brain and carries motor messages to rest of body
foramen magnum
hole at base of skull where spinal cord meets brain
vertebrae
bone that protects spinal cord
where is grey and white matter in spinal cord and brain
spinal cord: grey surrounded by white
brain: white surrounded by grey
2 types of cells in nervous system
glial cells: non - conductive; supportive cells
Neurons: conductive transmit impulses and secrete neurotransmitters; carry out nervous response
parts of the neuron
dendrites, cell bodies, axons, axon terminal
Dendrites
branches extend from cell body
receive info from env or other neuron
cell body
part of neuron that looks like typical cell; contains nucleus and other important organelles
axon
long part of neuron
electrical impulses travel down axon
axon terminal
transmit info to either effector organ or another neuron
nerves
bundle of axons surrounded by connective tissue
ganglia
cluster of neuron cell-bodies
3 types of neurons
sensory - afferent
motor - efferent
interneuron - association neurons
Sensory neurons
relay info about internal/external environment received by sensory receptors to CNS
Interneurons
link between sensory and motor neuron; only in CNS
Motor Neurons
carries nervous impulse from nervous system to effector
effector
cells/tissues/organs that produce a physiological response when stimulated
SAME - DAVE
(sensory - afferent, motor - efferent; dorsal - afferent, ventral - efferent)
Reflex
involuntary response to a stimulus
Reflex arc
neural circuit through spinal cord that bypasses Bain to produce reflexive response to stimuli
nerve pathway of reflex arc
stimulus —> sensory neuron —> interneuron —> motor neuron —> effector
Examples of reflexive responses
achilles tendon reflex, patellar reflex, pupillary reflex
electrochemical
conduction of charges via movement of charged chemical substances (ions)
nerve impulses are electrochemical messages
membrane potential
difference of charge across a cell membrane (exterior and interior axon)
resting membrane potential
difference in charges across cell membrane when neuron is at rest (-70mV)
How do ions cells travel in and out of the membrane
facilitated diffusion through ligand gated channels
How does K+ diffuse
tendency to diffuse out of cell
How does Na+ diffuse
tendency to diffuse into cell
compare diffusion of K+ and Na+ at rest
more K+ diffuse out of cell than Na+ diffuse into cell
relative polarity of outside and inside of cell at rest
outside is positive and inside is negative
What is an Action Potential
nerve impulse
occurs when a neuron recieves a stimulus
What happens to membrane and polarity when a neuron receives a stimulus
cause gated Na+ channels to open and K+to close —> influx of Na+ into cell —> accumulation of positive charge inside cell membrane relative to outside
Depolorization
charge reversal of membrane
What happens when overall membrane potential is positive
happen at +40mV
Na+ channels shut
k+ channels open —> restore membrane potential back to resting state
Repolarization
process of restoring membrane potential to resting state
What is hyperpolarization and why does it happen
state of excess interior negative charge
during depolarization K+ channels have delay in closing causing overshoot of K+ out of cell —> causes interior of cell membrane to become excessively negatively charged in comparison to resting membrane potential
How is hyperpolarization returned to resting membrane potential
sodium - potassium pump kicks in and pumping Na+ out of cell and K+ into cell
Refractory period
time taken for membrane potential to be restored after depolarization/repolarization
How does action potential move down neuron
from cell body to axon terminal
as one region of axon becomes depolarized, the region immediately before it begins to depolarize
in axons of myelinated neurons where are gated ion channels concentrated
Nodes of Ranvier
causes action potential to jump from node to node
Threshold level
level to which membrane potential must depolarize in order for action potential to occur
All or non response
nerve or tissue respond completely or not at all to stimulus
Synaptic Cleft
spaces between neurons or between neurons and effectors
presynaptic neuron
comes before synapse
postsynaptic neuron
comes after synapse
Where are neurotransmitters released from
vesicles
neurotransmitters
chemical messenger synthesized either locally in the axon terminal or in the cell body
Explain how neurotransmitters go form one neuron to another
vesicle combine with presynaptic end plate because both are phospholipids —> neurotransmitters released —> lock and key with receptors on postsynaptic neuron to induce electrochemical response by opening ion gated channels.
2 types of neurotransmitters
small molecule neurotransmitter: very small; sometime amino acid
Neuropeptides: larger protein complex made up of 3 or more amino acids
excitatory neurotransmitters
cause ligand gated sodium ion channel to open —> lead to membrane potential more positive —> leads to depolarization and production of an action potential down post synaptic neuron
inhibitory neurotransmitter
cause ligand-gated potassium ion channels to open —> leads to cell becoming hyperpolarized —>prevent production of an action potential down neuron
Acetylcholine
excitatory neurotransmitter; induces skeletal muscle contractions
What enzyme is used to break down acetylcholine
cholinesterase and broken down into acetate and choline
what is reuptake
process of acetate and choline taken back up the pre-synaptic vesicles
How is more acetylcholine created
choline stored and combined with acetyl CoA (from cell respiration) to produce more acetylcholine
chemoreceptors
detect chemical change
mechanoreceptors
detect things like stretch movement, blood pressure change
sensory neuron
supply nervous system with info about external environment and conditions of internal env
thermoreceptor
detect change in temp
epidermis
outermost layer of skin, makes contact with external env
sensory adaptation
occurs when a receptor becomes accustomed to the stimulus (habituation)
sclera
firm white outermost layer of eye
cornea
front bulging part of Sclera and bends light towards pupil
aqueous humour
fluid filled located in a chamber just behind the cornea
Choroid
very vascularized middle layer of eye
iris
circular coloured ring of muscle that controls pupil size
lens
transparent structure that focuses light on retina
ciliary muscles
controls the shape of the lens