NURS 3444. Exam 4 (NM and MS)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
The nurse is providing postoperative care for a 14-month-old girl who has undergone a myelomeningocele repair. The girl's mother is extremely anxious and tells the nurse she is afraid she will never learn how to care for her daughter at home. Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate?
a. “I will help you become comfortable in caring for your daughter.”
b. “You will need to learn to collaborate with all the caregivers.”
c. “You must learn how to care for your daughter at home.”
d. “There is a lot to learn, and you need a positive attitude.”
a. “I will help you become comfortable in caring for your daughter.”
The nurse is educating a group of caregivers about fractures seen in children. One of the caregivers states, “I have heard that if a bone breaks it can cause permanent damage and stop the growth of the bone.” This statement is accurate if the break occurs in the:
a. Joint
b. Humerus
c. epiphyseal plate
d. xiphoid process.
c. epiphyseal plate
A group of students is reviewing information about bone healing in children. The students demonstrate understanding of this information when they state:
a. a fracture closer to the growth plate heals much slower than one in the metaphysis
b. the process of breaking down and forming new bone is decreased in children compared with adults
c. a child's bones heal more quickly than those of an adult
d. callus production is slower (but greater in amount) in children than in adults.
c. a child's bones heal more quickly than those of an adult
When is skeletal maturity reached in males?
17 years
When is skeletal maturity reached in females?
2 years after menarch
Wolff's Law
A bone grows or remodels in response to forces or demands placed upon it
Genu varum
Bowleg
- normal until age 2
- due to underdevelopment
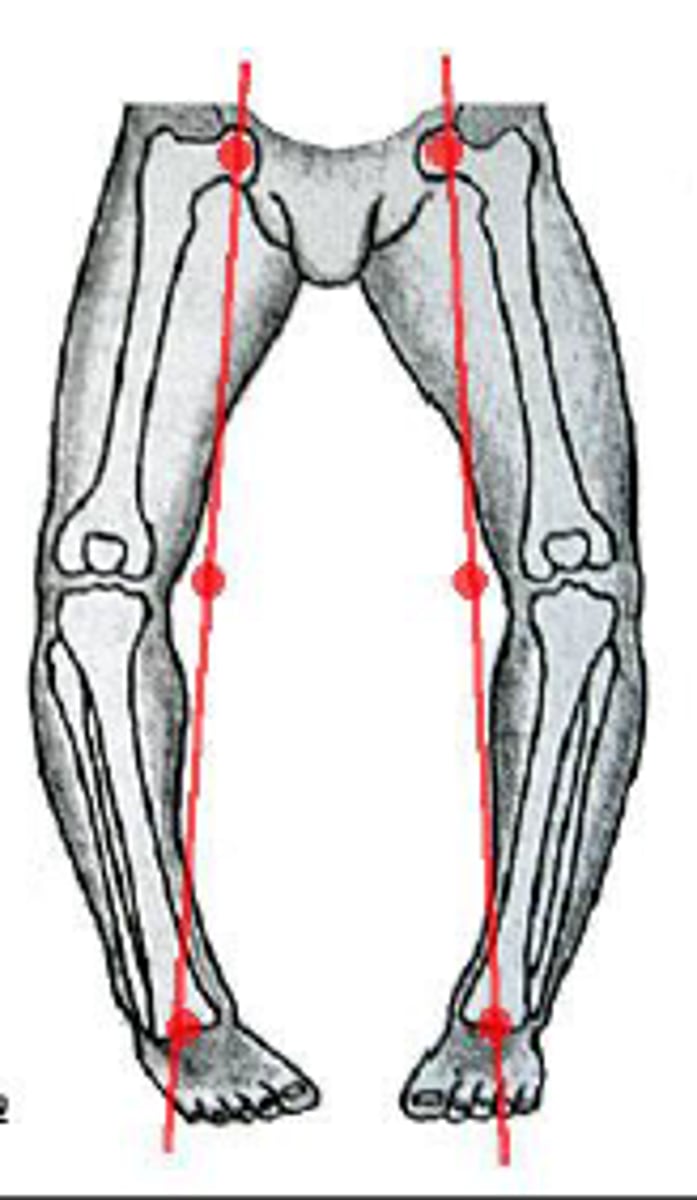
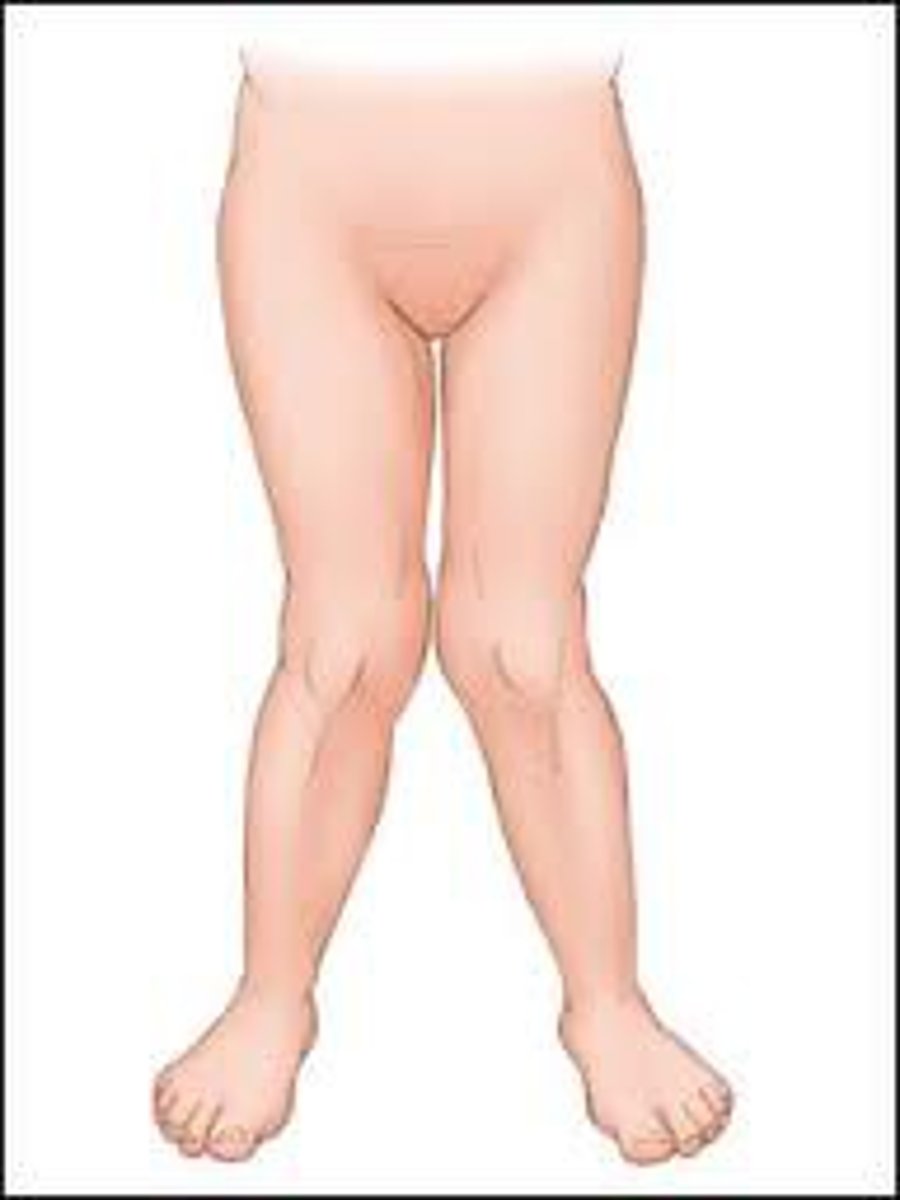
Genu valgum
knock knees
- common under age 7
- as child grow will become more slender and erect
Common causes of immobilized child?
- Congenital defects
- Neuromuscular condition
- Spica Cast
- Prolonged mechanical ventilation and sedation
- Traction
- Spinal fusion
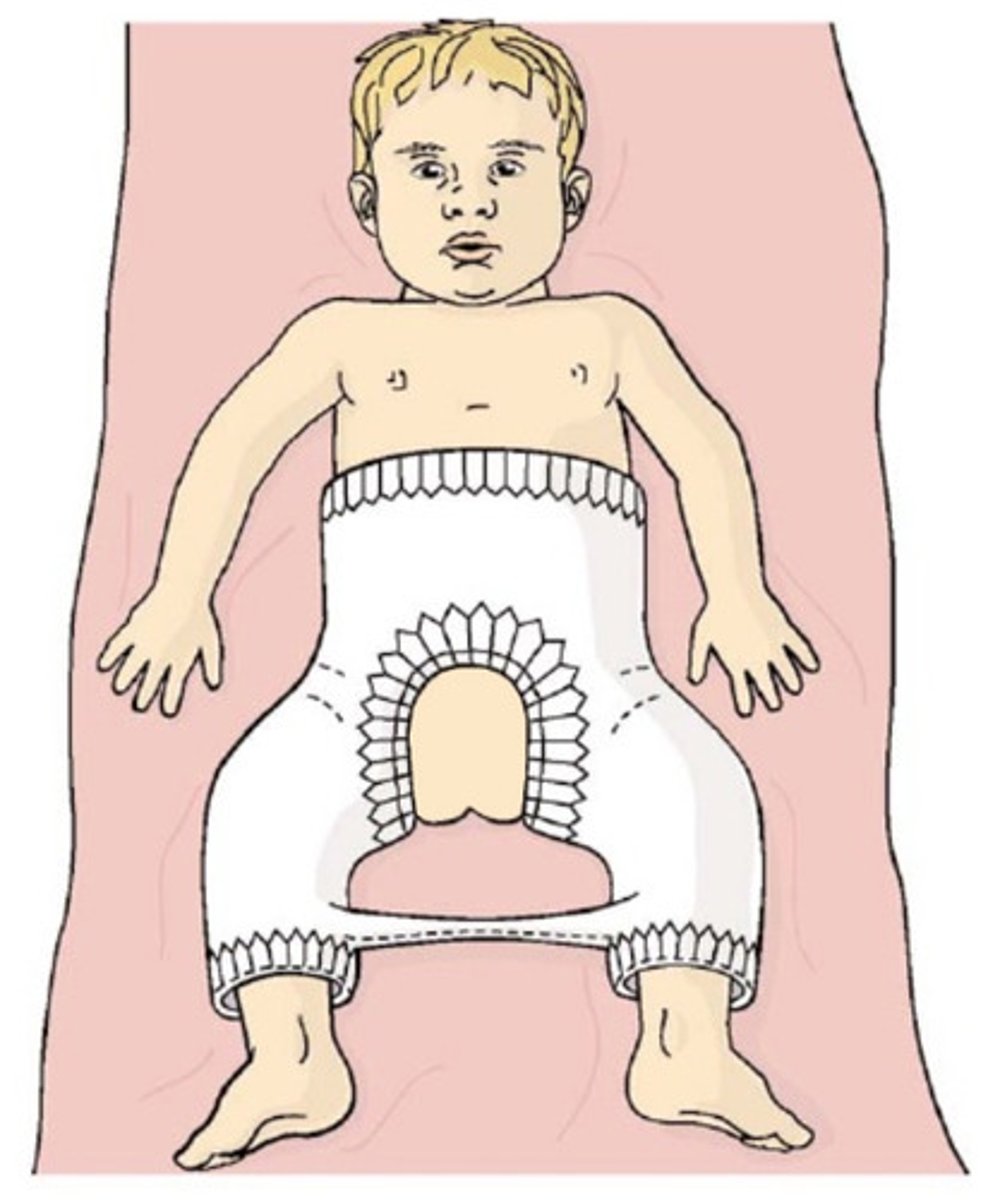
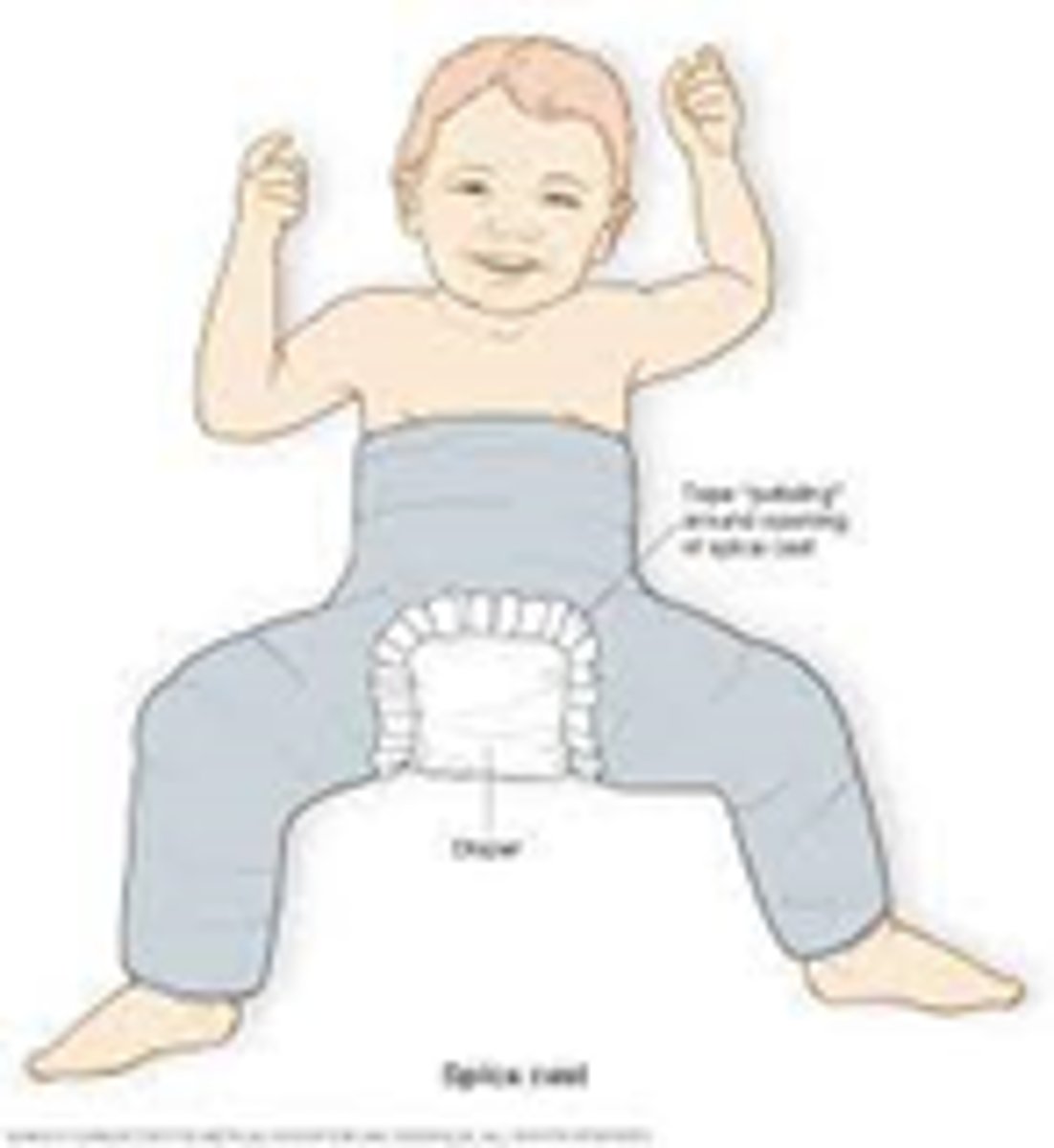
spica cast
encompassases abdomen, long cast on broken leg, short cast on other leg to stabilize child → often seen with femur fracture
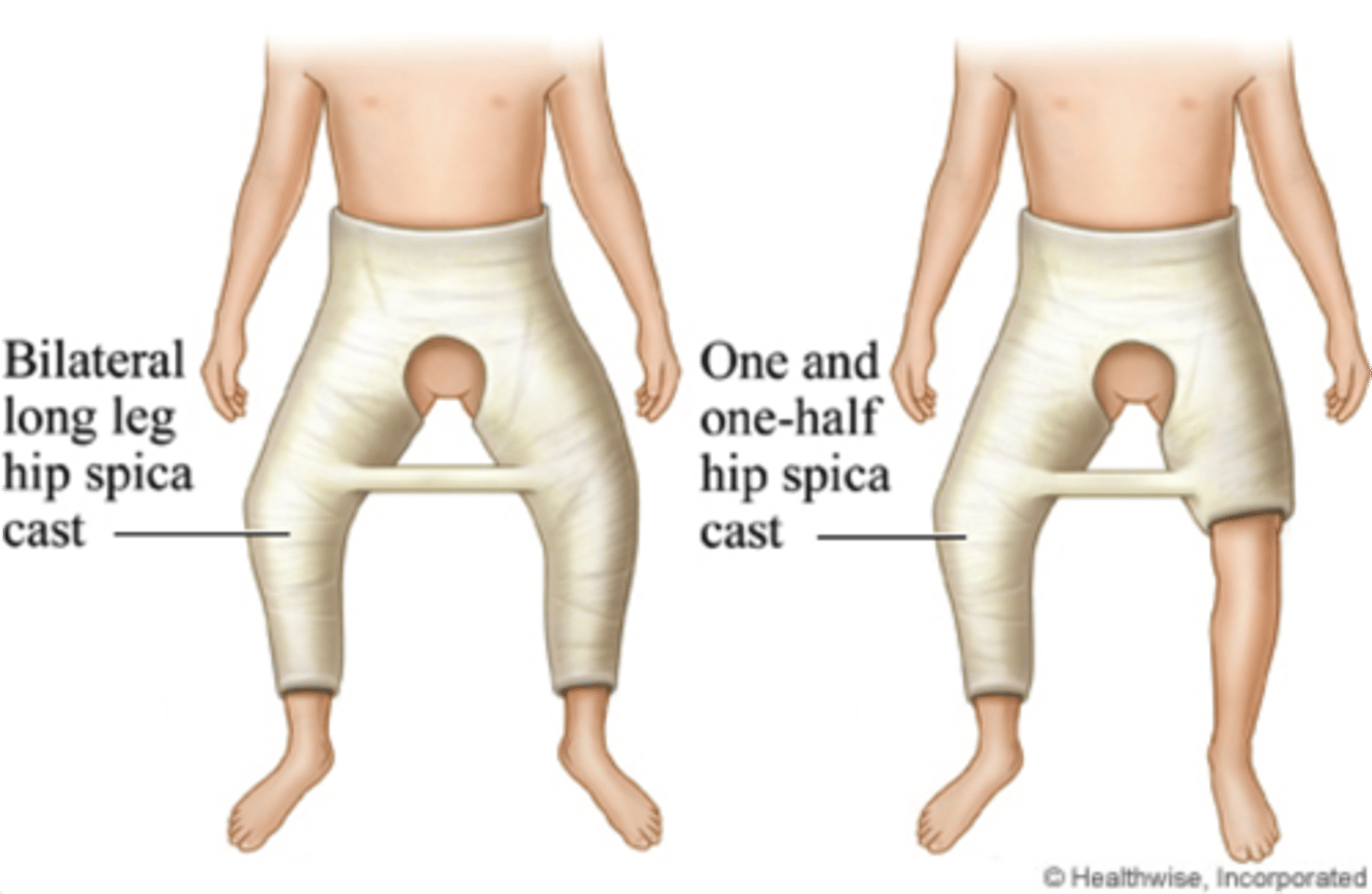
Double diapering with spica cast
- tuck a smaller diaper under the cast to prevent feces in the cast
- put another diaper on top of that
Immobilization impact on muscular system
atrophy and decreased strength
Immobilization impact on skeletal system
contractures
Immobilization impact on CV system
decreased perfusion, risk of clot (less than adult)
Immobilization impact on Resp System
increased risk of pneumonia, atelectasis, diaphragm may not have enough room if constipation
Immobilization impact on GI
constipation
Immobilization impact on renal
canaliculi, renal calcification
Immobilization impact on metabolism
lowers metabolism
Immobilization impact on neurosensory
always assess for sensation
Immobilization impact on integumentary
Skin breakdown, especially at edges of cast
Types of musculoskeletal injuries
- Contusion
- Dislocation
- Sprain
- Strain
- Fractures
S/S of fractures
- Swelling
- Pain or tenderness
- Deformity
- Diminished functional use of affected part
- Bruising
- Muscle rigidity
- Crepitus
What to assess for hx of injury with fracture?
- Story should match injruy
- Always ask child what happened
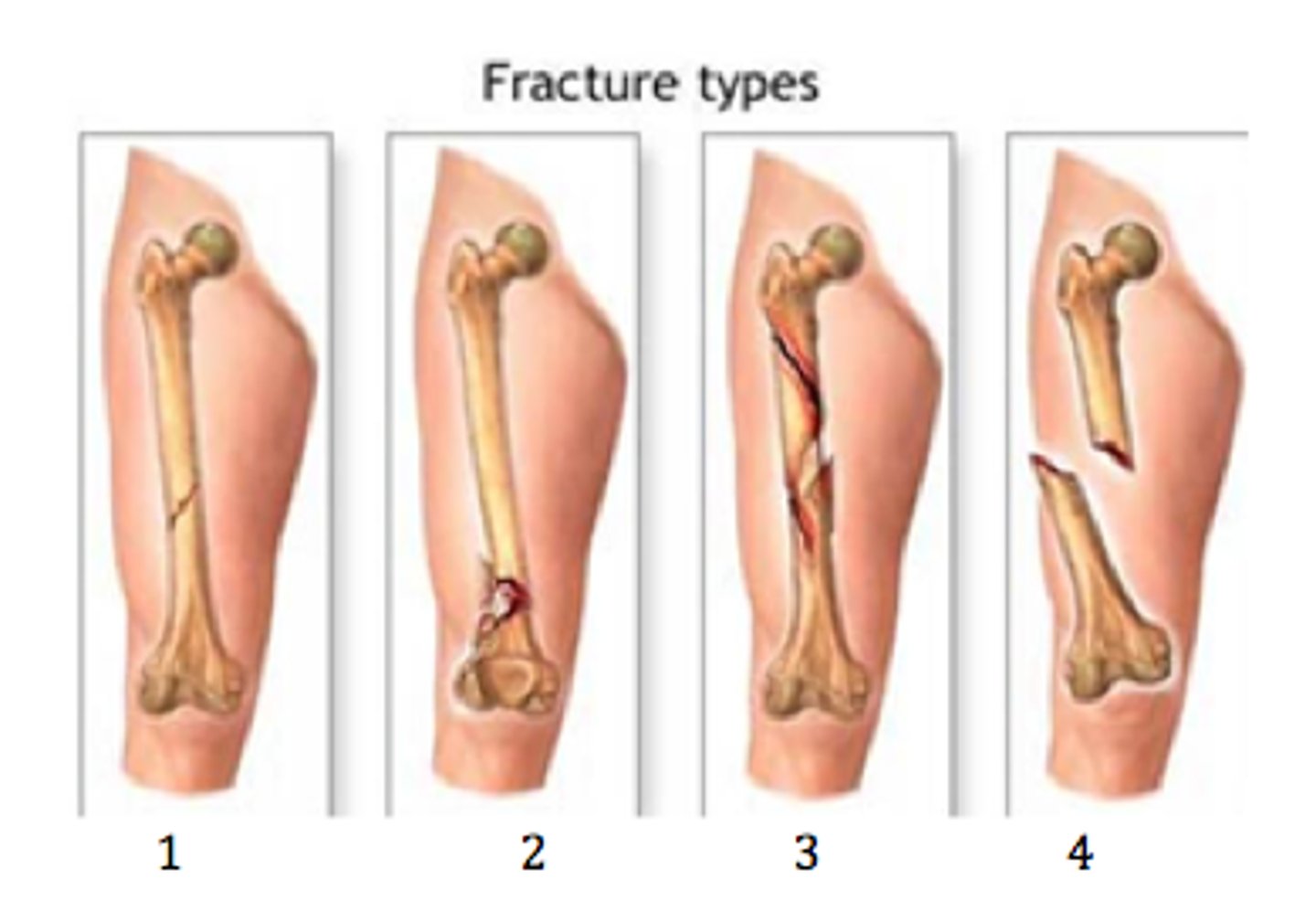
Types of fractures
1. oblique
2. comminuted
3. Spiral
4. Compound
What to note with spiral fracture?
must have two opposing forces to occur
- Child maltreatment → twist and pulling force
- Can also occur due to twist and pull from holding onto something or getting stuck in crib trying to climb out
5 P's of compartment syndrome
- pain
- pulse
- pallor
- paresthesia
- paralysis
Symptoms of compartment syndrome
Severe pain, decreased sensation weakness, paleness, unable to move
Treatment of compartment syndrome
fasciotomy
Application cast care
- Anticipatory guidance
- Distraction with application
- Petal edges PRN
- Teach CSM checks
Petal cast edges
Mole skin strips that wrap around legs and groin, etc. to protect cast from soiling
Removal cast care
Anticipatory guidance
- clutter sounds
- warmth
- caked skin
- atrophy
torticollis
head tilt due to shortening one sternomastoid muscle
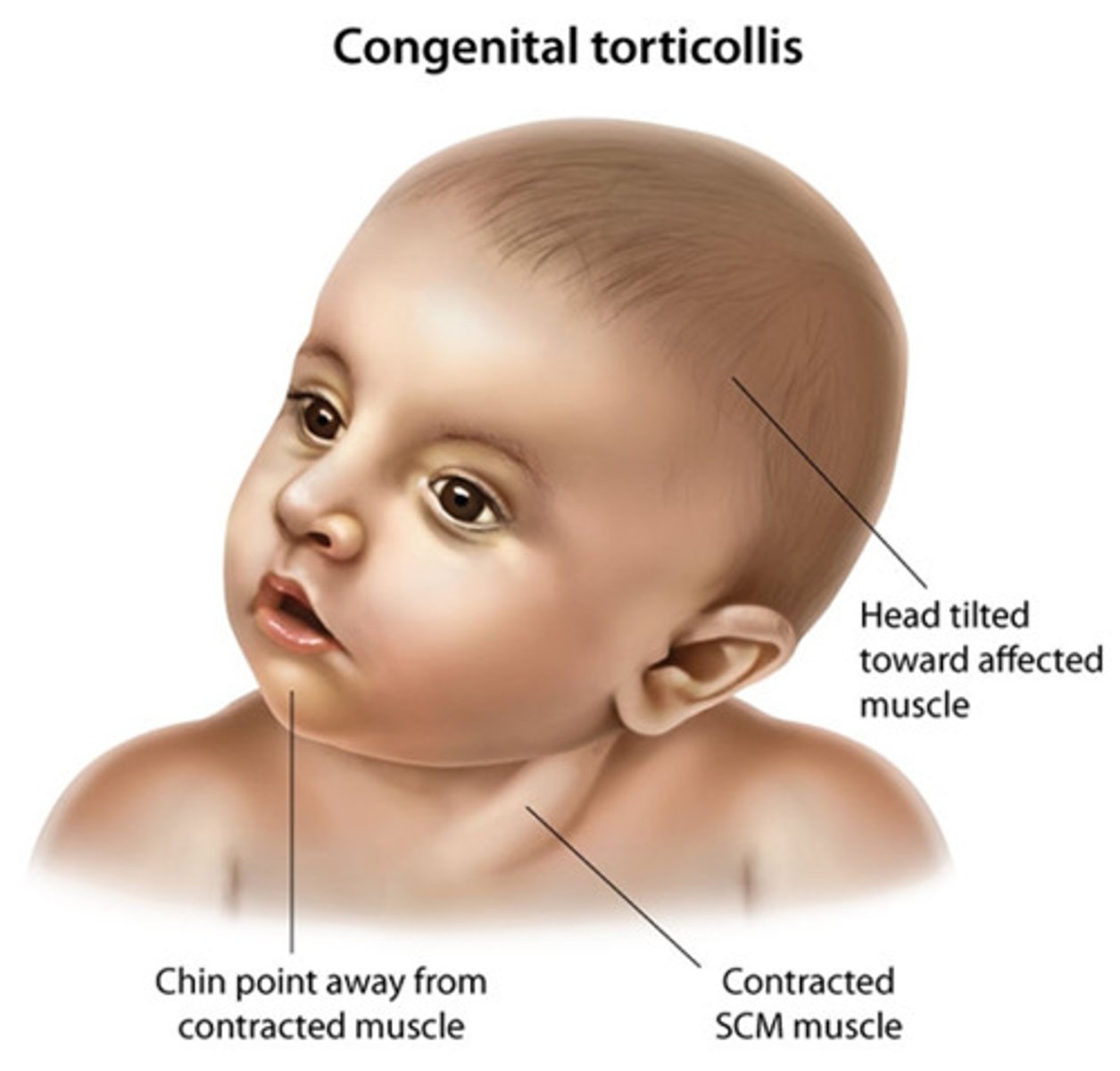
treatment of torticollis
gentle stretching exercise multiple times daily
Causes of Developmental Dysplasia of Hip
- females
- maternal hormones
- family hx of DDH
- in utero positioning
Infant symptoms of DDH
- Hip joint laxity
- +Ortolani
- +Barlow
- Shortening of thigh on affected side
- Asymmetric gluteal folds
Positive Ortolani Sign
Clunking with abduction of hips
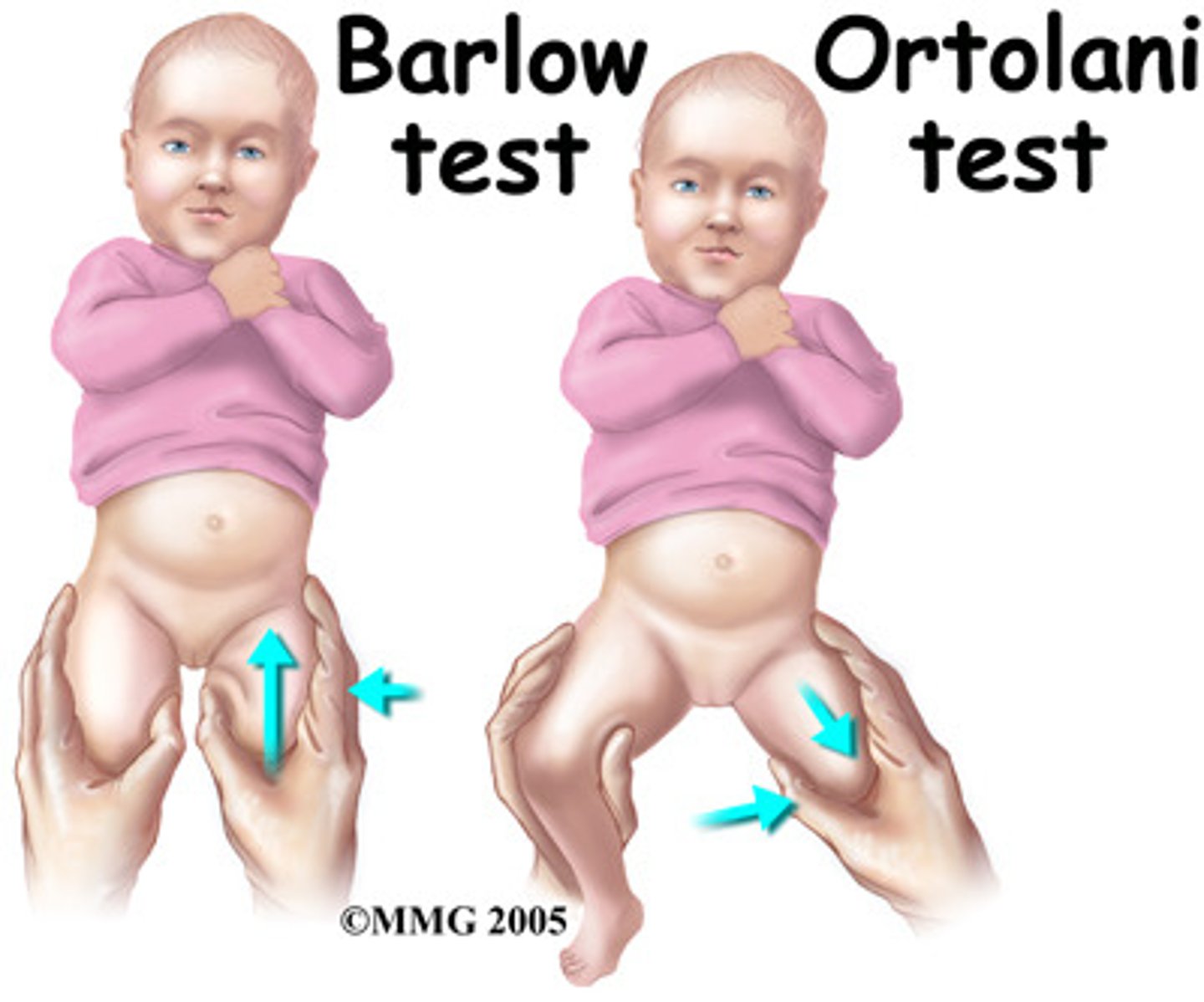
Positive Barlow Signs
Clunking with adduction of hips
Older infant and Child DDH symptoms
- Leg of affected hup appears shorter
- Waddling gait
- Lumbar lordosis (bilat)
- + Trendelenburg sign (pelvis tilts downward on normal side with weight bearing)
- Space between legs may look wider than normal
Treatment for DDH
- Pavlik harness
- Skin traction
- Spica cast
Pavlik harness
Used for child diagnosed between 0 and 6 months
- Wear all day, every day, for several months
- Adjusted with growth (every 1-2 weeks)
- Skin care (under contact points)
- Removal for bathing (may not be allowed)
- Neuro checks
- Normalcy
Skin traction
treat adduction contracture → stretches the associated soft tissue
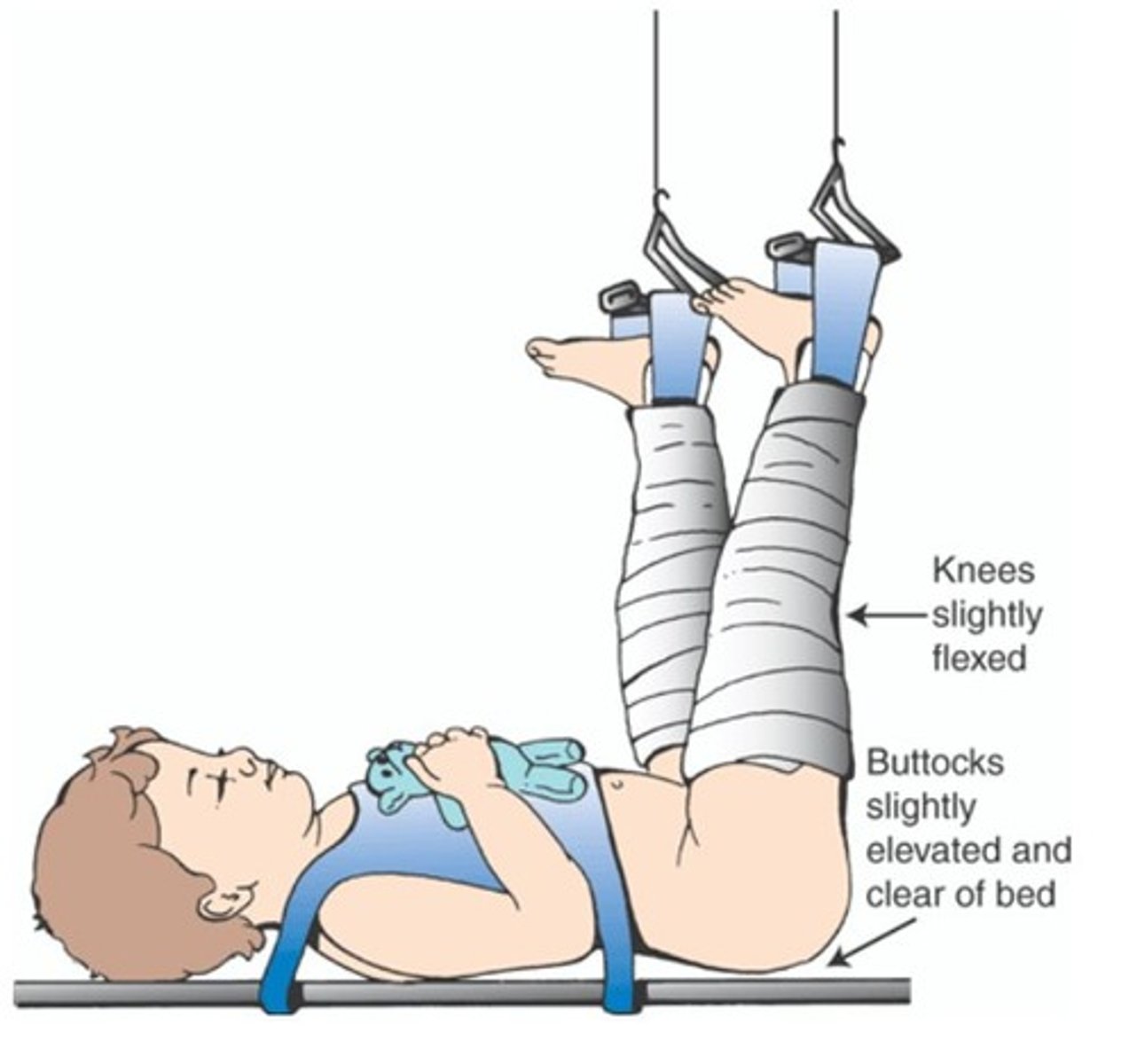
Use for spica cast
maintain external rotation (on for up to 12 weeks)
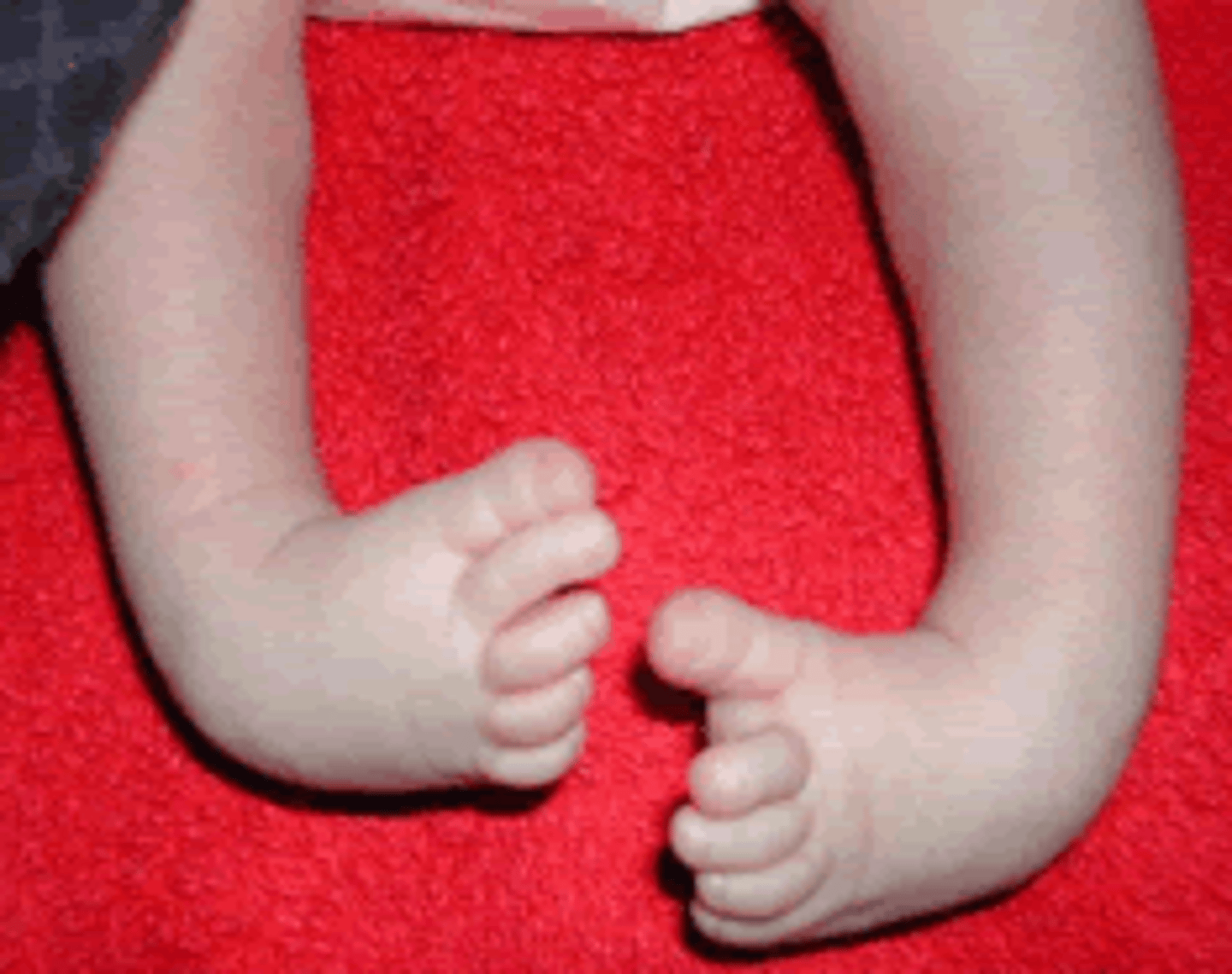
Symptoms of Clubfoot
- Foot and calf size variation (affected is smaller and shorter)
- Stiffness in the ankle or foot tendons
- Affected foot (feet) lack full ROM
Clubfoot treatment
- Serial casting (weekly with stretching)
- Heel Cord tenotomy
- Denis Browne bar and shoes
- If not effect, surgical pinning
Denis-Browne Bar
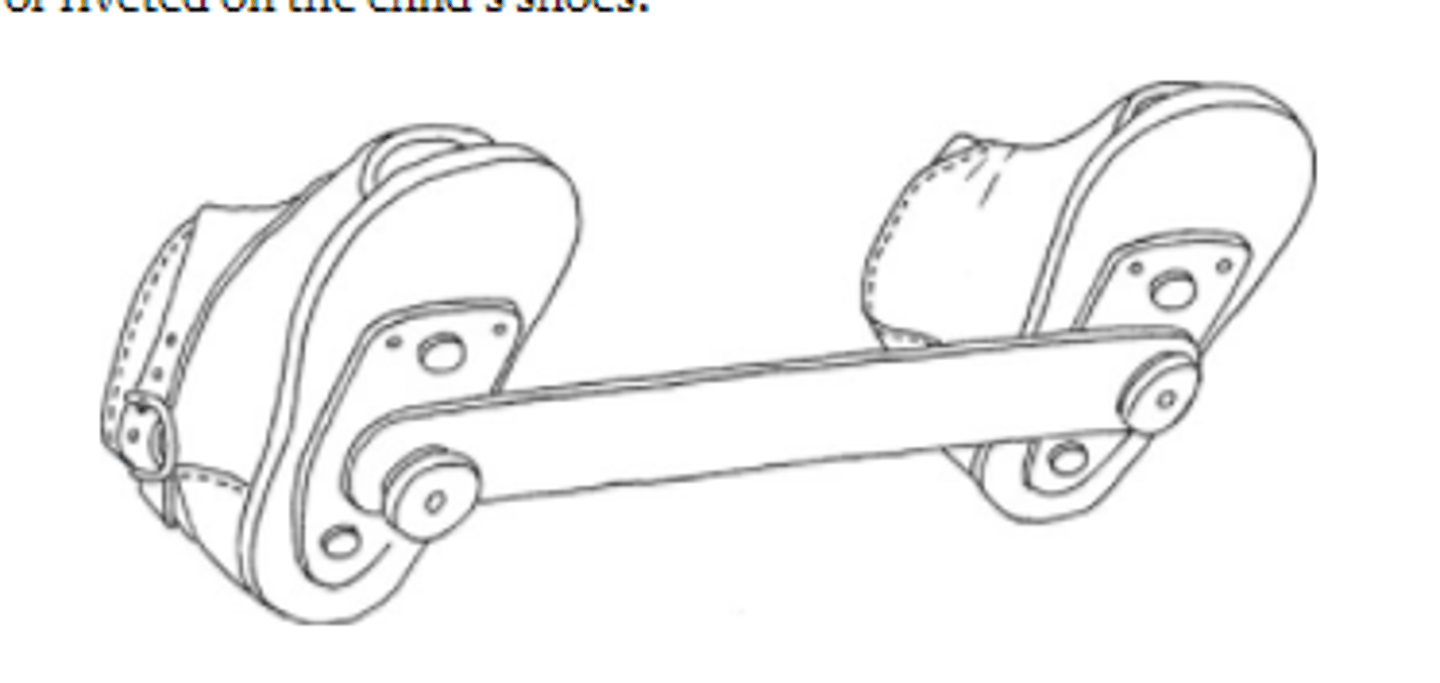
Progression of congenital clubfoot treatment
- Serial Casting
- Manipulation of foot → stretch muscles
- Heel cord tenotomy with cast → 3 weeks
- After 6 weeks - Bracing w/ dennis browne bar (maintain alignment)
23 hours a day initially, then 12 hours a day until approx age 5 years
osteogenesis imperfecta
inherited condition of deformed and abnormally brittle bones
Assessment of Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Blue sclera
- Hearing loss
- Dentinogenesis imperfect
- Growth restriction
Pamidorate
helps restore calcium and phosphorus into bone
- can cause immunosuppression (be careful w/ live vaccines)
pectus excavatum
- May cause cardiac and resp compression
- Severe cases - surgery with bar under sternum and ribs
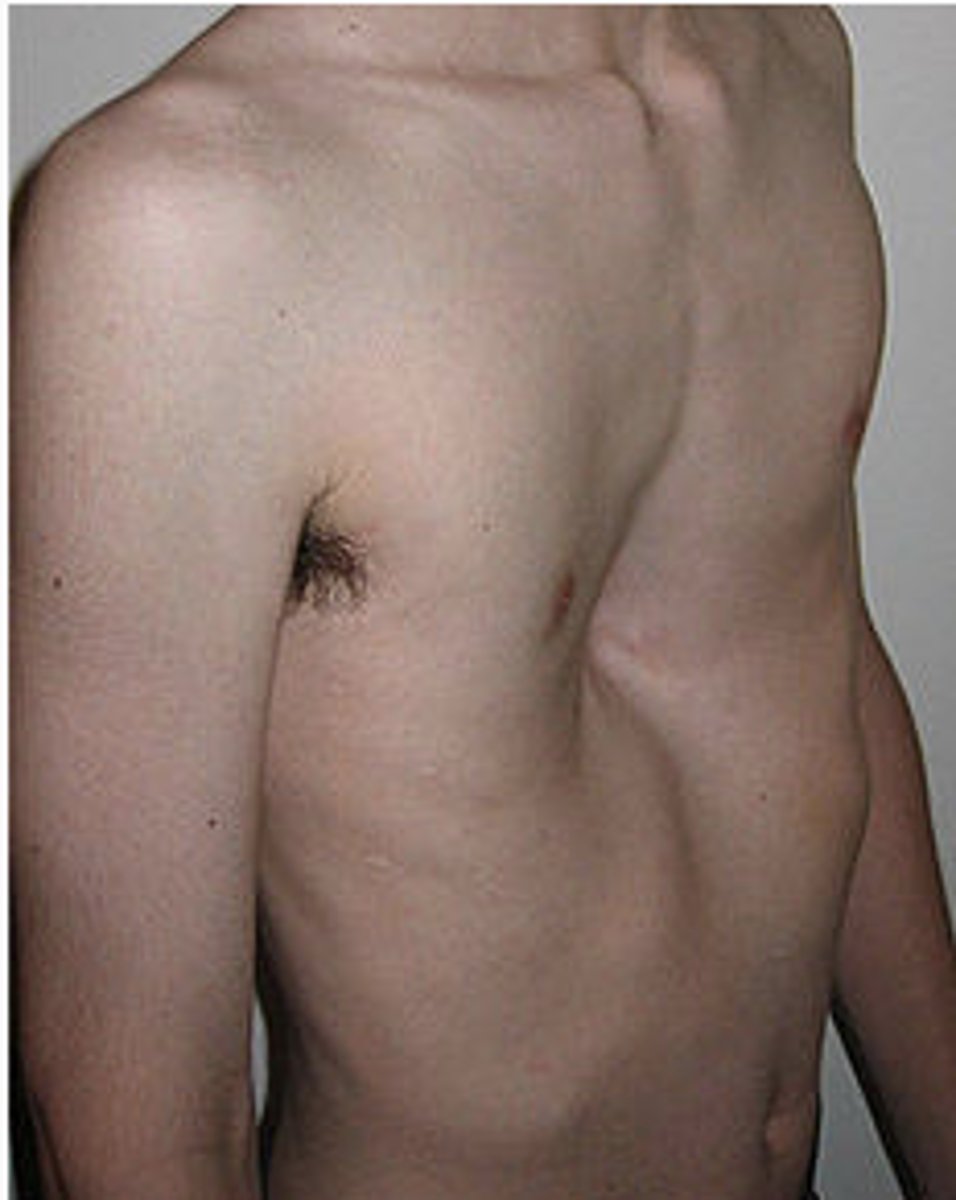
Pectus excavatum surgery consideration
- No rolling (no side lying for 4 weeks)
- Bar removal 2-4 years
When to do scoliosis checks?
Boys: 10 and 12
Girls: 13 or 14
Treatment
Based on severity
- mild (wait and see)
- moderate - 25-45 degrees (bracing)
- severe - 45+ degrees (spinal fusion surgery)
Spinal fusion Pre Op
blood work/blood loss plan
- Teaching (PCA, log-rolling, tubes)
Spinal fusion post op
- Circulation, Motion, Sensitivity (CMS) assessments
- Early recognition of complications (including neuro changes)
- PCA early mobilization, skin, I/O, resp, GI (constipation)
- Follow H/H
- Do well but it is a very long recovery
Spinal bifida occulta
no protrusion of meninges or cord
- Tuft of hair or dimple may be present
- Least severe
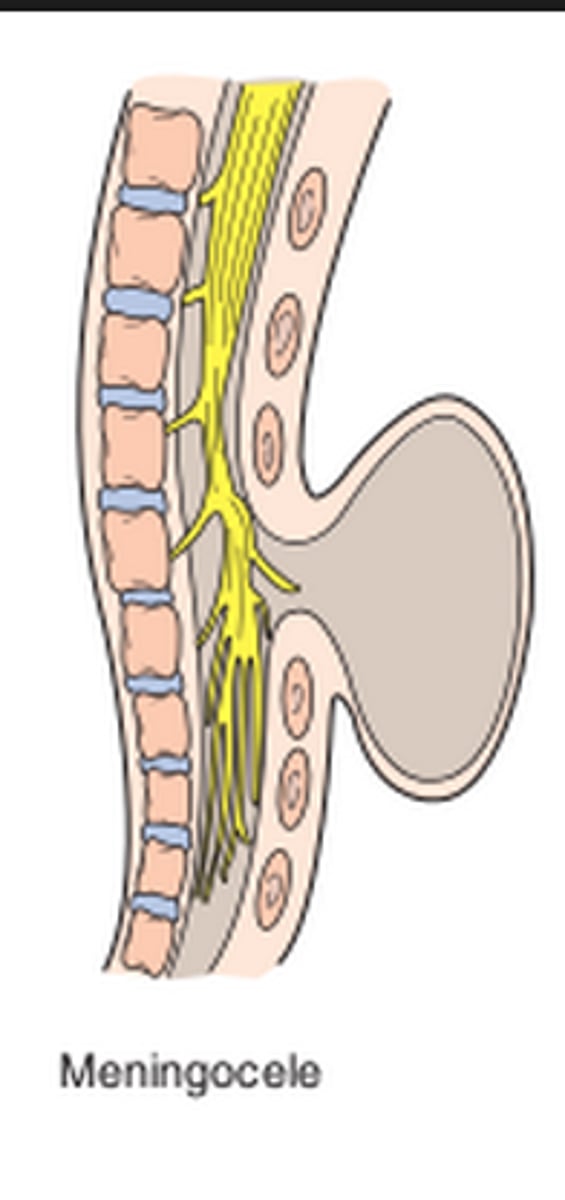
Meningocele
meninges herniate but cord intact
Myelomeningocele
nerves protrude with meningeal herniation
- can cause nerve impairment
- most severe
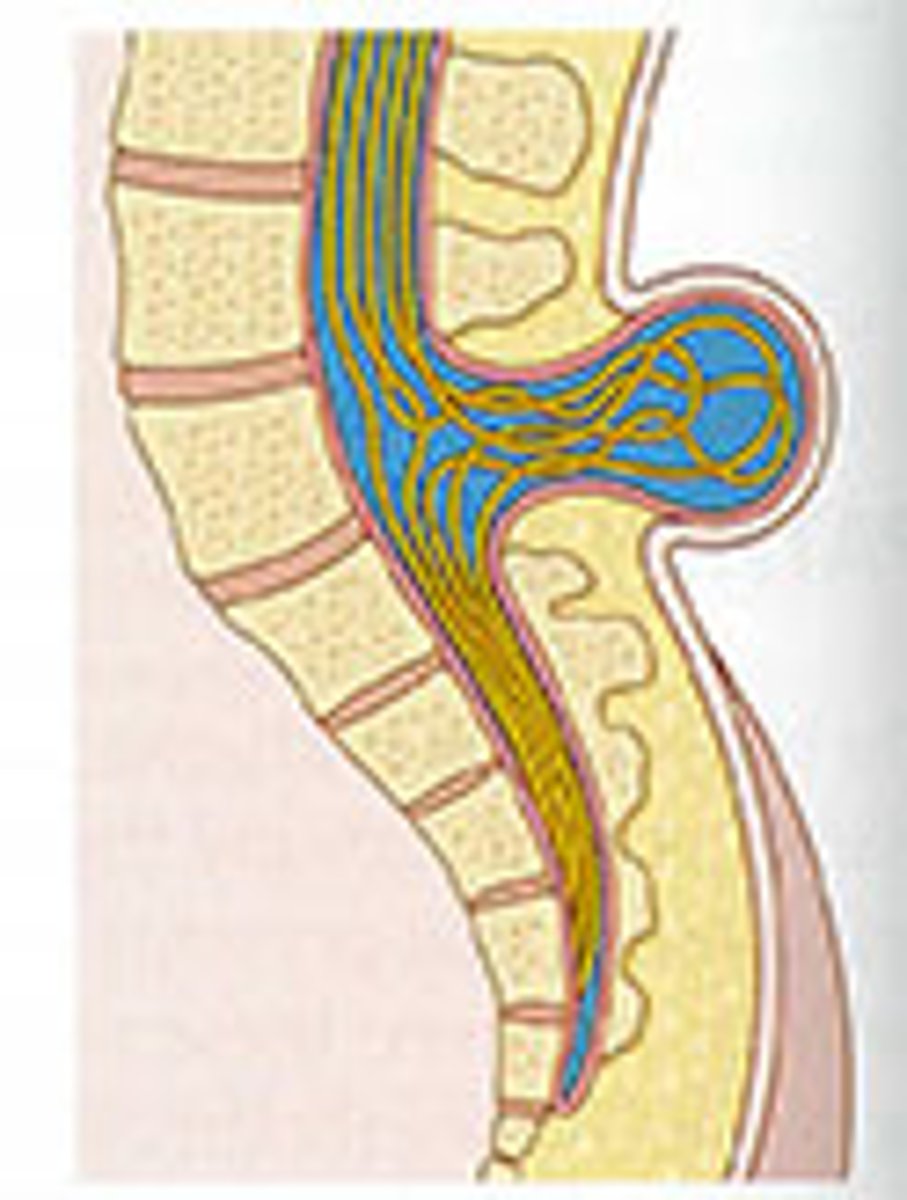
What it the biggest goal with myelomenigocele?
maintain the integrity of the sack
- keep sac moist with gauze
- keep pressure off
- frequently check sac integrity
What to not use with neural tube defects?
Latex
- repeated exposure to latex can cause latex allergy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
x-linked trait
- progressive muscle weakness and loss of abilities
- begin to meet most developmental milestones (age 3-7)
- loss of dystrophin
Symptoms of DMN
- Waddling gait
- Muscular enlargement (early) → muscular atrophy (later)
- Continue to lose muscle strength
- Loss of independent ambulation by age 12
- Immobility complications
- Mental impairments
- Will progress to atrophy of lung and heart muscles → death at young age
Therapeutic management of DMD
- Maintain optimal function in all muscles
- Prevent contractures
- Try to normalize things as much as possible
What is cerebral palsy caused by?
- area of brain not getting oxygen (lead to motor problems)
- still likely to have complete cognitive ability
Most common movement disorders of CP?
Spastic (80% of cases)
Clinical manifestation of CP?
- Delayed gross motor skills
- Abnormal motor development
- Altered muscle tone
- Abnormal posture
- Abnormal reflexes
- Associated disabilities (will still have normal cognitive)
Baclofen Pump
centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant to decrease spasticity and spasms
- refilled every 4-6 weeks
Side effects of baclofen
muscle weakness, fatigue, diaphoresis, h/a nausea or constipation
- Assess for hepatotoxicity
Diazepam
decrease muscle spasms with CP
Botulinum toxoid A
given intramuscular for the lower extremity (quads) relaxation for CP
Kyphosis
hunchback
- adolescence may have kyphosis due to posture
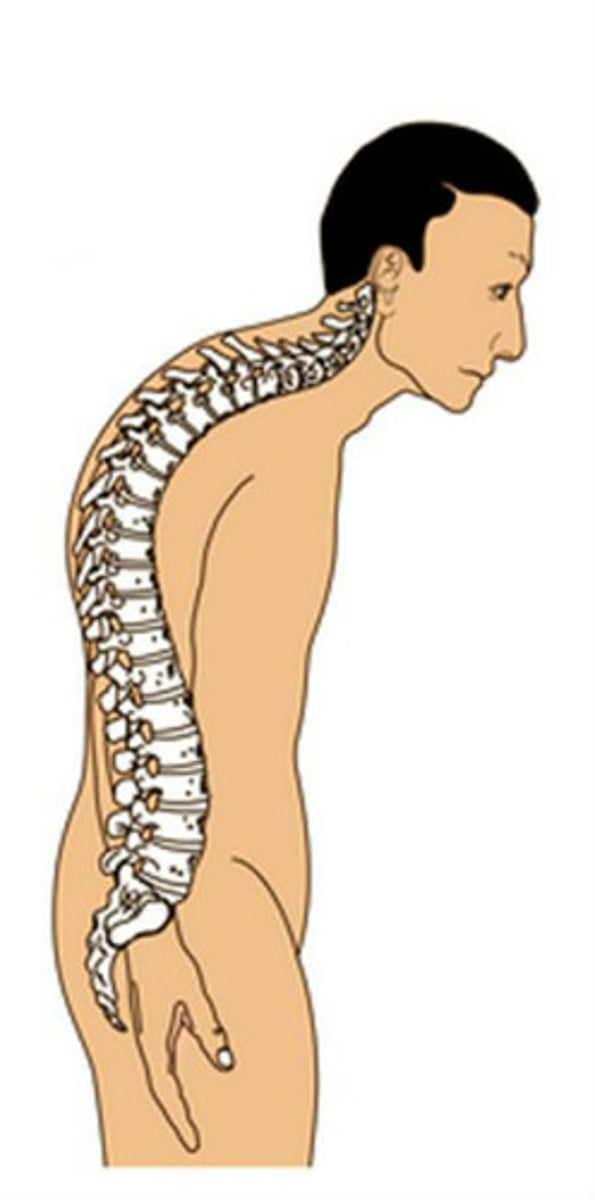
Lordosis
inward curvature
- expected finding in toddler
Complications of casting
neurovascular compromise, skin integrity impairment, soft tissue injury, compartment syndrome, infection
Baclofen
centrally acting muscle relaxant
- used to treat painful spasms and decrease spasticity in children with motor neuron lesions such as CP
Nursing Implications with Baclofen
- Assess motor function
- Observe for confusion, depression, or hallucinations
- Dosage must be tapered to prevent withdrawal syndromes
Neurovascular assessment with cast application
- Color (cyanosis)
- Movement
- Sensation
- Edema
- Quality of pulses
Petaling
cut rounded-edge strips of moleskin or another soft material with an adhesive backing and apply them to the edge of the cast
Call provider for cast if...
- Casted extremity is cool to the touch
- Child cannot move fingers or toes
- Severe pain occurs when child attempts to move fingers or toes
- Drainage or a foul smell comes from under cast
- Severe itching occurs inside the cast
- Child runs a fever greater than 101.5
- Skin edges are red and swollen
- Child complains of rubbing or burning under cast
- Cast gets wet and does not dry or is cracked, split, or softened
What drug for osteogenesis imperfecta?
Bisphosphonate
What drug for muscular dystrophy?
Prednisone (corticosteroids to slow progression)
Side effects of corticosteroids
- Weight gain
- Osteoporosis
- Mood changes
Grower's sign
child cannot rise from the floor in standard fashion because of increasing weakness
- sign of muscular dystrophy
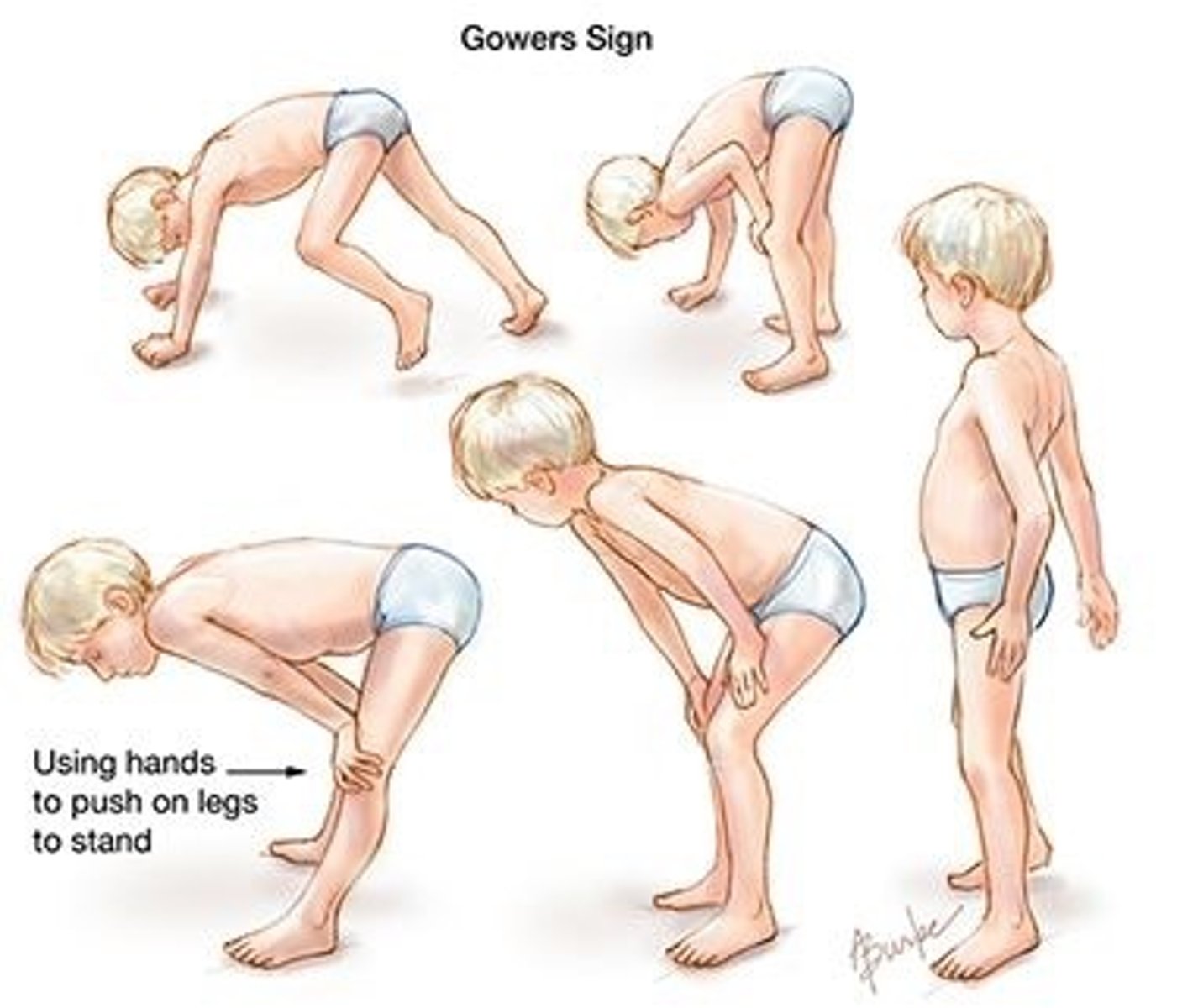
Absence of what with muscular dystrophy?
dystrophin
What medications for spasticity?
- Baclofen
- Dantorlene sodium
- Diazepam
Rickets
softening or weakening of bone
- may occur due to nutritional deficiencies
- limited exposure to sunlight
- impaired absorption of vitamin D