Kinetic theory
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
changes of state, solubility and diffusion
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
solubility
a measure of how easily a solute can dissolve into a solvent
saturated
a mixture where a solvent has dissolved as much solute as it can at a given temperature
solute
something that dissolves
solvent
something that a solute dissolves into
insoluble
a substance which can’t be dissolved
solution
a substance formed when a solute dissolves into a solvent
name 2 factors that can affect how easily a solute can dissolve
stirring and temperature
what happens when a solid sample of a mixture is heated?
parts of it melt at different temperatures
a pure substance has a melting and boiling point
fixed
mixture
two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically joined together
evaporation
the change in state from liquid to gas
chromatography
a separating technique used to separate mixtures that have different solubilities
filtration
a separating method to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid
crystals
the regular shaped structure of a solid. These are seen when a solvent is evaporated from a solution
filter paper
the thick paper used in chromatography and filtration
boiling point
the specific point at which a substance changes in state from a liquid to a gas
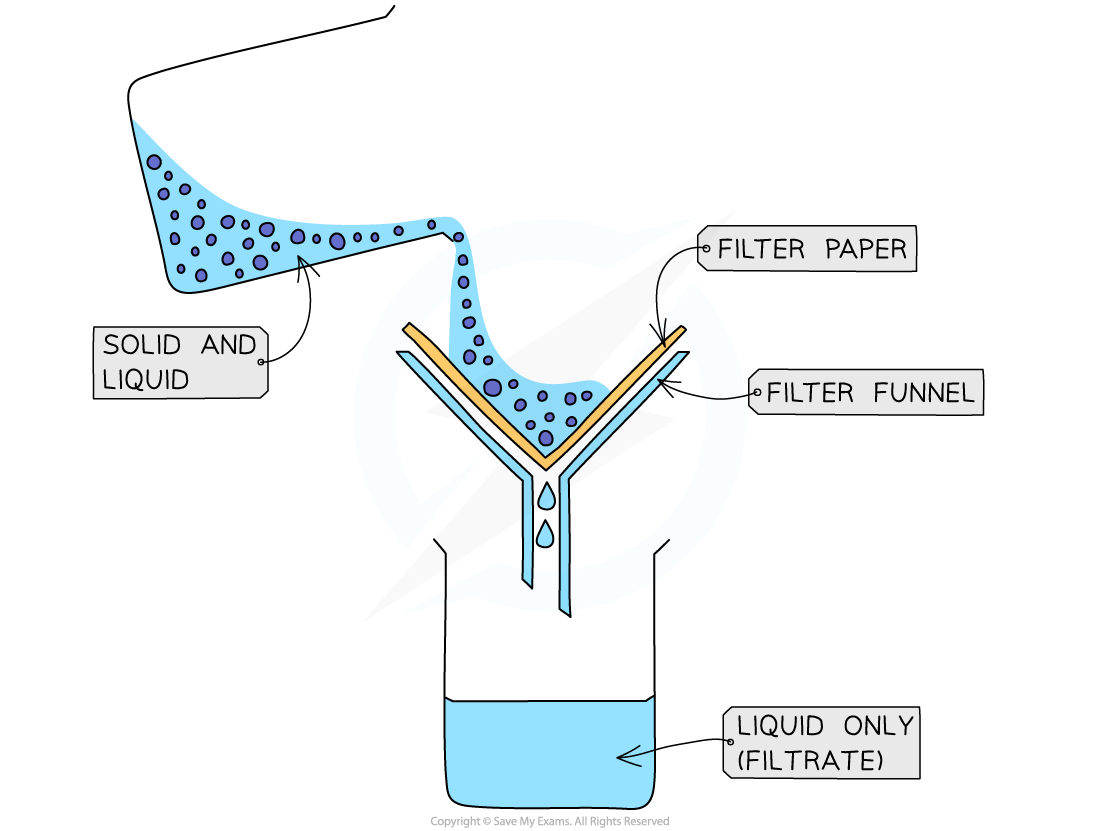
filtration
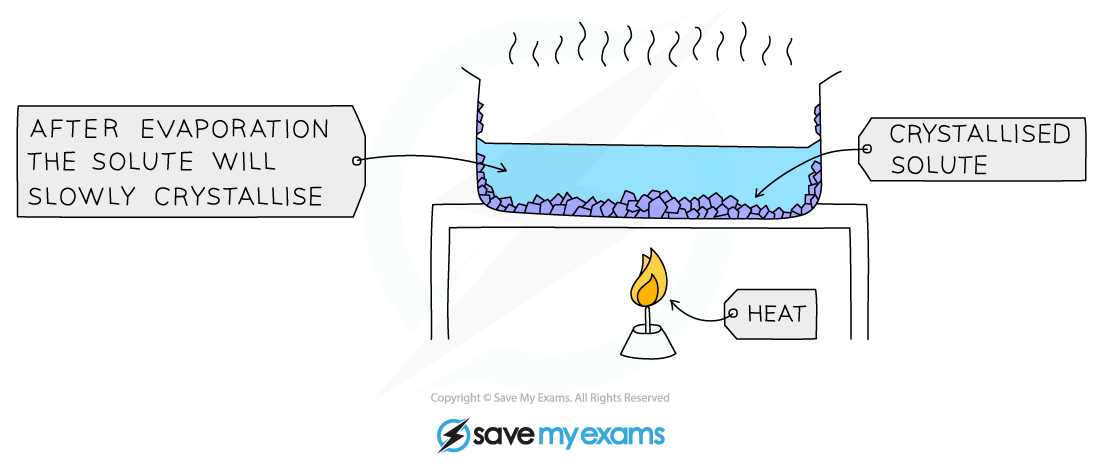
crystallisation
crystallisation
used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution, when the solid is much more soluble in hot solvent than in cold
decanting
used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid
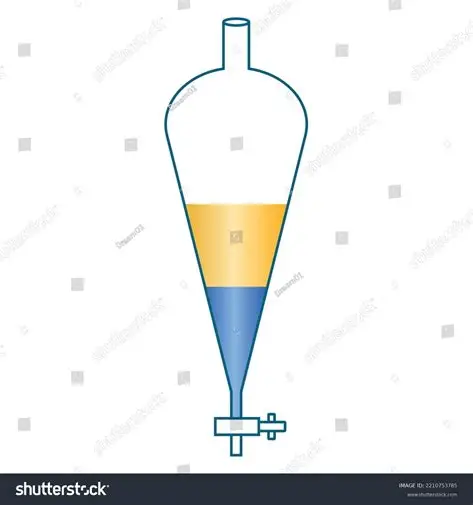
separating funnel
separating funnel
used to separate liquids with different densities
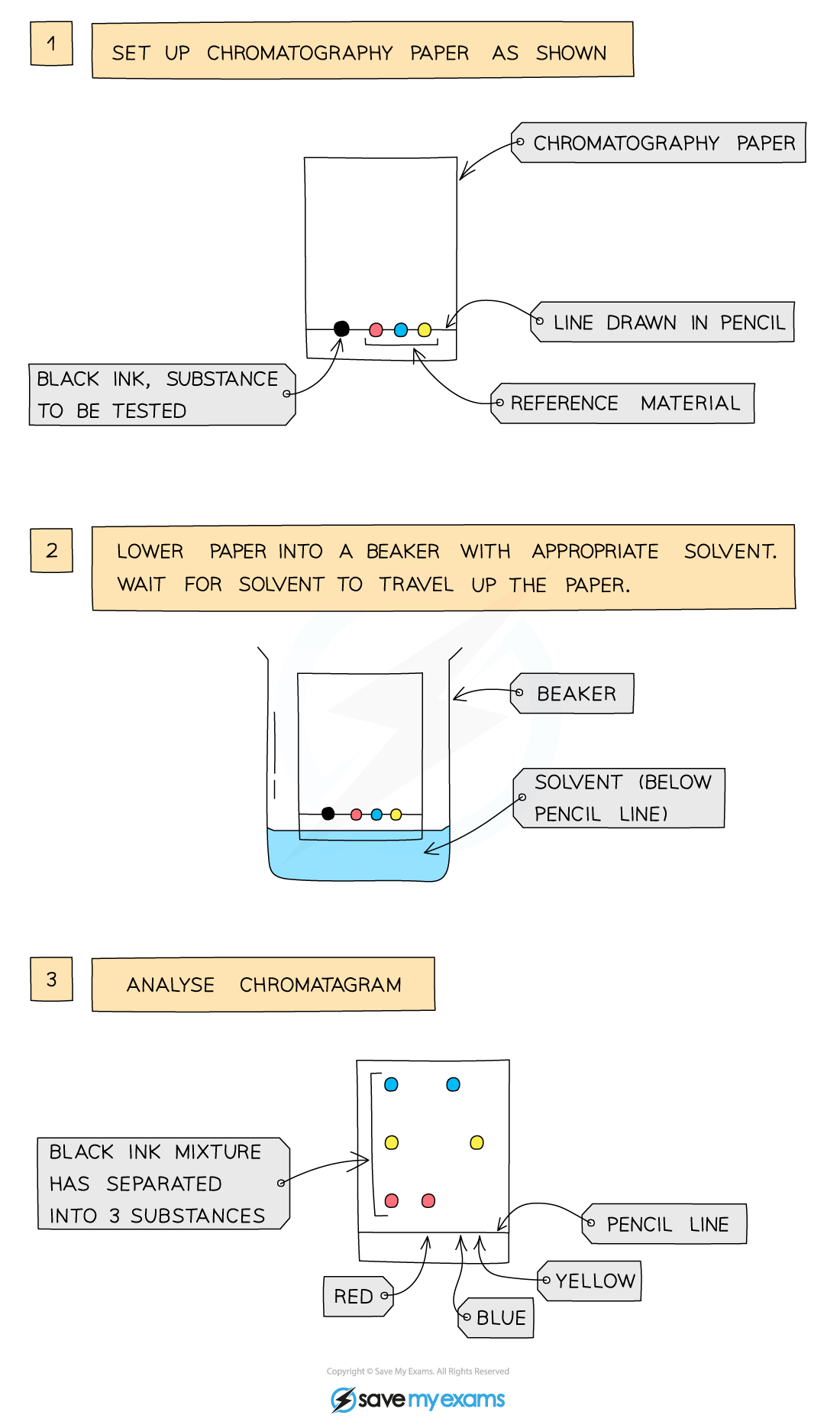
chromatography
distillation
separates two liquids with different boiling points
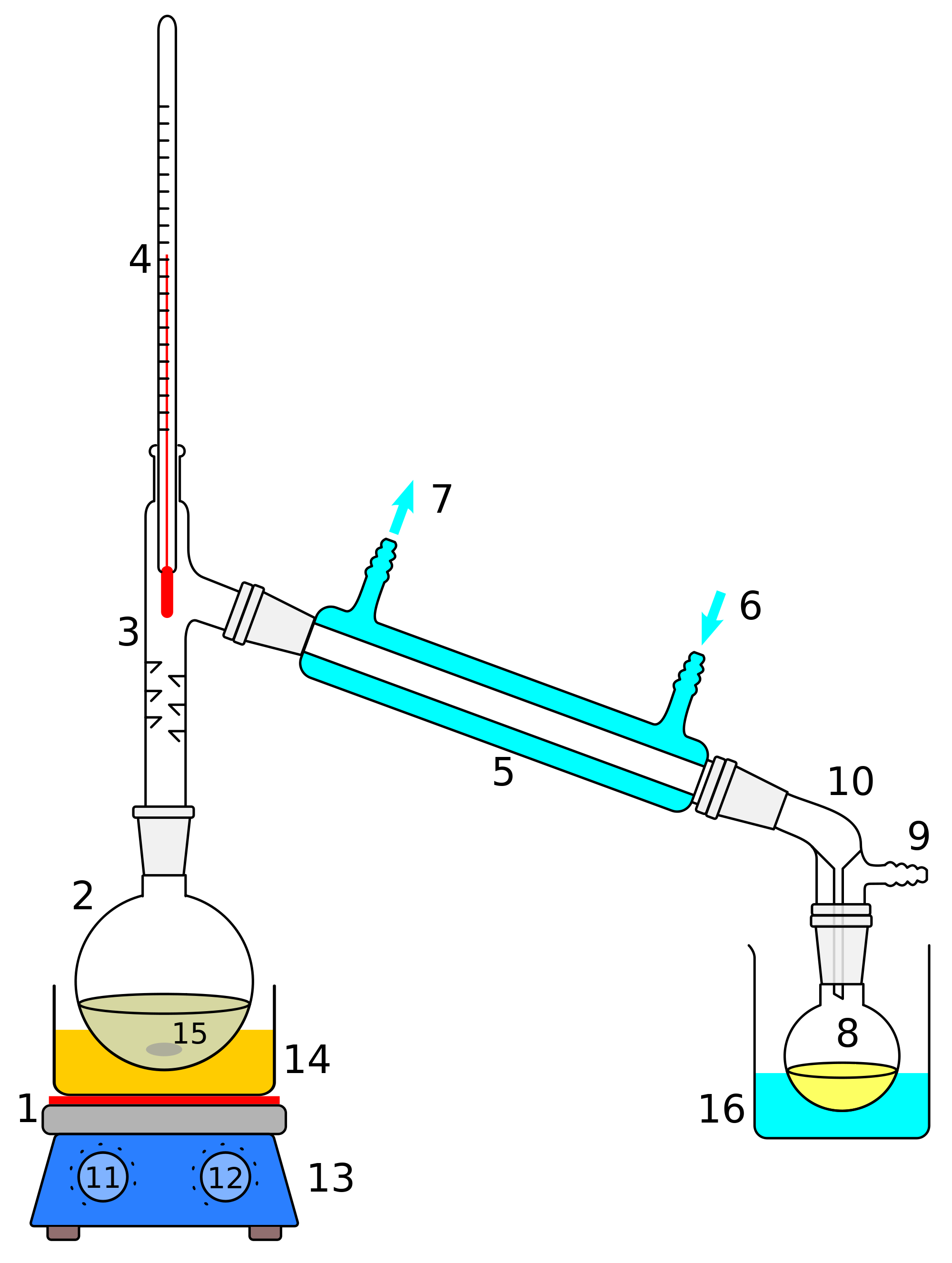
distillation
fractional distillation
separates multiple substances with different boiling point
how does fractional distillation differ from distillation?
distillation separates two substances, fractional distillation separates many substances
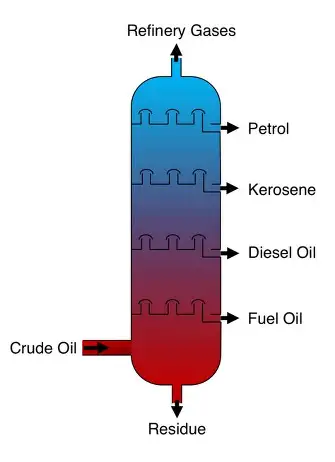
fractional distillation
solid to liquid
melting
liquid to gas
evaporation
gas to liquid
condensation
liquid to solid
freezing
solid to gas/ gas to solid
sublimation
describe the arrangement of particles in a solid
particles are in a regular arrangement, touching each other and are vibrating.
describe the arrangement of particles in a liquid.
particles are in an irregular arrangement, they flow and mostly touch.
describe the arrangement of particles in a gas.
particles are in an irregular arrangement, they flow and are separate (don’t touch)
what does each spot on a chromatography practical represent?
a pure sample
why does each ink sample have several dots after the experiment?
a mixture contains several pure substances, which move different distances, so has several spots.
what does it mean if a chromatography spot travels a long distance?
substance is very soluble and has an affinity for the mobile phase
what does it mean if a chromatography spot travels a short distance?
substance is not very soluble and has an affinity for the stationary phase.
what does Rf stand for
retention factor
give the equation to find the Rf
Rf=distance travelled by pure substance / distance travelled by the solvent