Arthropods Pt 3
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANS 389C
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
what is Order Psocodea also known as?
Order Phtheroptera; lice
historically, lice were grouped into 2 main types. what were they?
sucking lice (Anoplura) - found only on mammals
chewing lice (Mallophaga) - the name means “wool eaters”, but this group is not scientifically accurate anymore
scientists now only recognize 4 suborders of Order Psocodea. what are they?
anoplura
Rhynchophthirina
Ischnocera
Amblycera
anoplura
sucking lice that live on mammals only
Rhynchophthirina
rare lice, found on elephants and warthogs in Africa
Ischnocera
mostly chewing lice on birds, but some species are found on mammals
Amblycera
chewing lice found on birds and some mammals in South America and Australia
all parasitic lice are…
permanent ectoparasites
obligate parasites
host specific
what are parasitic lice called?
Phthiraptera
list some morphological features of Phthiraptera
small
various colors
wingless
dorsoventrally flattened
stout legs and claws
what do Phthiraptera feed on?
dead skin
feathers
sebaceous secretions (skin oils)
blood
most lice have similar ___ _____
life cycles
how many eggs do females lay in a lifetime (about 1 month)?
20-200 eggs
eggs are called _____
nits
where are nits located?
glued to hair or feathers
how many molts do nymphs go through before becoming an adult?
3
what is the total time from egg to adult in lice?
2-3 weeks
describe features of sucking lice
have piercing mouthparts
feed on blood
describe features of chewing lice
have cutting and grinding mouthparts
feed on skin, hair, feathers, scales, scabs
the level of impact a louse has on a mammal depends on..
the severity of the infestation
(true/false) louse populations can increase dramatically in a short time
true
name some clinical effects of louse infestations
pruritus
alopecia
self mutilation
weight loss
anemia
how are lice generally transmitted?
through direct physical contact
when do lice become more active?
in the winter
what family contains the largest of lice in domestic animals?
Family Haimotopinidae
what mammals do Haimotopinidae infest?
cattle, pigs, horses
what family infests cattle, sheep, horses and deer?
Family Bovicolidae
order Siphonaptera are also known as
fleas
what stage(s) of Siphonapteras are parasitic?
adult only
what is the feeding type in Siphonaptera?
obligate blood-feeding
over ___% of Siphonaptera live on mammals
95%
list morphological features of fleas
dark brown to black
small, wingless
bodies are laterally compressed (narrow)
third pair of legs are very long
why are the third pair of legs on fleas very long?
they are designed for jumping
(true/false) fleas are able to parasitize a range of different hosts
true
do female, or male fleas feed more?
female fleas feed more
what effects can blood feeding have on a host?
pruritus
skin inflammation
anemia
what are the 4 stages that fleas go through?
egg → larva → pupa → adult
describe appearance of flea eggs
oval shaped, smooth
where are flea eggs laid?
on host
when do flea eggs hatch?
they hatch dependent on temperature; could take 2 or less weeks to hatch
describe appearance of flea larvae
maggot-like, brown head, bristles
what do flea larvae feed on?
organic debris
how many times does a flea larvae molt until it pupates?
2
the time for a flea to complete its lifecycle depends on _________ and ________
temperature and humidty
what mammals does cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions occur in?
dogs, cats, poultry
what’s an example of fleas affecting public health in humans?
Bubonic Plague — bacteria called Yersinia Pestis
what family parasitizes many types of mammals and is found worldwide?
Family Pulicidae
what is the name of dog and cat fleas?
Ctenocephalides
arachnids are a diverse group of ______-_______ arthropods
land-dwelling
(true/false) arachnids are usually ominvores
false, they are usually carnivores
do arachnids have antennae or wings?
no
do arachnids have simple eyes or compound eyes (like insects)?
simple eyes
what is the main group of veterinary importance in Class Arachnida?
Subclass Acari (mites and ticks)
list morphological features of Acari
very diverse
most are tiny
body looks sack-like, because segments are fused together
not clearly divided
how many legs do adult Acari have?
4
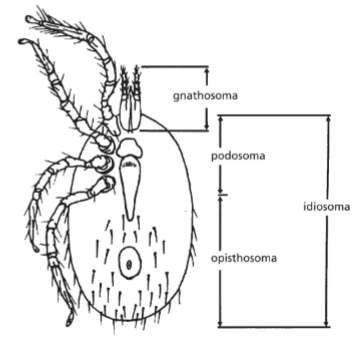
what are the names of Acari’s body segments?
gnathosoma
idiosoma
parasitic mites largely inhabit the _____
skin
what do parasitic mites feed on?
blood, lymph, skin debris, sebaceous secretions
how do parasitic mites feed?
puncture skin
scavenge on skin surface
feed on wounds
what are mite infestations called?
Acariasis
Acariasis can cause severe skin disease called _____
Mange
what are symptoms of Mange?
itching, hair loss, thickened skin
how long do mites stay on host?
usually their whole life
how are mites spread?
mostly spread by direct contact between animals
mites may be intermediate hosts for ________
tapeworms
what are the 4 stages of a mites life cycle?
egg → larva → nymph → adult
how many legs do mite larvae have? nymphs? adults?
larva - 6 legs
nymph - 8
adult - 8
how long does it take a mite to complete its life cycle?
less than 4 weeks
describe appearance of Family Sarcoptidae
round bodies, flattened ventrally
legs embedded in body (appearance of short legs)
what type of mite burrows into the skin?
Family Sarcoptidae
what genera of Family Sarcoptidae are of veterinary importance?
Sarcoptes
sarcoptic mange
Notoedres
mainly affects cats and rodents
Trixacarus
mange in guinea pigs and dogs
do Psoroptidae burrow into the skin?
no
describe appearance of Family Psoroptidae
oval-shaped bodies
legs are longer than the burrowing mites
what genera is of Family Psoroptidae are of veterinary importance?
psoroptes
psoroptic mange
cattle, sheep, rabbits
chorioptes
mild mange, often on legs and tails
otodectis
ear mites in dogs and cats
what order within Class Arachnida is a large and diverse group of mites that are found in many environments and varied forms?
Order Trombidiformes
what families in Order Trombidiformes are of veterinary importance?
Demodicidae and Cheyletiellidae
what family contains Genus Demodex
Family Demodicidae
where can Demodex mites found?
in many animals, including humans
where do Demodicidae live?
in hair follicles and sebaceous glands
(true/false) Demodicidae are not host specific
false, they are host specific
what species of Family Demodicidae are of veterinary importance?
Demodex canis and Demodex gatoi
most mites in Family Cheyletiellidae are ________, but some species are _________
predators; ectoparasites
what animals do Cheyletiellidae affect?
dogs, cats and rabbits
can Cheyletillidae be tranferred to humans?
yes
what is another name for Family Cheyletiellidae?
“walking dandruff”
Order Ixodida are also known as…
ticks
ticks are obligate blood-feeding _________
ectoparasites
what do ticks feed on?
mammals and birds
(true/false) ticks are larger than mites
true
how often do ticks feed?
infrequently, with long gaps between meals
what are the 2 families of interest in Order Ixodida?
Ixodidae and Argasidae
Ixodidae (hard ticks)
have a hard plate (scutum) on their back
in males, it covers the whole back
in females, larvae, and nymphs, it only overs a small part so the body can swell during feeding
Argasidae (soft ticks)
no scutum
include bird ticks and tampans
what are some symptoms of tick bites?
irritation and inflammation
allergic reactions (hypersensitivity)
anemia (if many ticks are feeding)
reduced production (weight loss, milk drop)
what can tick saliva cause?
toxicosis
tick paralysis
most importantly, ticks are vectors of disease:
viruses
bacteria
Rickettsiae
protozoa