Organic Chemistry II Exam 1: Chapter 14 "Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes"
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Conjugation
This occurs whenever p orbitals can overlap with three or more adjacent atoms. For example, the p orbital at the allylic position in relation to the double bond
Delocalize
Having three or more p orbitals on adjacent atoms allows p orbitals to overlap, allowing the electrons to do this
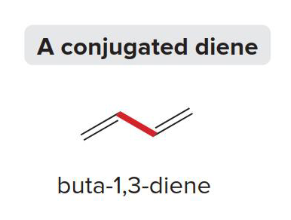
Conjugated Diene
This type of diene has pi bonds (p orbitals) with electrons that are able to delocalize due to overlap (aka, two double bonds joined by one pi bond). The electron rich area is spread out throughout the entire system
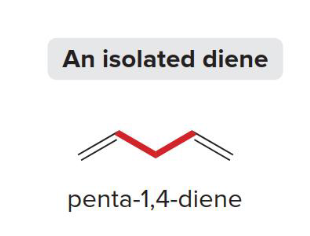
Isolated Diene
This type of diene has pi bonds (p orbitals) with electrons that are not able to delocalize due to the pi bonds being too far apart and separated by at least one sp3 carbon. The electron rich areas are localized in the pi bonds.
Conjugation (p orbital overlap)
In an allyl carbocation, _______ stabilizes the molecule and makes it more stable by lowering the overall energy
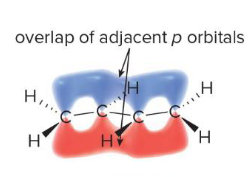
Delocalizes
Conjugation ________ electrons, creating resonance structures that increase stability
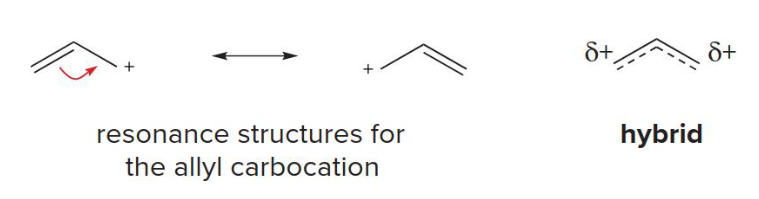
2nd
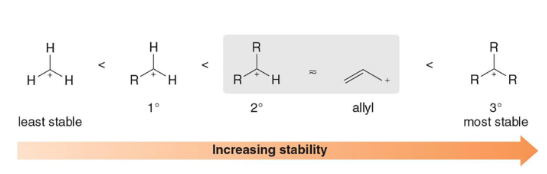
The stability of an allyl carbocation (delocalized) is comparable to a more highly substituted ___ degree (localized) carbocation
Resonance
Three Atom “Alyll” System: X=Y-Z*
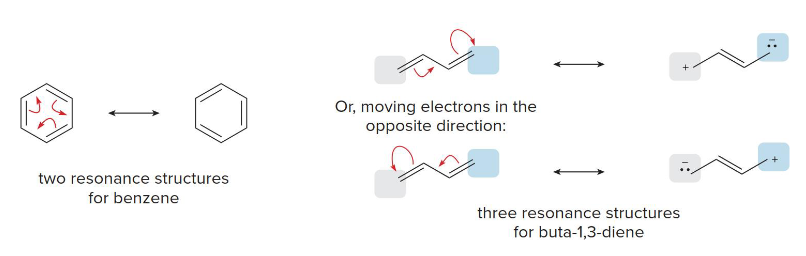
Conjugated Double Bonds
Cations Having a Positive Charge Adjacent to A Lone Pair
Double Bonds Having One Atom More Electronegative Than theT Other
These are all common examples of what?
Three Atom “Alyll” System: X=Y-Z*
This is an example of what kind of resonance system?
( [*] can be a radical, charge, or lone pair)
![<p>This is an example of what kind of resonance system?</p><p>( [*] can be a radical, charge, or lone pair)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ce5c052-3c43-4fe9-9771-d99fd0a14b23.png)
Conjugated Double Bonds
This is an example of what type of resonance system?
Cations having a positive charge adjacent to a lone pair
This is an example of what type of resonance system?
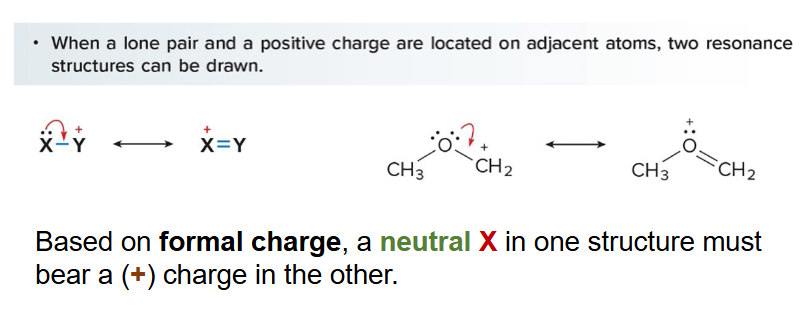
Double Bonds Having One Atom More Electronegative Than the Other
This is an example of what type of resonance system?

Hybrid
This resembles the most stable resonance structures
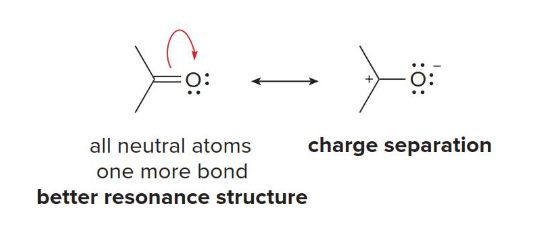
bonds; charges
The first rule of relative stability of resonance structures: Resonance structures with more (bonds/charges) and fewer (bonds/charges) are better
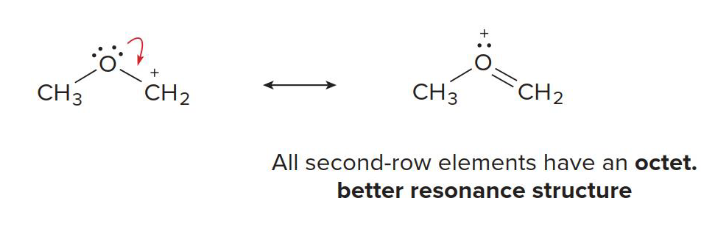
octet
The second rule of relative stability of resonance structures: Resonance structures in which every atom has an _____ is better
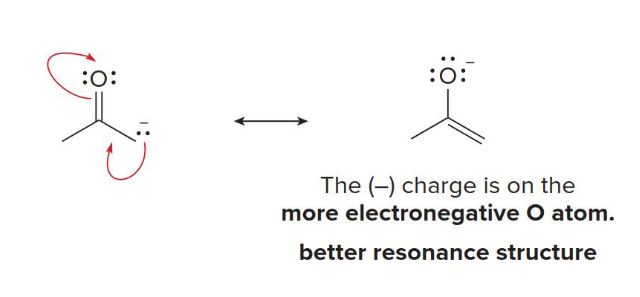
negative
The third rule of relative stability of resonance structures: resonance structures that place a _______ charge on a more electronegative atom are better
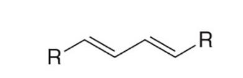
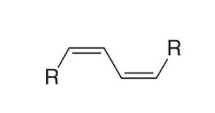
double trans bonds (Trans, trans-1,3-diene / (E,E)-1,3-diene)
This image is an example of a diene with (double trans bonds/double cis bonds/one trans, one cis bond) conformation
double cis bonds (cis,cis-1,3-diene / (Z,Z)-1,3-diene)
This image is an example of a diene with (double trans bonds/double cis bonds/one trans, one cis bond) conformation
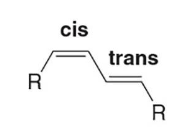
on cis, one trans bond (cis,trans-1,3-diene / (Z,E)-1,3-diene)
This image is an example of a diene with (double trans bonds/double cis bonds/one trans, one cis bond) conformation
rotation
The switch between s-cis conformation and s-trans formation occurs from _________ around the C-C bond that joins the two double bonds
conjugated
Four features distinguish _______ dienes from isolated dienes
The C-C bond joining the two bonds is unusually short
They are more stable than similar isolated dienes, and release less energy when broken
Some reactions of conjugated dienes are different from reactions of isolated double bonds
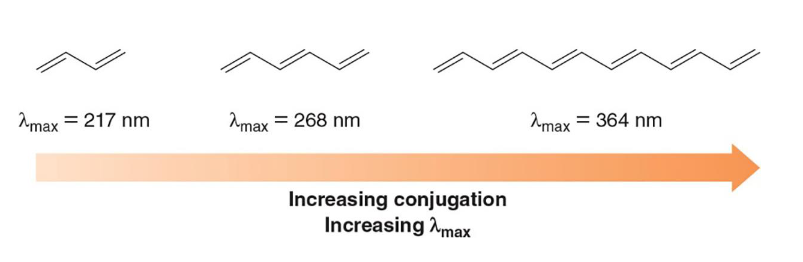
Conjugated dienes absorb longer wavelengths of ultraviolet light
shorter
A bond between two sp2 C bonds is (shorter/longer) than a bond between two sp3 C bonds

more
Conjugated dienes are (more/less) stable than isolated dienes, and less energy is released when they’re broken
less
In electrophilic addition of H-BR in isolated dienes, H bonds to the ______ substituted carbon and Markovnikov’s rule is followed
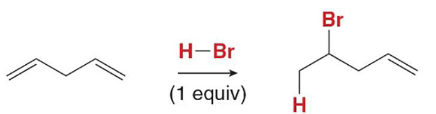
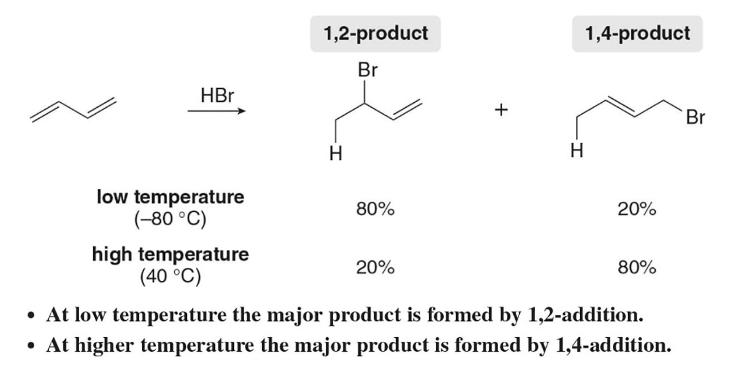
two (1,2 and 1,4 product)
In electrophilic addition of H-BR in conjugated dienes, ____ products are created. The amount of each formed depends greatly on reaction conditions
Diels-Alder Reaction
An addition reaction between a 1,3-diene (cis) and an alkene (dienophile) to form a new six membered ring. Often used to used to create steriods
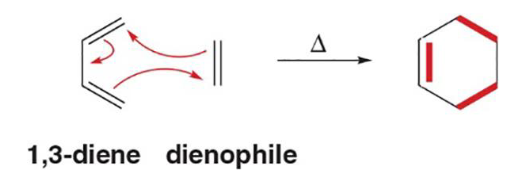
s-cis
S-trans 1,3-dienes are very unreactive in Diel's-Alder reactions, and must be configured to ______ first
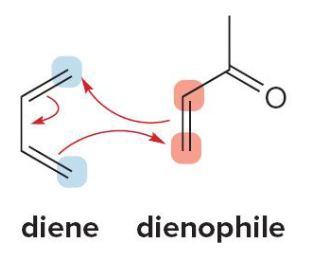
Dienophile
Electron withdrawing substituents in the (dienophile/diene) increase the reaction rate because it acts as an electrophile
Nucleophile
electron rich entities that donate electrons
Electrophiles
Electron deficient entities that seek to accept electrons
nucleophile
In a Diels-Alder reaction, diene acts as the (nucleophile/electrophile)
electrophile
In a Diels-Alder reaction, dienophile acts as the (nucleophile/electrophile)
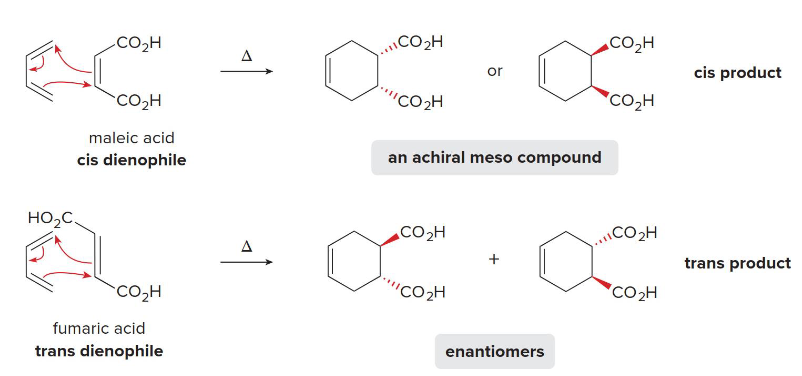
T
The stereochemistry of a dienophile is retained (T/F)
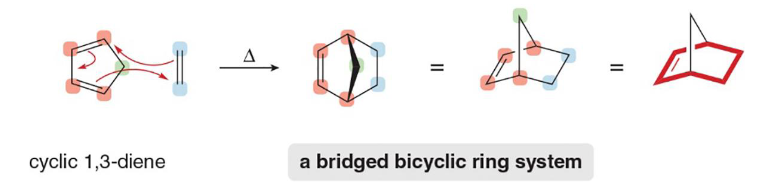
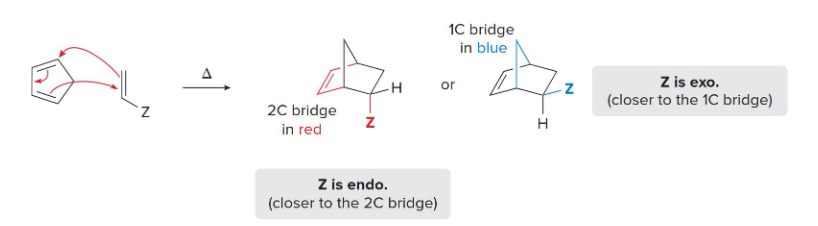
bridged
In a __________ ring system, one non-adjacent atom is above the two rings and shared

endo
In a bridged ring system, (endo/exo) product is preferred and energetically favorable
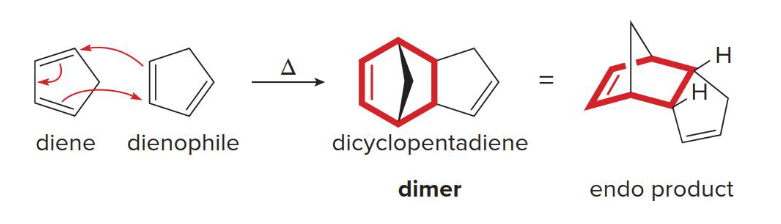
T
1,3-cyclopentadiene readily undergoes Diels-Alder reaction with itself, and undergoes retro Diels-Alder reaction when heated (T/F)
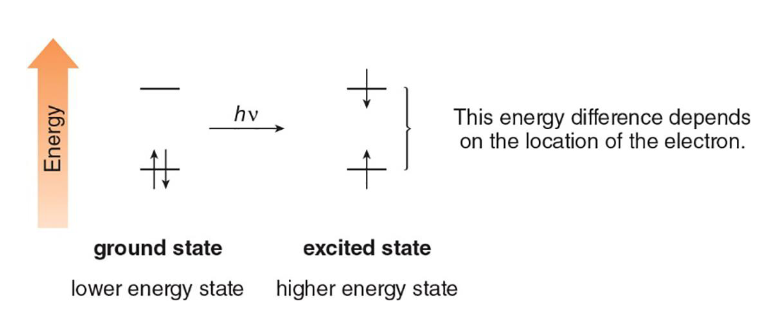
ultraviolet
The absorption of this type of light by a molecule can promote an electron from a lower electronic state (ground) to a higher one (excited)
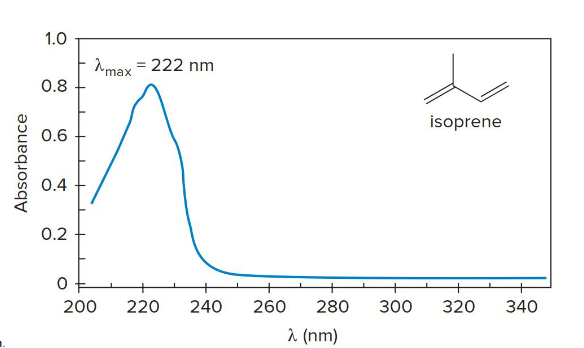
UV spectrum
A plot of the absorbance of UV light versus wavelength.
conjugated
When molecules have 8 or more __________ pi bonds, the absorption shifts from UV to visible region (thus giving off colors, like lycopene which absorbs all colors but red, giving tomatoes their color)