Lipogenesis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is lipogenesis?
The process of synthesizing triglycerides and fatty acids from smaller precursors
What are triglycerides and their structure?
What: Primary form of energy storage in animals
Structure: 3 fatty acids esterified to a glycerol backbone
Where does lipogenesis occur?
Liver and adipose tissue during fed state (after meal)
What are the 5 steps in lipogenesis?
Glucose metabolism and acetyl-CoA production
Cytoplasmic Acetyl-CoA formation
Formation of Malonyl-CoA
Fatty acid synthesis
Triglyceride assembly
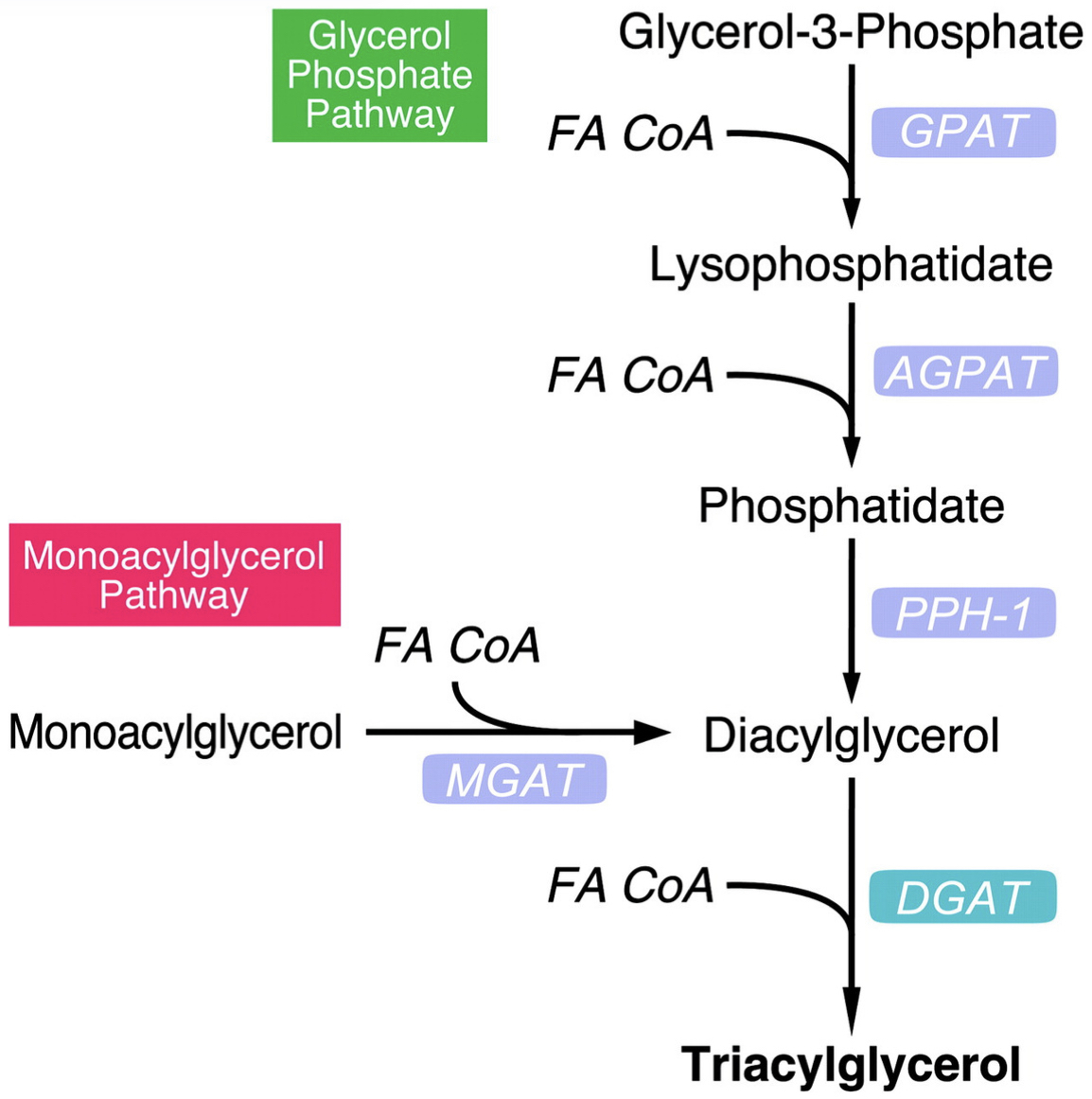
Triglyceride Assembly
How are FA activated
Forms
How is triglycerides formed
How are TGs stored
How are FA activated: By CoA
Forms: Fatty acyl-CoA
How is triglycerides formed: Glycerol-3-phosphate derived from glucose metabolism is esterified with fatty acyl-CoA
How are TGs stored: In lipid droplets within adipocytes or exported as VLDL from the liver
Regulation of Lipogenesis
How is it activated?
Activated by:
Insulin because it promotes
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity, glucose uptake and glycerol-3-phosphate availability
High carbohydrate diets because it increases glycolysis and Acetyl-CoA availability
Citrate since it is an allosteric activator of ACC
Regulation of Lipogenesis
How is it inhibited?
Inhibited by:
Glucagon and epinephrine due to cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC
Long chain fatty acyl-CoA
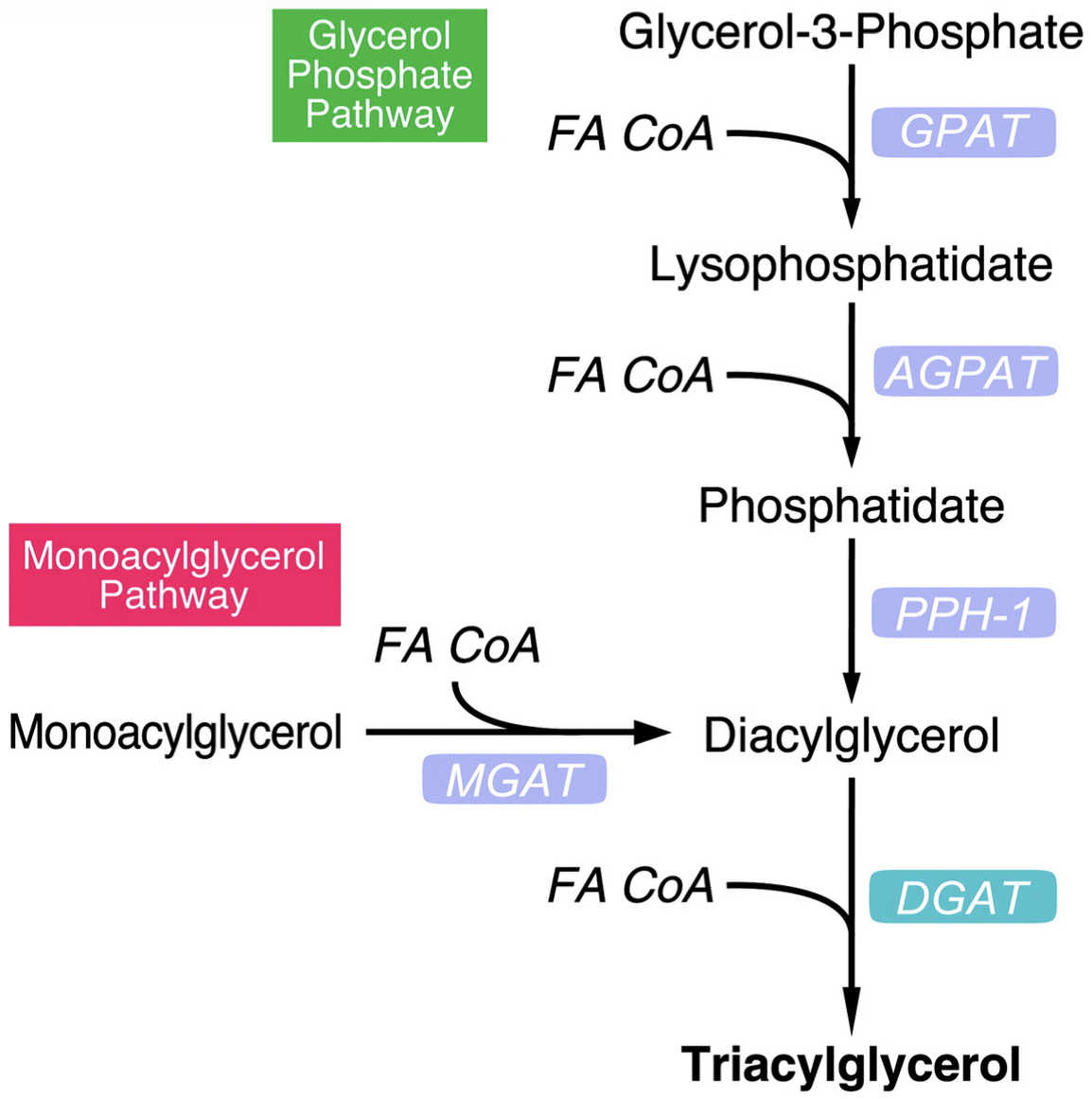
The process
The process