3.3.3 Economies & diseconomies of scale
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Costs in the long run are explained by economies & diseconomies of scale
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
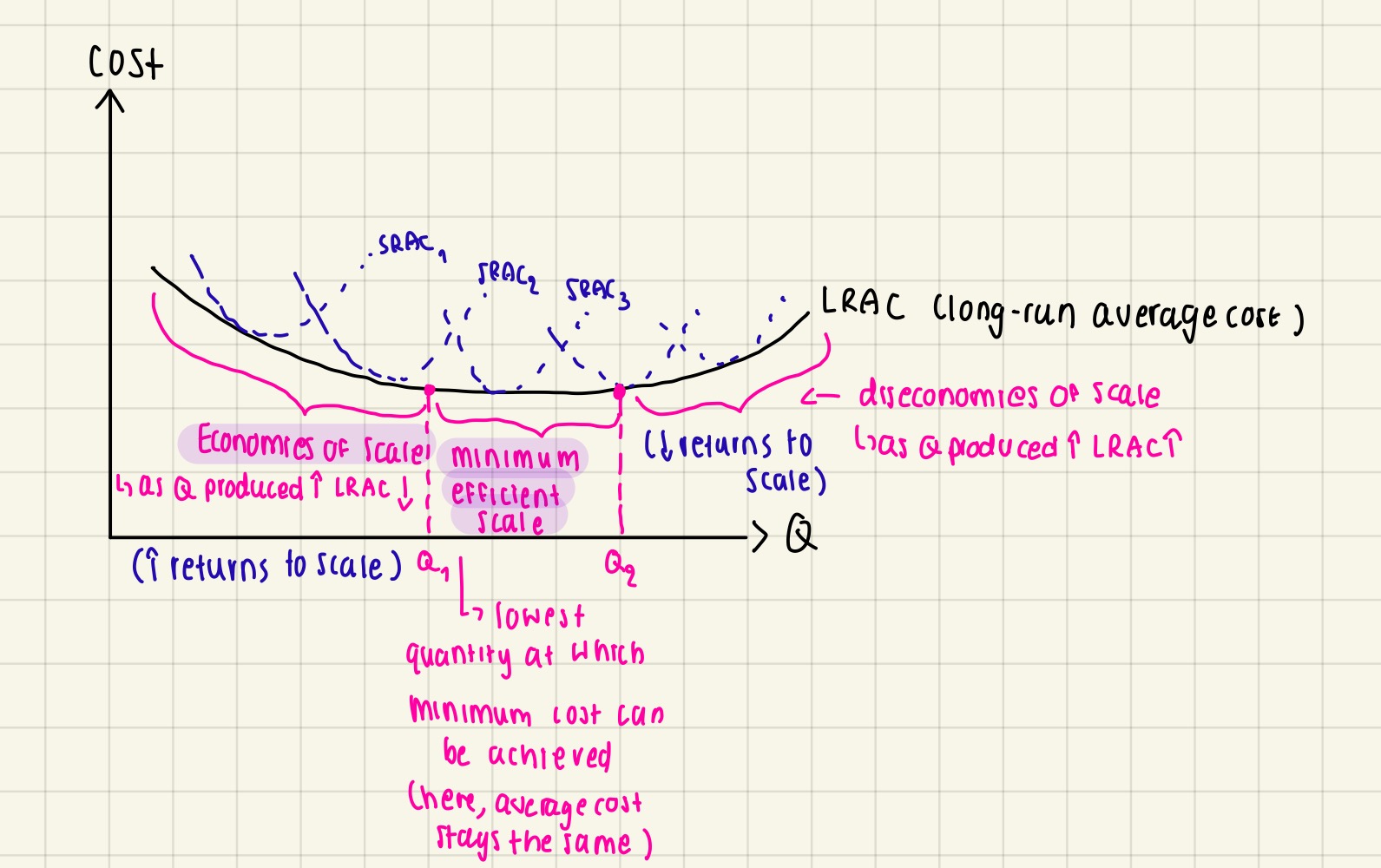
Graph explaining how economies & diseconomies of scale make up the LRAC graph (not important, don’t memorise the graph)
Once AC starts to increase, entrepreneur realise he might increase more fixed factors to reduce average cost
Therefore, new set of factors of production creating new SRAC
(Don’t have to memorise this)
When output increases more than input (due to efficiency - ie. Labour) → increase returns to scale
But a further increase in input → leads to inefficiency → less output produced compared to the input → decrease returns to scale
Types of economies of scale: Distinction between internal & external economies of scale
Internal economies of scale = factors which are improvement in production process / factors of production (ie. Better labour / machineries) resulting in LRAC decrease, changes in LRAC occur only within an individual firm
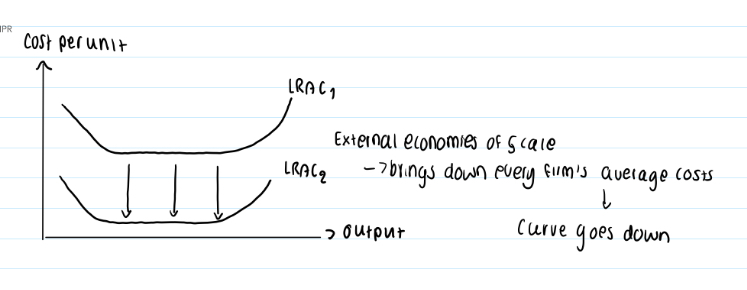
External economies of scale = factors in improvement in factors about industry / environment (ie. Regulation, location with good infrastructure) benefiting all firms in the industry when an industry as a whole grows → brings down every firm’s average costs within the industry → curve goes down
Types of internal economies of scale
Technical = large firms use bigger scale machinery → decrease average cost
Managerial = large firms employ specialist managers who are more productive
Financial = large firms can borrow loans at lower interest rates as they are seen as less risky by banks & investors
Purchasing = monopoly behaviour / negotiation power / can buy in bulk & gain discounts from suppliers
Suppliers do discounts to not lose this huge customer as the customer would likely to stay with them due to the discount → long term profit for the suppliers…
Marketing = Large firms can afford big advertisement → more people attracted to the good → more goods sold → can spread cost of advertisement over a greater volume of sales → lower average cost
Therefore, all of these: When increase quantity, these economies of scale (types of economies of scale) increases / sets to decrease LRAC
Take note that these factors all begin with ‘large firms…’ as increase in output can mostly be obtained by large firms only
Types of diseconomies of scale: internal diseconomies of scale & external diseconomies of scale
Internal diseconomies of scale = diseconomy of scale that happens because of firm’s own growth, factors that cause a single’s firm LRAC to increase as output increases
External diseconomies of scale = diseconomy of scale that caused without any action by the firm itself as it grows, factors that cause all firms in the industry’s LRAC to increase as their output increases
Types of internal diseconomies of scales (asked this more than external)
Poor-coordination
Large firms may be hard to manage if operating in different countries, different time zones → hard to coordinate → productivity decreases → AC increases
Demotivation
Large firms are impersonal & workers feel unvalued → workers feel alienated → productivity decreases → AC increases
Control
Hard to monitor productivity / quality of large workforce
Example of external diseconomies of scale
congestion - higher transport costs
External economies of scale (3 marker + mcq)
definition of external economies of scale
explain the data
graph resulting from external economies of scale
Diseconomies of scale (3 marker + mcq)
definition of diseconomies of scale
Poor-coordination point
Graph showing LRAC curve (as output increases, LRAC increases)