CH 5/6: Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What are the steps for naming alkenes?
1) recognize that the alkene(s) is the highest priority in the molecule
2) number the longest parent chain, which assigns the C = C as the lowest # possible.
2a) Lowest locant of the C = C is placed either before the parent name or before the “ene” suffix.
3) name the parent chain, which changes the “ane” to “ene”.
4) List the numbered substituents before the parent name in alphabetical order.
What is the definition of a locant in alkene nomenclature?
a single # representing the position of the C = C bond.
What do addition reactions do to alkenes?
adding 2 groups across the pi bond
What is the role of the pi bond (C=C) in electrophilic addition reactions? Clarification: this question relates to alkenes
acts as an electron pair donor (base/Nu).
What is hydrohalogenation?
the addition of a H atom and halogen across a pi bond
What does Markovnikov's Rule state regarding hydrohalogenation?
Hydrohalogenation is regioselective, so H atoms tend to go on the less substituted carbon, while the halogen tend to go on the more substituted carbon.
What happens if an alkene is not symmetrical during hydrohalogenation? What determines the major product?
Two isomer products form. Markovnikov rule determines the major product.
If an alkene is symmetrical, then the reaction will produce ___ product.
one
For hydrohalogenation, the reaction prefers a ______ carbocation . Therefore, a ________ carbocation is preferred over a _________ carbocation.
stable; tertiary, secondary
An alkene reacting with a strong acid (HBr, HCl, and HI) indicates the product will be ___________ addition.
Markovnikov
An alkene reacting with a strong acid (HBr, HCl, and HI) and a peroxide (ROOR) indicates the product will be ____-___________ addition.
anti-markovnikov
For radicals, they prefer more/less substituted carbocation.
more
Peroxide (ROOR or H2O2) are ____ reactive and generate ________. They cause an ____- markovnikov product.
very, radicals; anti
What is the stereochemistry of hydrohalogenation reactions?
racemic mixture
What are the mechanism steps for hydrohalogenation reactions?
1) protonation —> pi bond attacks the H atom of H—X (HBr, HCl, and HI)
2) most substituted carbocation intermediate forms and halide ion (Cl-, Br-, and I-) attacks the carbocation
3) haloalkane forms
What is acid-catalyzed hydration?
Markovnikov addition of H atom and -OH ion across pi bond
alkene reacting with diluted sulfuric acid (H2SO4) results in a ___________ addition product.
markovnikov
Acid-catalyzed hydration needs ___-____________ acid as a catalyst, which are _____, _____, and ____.
non-nucleophilic, H2SO4, H3PO4, TsOH
What is the mechanism steps for acid-catalyzed hydration?
1) protonation —> alkene attacks the H atom of H3O+ (hydronium ion)
2) carbocation intermediate forms and H2O attacks the carbocation
3) deprotonation —> e- pair from the oxygen atom of H2O attacks the H atom of oxonium ion
4) alcohol product forms
What is the stereochemistry of acid-catalyzed hydration?
If a NEW chiral center is forms, a racemic mixture forms.
What is an oxymercuration-demercuration reaction?
Markovnikov addition of H and -OH in an anti-fashion and w/o rearrangement
What does adding atoms in an anti-fashion mean?
one atom is wedge while the other atom is dash
What is a hydroboration-oxidation reaction?
Anti-Markovnikov addition of H and OH added in a syn fashion and w/o rearrangement
What does adding atoms in an syn-fashion mean?
both atoms are either dashed or wedged
What is catalytic hydrogenation?
addition of H2 across a pi bond
Hydrogenation requires a _____ catalyst.
metal
Hydrogenation is a _____________ reaction, which only results in a ___ addition product.
stereospecific, syn
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
it does not dissolve in solution, such as Pt or Pd metals
What is a homogeneous catalyst?
it does dissolve in solution, such as using a ligand with a metal
What is a halogenation reaction?
anti-addition of X and X across a pi bond, but is only practical with Cl2 and Br2
Halogenation uses a _______________ solvent, which are either ______ or ____.
nonnucleophilic, CH2Cl2 or CCl4
What is the mechanism steps for halogenation? Hint: similar to epoxides under acidic conditions
1) Alkene attacks bromide 1 of the molecular bromine, bromide 2 is kicked out, and bromide 1’s e- pair attacks the more substituted carbon of the alkene, forming a bridged bromonium ion.
2) Bromide ion attacks the backside of the more substituted carbon.
3) Anti-addition product forms.
What is a halohydrin reaction?
Markovnikov addition of X and OH in an anti-fashion
Why does water act as a Nu over the bromide ion in halohydrin?
there are more water molecules than bromide ions, so water outcompetes the bromide ion for the bromonium ion
What is the mechanism steps for halohydrin reactions?
1) Alkene attacks bromide 1 of the molecular bromine, bromide 2 is kicked out, and bromide 1’s e- pair attacks the more substituted carbon of the alkene, forming a bridged bromonium ion.
2) e- pair from the oxygen of H2O attacks the most substituted carbon.
3) deprotonation —> e- pair of O atom of H2O attacks attacks the H atom of the R-OH2+ (oxonium ion).
4) anti-addition product forms
What is an anti-dihydroxylation reaction?
anti-addition of 2 OHs across pi bond involving a 2-step process: epoxidation and hydrolysis
What reagent is used for the epoxidation step in anti-dihydroxylation?
peroxy acid (RCO3H)
What is the mechanism steps for anti-dihydroxylation reactions?
1) epoxidation —> look at the image
2) protonation —> e- pair of epoxide ring attacks the H atom of the H3O+ (hydronium ion)
3) e- pair of the H2O attacks the least substituted carbon and one of the O atom’s bond breaks
4) deprotonation —> H2O attacks the H atom of the R—OH2+ (oxonium ion)
5) anti-addition product forms
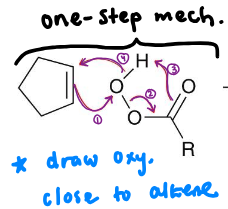
What is a syn-dihydroxylation reaction?
syn-addition of 2 OHs across pi bond involving a 2-step process: addition of OsO4 and reduction
Why is KMnO4 preferred over OsO4?
KMnO4 can be used under mild condiions while OsO4 is expensive and toxic.
What are the steps for naming an alkyne?
1) Identify that alkyne is the highest priority group in the molecule. Note: alkynes and alkenes have = priority.
2) Number the longest parent chain that assigns the alkyne the lowest number
3) Name the parent chain, changing -ane to -yne
3a) Place the locant before the parent name or before the -yne suffix
4) Name the substituents
5) List the substituents before the parent name in alphabetical order
Why is acetylene a strong acid? How does it relate to terminal alkynes?
Despite the fact that nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon, acetylene’s hybridization has more s character, making it more acidic.
The more s character, the more acidic the alkyne.
How can you turn acetylene from a strong acid to a weak base (acetylide ion)?
Deprotonation by strong bases such as NaNH2 or NaH
How can you create an alkyne?
alkyl (geminal or vicinal) dihalide reacting w/ a sB via E2
Why is 3 (excess) NaNH2 needed for terminal alkynes?
shifts the equilibrium toward the elimination products
rxn can go to completion
What is needed to produce neutral alkyne?
aqueous workup, using water
what is alkylation of acetylide (or alkynide ion)?
alkynide ion reacting w/ a primary or secondary alkyl halide via SN2
acetylenic alcohol formation mech
1) R’ — C(triple bond)C (acetylide ion) attacks the R2C=O (carbonyl carbon)
2) alkoxide ion forms
3) protonation —> alkoxide ion attacks the H atom of H3O+ (hydronium ion)
4) acetylenic alcohol forms
acetylenic alcohol formation w/ aldehyde
secondary alcohol
acetylenic alcohol formation w/ ketone
tertiary alcohol
How do addition reaction of alkynes differ from alkenes?
exothermic rxn
Depending on the reagent:
pi bonds become 2 sigma bonds or 4 sigma bonds
1-2 molecules may be added
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes Mechanism
1) Alkene attaches to metal catalyst surface. Hydrogen atoms attach to metal catalyst surface.
2) protonation —> bond of the C atom attacks the H atom and bond of H atom attacks the metal catalyst surface (2x)
3) cis alkene forms via syn addition
4) protonation —> bond of the C atom attacks the H atom and bond of H atom attacks the metal catalyst surface (2x)
2) alkane forms
What reagent is used for reducing an alkyne to a cis alkene?
H2 and Lindlar’s catalyst
What reagent is used for reducing an alkyne to a trans alkene?
Na (s) and NH3 (l)
Dissolving Metal Reduction
1) Nu attacks —> sodium atom attacks the carbon atom of the alkyne and the alkyne homolytically splits
2) radical anion intermediate forms and protonation —> radical anion attacks the H atom of the ammonium
3) radical intermediate forms and sodium atom attacks the radical intermediate
4) anion forms and protonation —> anion attacks the H atom of the ammonium
5) trans alkene forms
Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes Mechanism
1) bond of the strong acid attacks the alkyne and protonation —> alkyne attacks the hydrogen atom of H—X
STOP HERE IF IT IS ONLY HX reagent. CONTINUE IF IT IS EXCESS HX reagent.
2) protonation —> alkene attacks the hydrogen atom of H—X, halogen is kicked out
3) carbocation forms and halide ion attacks the carbocation
4) dihalide forms on the most substituted carbon and dihydrogen forms on the least substituted carbon
What are the 2 hydration mechanism of alkynes?
1) mercuric ion-catalyzed hydration
2) hydroboration-oxidation
What is reagents are used for the mercuric ion-catalyzed hydration?
H2SO4, H2O and HgSO4
What is mercuric ion-catalyzed hydration of alkynes?
Markovnikov addition of H and OH involving the formation of an enol intermediate and keto-enol tautomerization (using hydronium ion and water)
How does hydroboration-oxidation differ for alkenes and alkynes?
Alkynes: formation of enol, tautomerization of enol into an aldehyde for terminal alkynes) or ketone (for internal alkynes)
What is tautomerization?
structural isomers that can interconvert
Tautomerization is ____-catalyzed.
base (-OH)
If the reagent is excess X2, then what is the product for a halogenation reaction of alkynes?
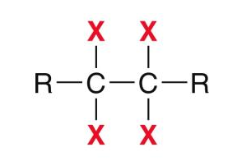
If the reagent is one equi. of X2, then what is the product for a halogenation reaction of alkynes?
major product: trans alkene
minor product: cis alkene
What is the purpose of NaH and NaNH2?
deprotonation