AP HUG Unit 6 Vocab/Concepts
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Urbanization
The creation and movement of people into cities
Processes that drive urbanization
Transportation
Communication
Population growth
Migration
Economic development
Government policies
Government factors that affect urbanization
Safety
Good schools
Accessible transportation
Entertainment options
Cash grants
Rebates
Tax credits
Sustainability issues of urbanization
Environment
Urban/suburban sprawl
Resources/energy
Sanitation
Population pressure
Urban sprawl
The growth of cities outward or vertically, creating issues like a lack of greenery or traffic
Types of infrastructure
Communication systems
Roads, highways, public transportation
Airports, ports, railway hubs
Educational systems
Hospitals
Water and sewage systems
Electrical grids
Internet services
New urbanism
A counter to urban sprawl creating:
Mixed-use neighborhoods
Walkable areas
Residential areas confined to the sky instead of outward
More affordable housing
Use of public transportation
Aims for environmental sustainability
Positive effects of new urbanism
Ease of accessibility to services, recreation, and jobs
Increased sense of community
Less travel time and reduced traffic
Decreased energy/fuel use, decreased air pollution
Increased real estate values
Revitalization of urban landscapes
Preservation or conservation of parks
Curbing urban spawl through more efficient land use
Brownfields
Sites that have been abandoned and contain some level of environmental contamination
Greenbelt
Undeveloped and often plant-filled area around urban environment
Smart growth
Policies to preserve farmland by using land more efficiently and sustainably
Slow growth
Policies to preserve farmland by managing or limiting growth
Properties of the central city
Completely urban, typically older and built with the CBD
Suburbanization
The movement of people out of the central city into suburbs, beginning in America with the invention of the Ford Model T (suburbs now house 1/2+ of all Americans)
Suburb
A residential area typically outside of the central city, with population less concentrated but cities are still advanced
Ex: Thousand Oaks
Agricultural village
A village based on subsistence agriculture
Ex: Early Fertile Crescent villages
Social stratification
The birth of social classes
Leadership class
Makes decisions, becomes elite of agricultural villages as mediators
Five Hearths of Urbanization
Mesopotamia, Nile River Valley, Indus River Valley, Huang He and We River Valleys, and Mesoamerica
Site and situation
Site: What are the physical properties and resources of a place? Situation: What is happening or coming to a place? How is it connected to other places? (Both determine location of cities and trade)
Forward capital
A new capital moved symbolically and sometimes to encourage urban growth
Ex: Brazil’s capital moves from Rio de Janeiro to Brazilia
Properties of Greece
A collection of city-states
Cities built on an acropolis (mound where important buildings are like Parthenon)
Many agoras (market around acropolis)
Everything else outside of those 2 main areas
City-state
A city that also makes up a state, often with its own government
Properties of Rome
First civilization to really capitalize on infrastructure (by roads, sewers and aqueducts)
Cities have a forum (area in center of city, like a modern downtown)
Sunbelt Phenomenon
The movement of US industry and population from the northern states like Ohio to the sunbelt states like Mississippi and Louisiana
Gravity Model
A model predicting the degree of interaction and mobility of places based on their distance and population (can be political, religious, economic, etc.)
Christaller’s Central Place Theory
Central places have a hexagonal zone of influence
There are different orders of services, market areas, and thresholds
Not as applicable today, but still works in some areas
Assumes land is isotropic, there are many central places nearby, and business competition is even
Also assumes that resources, buying power, population, and transportation costs are evenly distributed
Hinterland
Rural area supported by central place
Edge cities
Cities on the edge of major urban centers, often attract visitors for entertainment purposes
Ex: Inglewood, Irvine, Anaheim
Exurb
Residential areas near the suburbs that house the wealthier people (sometimes gated communities, farther from the central city, and commuter zone)
Boomburb
Rapidly growing suburban cities, often different or more modernized than older suburbs
Range
How far people are willing to travel for a service
Threshold
The minimum amount of people a service requires to be profitable
Order of services
Levels of services that are classified by range and threshold
(Higher-order services like sports teams need larger populations)
Market/trade area
Region around a city that is dependent on the goods and services of that city
Rank-size rule
The 2nd-largest city has 1/2 the population of the largest city, then the 3rd-largest has 1/3, etc.
Ex: Germany’s city populations
Primate city
A city that has a much larger population than any others in the area, skewing the rank-size rule
Ex: Mexico City
Central business district
The primary area of economic activity, often referred to as “dowtown”
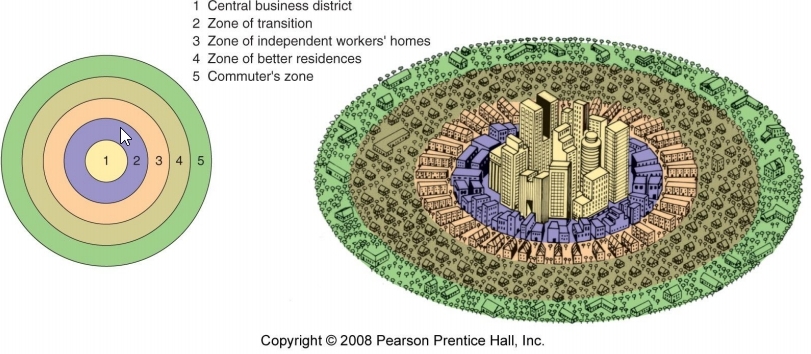
Burgess’s Concentric Zone Model
5 concentric circle zones, each wrapping around each other
Zones are:
CBD
Transition zone (mixed use)
Worker’s homes (poor people)
Better homes (rich people)
Commuter zone (often middle-class people)
No longer as accurate due to gentrification, economic change, and transportation change (only applies to American cities and is opposite of international cities)
Hoyt Sector Model
There are sectors like pizza slices surrounding the CBD
These sectors form along transportation routes
Each with their unique business or socioeconomic class (industrial areas are opposite rich areas)
Outdated due to being based on railcars and not accounting for the loss of the CBD’s importance

Functional zonation
The division of land into areas with different functions
Ex: Splitting of a large plot of land into one area for schools, one area for residential buildings, and another area for mixed use
Harris and Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
Not everything comes from original CBD, but uninterrupted urban development pops up in other CBD-like shopping areas, transportation hubs, etc. (may become CBD in future)
Ex: Denver

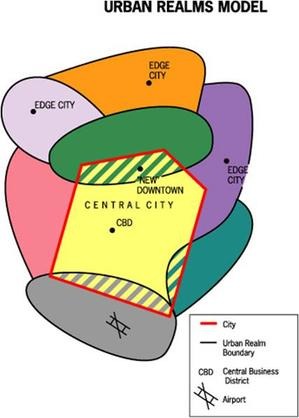
Urban Realms Model
Major city surrounded by overlapping edge cities (“Dowtown” may change)
Ex: LA
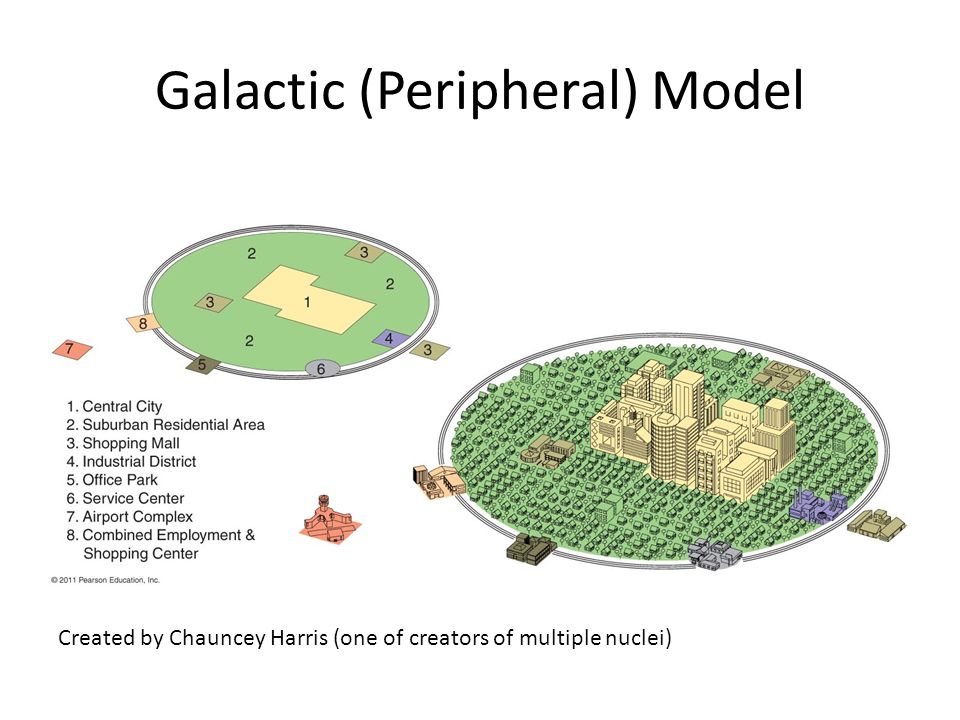
Galactic City Model
A combination of the Multiple Nuclei Model and the Urban Realms Model, including edge cities that appear after a gap for transportation and multiple areas of economic development (edge cities orbit central city)
Ex: Atlanta
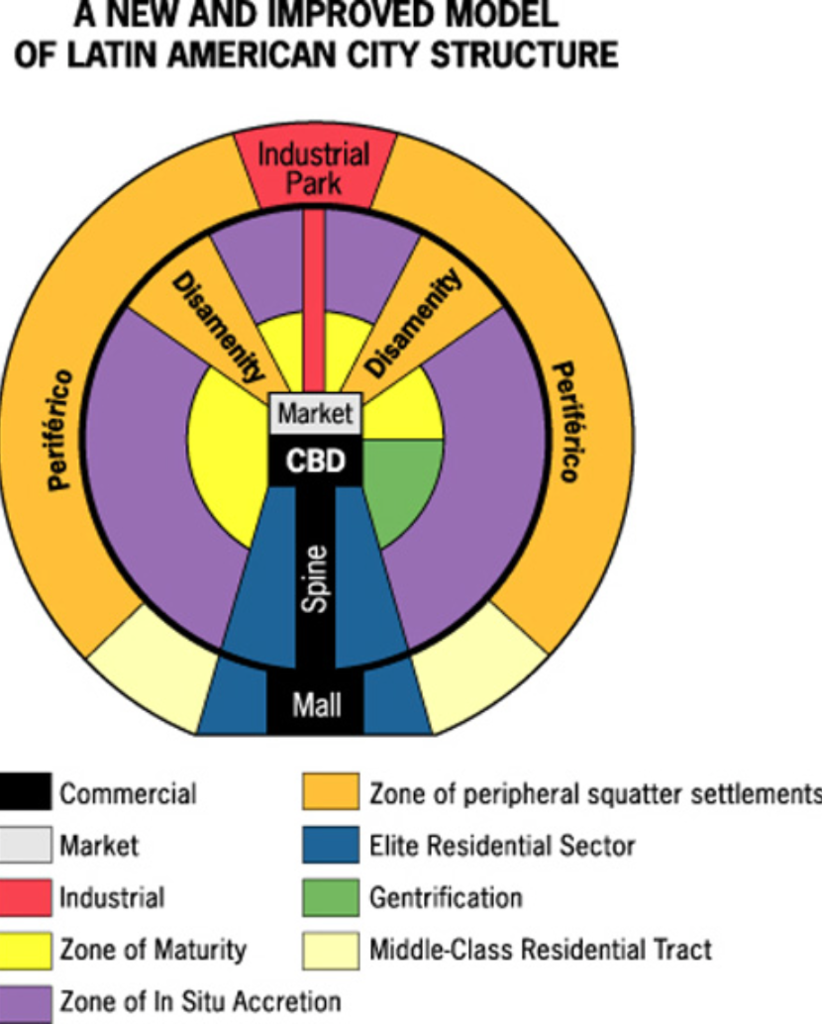
Griffin-Ford Model
Latin American cities have a CBD and mall district, with many other districts
High-income housing surrounding spine of mall district
Industrial area on the outskirts
Zone of maturity and/or area of gentrification borders the CBD/market
Outside zones of maturity and areas of gentrification is low and middle income housing (zone of situ accretion)
Disamenity zone across from spine
Periférico outside zone of situ accretion (squatter settlements)
Disamenity sector
The poorest part of the city in which the government cannot provide safety or resources (typically ruled by drug cartels or gangs)
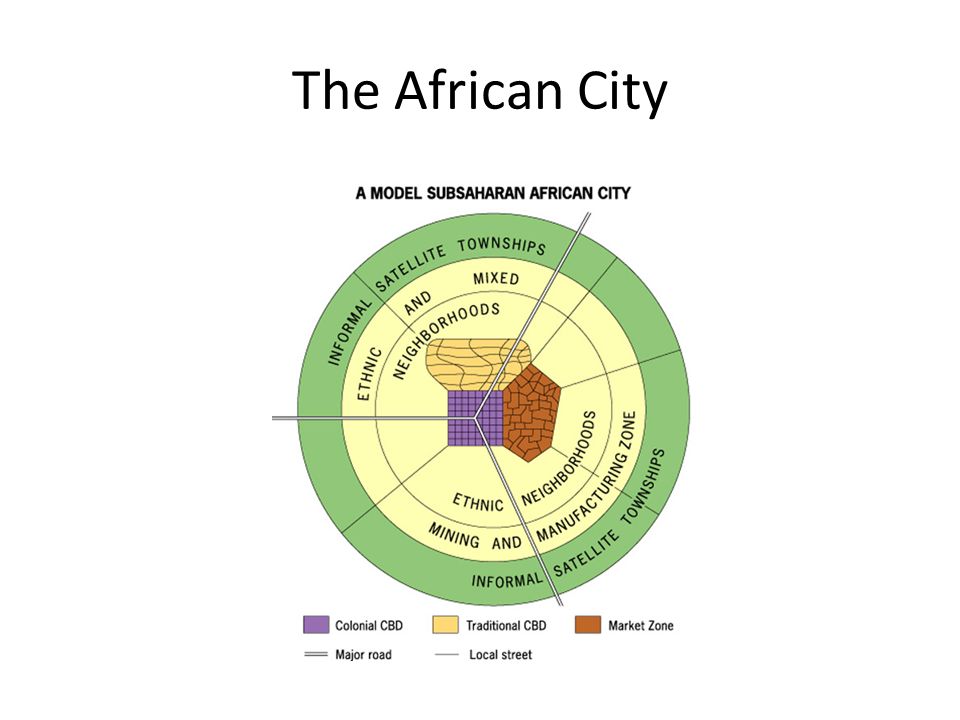
African City Model
City is a combination of concentric rings and sectors built along transportation lines
Rings: Ethnic neighborhoods, mining areas, squatter settlements
3 CBDs: colonial CBD, new CBD, and market (Infrastructure disappears as you move away)
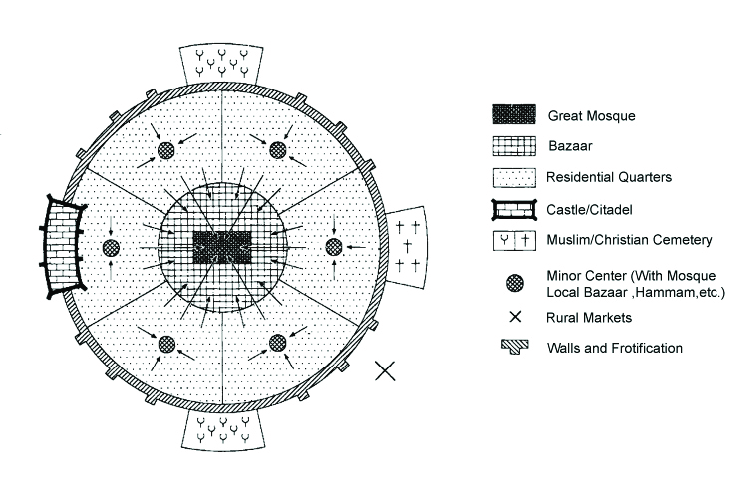
Middle Eastern City Model
Great mosque surrounded by bazaar
Bazaar sourrounded by residential quarters with many minor centers
Enclosed by walls/fortification with holes for Christian/Muslim cemeteries and castle/citadel
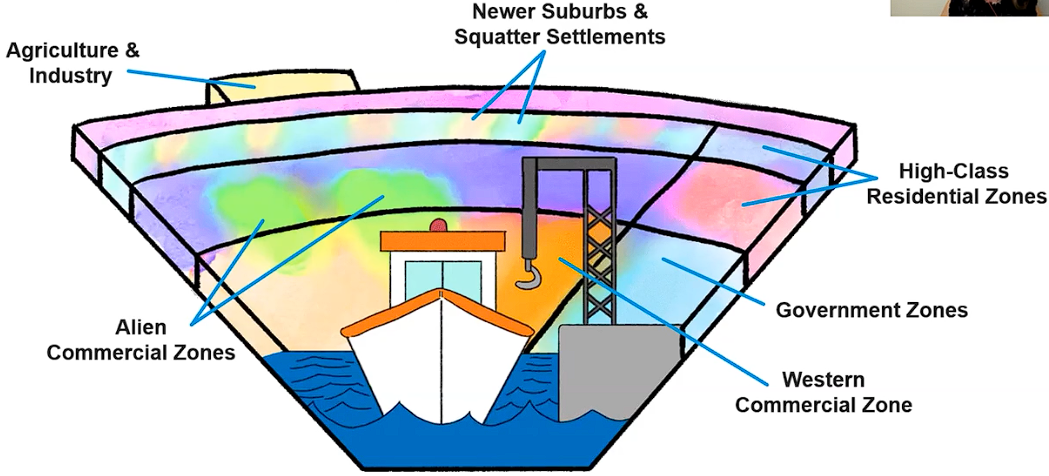
McGee Model
Port city model for SE Asian cities, with vectors of economic activity stemming from a semicircle port area/CBD
Alien commerical area (European/Western merchants)
Western commercial zone (Chinese merchants)
Government zones near commercial zones and port
High-income housing
Newer suburbs mixed with squatter settlements
Agriculture and industry on outskirts
Effect of age of exploration
Made port cities more important
Ex: Tokyo, Jakarta, Mumbai
Second Urban Revolution
Ties to Industrial Revolution and Second Agricultural Revolution
Cities began to exist near power sources like water and coal
Cities were disgusting and messy (slums, pollution, factories with minimal conditions)
People unionized and fought for better conditions
Borchard’s Epochs
Sail-wagon: Form entrepots (port cities) 1790-1830
Iron horse: Locomotive 1830-1870
Steel rail: Trains 1870-1920
Auto-air amenity: Planes, cars, etc. 1920-1970
High technology: Modern day 1970-present
Shantytowns/squatter settlements
Poor towns, with little or no regulation on boundaries and often hand-made homes and roofs with an informal economy (caused by rapid urbanization, demand for affordable housing, and failure to enforce land use policies)
Flaws of squatter settlements
Political
Land ownership
Infrastructure
Crime
Environmental
Pollution
Soil erosion
Social
Infrastructure
Medical care
Education
Core cities
Cities constantly made and remade
Commercialization
Making the central city pretty again
Redlining
Refusing loans to poor areas or target groups to force housing or business sales (illegal in US)
Blockbusting
Scaring white people by having other ethnicities that they dislike move into a neighborhood, causing them to move out and sell their homes (triggers white flight)
White flight
When white people move out of neighborhoods with more ethnic diversity, typically those with African Americans
Gentrification
When the homes of poor people are bought out and they are displaced, then developers improve the homes and sell them for a higher price (often makes it so that former residents cannot return)
Effects of gentrification
Positive:
Property value increase
Investment opportunities
Infrastructure
Architectural or aesthetic enhancement
Negative:
Uneven development
Tenants cannot afford higher price
Displacement of groups of people
Local businesses cannot support higher prices
Tear-downs
When houses are torn down to build newer ones, typically McMansions
McMansion
Houses built with an attempt to take up as much space as possible, typically in the suburbs after tear-downs (looks like multiple houses in one)
Micropolitan
10,000-50,000 people
Metropolitan
Greater than or equal to 50,000 people
Megacity
10+ million people
Metacity
20+ million people
Megalopolis
Cities connected by nonstop urban development
Ex: LA
World city
A city that functions at the global scale and runs the global economy
Ex: Tokyo, London, NYC
Networks used by global cities to influence the world
Manufacturing and trading networks
Transportation networks
Banking networks
Communication networks
Entertainment and media hubs
Governmental agencies
Spaces of consumption
Cities that are transformed into tourist attractions
Ex: Hollywood