FSM EOT
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
knowledge of a food service dietitian
nutrient requirements
food legislation, regulation and standards
food preparation (recipes)
food service systems (menu ordering, procurement, preparation, plating, distribution and ware washing)
methods of data collection (KPIs)
change mment
Skills of a food service dietitian
advocacy for pts through menu planning, procurement, mment
translate knowledge into food safety and nutrition guidelines
develop and assess recipes and menus
utilise meal mment systems
develop, implement and assess the results of quality audits
adapt written and verbal communication to audiences
activities of a food service dietitian
develop and analyse recipes
develop and analyse menus
monitor for the impact of changes
monitor the quality of services
develop training programs for staff
lease with key stakeholders
advocate for improved food services
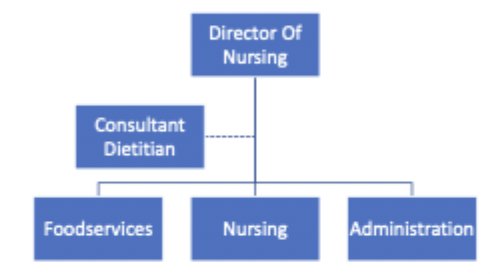
dietitian as consultant
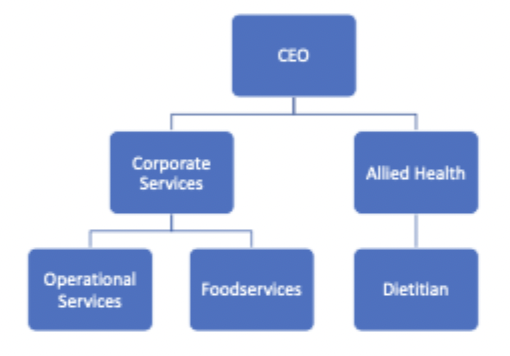
dietitian alongside
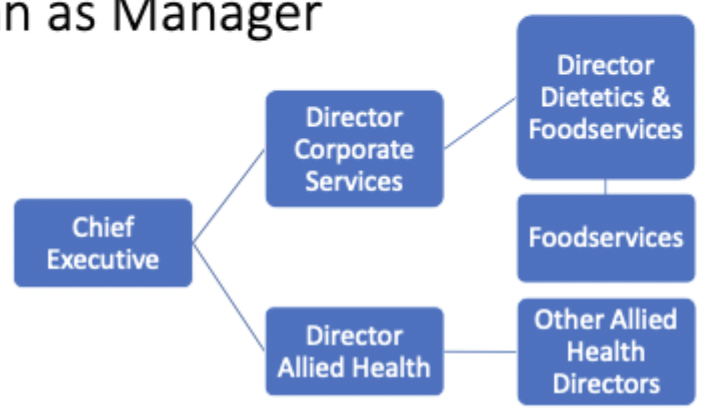
dietitian as manager
open vs closed system
open - interacts w environment
closed - do not interact w environment
systems thinking
key concepts of systems thinking
holistic approach
interconnectedness and interdependence
systems and subsystems
boundaries and environment
feedback loops
aims/goals/purpose of food system
produce safe nutritious meals of desired quality/quantity that meets client’s needs (social, cultural, medical)
happy/productive workforce
environmental sustainability
meet organisational and financial goals
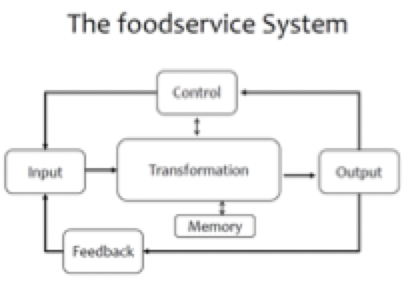
transformation
the processes that convert inputs unto outputs
mment functions - planning, organising, staffing, leading, controlling
functional systems - procurement/purchasing, preparation and production, distribution and service, hygiene and maintenance
linking processes - decision making, communication, training
inputs
human - labour, skills
materials - food, supplies
facilities - space, equipment
operational - money, time, utilities (electricity, water), info
outputs
meals - quantity (standardised recipes), quality (meets safety standards)
client satisfaction
client needs - cultural, social, medical, nutritional
staff satisfaction and performance
financial accountability
sustainability - procurement, waste, donation
financial - budget targets
control
aims
standards
standardised menus
policies/procedures
programs
contracts
food control plans
audits
external controls - contractor, laws, regulations, FSANZ
memory
records
financial
staff
forecasting
inventory
procurement
staff memory
IT programs
software - holds feedback, survey results, KPIs
feedback
assessment of food service system
internal - client feedback, performance measures, plate waste, order frequency, audits
external - food service regulators, supplier feedback, union
continuous quality improvement cycle
plan - identify problem
do - benchmarking, collect data
check - compare to other FS and predictions
act - what changes next?
external quality systems
food safety
national food standards - FSANZ
state legislation - food act (QLD) 2006
systems safety
national safety and quality health service standards (accreditation standards)
internal quality systems
controls, memory, feed back
production waste
client feedback
audits
KPIs
inputs, transformation, outputs
recruitment processes
staff training audits
staff surveys
food procurement contracts
food quality (ingredients)
HACCP
KPIs
food safety standards
budget
resources used in QLD to improve food services
FS best practice
FEEDS
food quality: what are you measuring
patient acceptance of food
quality of the food/meals
efficiency of system
safety of food - allergens, therapeutic, bacteria
how to test patient acceptance of food
acute hospital foodservice patient satisfaction questionnaire
resident foodservice satisfaction questionnaire
hospital food experience questionnaire
meal assessment tool
meal quality audit tool
plate waste there food o
other food service measures
accuracy and non-patient waste
therapeutic diet accuracy
meal accuracy
production waste
quality and efficiency
staffing efficiency
cost per meal
meals per hour or meals per FTE
total cost of the system
nutrition care process
ADIME
CQI - NCP - assessment
plan, do and check
data from surveys, admin data sets, epidemiological or research studies
KPIs
CQI - NCP - Diagnosis
act
dietitian identifies problem needing to be treated
CQI - NCP - int, M and E
occurs through change mment when you make int, plan for change, monitor change, evaluate outcome
CQI tools
patient satisfaction
resident satisfaction (aged care)
meal assessment tool
plate waste
Meal quality audit tool
basic functions of management
planing
organising - determine objectives, work needed?
staffing - recruitment and retention
directing and coordinating - decision making, communication, follow up
reporting - inform everyone through records, research, reports, audits, inspections
budgeting - planning, accounting, controlling
why do we need change
shift from hospital care to outpatient
reduced lengths of stay in hospital
aging population
changes in gov
improvement in tech, food ordering, equipment, delivery systems
increasing costs of food and energy
economic climate
geopolitical events
environment e.g. climate change
pathogens and disease
change to transport and infrastructure
workforce changes
regulation and legislation change - alleged labelling
key components of change mment
communication - explain reasons and benefits of change
training and support
stakeholder engagement
monitoring and feedback
Lewis model of change
unfreeze
outline changes
speak w mment
develop presentation materials
consider employee reactions
connect changes to company goals
emphasise your support
change
determine how to measure progress
allow for increased communication for staff questions
contact staff who need more help
create anonymous surveys to collect feedback
refreeze
develop incentives and rewards
implement training programs
praise employees
kotter’s 8 step change mment framework

Prosci change mment
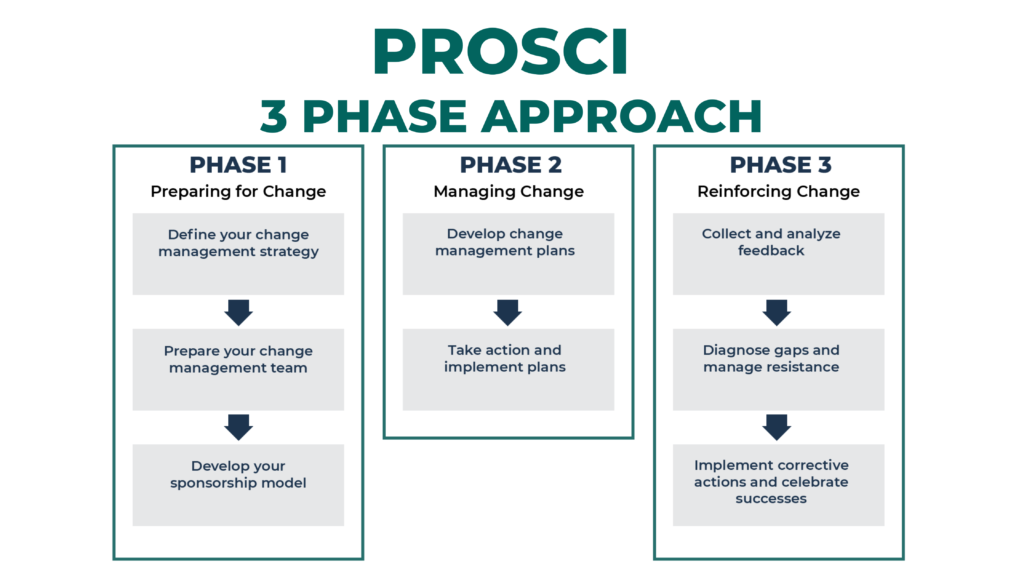

simple change management approach
phase 1 - prepare
understand why of change
plan for change
commence stakeholder engagement
phase 2 - manage
change resources
delivery change
monitor and adjust
phase 3 - sustain
assess change
embed change
monitor change
leadership theory; 5 dimension theory of leadership styles
a leader that can be flexible in
degree of control
concern for productivity
concern for people - clients and employees
structure
risk taken in decision making
attributes of successful FS manager - technical expertise and knowledge
standards, policies and procedures
process paperwork
manage work with resources allocated
environmental protection laws
political environment
marketing
CQI - surveys
work redesign, productivity, benchmarking
cost-containment measures
sustainability
disaster and emergency planning
cultural/generational diversity
attributes of successful FS manager - interpersonal skills
communication
empathy
understanding
ethical conduct
motivation
mentoring
trust
intelligence
share vision, goals, objectives
self-confidence
delegating
formal vs informal leader
formal - job title
informal - naturally forms
leadership styles
autocratic - unilateral decision making. effective in quick decision making but can lead to low morale of overused
democratic - e.g. participative leadership. encourages input from team members. fosters sense of ownership, can lead to higher job satisfaction, may slow down decision making
transformational - inspires and motivates team through shared vision and enthusiasm. focus on change and innovation, often leading to high levels of engagement and performance
transactional - system of rewards and punishments. effective in achieving short term tasks and maintaining routines. may not encourage creativity or long-term growth
laissez-faire - hands off approach, gives team members high degree of autonomy. can be empowering for self-motivated employees but may lead to lack of direction/accountability
servant - prioritises needs of team, focus on development and well-being. can build strong supportive relationships, can be less effective in high pressure situations
standard 3.3.3 for food premises and equipment
div 1 - interpretation and application
div 2 - design and construction of food premises
adequate space
can be cleaned and sanitised
reduces dirt, dust, pests
audit: windows sealed, self-closing doors, no holes for pests, storage space?
div 3 - floors, walls and ceilings
can be cleaned
can’t absorb grease, food particles
no water ponding
no harbourage of pests
audit: cracks/chips, wall joints sealed, cleanable materials?
div 4 - fixtures, fittings and equipment
no contamination
easily cleaned
no harbourage of pests
surfaces around can be easily cleaned
supply of hot/cold potable water?
div 5 - miscellaneous
enough storage w no contamination
toilets - ‘hands-free’ hand washing
food transport - safe food, can be cleaned
Workflow and functional areas
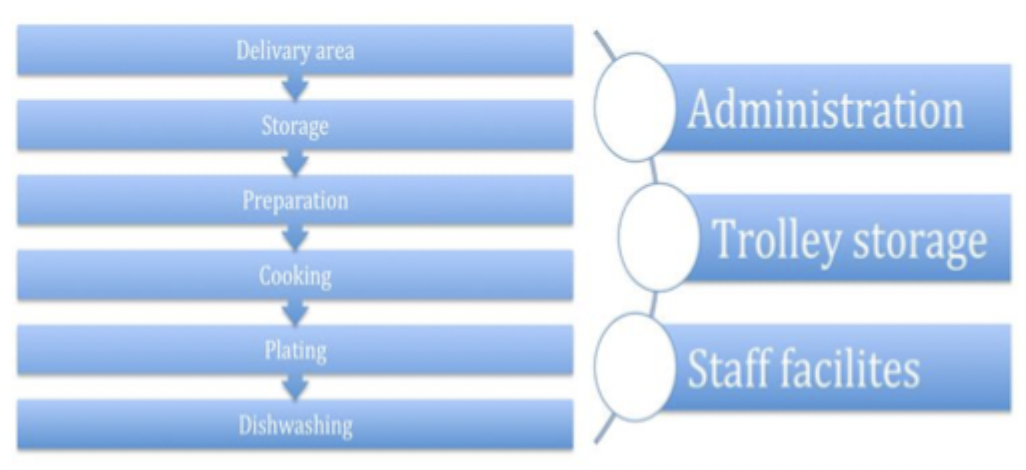
understand why we have workflow, seperate clean and dirty e.g. GCUH
workflow issues in different sized kitchens
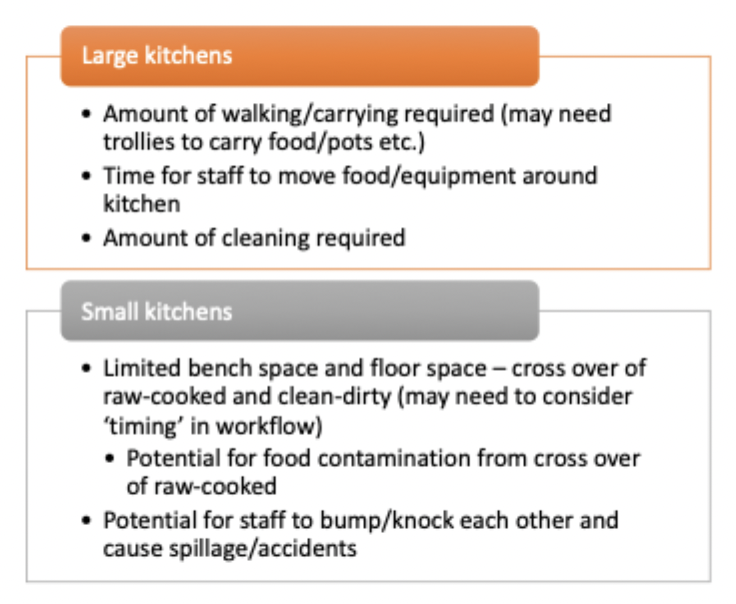
How are the menu, kitchen design and workflow related?
menu
standard recipes, production processes
ingredients and storage (dry, cold, frozen)
equipment
task delegation/flow
shift/break times
how does workflow influence food safety
receiving/delivery
storage
preparation
cooking
holding/plating
serving
cooling - leftovers, bacteria
reheating
packaging
distribution
equipment - cooking ovens
convection - <40 meals
commercial convection oven - smaller than combo
combination/combi oven - steams, up to 40 trays
equipment - alternative cooking items
induction heating/hob - like home stove
bratt pan - tilting fryer: shallow pan, poach, stir fry

oven w cooktop
salamander - grill

steam jacketed pans - like double boiler (soups, casseroles)

blast chiller - extend product life
plating equipment - warmers, chillers, shelves, bays for serving
food delivery - carts/trollies (can have hot cold side), retherm trollies
thermal dinnerware - keeps food hot for longer
hostess trolleys - bur lodge and regethermic (decentralised, rolled to ward to self-serve/serve at ward)
robotic trolley delivery
pot washer
dishwasher - pass through (short cycle times), flight (high volume, magnets for cutlery, different compartments)
production, plating and distribution systems table
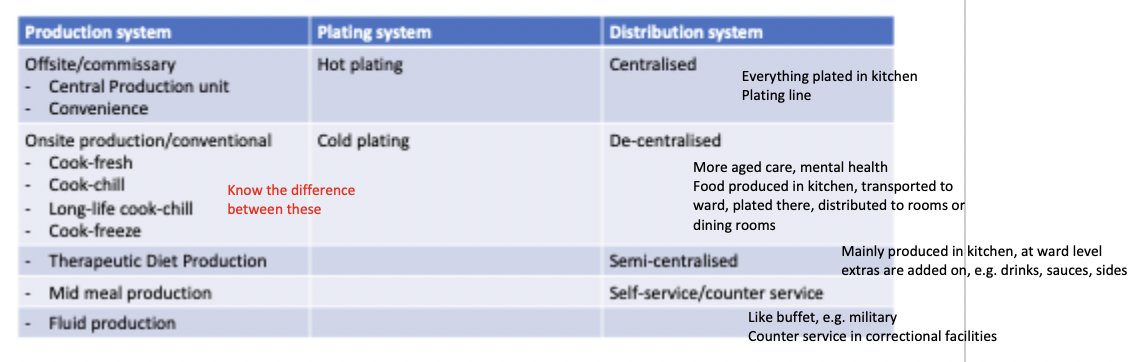
production systems
central - meals prepared for multiple facilities and transported
convenience - bought from supplier, heated etc. on site
cook-fresh - cooked fresh, served immediately
cook-chill - cook fresh, rapidly chilled <3C, can be held fro 5 days
long-life cook-chill - cook fresh, vacuum sealed before chilling. shelf life 20-45 days
cook-freeze - cook fresh, blast frozen to -20C. shelf life 12 months
therapeutic - big hospitals have seperate area - allergens, cultural, religious
mid meal
bought in preprepared - supplement w things on site
special diets maybe prepared on site
drinks prepared in ward pantry’s (tea, cordial…)
fluid
clear/full - portion packs cheaper
special reqr - e.g. ONS - purchased
instant formula - made in dedicated room (cross contamination)
plating systems
plating
hot - food cooked or reheated and put on plates hot
cold - plated cold, need cold environment, retherm trolley
distribution systems
centralised - food is plated in central area
decentralised - plated from bulk trolleys or servers onto plates in ward/ding room

semi-centralised - plated centrally, finished at ward (e.g. add toast so not soggy)
self service
mid meal - usually de centralised, from trolleys at ward pantry
room service - always hot-plates, could be cook-fresh, cook-chill or cook-to-order, centralised distribution
factors to consider when planning menu
external environment - gov, budget, laws, availability, seasons, suppliers, sustainability
internal - mment, labour changes, standards, size, staff
people - pt demographic, nut reqr, cultural
why plan menus
improve nut intake
predictability
labour
costs
budget
purchasing
maximise efficiency
variety, less repetition
types of menus
a la carte (restaurants, room service, cafeteria)
cyclic
week/fortnight
non-selective
selective - choice every meal
semi-selective - some choice, some fixed
single use - ramadan Christmas
menu standards - aged care
14 day min menu
35 choices
14 x full
21 easy to chew (at least 1 vegetarian choice every day)hot, cold and fortified breakfast every day
protein at all 3 meals
supplementation available
finger food available
fortified soup
moulds where possible
HPLE for wt mment residents
fish 3x per week
25-35g/d of fibre
allow input from residents
menu standards - acute long stay
min 35 hot main meals
choice of 3 main meals and 3 mid meals each day (at least 2 mid meals are substantial)
fortified hot cereal and soup
hot protein breakfast for all texture levels - full, easy to chew, minced moist, pureed
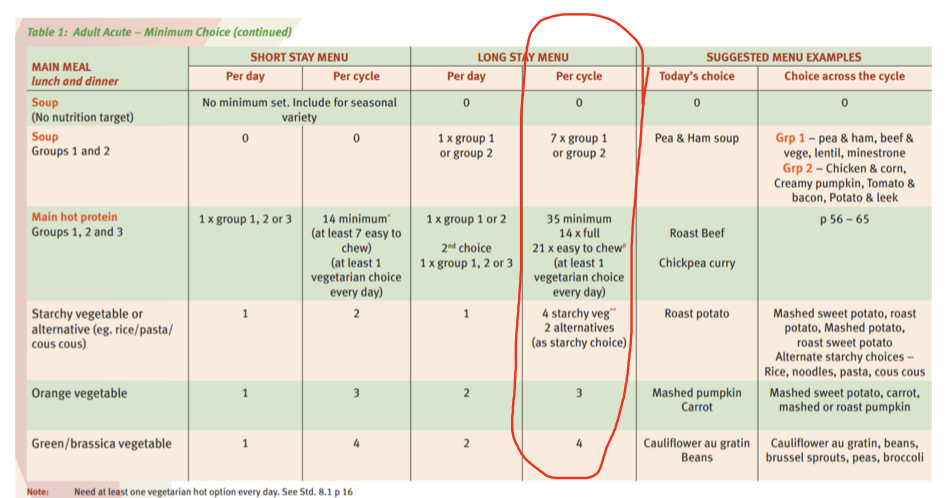
minimum menu choice - long stay adult acute (QHNSMM)
per cycle
7 soups
main hot protein
35 minimum
14 x full
21 x easy to chew
(at least 1 veg choice every day)
4 starchy veg (sweet/potato/mash) & 2 alternatives (rice, noodle, pasta)
3 orange veg
4 green/brassica veg (cauliflower, beans, Brussel, peas, broccoli)
why plan integrated menus
(includes common therapeutic diets w/in general menu)
more available for those w restrictions
supplies - less waste, storage
efficiency - less items, less time
less cost
assessing a menu
3 steps
verify info about menu and FS
verify info about people you are feeding
use appropriate tools to assess menu that meets standards/policies
QHNSMM
QH menu assessment tool
AGHE
therapeutic diet guidelines
menu analysis software - e.g. foodworks
DA food allergy intolerance menu assessment tool
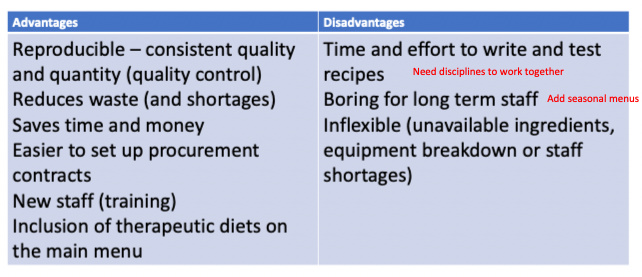
standardising recipes - advantages/disadvantages
standardising recipes - integrated vs non-int menus
int combines multiple diets - no added sugar, no added salt, HPHE, low fat (KJ), tex mod, high fibre, veg, gluten, lactose
steps to developing bulk standardised recipes
yield
weights (g) or measures (cup)
use easy figures - whole or half
standard abbreviations tsp, tbsp
list ingredients in order used
concise method
directions for serving
OR
watch cook
ingredients, quantity
procedures
equipment
go over w cook, change if needed
others cook w recipe, change if needed
mid meal groups
HPHE
LPHE
healthy snack
food safety program
hazards HACCP
food safety program needs to be audited
control reqr
storage, processing, packaging, distribution, disposal, recall
standard - food premise and equipment
layout reduces contamination
premise, fixtures, fittings, equipment, transport vehicles can be cleaned, water, ventilation, storage etc.
food safety program for vulnerable populations
must have documented and audited program
must be available on premise for staff
audited within 6 months of opening!
audits
staff
cleanliness
CCPs
support processes documented? - training, cleaning, pests, temps,
what is procurement
process for ordering
product info form PIF
process for receiving
inventory control
procurement - purchasing
ordering - identify product, characteristics (shelf life, delivery, size etc.), assess reqr, contracts
PIF - gives details: supplier, description, ingredients, country of origin, nutritional, allergen, shelf life
receiving - demo, correct product, storage
inventory control - FIFO, records in system, when stock reduced refill
FSP support programs in the tool

hour rule
0-2 hrs use immediately to fridge <5C
2-4 hrs use immediately
>4hrs throw away
military
dietitian role
production distribution
nut reqr
unique considerations
nut, FSM, therapeutic, education,
self-service, private contractors
reqr
PALs
gender
age
field kitchens, ration packs, allergies, culture, logistics, ration packs
correctional facilites
dietitian role
production distribution
nut reqr
unique considerations
menu planning, therapeutic, nut ed, FS
centralised or counter service (lower security)
meet basic needs, diet guidelines, mental health
cost effective, security levels, alc, Vegemite, coffee, bones, allergens, no luxury items
child care
dietitian role
production distribution
nut reqr
unique considerations
puree, solid
unique - growth level, iron, cultural, breast milk, high risk allergies, involve children in food prep
aged care
dietitian role
production distribution
nut reqr
unique considerations
nut reqr QHNSMM
unique - texture, malnt, dining room , aged care quality standards
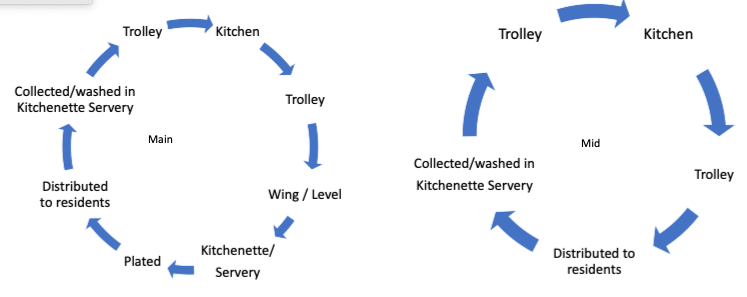
food service cycle main vs mid aged care
dysphagia
causes
incidence
nut impact
IDSSI and purpose
swallowing difficulty
stroke, cancer, ABI, Muscular sclerosis
hosp - ICU 7.9%
older pts/rehab - 50%
community 65+ 15-30% (lots of silent aspiration)
aged care 50%
reduced food intake
dehydration malnt
QoL
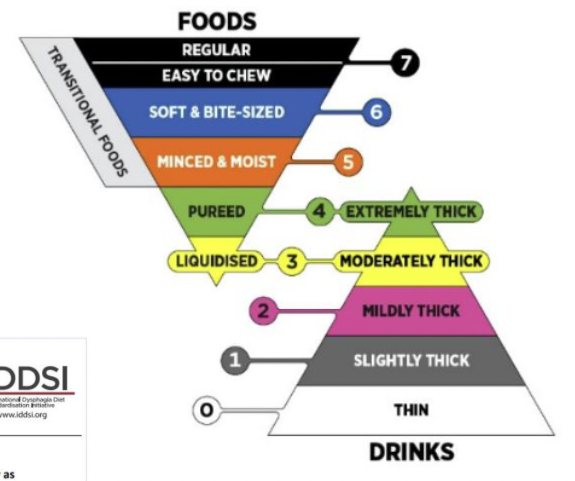
text-mod diets
standard initiative
IDDSI chart
test methods
spoon, fork, syringe flow
allergen labelling
ingredients
summary statement
warning statement - uncommon ingredient, warn of allergen chance
advisory statement
exemptions - glucose syrup gluten
food allergen mment in FS
identify - CCPs
assess
manage - CQI
audit
support programs - trainmen etc.
tips for sustainable health care
local produce, products
seperate organic, recyclable landfill
equipment low energy
minimise water usage, utilise grey water
menu planning - e.g. reduce meat