Med Imaging E2: skeletal part 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
what views on plain films are needed for joints, hands, or feet?
oblique (AP and lateral)
What would you use for evaluation of fine bone structure (esp. in skull, spine, pelvis, occult fx)?
CT scan
What would you use for evaluation of soft tissues like muscles, organs, ligaments, cartilage, spinal cord?
MRI
What would you use for evaluation of bone metastases and osteomyelitis?
nuclear medicine- bone scan
What is articular surface involvement?
fracture extends into joint surface- can affect joint function and may lead to arthritis if not tx properly
what is displacement?
describes the extent to which the broken bone fragments have moved from their original position; measured in terms of mm or percentage of bone’s width
what is angulation?
refers to angle formed b/t fractured bone fragments
indicates how much the bone fragments have tilted relative to each other
what is rotation?
describes twisting of bone fragments around axis of bone
can affect alignment and function of limb
what is shortening?
occurs when bone fragments overlap, causing overall length of bone to be shorter
can impact limb length and function
what is fragmentation?
refers to number of pieces the bone has broken into
ex: simple fx has 2 fragments; comminuted fx has multiple
what is soft tissue involvement?
describes extend of damage to surrounding muscles, ligaments, nerves, and skin
can complicate healing process and affect overall tx plan
what type of fracture is this?
compression
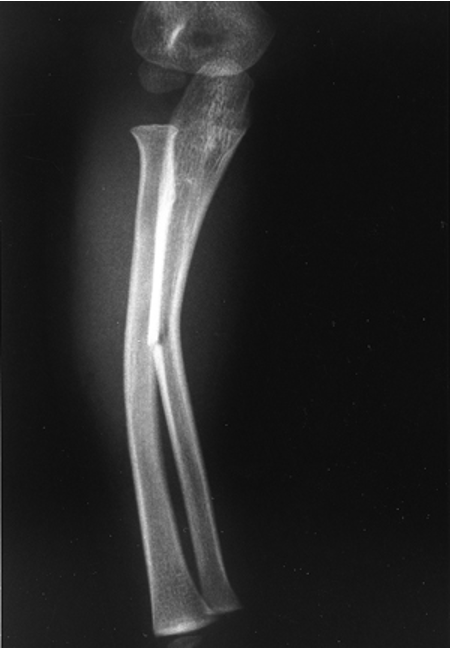
what type of fracture is this?
greenstick
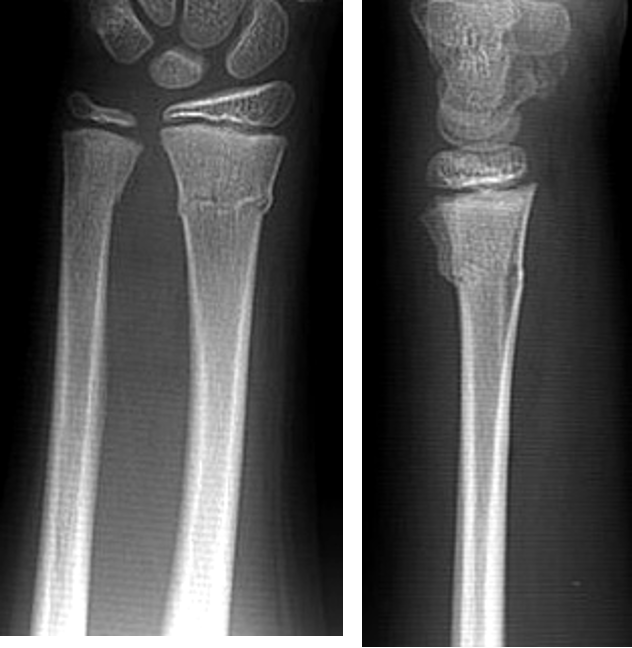
what type of fracture is this?
torus
what is a pathologic fracture?
fracture in bone due to a tumor or metabolic disorder
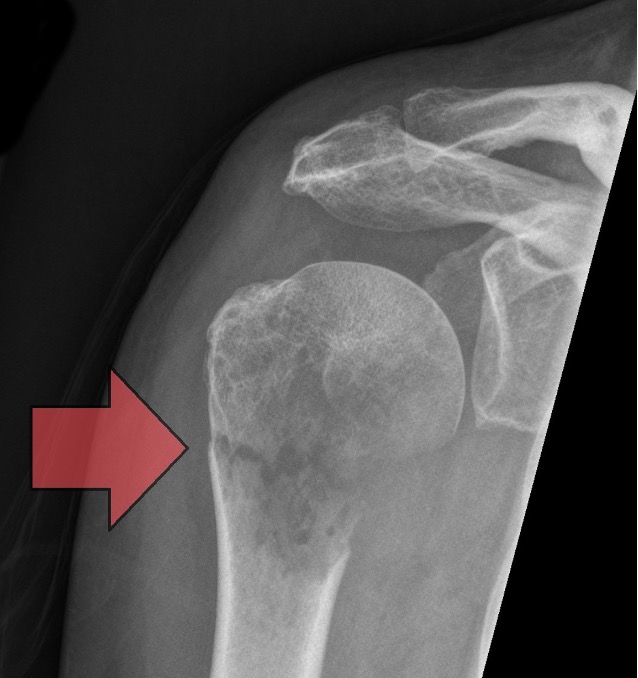
what are salter-harris fractures?
fracture through growth plate
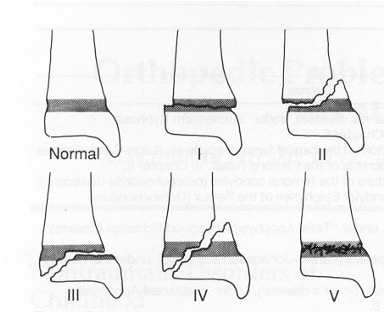
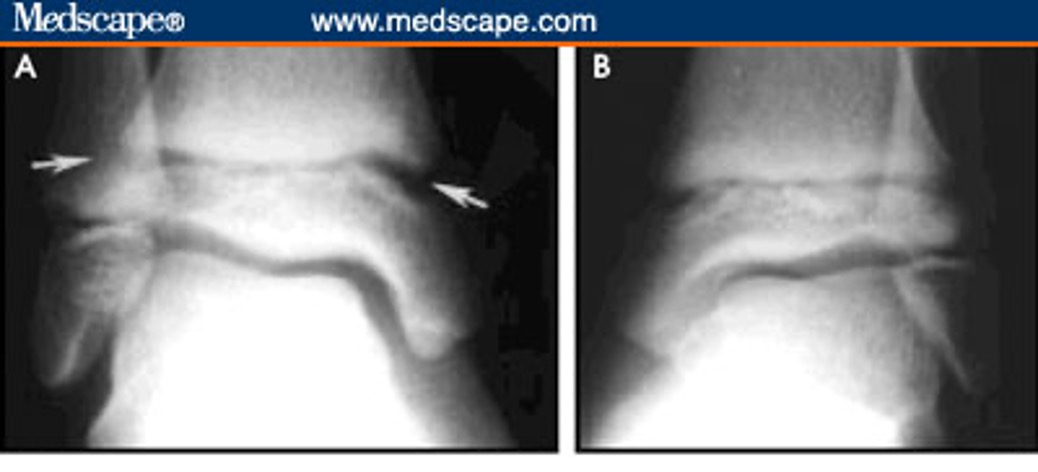
what type of salter Harris fracture is this? what kind of tx is needed?
I; cast or boot
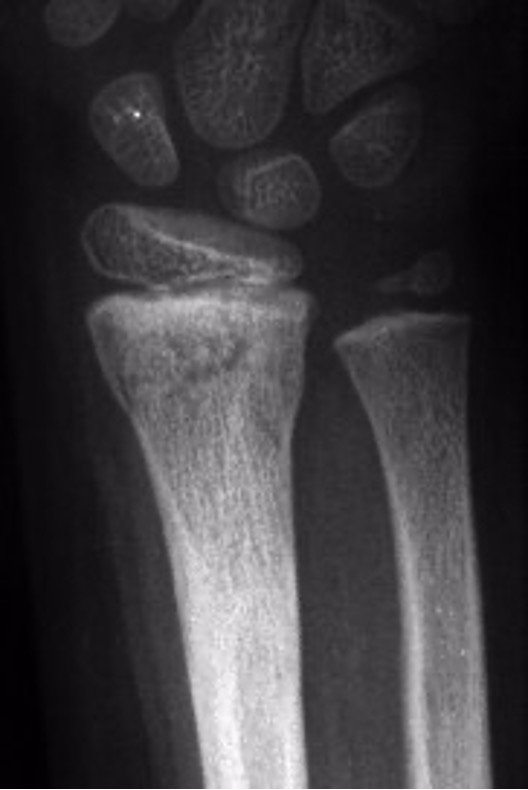
what type of salter Harris fracture is this? what kind of tx is needed?
II; cast or boot + closed reduction if misalignment
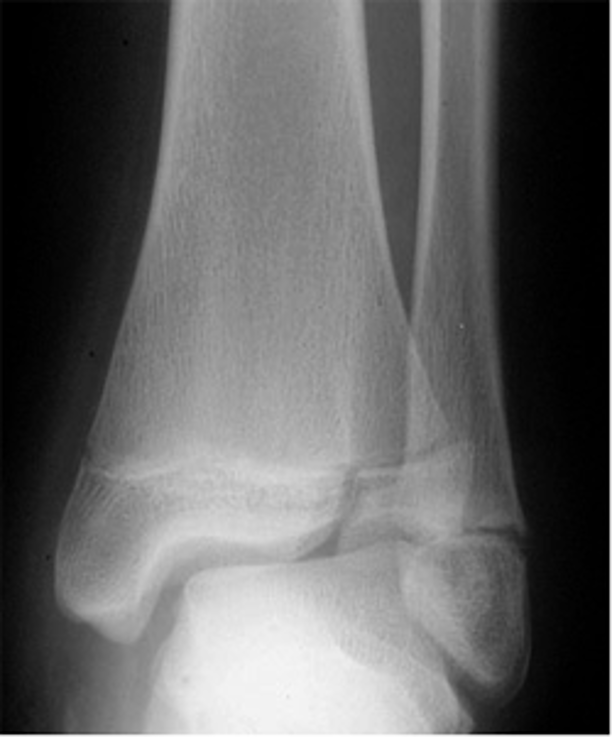
what type of salter Harris fracture is this? what kind of tx is needed?
III; usually open reduction internal fixation
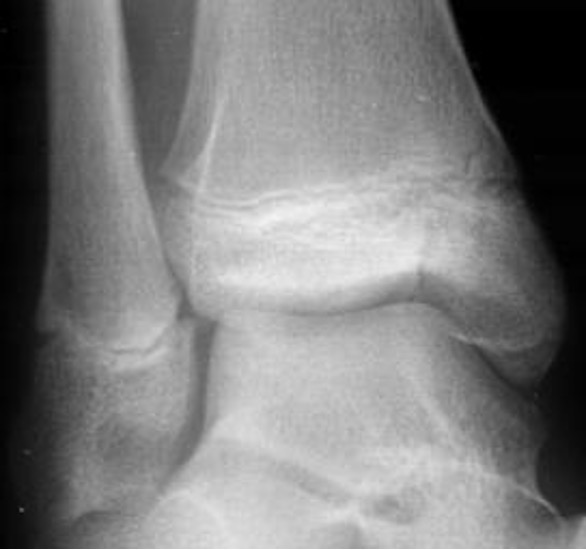
what type of salter Harris fracture is this? what kind of tx is needed?
IV; open reduction internal fixation
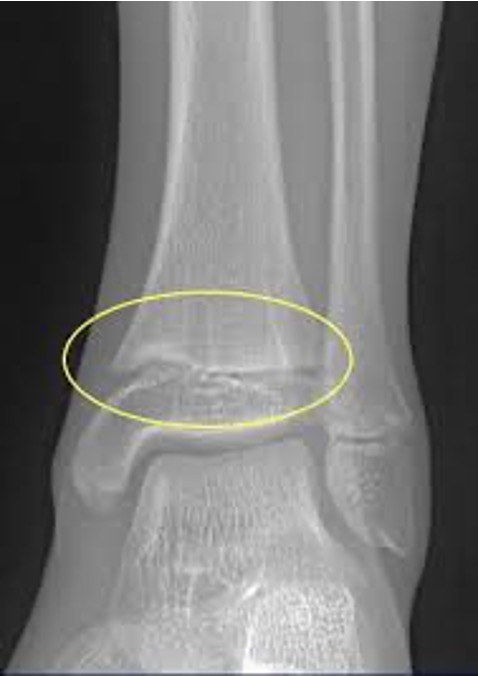
what type of salter Harris fracture is this? what kind of tx is needed?
V; often delayed dx, must realign in most cases
what does C-spine lateral view plain film evaluate?
alignment, spacing, soft tissues and vertebrae
what does C-spine AP view evaluate?
alignment and oblique fractures
what does what does C-spine oblique view evaluate?
neural foramina narrowing and alignment of facet joints
what does C-spine odontoid view evaluate?
C1-C2 relationship (mouth open)
what does C-spine swimmer’s view evaluate?
C7-T1
what is the normal appearance of C-spine?
normal curve seen well on lateral view
what are the 5 lines that should be evaluated on lateral view of the c spine?
anterior soft tissue line
arterial spinal/vertebral line
posterior spinal/vertebral line
spinolaminal line
spinous process line
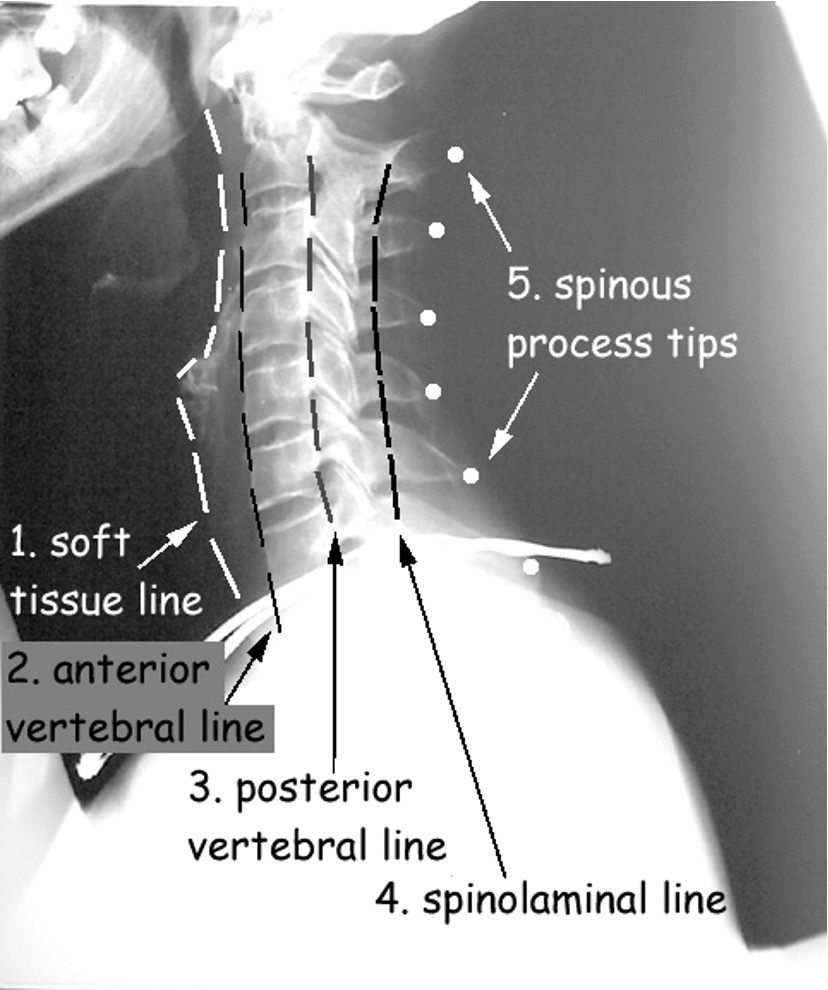
describe how the soft tissue line should appear
at C3- should be between 4-4 mm (may be up to 7mm on portable film)
below C4- ranged from 10-20 mm
if soft tissue line is wider than adjacent vertebral body, what may be present?
pathology
what should be visible on lateral view of c-spine?
all 7 vertebral bodies and C7-T1 joint space
What should be ordered if you cannot visualize C7-T1 on lateral view?
swimmers view
what are the most common sites of spinal fractures?
C1-C2, C5-C7, T9-L2
what are indications for imaging in spinal trauma?
pain, neuro deficits, altered level of consciousness
if a head CT is indicated, what should also be done at the same time (in spinal fractures)?
c-spine CT
what is Jefferson’s fracture?
burst fx of C1
due to axial loading of head being smashed down onto spine
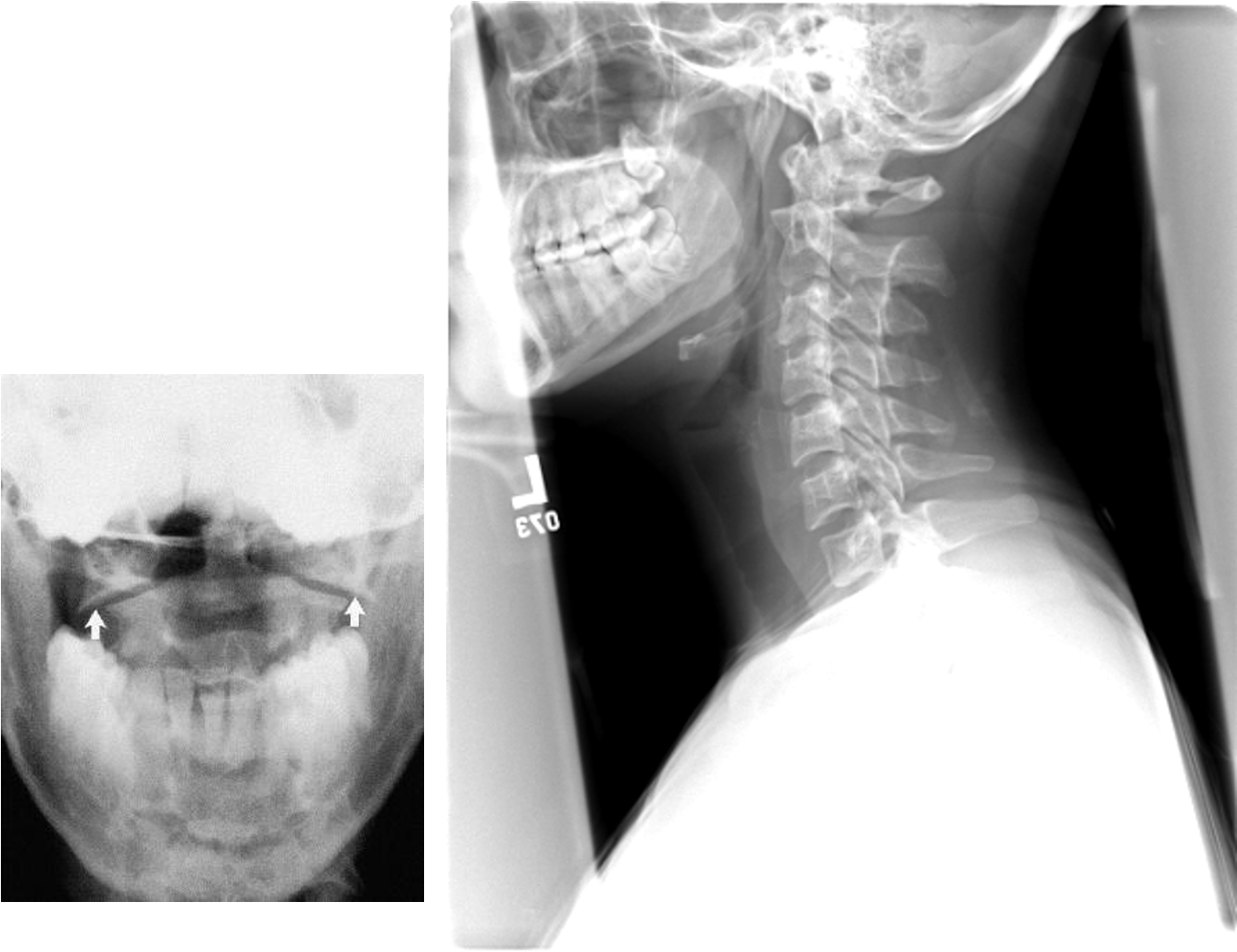
what fracture would you expect after diving in a shallow pool?
Jefferson’s fracture
what is odontoid fracture?
fx of odontoid process of C2
caused by subluxation of C1 and C2
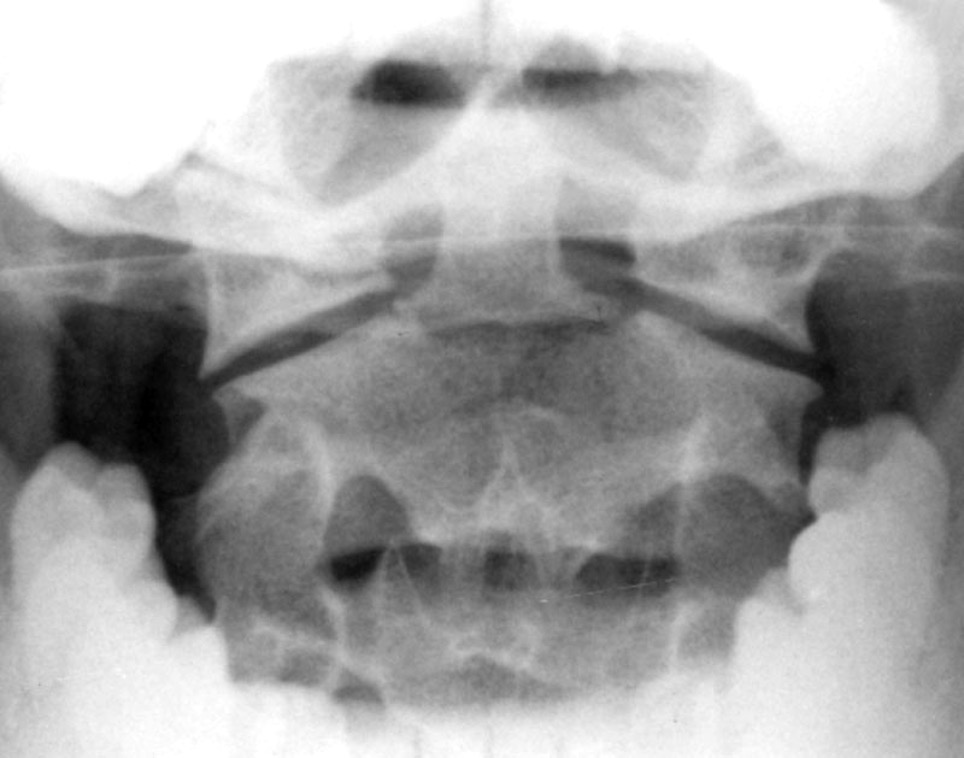
what is hangman’s fracture?
fx of posterior aspects of C2
hyperextension injury, often w/ spinal cord compromise; subluxation of C2 over C3
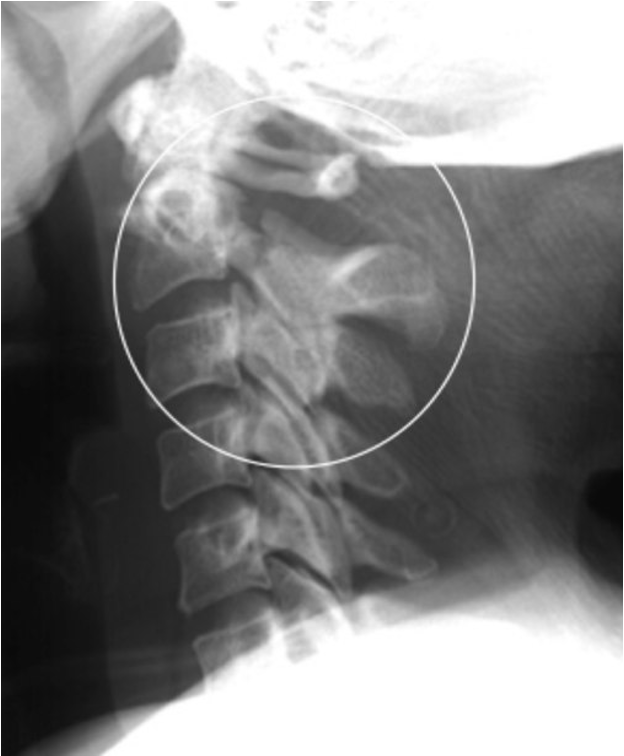
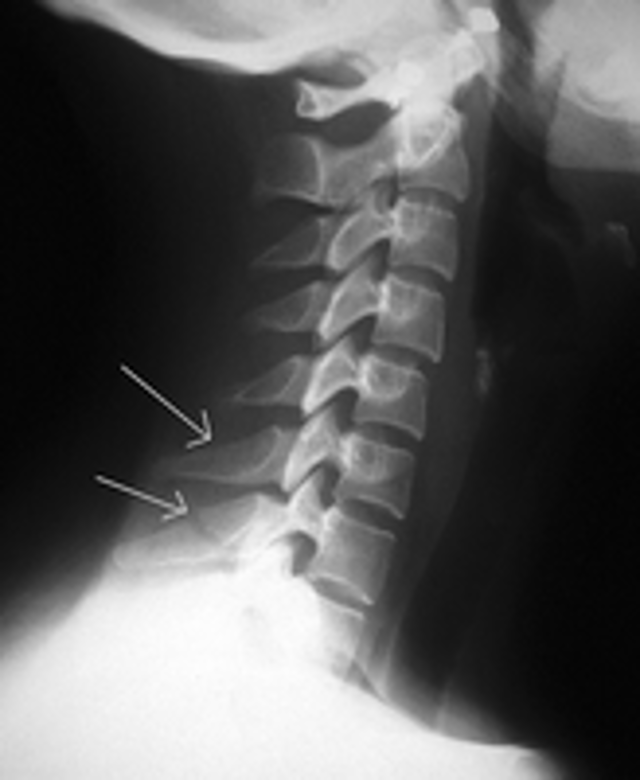
what is clay-shoveler’s fracture?
fx of spinous process of C6, C7, T1, or T2
hyper flexion injury- reflex muscle pull on spinous process
what is indicated for evaluation of suspected herniated disk, radiculopathy, or if neurologic deficit is present?
MRI
what are signs of C-spine degenerative changes?
dec disk space, sclerosis, and spurring of margins of vertebral bodies
what are common areas where degenerative changes occur in the C-spine and appear by age 30-40?
C4-C7
why are the upper thoracic vertebrae often difficult to see on lateral view?
bc of the shoulders
what is thoracic spine trauma usually due to?
MVA or osteoporosis
The ______ view should be evaluated for alignment and the _____ view should be evaluated for subluxation in thoracic spine trauma
AP; lateral
compression fractures of middle and lower thoracic spine are common due to _____
osteoporosis (also caused by.a fall)
what are the 3 most common degenerative changes in the thoracic spine?
spurs (hypertrophic osteophytes)- no clinical significance
calcification of anterior spinal ligament (DISH)- no clinical significance
calcification of intervertebral disc - result of trauma, hypercalcemia or other dz
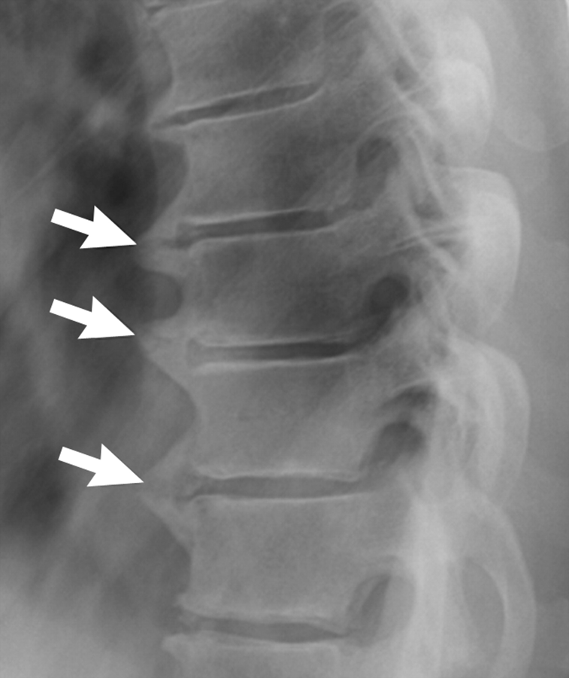
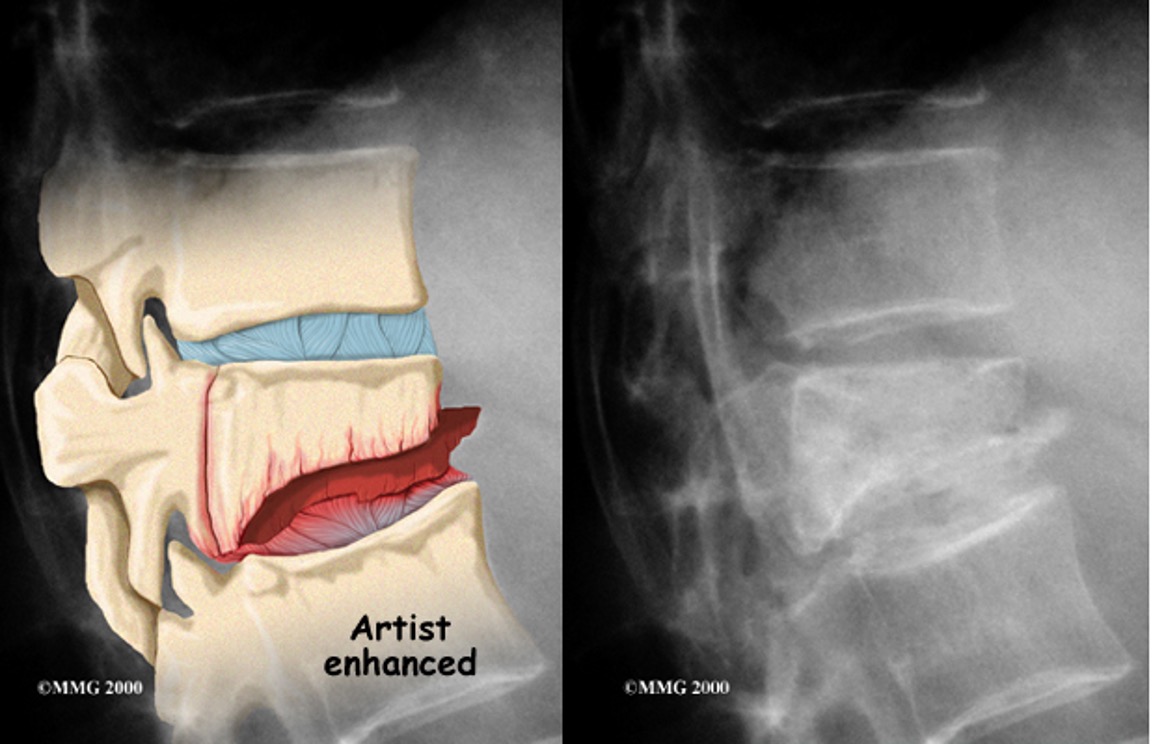
what is this?
diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
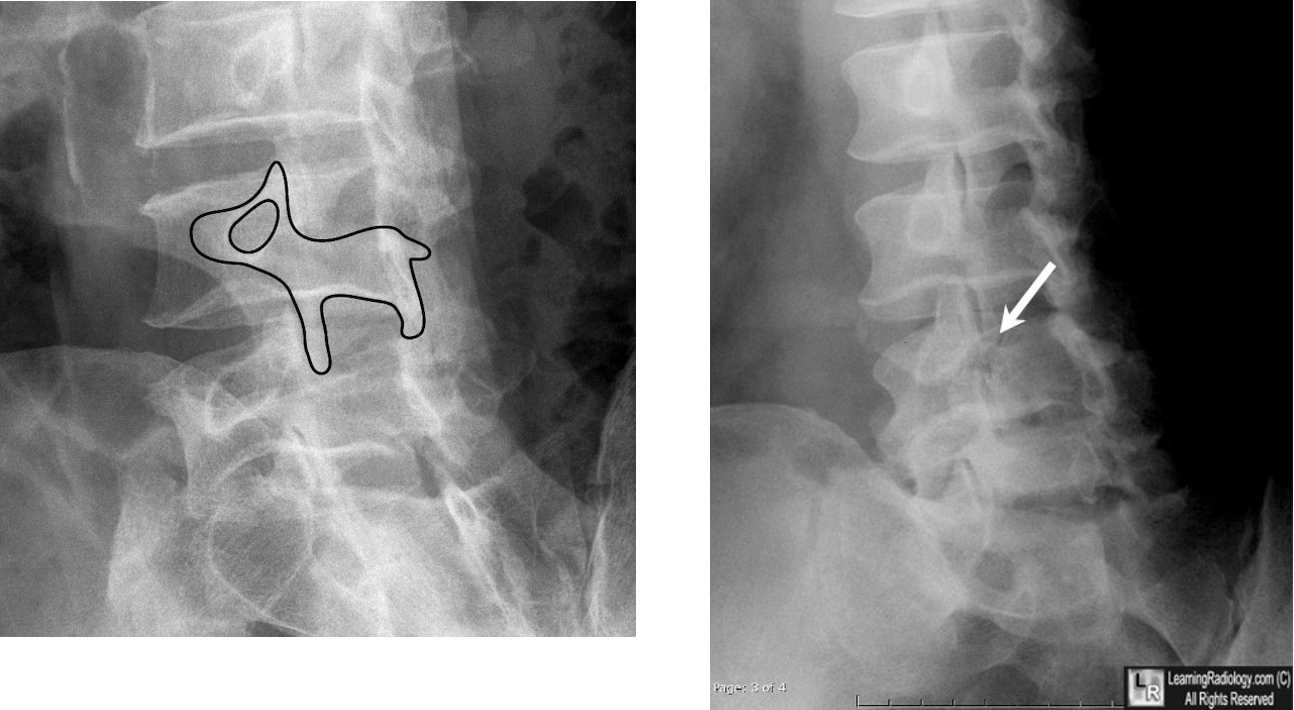
what does scottie dog indicate?
fracture of pars interarticularis (sponylolysis)
(collar on scottie dog)
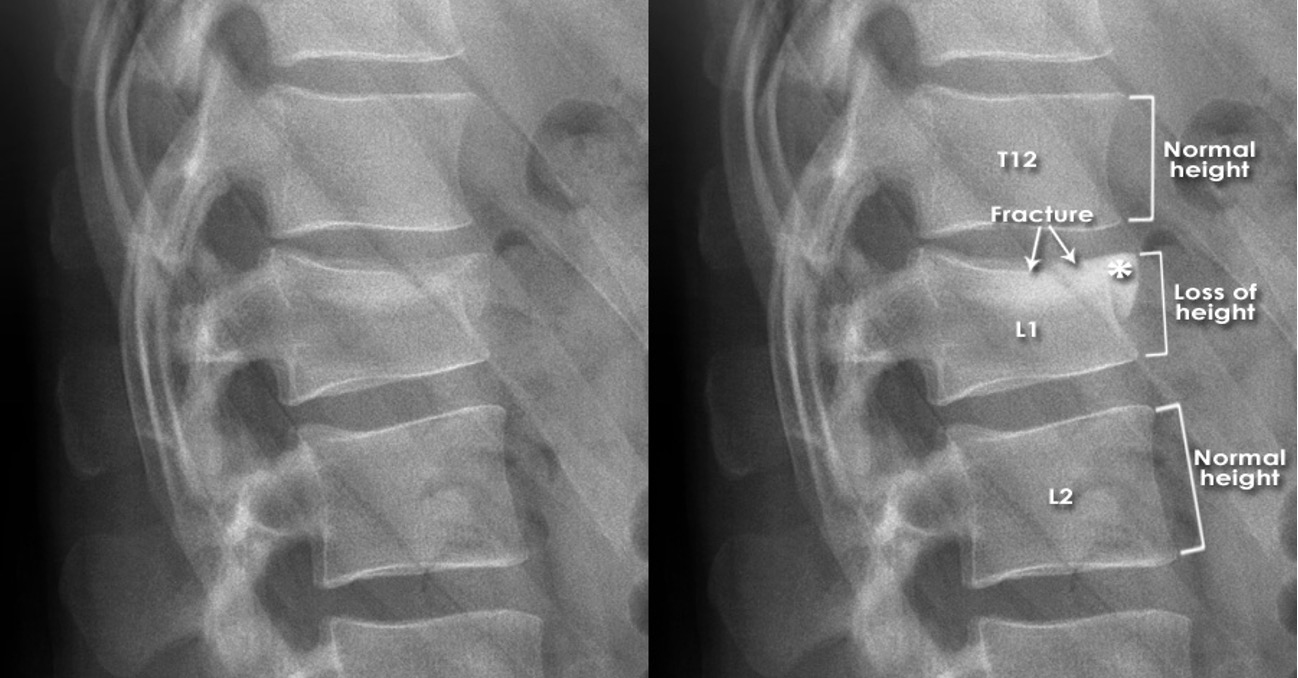
what is this?
wedge compression fracture
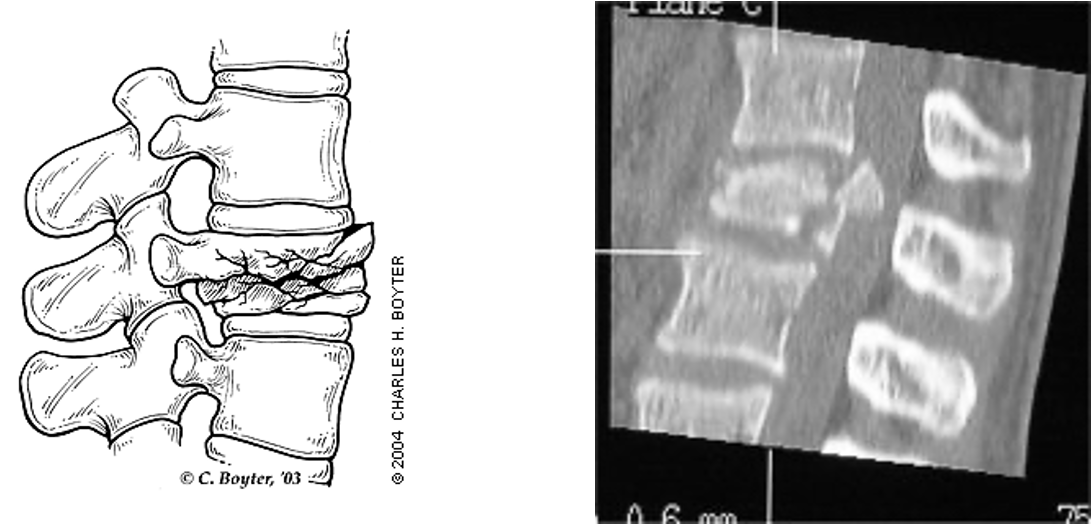
what is this?
compression burst fracture
what is the best study for suspected herniated or bulging/protruding discs?
MRI
what patients do spinal infections usually occur in?
diabetic or post operative
how does a spinal infection appear compared to a tumor?
infx: destructive process that involves or crosses a disk space
tumor: does not involves the disk space
when is imaging indicated w/ spinal infx?
localized pain, elevated ESR, fever, elevated WBC’s, or positive blood culture
(MRI preferred over CT if possible)
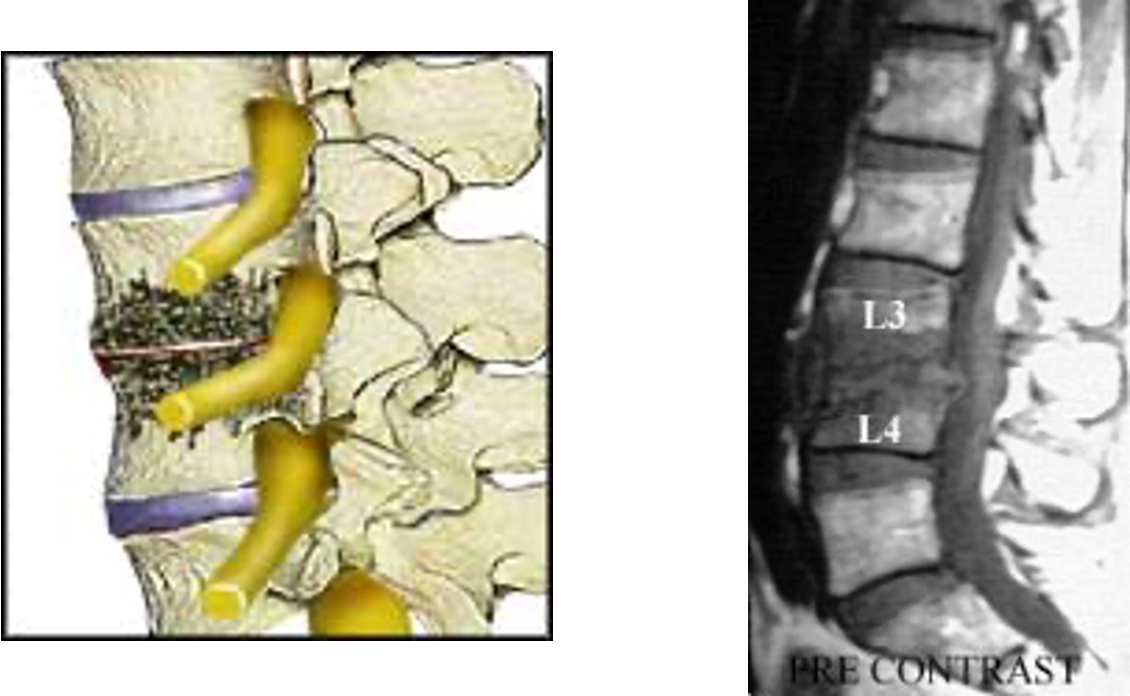
what is this?
spinal infx (involve disc space)
what is the most common neoplasm in the spine?
metastatic disease from cancer somewhere else in the body
what are lytic lesions in the spine?
decreased bone density- appear black
ex: lung, renal, breast cancers or multiple myeloma
what are sclerotic lesions?
increased bone density- appear white
ex: prostate or breast cancer
what is the best study to look for bone metastases?
bone scan
Why do metastases most frequently occur in the skull, ribs, spine, pelvis, and proximal humerus/femur?
bc they arise in the red marrow and these bones have more RBCs in the marrow than other bones
what are indications for a bone scan?
initial staging of lung/breast/prostate cancer
bone pain w/ cancer
elevated alkaline phosphatase
to evaluate the response to chemo
what is ankylosing spondylitis?
form of spondyloarthritis; bamboo appearing spine caused by calcifications bridging over the disk spaces
may cause eventual fusion of the spine
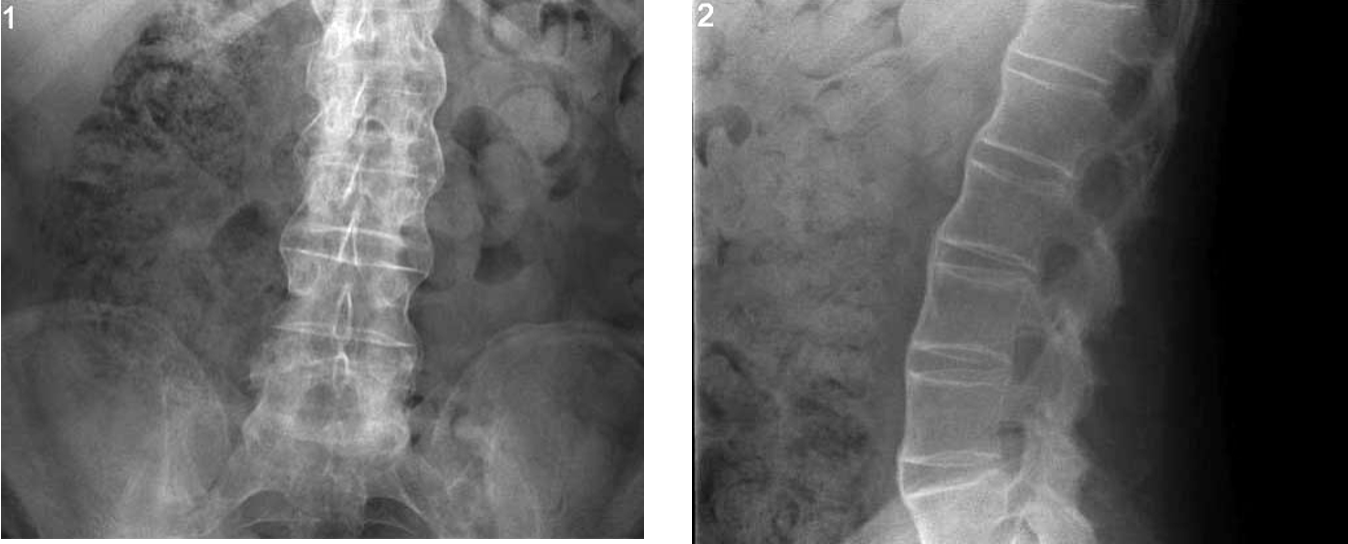
what is primary osteoporosis?
age related strider in which density of bone mass is reduced leading to inc risk of fracture caused by aging or estrogen deficiency
what is secondary osteoporosis?
osteoporosis results from other causes such as hyperparathyroidism, excess glucocorticoids, malabsorption, etc
When do plain films show osteopenia?
not until bone loss is more than 30%
What is the preferred method to measure bone density?
dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
what does DEXA measure?
bone density of femoral head and lumbar spine
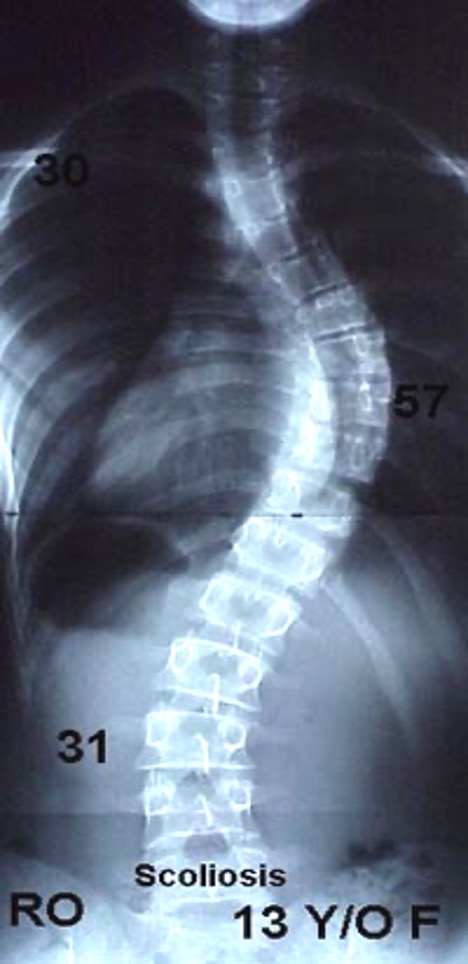
what is this?
scoliosis
what is indicated in joint pain?
plain films
when is MRI indicated in joint pain?
plain films are negative and presence of dec motion, joint effusion, or acute muscle spasm or if aseptic necrosis is suspected
what is the most common joint disease?
osteoarthritis
what can be used to evaluate arthritic changes?
plain films of hand
what is osteoarthritis?
joint space narrowing and osteophytes especially involving the distal interphalangeal joints
what is rheumatoid arthritis?
joint space narrowing, subchondral cysts, erosions at the lateral edges of the joints, and ulnar deviations at the MCP joints
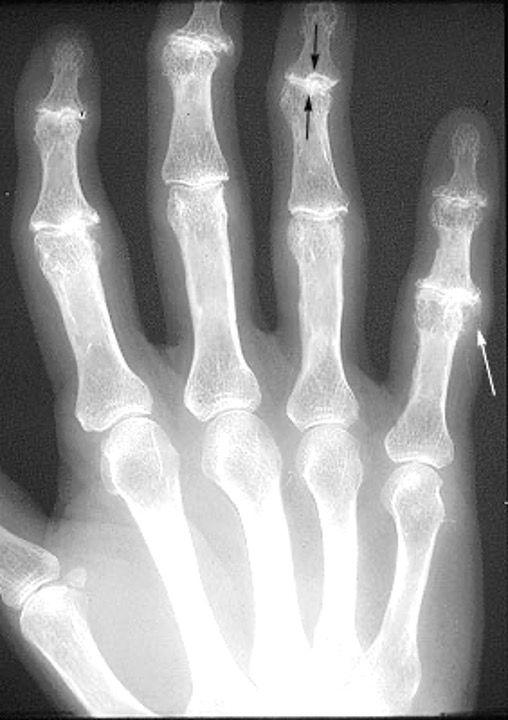
what is this?
osteoarthritis- sclerosis of DIP joints and osteophyte of PIP joint in 5th digit
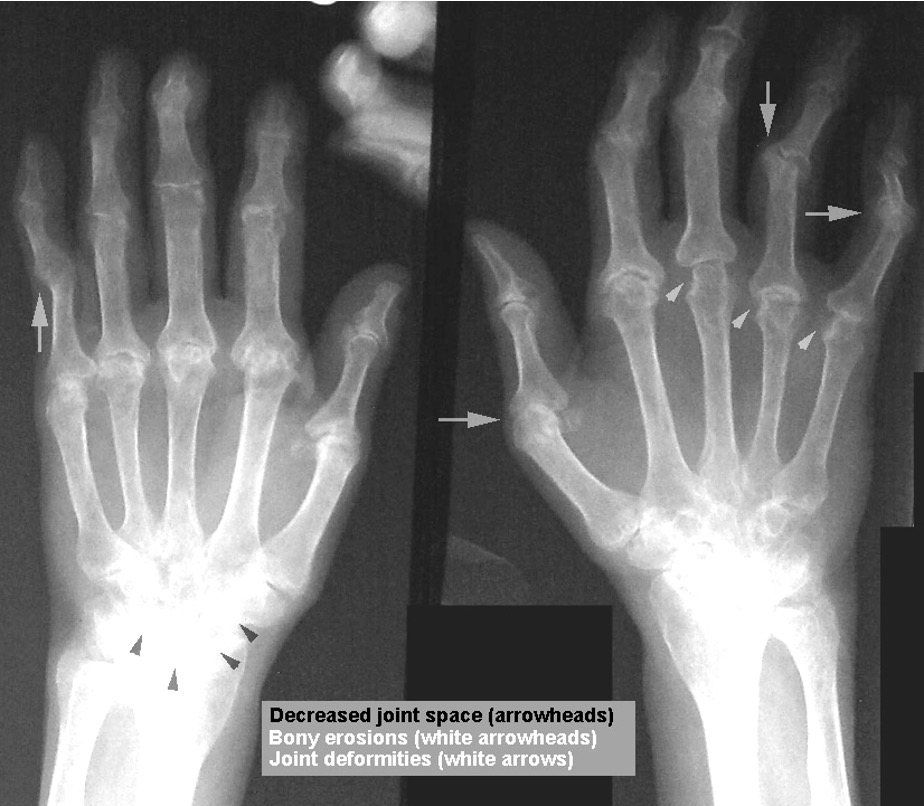
what is this?
rheumatoid arthritis
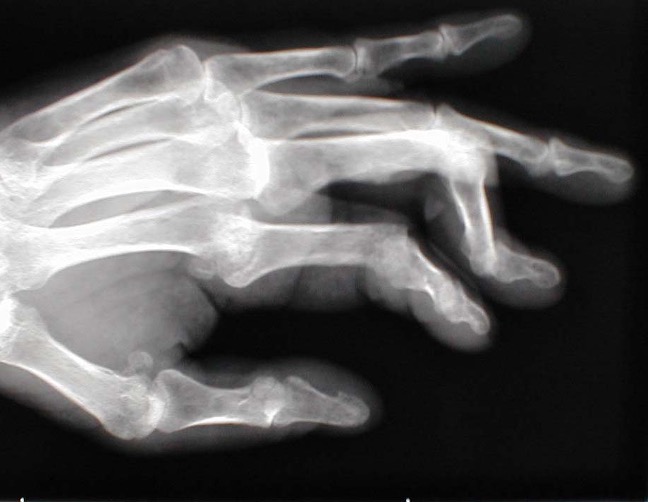
what is this?
boutonniere deformity
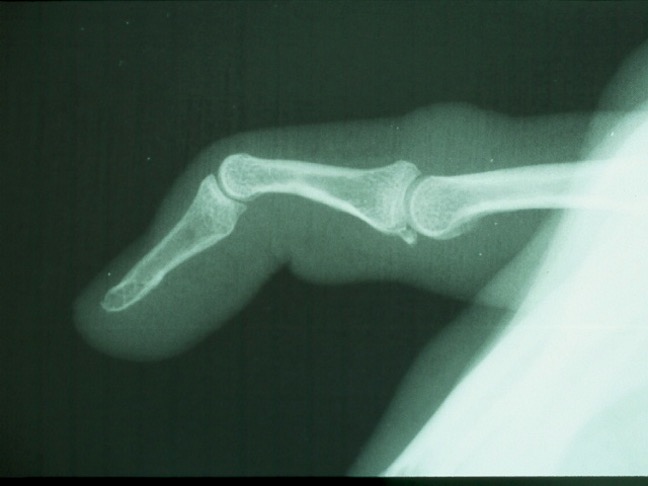
what is this?
swan-neck deformity
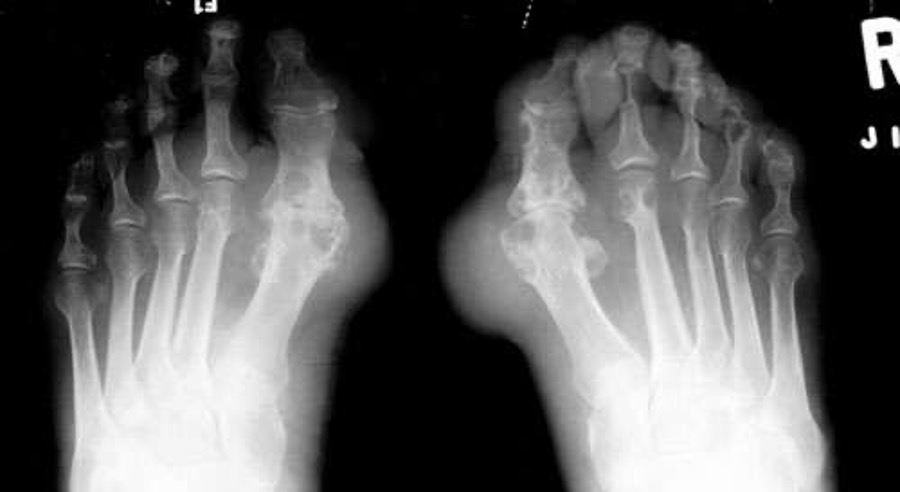
what is this?
gout- usually only involves first MTP joint
what is periostea reaction?
thickening of periosteum - appears white on xray
seen w/ normal healing fractures, osteomyelitis, benign and malignant tumors
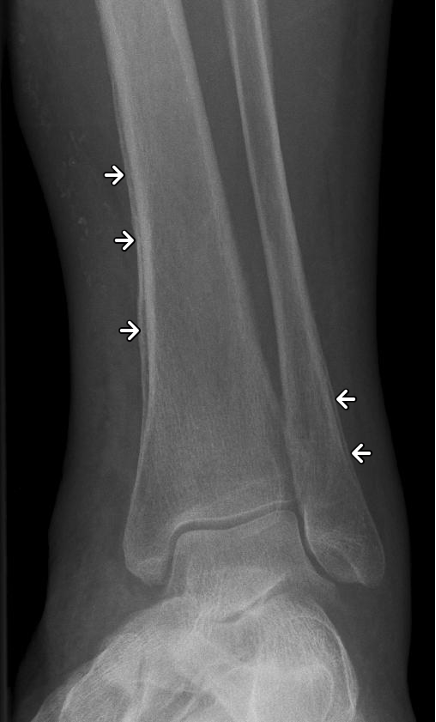
what is a radiating periostea reaction (sun-burst) worrisome for?
malignancy
what lesions should be considered malignant?
any lytic lesion w/o sclerotic margin
what do benign bone lesions look like?
small size, no periostea reaction, sharp zone of transition b/t bone and lesion, thin well defined sclerotic margin
what do plain films show in osteomyelitis?
focal loss of calcium, bone erosion, or periostea reaction
what imaging is indicated in osteomyelitis?
MRI or bone scan if plain films are negative continuously
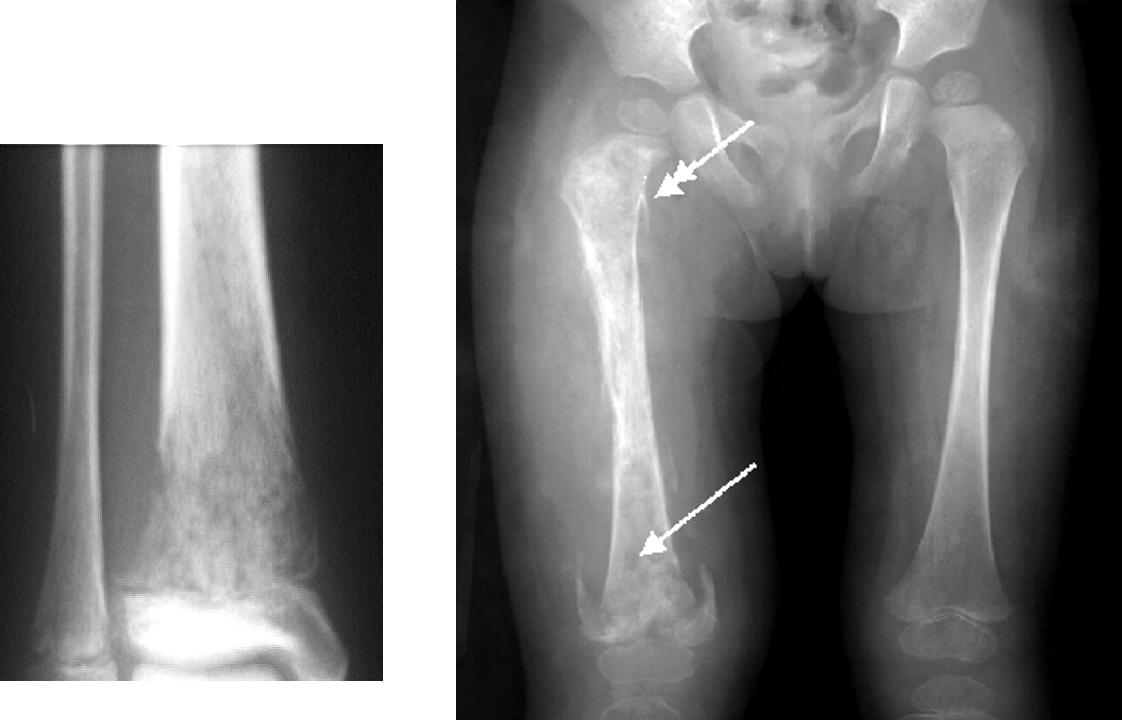
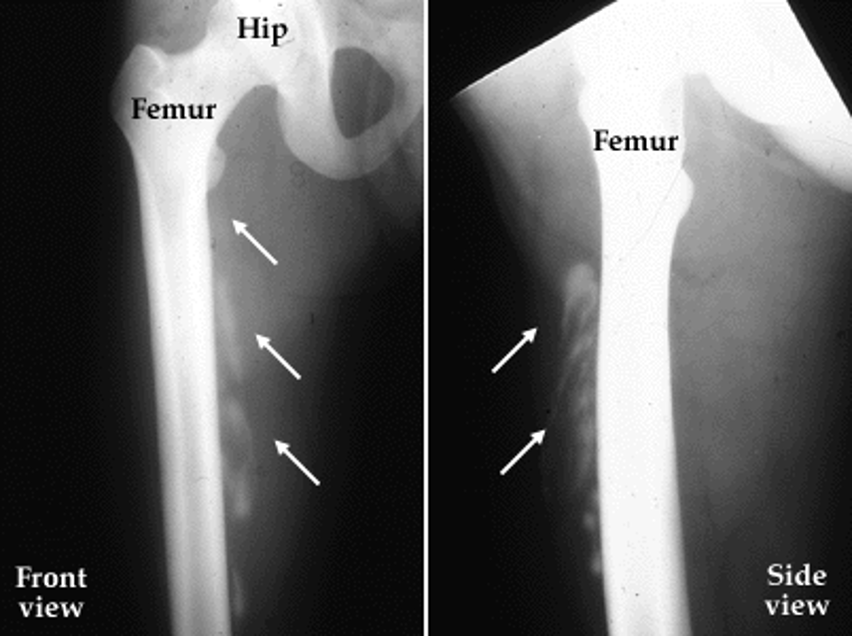
what is this?
osteomyelitis
how is septic arthritic, an acute bacterial process, diagnosed?
joint aspiration
plain films indicated- destruction of single joint space on both sides of the joint
what is myositis ossificans?
calcification of soft tissues after trauma; may require surgery to remove