1.1 The importance of circulatory systems and 1.2 Water as a solvent
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is mass flow? (1)
Mass flow refers to the circulation of blood to maintain a concentration gradient.
What are mass flow systems? (1)
A mass flow system is a mechanism that transports substances in bulk over long distances, driven by a pressure gradient.
What is the mass transport system in mammals? (1)
In mammals, the mass transport system is the circulatory system.
How does the surface area to volume ratio (SA:V) change with the size of an organism? (1)
As the size of the organism increases, the SA:V ratio decreases and therefore smaller organisms will have a larger SA:V ratio.
How does the surface area to volume ratio (SA:V) effect rate of diffusion? (1)
The smaller the SA:V, the lower the rate of diffusion.
How do you calculate the surface area of a cube? (1)
Surface area = 6a², where a is the length of a side.
How do you calculate the volume of a cube? (1)
Volume = a³, where a is the length of a side.
Why do organisms need to exchange substances with the environment? (3)
- To remove waste products (e.g. carbon dioxide, urea).
- To allow the uptake of oxygen and glucose for aerobic respiration.
- To exchange heat with the surroundings.
Why do unicellular organisms rely on diffusion for exchange? (2)
- They have a short diffusion distance from the cell surface to the centre.
- They have a larger SA:V ratio, allowing for efficient exchange.
How does increasing body mass affect oxygen consumption per gram of tissue? (1)
As body mass increases, the rate of oxygen consumption per gram of tissue decreases.
Why do larger organisms have a lower oxygen consumption rate per gram of tissue? (1)
Because they require less energy to maintain body temperature, resulting in lower oxygen demand per gram.
What must be considered when comparing heat loss between organisms? (1)
Heat loss should be compared per unit of body mass to ensure a valid comparison.
Why do large organisms lose less heat than smaller ones? (1)
They have a smaller SA:V ratio meaning they have less surface area exposed per unit of volume, which reduces the rate of heat loss through their surface.
Why is a transport system needed in humans? (2)
- Humans have a low surface area to volume ratio.
- Therefore diffusion alone is insufficient for transporting substances.
What are the key features of an open circulatory system? (4)
- Blood flows within open-ended vessels.
- Blood is released into the body cavity and bathes organs and tissues.
- A simple heart pumps blood towards the head and draws it back in when relaxed.
- Substances diffuse quickly in and out of cells.
What organisms are open circulatory systems found within? (1)
This system is common in organisms with a large surface area to volume ratio (e.g. insects).
What are the key features of a closed circulatory system? (3)
- Blood remains enclosed in vessels, allowing pressure to build up and move blood faster.
- Narrow vessels maintain high blood pressure.
- They are efficient for delivering blood to organs and tissues.
What organisms are closed circulatory systems found within? (1)
They are found in all vertebrates, including fish, birds, and mammals.
What are the key features of a single circulatory system? (3)
- Blood passes through the heart only once per complete circuit.
- Blood travels under pressure from the heart to gill capillaries, where it gains oxygen.
- It then flows through systemic capillaries before returning to the heart.
What organisms are single circulatory systems found within? (1)
This system is found in fish.
What are the key features of a double circulatory system? (4)
- The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood around the body (systemic circuit).
- The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs (pulmonary circuit).
- The left side has thicker muscle to create higher pressure for body circulation.
- The right side creates lower pressure to protect delicate lung tissue.
What is the benefit of a double circulatory system? (1)
It increases the speed and efficiency of blood flow while maintaining safe pressure to the lungs.
Draw a diagram of the dipole nature of water. (2)
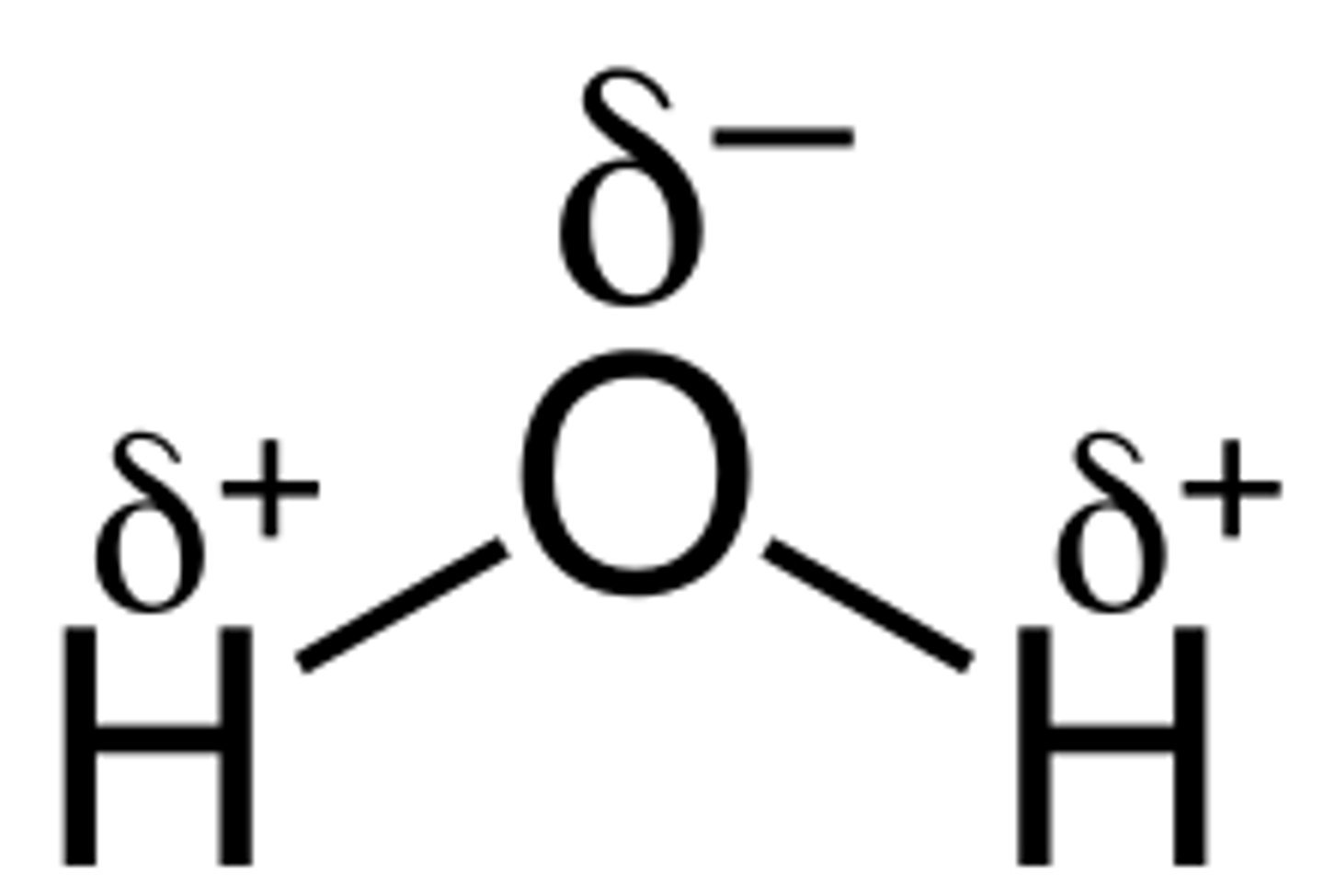
What type of bonds hold hydrogen and oxygen together in a water molecule? (1)
Covalent bonds hold hydrogen and oxygen together in a water molecule.
What is the general structure of a water molecule? (1)
One oxygen atom is joined to two hydrogen atoms by shared pairs of electrons.
Draw the general structure of a water molecule. (2)
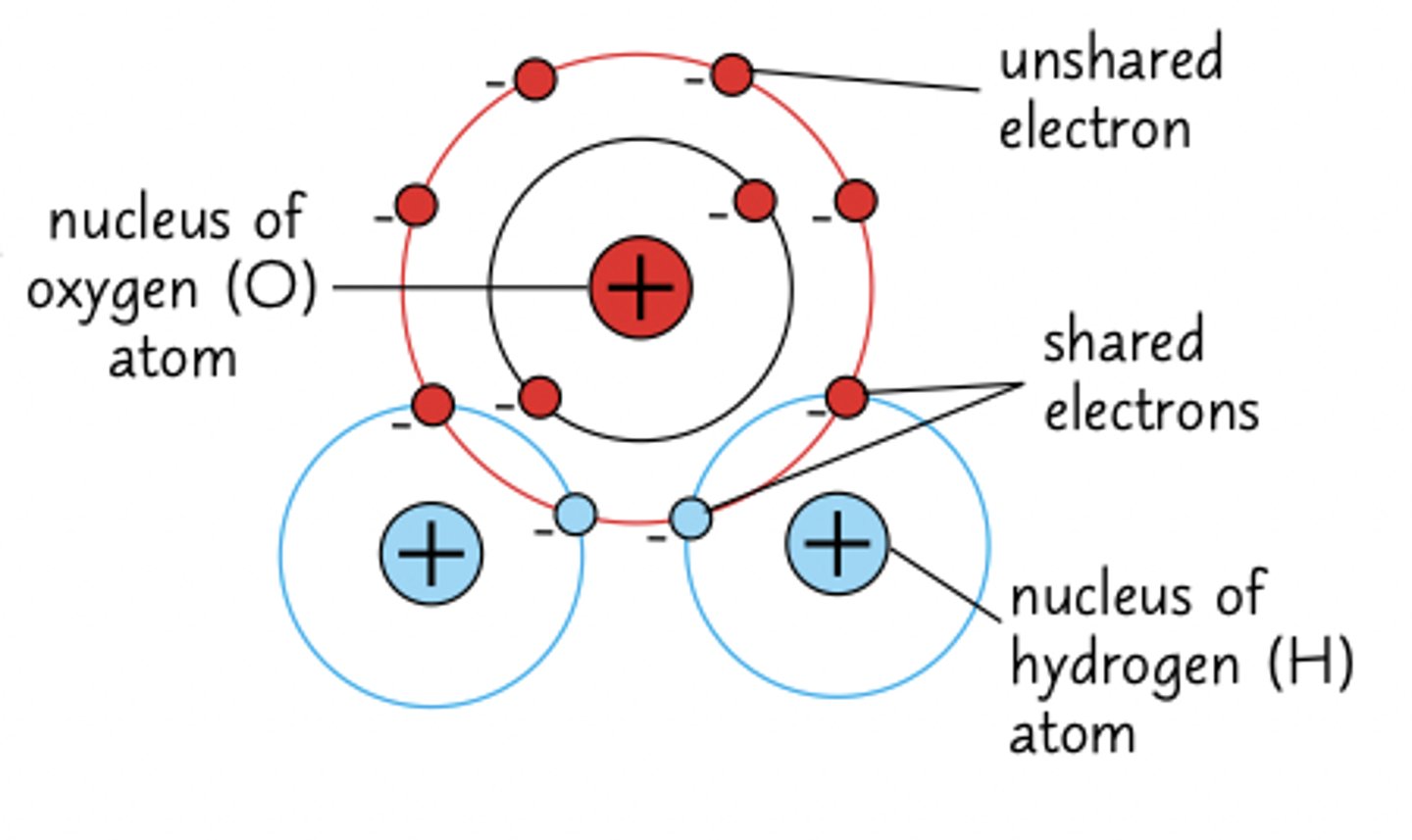
Why do hydrogen atoms have a partially positive charge in water? (1)
Electrons are pulled towards the oxygen atom, leaving the hydrogen atoms with a partial positive charge.
Why do oxygen atoms have a partially negative charge in water? (1)
Oxygen has two lone (unshared) electron pairs, making it partially negative.
How do water molecules attract one another? (2)
- The slightly negatively-charged oxygen atom attracts the slightly positively charged hydrogen atoms of other water molecules.
- These interactions are known as hydrogen bonds.
Why is water classed as a dipolar molecule? (1)
The uneven charge distribution of oxygen and hydrogen means water is classed as a dipolar molecule.
What is cohesion? (1)
Cohesion is the attraction between molecules of the same type.
What is an example that demonstrates cohesion between molecules? (1)
Between two water molecules.
What are the three main properties of water? (3)
1. Good solvent.
2. Strong cohesion.
3. High latent heat of vaporisation.
Why is water a good solvent? (2)
- Water molecules are dipolar, so they surround and attract ions, separating them.
- Water forms hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules, helping them dissolve and be transported.
How can water dissolve ionic substances such as NaCl? (1)
The partial charges on water molecules surround Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions, separating them so they dissolve.
Why does water have strong cohesion? (2)
- Water is a dipolar molecule, so water molecules stick together with hydrogen bonds.
- This makes water a cohesive liquid, allowing it to flow well.
Why is water's strong cohesion an important property? (1)
It is important in mass transport systems like xylem in plants.
Why does water have a high latent heat of vaporisation? (2)
- Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation because a large amount of energy is required to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules during evaporation.
- As water evaporates, it absorbs a significant amount of heat energy from its surroundings.
How does water's high latent heat of vaporisation contribute to its cooling effect? (2)
- During sweating, water droplets on the skin absorb heat energy from the body.
- When the sweat evaporates, it carries this heat away from the skin's surface, resulting in a cooling effect that helps regulate body temperature.
Why is ice less dense than water? (2)
- When water freezes, hydrogen bonds form between molecules.
- These bonds hold molecules further apart from one another, reducing the density of ice.
How do the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium? (3)
- Water is a solvent.
- Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules and solute molecules.
- Water is liquid so it has the ability to flow.