APHY 164 - Cardiac Output
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
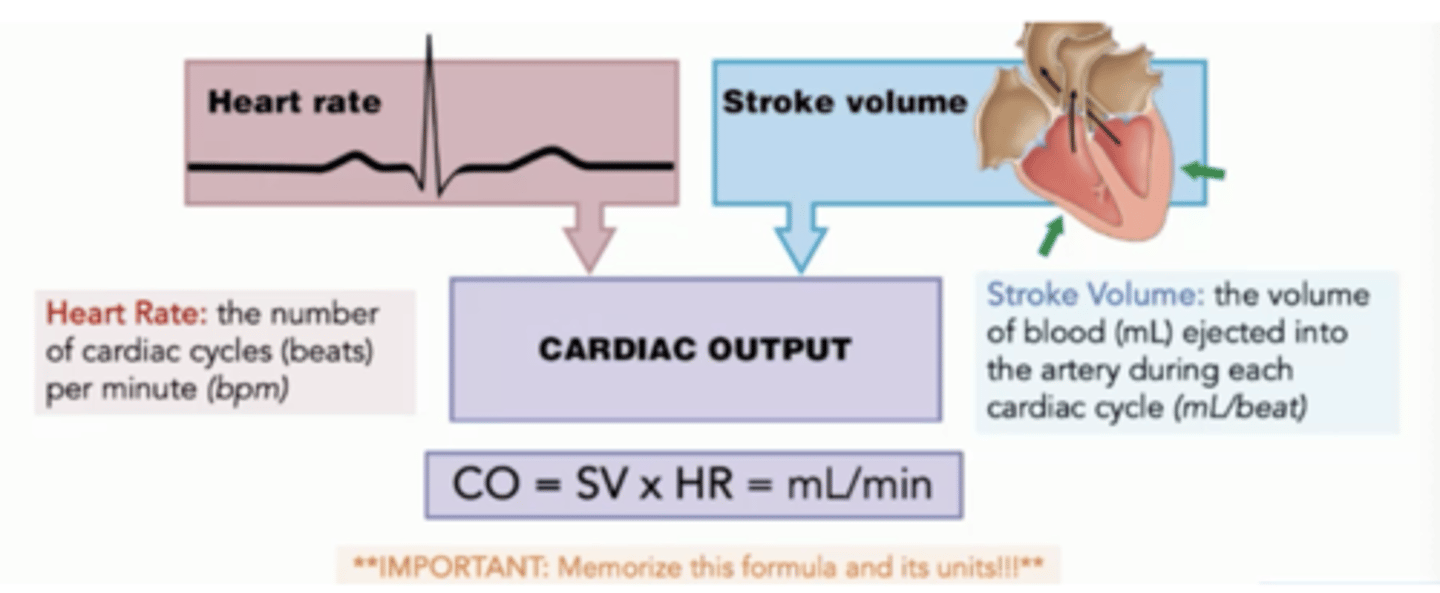
Cardiac Output (CO)
The amount of blood pumped by a single ventricle in one minute. HR x SV = CO
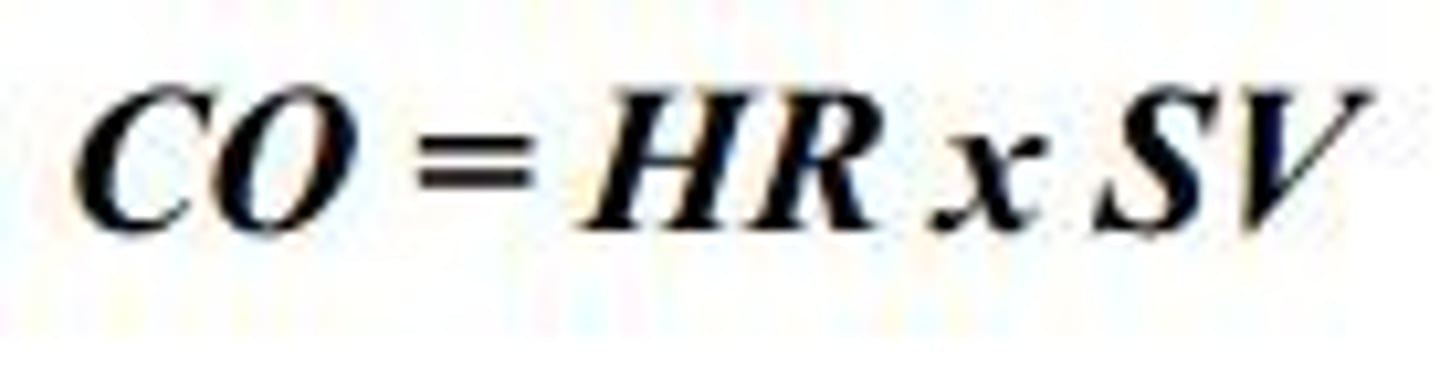
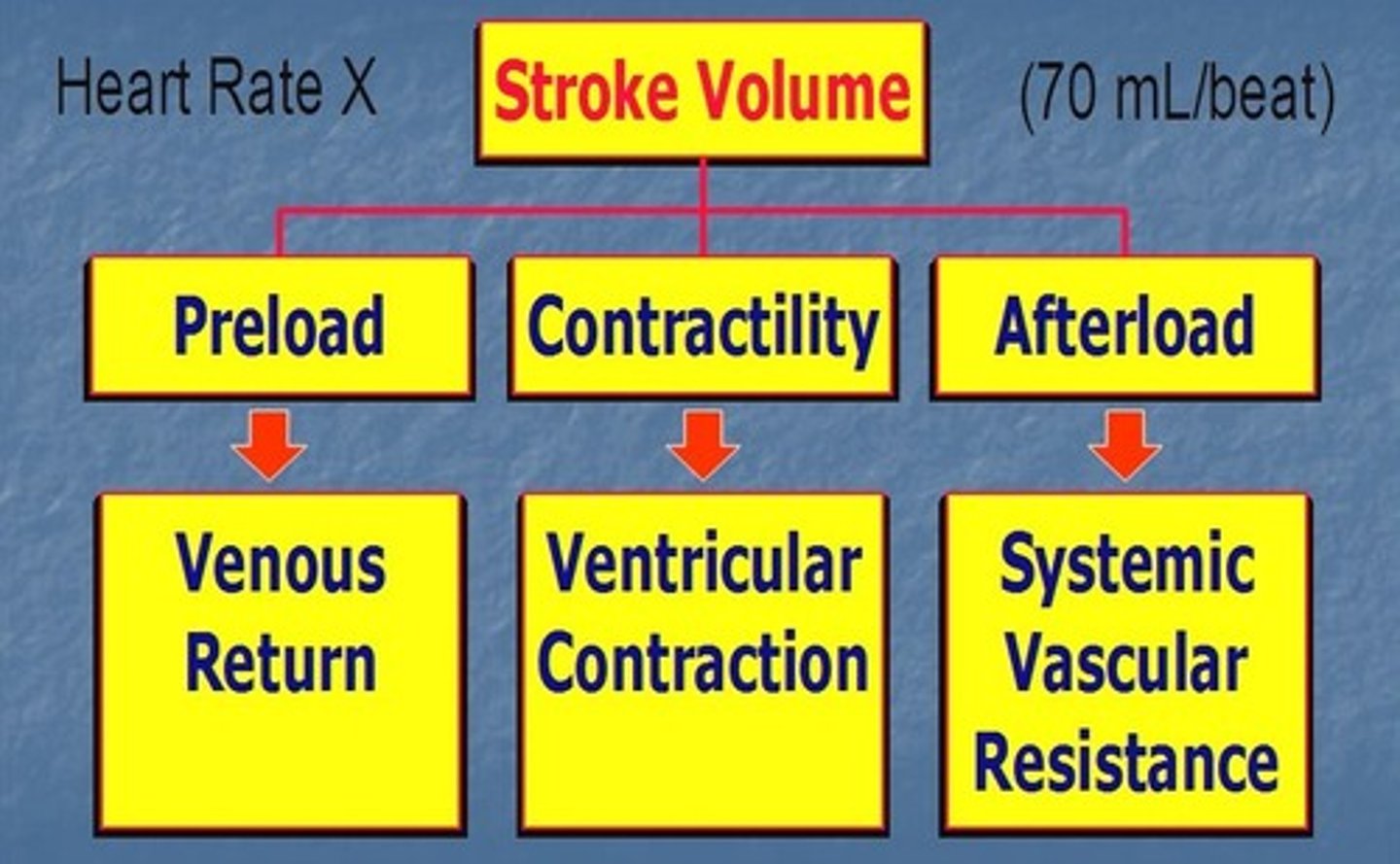
Stroke Volume (SV)
The amount of blood ejected from a ventricle in one heartbeat (contraction).
Heart Rate (HR)
number of heart beats per minute
Cardiac Output (CO) equation
CO = heart rate (HR) x stroke volume (SV), healthy individual 5L/min
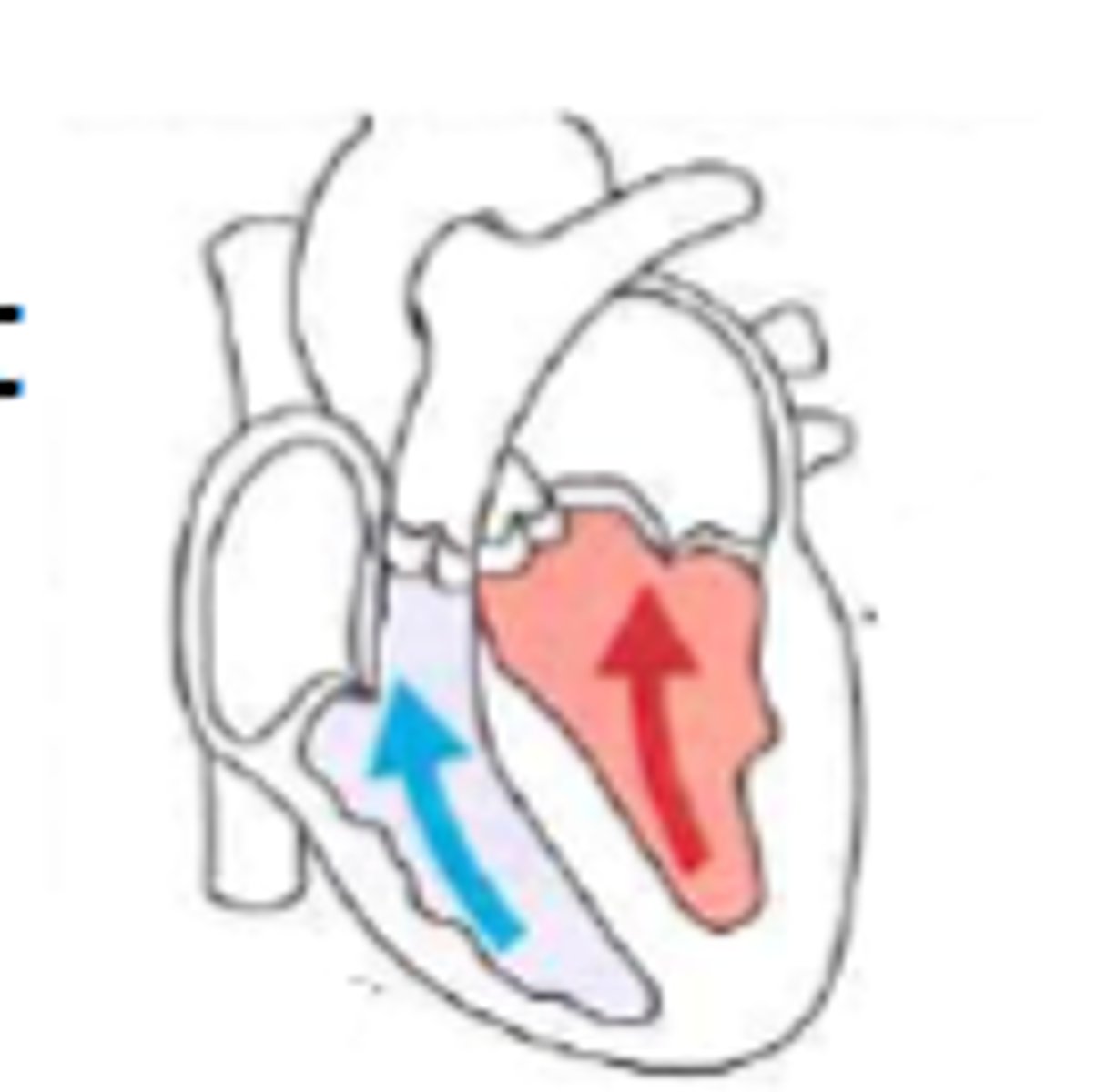
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
volume of blood in each ventricle at end of ventricular diastole (relaxation/filling)
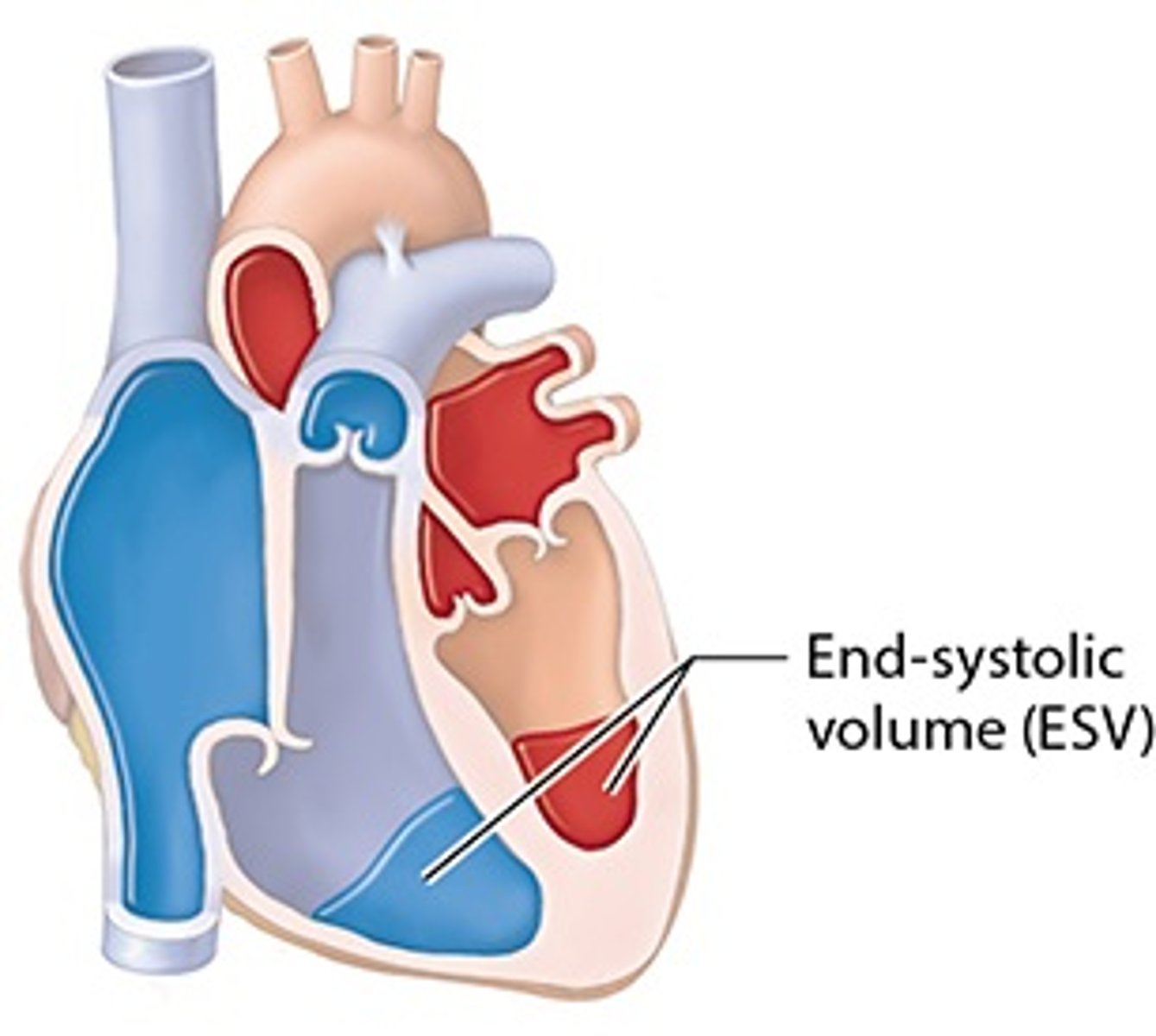
End Systolic Volume (ESV)
volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after systole (contraction)
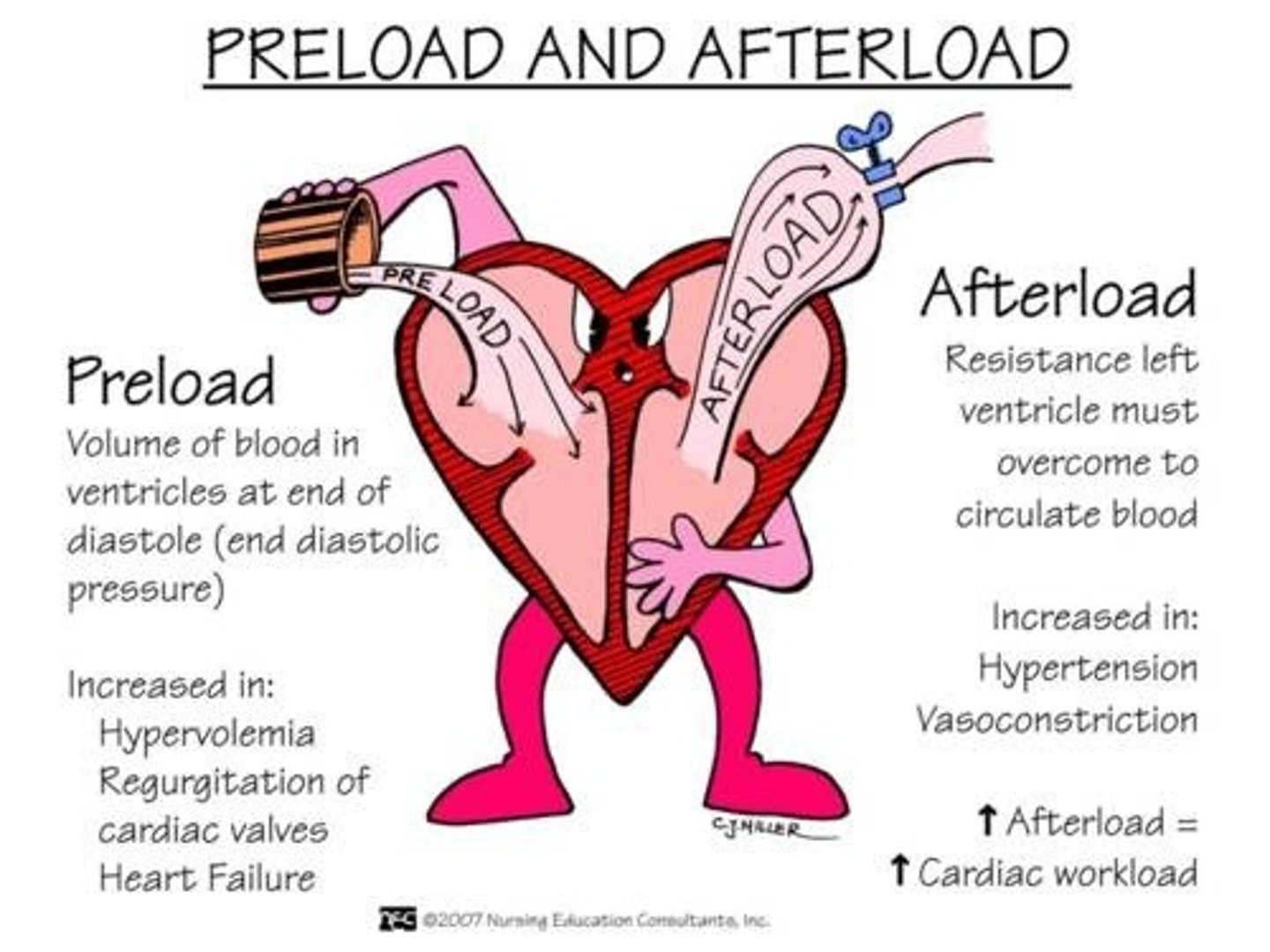
Preload
degree of stretch of the cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole (relaxation/filling)
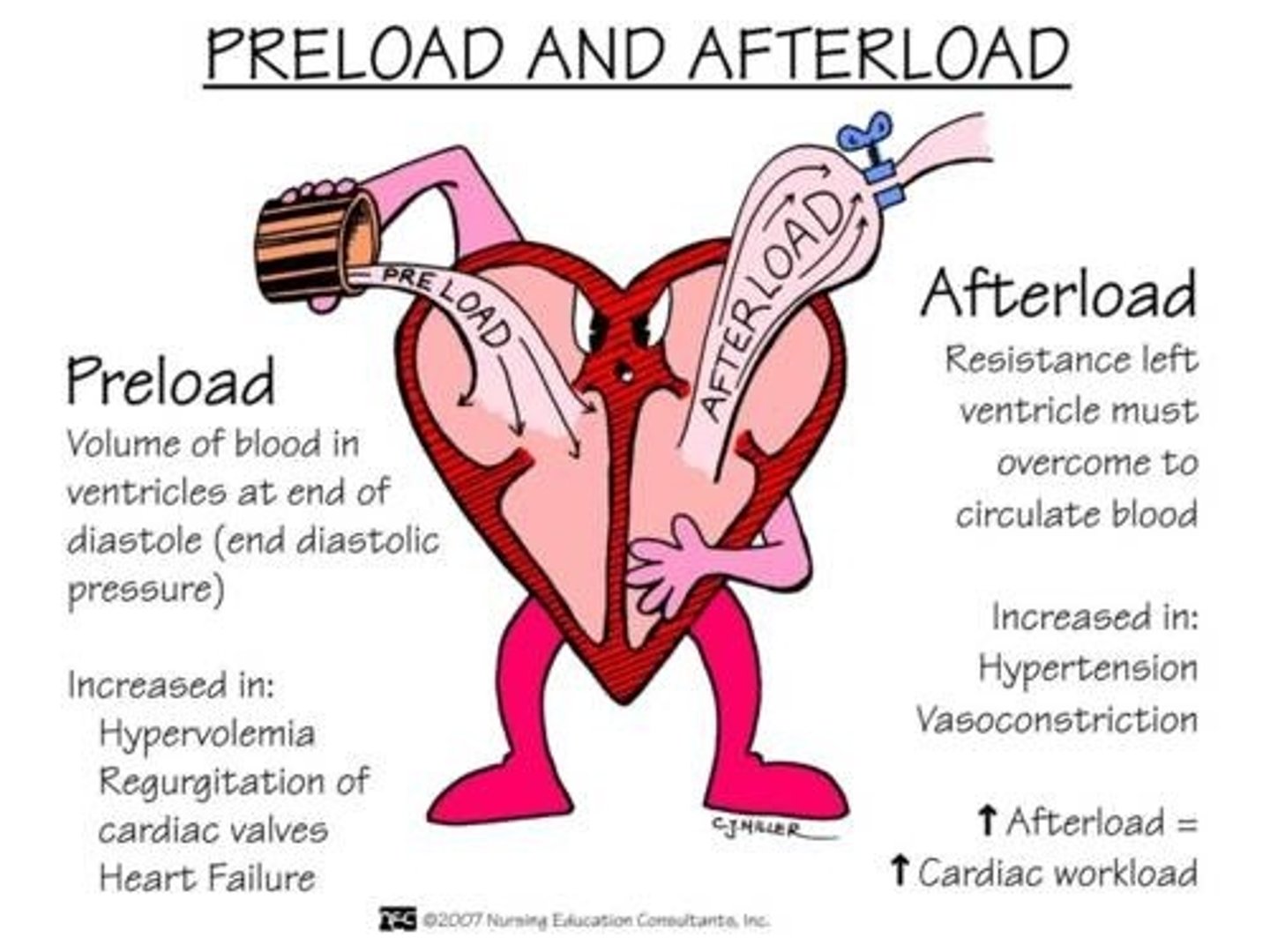
Afterload
the amount of resistance to ejection of blood from the ventricle
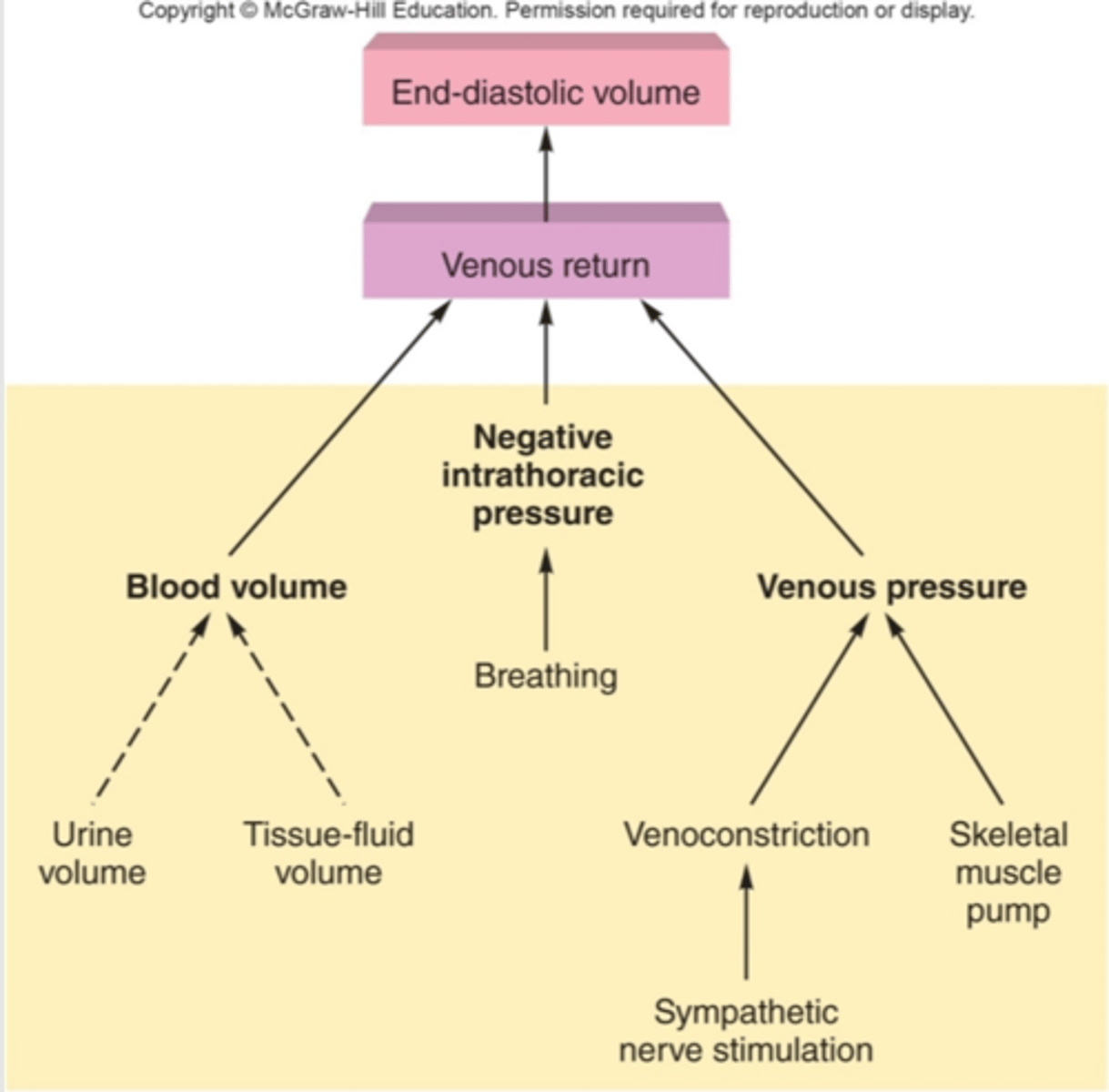
Venous Return
the amount of blood returned to the heart, determines preload
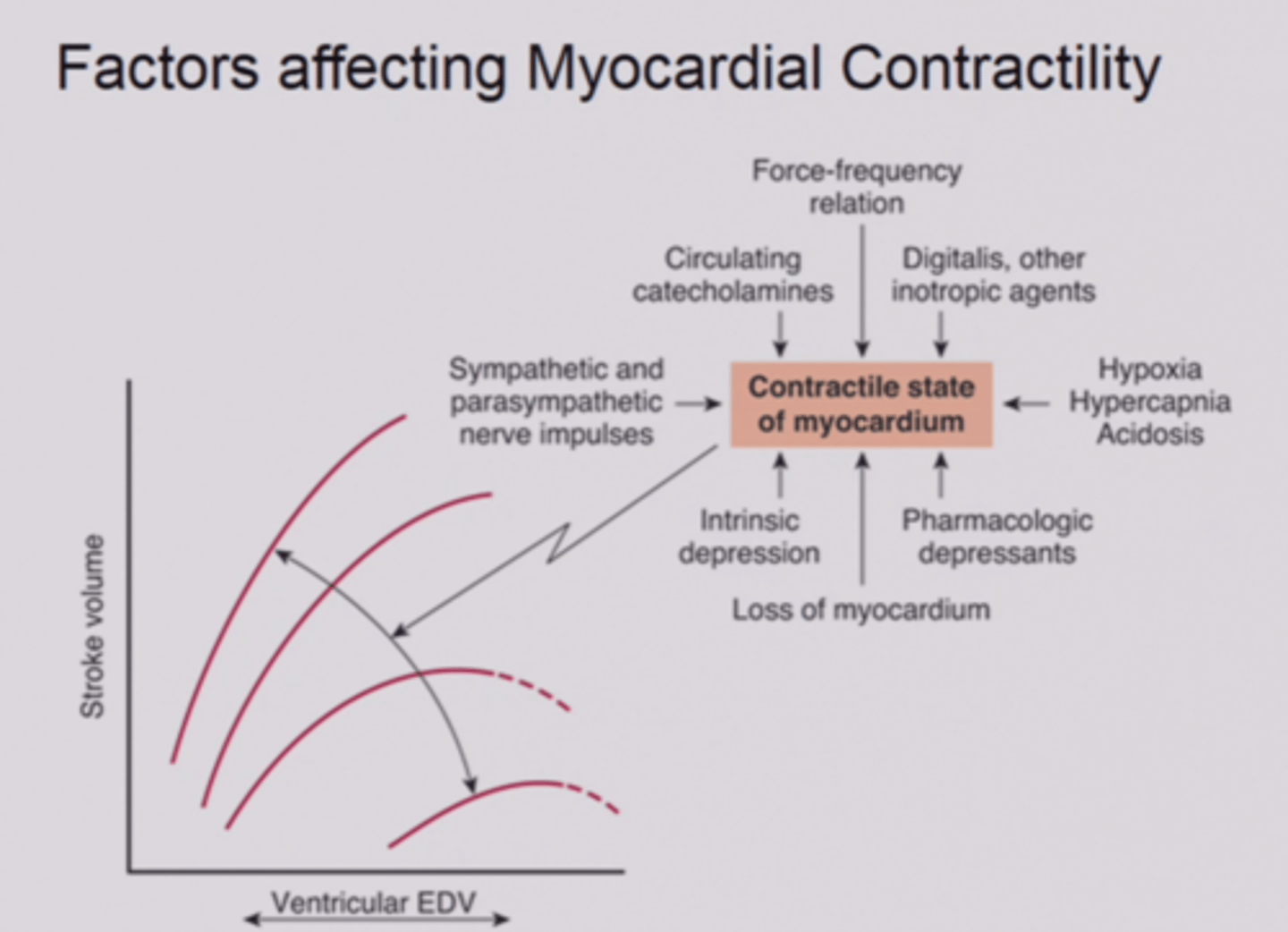
Positive ionotropic agents
Increase the strength of heart muscle contractions, increase the levels of calcium -> increases number of cross bridges -> increases the force of contraction
Negative ionotropic agents
decrease the strength of heart muscle contractions, decrease the levels of calcium -> decreases number of cross bridges -> decreases the force of contraction
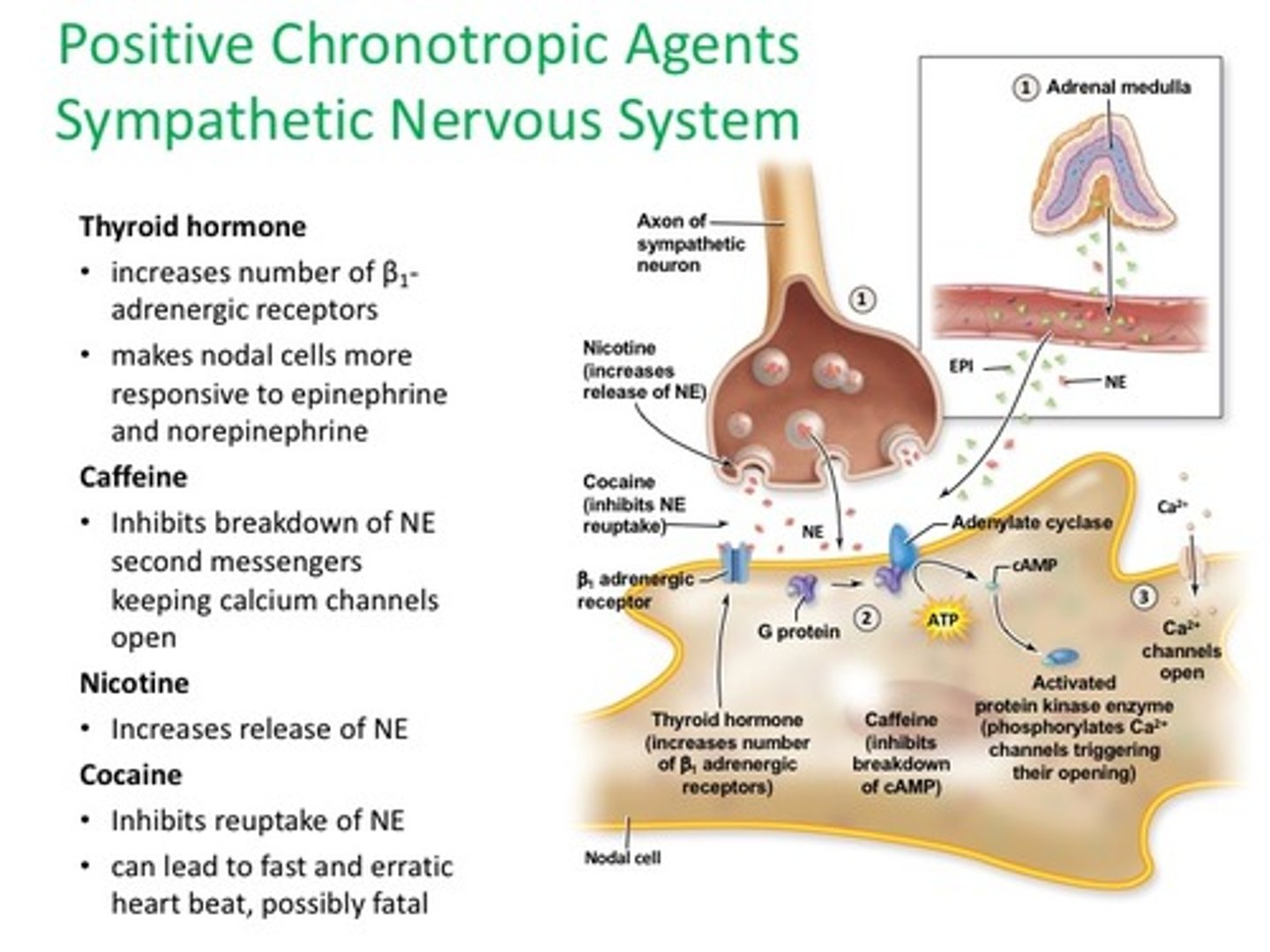
Positive chronotropic agents
factors that increase the heart rate
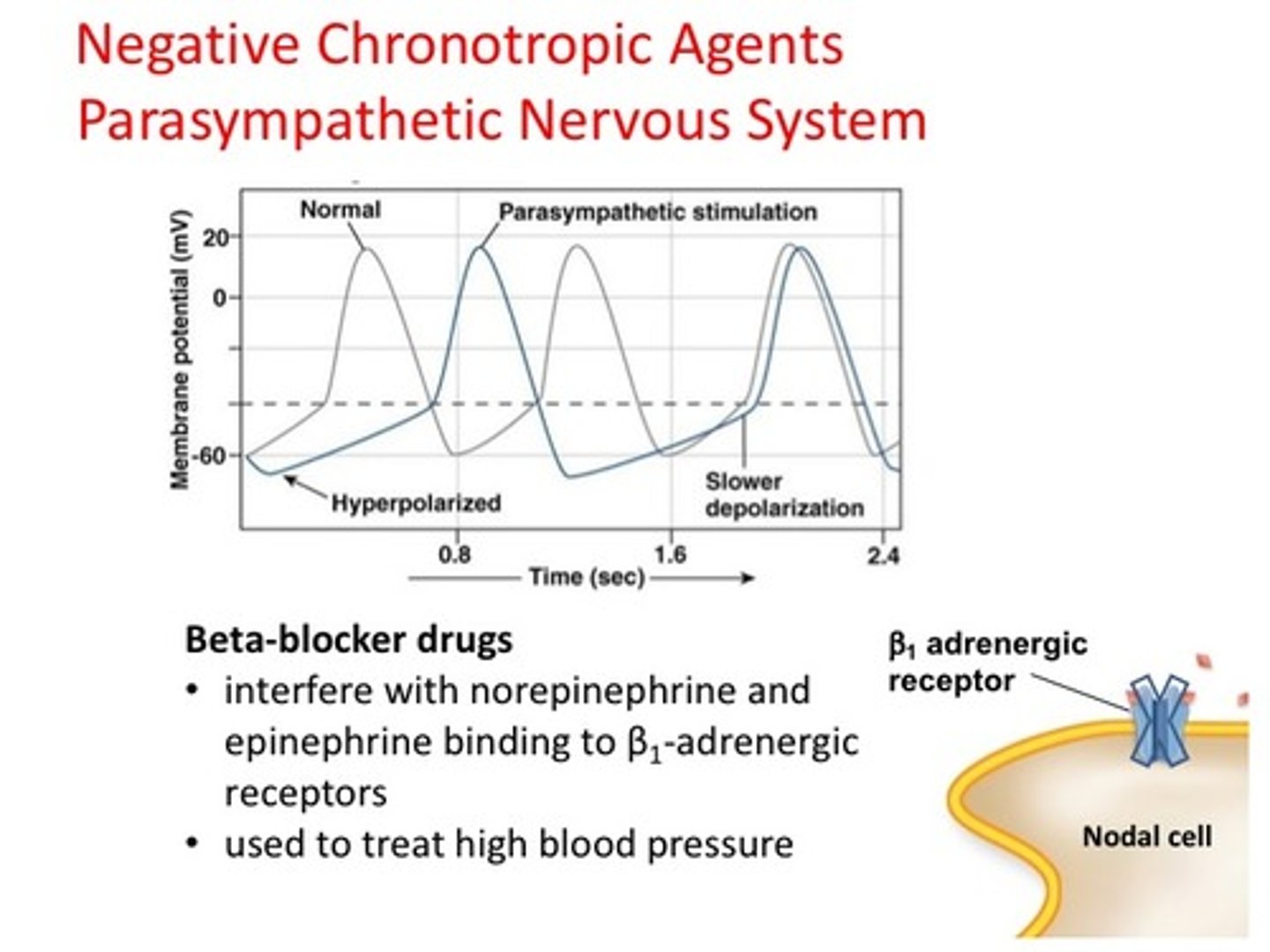
Negative chronotropic agents
factors that decrease the heart rate
Contractility of the heart
The strength of contraction of the heart muscle at any given end-diastolic volume
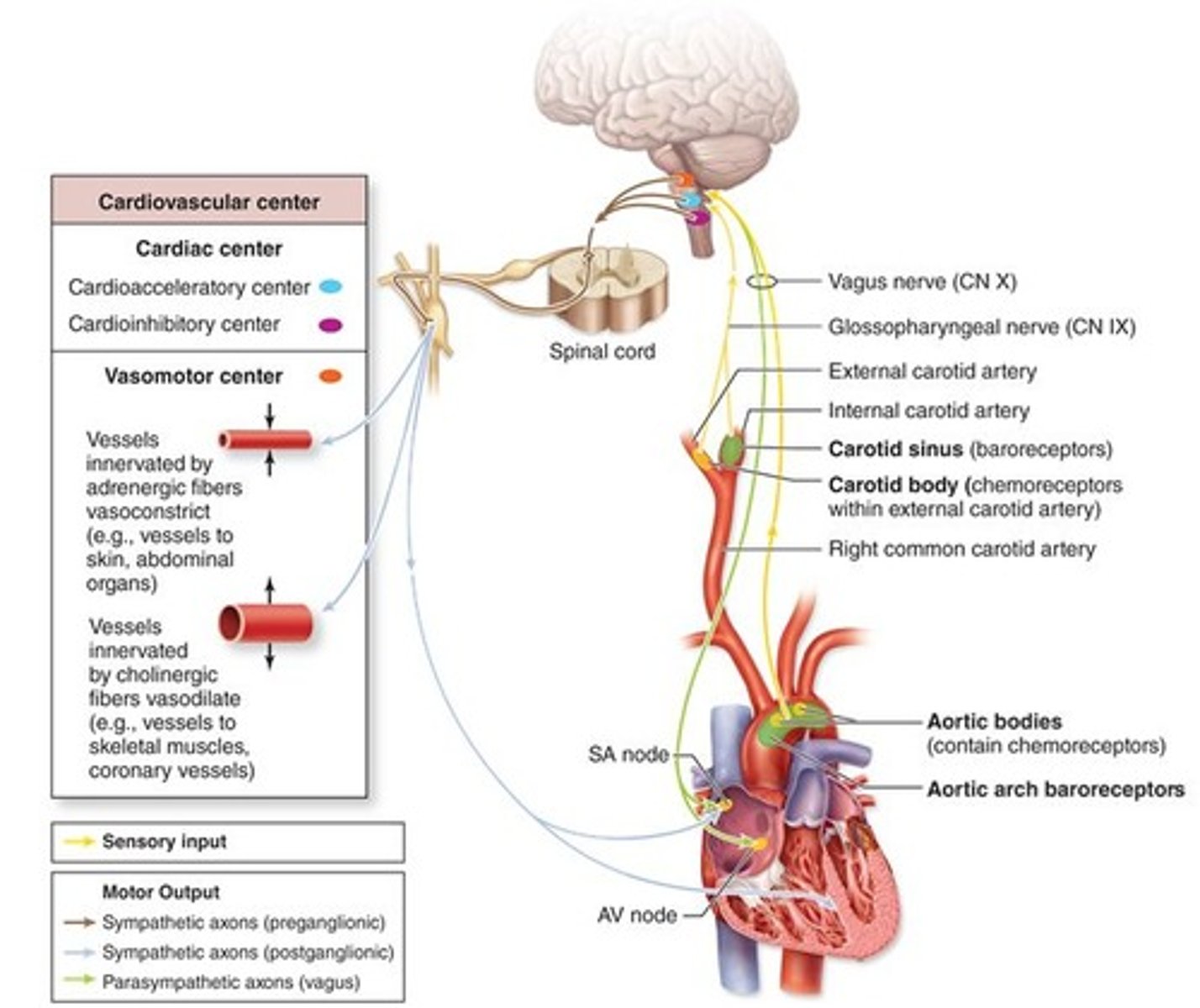
Cardioacceleratory center
sends signals through sympathetic nerves to increase both heart rate and force of contraction, stimulates SA and AV nodes, heart muscle, and coronary arteries
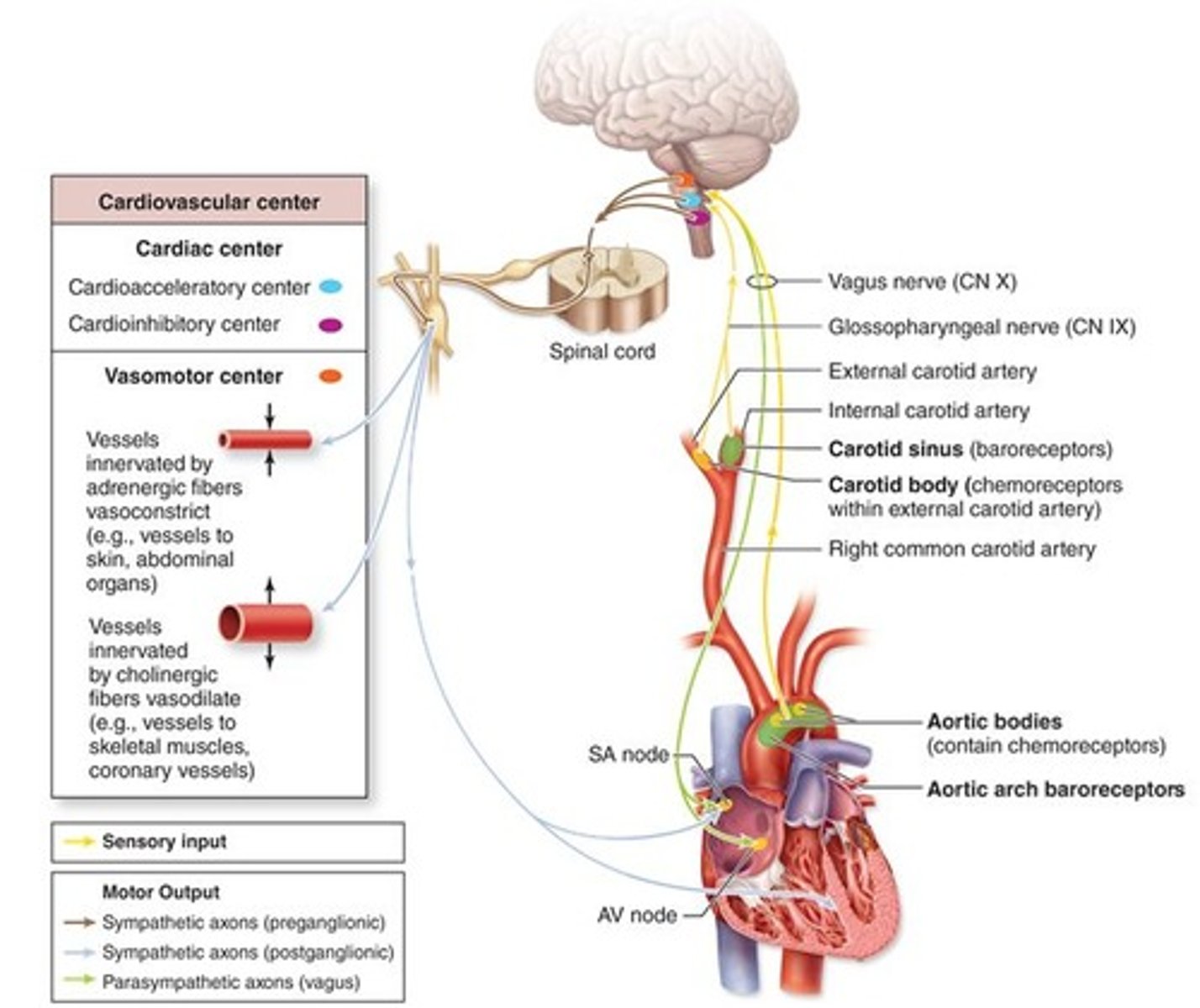
Cardioinhibitory center
sends signals through parasympathetic vagus nerve to decrease heart rate, inhibits SA and AV nodes