GENETIC VARIATION AND GENETIC CHANGE VOCABULARY
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:41 PM on 9/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
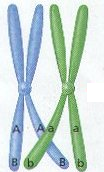
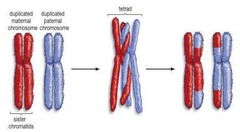
crossing over
when parts of two chromatids cross over each other before meiosis I at a point of crossing over called the chiasma
2
New cards
recombination
the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes producing recombinant chromosomes
3
New cards
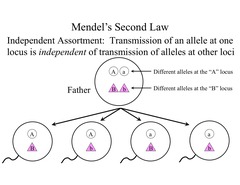
independent assortment
each chromosome pair is sorted independently of the other pairs during meiosis
4
New cards
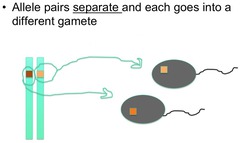
segregation
the two members of any pair of alleles at a given locus separate and pass unchanged into different gametes
5
New cards
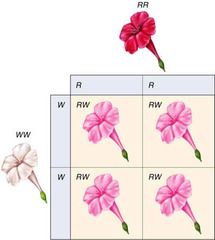
incomplete dominance
the action of one allele does not completely mask the action of the other and heterozygous offspring is intermediate in phenotype between the parental phenotypes
6
New cards
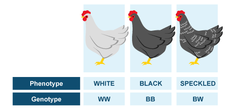
codominance
both alleles in a heterozygous organism are dominant so both alleles are fully and equally expressed
7
New cards
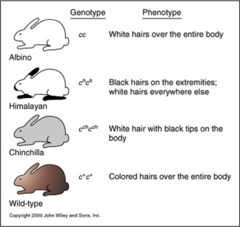
multiple alleles
three or more forms of ONE gene leading to 3 or more possible phenotypes for a particular trait
8
New cards
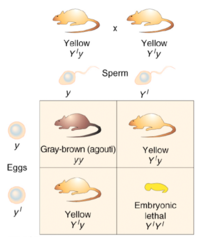
lethal alleles
alleles that cause an organism to die but only when present in homozygous condition
9
New cards
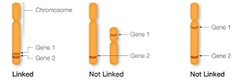
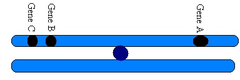
linked genes
genes that are located close together on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together
10
New cards
genetic diversity
the range of different genes and different alleles present in the gene pool of a population AND their relative frequency.
11
New cards
allele frequency
% or number of each allele in a gene pool
12
New cards
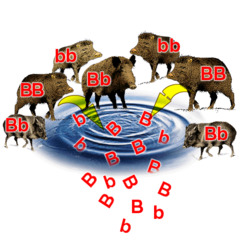
gene pool
all the alleles of all the genes that exist in a population at any one time
13
New cards
genetic change
the change in the frequency of alleles in a population's gene pool
14
New cards
natural selection
the differential survival and differential reproductive success of individuals whose characteristics are best suited to the environment at a given time
15
New cards
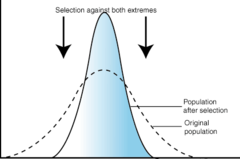
stabilising natural selection
selection for those individuals with average phenotypes and selection against those with extreme phenotypes
16
New cards
directional natural selection
selection for one end of a phenotypic range at the expense of the other
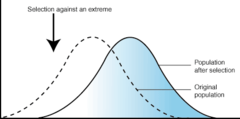
17
New cards
disruptive natural selection
selection against the average and for the extremes
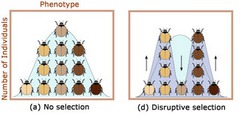
18
New cards
genetic drift
the change in allele frequency in a gene pool due to chance
19
New cards
founder effect
loss of genetic variation when only a few individuals colonise a new area AND allele frequencies in the new gene pool are not representative of the original population
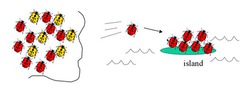
20
New cards
bottleneck effect
loss of genetic variation [change in allele frequencies in a population's gene pool] when a large population decreases in numbers to become a small population and then increases again
![loss of genetic variation [change in allele frequencies in a population's gene pool] when a large population decreases in numbers to become a small population and then increases again](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b44b7d4f7f584d03ad5411ef93c59a89.jpg)
21
New cards
migration
when individuals move from one population to another
22
New cards
gene
a length of DNA, bounded by start and stop codes, that codes for a specific polypeptide chain, that then folds to form a functional protein
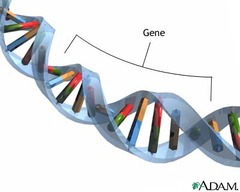
23
New cards
somatic mutations
not inheritable and occur in any cell in the body except the gametes
24
New cards
gametic mutations
occur in the gonads when gametes are formed so can be passed onto offspring
25
New cards
gene mutation
sudden and permanent change to the base sequence of a gene

26
New cards
evolution
the change in allele frequency in a population's gene pool from generation to generation
27
New cards
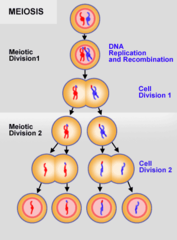
meiosis
cell division to produce gametes
28
New cards
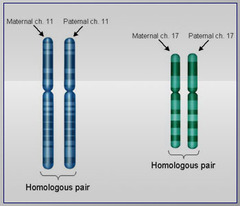
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes that have the same genes and the same structure
29
New cards
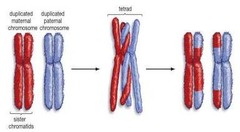
recombination
one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another shuffling allele combinations
30
New cards
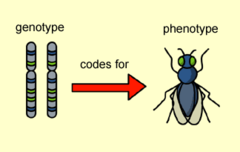
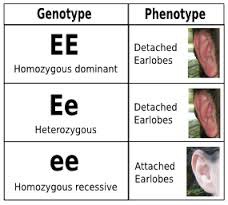
phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
31
New cards
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
32
New cards
selection pressure
environmental factors that favour certain phenotypes

33
New cards
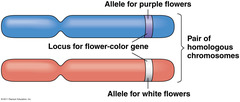
allele
alternative form of a gene.
34
New cards
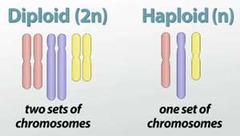
haploid cell
cell containing only one set of chromosomes (n).
35
New cards
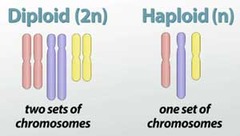
diploid cell
cell with chromosomes that come in homologous pairs, one set inherited from each parent
36
New cards
unlinked genes
genes that are found on different chromosomes