2.3- growth and development- sites and types
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is primary growth?
Is produced by bone formation on the surface of the bone
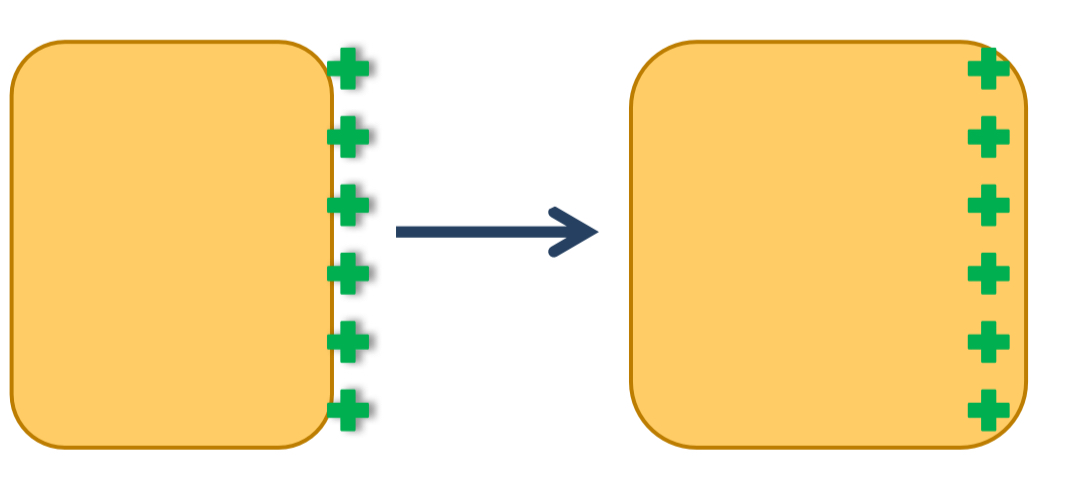
What are the 3 main types of growth at the sutures of the cranial vault?
Primary
Secondary growth
Remodelling
Which mechanisms occur on the surface and sutures of bones?
Primary growth, primary displacement, active displacement
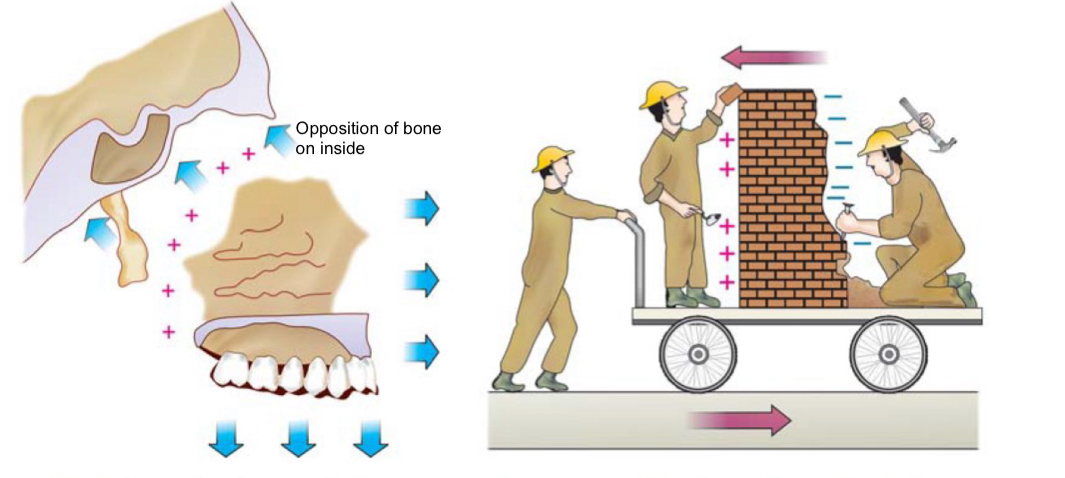
What is primary displacement?
Bone moves to another position due to deposition, resorption and when space is created by enlarging bones
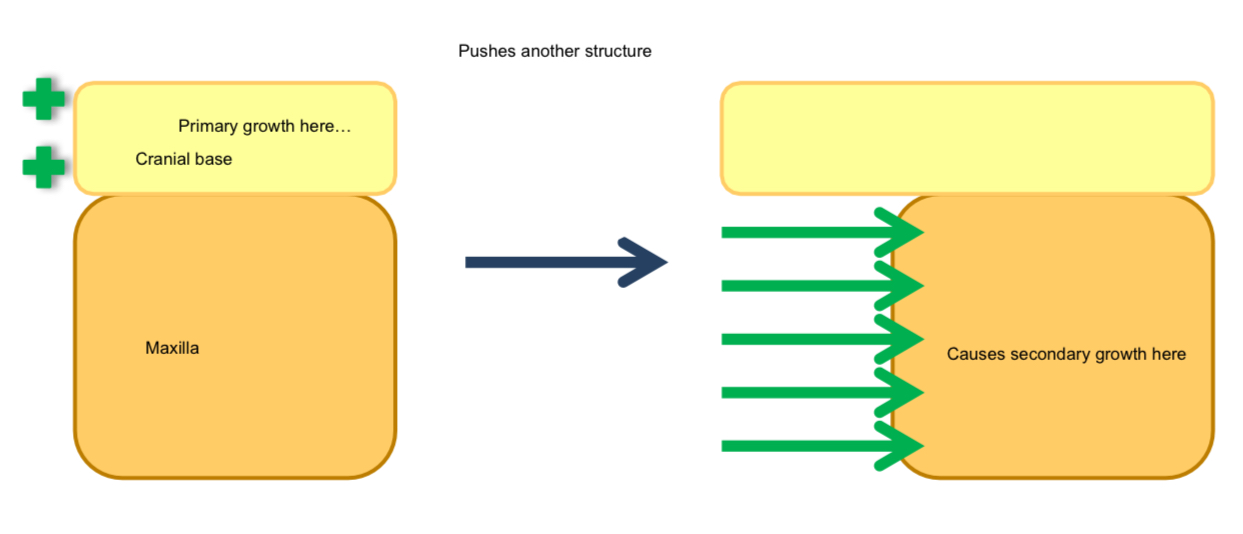
What is secondary growth/passive displacement?
Bone appears to grow due to growth of adjacent bones, which transports the bone into a new position
What are the types of growth of adjacent bones?
Secondary growth, secondary displacement, passive displacement
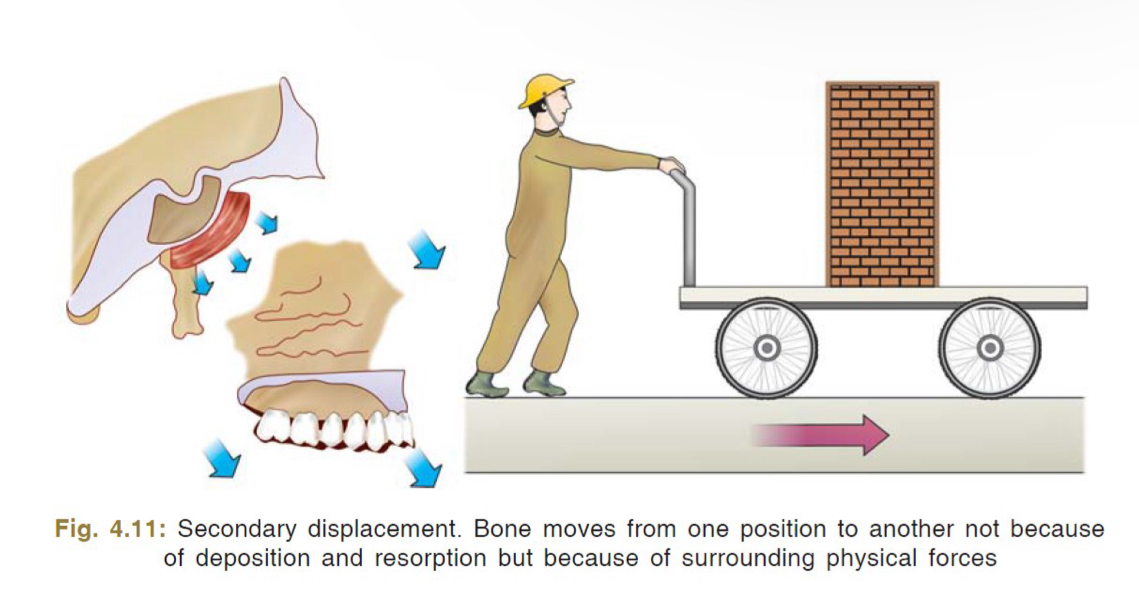
What is secondary displacement?
Bone moves to another position, due to surrounding physical forces not deposition or resorption
What is surface remodeling?
Changes in the shape and size of the bone due to apposition and resorption
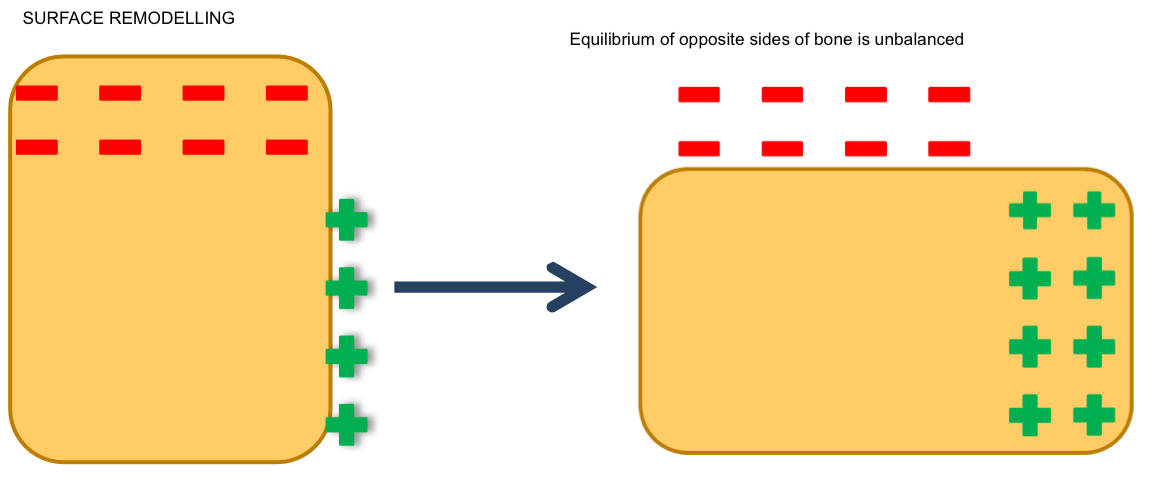
What are examples of remodelling mechanisms that occur on outer and inner surfaces of the cranial vault?
Remodelling
Cortical drift
Active displacement
What is the cranial vault made up of?
Flat bones formed by intramembranous bone formation
Where does the growth of the bone of the cranial vault occur?
At the cranial sutures- periosteum
At birth what happens to the skull bones/cranial vault?
separated by fontanelles- loose connective tissue, allows deformation during childbirth
What happens to the skull bones after birth (post natal growth)?
Apposition along the edges of fontanelles- closes soft spots
Bones remain separated by thin sutures, fuse in adult life
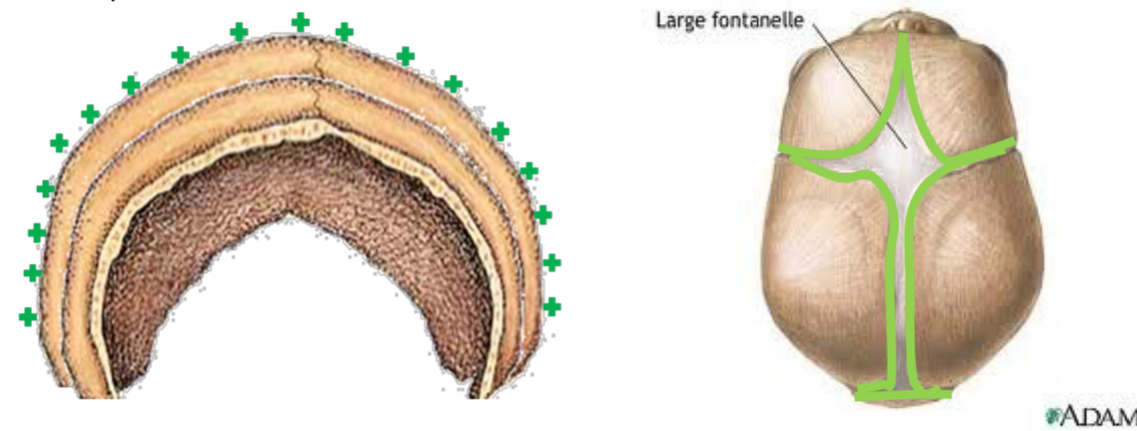
What are the mechanisms of growth in the cranial vault?
Apposition of new bone at sutures
Remodelling- allows for changes in contour during growth, bone removed from inner surface and new bone added to exterior
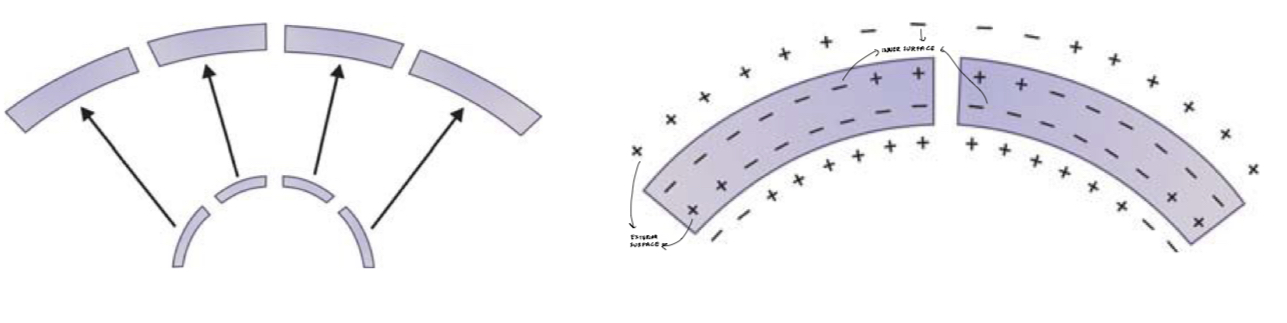
How does growth at the sutures of cranial vault occur?
Primary growth at coronal, sagittal, parietal, temporal, occipital sutures- to accommodate rapid brain expansion
As brain expands, bones are displaced outwardly
Intramembranous sutural growth replaces fontanelles
What kind of growth occurs at the outer and inner surfaces of the cranial vault?
Periosteal and endosteal remodelling
Resorption at endosteal lining and apposition at periosteum causes overall thickness of medullary space
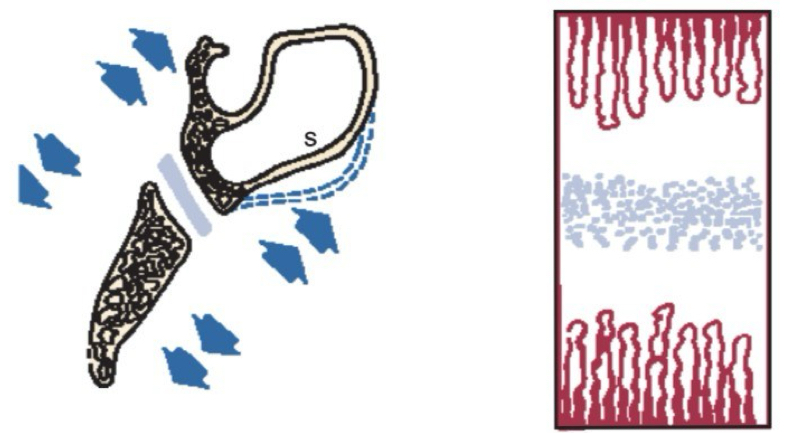
What is the structure within a synchondrosis?
2 sided epiphsyeal plate
Cellular hyperplasia in centre
Bands of maturing cartilage cells extends in both direction
Mature cartilage eventually replaced by bone
Where is the intersphenoidal synchondrosis located?
Between anterior and posterior portion of sphenoid
Doesn’t contribute to growth after birth
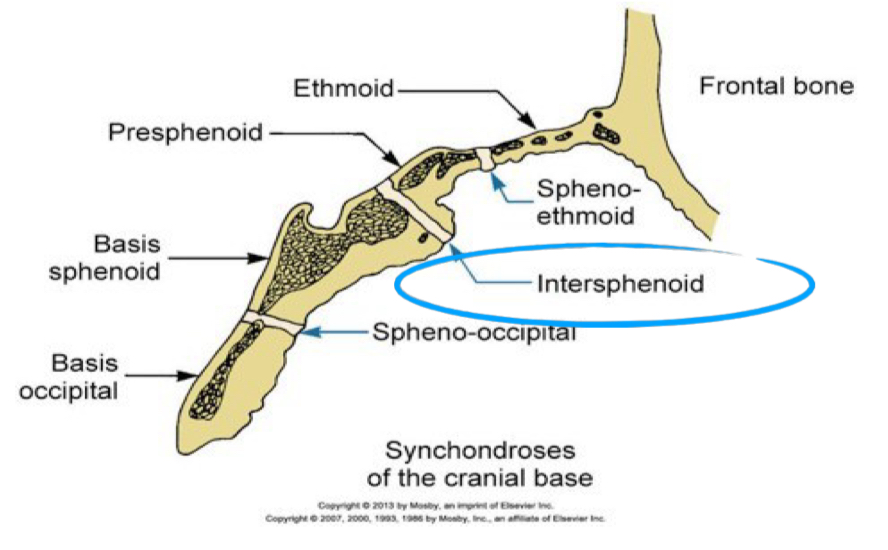
Where is the sphenoethmoidal synchondrosis?
Between sphenoid and ethmoid bone
Max activity from birth to 7 yrs- passive displacement
Where is sphenoccipital synchondrosis?
Between sphenoid and occipital bone
Doesn’t ossify till 13-15 yrs so major determining factor of vertical development of upper half of face and position of superior dentoalveolar complex in sagital plane
What is a synchondrosis and where is it found causing growth in?
Cartilaginous joint where hyaline cartilage divides and becomes bone
Found between and within the ethmoid, sphenoid, and occipital bones- causes growth of cranial base
Why does what happens to cranial base affect the structure, dimension and placement of various facial parts?
Acts as a template from which the face develops and other bones grow
In the embryo stage how is the maxillary bone formed and give a type of the cartilage?
Apposition- growth cartilages help make the head longer and help move maxilla forward but don’t actually become the maxilla
Malar cartilage completely disappears and replaced by bone before birth
What happens to the maxilla in postnatal development?
connects to the rest of the skull at sutures
Surface remodelling
Is pushed forward by growth of cranial base
In the maxilla, what occurs after the cranial push at the sutures?
The posterior and superior sutures allow it to grow down and forwards
Apposition occurs during the movement
Sutures remain same width but increase in length
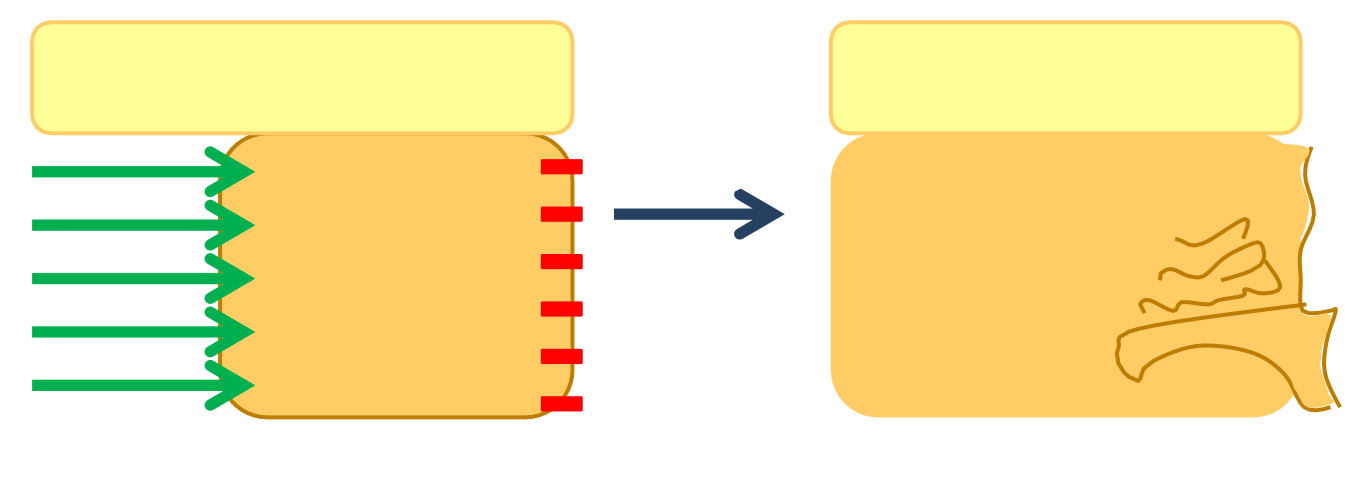
What occurs as the maxilla grows downward and forward?
Front surfaces are remodelled
Bone removed from anterior surface which moves forwards
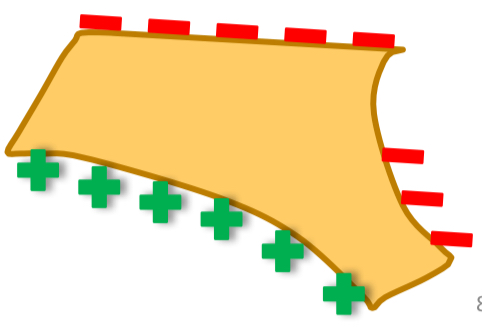
What is the additive effect of the palate bone?
Nasal side bone removed, added to oral side- thickens palate
Anterior part of alveolar process is a resorptive area so it cancels out some forward growth
How does the growth of the nasomaxillary complex occur, how does nose grow?
Passive displacement
Nose grows more rapidly than rest of face
Proliferation of lateral cartilages alters shape of nose
Where does the mandible develop?
In same area as cartilage of 1st pharyngeal arch-Meckels, which disintegrates as mandible develops
What are the points about post natal growth of mandible?
Endochondral and periosteal activity
Displacement of TMJ is a minimal role
Cartilage covers surface of Condyle at TMJ - hyperplasia, hypertrophy, endochondral replacement
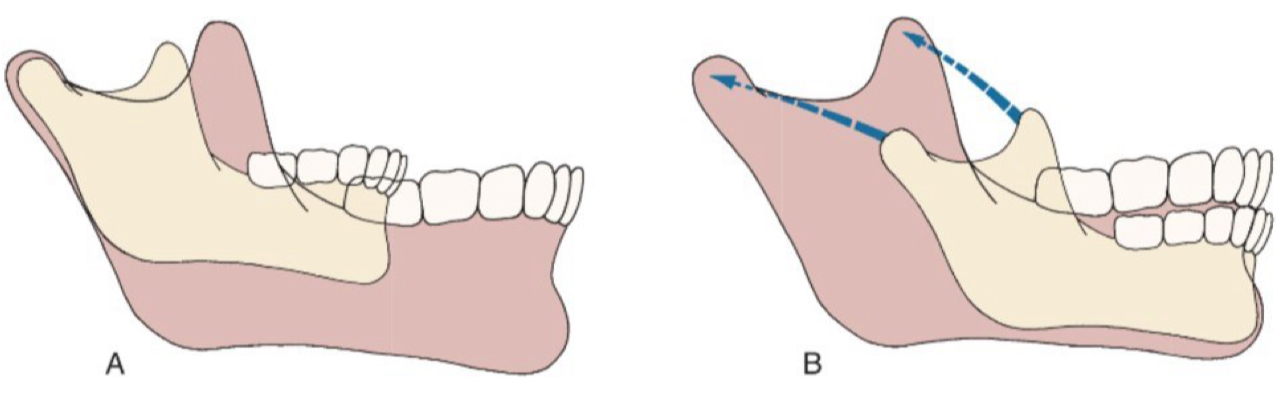
What are the growth sites of the mandible?
Chin - inactive, translated forward and downward
Mandible body- grows by periosteal apposition
Ramus- endochondral replacement
What is an area of resorption in the mandible?
Anterior border of the chin
What is the order in which growth is completed in the different planes of space and which age is each completed?
Width, length, height
W 10-12
L 14-16
H 18-20