3-Digestion and Absorption of Lipids and Vitamins
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
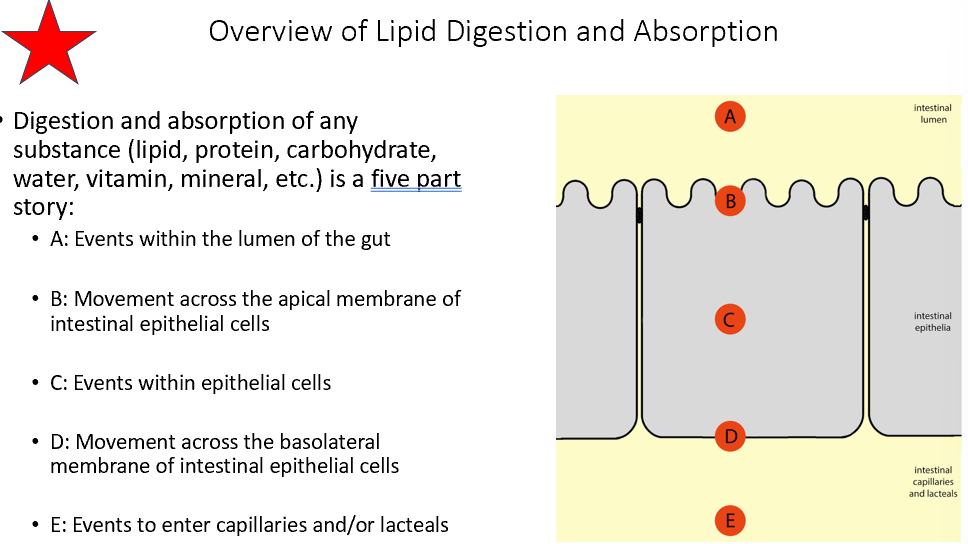
Lipid Digestion/Absorption Areas of Events (cell wise)
Lumen of the gut
Move across apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells
Events w/in the cells
Move across basolateral membrane of epithelial cells
Events to enter capillaries/lacteals
Lipid Subtypes and Characteristics
Triacylglycerol (TAG)
long term fuel storage, insulation
Phospholipid
modified TAG
cell membranes
Steroid
hydrocarbon rings
cell membranes
hormones
Dietary Fat means:
TAG, phospholipids, steroids
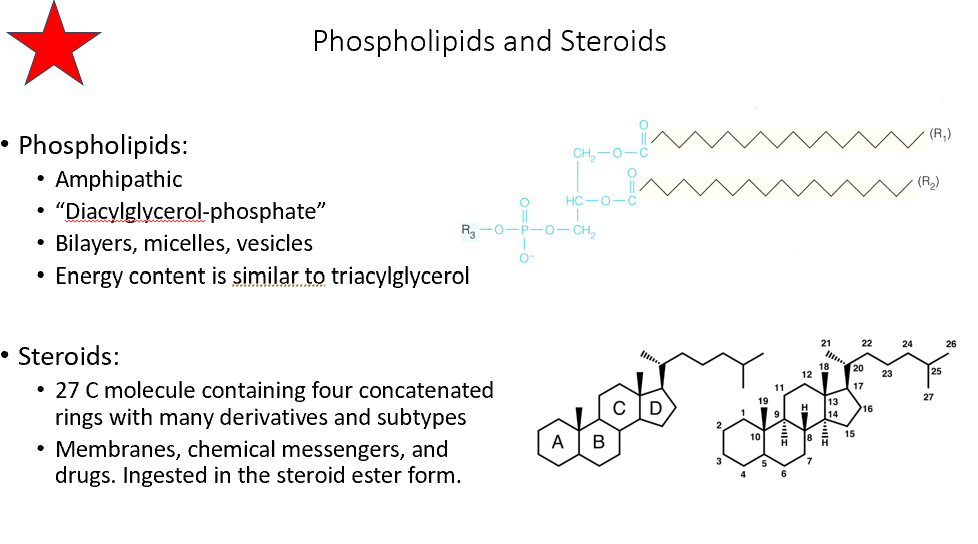
Phospholipids
Amphipathic
Make up bilayers and micelles
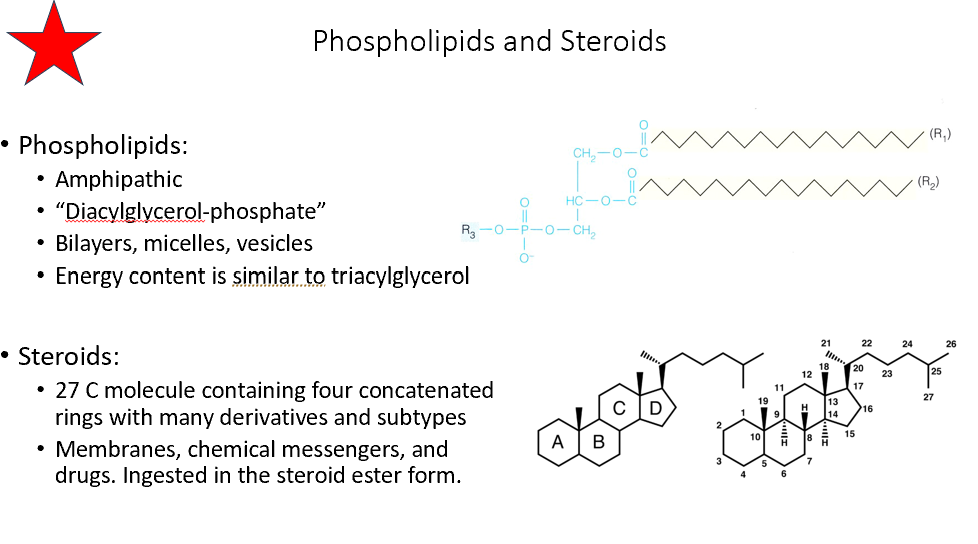
Steroids
27 C molecule with 4 rings
Membranes, messengers, drugs
Ingested as steroid esters!
What does it mean when an athlete “bonks”?
Limited carb storage
Glycogen stores are decreased → body fatigues and burns fat instead
Fat takes longer to deplete
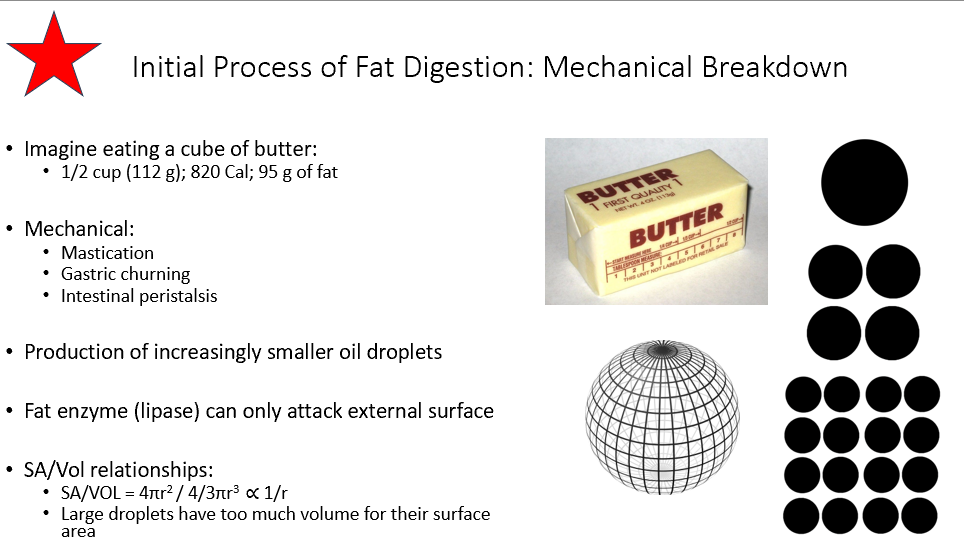
Mechanical methods of breaking down fat
Mastication
Gastric Churning
Intestinal Peristalsis
Why do we need to break fats down into increasingly smaller oil droplets?
Fat enzyme (lipase) can only attack external surface
Dietary Protein in the stomach
Some amphipathic character
Bile Salts and Lecithin
Made in the liver
Sometimes stored in gallbladder
Released via common bile duct → duodenum
Bile Salts
Cholesterol-derived amphipathic molecules
95% reabsorbed before the large intestine (ileum)
Emulsification and micelle formation
Lecithin
Phospholipid (diacylglycerol phosphate) derivatives
Essential in emulsification of fats
What allows bile salts and lecithin to emulsify things?
Amphipathic nature!
Emulsification increases SA by 1000x.
Lipase Reaction
TAG → MAG + 2 FA
Lingual Lipase
Fat digestion in mouth, continues in stomach
Works best at pH 5
Does NOT require bile salts or colipase
Gastric Lipase
Additional digestion
Pancreatic Lipase
Works best at pH 8
Secreted by pancreas → duodenum
Most important lipase!
Does require colipase & bile salts
Other Lipases (besides lingual, gastric, and pancreatic)
Cholesterol Esterase
Phospholipase A2
Cholesterol Esterase
Digests most all lipids
Cuts ester bonds in fats, cholesterols, and phospholipids
Phospholipase A2
Cleaves fatty acids from middle carbon of glycerol backbone of a phospholipid
Colipase (purpose, secreted as, activated by, functions (2))
Protein needed for pancreatic lipase to function
Secreted as procolipase (inactive form)
Activated by trypsin (in the duodenum)
Functions:
Cofactor
Allows pancreatic lipase access to emulsified fat droplets (moves bile salts/lecithin away)
What reverses the reaction of lipases?
The emulsification capacity of bile salts helps pull digested fat away from the main fat droplet.
Packaging of Lipids with Proteins and Lecithin
Smooth ER
Lipids/TAG are reconstituted
Rough ER
Lipids coated with apolipoprotein and phospholipid
Chylomicrons are formed
Golgi
Chylomicrons are packaged in vesicles for exocytosis
What happens in packaging of lipids if you don’t have apolipoprotein?
Abetalipoproteinemia: inability to absorb dietary fat/fat soluble vitamins.
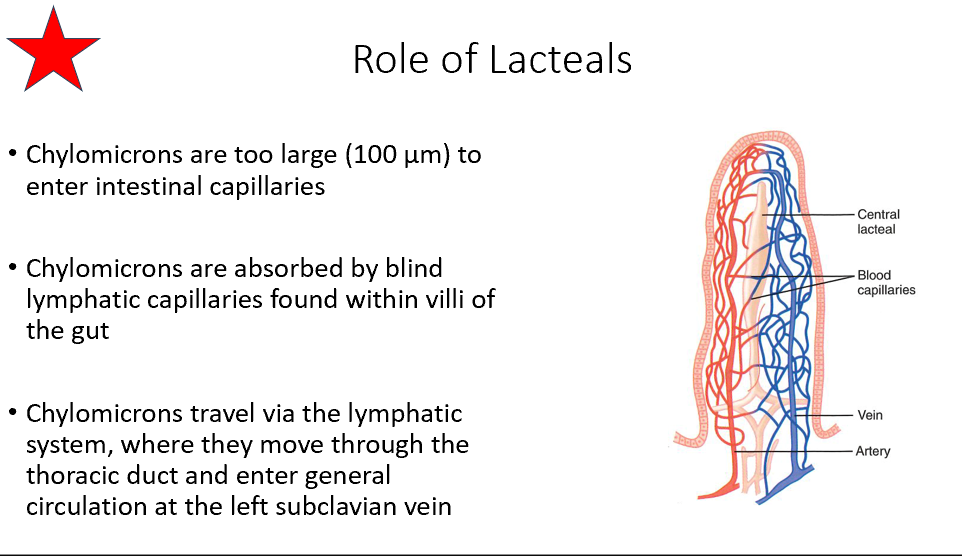
Lacteals
Chylomicrons are too big for intestinal capillaries
They use lacteals in the villi of the gut instead
Chylomicrons travel via lymph system through thoracic duct → left subclavian v. → general circulation
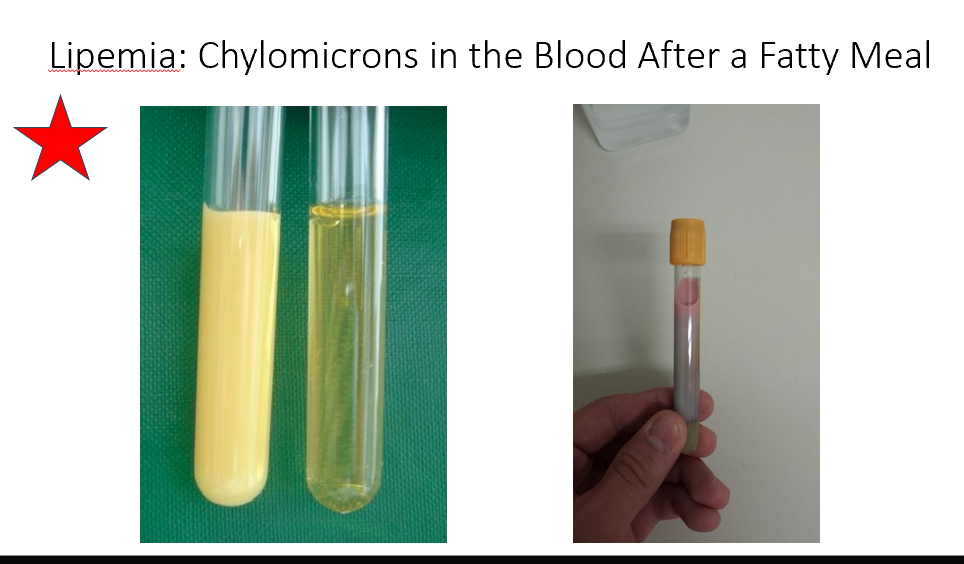
Lipemia
Chylomicrons in the Blood After a Fatty Meal
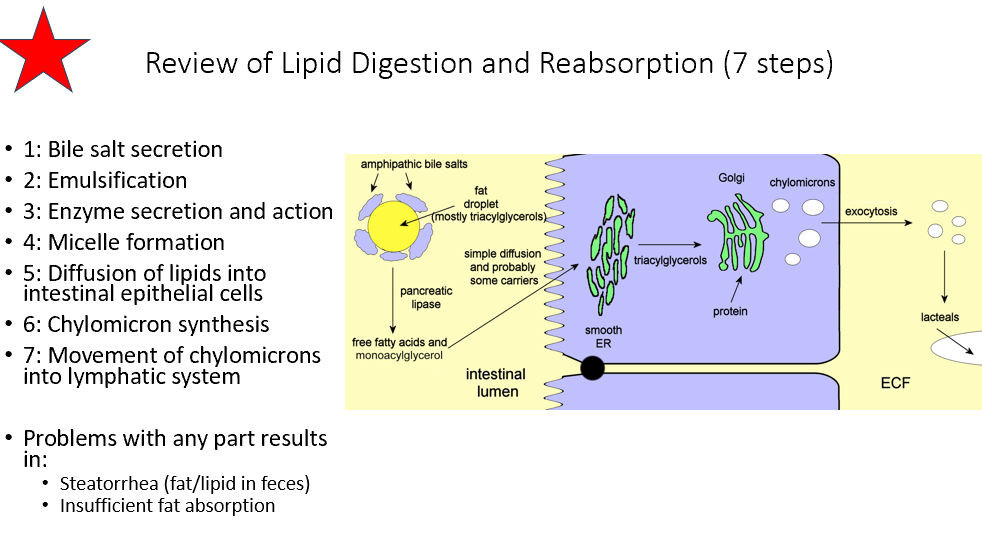
Lipid Digestion/Reabsorption Steps
1: Bile salt secretion
2: Emulsification
3: Enzyme secretion and action
4: Micelle formation
5: Diffusion of lipids into intestinal epithelial cells
6: Chylomicron synthesis
7: Movement of chylomicrons into lymphatic system
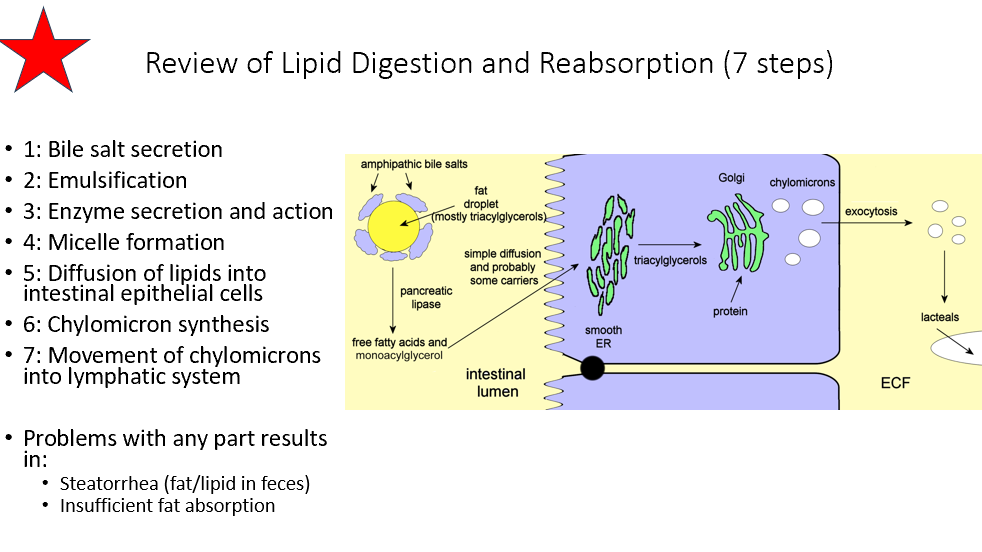
What happens if there’s a problem with any portion of lipid digestion/reabsorption?
Steatorrhea (fat/lipid in feces)
Insufficient fat absorption
What are the water soluble vitamins?
B’s and C’s are Watery!
C (ascorbic acid) is for “Collagen not Colds”
B1 (thiamine) is “To enter The TCA cycle for aTp synthesis”
B2 (riboflavin) is “Very Vital for FAD and makes PEE TOO yellow”
B3 (niacin) is “Needed for NADH”
B5 (pantothenic acid) is for “Pent up CoA entering the TCA”
B7 (biotin) is for “Biotin binds avidin”
B9 (folate) is for “Future Fetus”
B12 (cobalamin)
Vitamin C
C (ascorbic acid) is for “Collagen not Colds”
Vitamin B1
B1 (thiamine) is “To enter The TCA cycle for aTp synthesis”
Vitamin B2
B2 (riboflavin) is “Very Vital for FAD and makes PEE TOO yellow”
Vitamin B3
B3 (niacin) is “Needed for NADH”
Vitamin B5
B5 (pantothenic acid) is for “Pent up CoA entering the TCA”
Vitamin B7
B7 (biotin) is for “Biotin binds avidin”
Vitamin B9
B9 (folate) is for “Future Fetus”
Vitamin B12 (facts, procedure requiring more?)
B12 (cobalamin) requires intrinsic factor (secreted by parietal cells of the stomach) and is absorbed at the ileum.
Gastrectomy requires extra oral B12 or B12 injections to avoid deficiency.
What are the fat soluble vitamins?
Kool ADE man is fat!
A (retinol) is for “Ayes”
D (cholecalciforol) is for “Darn strong bones”
E (tocopherol) is for “Excellent ‘Embranes”
K (phytonadione) is for “Klotting”
Vitamin A
A (retinol) is for “Ayes”
Vitamin D
D (cholecalciforol) is for “Darn strong bones”
Vitamin E
E (tocopherol) is for “Excellent ‘Embranes”
Vitamin K
K (phytonadione) is for “Klotting”
How are fat soluble vitamins absorbed?
Similar to lipids!
Emulsified, micelles, across membrane, absorbed into lacteals!
Any fat digestion/absorption dysfunction is likely to cause what?
Fat soluble vitamin absorption deficiency
Orlistat
Gastric and pancreatic lipase inhibitor
Steatorrhea “treatment effects” are a type of aversion therapy
Pellegra is associated with what? What are the signs to look for?
Pellegra (niacin or B3 deficiency)
3 Ds: dermatitis, dementia, and diarrhea