Fake News, Real Science Final Exam
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Data visualizations
Visual representations of data to help interpret trends and patterns.
Earth's energy budget diagram
A system model showing incoming and outgoing energy flows on Earth.
Feedback loops in Earth systems
Processes where a change in one part of a system causes further change (positive or negative).
Scientific uncertainty
The idea that all scientific measurements and models include a degree variability
Climate forcings
External factors (like greenhouse gases, solar radiation) that influence Earth's climate system.
Earth's radiation budget
Balance between incoming solar energy and outgoing infrared energy.
Climate models
Simulations that predict future climate patterns based on data and assumptions.
Uranium enrichment
Increasing the percentage of U-235 for reactors or weapons.
Risks of nuclear energy
Includes reactor accidents, waste storage issues, and long-term radioactive contamination.
Pros and cons of nuclear energy
Pros: Low carbon emissions, high energy output; Cons: Waste disposal, accident risks.
Characteristics of science
Testable, falsifiable, reproducible, peer-reviewed.
Science vs. pseudoscience
Science follows evidence and testing; pseudoscience relies on beliefs without testing.
Demarcation of science
Separating legitimate science from pseudoscience based on falsifiability.
Falsification
The ability for a theory to be proven wrong by evidence.
Peer review
The process where other experts evaluate scientific research before publication.
Fallacious reasoning
Flawed arguments that misuse logic or reasoning.
Types of fallacious reasoning
Straw man, slippery slope, ad hominem, false dilemma.
Science as processes
Methods of inquiry like experiments and observations.
Science as social practices
Collaborative, structured systems for producing scientific knowledge.
How science guards against enduring error
Through peer review, replication, transparency, and critical scrutiny.
Scientific expertise
Knowledge based on years of study and peer evaluation.
Scientific consensus
General agreement among scientists based on collective evidence.
Competent outsider
A knowledgeable non-specialist who can still engage meaningfully with scientific ideas.
System 1 thinking
Fast, intuitive, automatic decision-making.
System 2 thinking
Slow, effortful, logical decision-making.
System 1 heuristics
Mental shortcuts used to make quick judgments.
How to create a system model
Identify system parts, flows, and feedbacks, and draw connections.
How to interpret a system model
Understand how changes affect different parts of the system.
How to use a system model for prediction
Predict outcomes by simulating changes in variables.
Positive feedback loop
A process that amplifies change and destabilizes a system.
Negative feedback loop
A process that stabilizes a system by counteracting changes.
Strength of an argument
How well claims are supported with logic and evidence.
Author qualifications
Assessment of the author's expertise or credibility on the topic.
Evidentiary support
Quality and amount of evidence backing claims.
Potential bias
The presence of a slant or prejudice in information presentation.
Definition of rhetoric
The art of persuasion using effective language.
Common types of arguments
Logical arguments (logos), ethical appeals (ethos), emotional appeals (pathos).
Formal debate structure
Introduction, arguments, rebuttals, and conclusion, following structured rules.
Misinformation
False information shared without intent to deceive.
Disinformation
False information deliberately shared to mislead.
AI and misinformation
Artificial intelligence tools that can generate and spread false content.
Toolkit for debunking conspiracy theories
Fact-checking, source validation, logical analysis.
Definition of media framing
How media outlets shape the presentation of news to emphasize certain aspects.
Conducting a frame analysis
Identifying themes, perspectives, and emphasis patterns in media coverage.
What is science?
A systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science education in an age of misinformation
The study and practice of teaching science effectively amidst widespread confusion on the topic.
Demarcation of science
The philosophical and methodological criteria distinguishing science from non-science or pseudoscience.
Falsification
The principle that scientific theories must be testable and refutable; a theory is scientific if it can be proven false.
Peer review
The evaluation of scientific work by others who are experts in the same field to ensure validity and quality before publication.
Difference between peer-reviewed and media articles
Peer-reviewed articles are evaluated by experts and are considered credible scientific sources; media articles are not peer-reviewed and may lack scientific rigor.
Fallacious reasoning
Flawed logical arguments that undermine the validity of reasoning, often leading to incorrect conclusions.
Types of fallacious reasoning
Common logical fallacies include straw man, slippery slope, ad hominem, false dilemma, and hasty generalization.
Science as a body of knowledge
The accumulation of scientific facts, theories, and principles over time.
Science as processes
The methodologies and procedures used to conduct scientific research and experimentation.
Science as social practices
The collaborative and communicative aspects of scientific work within the scientific community and society.
How science guards against enduring error
Through mechanisms like peer review, replication of results, and ongoing scrutiny, science minimizes persistent errors.
Scientific expertise
Specialized knowledge and skills acquired through education and experience in a scientific field.
Scientific consensus
General agreement among scientists based on collective evidence and reasoning.
Competent outsider
An individual who, while not a specialist in a particular scientific field, possesses sufficient knowledge to understand and evaluate scientific information.
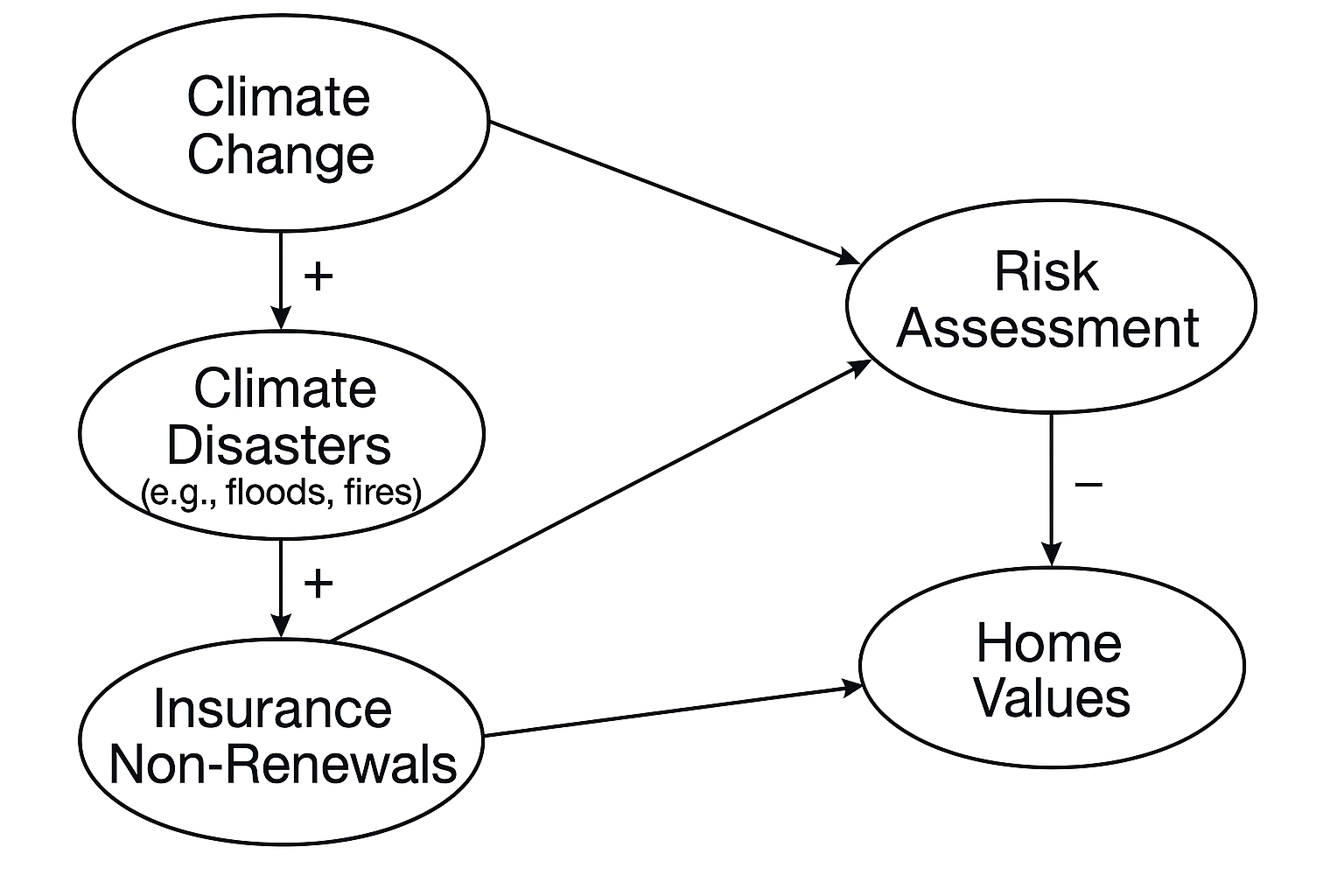
Insurance Non-Renewal
The decision by insurance companies not to renew existing policies, often due to heightened risks such as extreme weather.
Climate-Related Disasters
Natural events intensified by climate change, such as wildfires, hurricanes, and floods.
Insurance Market Withdrawal
The process of insurance companies exiting specific markets or regions due to high risk.
Risk Assessment (Insurance Context)
The evaluation of potential risks to determine insurance coverage and premiums, now updated for climate risks.
Insurance Affordability Crisis
A situation where insurance premiums become too expensive for many homeowners, especially in high-risk areas.
Federal and State Insurance Programs
Government-backed insurance initiatives providing coverage when private insurers withdraw (e.g., California FAIR Plan).
Climate Risk Modeling
The use of data and simulations to predict how climate change impacts regional insurance risk.
Real Estate Market Impact (from Insurance Loss)
The loss of property value and reduced market activity caused by insurance availability problems.
Regulatory Responses to Insurance Crisis
Actions by government bodies to stabilize insurance markets and protect homeowners in climate-affected areas.
Climate Adaptation Strategies
Measures homeowners and communities take to reduce vulnerability to climate-related risks and maintain insurability.
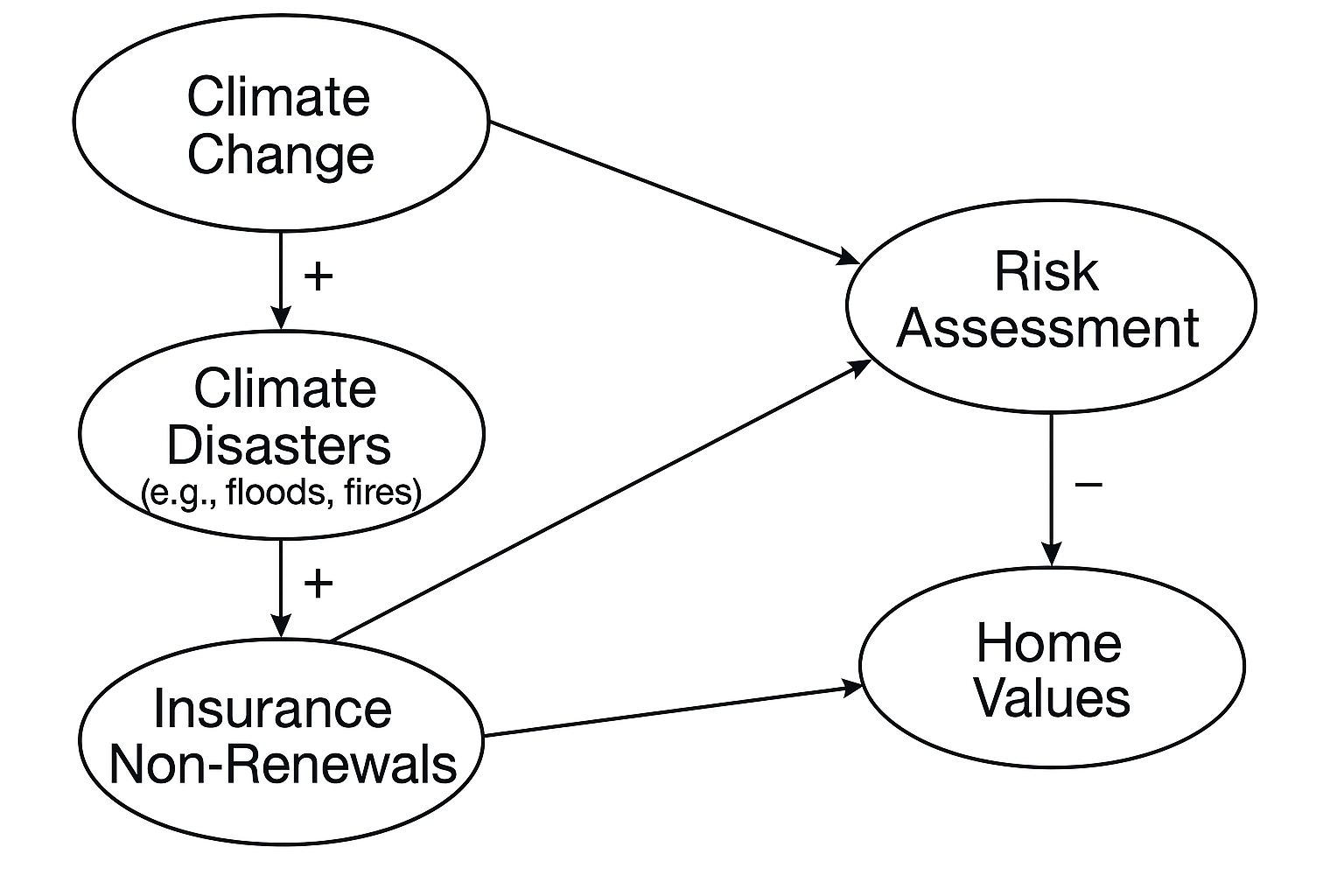
What type of feedback loop exists between "Insurance Non-Renewals" and "Economic Uncertainty"?
Positive feedback loop.
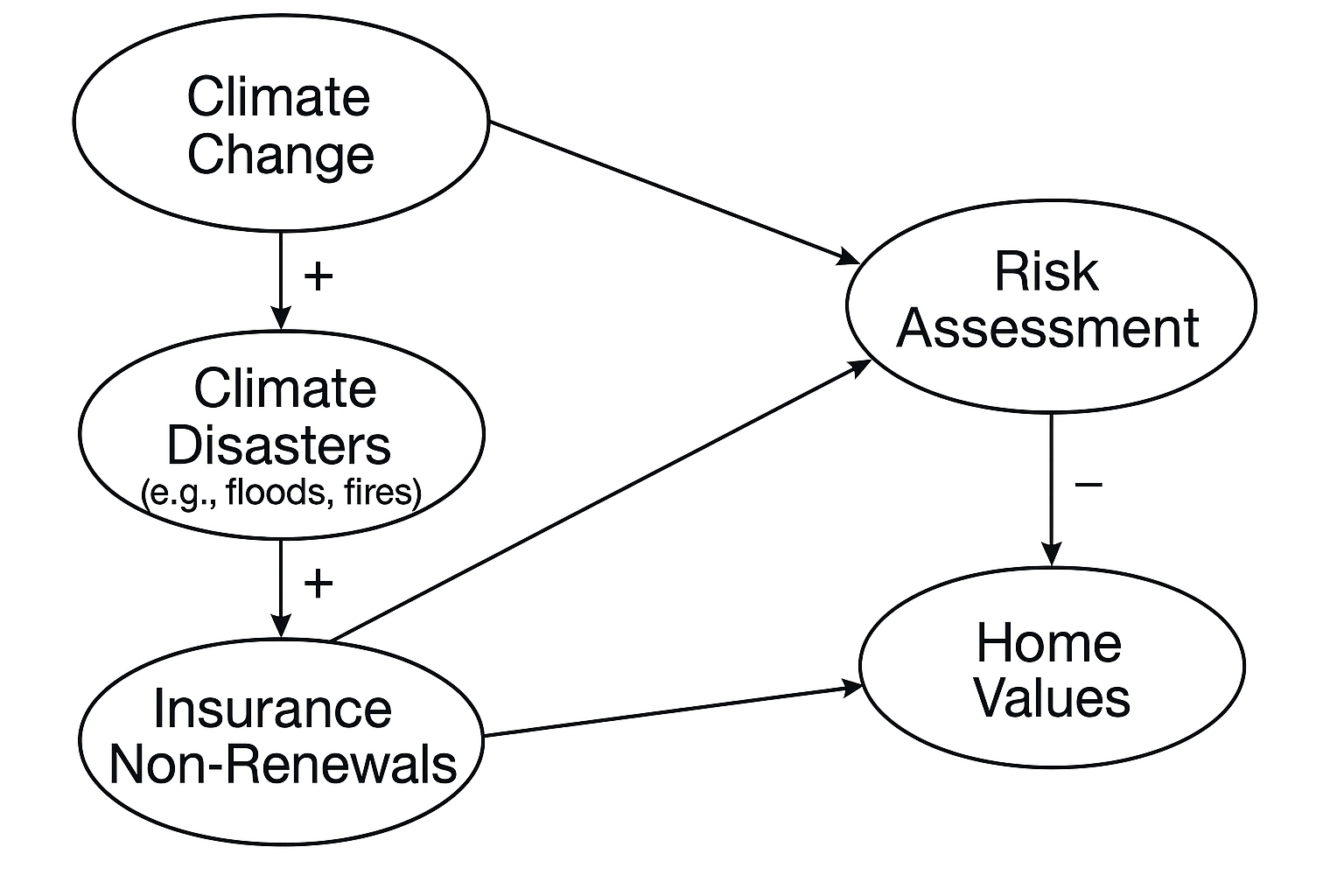
If Greenhouse Gas emissions decreased, what would happen to Risk Assessments?
Risk Assessments would likely decrease.
Which link represents a negative correlation?
"More Insurance Non-Renewals → Decreased Home Values."
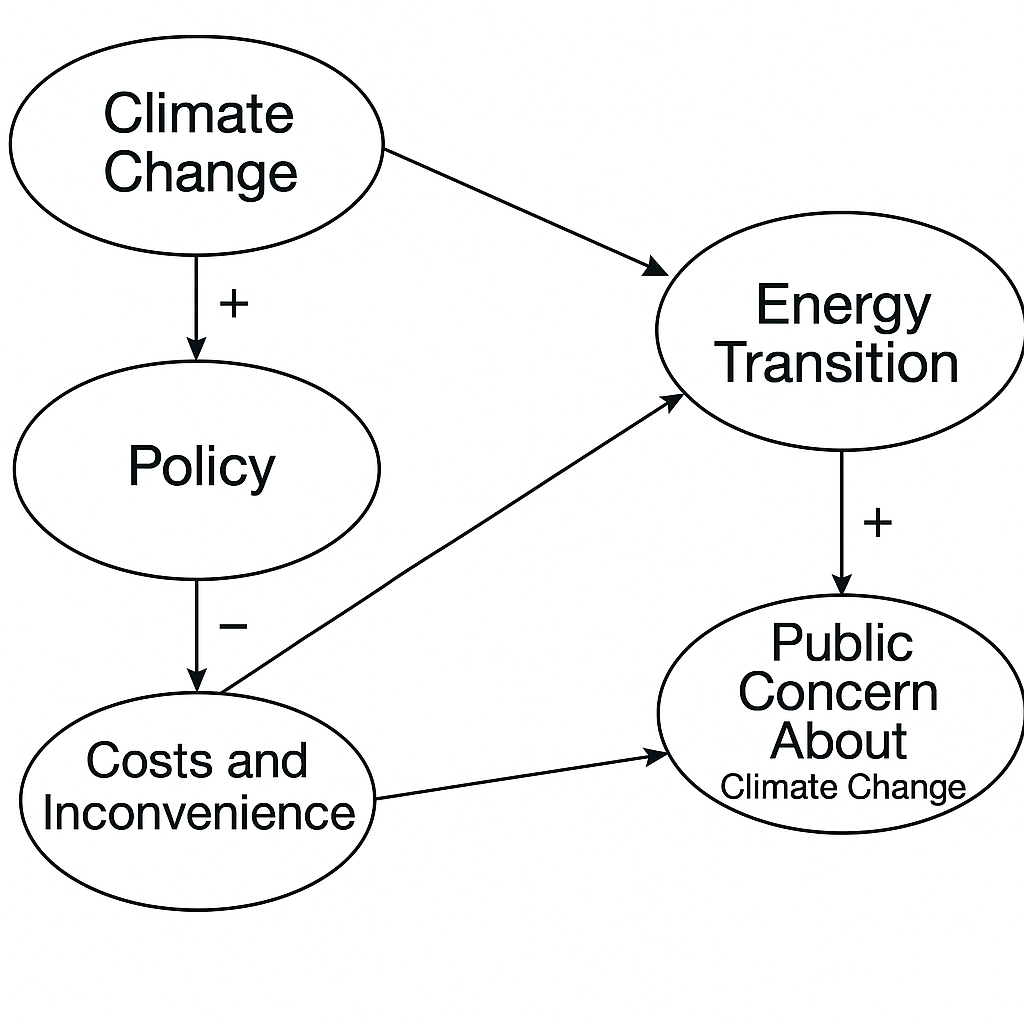
What happens to climate change if public polices increase?
It goes up
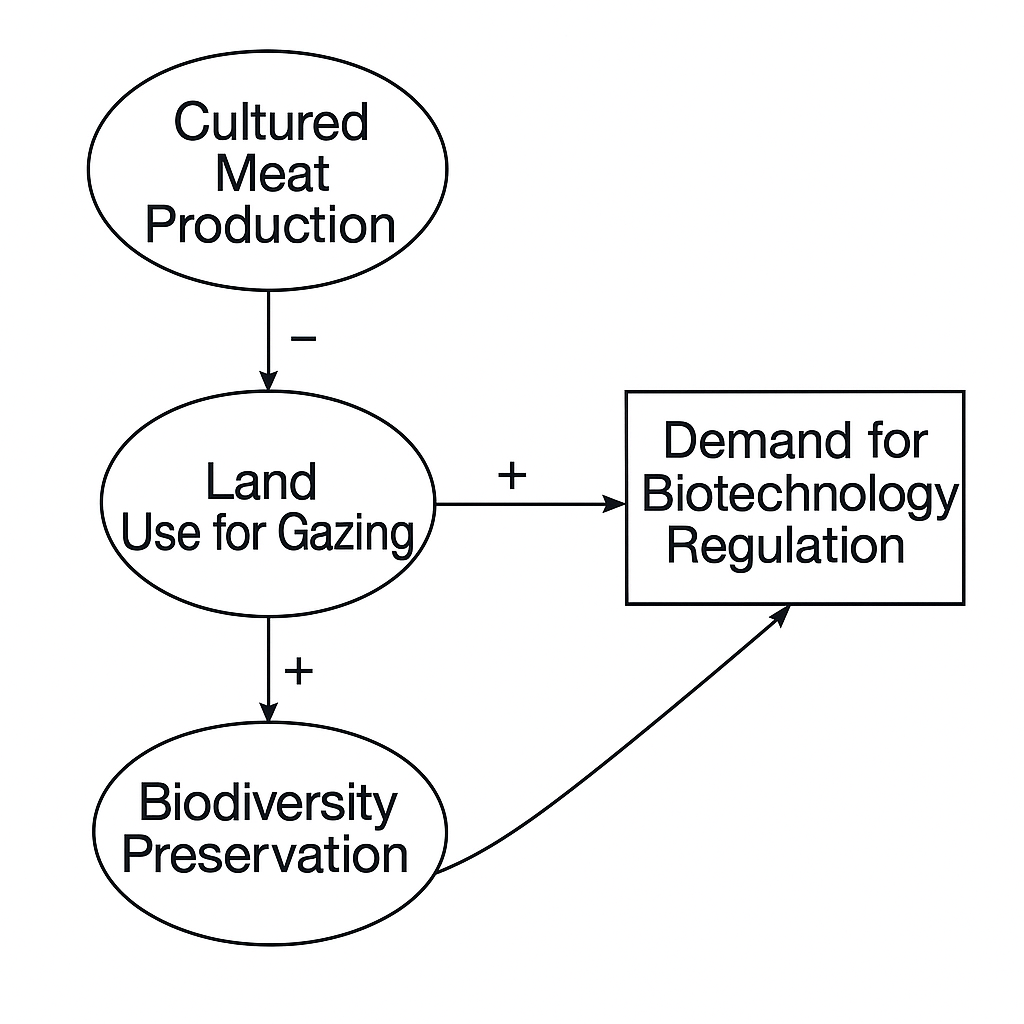
How would an increase in demand for biotechnology regulation affect future cultured meat production?
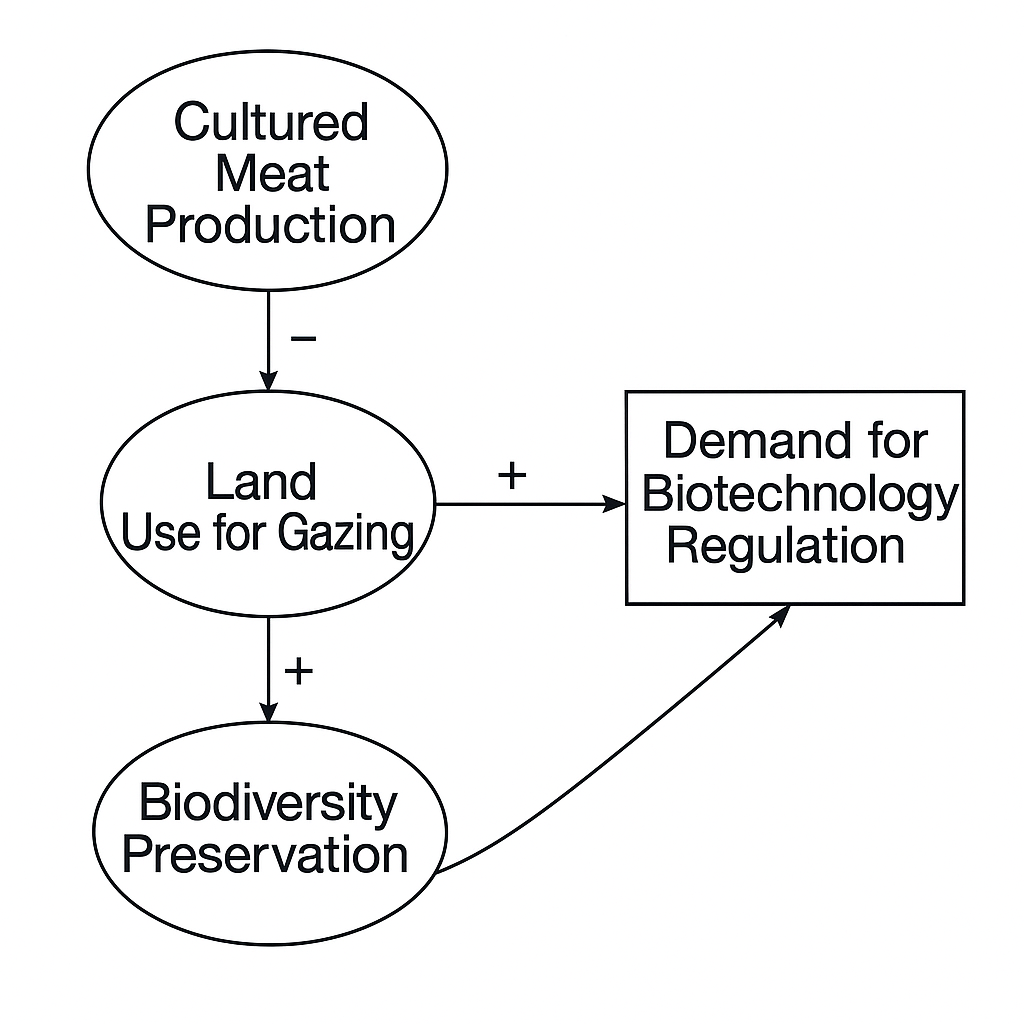
What is the chain of indirect relationships from Cultured Meat Production to Extinction Rates?
Cultured Meat → Less Grazing Land → More Biodiversity → Fewer Extinctions.

Which link shows a positive social impact?
Decreased Land Use → Increased Biodiversity Preservation.
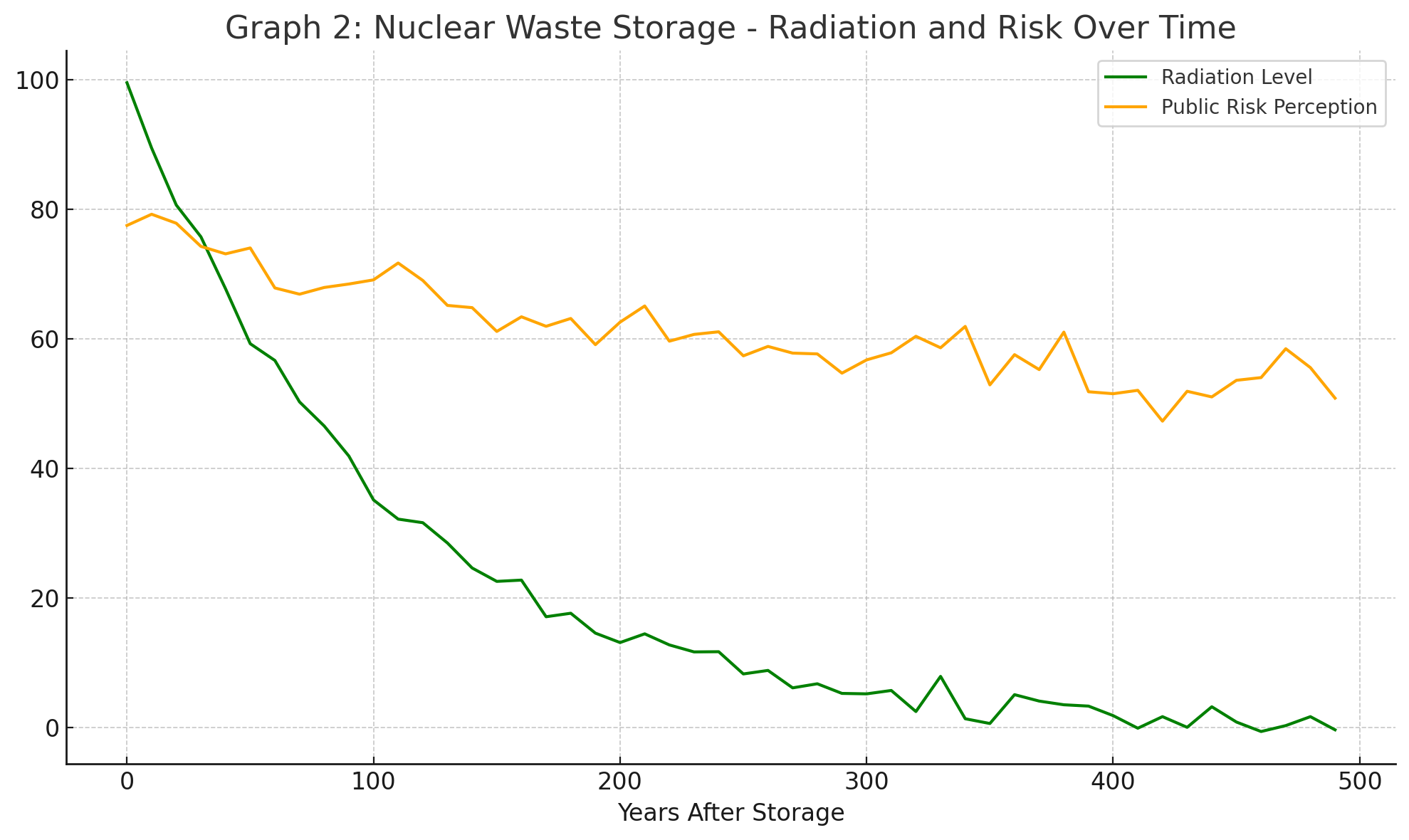
How does public risk perception change compared to radiation level over time?
Declines slower
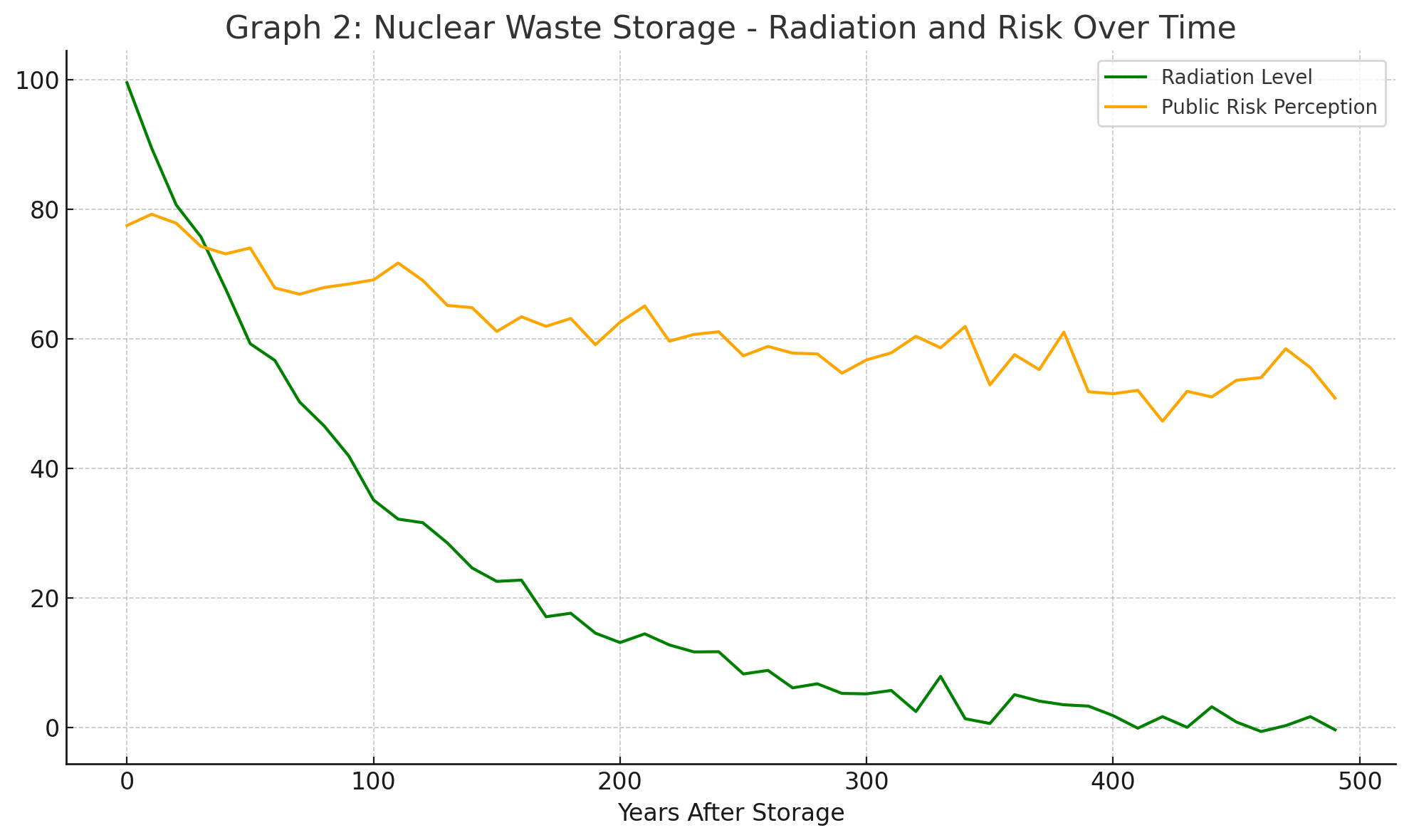
What shape best describes the curve for radiation level decrease?
Exponential decay
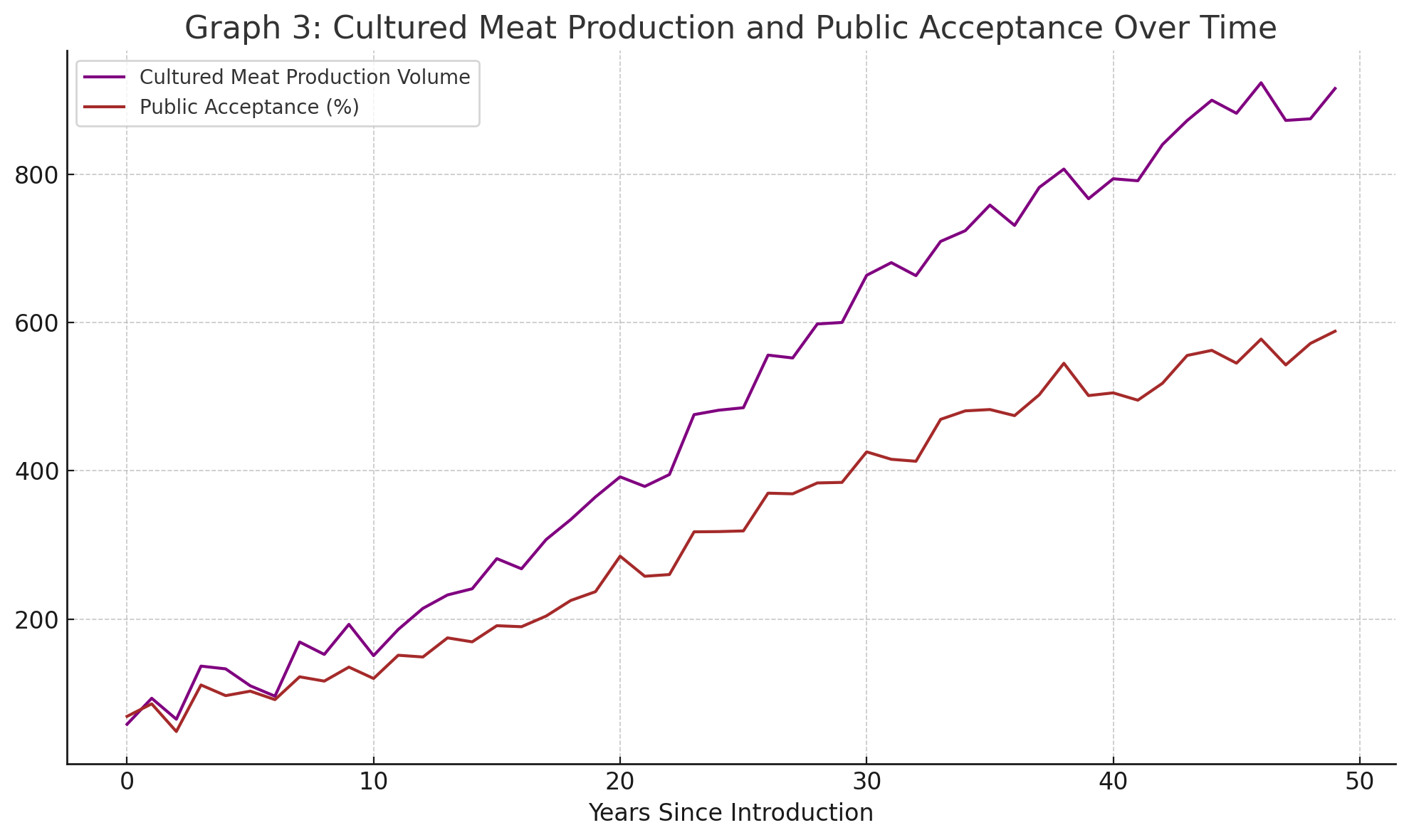
What is the gap between production volume increase and public acceptance increase called?
Lag
Which claim is an example of pseudoscience?
Cold fusion without experimental replication
Which of the following best illustrates the WYSIATI heuristic?
Basing climate opinions only on today's weather
Source amnesia is best demonstrated by:
Forgetting whether a story was from a credible origin
What is the main difference between observational and inferred data?
Observational data comes from direct measurement; inferred data is based on reasoning
Which of the following is an example of a framing effect in data visualization?
Showing a rising trend by changing the y-axis scale
Why must scientific findings always be considered tentative?
Future evidence could modify current conclusions
Nuclear fission
Splits atoms to release energy
Radioactive decay
Spontaneous emission of particles or energy.
Disinformation
False information shared with intent to deceive
Stories over Statistics
Relying on anecdotes instead of data
WYSIATI
What You See Is All There Is
Nuclear colonialism
Powerful countries exploit the resources and land of less powerful nations for nuclear development and testing
Light Water Reactors
Use low-enriched uranium
Advanced Reactors
HALEU (5–20% U-235), more efficient, smaller size
“Global Warming” alternatives
Climate crisis, climate disruption, global heating
Framing Techniques
Word choice, metaphors, analogies
Climate Crisis
A term emphasizing the urgent, severe impacts of human-driven climate change
Greenhouse Effect
Trapping of the sun’s heat by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Half-life
Time required for half of a radioactive substance to decay
Most dangerous radiation
Gamma radiation
What is the half-life of Uranium-238?
4.5 billion years