biology chpater 22 cloning and biotechnology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
vegetative propagation:
plant cuttings are taken and planted to give new shoots
involves parts of the plants like bulbs, runners, rhizomes and stem tubers
used in horticulture to make new plants cheaply
the plants will be genetically identical
propagation from cuttings of stems is also much faster, and rooting powder is applied.
Natural cloning in plants
micropropagation:
making large numbers of genetically identical offspring from a single parent plant using tissue culture
take a sample of plant tissue
sample is sterilised with beach or ethanol
explant is placed in sterile culturing medium with plant hormones to stimulate mitosis, which forms a callus
callus separated to medium to grow plantlets
artificial cloning in plants
advantages:
rapid productin
disease free plants
large numbers
reliably increase endangered plant numbers
disadvantages:
produced monoculture
expensive
plantlets are vulnerable to disease
advantages and disadvantages of micropropagation
in invertebrates, starfish can clone parts of their body when cut off
vertebrates clone with twins in the womb
natural animal cloning
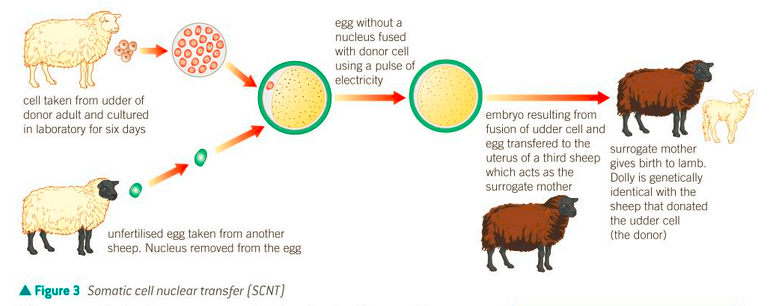
two types are twinning or somatic cell nuclear transfer
Twinning:
Early embryos are artificially split
used by farmers to produce maximum offspring from cows
Somatic cell nuclear transfer:
nucleus is removed from a somatic cell of an animal and the nucleus from a different ovum
nucleus from somatic cell is placed into ovum and given electric shock so it fuses
embryo is transferred to a third animal
new animal is clone of the animal which the somatic cell was from but mtDNA comes from egg
two types of artificial cloning in animals
advantages:
more offspring made
SCNT allows cloning of specific animals with desired traits
useful in pharming for human medicines or proteins
disadvantages:
inefficient
short live spans and health problems
many fail to come to term
advantages and disadvantages of animal cloning?
when biological organisms to synthesise breakdown, or transform materials for people
what is biotechnology?
use of biological systems to remove soil and water pollution
natural organisms break donw organic material making CO2 and water
what is bioremediation?
no welfare issues to consider
wide range of microorganisms
short life cycel and rapid growth rate
nutrient requirements are very simple
growth conditions are simple like low oxygen and low temps
why are microorganisms used for biotechnology?
microorganisms have an indirect effect as they make one thing that is turned into food
for example bread is made from yeast
what does indirect food production entail?
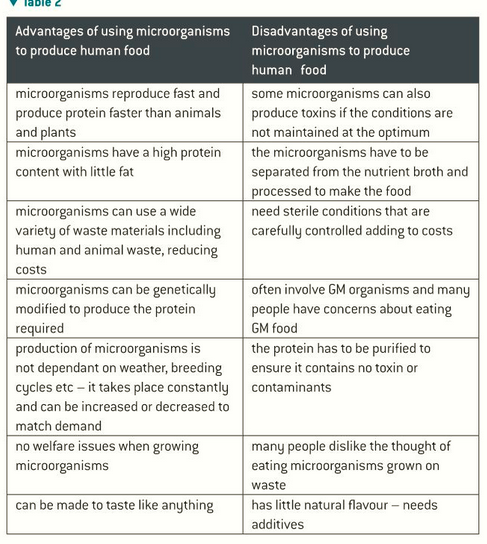
Microorganisms directly make food such as Quorn
Advantages: fast and wide variety of waste materials can be made
Disadvantages: little flavour, involves GM, need sterile conditions, people don’t want to eat
direct food production from microorganisms
penicillin and insulin are made using GM
what medicines are made using biotechnology?
asceptic technique needs to be used
inoculating broth where the bacteria and nutrients both are mixed then incubated
wire inoculating loop must be sterilised by fire and ethanol
can be done in agar or in a lab
how to culture microorganisms
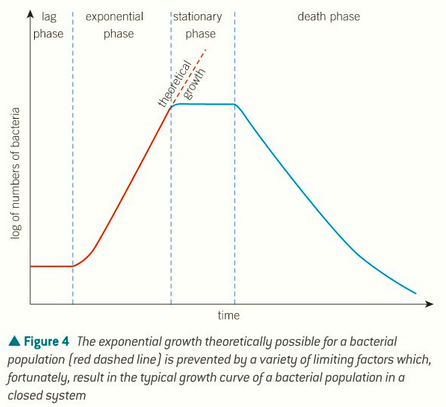
lag phase - bacteria adapt to new environment
log or exponential phase = birth rate>death rate
stationary phase - total growth rate is 0, birth rate = death rate
death phase - death rate > birth rate
what does the bacterial growth curve look like?
nutrient availability
oxygen and temp levels
build up of waste products
change in pH
limiting factors for bacterial growth
N = N₀ * 2ⁿ, where N is the final number of bacteria, N₀ is the initial number, and n is the number of generations or divisions
what is the formula for size of bacterial colonies?
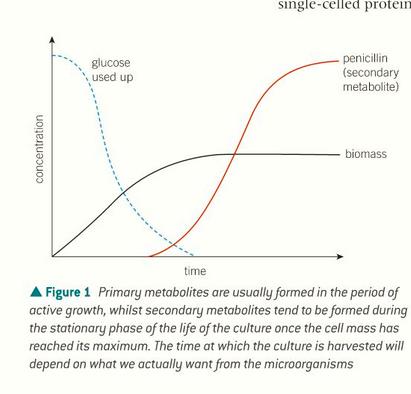
Primary metabolites are essential for an organism's basic survival formed during active growth (made in log phase)
Secondary metabolites are not directly involved in these processes but, play roles in defense, adaptation, and other specialized functions (made in stable phase)
what are primary and secondary metabolites?
batch and continuous
what are the two types of bioprocesses?
inoculated in a fixed volume medium for a fixed amount of time
waste and products build up
process stopped before death phase
batch fermentation
sterile nutrient medium
nutrient medium is added continuously to culture
once it reaches exponential growth, cultured broth is continuously removed
continuous fermentation
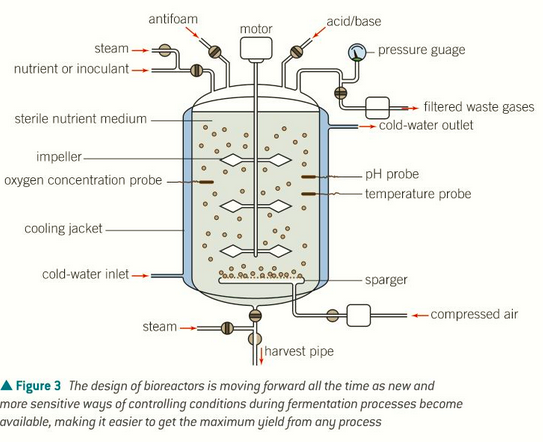
temperature, nutrients and oxygen, asepsis, mixing
how do you control bioreactors?
less wasteful and cheaper
more efficient and specific
less unwanted products
advantages of isolated enzymes
easier to isolate since they are secreted
there are fewer types so easier to identify
sometimes used when a specific enzyme is only found inside cells
why are extracellular enzymes mainly used?
when are intracellular enzymes also used?
enzymes that are attached to an inert support system to which the substarte passes over
what are immobilised enzymes?
advantages:
reused which is cheaper
easily separated from product
greater temp tolerance
allows for efficient controlled reactions
disadvantages:
reduced efficiency
higher initial costs of materials and bioreactors
advantages and disadvantages of immobilised enzymes
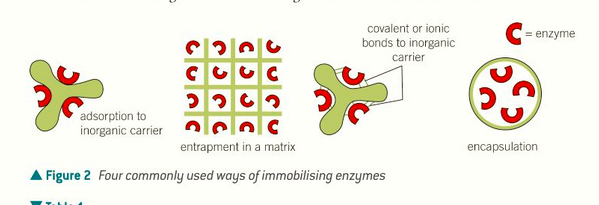
adsorption: stick enzymes to inorganic carriers, simple and cheap but enzymes easily lost
ionic or covalent bonding: bond to carriers using these bonds, strongly bound and very accessible to substrate, active site may be modified
entrapment in a matrix: widely applicable but active site is not easily available
membrane entrapment (encapsulation): simple but expensive
methods of immobilising enzymes?
penicillin acylase - semi-synthetic penicillins to treat bacteria resistant penicillins
glucose isomerase to convert glucose to fructose
lactase
examples of immobilised enzymes uses