16. The First World War
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
WWI
first large-scale international since the Napoleonic Wars;
all great powers including => Japan, Italy and the US - involved
gigantic economic, social and demographic consequences
the war resulted in the downfall of 4 empires: Germany, Austria- Hungary, Russia and the Ottoman Empire
Started by a spark: the assassination of Francis Ferdinand in Sarajevo → 18 June 1914
First Large-Scale Global War Since the Napoleonic Wars
WWI the first truly global conflict including all major powers of the time
1) Allies: France, Britain, Russia → later joined by Italy, Japan and the US
2) Central Powers: Germany, Austro- Hungary, Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria
38.2 Million Causalities
→ Approx. 10 million deaths, 7 million civilian deaths, and 21 million wounded
→ massive loss of life due to trench welfare, new weapons (machine guns, poison gas) and disease
Gigantic Consequences
Economic: European economies were devastated; massive war debts and inflation
Social: Rise of pacifism, trauma (shell shock; psychological trauma experienced by soldiers due to the intense stress of battle) and disillusionment
Demographic: A ‘lost generation’ of young men; population imbalances in many countries
Collapse of 4 Major Empires
→ the war resulted in the downfall of 4 empires
German Empire → Became Weimar Republic
Austro- Hungarian Empire → Split into Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia and others
Russian Empire → Overthrown in 1917; led to the Bolshevik Revolution and USSR
Ottoman Empire → Dissolved; led to the modern Middle East and the Republic of Turkey
The Spark => Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
28 June 1914
Sarajevo, Bosnia (then parts of Austria- Hungary)
Assassin: Gavrilo Princip, a Bosnian Serb nationalist linked to the group Black Hand
Triggered a chain reaction of alliances and declarations of war, starting with Austro- Hungary declaring war on Serbia
Rivalries and Alliences
→ Situation herited from the Napoleonic Wars and the Vienna Congress
→Otto van Bismarck: ‘All international politics reduces itself to the formula: Try to be à’ trois as long as the world is governed by the unstable equilibrium of five great powers’
Military Alliances in 1914
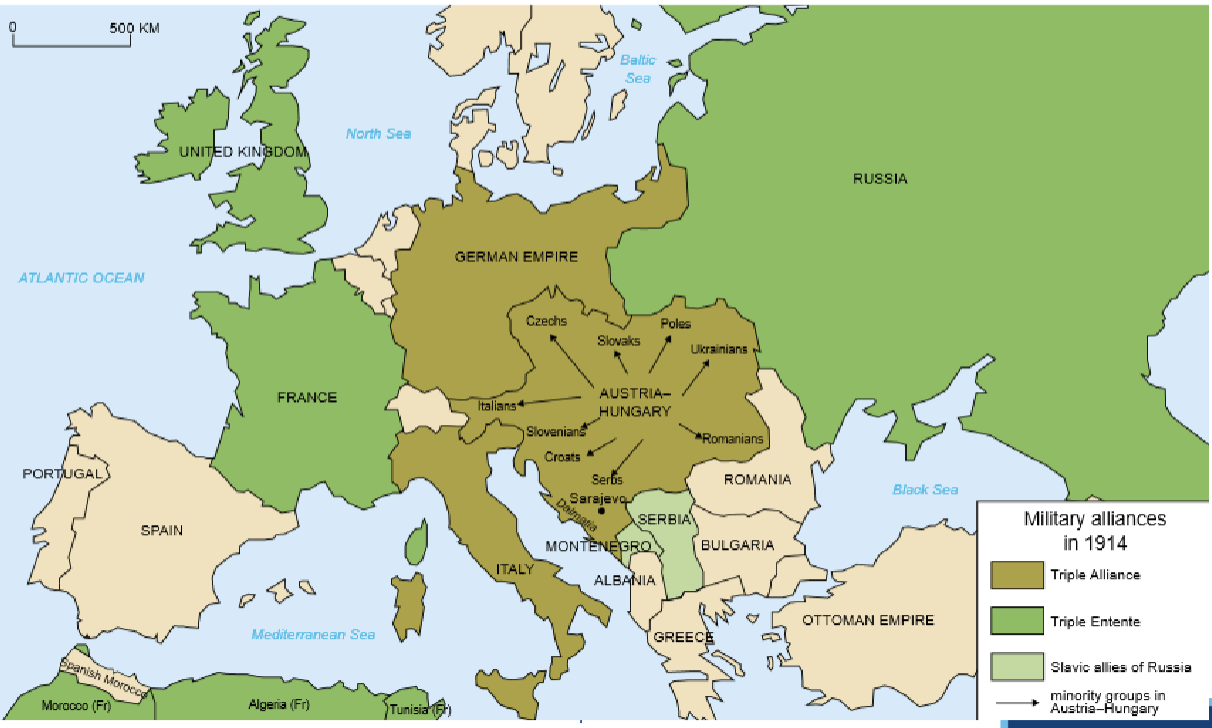
WWI Rivalries
classic rivalries were those between 1) France and Germany, since the War of 1870- 71 → the lost of Lorraine- Alsace and 2) Austria- Hungary and Russia, over influence in he Balkans, flamed by Pan- Slavism and aspiring for a free maritime passage to the Mediterranean
Triple Alliance
Germany + Austria- Hungaria + Italy (1882)
→ primarily directed against Russia
→ + Germany’s fear to be ‘sandwiched’ between France and Russia
1879: Dual alliance between Germany and Austria- Hungary to counter further Russian expansion in the Balkans. to fill the vacuum left by the waning Ottoman Empire → they were joined by Italy in 1882
Triple ENTENTE
France, Great Britain and Russia (1905)
resulted most and for all from the French strife to end isolation in European geo-politics
Heavy French investments in Russia since the late 1880s
in 1892 Russia and France had signed military treaty followed by a formal Dual Allience in 1894
→ they were joined by traditionally neutral Britain as they feared German expansion more than French rivalry in the colonies
WWI Mounting tensions
Arms race since 1905: in the wake of the humiliating Russian defeat against Japan → Russo- Japanese War (1904-1905) → Germany and Britain - accelerated military buildup
naval arms race + continental militarisation: all major powers increased army sizes and stockpiled weapons, creating a climate of suspicion and readiness for war
1905: The First Moroccan Crisis
Germany challenged French influence in Morocco to test the strength of the Entente Cordiale (Britain- France alliance)
Kaiser Wilhelm II - visited Tangier and declared support for Moroccan independence
Algeciras Conference (1906), where most powers sided with France. Germany was diplomatically isolated.
1908: Annexation of Bosnia- Herzegovina by Austria-Hungary in 1908, which it had occupied since 1878
angered Serbia and Russia, who supported supported Slavic unity and opposed Austrian expansion
tension rose in the Balkans, especially between Austria- Hungary and Serbia
1908 coup d’etat by Young Turks in the Ottoman Empire
the Young Turks (reformist nationalist group) staged a coup d’etat
aimed to modernise and centralise the empire, which alarmed neighbouring powers
this revolution weakened Ottoman control over its territories, increasing instability in the Balkans
1911: Second Moroccan Crisis
France sent troops to Fez to suppress a rebellion and strengthen its control over Morocco
Germany responded by sending the gunboat Panther, claiming to protect german interests
outcome = another diplomatic defeat for Germany; France gained more control in Morocco and Germany received minor compensation in Central Africa
=> increasing British hostility toward Germany, pushing Britain and France closer together
The First Balkan War
1912
the Balkan League: Serbia, Bulgaria, Greece, Montenegro
vs the Ottoman Empire
Goal: to drive the ottomans out of their remaining European territories
Outcome:
→ the Balkan League won
→ the Ottoman Empire lost most of its European land
→ Albania was created (With support from Austria-Hungary and Italy) to block
Second Balkan War
1913
Serbia, Greece, Romania + Ottoman Empire
vs Bulgaria
Cause: Dispute over the division of territory won in the First Balkan War, especially Macedonia
Outcome:
→ Bulgaria was defeated
→ Serbia and Greece gained more territory
→ Bulgaria became resentful, setting the stage for its alliance with the Central Powers in WWI
Impact on South Slav Nationalismm
Serbia emerged stronger gaining land and prestige but also frustrated because the creation of Albania blocked its access to the sea
this fueled South Slav (Yugoslav) nationalism, especially among Serbs who wanted to unite all Slavic peoples in the Balkan- including those under Austro-Hungarian rule - like Bosnia
This nationalist tension contributed directly to the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914 sparking WWI
Countdown to War - July 1914
→ 23 July 2914
Austria- Hungary issued an ultimatum to Serbia, blaming it for the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
the ultimatum was intentionally harsh → designed to provoke rejection
Austria was hesitant at first, but was encouraged by Germany’s ‘blank cheque’ — a promise of full support
→ 25 July 1914
Serbia responded partially accepting the ultimatum but Austria found it insufficient
Tsar Nicholas II of Russia ordered partial mobilisation to support Serbia, a fellow Slavic nation
→ Late July 1914
Britain attempted last-minute diplomacy to prevent war - proposing a conference, but it failed
Germany and Austria- Hungary pushed forward with military plans
→
The von Schlieffen Plan (Germany’s War Strategy)
Goal: avoid two- front war by defeating France quickly and then turning east to fight Russia
Assumption: Russia would take 2 weeks to mobilise its army
Strategy:
→ bypass France’s strong eastern defences
→ invade through Belgium (and possibly the Netherlands) to strike France from the north
→ encircle Paris and force quick surrender
attack the french from their vulnerable north-side
Great Britain would never accept the violation of Belgian Neutrality but Germans were prepared to run that risk
The start of the WWI
28 july 1914 => Austria- Hungary declared war on Serbia, although the Serbian government had been prepared to give in on most points of the Austrian ultimatum
the next day => Russian tsar ordered a full- scale mobilisation
on 31 July Germany declared war on Russia and the next day invaded the Grand- Duchy of Luxembourg
on 3 August Germany declared war on France and it invaded Belgium
In reaction to the violation of the Belgian neutrality, on 4th August the British declared war on Germany
Violation of Belgian Neutrality
Belgium was neutral under IL
Britain had pledged to defend Belgian neutrality (treaty of London, 1939)
Germany invaded anyway, expecting Britain might stay away
Result: Britain declared war on Germany on 4 August 1914
The von SCHIEFFEN PLAN and its early execution
og plan
Germany aimed to quickly defeat France by invading through Belgium and possibly the Netherlands
they shift forces east to fight Russia, assumption it would mobilise slowly
Modification of the plan
Germany did not invade the Netherlands
diverted more troops to defend Alsace- Lorraine
these changes weakened the right wing, making the plan less effective
Battle of the Marne (Sept 1914)
German forces advanced to the Marne River, just 50km from Paris
Allied counterattack (mainly French and British) pushed them back
German retreated to the Aisne river, around 60km north
Resulted in a stalemate and the beginning of trench warfare on the Western Front
—> continuation of the ww1
in Flanders and Artois the German advances were halted
by November both sides digged in their trenches => from then onward, the front line, running from the Franco- Swiss border in the southeast to the Flemish coast in the northwest => would hardly move for another four years
during the next years → both sides would try to break through enemy lines but all of these efforts failed at a horrendously high coast of causalities
The War becomes global
by the end of 1914, Japan entered on the Allied side
→ seized German colonies in the Pacific and Shandong Peninsula in China
→ motivated by imperial ambitions and alliance with Britain
→ Anglo-Japanese Alliance 1902
a year later, Italy joins the Allies (1915)
→ initially part of the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary => switched sides in May 1915
→ promised territorial gains (e.g. South Tyrol, Dalmatian coast)
→ fought Austria- Hungary along the Isonzo Front (12 battles, high causalities, little gains)
Ottoman Turkey
→ joined in November the German- Austrian alliance (in opposition to its old Russian enemy)
→ key event: Gallipoli Campaign (April 1915- Jan 1916)
allied attempt (mainly British, ANZAC forces) so seize the Dardanelles and knock the ottomans out of the war
Failed campaign with heavy losses; boosted Turkish nationalism and rise of Mustafa Kemal Atarurk
Allied Success in Africa and Middle East
→ africa: allies captured most German colonies (togoland, german southwest africa, cameroon)
→ Middle east: Arab revolution (1916-1918); targeted ottoman control in the Arabian Peninsula and Syria; British forces captured Bagdad and Jerusalem (1917)
1917 as the turning point of WWI
US enters the War on 6 April 1917
→ triggered by the Zimmermann Telegram: Germany proposed a military alliance with Mexico against the US
→ Combined with unrestricted submarine warfare, this pushed the US to declare war on Germany
→US entry brought fresh troops, resources and morale to exhausted Allies
Russian Revolution
→ 15 March 1917: Tsar Nicholas II abdicated after mass protests and military mutiny (Feb Revolurion)
→ a provisional government took over but continued the war
→ 6 now 1917 → Bolsheviks seized power in the October Revolution, led by Vladimir Lenin
=> Treaty of Brest- Litovsk: signed between bolshevik Russia and Central Powers
Russia exited the war, giving up vast territories = Ukraine, Belarus, Baltic states
Allowed Germany to shift troops to the Western front, but US soon tipped the balance
1918
→ German Spring Offensive (March - July 1918)
also called the Ludendorff Offensive
Germany launched a last major push on the Western Front before American forces could fully arrive
Initial success: broke through Allied lines and advanced rapidly
halted by July 1918→ especially after the second battle of Marne
Marked the turning point: Allies began a sustained counteroffensive
→ Collapse of the German Regime (Oct- Nov 1918)
Military failures, economic hardship and civil unrest led to the collapse of morale
oct 1918: German generals urged the Kaiser to seek peace
Early November: Kaiser Wilhelm I abdicated ( 9 nov); a republic was declared in Germany
→ Armistice Signed - 11 nov 1918
signed in a railway carriage in Compiegne, France
came into effect at 11 am, 11 nov 1918
marked the end of fighting on the Western Front, though a formal peace treaty (Treaty of Versailles) came later in 1919
Outcomes of WWI
for 1500 days on a row → about 6000 people were killed every day
in all 9.4 million men were killed or ‘disappeared’ and 21,2 million were wounded and 7,6 million prisoners of war were taken
Europe became a continent of widows and spinsters
psychological effect
enormous economic damage