Applied Kinesiology quiz 1
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
kinesiology
study of human motion or human movement
anatomic kinesiology
study of the human musculoskeletal system and musculotendinous system
structural kinesiology
study of muscles as they are involved in the science of movement
what does the american kinesiology association define kinesiology as
the academic discipline which involves the study of physical activity and its impact on health society and quality of life
what does the fundamental position of the human body consist of
standing upright
arms at sides
head facing forward
feet facing forward
what does the anatomical position of the human body consist of
standing upright
arms out at sides
head facing forward
feet facing forward
palms facing forwards
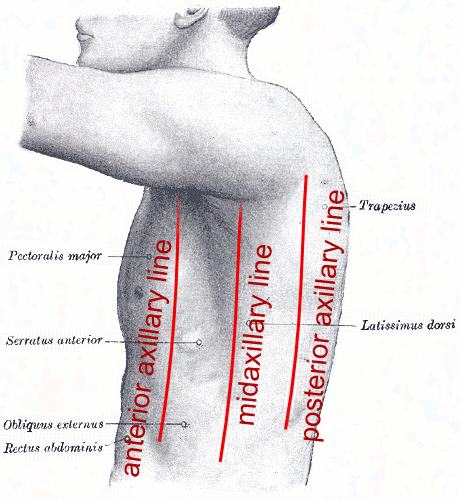
mid-axillary line
a line running vertically down the surface of the body passing through the apex of the axilla (armpit)
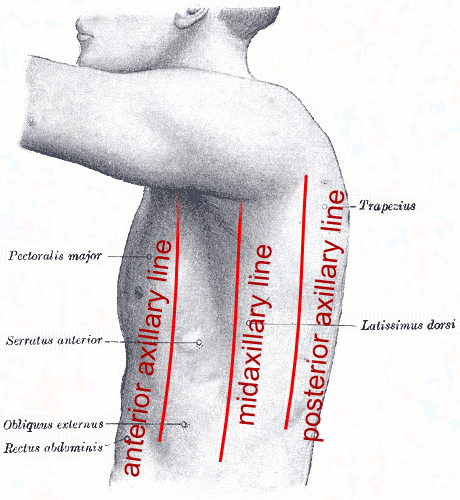
anterior axillary line
a line that is parallel to the mid axillary line and passes through the anterior axillary skinfold
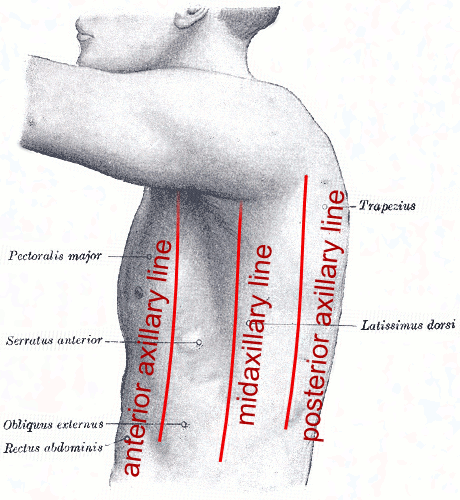
posterior axillary line
a line that is parallel to the mid axillary line and passes through the posterior axillary skinfold
mid clavicular line
a line running vertically down the surface of the body passing through the midpoint of the clavicle
mid inguinal point
a point midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis
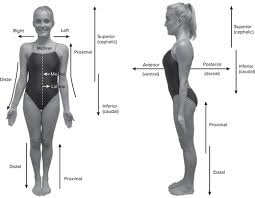
anterior(ventral)
in front
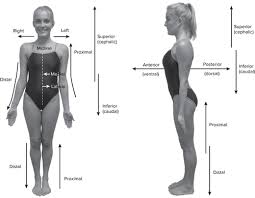
posterior(dorsal)
behind
inferior
below
superior
above
medial
toward inside or midline
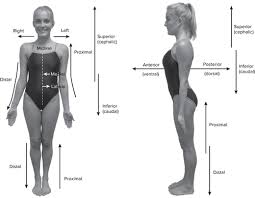
lateral
toward outside
proximal
nearer to the center of the body or the point of attachment
distal
away from the center of the body or from the point of attachment
dorsal
back
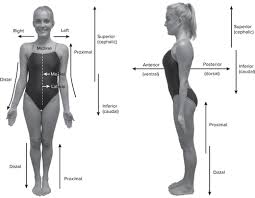
ventral
front
prone
position where a person lies face down on their stomach
supine
the position where a person or animal lies face up on their back
dexter
relating to or on the right side of something
sinister
relating to or on the left side of something
plane of motion
imaginary two dimensional surface through which a limb or body segment is moved
motion occurs __ __ _______ _ _____ revolving around an ____
in or through a plane; axis
there is a 90 degree relationship between a plane of motion and its ___
which is perpendicular to the plane motion
axis(or axes)
line passing perpendicularly through a plane
motion occurs in a plane
around an axis
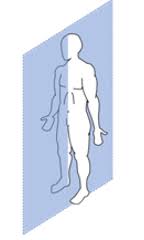
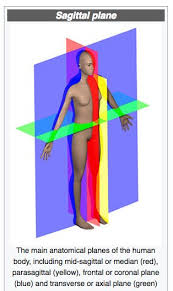
sagittal plane
vertical plane that divides the body into medical and lateral parts
common movements: flexion and extension
ex: sit up
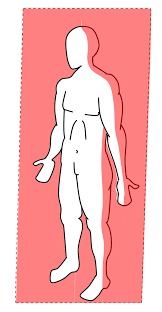
frontal (or coronal) plane
vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
common movements: adduction and abduction
ex: jumping jacks
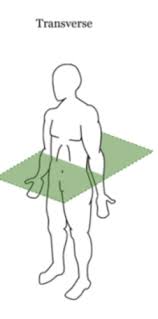
transverse plane
horizontal plane that divides the body into inferior and superior parts
common movements: pronation and supination
ex: turning a door knob
center of mass (com)
the point at which all three mid cardinal planes intersect
biomechanical definition
point about which all mass acts
flexion
reduce the angle between two bones at a joint
ex: lifting the weight reduces the angle at the joint
extension
increases the angle between two bones at a joint
ex: lowering the weight to increase the angle at the joint
abduction
moving a segment away from the midline of the body
adduction
moving segment towards the midline of the body (adding it to the body)
pronation
when the palm is moved to face down or posteriorly
supination
when the palm is moved to face up or anteriorly
medial rotation
rotation toward the midline
ex: sideways band pulls inward
lateral rotation
rotation away from the midline
ex: sideways band pulls releasing
circumduction
a cone of movement that does not include any rotation
occurs when flexion and extension movements are combines with abduction and adduction movements'
ex: tracking an imaginary circle in the air with your index finger
dorsiflexion
bringing the top of the foot toward the lower leg or shin
plantarflexion
pushing the top of the foot away from the lower leg or shin (planting the foot)
inversion
when the sole of the foot is turned inward(as when you roll your ankle)
eversion
when the sole of your foot is turned outward or away from the median plane of the body
function of the skeletal system
protection of heart lungs brain etc
support to maintain posture
movement by serving as points of attachment for muscle and acting as levers
mineral storage such as calcium and phosphorus
hematopoiesis- process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow
articular cartilage
smooth surface for movement of joints
reduces friction
provides cushioning to absorb shock
compact bone (cortical bone)
spongy bone (trabecular or cancellous bone) is surrounded by what
activity
strength and thickness of bones depends on ___
joints
bones of skeleton are connected by
periosteum
membrane covering the surface of bone which contains
blood and lymph vessels
nerves
osteoblasts- bone forming cells
osteoclasts- bone resorbing cells
epiphyseal plate (growth plate)
thin cartilage plate separates diaphysis and epiphyses
calcium carbonate
calcium phosphate
collagen
water
what are bones composed of
60-70%
how much bone weight is calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate
25-30%
how much of bone weight is water
tension
collagen provides some flexibility and strength in resisting ___
collagen
aging cause progessive loss of ___ and increases brittleness
pliable, brittle
if mineral is removed, bone is too____. If collagen is removed bone is too ___
circumferentially and longitudinally
bone grows both ____ and ____
longitudinal growth
occurs at the epiphyseal plate and seals at 18-25 years old
circumferential growth
results from an increased cross sectional area and remain metabolically active throughout lifespan
condyle
rounded process of a bone that articulates with another bone
epicondyle
a small condyle
facet
small faily flat smooth surface of a bone generally an articular surface
foramen
a hole in a bone through which nerves or vessels pass
fossa
a shallow dish shaped section of a bone that provides space for an articulation with another bone or serves as a muscle attachment
process
a bony prominence
tuberosity
a raised section of bone to which a ligament tendon or muscle attaches usually created or enlarged by the stress of the muscle’s pull on that bone during growth
collagen
provide strength but lack flexibility
elastin
can stretch and provide flexibility to return to their former shape but lack strength
long bones
composed of a long cylindrical shaft with relatively wide protruding ends
shaft of a bone contains the medullary canal
ex: phalanges, metatarsals, metacarpals, tibia, fibula, femur, radius, ulna, and humerus
short bones
small cubical shaped solid bones that usually have a proportionally large articular surface in order to articulate with more than one bone
ex: carpals, tarsals
flat bones
usually have a curved surface and vary from thick where tendons attach to very thin
ex: ilium, ribs, sternum, clavicle, scapula
irregular bones
include bones throughout entire spine and ischium, pubis, and maxilla
sesamoid bones
small bones embedded within tendon of a musculotendinous unit that provide protection and improve mechanical advantage of musculotendinous units
ex: patella 1st metatarsophalangeal, 1st metacarpophalangeal
tension
compression
bending
shear
torsion
what are the different types of tissue loading
tension loading
tissue is loaded along its long axis pulling the tissue in opposite directions
compression loading
the tissue is loaded along the long axis pushing the tissue towards the center
bending loading
forces acting in opposite directions causing tension on the longer side and compression on the smaller side
shear loading
forces acting in opposite directions across the long axis of the tissue
torsion loading
forces cause a rotation force along the long axis of the tissue
diarthrodial
freely movable joints
amphiarthrodial
slightly movable hoints
synarthrodial
immovable joints
joint
location at which two or more bones connect or come into contact with each other
articulation
the connection of bones at a joint usually to allow movement between surfaces of bone
can be point of contact between- cones, cartilage and joints, teeth and bones
arthrology
scientific study of joints concerned with the anatomy function dysfunction and treatment of joints
structural classification- based on interposed structure
biomechanical classification- based on number of bones and its biomechanical properties
functional classification- based on movement
joints are categorized based on
fibrous joints
joint joined by collagen
ex: sutures of skull
cartilaginous joint
joint joined by cartilage
ex: manubrio-sternal joint
synovial joint
not directly joined the bones have synovial membrane synovial cavity filled with synovial fluid articular capsule and associated connective tissue and ligaments
ex: hip joint shoulder joint knee joint elbow joint
simple joint
two surfaces articulate
ex: joints of the phalanges
compund joint
three or more surfaces articulate
ex: wrist joint
complex joint
two or more surfaces articulate in addition to the presence of an articular disc or meniscus
ex: knee joint
synarthroidal
immovable
ex: suture(cranial bones), gomphosis(teeth fitting into madible or maxilla)
amphiarthrodial
slightly movable
syndesmosis
two bones joined together by a strong ligament or an interosseous membrane that allows minimal movement between the bones
ex:between the tibia/fibula (interosseous membrane)