limbic system
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
functions of limbic system
- olfaction
- emotional responses + behavioral activity
- memories + learning
what is the role of cingulate gyrus and septal area?
memory and ANS
what is the role of parahippocampal gyrus?
memory processing
what is the role of the hippocampal formation?
memory
what is the role of the amygdaloid nucleus/bdu?
emotional response, behavior, smell
hypothalamus includes
- mammillary bodies
- ANS nuclei
what is the role of the hypothalamus?
homeostasis
what is the role of the anterior nucleus of the thalamus?
memory
what is the role of the mediodorsal nucleus?
emotions and behaviors
septal area includes
septum pellucidum and paratermial gyrus
septal area plays a role in what pathway?
reward
subcallosal area aka
parolfactory area
what is the role of the nucleus accumbens?
reward, motivation, and decision making
anterior part of the cingulate gyrus contains
inhibitory control center
what is the role of the Orbitofrontal cortex (OFC)?
- social behavior
- second thoughts or caution before undertaking an actions
what may become abnormal in drug addicts who cannot control their addiction although aware of consequences?
Orbitofrontal cortex (OFC)
Subcallosal part of cingulate gyrus (SCC) is associated with?
sadness
deep brain stimulation of what area of the brain is used for relief of severe depression?
Subcallosal part of cingulate gyrus (SCC)
what sends information from the hippocampus to the septal area and mammillary bodies?
fornix
what sends information from the amygdala (around corpus collosum) to the hypothalamus and septal area?
stria terminals
what pathway sends information from the ventral amygdala to the hypothalamus, septal area and mediodorsal nuclei of the thalamas?
Ventral amygdalofugal pathway
what sends information from the septal area to the habenulla?
Stria Medullaris thalami
what tract sends information from the mammillary bodies to the anterior nucleus of the thalamus?
Mammilothalmic tract
what sends information from the prefrontal cortex through the hypothalamus to the reticular formation of the brainstem?
medial forebain bundle
what part of the brain is in charge of consolidation of new declarative memories like knowing facts and remembering events?
hippocampus
what are the three parts of the hippocampus?
- dentate gyrus
- hippocampus proper
- subiculum
dentate gyrus contains what fibers/information
afferent information coming in
hippocampus proper contains what fibers?
efferent leaving
subiculum contains what fibers?
efferent leaving
what area of the brain receives input from the the cortical association areas that deals with multiple sensory perceptions via cingulum?
Entorhinal part of parahippocampal gyrus
what connects the hippocampi in the right and left hemispheres?
hippocampal commissure
what plays a role in fearful emotions?
amygdala
where is the amygdala located?
beneath uncus near dorsomedial tip of temporal lobe
what is the role of the medial amygdala?
olfaction
what is contained in the central amygdala?
Hypothalams and brainstem nuclei
what is the link between experiences of expression of cortical areas?
basolateral amygdala
where are the head of the caudate nucleus and putamen continous?
Accumbens nuclei
septal area consist of
Paraterminal gyrus and subcallosal area
accumens and septal nuclei are associated with
reward mechanisms and pleasure
what is the role of the septal region?
pleasure phenomena and sexual feelings
Euphoria associated with use of psychostimulants is due to/from
- Accumbens nucleus
- Dopaminergic projections from ventral tegmental area
what area of the brain remembers smells?
Parahippocampal Grus
what area of the brain is in charge of emotional responses to smell?
amygdala
papez circuit
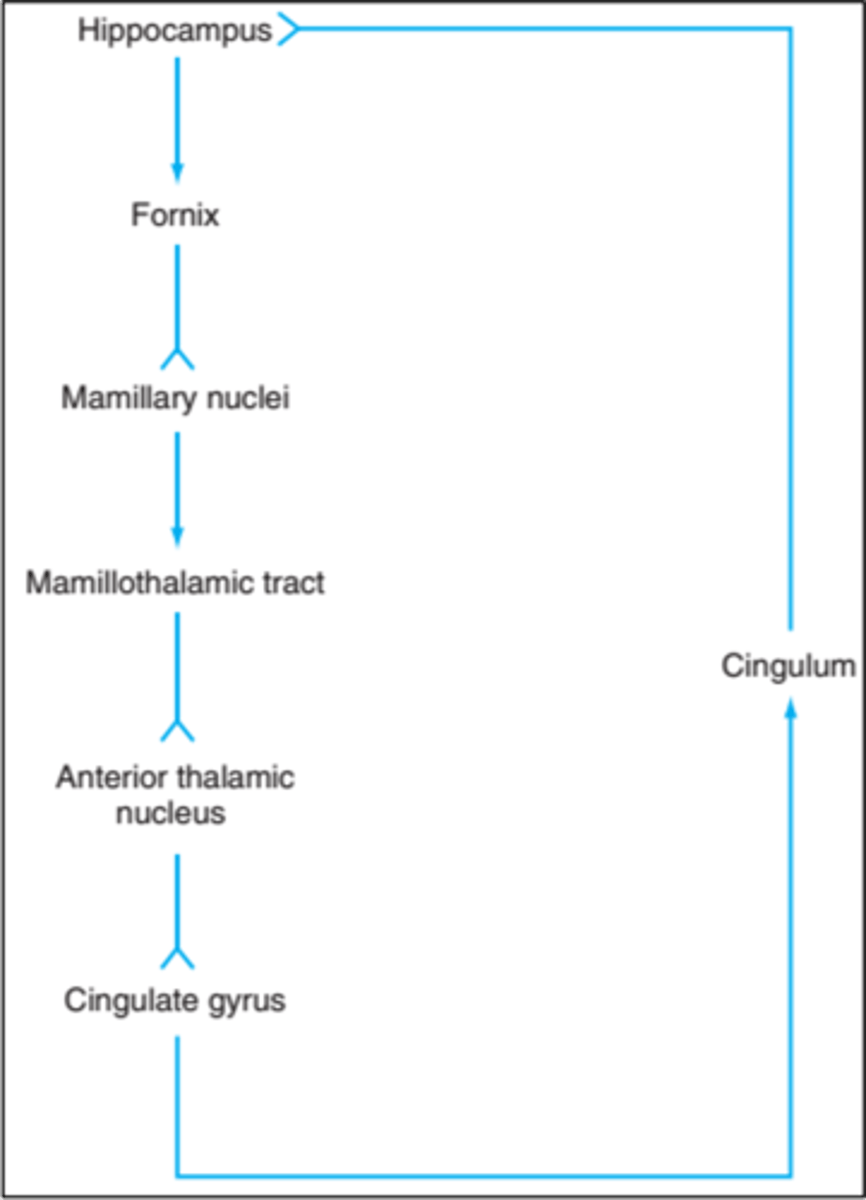
what communicates with the prefrontal cortex linking our memories and past experiences with our decision making?
papez circuit
When items of information are important or desire to remember the hippocampus emits signals that reverberate over and over in the Papez circuit until they are
stored in the areas of the cerebral cortex for long-term memory
what area of the brain is damaged if there is profound loss of recent or short-term memory and ability to learn?
hippocampi
people who have damage to their hippocampi
- Cannot remember anything that has occurred longer than a few minutes beforehand (anterograde amnesia)
- Memories of distant past remain intact
subcortical afferent pathway of the amygdala is important in
infancy and childhood
what area of the brain is responsible for response to pleasant or unpleasant odors?
Corticomedial amygdala
Signals sent via medial dorsal thalamic nucleus to orbitofrontal cortex are involved with?
perception of emotions
Signals sent via central nucleus to hypothalamus eliciting expression of emotions via what pathways?
autonomic and motor
Human behavior is based chiefly on nonolfactory experiences projected from ______ ________ to _________ __________
cerebral cortex; basolateral amygdala
information sent to the hypothalamus from the ventromedial nucleus is for
satiety
information sent to the hypothalamus from the lateral hypothalamus nucleus is for
hunger
what areas of the brain play a role in sexual behavior?
information to the hypothalamus - paraventricular nucleus (oxytocin) increase sexual drive, Medial preoptic nucleus (gonatotropin releasing hormone) increases testostorin and can increase sex drive
what happens if there is bilateral lesions to the amydala?
Behavioral alterations, especially a profound loss of fear
mesolimbic pathway
information to the septal area and hypthalamus is sent to the ventral tegmental area/nuclei (lots of dopaminergic neurons) sends information to Nucleus Accumbens
Mesocortical pathway
information to the septal area and hypthalamus is sent to the ventral tegmental area/nuclei (lots of dopaminergic neurons) to the prefrontal cortex
Surgical lesions of amygdalae in patients who struggle with?
socially unacceptable aggressive behavior to cause placid behavior (not easily excited or upset)
loss of neurons in what areas of the brain are associated with alzeimers?
hippocampus and adjacent parahipocampal cortex
loss of connections between hippocampus and adjacent parahipocampal cortex with ______ accounts for the loss of recent memory that is associated with alzheimer's?
neocortex
kluver-bucy syndrome is characterized by
- Placidity in which fear and anger are no longer shown
- Hyperorality is the tendency to exam objects excessively by mouth, even dangerous things
- Hypersexuality with suggestive behavior and inappropriate attempts at sexual contact
- Hyperphagia is eating excessive amounts even when not hungry or when objects are not actually food
- Visual agnosia is the inability to recognize objects by sight
Wernicke - Korsakoff can be caused by
chronic alcoholism and associated nutritional deficiency (vitamin B1, thiamine)
most frequent alterations for •Wernicke - Korsakoff occur in
the medial parts of the medial dorsal thalamic nuclei
Wernike encepalopahy is characterized by
- Confusion
- Inability to coordinate voluntary movemtns
- Visual changes and additional eye problems
if Wernike encepalopahy goes untreated it will develop into
Korsakoff syndrome -- long-term memory disorder