Lecture 11: Parasitism
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are characteristics of a parasite?
lives in or on another organism (host)
consumes host resources or some tissues
some use the host to infect another host or to reach other habitats
different degree of host specificity
lots of parasites are nonpathogenic (harmless)
What is an infection?
invasion of body tissues by other organisms
What is a pathogen?
parasite that causes an infectious disease (symptoms). Harms host
T/F all parasites are pathogenic
False, not all are pathogenic
T/F Parasites are always a bad thing
false, not always a bad thing
What are the modes of transmitting parasites?
exchange of body fluids or tissues
vectors
skin penetration
ingestion
breathing in spores and general airborne
physical contact
What are vectors?
an insect or animal that transmit disease to other animals or humans
What is an example of a vector?
mosquitos
What are ectoparasites?
Mostly arthopods (ticks, mites, lice, fleas, etc.), some leeches, lampreys, some nematodes on plants
Nematodes can be ectoparasites for who?
for plants, not humans
Most ectoparasites do what?
suck the blood and then leave
What types of endoparasites are there?
intracellular and intercellular
What are intracellular endoparasites?
live inside the cells of a host
What are intercellular endoparasites?
live in spaces between cells of a host
What are examples of endoparasites?
viruses
prions
protozoans
bacteria
fungi
helminths
What are prions?
they begin as beneficial brain protein. It folds into an incorrect shape and becomes pathogenic
How do prions replicate?
by coming into contact with other proteins
What are examples of prions?
bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad cow disease)
chronic wasting disease in deer, elk, and moose
Are prions living organisms?
No
How do some researchers feel about prions?
some say they are not parasites since they are not living organisms
What are viruses?
Composed of genome of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid
How do viruses reproduce?
within cells using the cells metabolic pathways
What examples of viruses?
HIV: AIDS
H5N1 (“bird flu”): jumps to humans
west nile virus
COVID-19
How is the west nile virus transmitted? and who does it affect?
by mosquitos
affects birds and humans
Where was HIV initially found?
in chimps
Do parasites intend to kill hosts? Why or why not?
They do not because it is not beneficial for them to lose their host
What are bacteria?
single-celled prokaryotes
Do bacteria have a nucleus?
No
What are examples of bacterial infections?
anthrax
plague
pneumonia
salmonella
leprosy
What are protozoans?
unicellular eucaryotes, some colonial
What are examples of protozoans?
trypanosoma
giardia
Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes
eukaryotes have a nucleus and organelles and prokaryotes do not
What are fungi?
eukaryotic unicellular and multicellular organisms
What are examples of fungi?
chytridiomycosis
white-nosed bat syndrome
What are helminths?
“worms”: platyhelminthes, nematoda and acanthocephala
Which are the most diverse helminths?
flatworms and roundworms
Do we need a microscope to see helminths?
generally no
What are the main types of hosts in the helminths life cycle?
intermediate host and definitive (final) host
What is an intermediate host?
a host needed in the course of the parasite’s life cycle in which there is development to a next larval stage. The parasite may multiply asexually
what is a Definitive (final) host?
host in which the parasite sexually matures and exhibits sexual reproduction
T/F parasites need multiple hosts in their lifetime
true
Explain the complex life cycle of endoparasites known as clonorchis sinensis
the host of this parasite needs to be a snail at some point, if not they die. Therefore, they need to have the ability to recognize hosts
What are the mechanisms of parasite transmission?
Horizontal transmission and vertical transmission
What is horizontal transmission?
when a parasite moves between individuals other than parents and their offspring
What is an example of horizontal transmission?
a mosquito biting a bird and transmitting parasites to it
What is vertical transmission?
when a parasite is transmitted from a parent to its offspring
What is an example of vertical transmission?
a mother nesting w/ her chicks and the mother passes parasites to chicks
or mother is pregnant, passes parasites to offspring bc it crosses the placenta
Anything coming from mom or dad=
vertical transmission
anything coming from anything other than mom or dad=
horizontal transmission
What are factors that influence parasite-host dynamics?
mode of entering the host
population density (higher = closer contact)
host’s immune system
ability of parasite to jump between species
existence of reservoir specices
in human populations: hygiene and modern traveling can be important
implant: monocultures
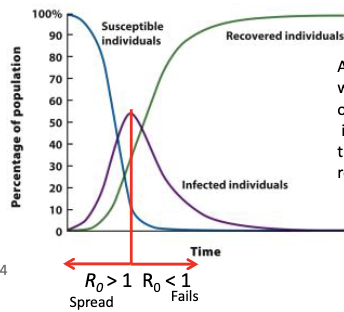
Explain this model. and what does R0 mean?
model on dynamics of a nonlethal infection over time
the disease spreads whenever the number of newly infected individuals is greater than the number of recovered individuals
R0= reproductive ratio: number of secondary cases produced by primary cases
Explain parasite adaptation in snails.
infected by platyhelminthes
host acts differently because it is under the influence of the parasite
snails begin to move upward
eyestalks are enlarged and banded
in effect are easily noticed by birds
Explain parasite adaptation in yellow dungflys.
yellow dungfly is infected by fungus
the fungus causes the fly to perch upside-down on an upper leaf of a plant
spores are released, wind infects more flies
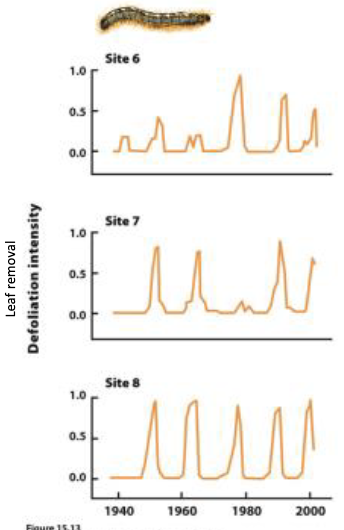
Explain these graphs.
forest tent caterpillars have population densities that cycle every 10-15 yrs
viruses increase abundance shortly after caterpillar densities increases
many caterpillars die
high density= more transmission= mortality= prevalence of the disease declines
What is coevolution in host-parasite interactions?
two ore more species evolve in response to each other’s evolution
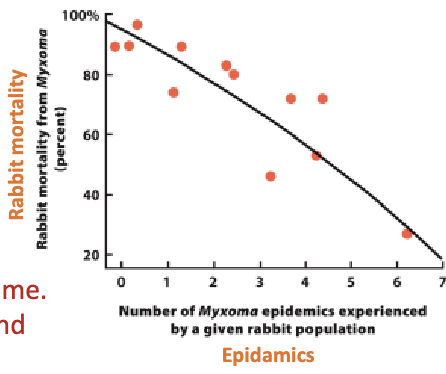
Explain this graph.
Decline of rabbit mortality over time. More resistant host population and less lethal pathogen
measures immune responses
Explain the invasive rabbits in Australia situation
Rabbits were not native to Australia and were brought over
too many reproduced and were becoming uncontrolable
they introduced a virus (Myxoma) to attempt to take them out
mortality rate was huge
rabbits that survived reproduced and passed on resistance
pathogen became less effective