BMS - Lecture 6 : Molecular motors, proteins in cell organisation and movement
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
movements of living things: organisms
muscle contraction
movements of living things: cells
pseudopodia
movements of living things: organelles & macromolecules in cells
cell division
2 key proteins of skeletal muscle
actin
myosin
what are fascicles
bundles of muscle fibres
whats a sarcomere
centre of contraction
what kind of cells do muscle fibres have
long
multinucleated
myofibrils consist of what type of filaments 2
thick
thin
myofibrils are surrounded by —— vesicles containing —- = —- —-
flattened
Ca2+
sarcoplasmic reticulum
myofibrils consist of what 2 bands
i band
A band
I band contains —- filaments of —-
thin
actin
A band contains —- filaments of —-
thick
myosin
tropomyosin & troponin are in —- filaments
thin
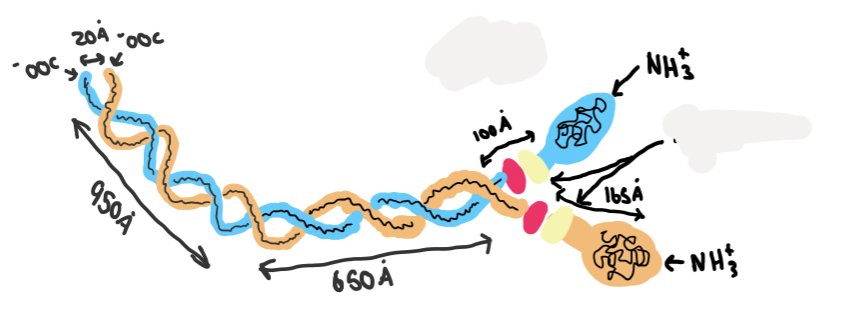
what structure is this
myosin
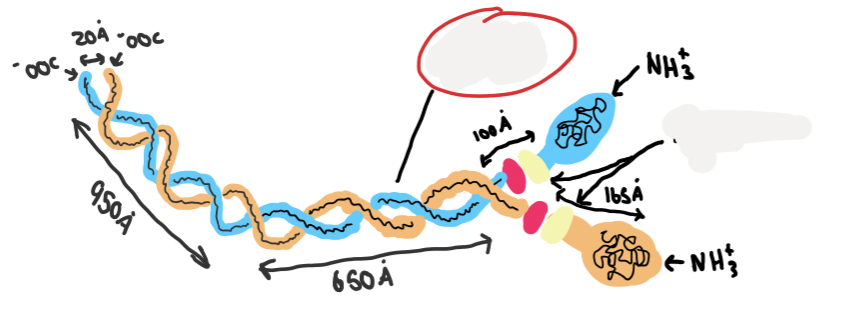
what structure is this
what is the name of the circled part
myosin
heavy chain
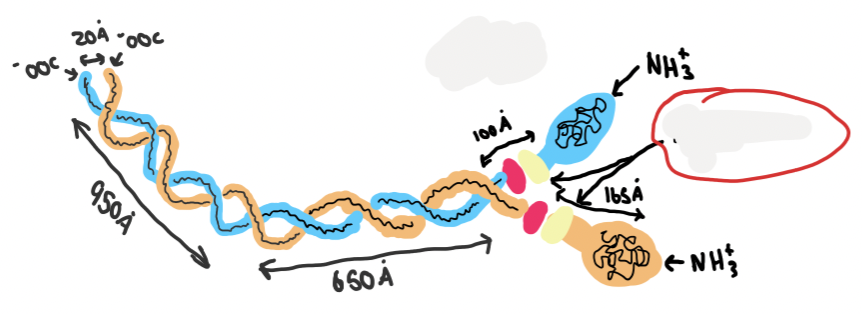
what structure is this
what is the name of the circled part
myosin
light chain
how many polypeptides does myosin tail consist on
6
each moysin head functions as a —- & as —- binding site
ATPase
ATP
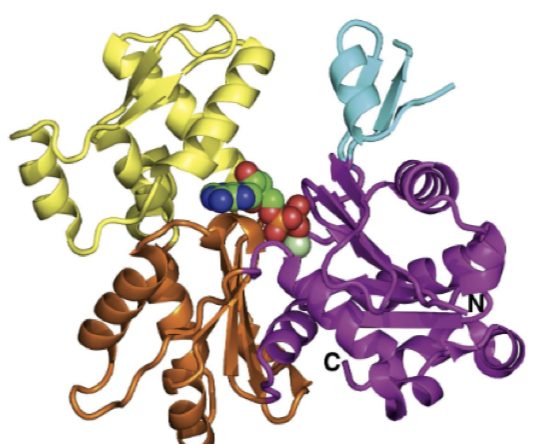
what structure is this
G-actin
how many protein domains does G-actin have
4
What is F-actin
fibrous polymer of actin
what is a dimer
linkage of 1 alpha-helices
how many subunits does troponin have
name them
3
troponin C
troponin I
troponin T
what does troponin I do 2
binds actin
prevents binding of myosin head
what does troponin C do
Binds Ca2+
what does troponin T do
binds tropomyosin
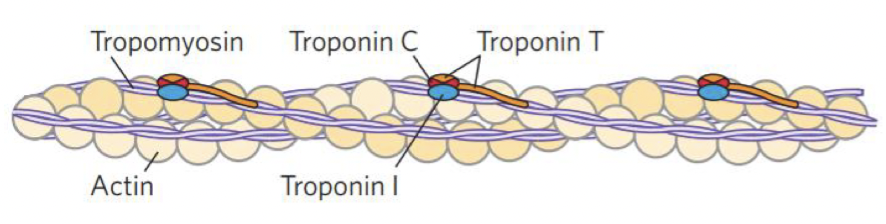
what structure is this
tropomyosin-troponin complex
what triggers muscle contraction
Ca2+
what is the most abundant cytosolic protein
actin
what are muscle stem cells called
satellite cells
what are satellite cells involved in
Muscle repair and regeneration
Maintenance of muscle tissue
Contribution to muscle growth and adaptation
what is one different between smooth muscle and skeletal muscle? hint. something to do with troponin C
calmodulin