Coelom, Viscera, Cardiovascular & Lymphatic Systems – Vocabulary Review
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards summarizing major cavities, serous membranes, peritoneal folds, heart anatomy, and key vessels/histology for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Coelom (Ventral Body Cavity)
Entire anterior body cavity containing thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Thoracic Cavity
Superior subdivision of the coelom; houses pleural cavities, pericardial cavity, and mediastinum.
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Inferior subdivision of the coelom; contains abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Peritoneal Cavity
Fluid-filled space within the abdominopelvic cavity that surrounds intraperitoneal organs.
Pleural Cavity
Serous cavity surrounding each lung.
Pericardial Cavity
Serous cavity surrounding the heart.
Mediastinum
Central thoracic region between lungs; contains heart, great vessels, esophagus, trachea, etc.
Visceral Pleura
Serous membrane directly covering the lungs.
Parietal Pleura
Serous membrane lining the thoracic wall and diaphragm around the lungs.
Visceral Pericardium (Epicardium)
Serous membrane forming the outer surface of the heart.
Parietal Pericardium
Serous membrane lining the fibrous pericardial sac.
Visceral Peritoneum
Serous membrane directly covering intraperitoneal abdominal organs.
Parietal Peritoneum
Serous membrane lining the abdominal wall.
Mesentery
Double layer of peritoneum suspending organs and providing vessels and nerves.
Mesentery Proper
Mesentery attaching jejunum and ileum to the posterior abdominal wall.
Mesocolon
Mesentery attaching transverse and sigmoid colon to the posterior wall.
Coronary Ligament
Peritoneal fold attaching the liver to the diaphragm.
Falciform Ligament
Peritoneal fold attaching liver to anterior abdominal wall; contains ligamentum teres.
Ligamentum Teres Hepatis
Fibrous remnant of the fetal umbilical vein within falciform ligament.(thicker part, thinner part is falciform)
Greater Omentum
Large peritoneal apron connecting stomach to transverse colon.
Lesser Omentum
Peritoneal fold connecting stomach and duodenum to liver.
Diaphragm
Muscular partition separating thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Aortic Hiatus
Diaphragmatic opening for the aorta.
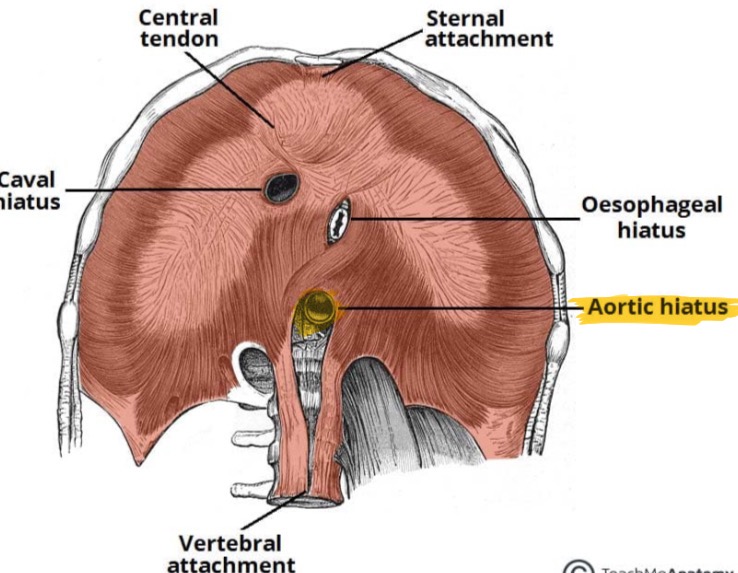
Esophageal Hiatus
Diaphragmatic opening for esophagus and vagus nerves.
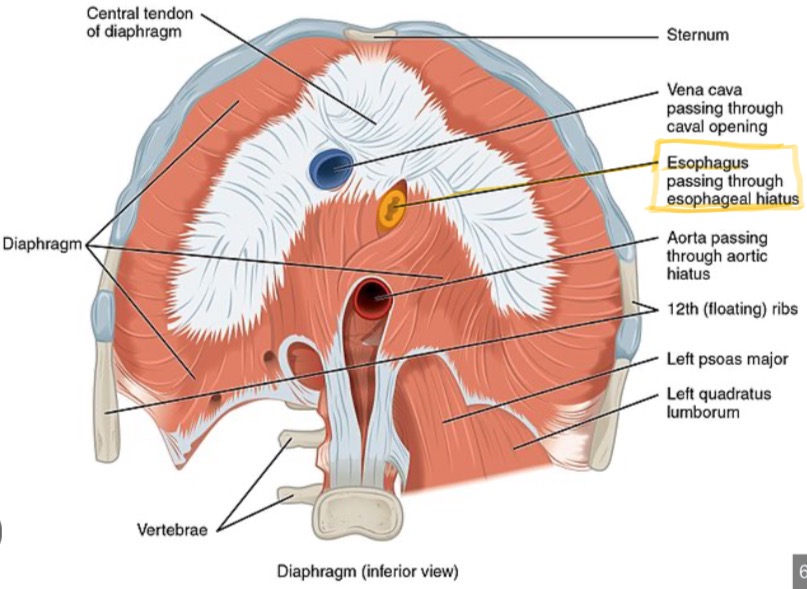
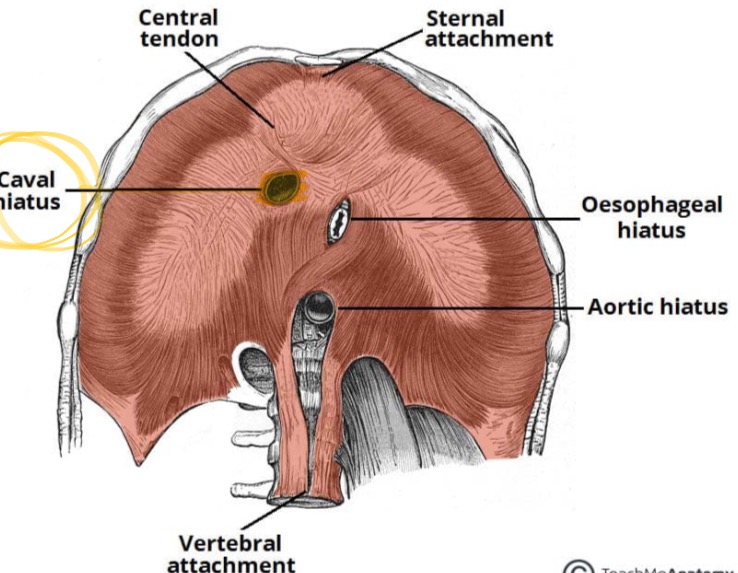
Caval Hiatus
Diaphragmatic opening for the inferior vena cava.
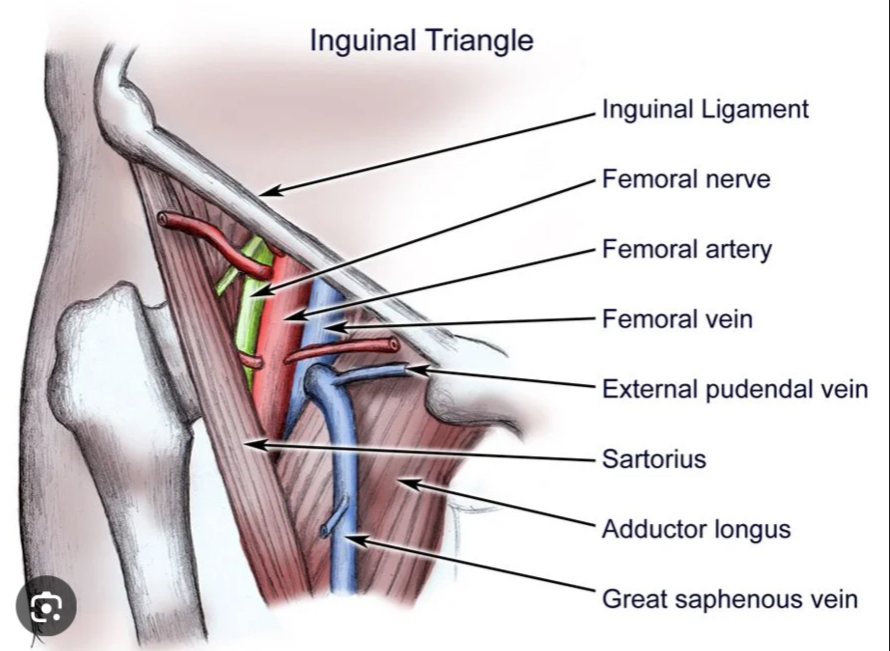
Femoral Triangle Contents
Femoral artery, vein, lymphatics, and nerve exit the coelom here.
Inguinal Canal Contents
Transmits spermatic cord (male) or round ligament (female).
Retroperitoneal Organs
Organs located behind parietal peritoneum (e.g., pancreas, kidneys, ascending colon).
Intraperitoneal Organs
Organs enveloped by visceral peritoneum (e.g., stomach, liver, jejunum).
Pericardial Sac (Pericardium)
Fibrous and serous layers enclosing and protecting the heart.
Fibrous Pericardium
Tough outer connective-tissue layer of the pericardial sac.
Epicardium
Outer layer of heart wall; same as visceral pericardium.
Myocardium
Thick muscular middle layer of heart wall.
Endocardium
Endothelial inner lining of heart chambers.
Apex of Heart
Inferior pointed tip of the left ventricle.
Coronary Sulcus
Groove separating atria from ventricles; houses coronary vessels.
Interventricular Sulcus
Anterior and posterior grooves marking ventricular septum externally.
Auricle
Small ear-like pouch of each atrium that increases volume.
Pectinate Muscles
Ridges of myocardium in atrial walls, especially auricles.
Chordae Tendineae
Tendinous cords anchoring AV valve cusps to papillary muscles.
Papillary Muscles
Conical ventricular muscles that tighten chordae tendineae during systole.
Trabeculae Carneae
Irregular muscular ridges lining ventricular walls.
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Valve between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk.
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Valve between left ventricle and ascending aorta.
Coronary Arteries
Right and left vessels supplying blood to the heart tissue.
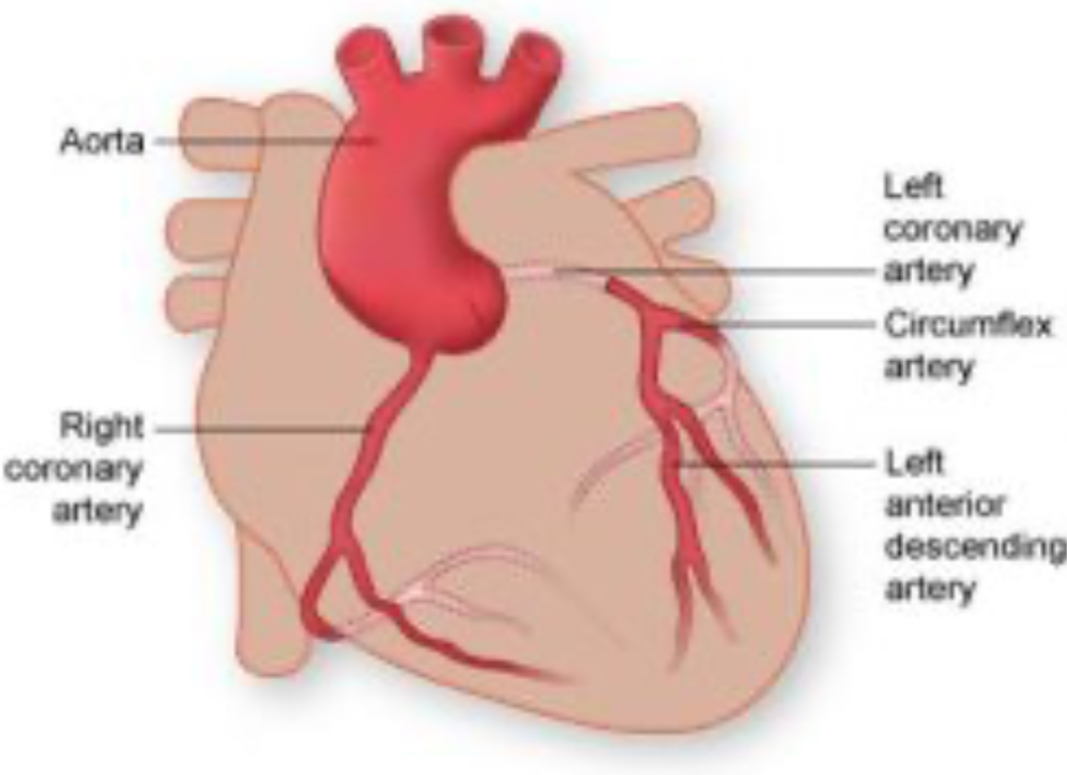
Coronary Sinus
Large venous channel draining cardiac veins into right atrium.
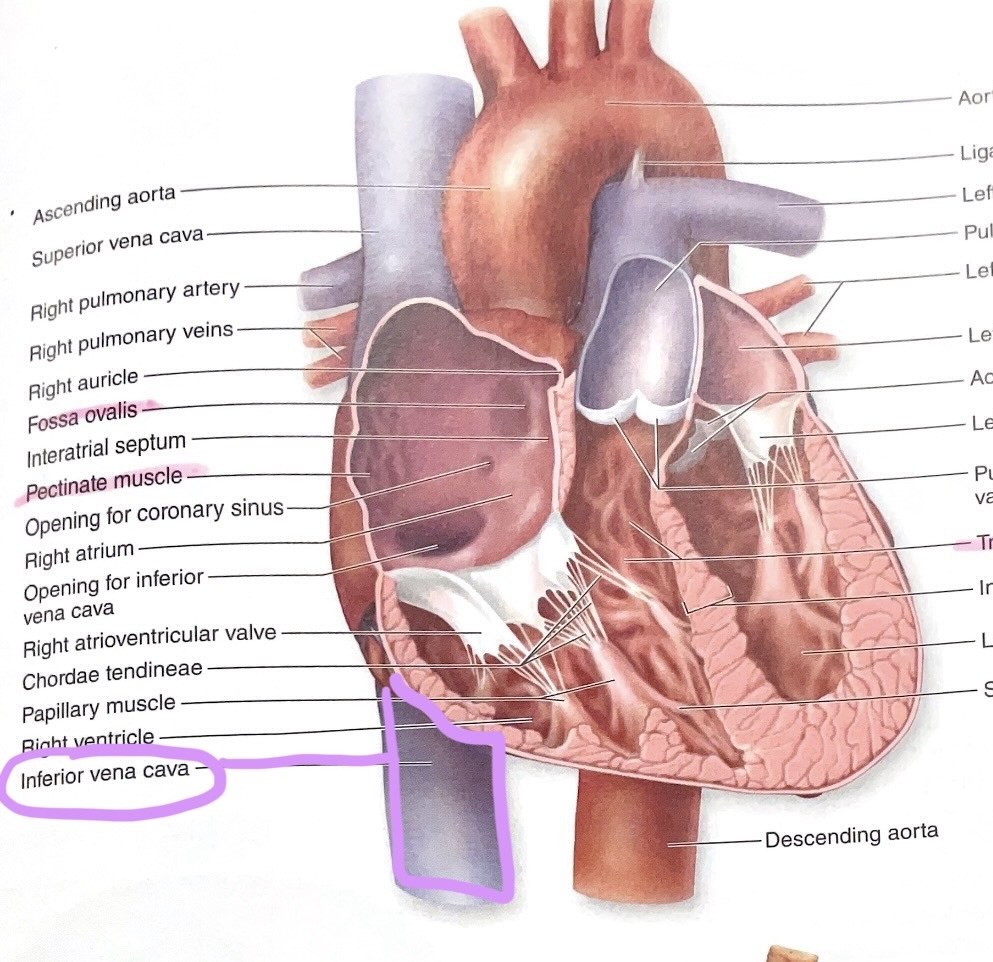
Fossa Ovalis
Depression in interatrial septum; remnant of fetal foramen ovale.
Ligamentum Arteriosum
Fibrous remnant of fetal ductus arteriosus between aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Pulmonary Trunk
Artery carrying deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs.
-
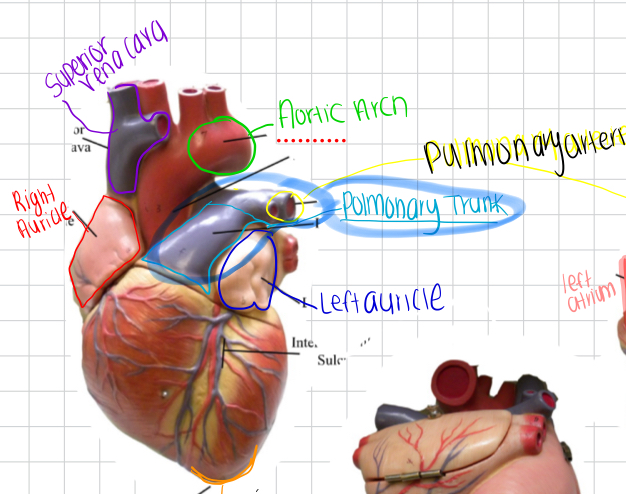
Ascending Aorta
First portion of the aorta leaving the left ventricle.
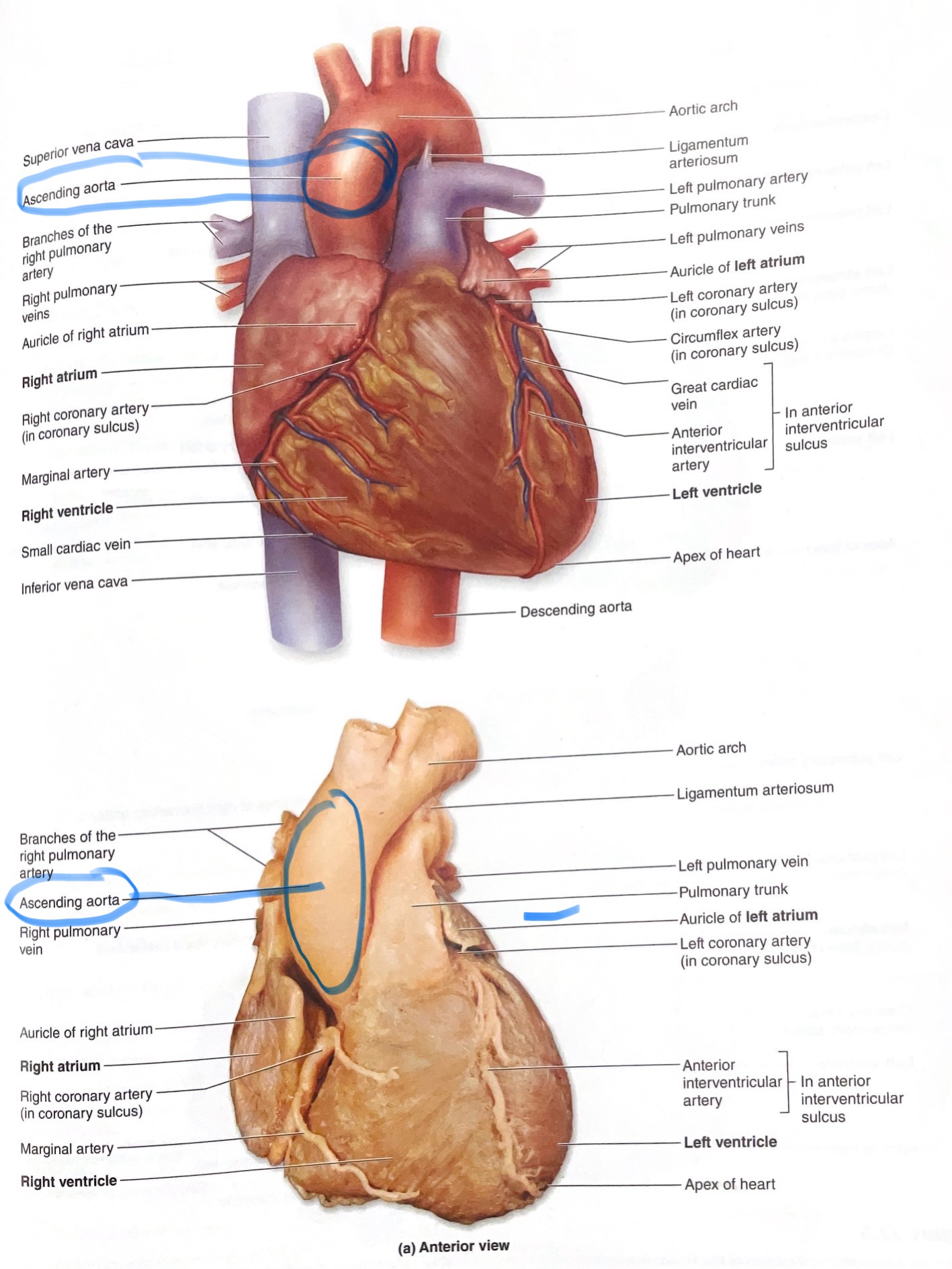
Superior Vena Cava
Vein returning blood from head, neck, and upper limbs to right atrium.
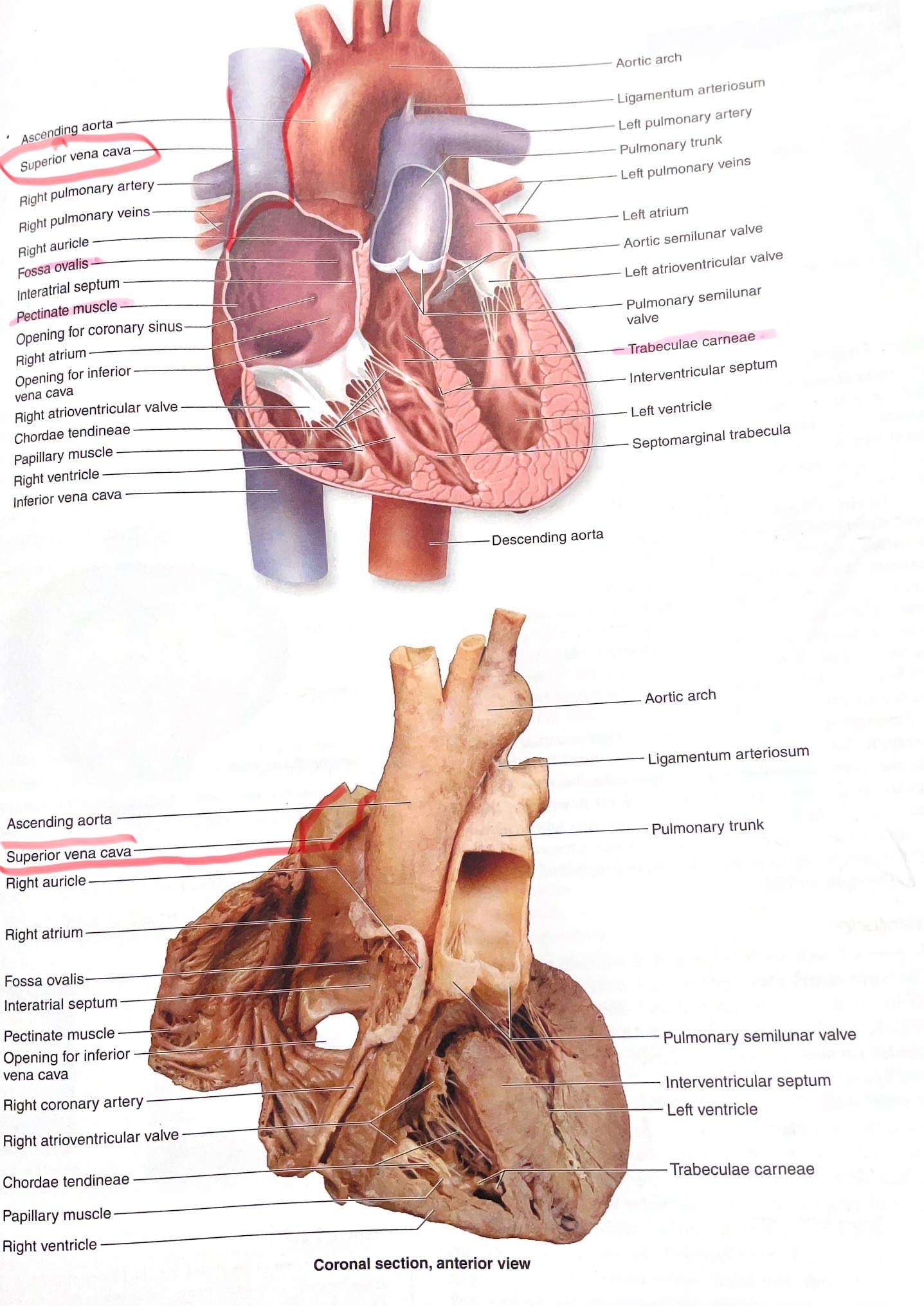
Inferior Vena Cava
Vein returning blood from abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs to right atrium.
Subclavian Artery
Artery supplying head, neck, and upper limb; gives off vertebral and thyrocervical branches.
Celiac Trunk
First abdominal aortic branch; gives gastric, splenic, and common hepatic arteries.
Renal Arteries
Paired arteries supplying the kidneys.
Hepatic Portal Vein
Vein conveying nutrient-rich blood from GI tract to liver.
Great Saphenous Vein
Longest superficial vein of the body; runs along medial lower limb.
Artery (Histology)
Thick-walled vessel with round lumen for high-pressure blood flow.
Vein (Histology)
Thin-walled vessel with large irregular lumen and possible valves.
Peripheral Nerve (Histology)
Bundle of axons lacking a lumen; shows dot-like axons within myelin.