Cerebral Hemispheres and Cortex (Neuroanatomy Lab) - Spring 2025
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
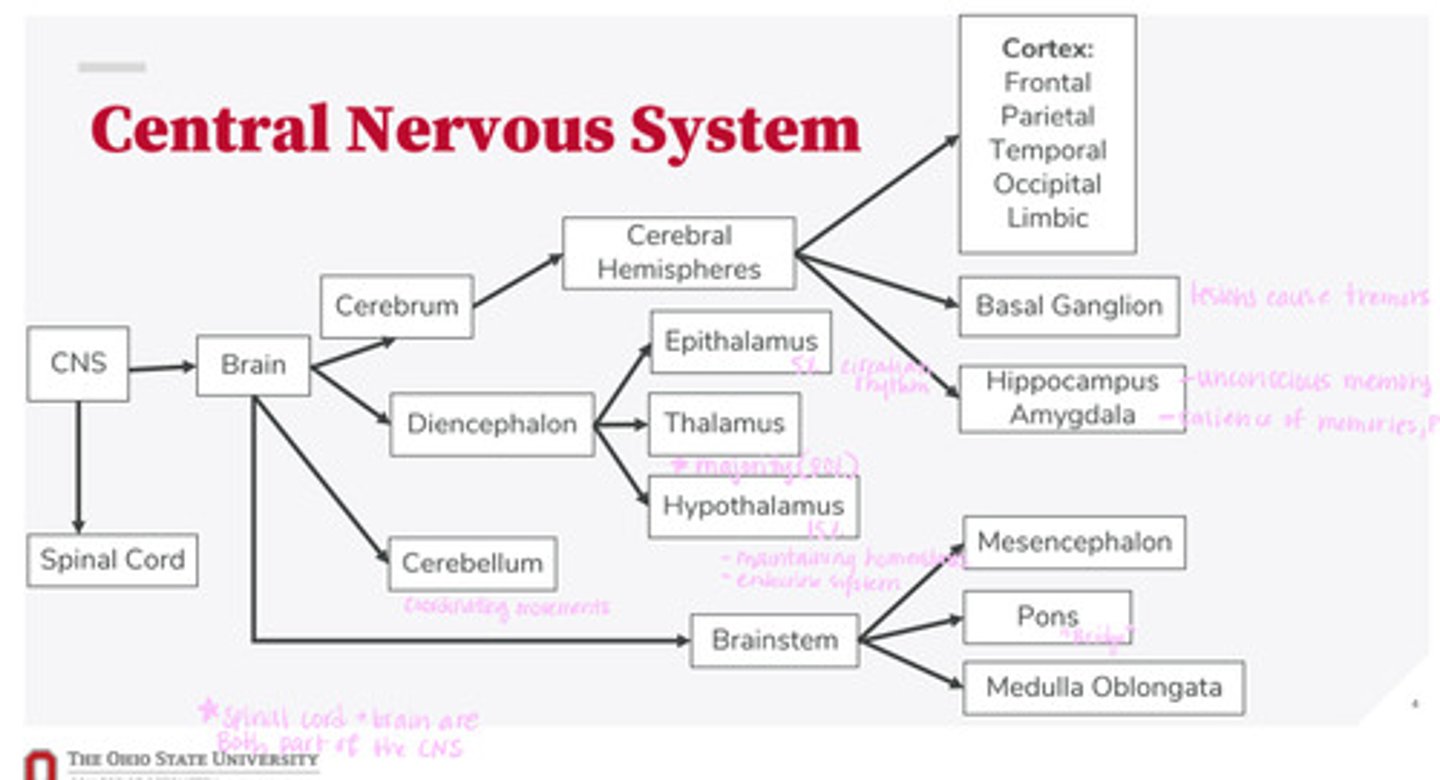
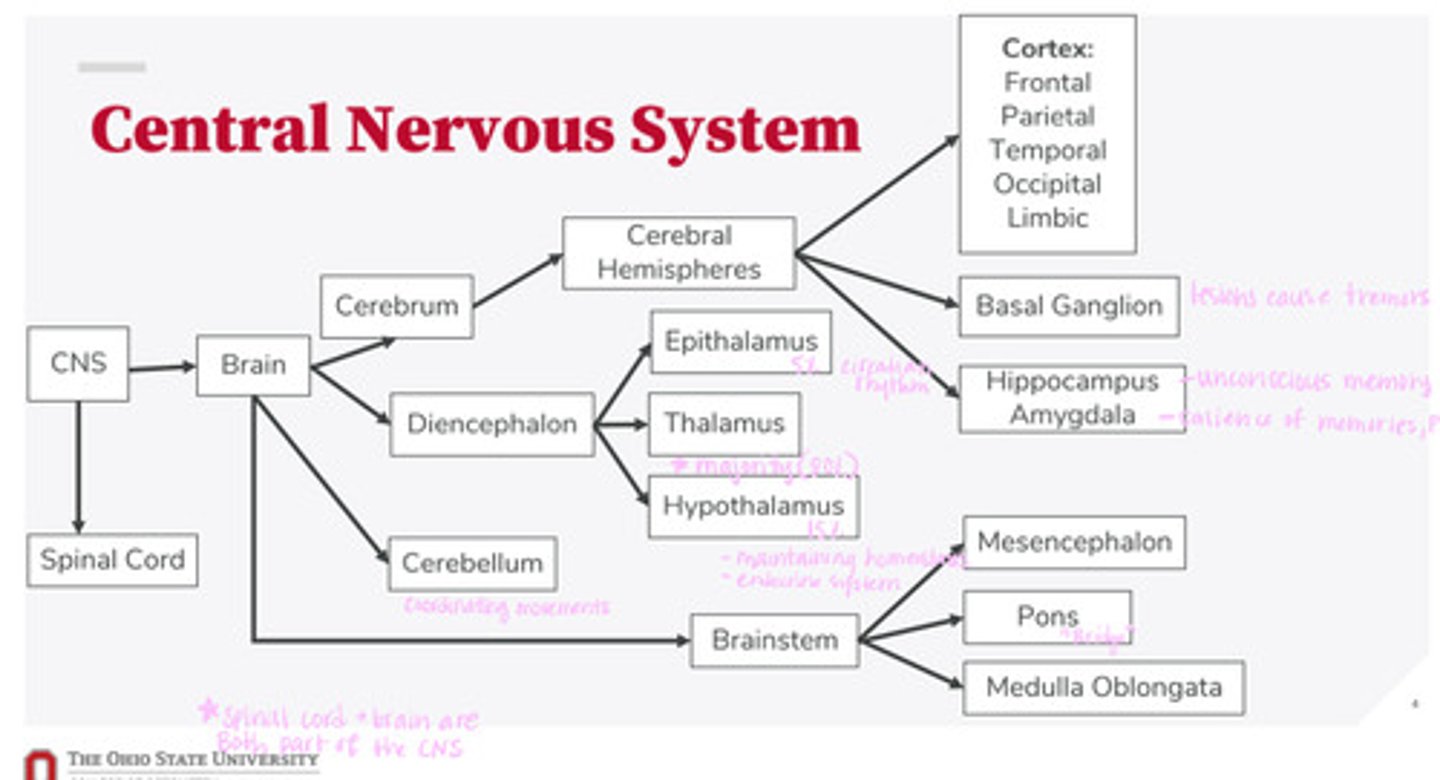
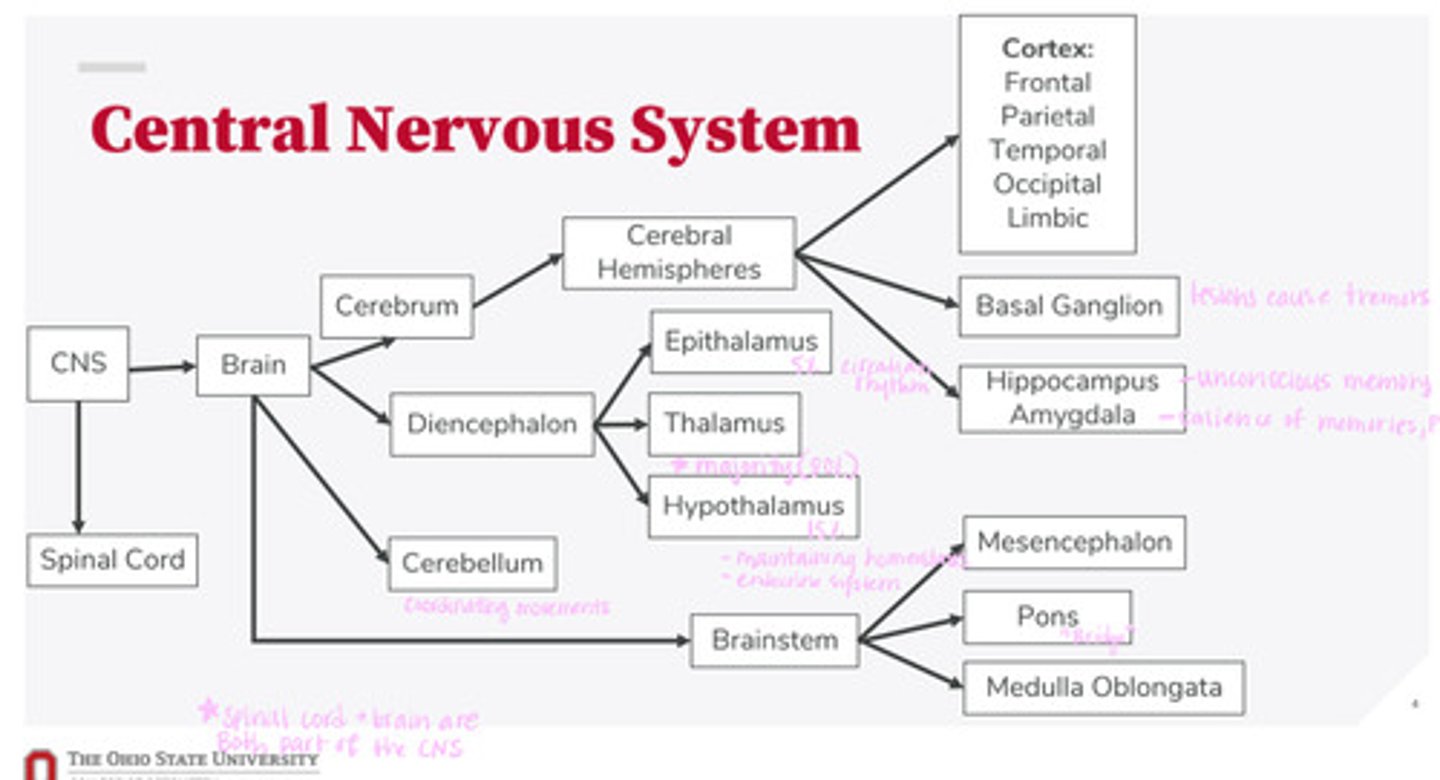
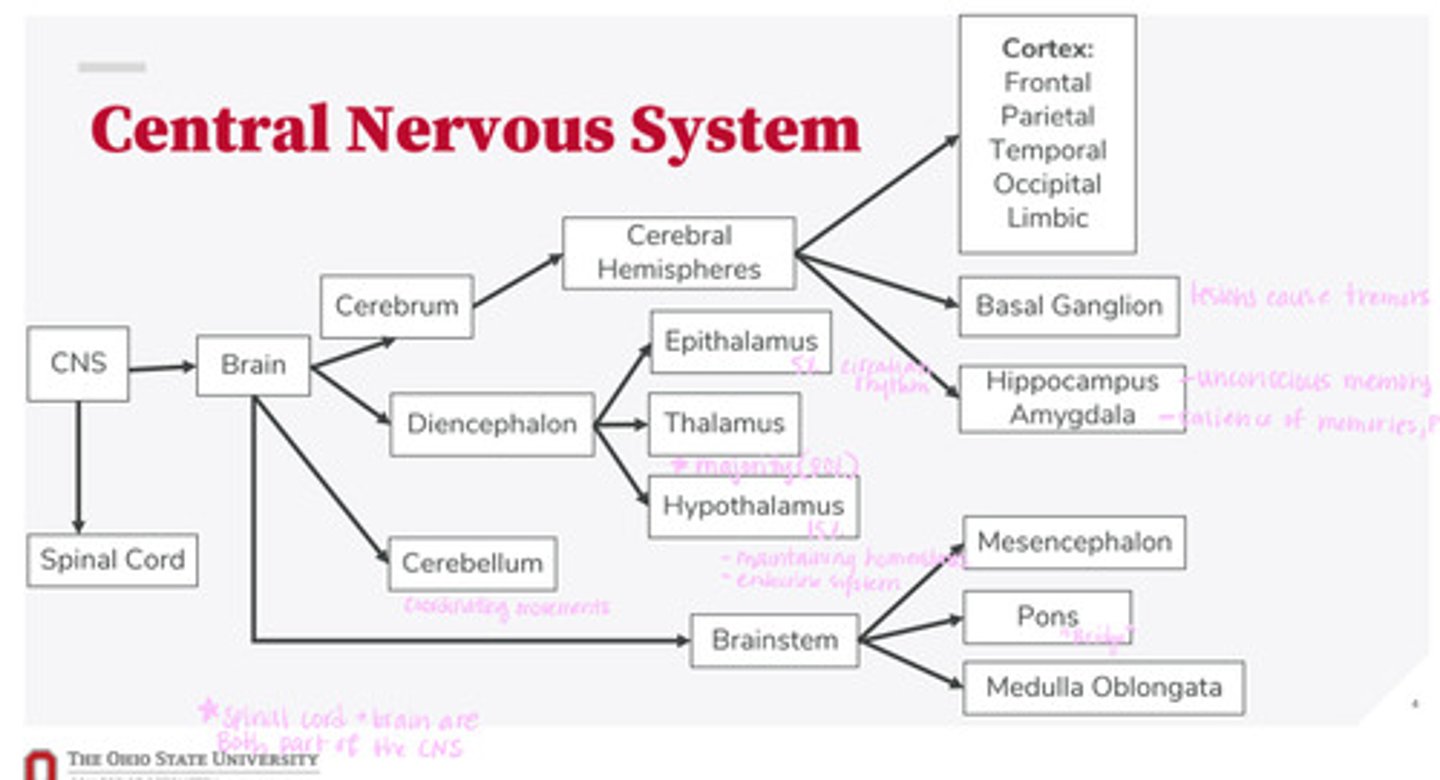
-brain
-spinal cord
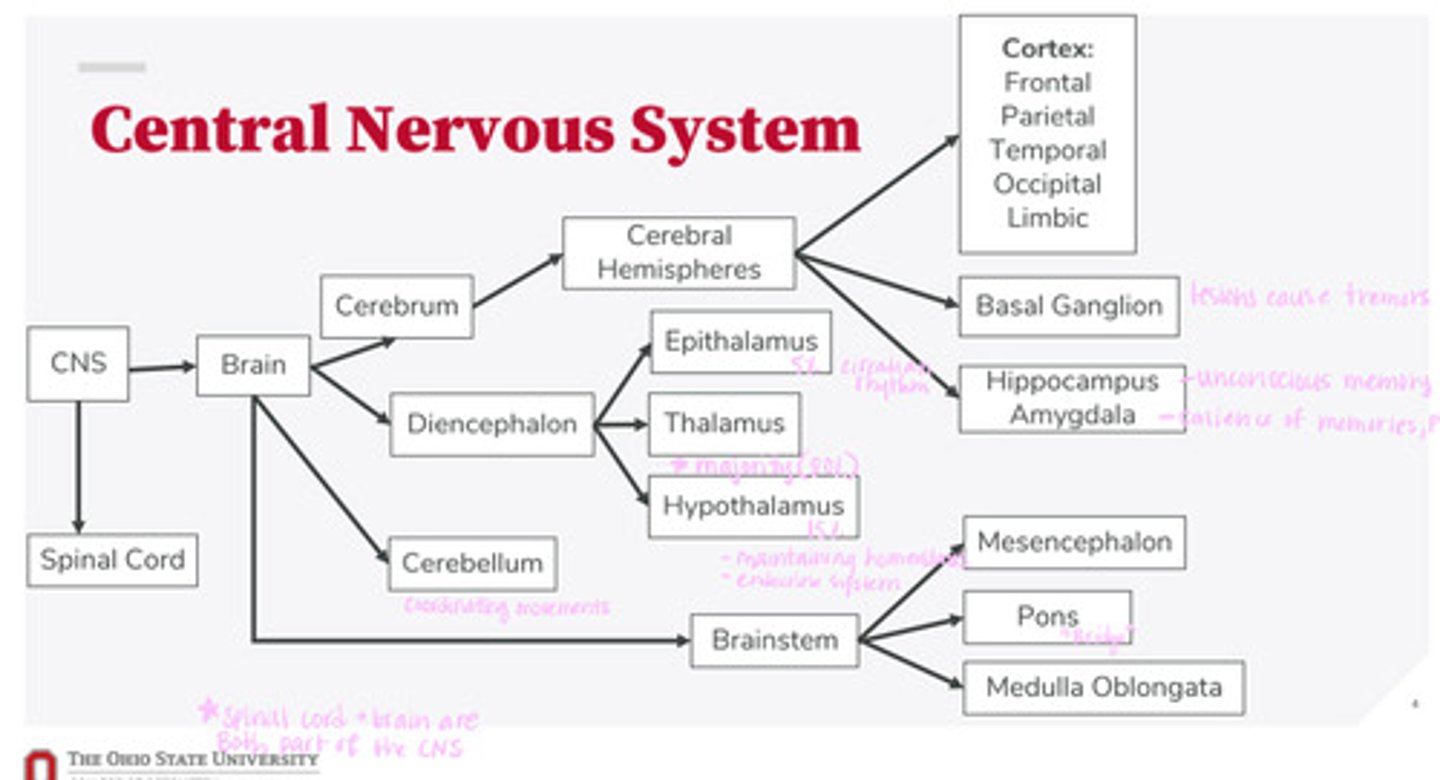
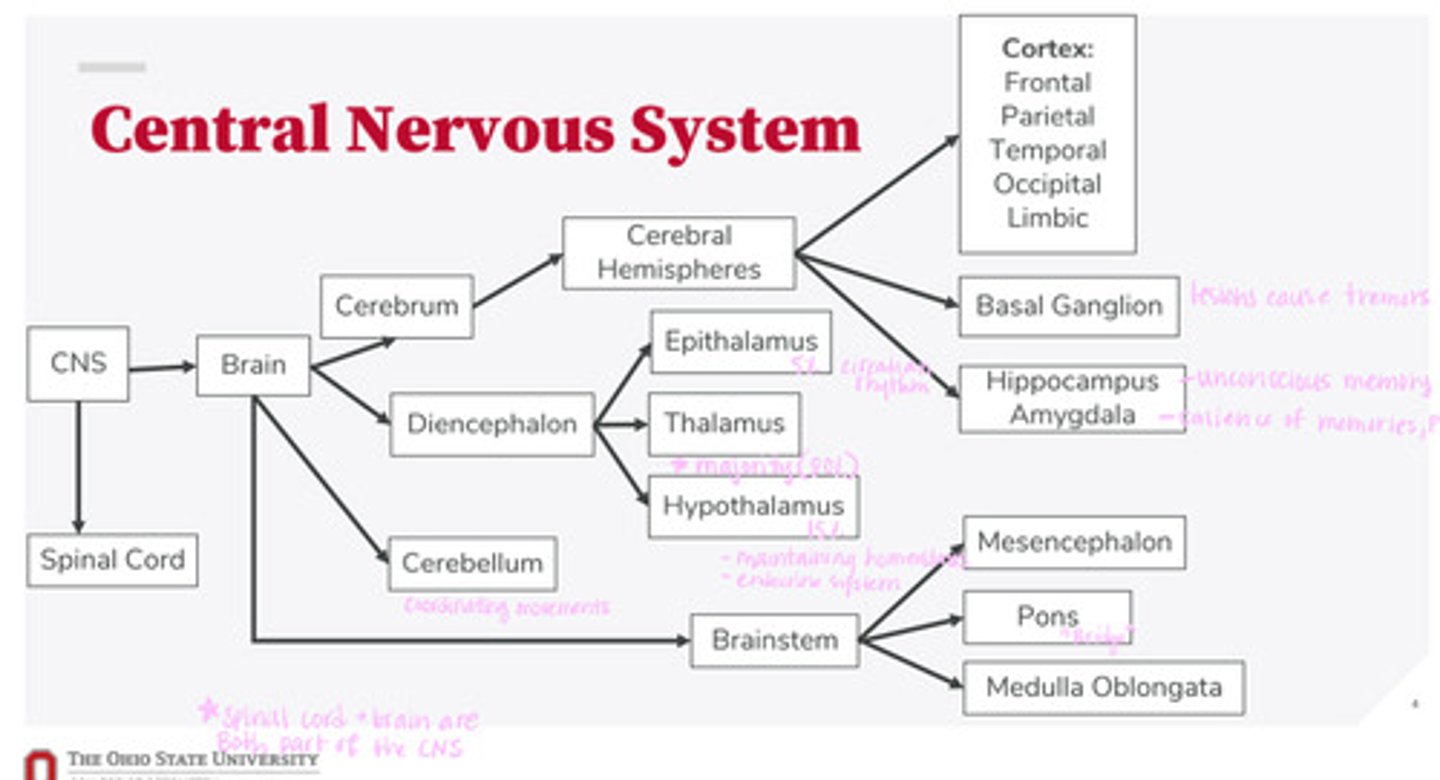
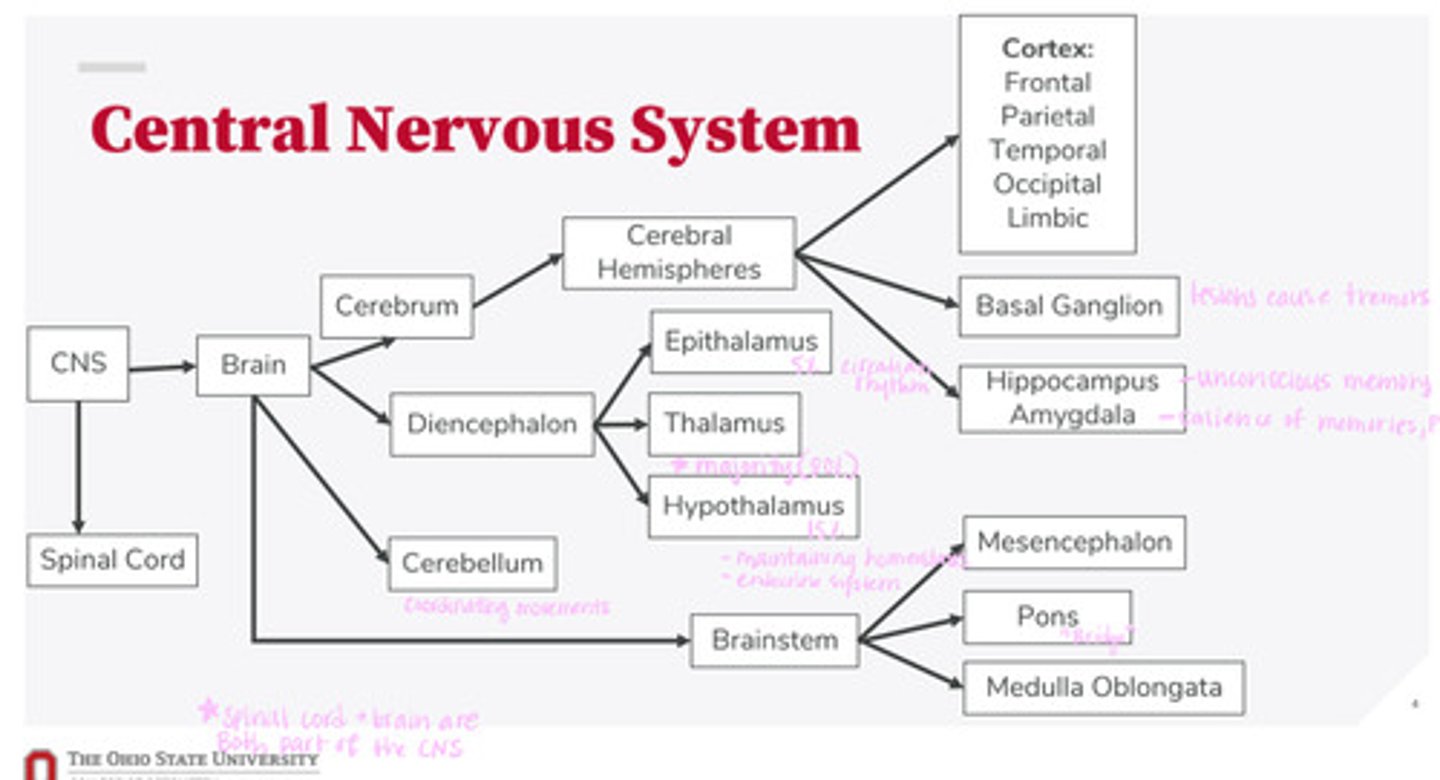
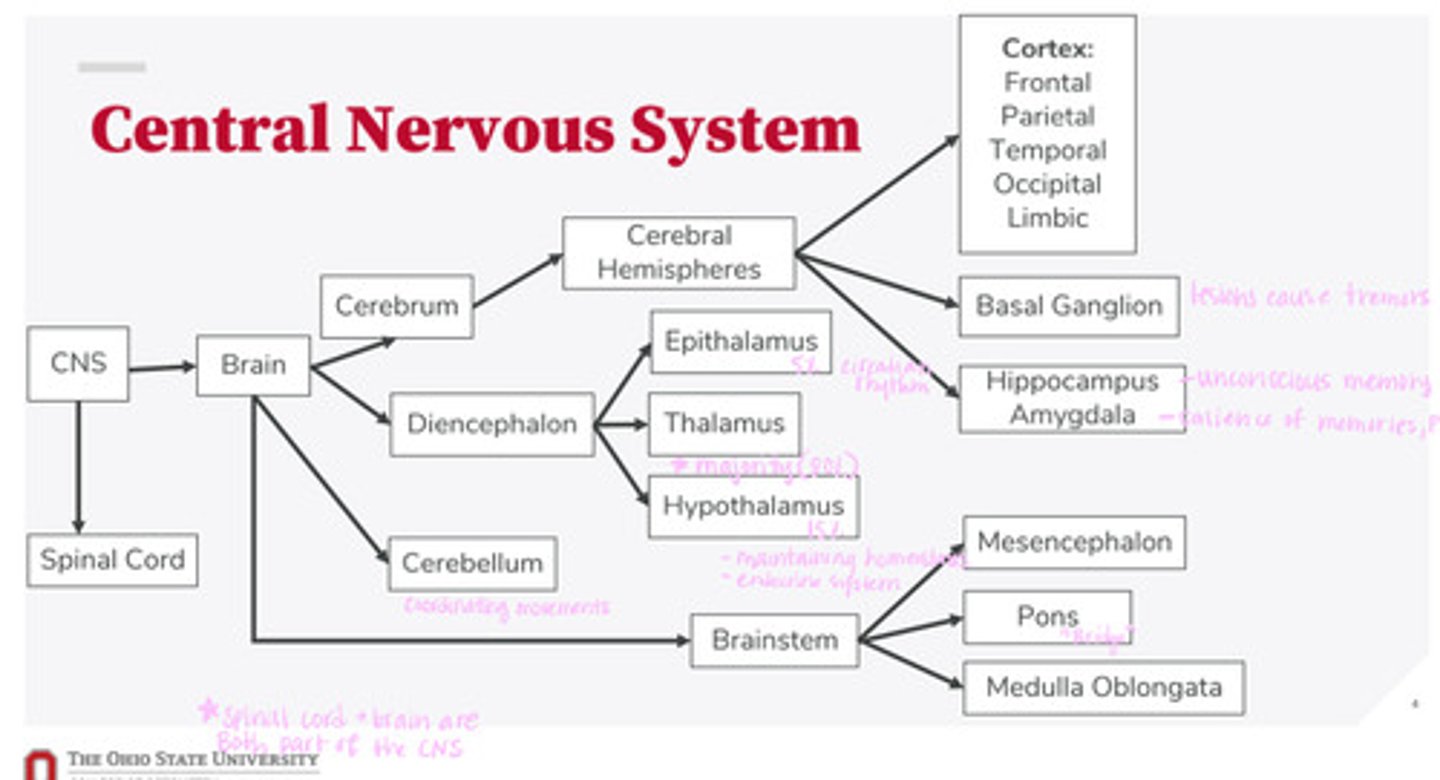
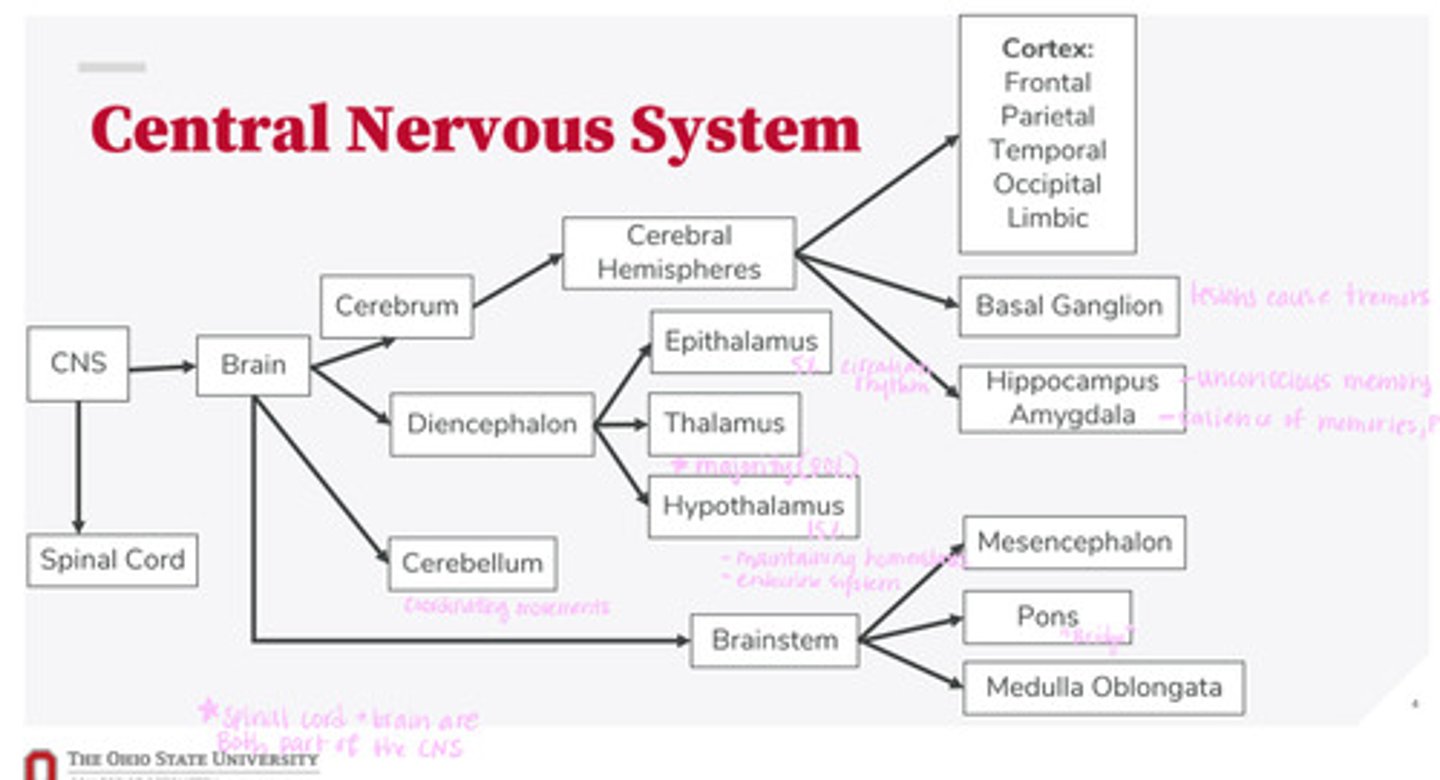
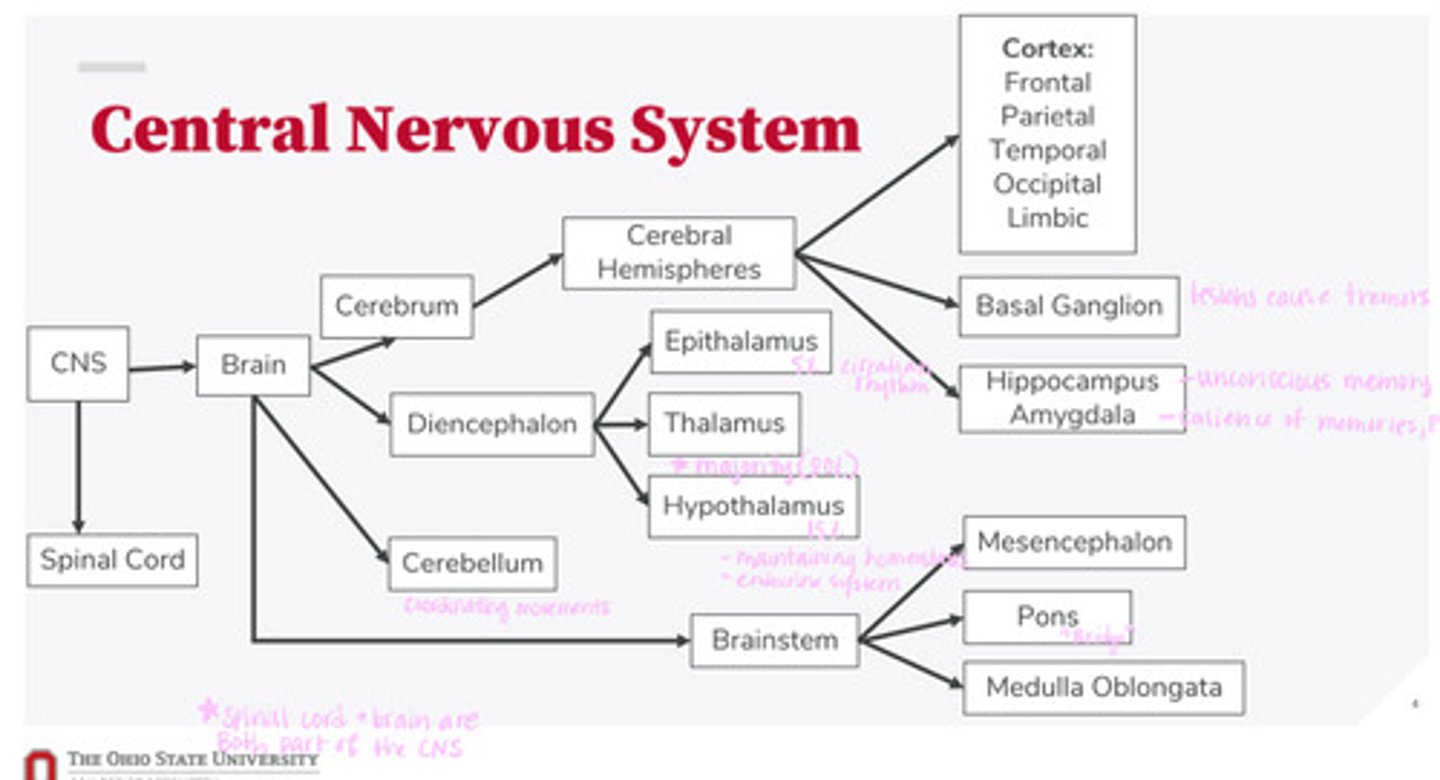
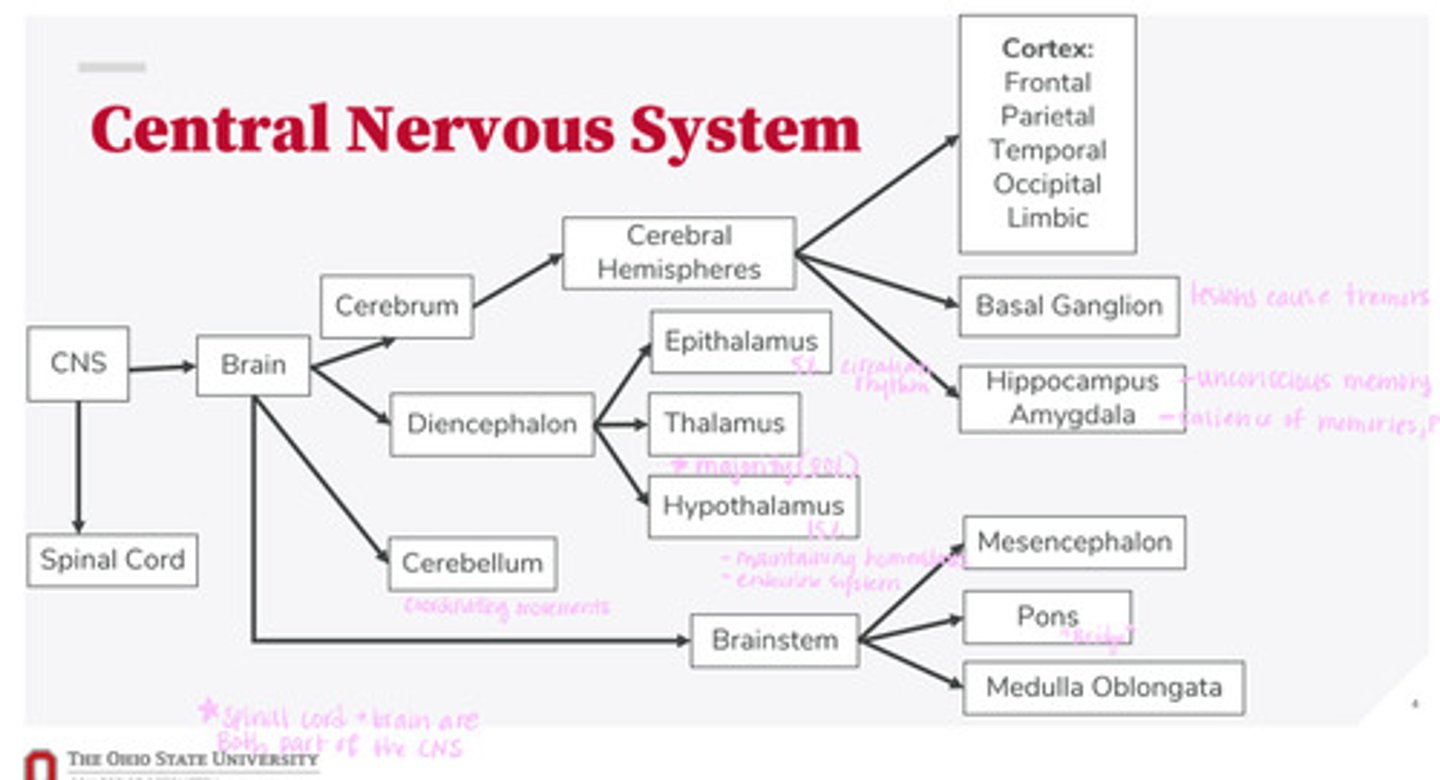
What are the 2 divisions of the CNS?
-cerebrum
-diencephalon
-cerebellum
-brainstem
What are the 4 divisions of the brain?
-epithalamus
-thalamus
-hypothalamus
What are the 3 divisions of the diencephalon?
-mesencephalon
-pons
-medulla oblongata
What are the 3 divisions of the brainstem?
-cortex
-basal ganglion
-hippocampus
-amygdala
What are the divisions of the cerebral hemispheres?
-frontal lobe
-parietal lobe
-temporal lobe
-occipital lobe
-limbic system
What are the divisions of the cortex?
coordinating movements
What is the function of the cerebellum?
thalamus
A majority of signals from the diencephalon flow into where?
-thalamus
-epithalamus
-hypothalamus
circadian rhythm
What is the function of the epithalamus?
-maintaining homeostasis
-endocrine system function
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
tremors
Lesions on the basal ganglion cause what?
hippocampus
What part of the brain is in control of unconscious memory?

amygdala
What part of the brain is in control of the salience of memories (PTSD)?
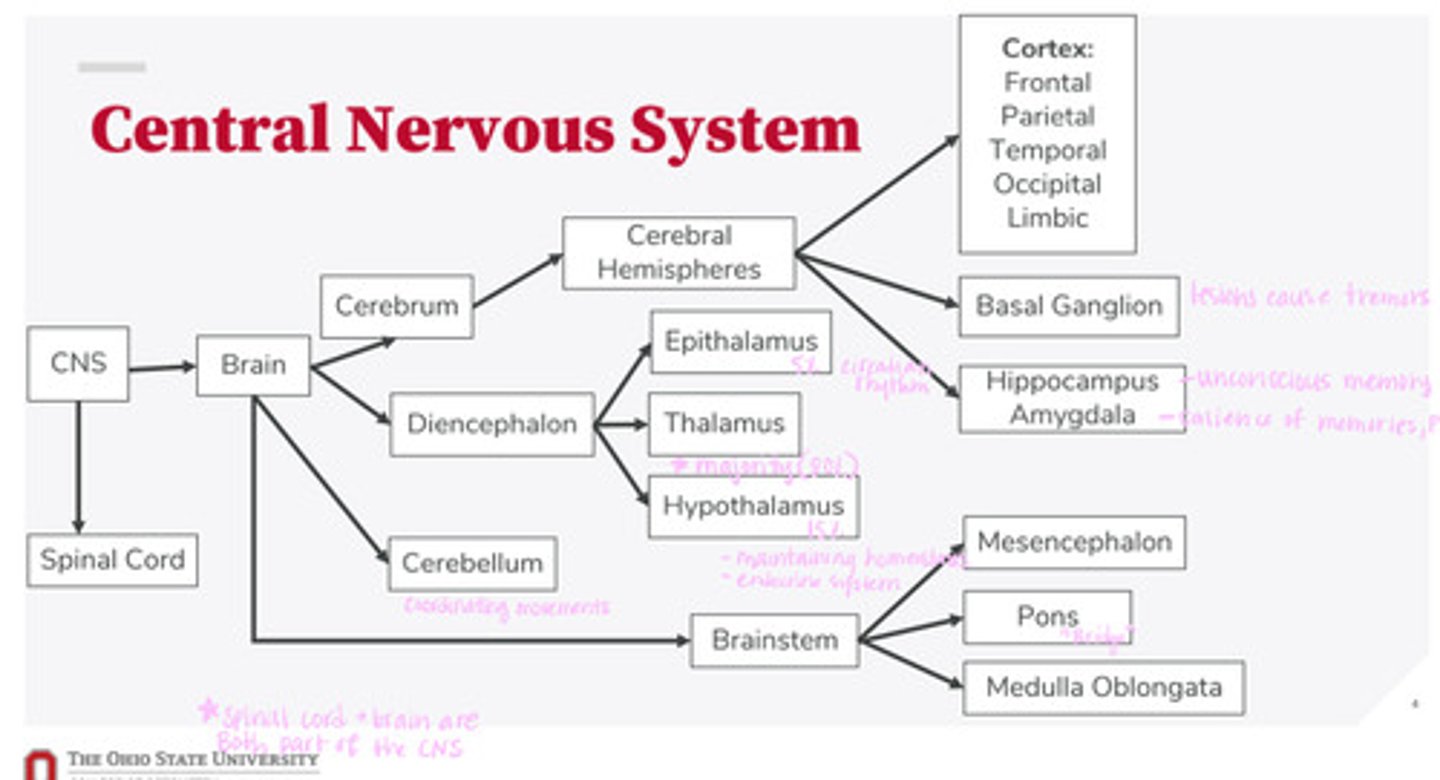
The bridge between the mesencephalon and the medulla oblongata
What is the function of the pons?
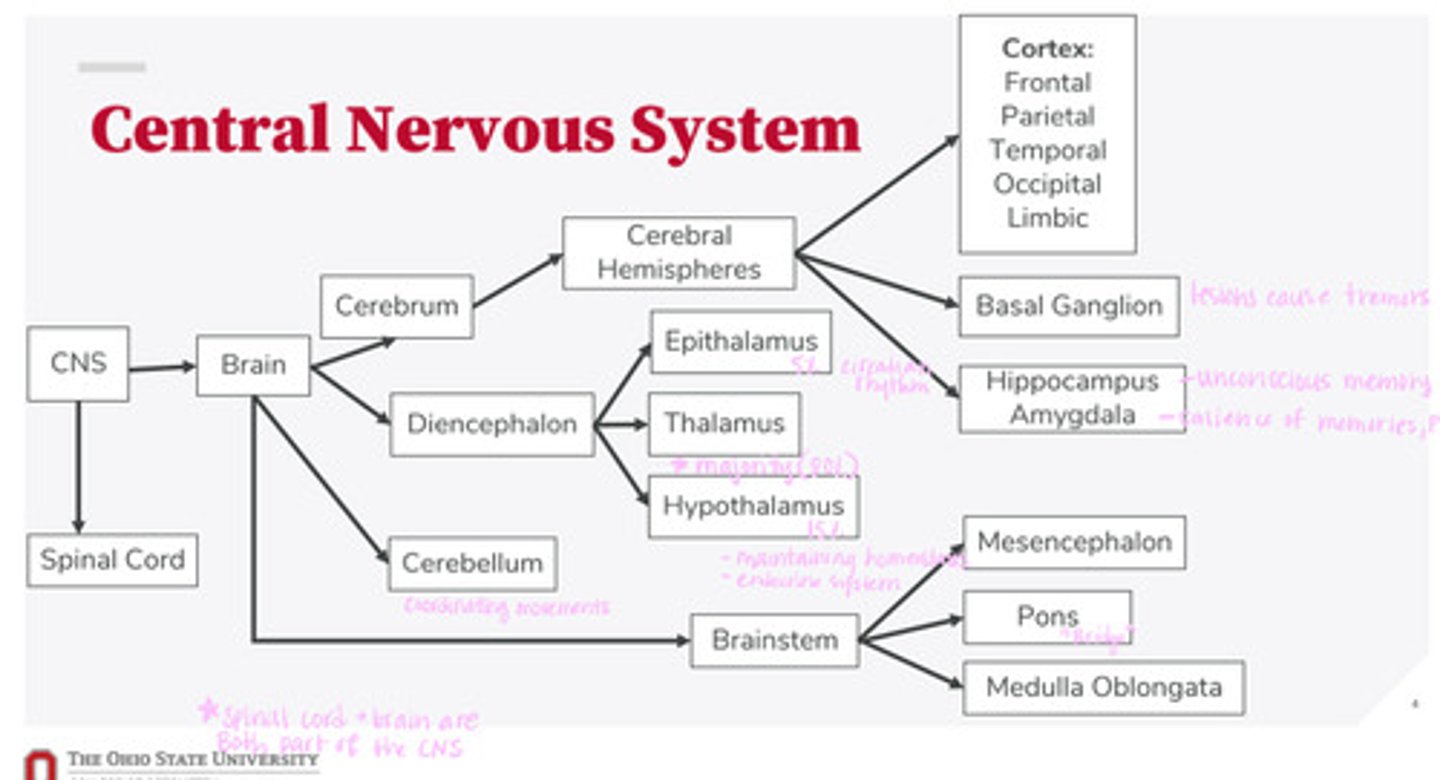
midbrain
What is the mesencephalon?
-forebrain
-midbrain
-hindbrain
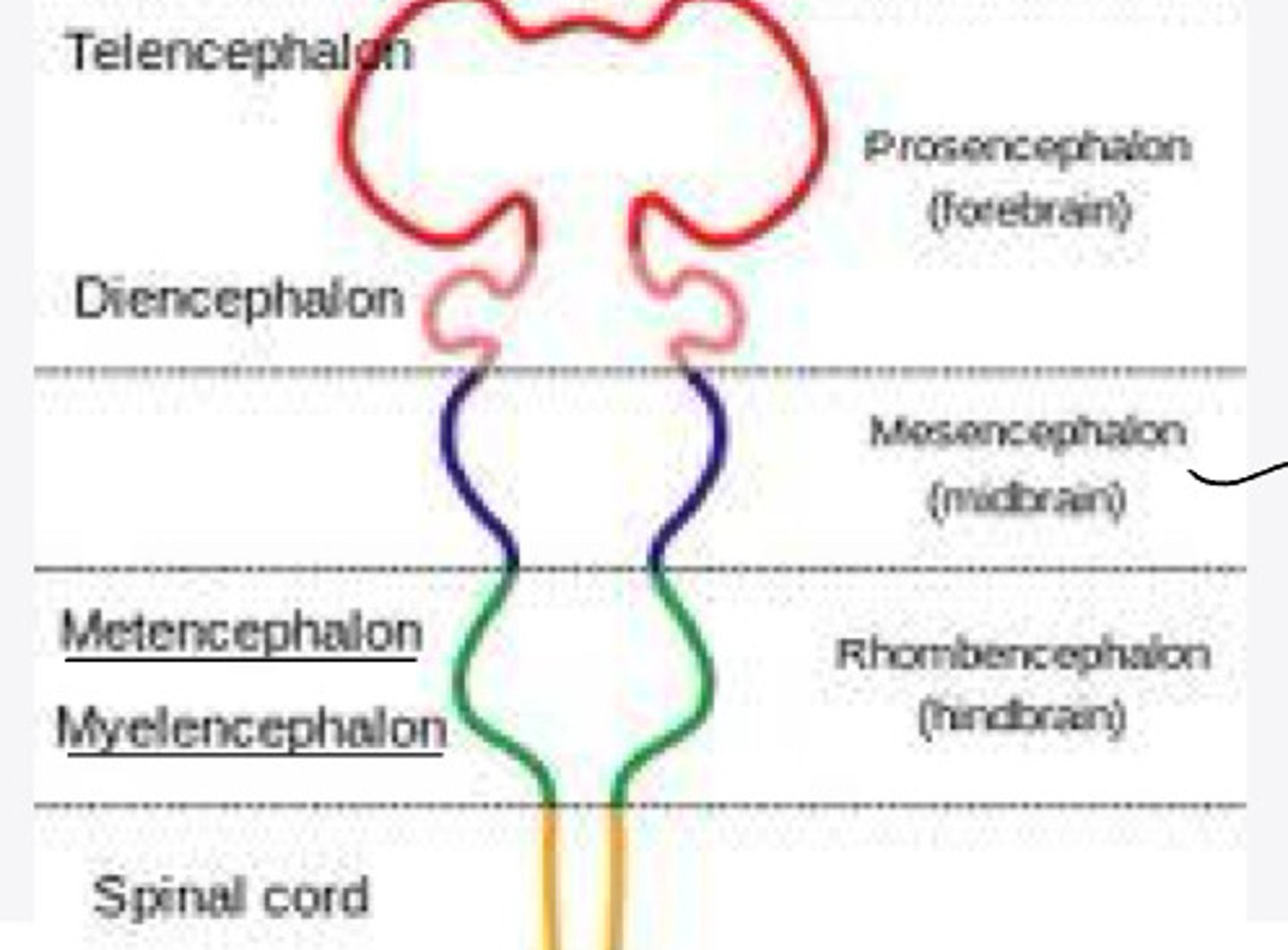
forebrain
What is the prosencephalon?
-forebrain
-midbrain
-hindbrain
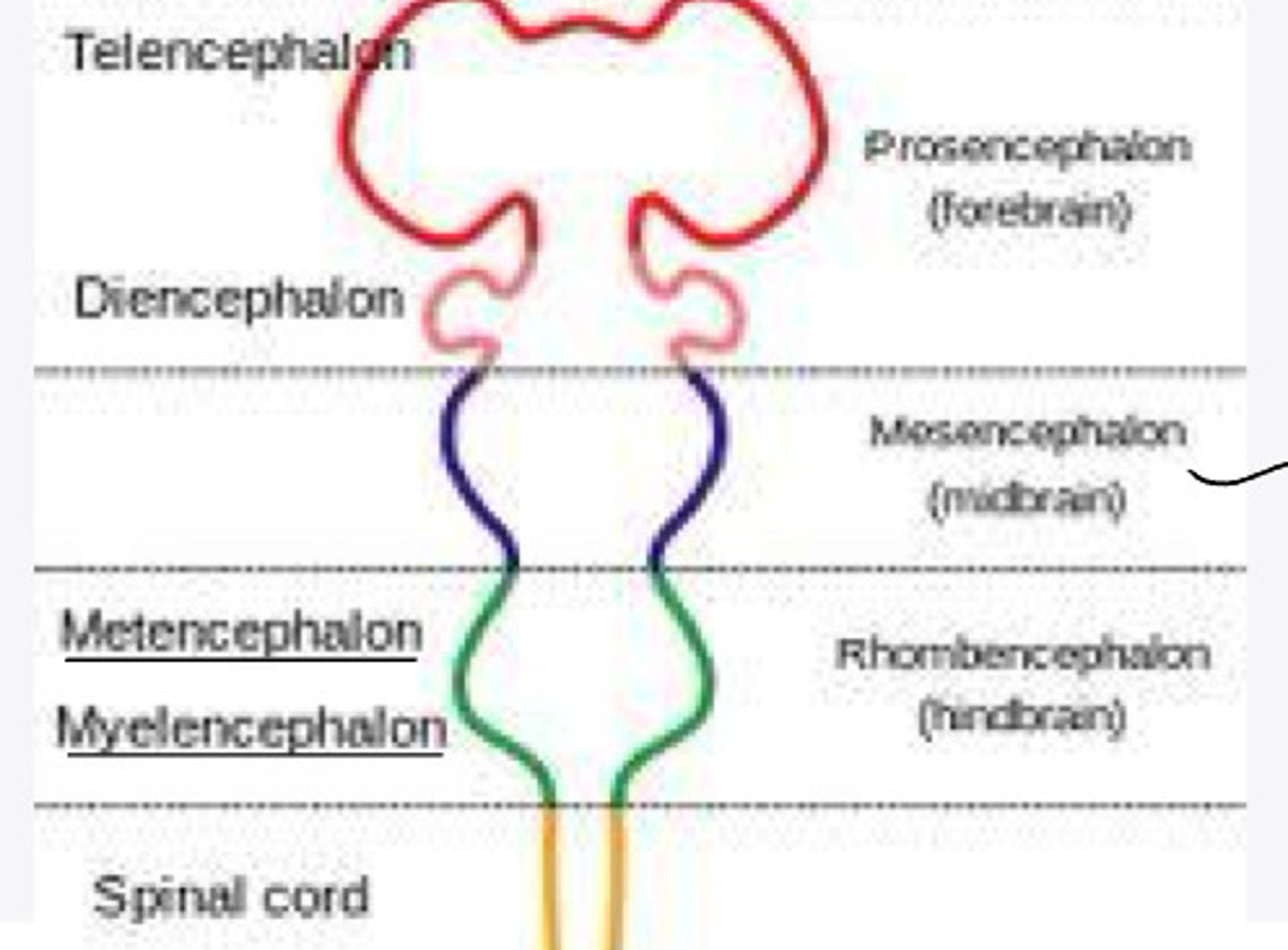
hindbrain
What is the rhombencephalon?
-forebrain
-midbrain
-hindbrain
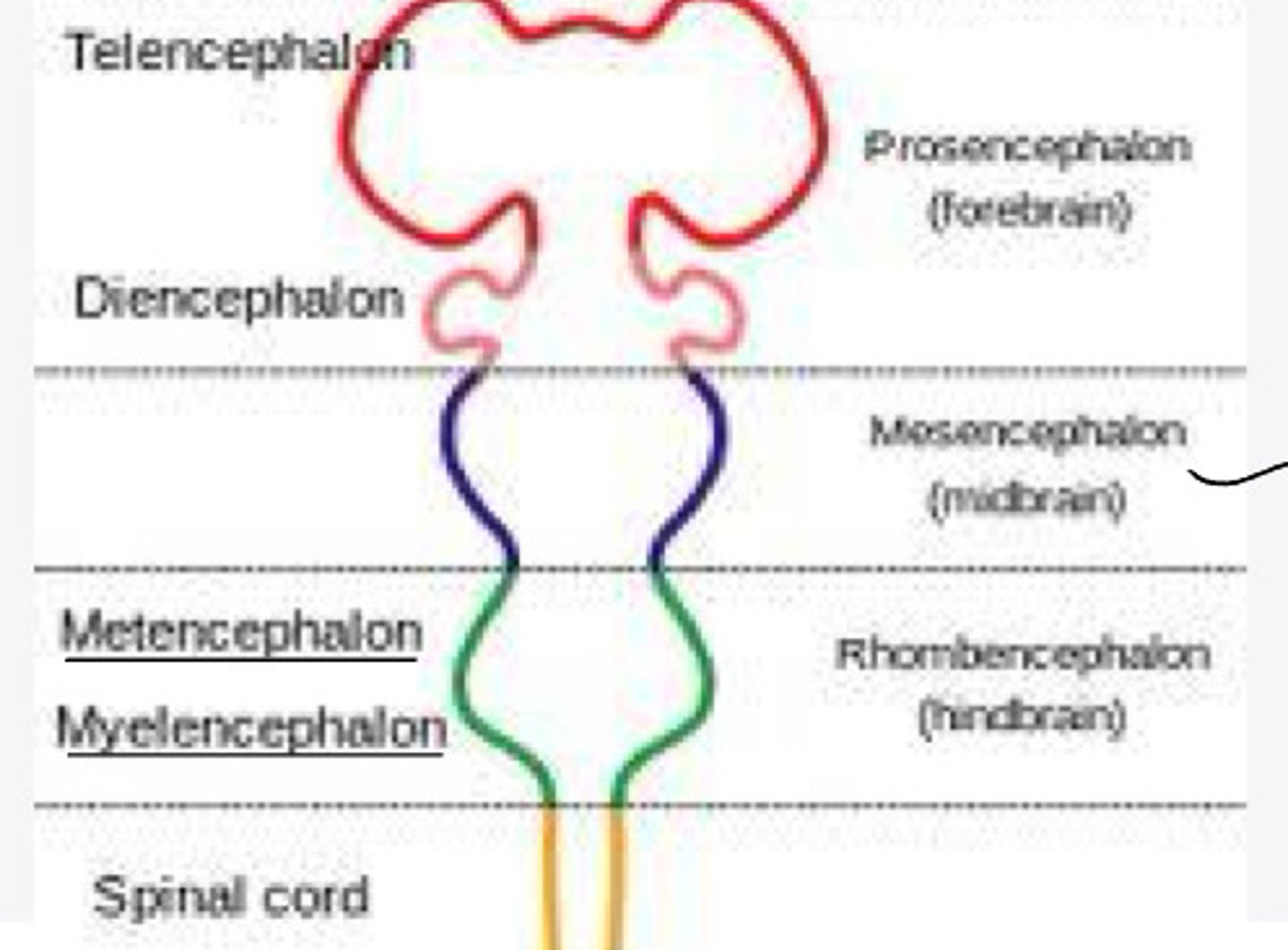
-telencephalon
-diencephalon
In embryology, the prosencephalon will differentiate into what 2 structures?
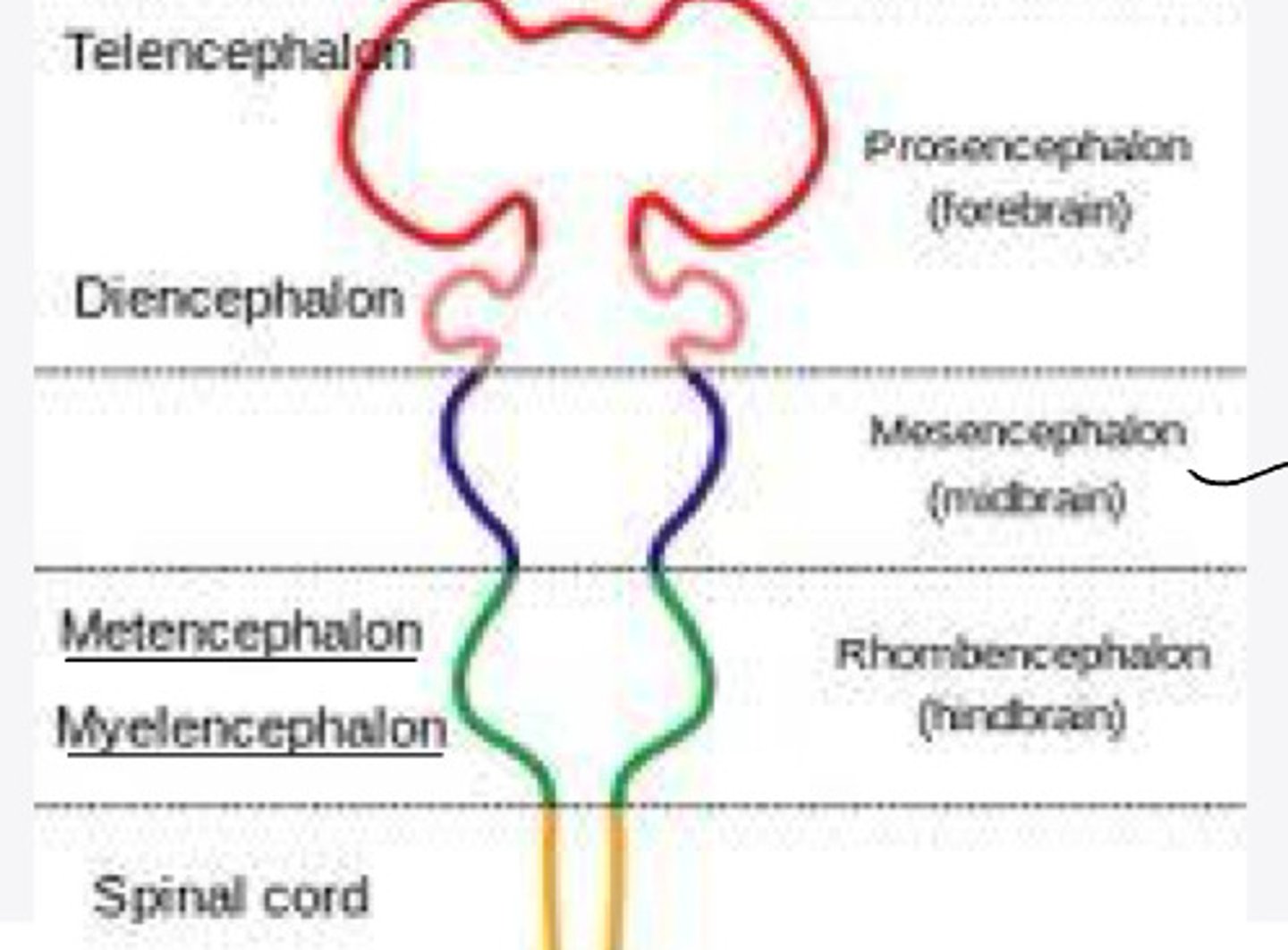
cerebral hemispheres
The telencephalon will differentiate into what structure?
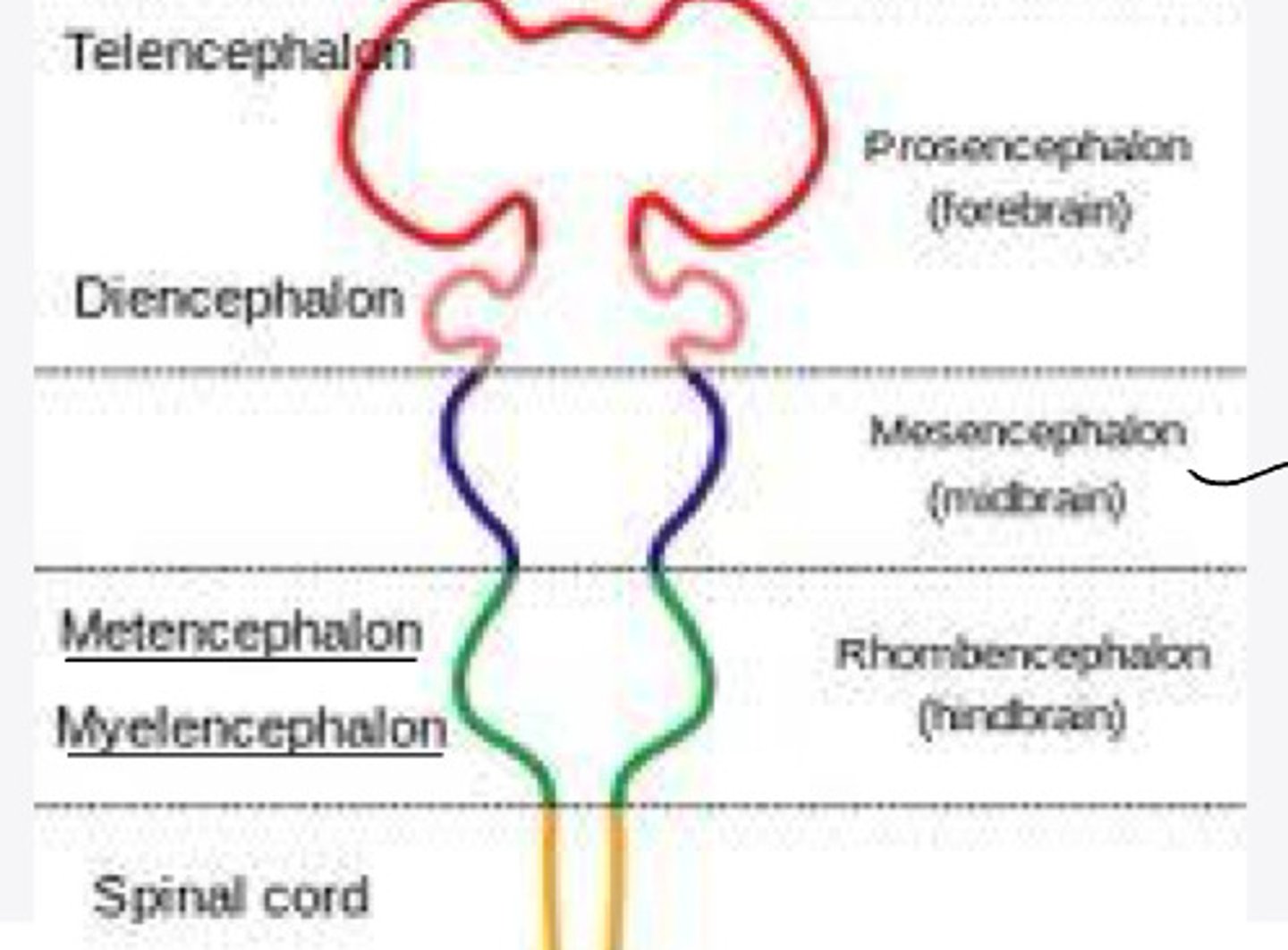
thalamus, epithalamus, hypothalamus
The diencephalon will differentiate into what structures?
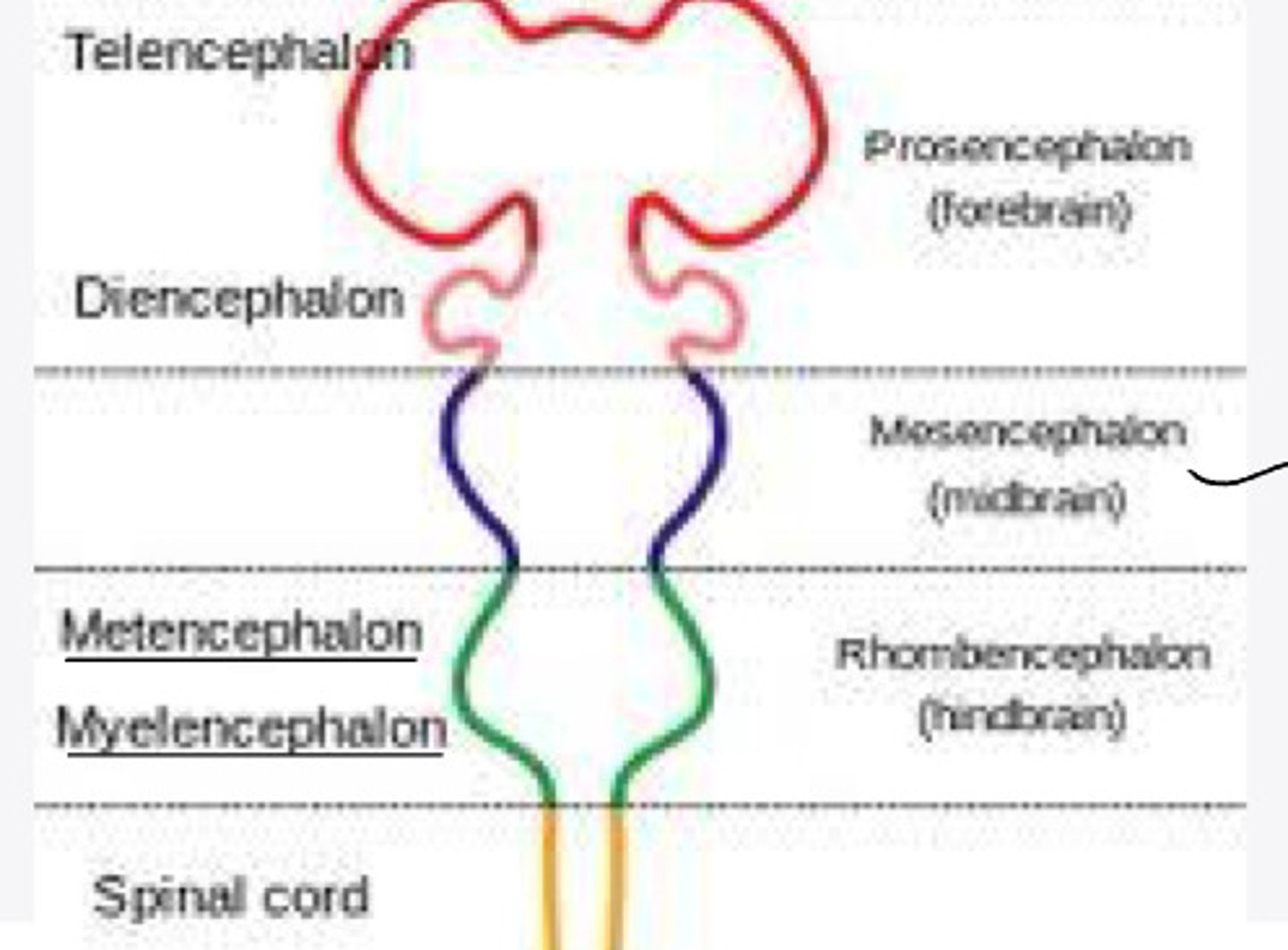
none
In embryology, the mesencephalon will differentiate into what structure?
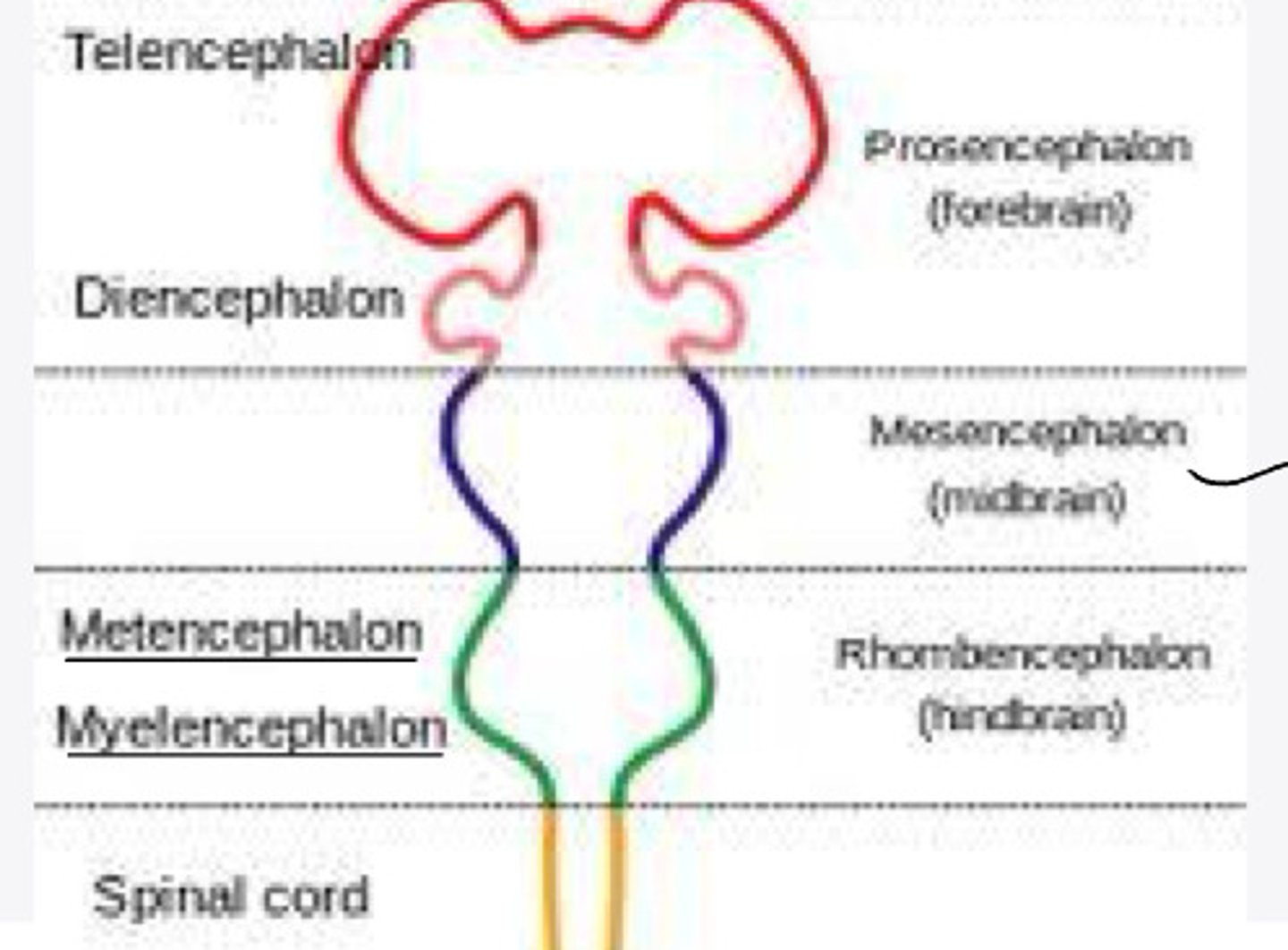
-metencephalon
-myelencephalon
In embryology, the rhombencephalon will differentiate into what 2 structures?
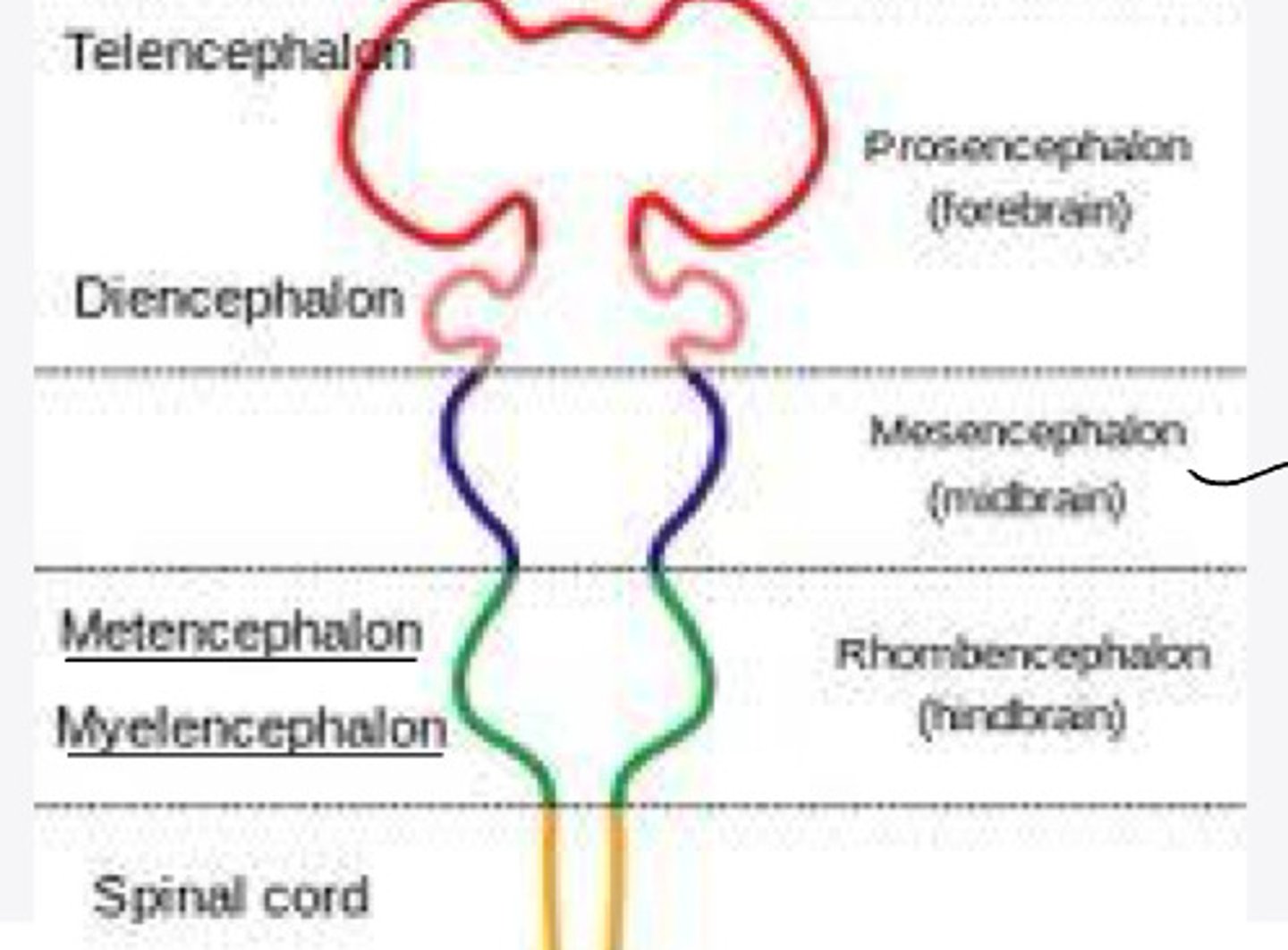
pons and cerebellum
The metencephalon will differentiate into what structures?
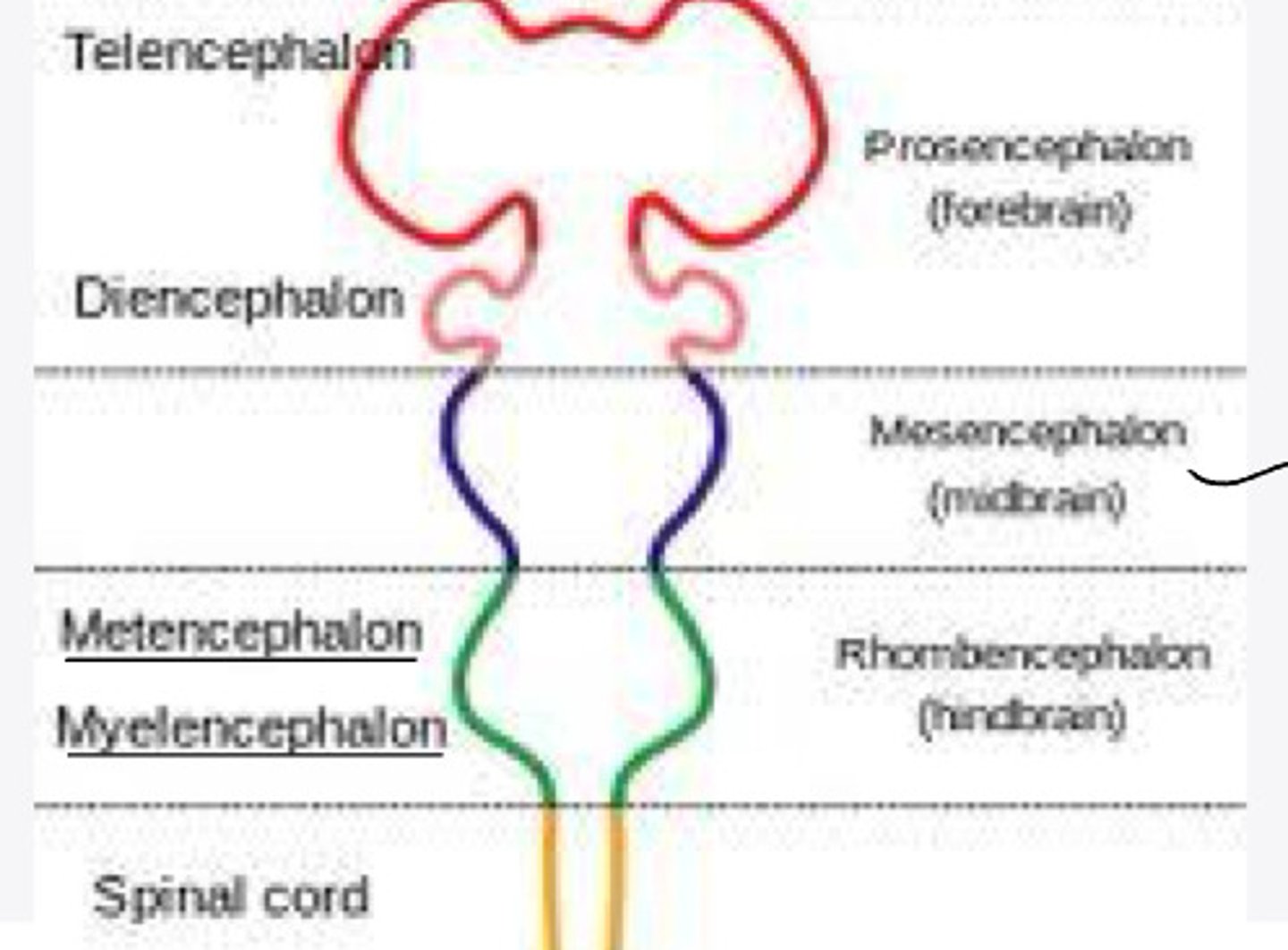
medulla oblongata
The myelencephalon will differentiate into what structure?
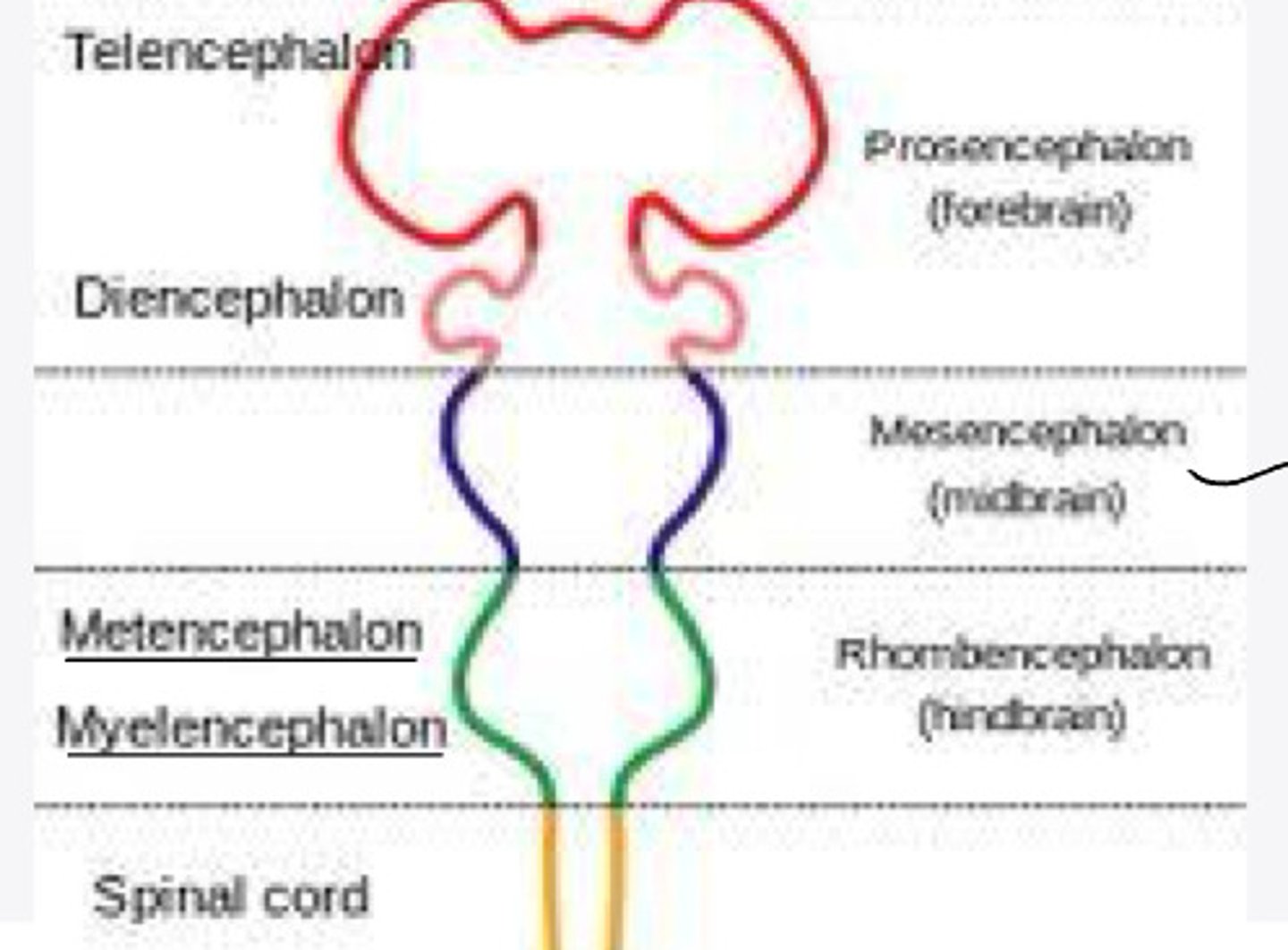
geri, sulci, lobes
What are the anatomical divisions of the cortex of the brain?

52 Brodmann areas
What are the histological divisions of the cortex of the brain?
motor cortex, premotor cortex, visual cortex, etc.
What are the functional divisions of the cortex of the brain?
While there is significant overlap between the 3 methods, they are not in 100% agreement
Are the 3 methods of classifying the cortex (anatomical, histological, and functional) in 100% agreement? Is there overlap in these methods?
no -- the left one is larger (in all Right handed individuals, some Left handed)
Are the right and left hemisphere equal in size? If no, which one is larger?
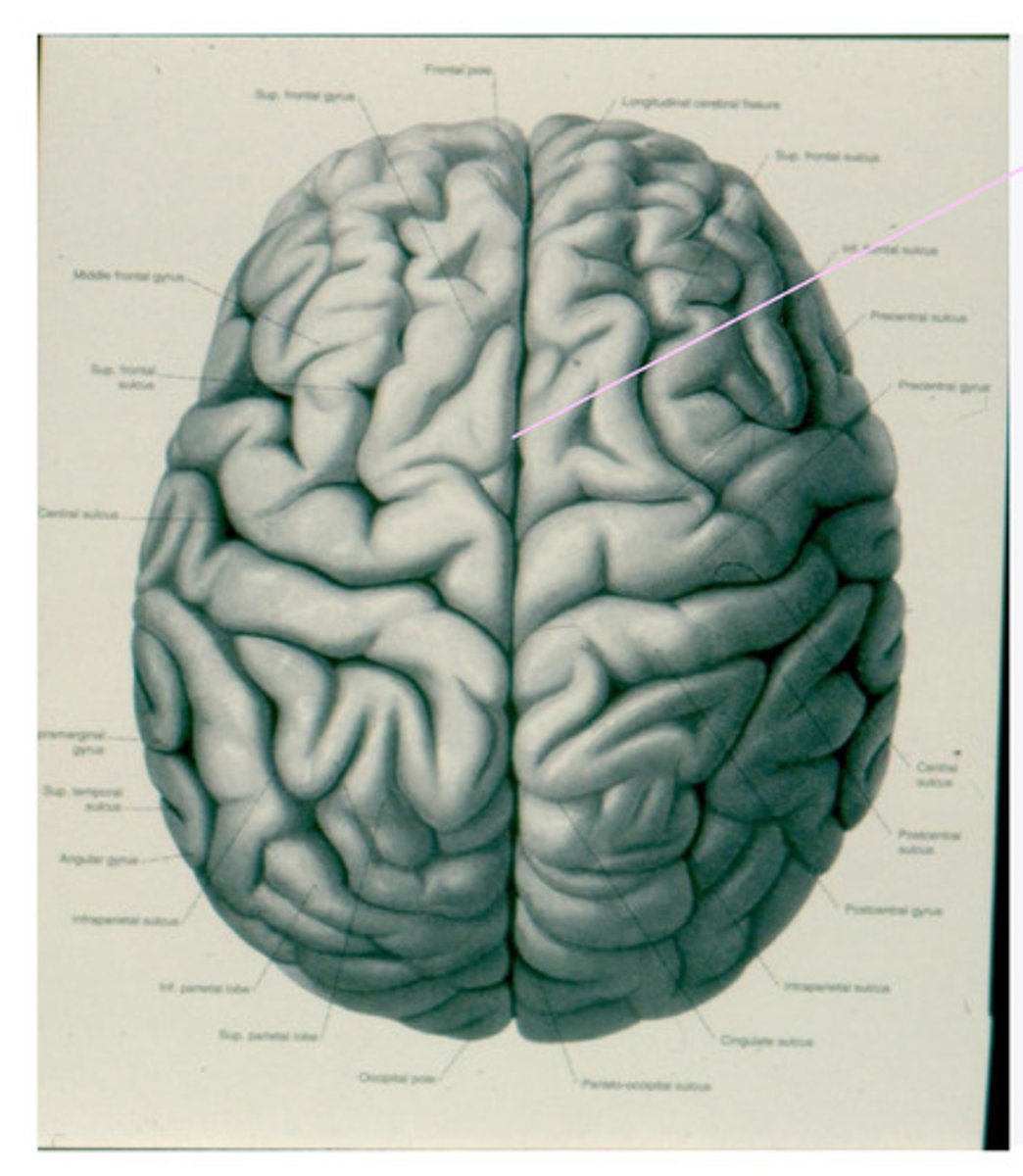
right hemisphere tends to be larger or equivalent in size to the left
In left handed individuals, which hemisphere is larger?
Yes
Do the right and left hemisphere of the brain try to inhibit each other?
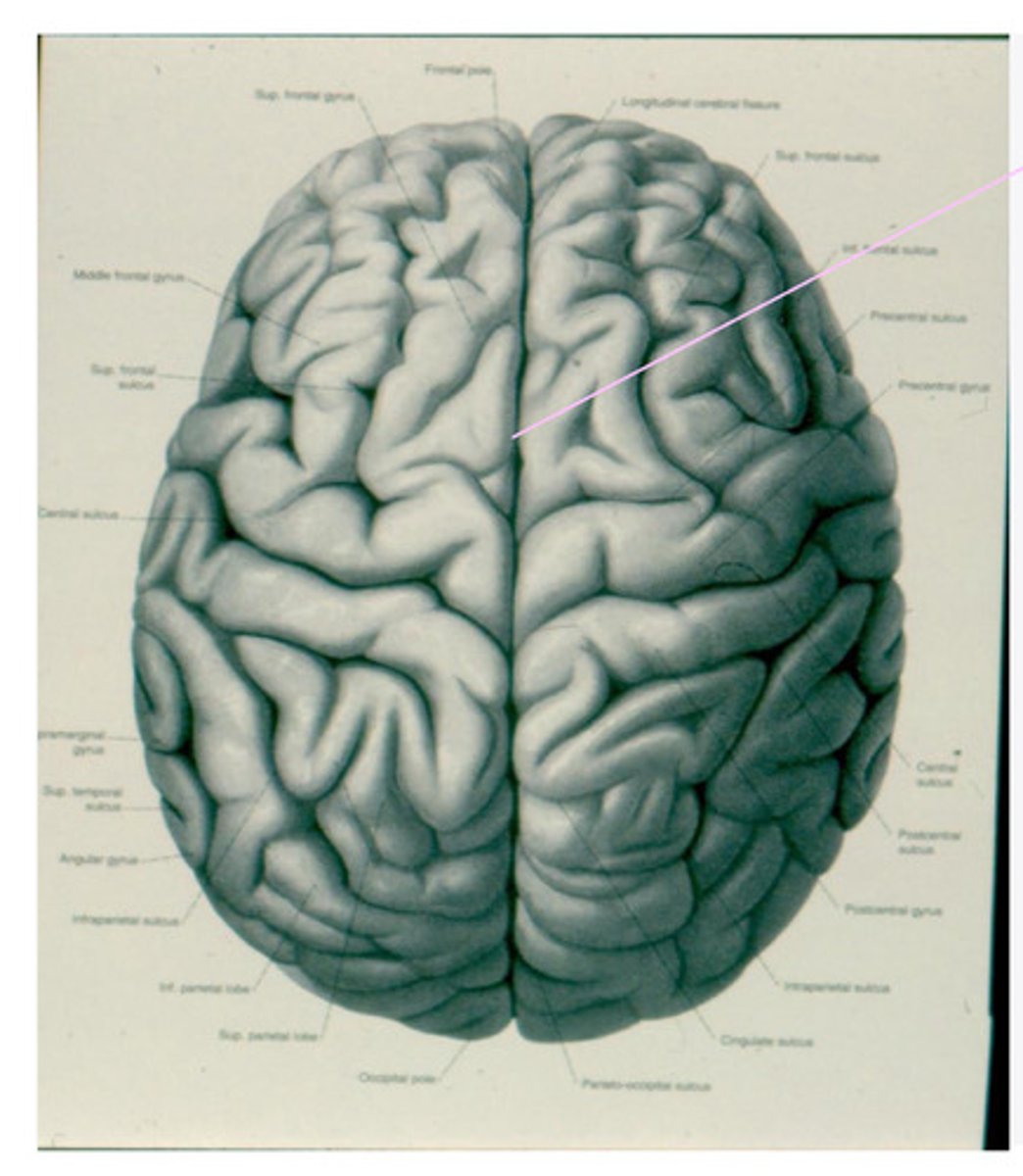
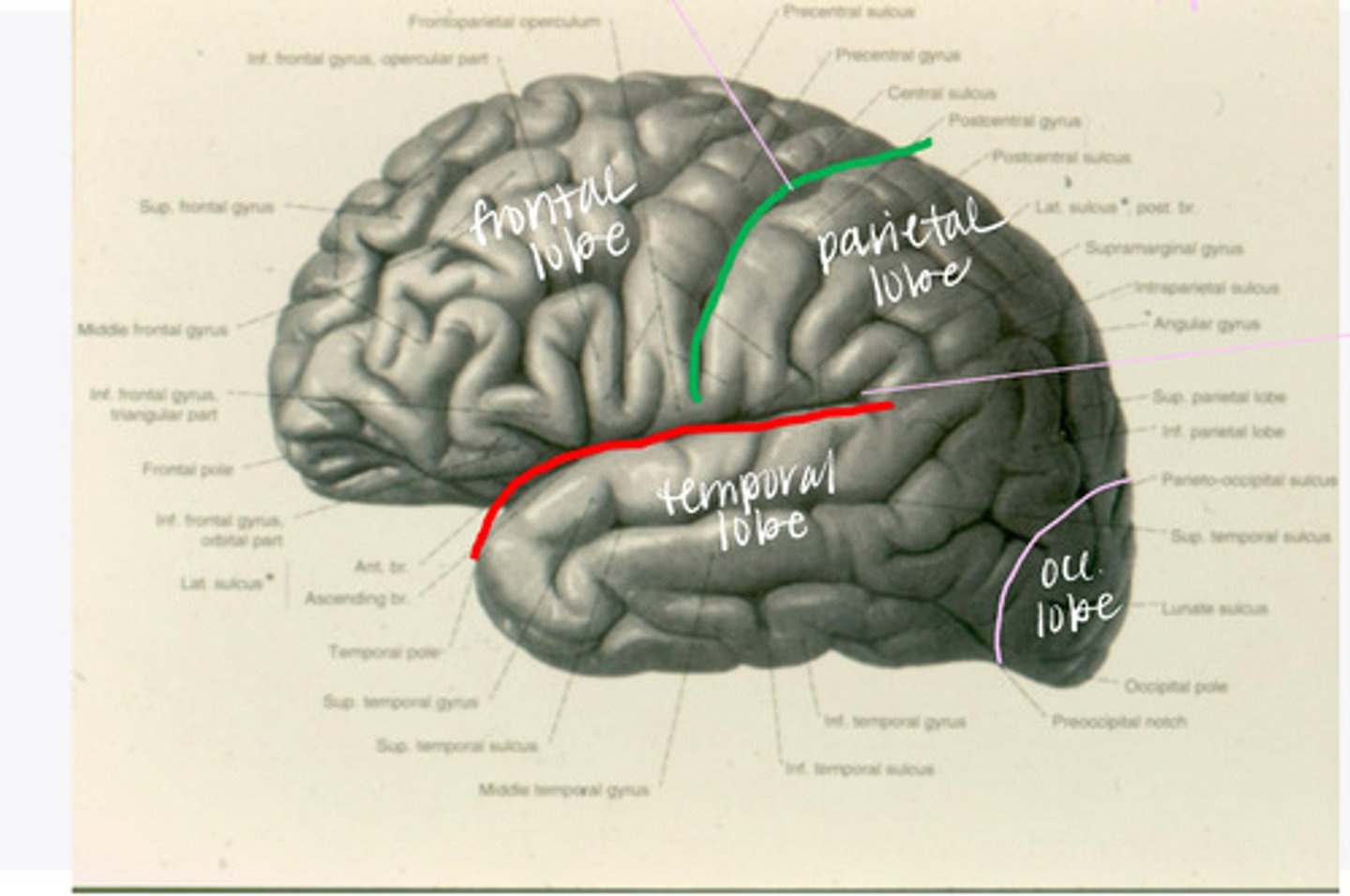
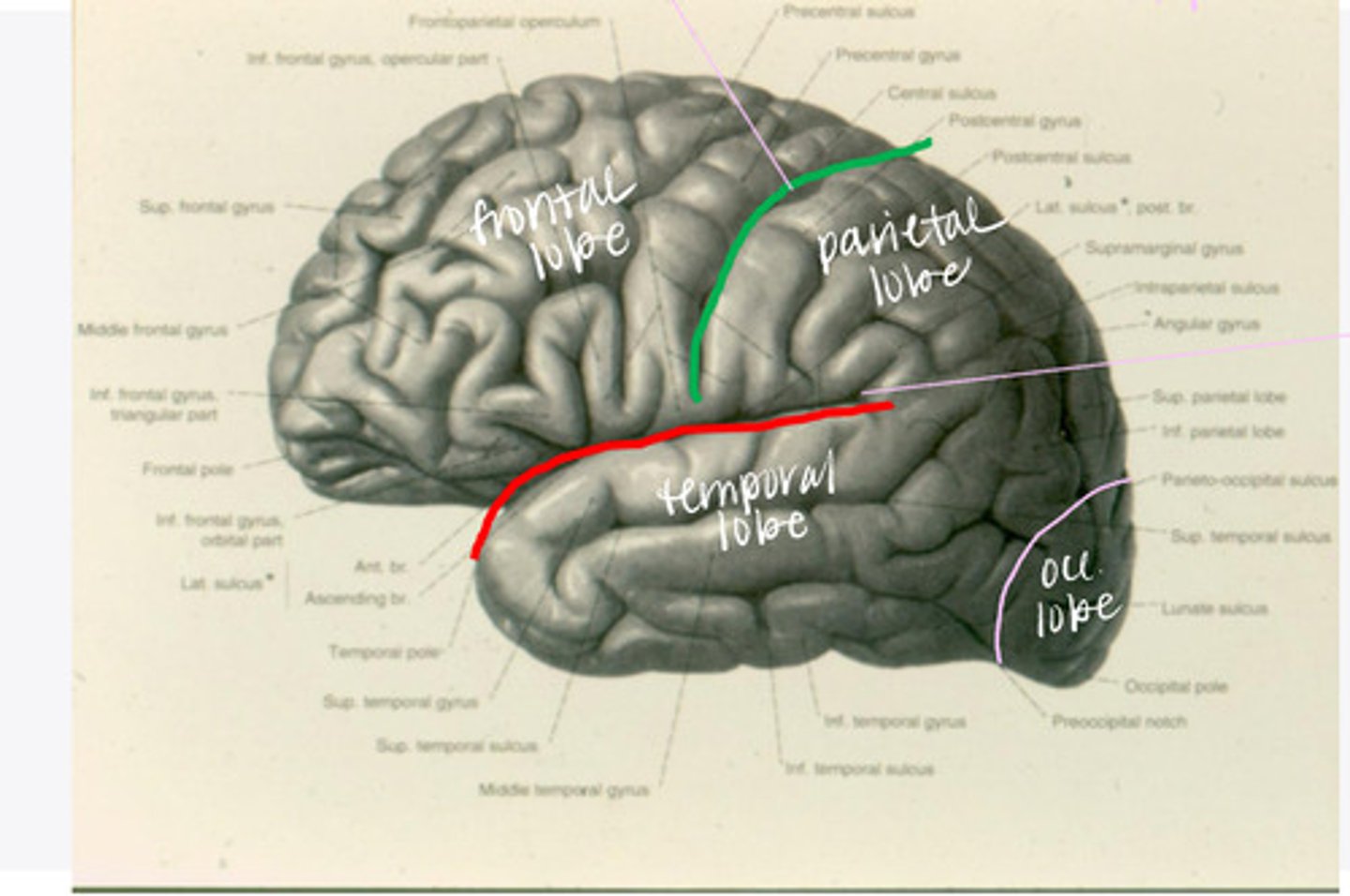
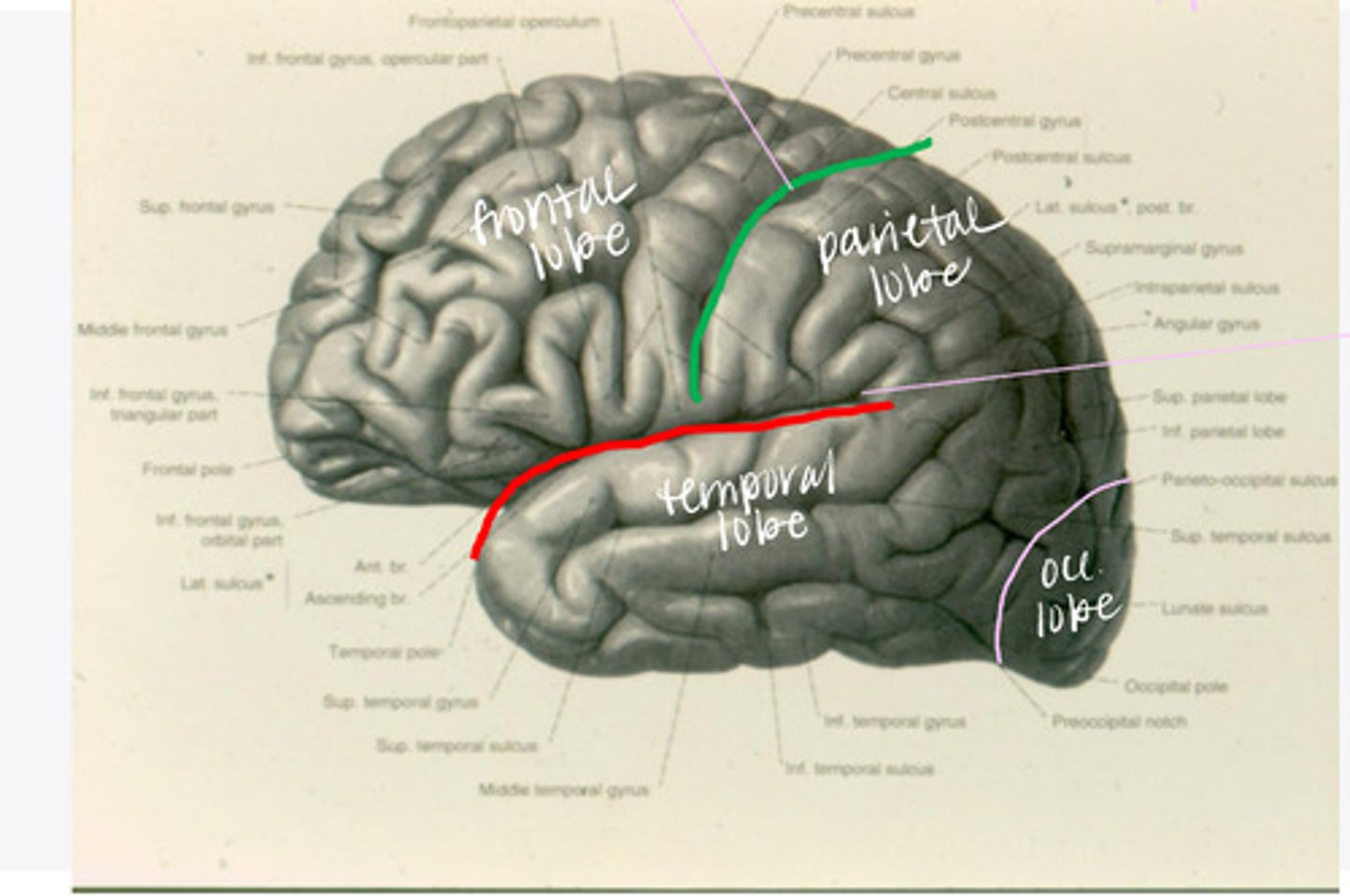
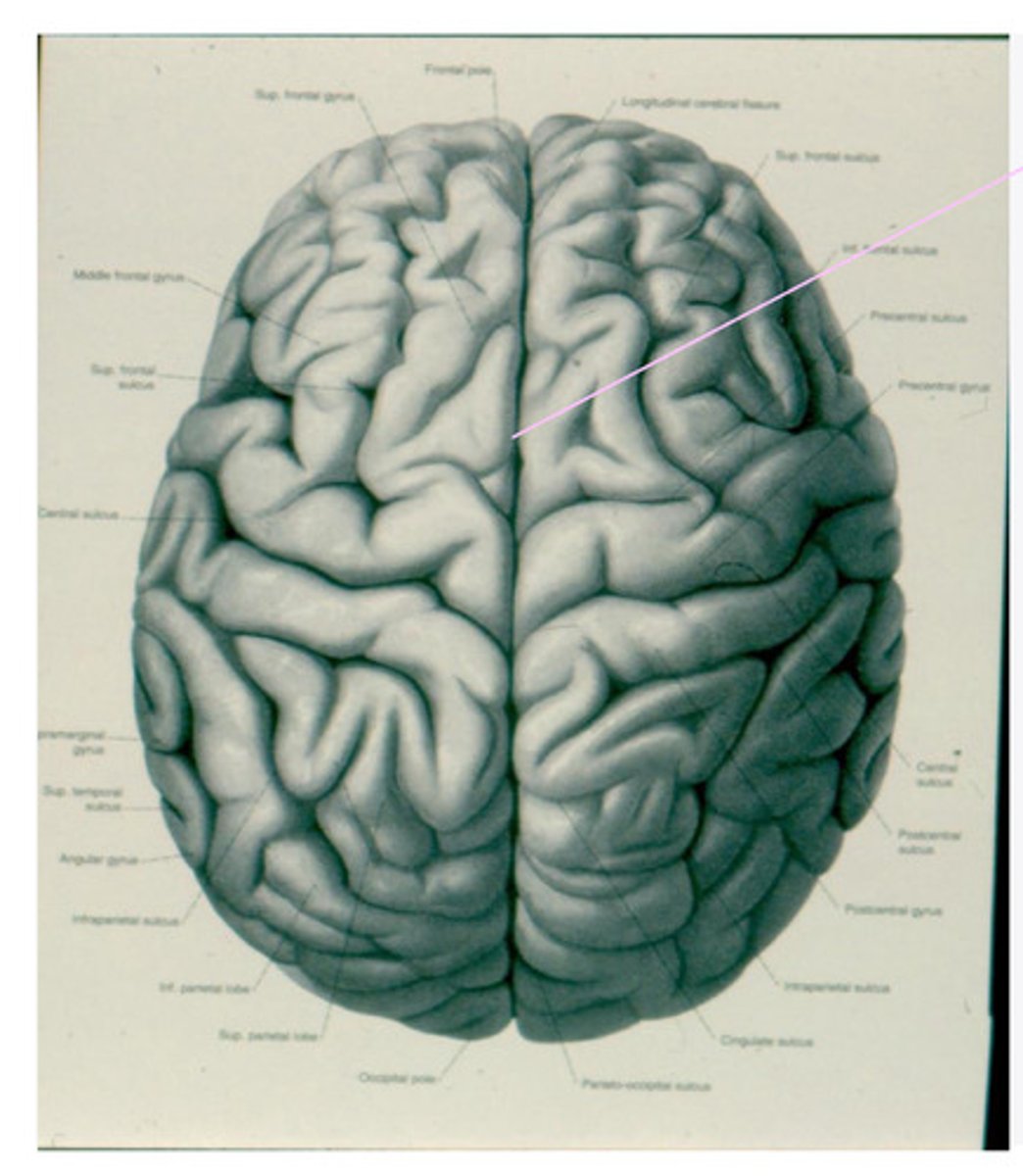
-frontal
-parietal
-temporal
-occipital
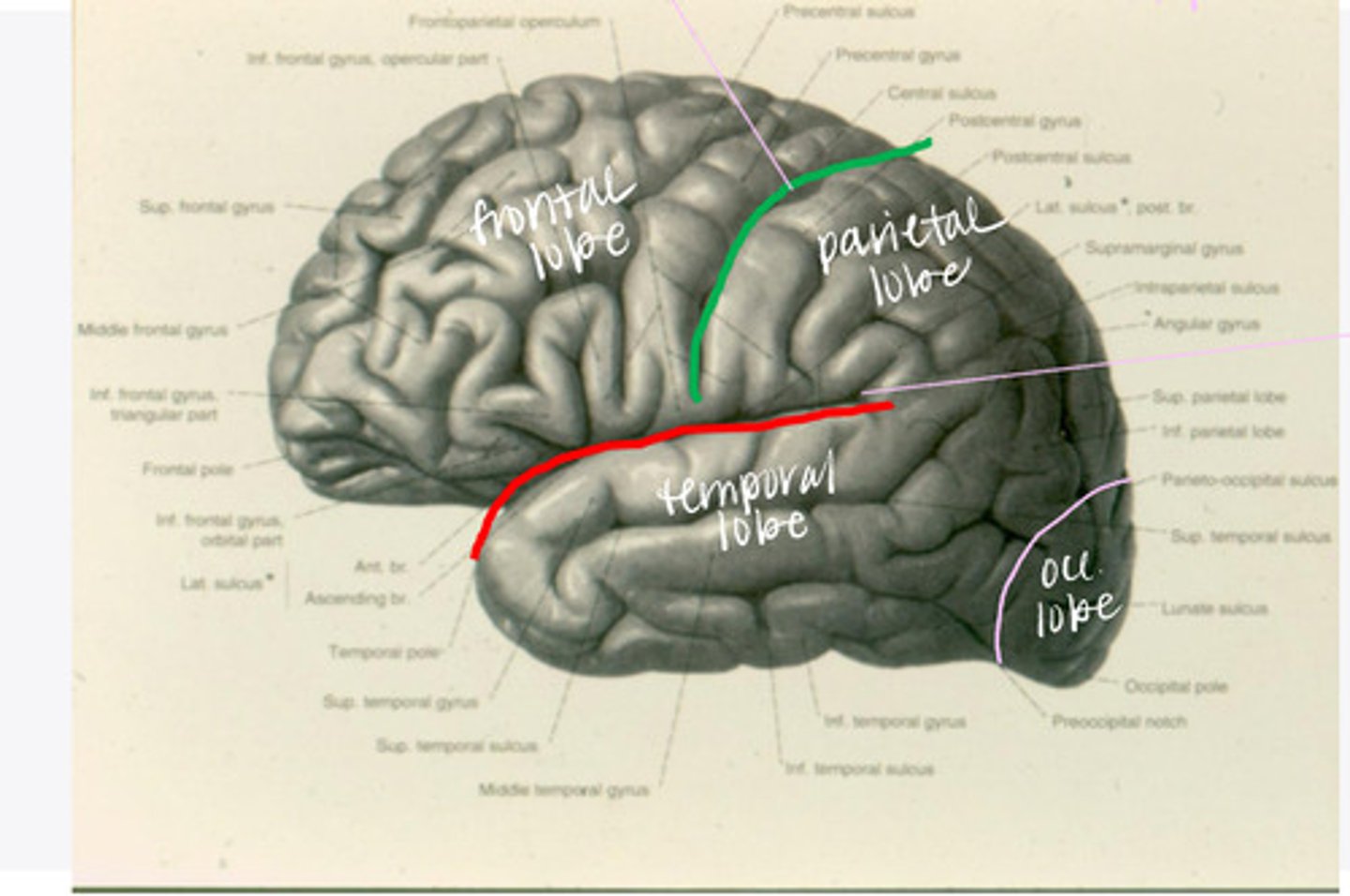
What are the 4 lobes of the brain?
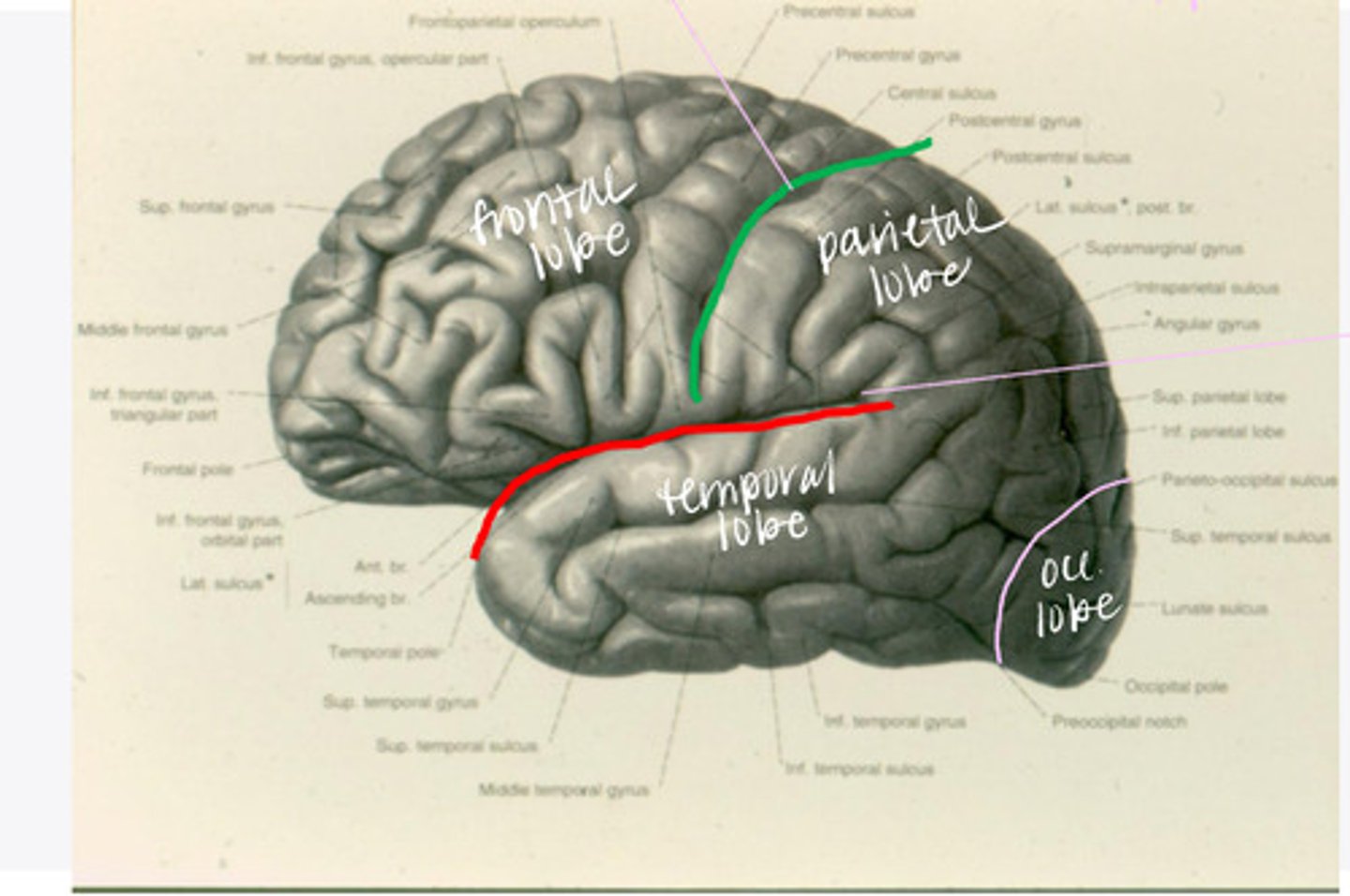
central sulcus
What sulcus differentiates the frontal from the parietal lobe?
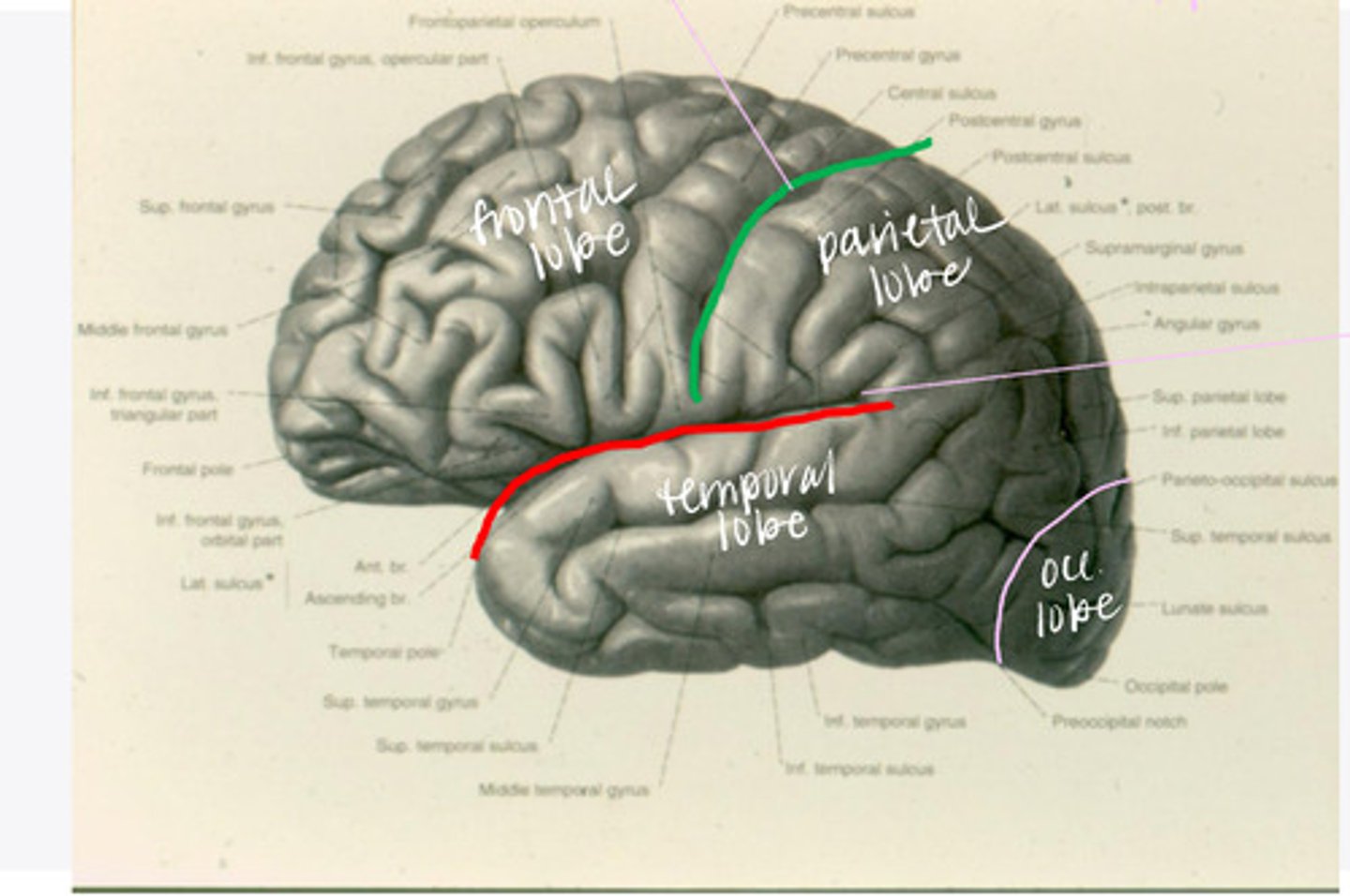
lateral sulcus
What sulcus differentiates the frontal from the temporal lobe?
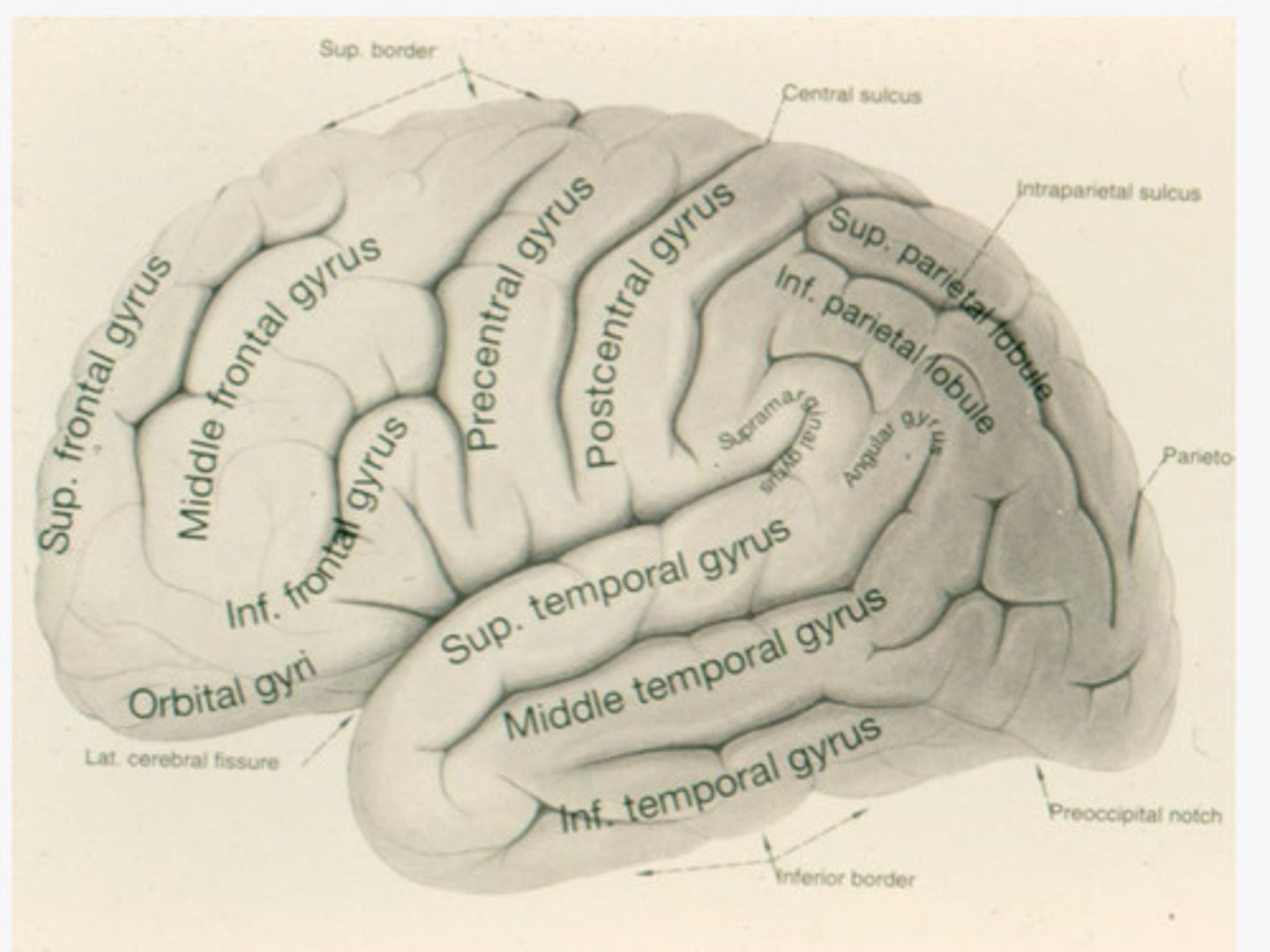
-precentral gyrus
-superior frontal gyrus
-middle frontal gyrus
-inferior frontal gyrus
The frontal lobe is divided into what 4 gyri?
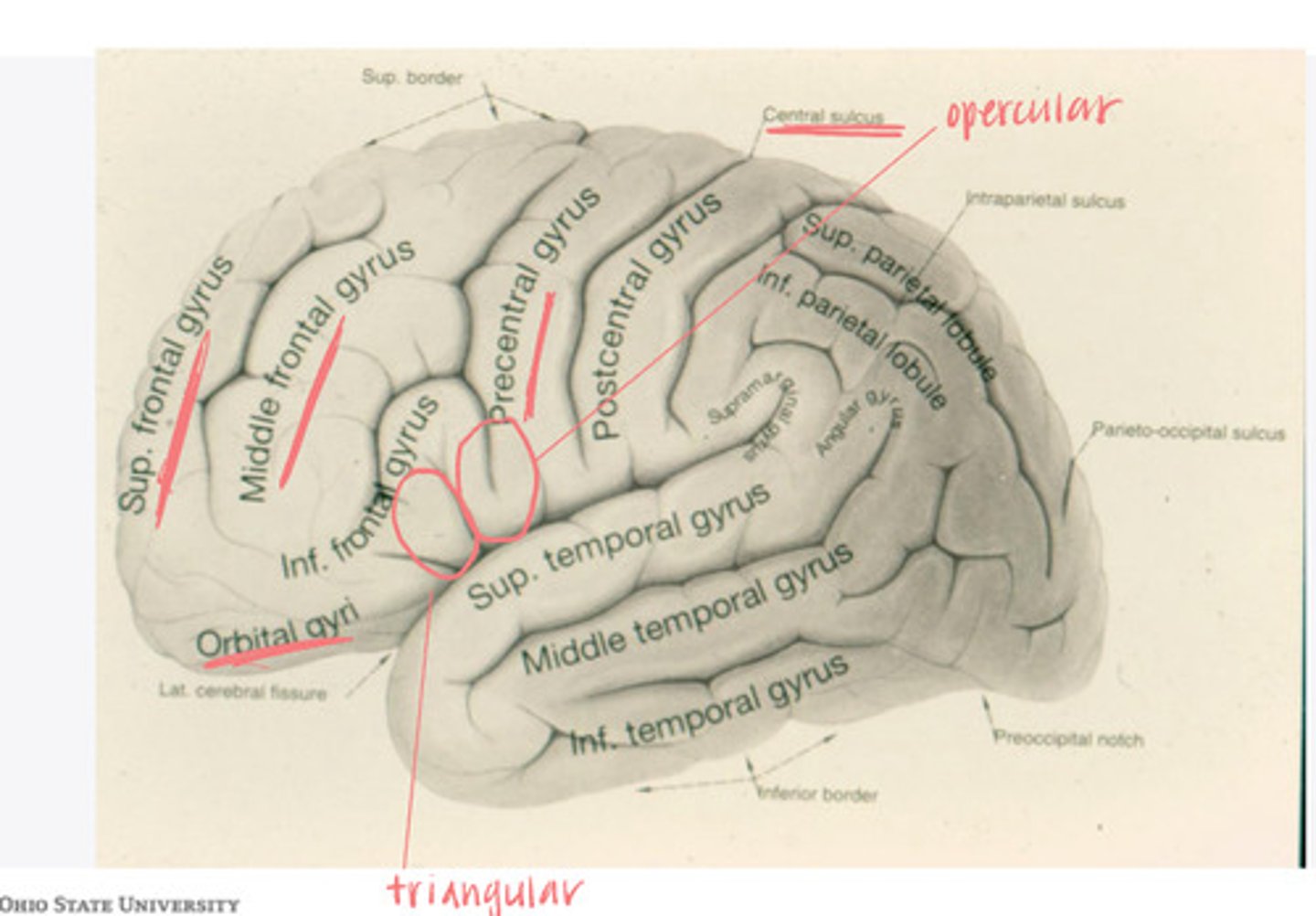
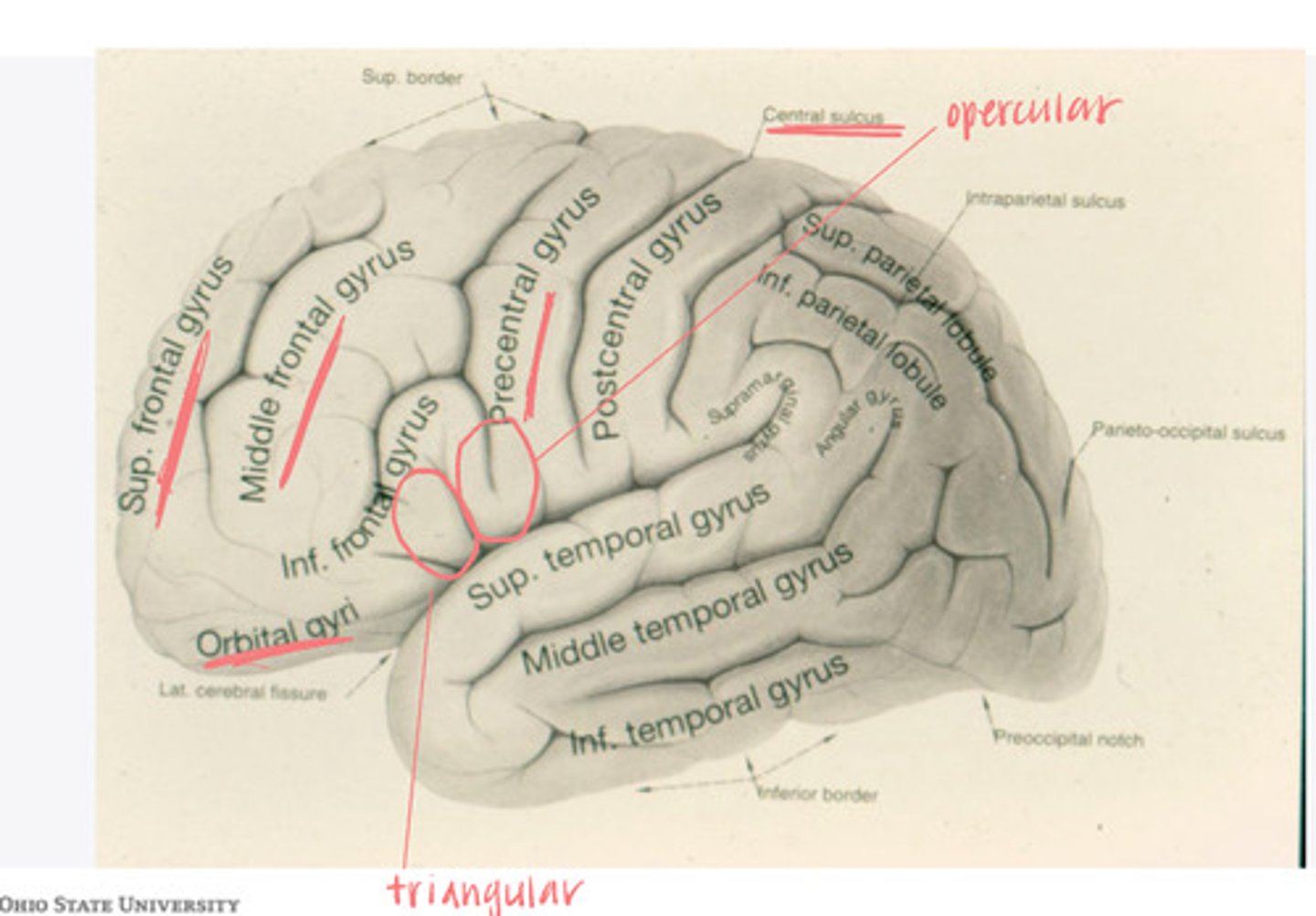
-opercular
-triangular
-orbital gyrus
What are the 3 divisions of the inferior frontal gyrus?
-post-central gyrus
-superior parietal lobule
-inferior parietal lobule
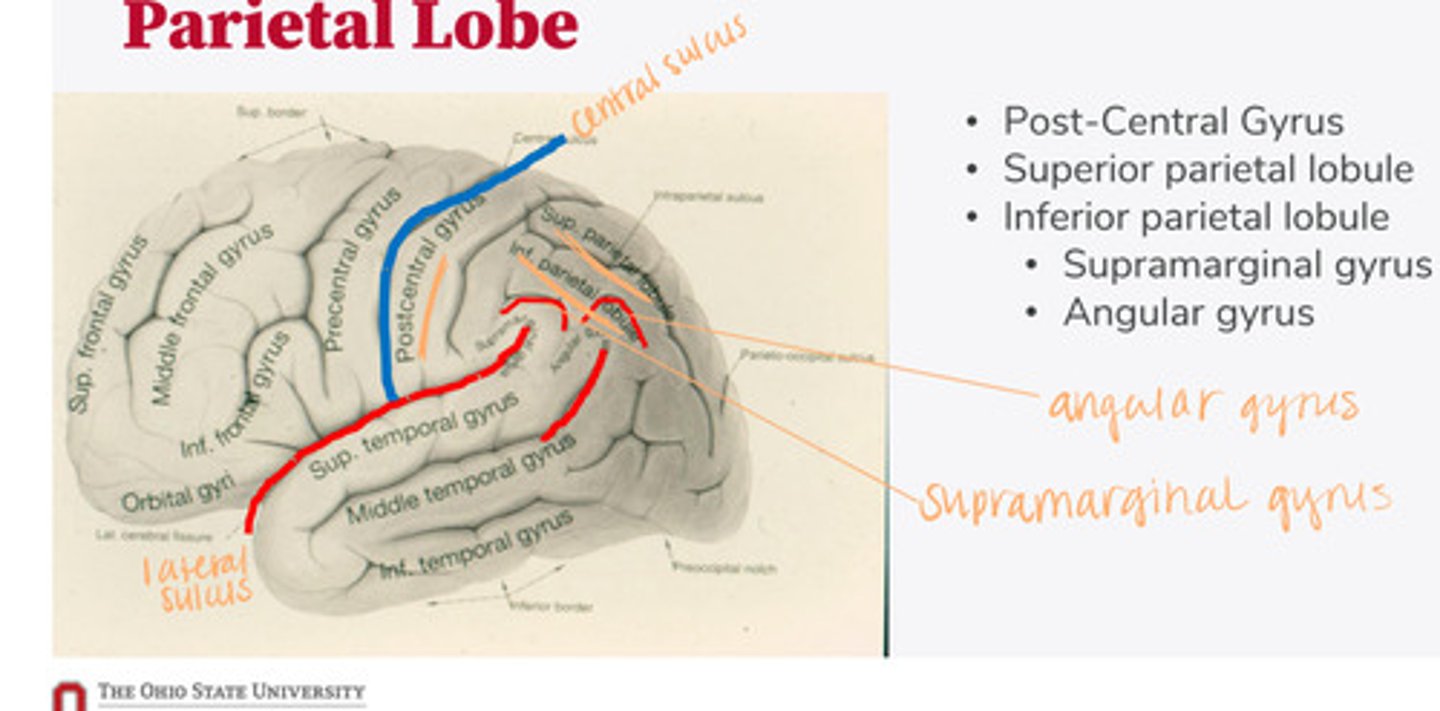
What are the divisions of the parietal lobe?
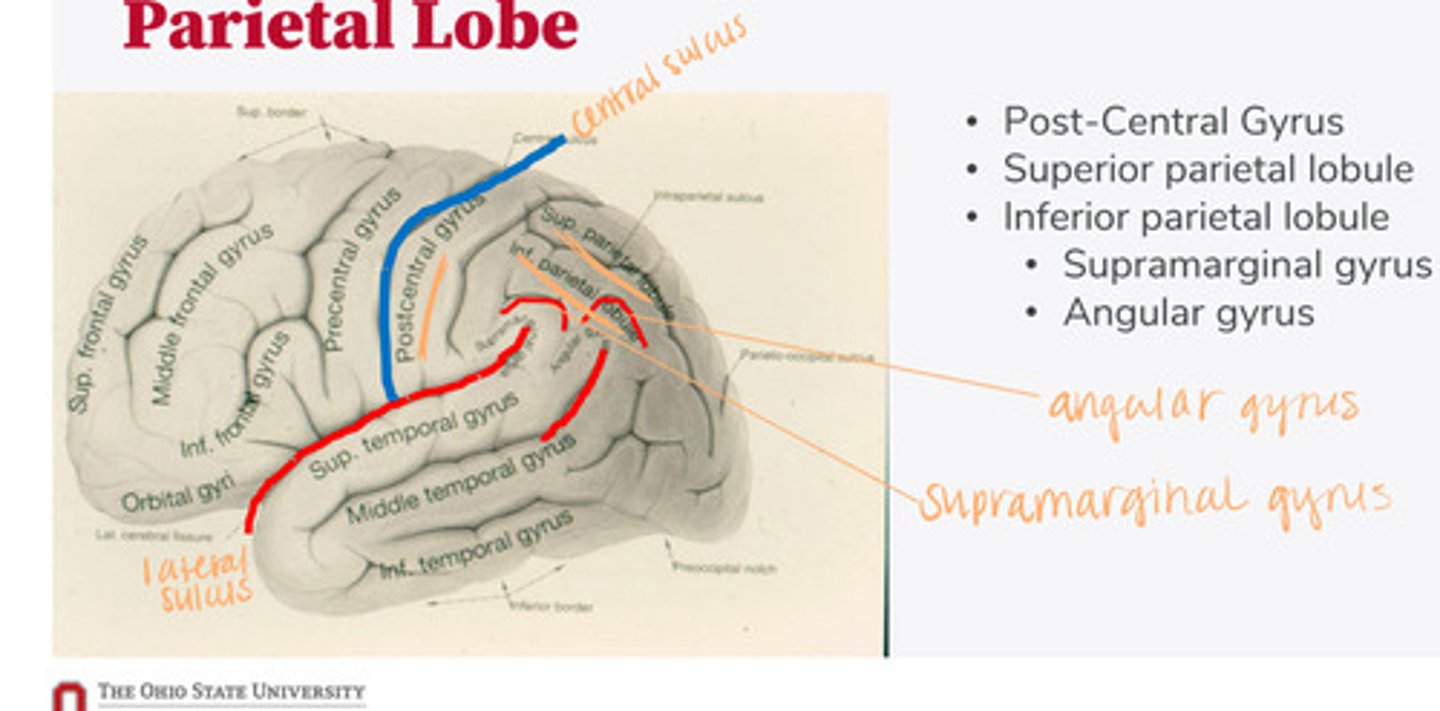
-supramarginal gyrus
-angular gyrus
What are the divisions of the inferior parietal lobule?
processing location and distance of vision
What is the primary sensory Cortex important for?

-superior temporal
-inferior temporal
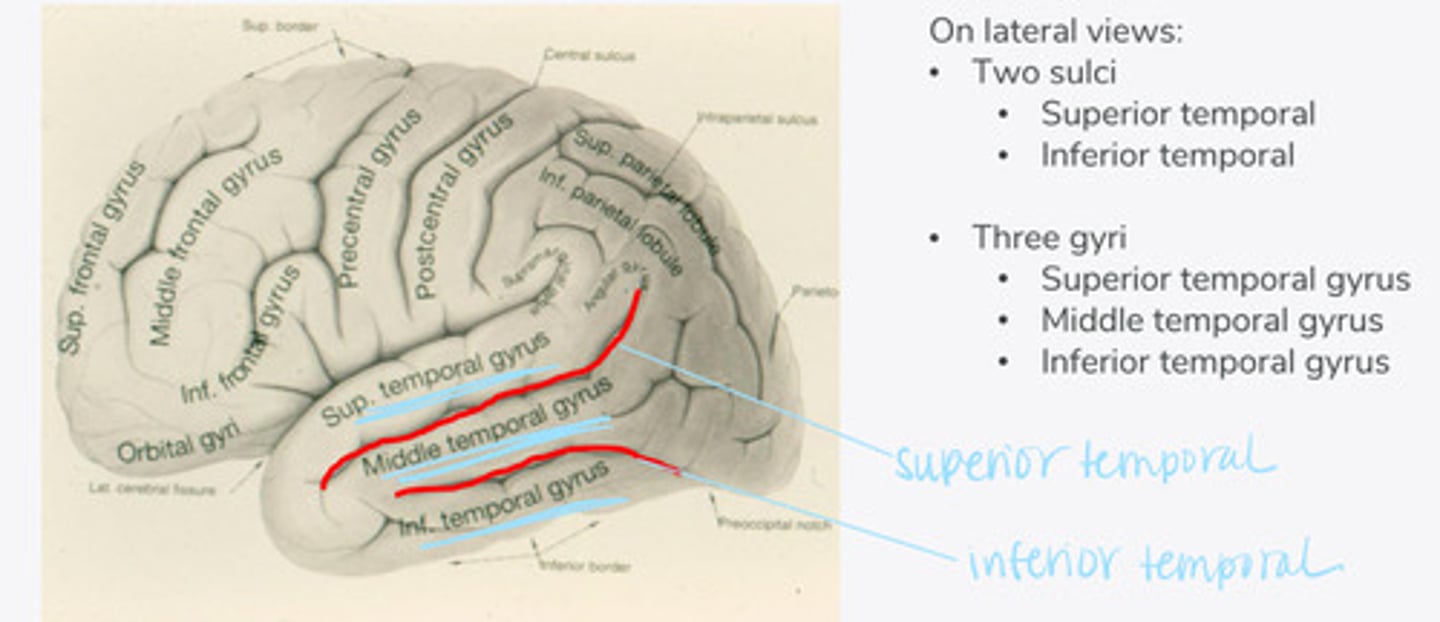
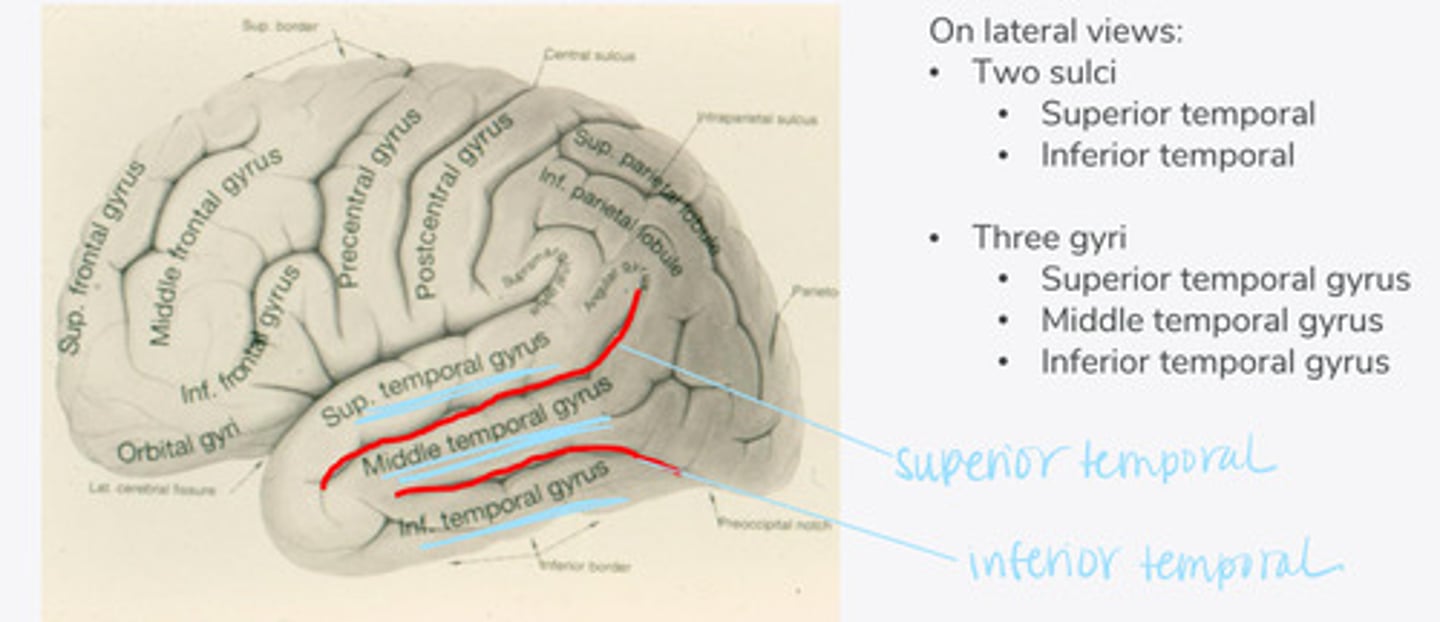
What are the 2 major sulci of the temporal lobe (on lateral view)?
-superior temporal
-middle temporal
-inferior temporal
What are the 3 major gyri of the temporal lobe (on lateral view)?
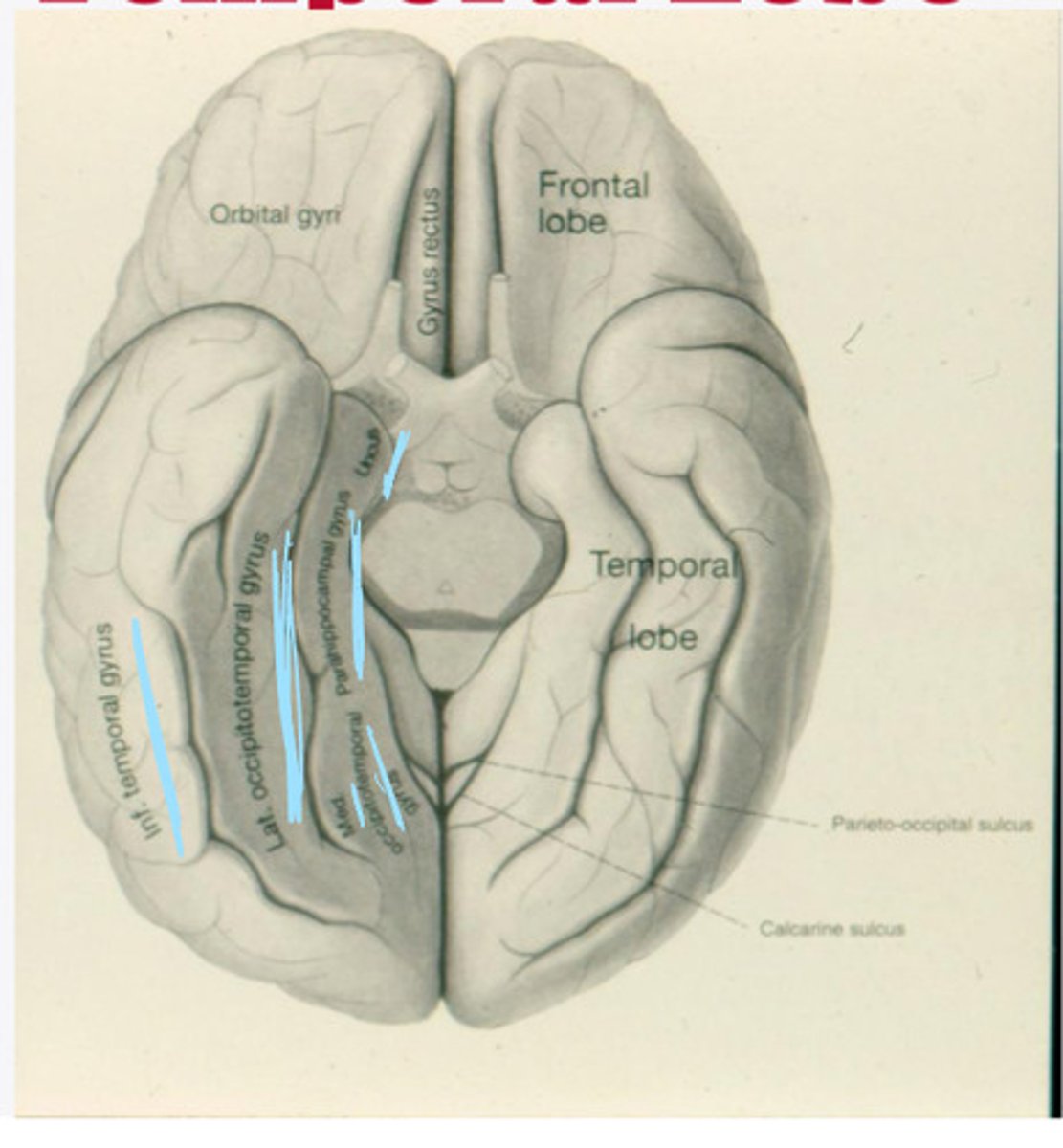
-inferior temporal
-lateral occipitotemporal
-medial occipitotemporal
-parahippocampal
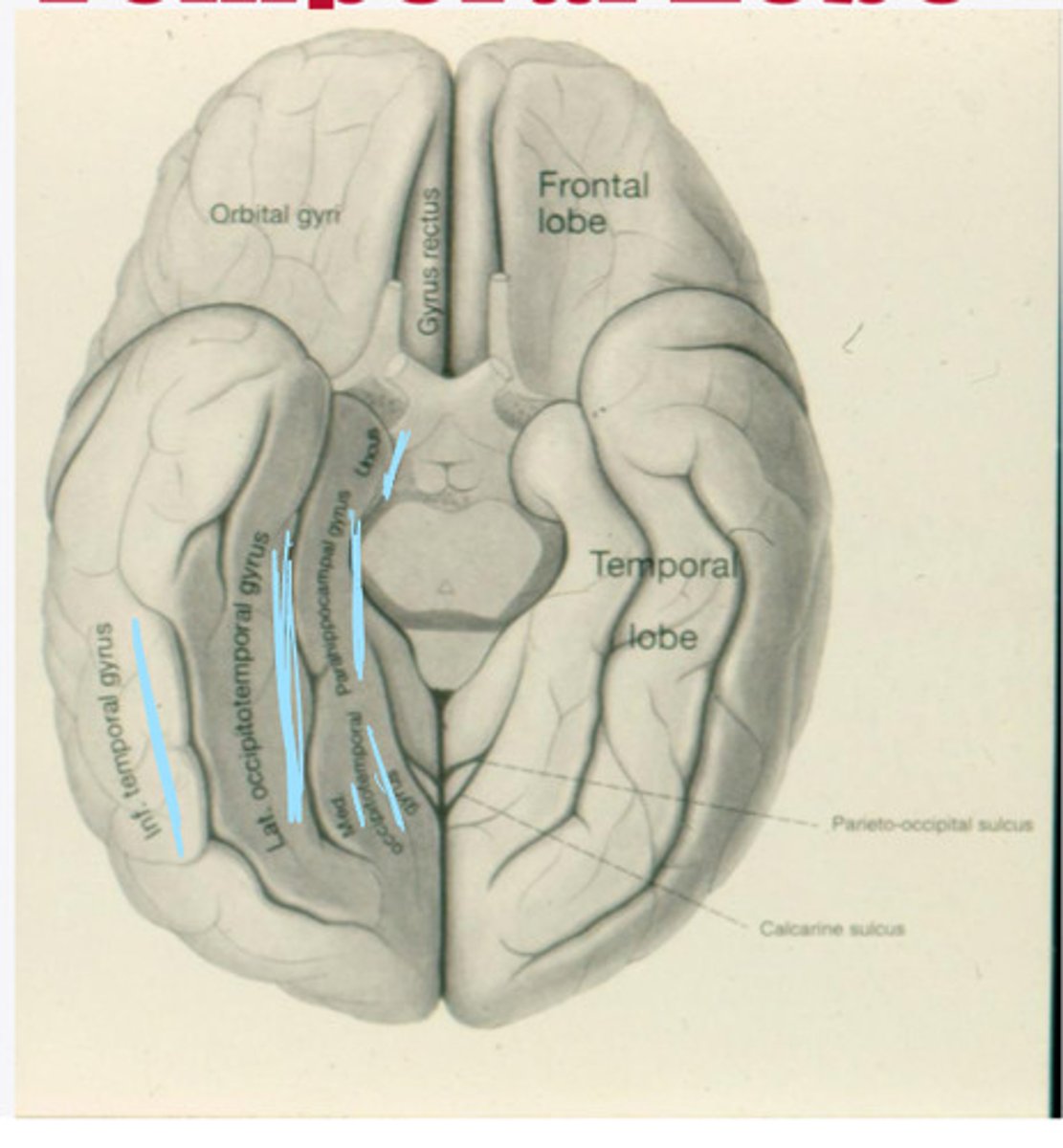
What are the 4 major gyri of the temporal lobe (from an inferior view)?
uncus -- goes to the hippocampus
What is an important structure/gyri connected to the parahippocampal gyrus?
-involved heavily in language and hearing
-imporant in visual identification
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
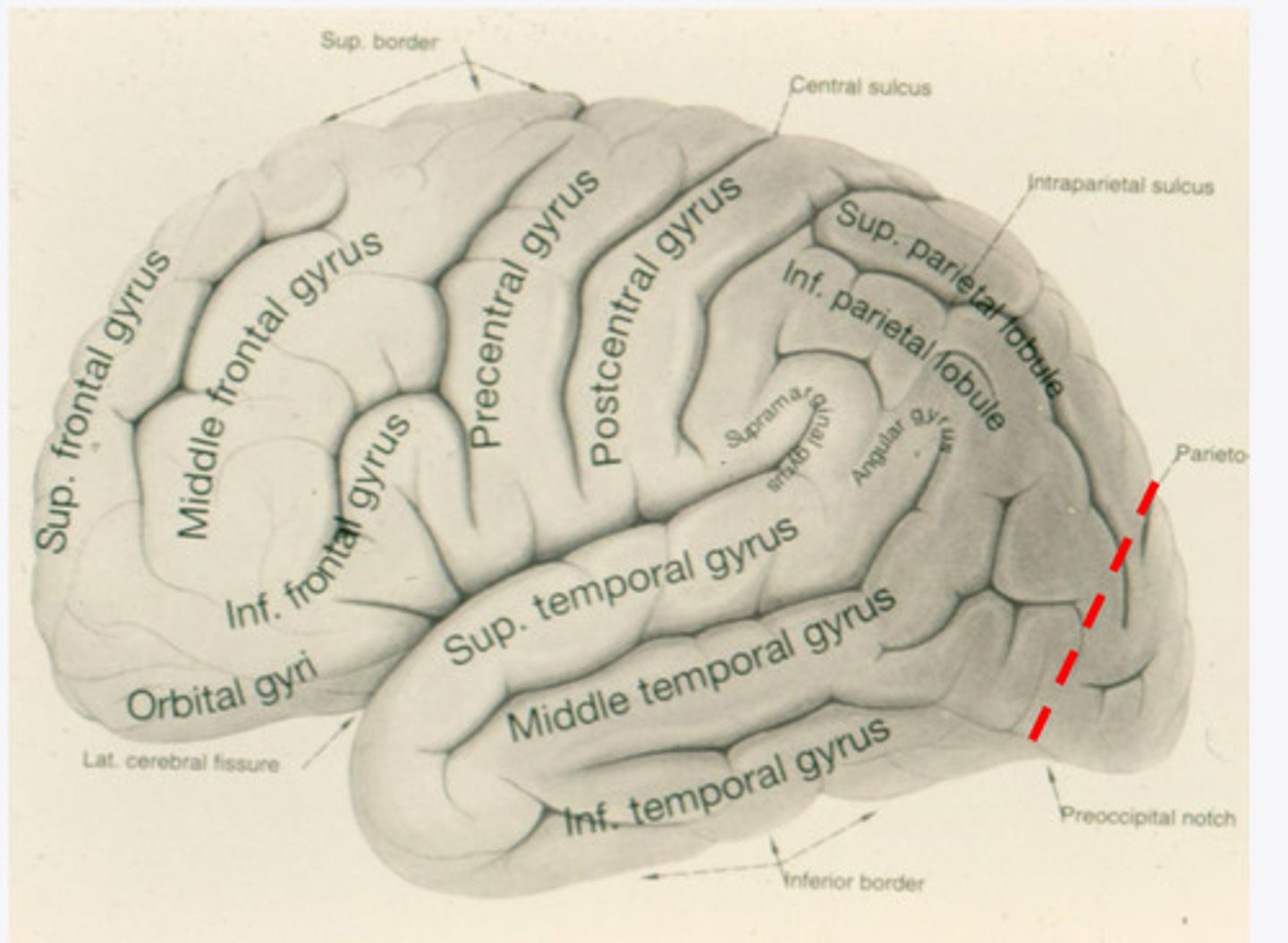
everything posterior to the line connecting the parietooccipital sulcus and the preoccipital notch
Where is the occipital lobe located in a lateral view of the brain?
posterior to the parietooccipital sulcus
Where is the occipital lobe located in a medial/mid-saggital view of the brain?
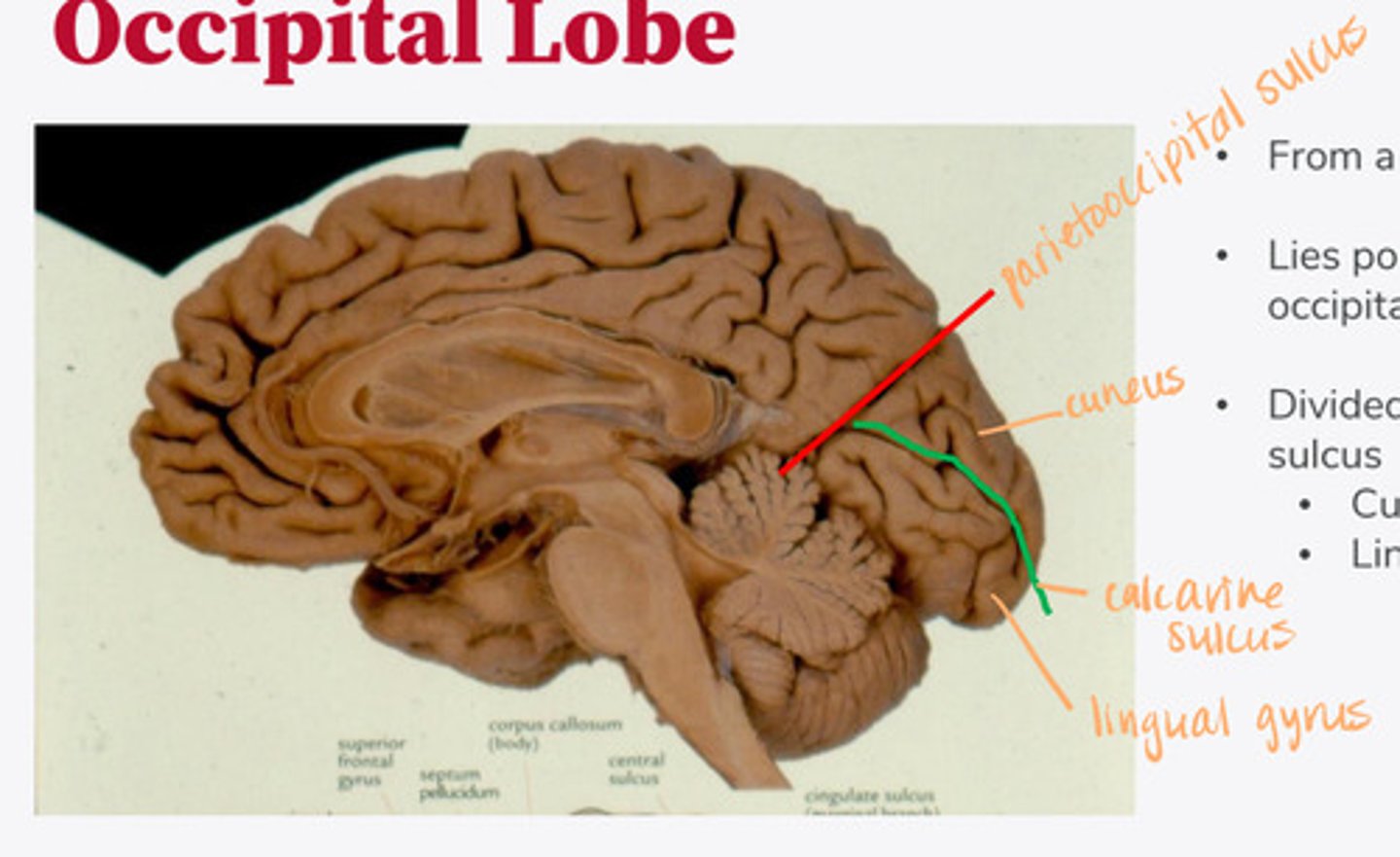
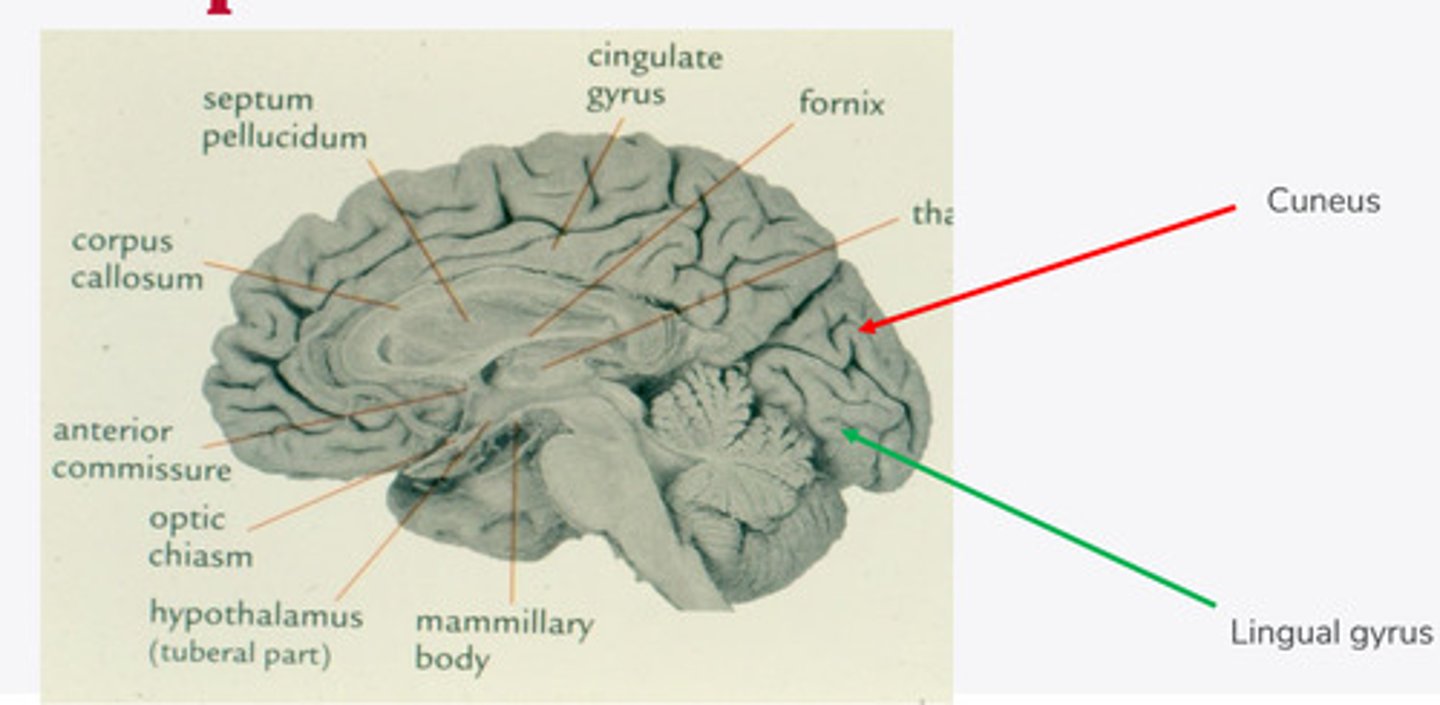
-divided in half by the calcarine sulcus
Cuneus = above
Lingual gyrus = below
In the midsaggital view, the occipital lobe is divided in half by what? What 2 lobes does it divide into?
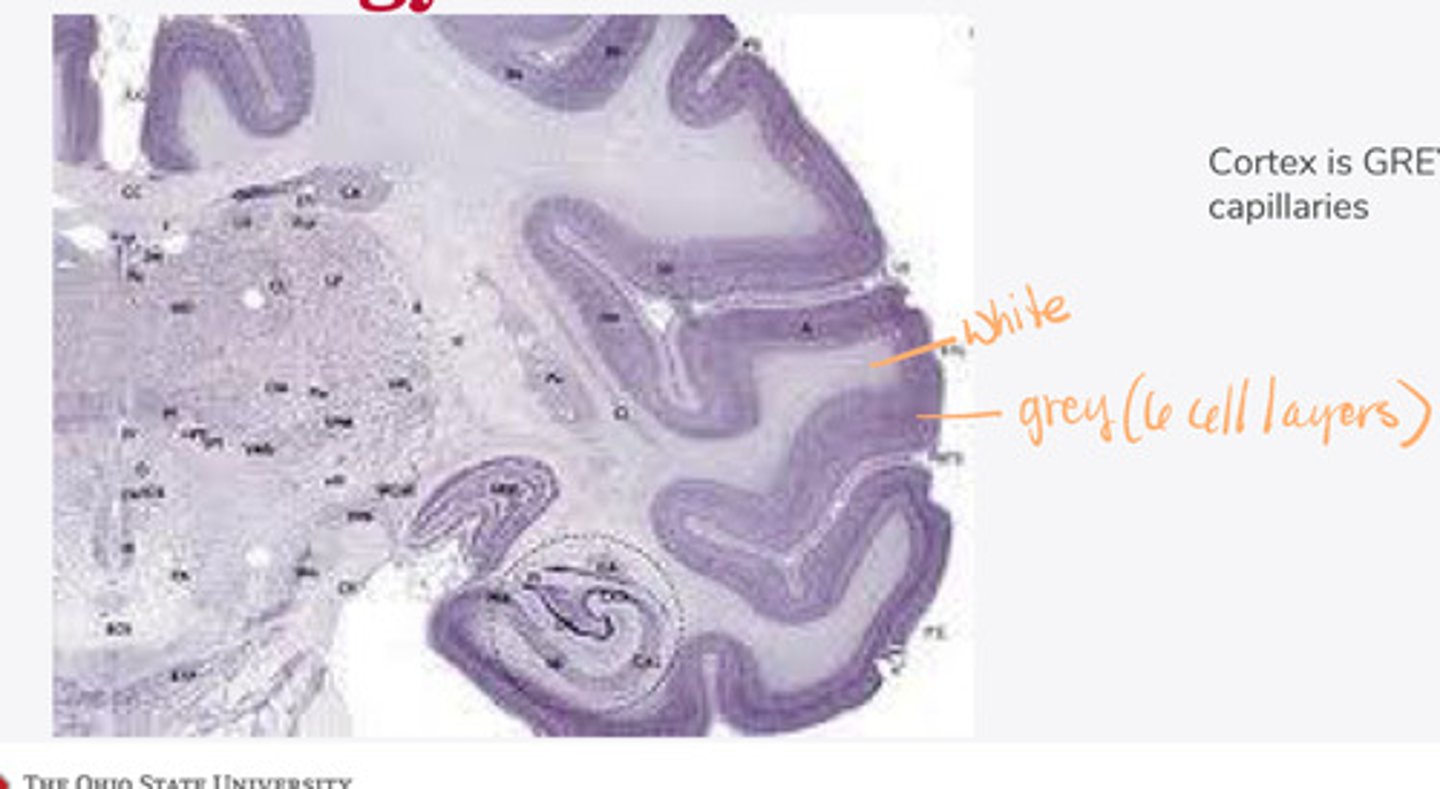
grey
Cortex of the brain is ______ matter with capillaries
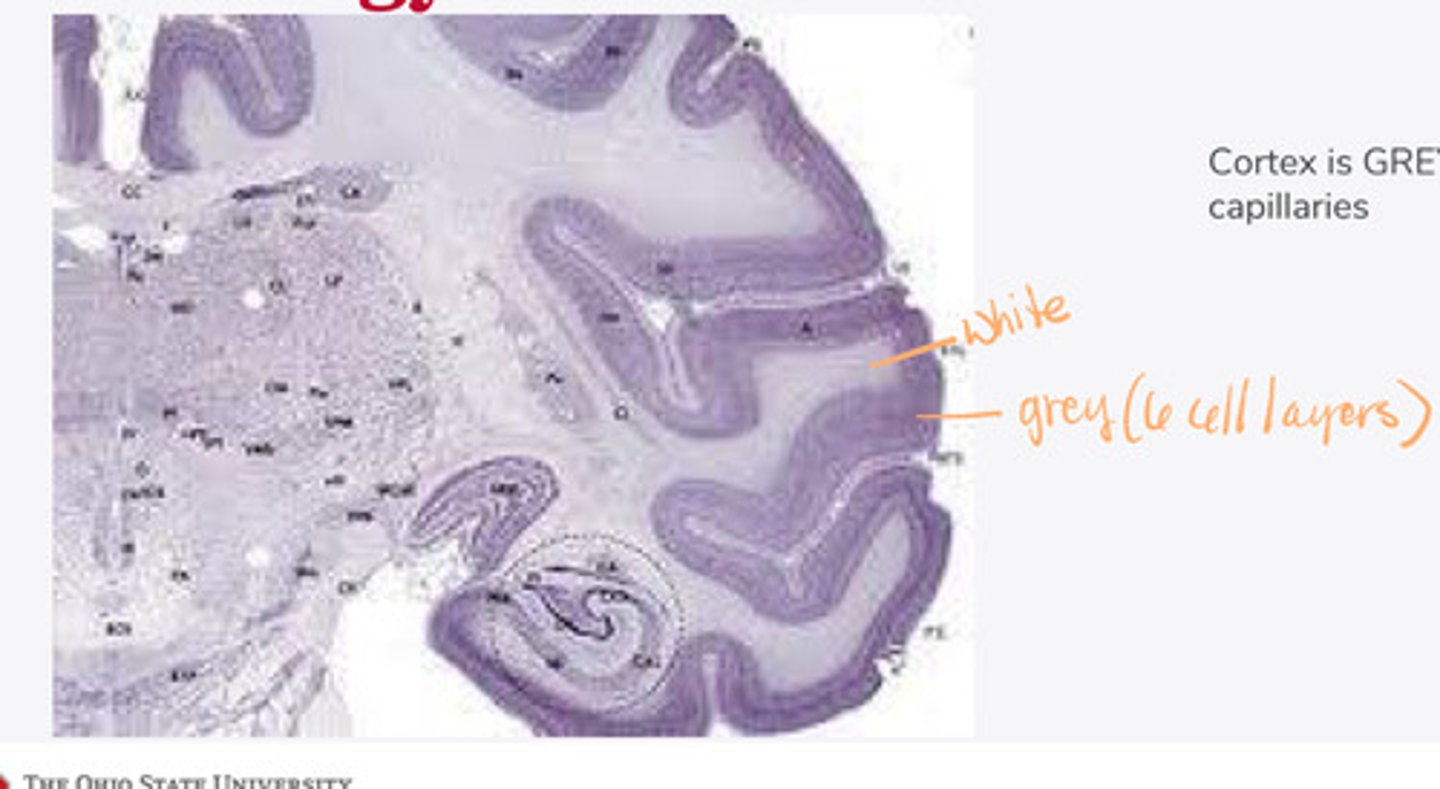
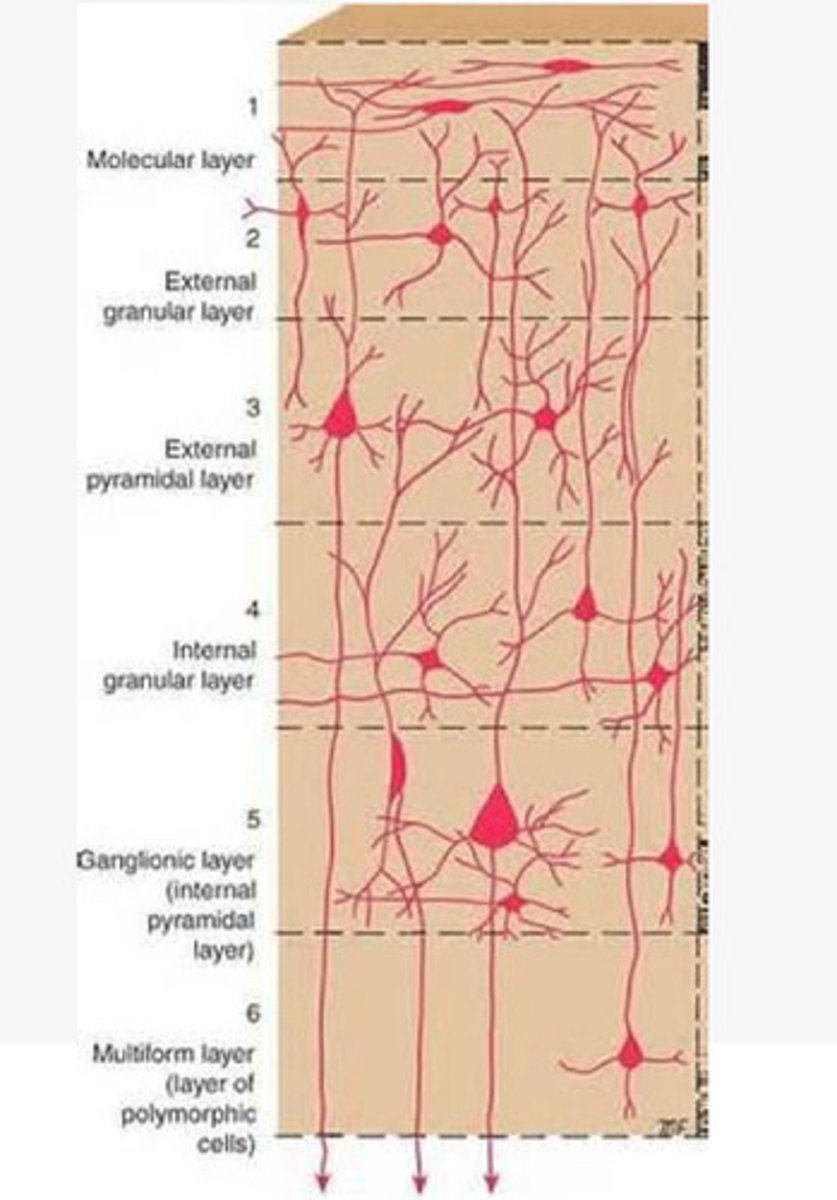
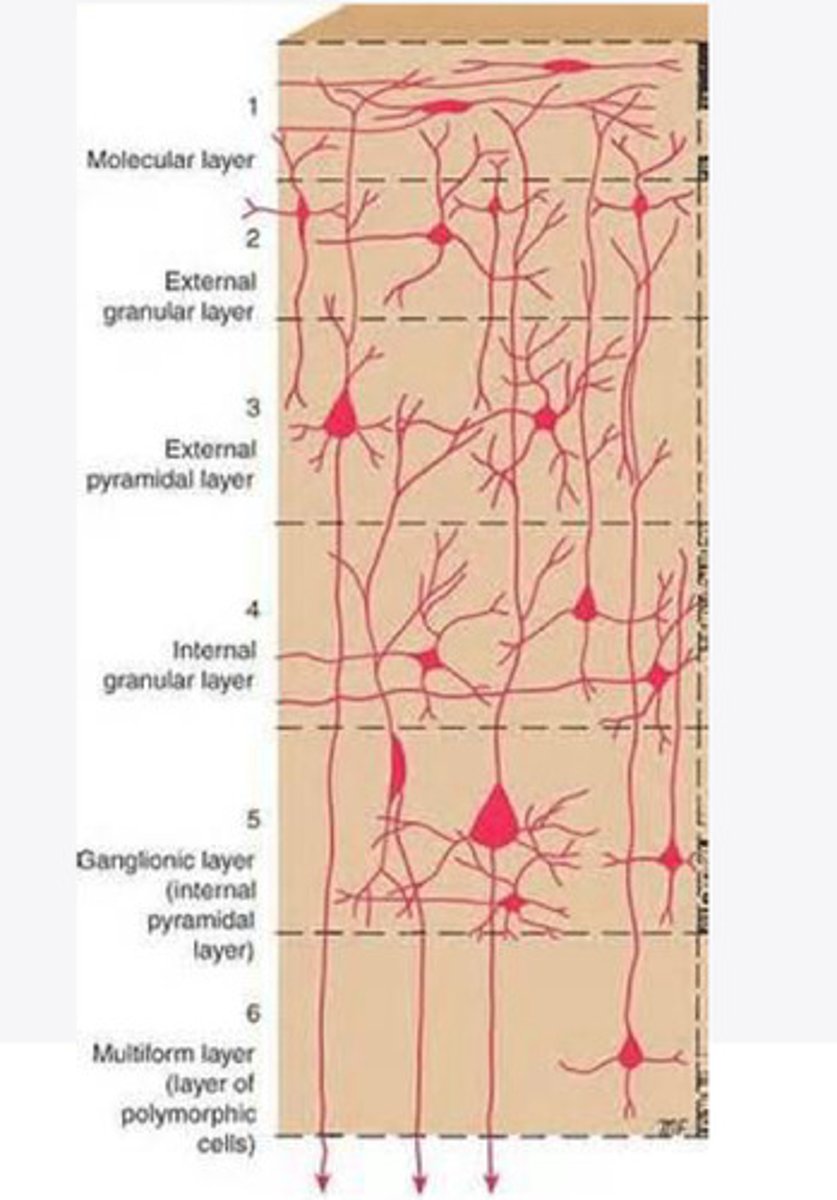
divided into 6 distinct layers, due to varying densities of cell body types within each layer
The cortex of the brain is divided into how many layers? Why is it divided into layers?
stellate, pyramidal
What are the 2 primary cell types in the cortex of the brain?
white
______ matter lies internal to the grey matter of the cortex of the brain
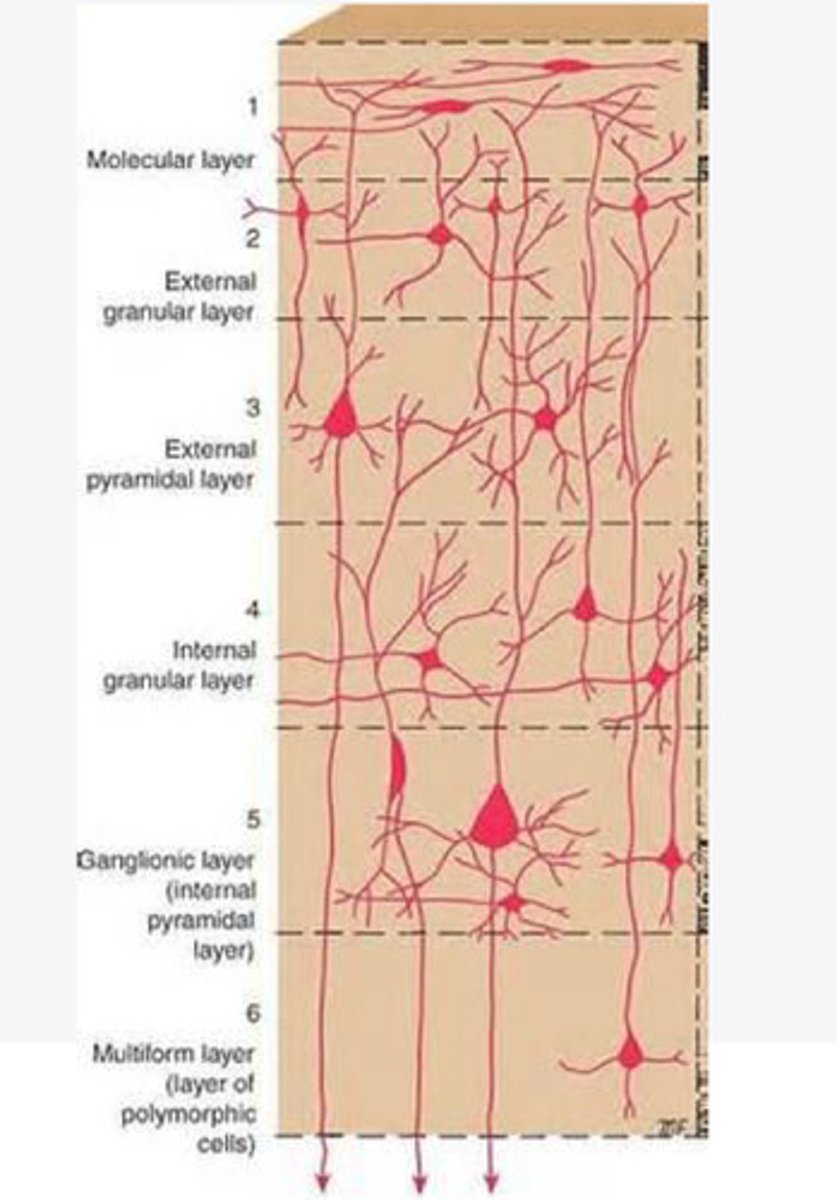
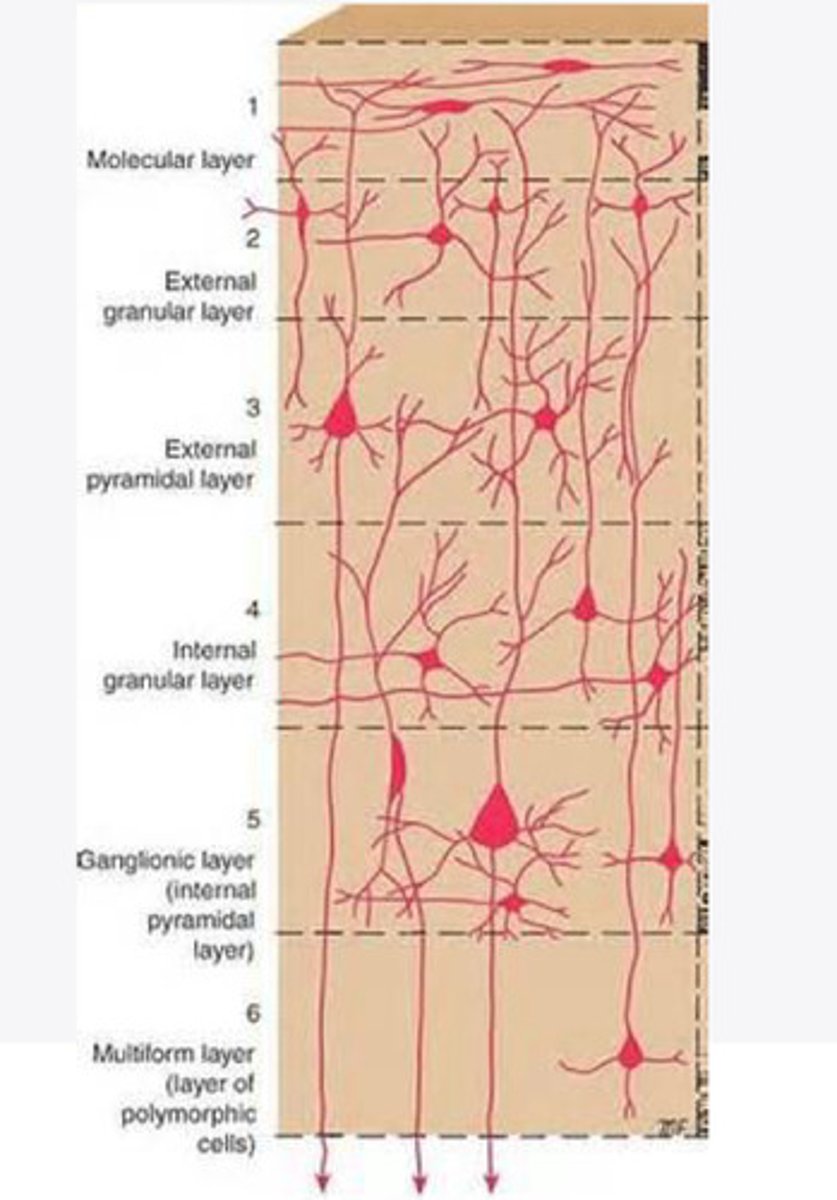
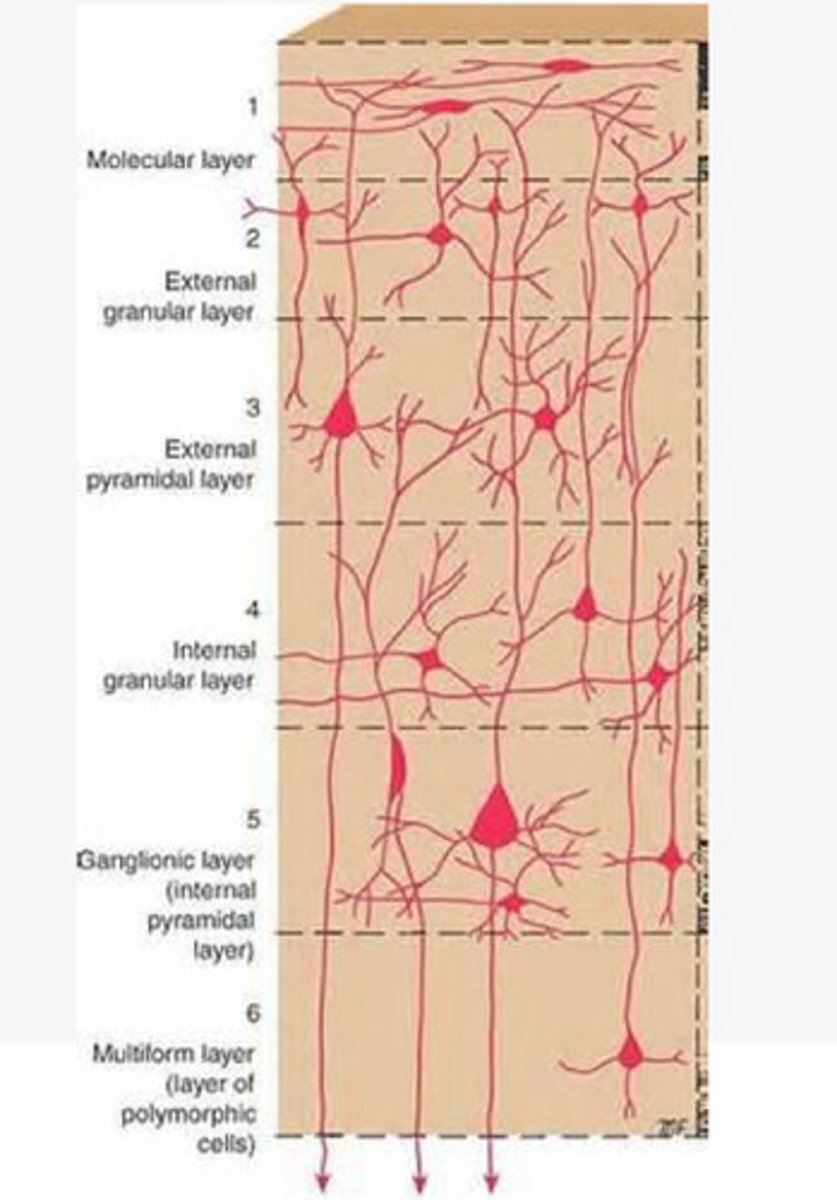
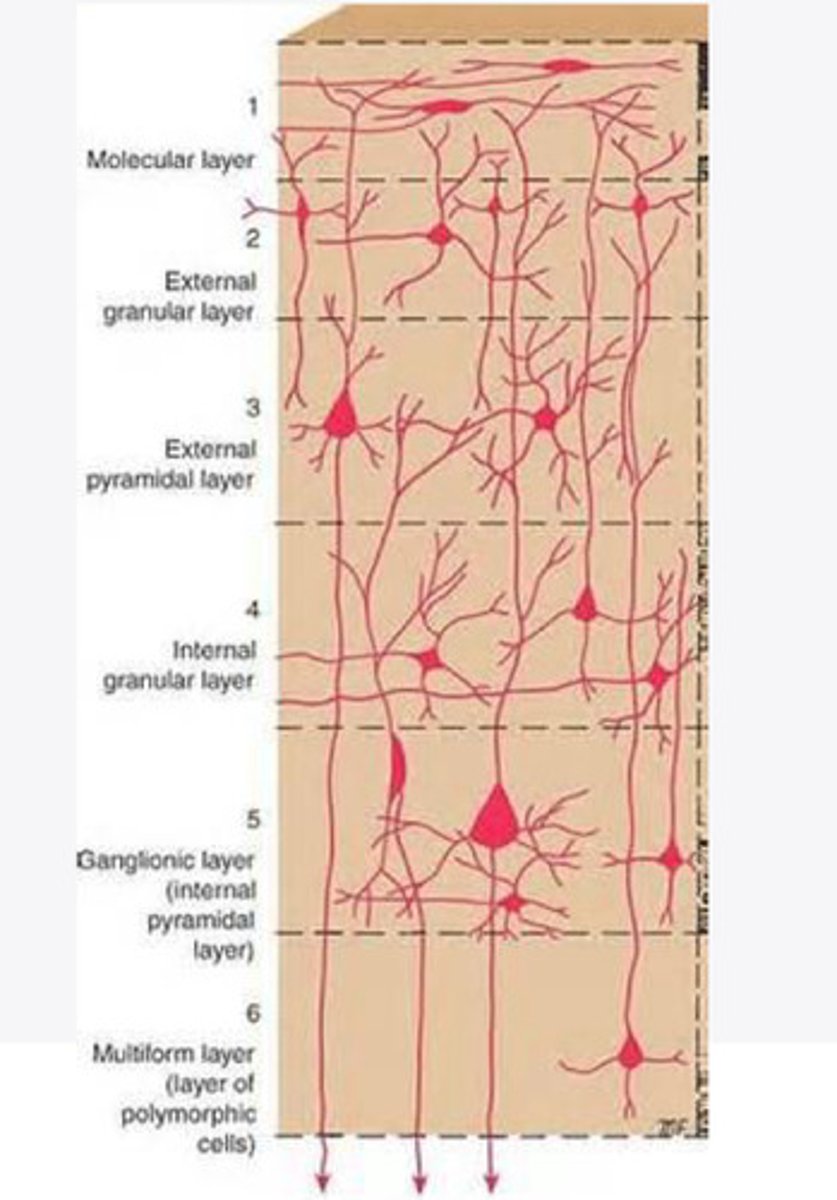
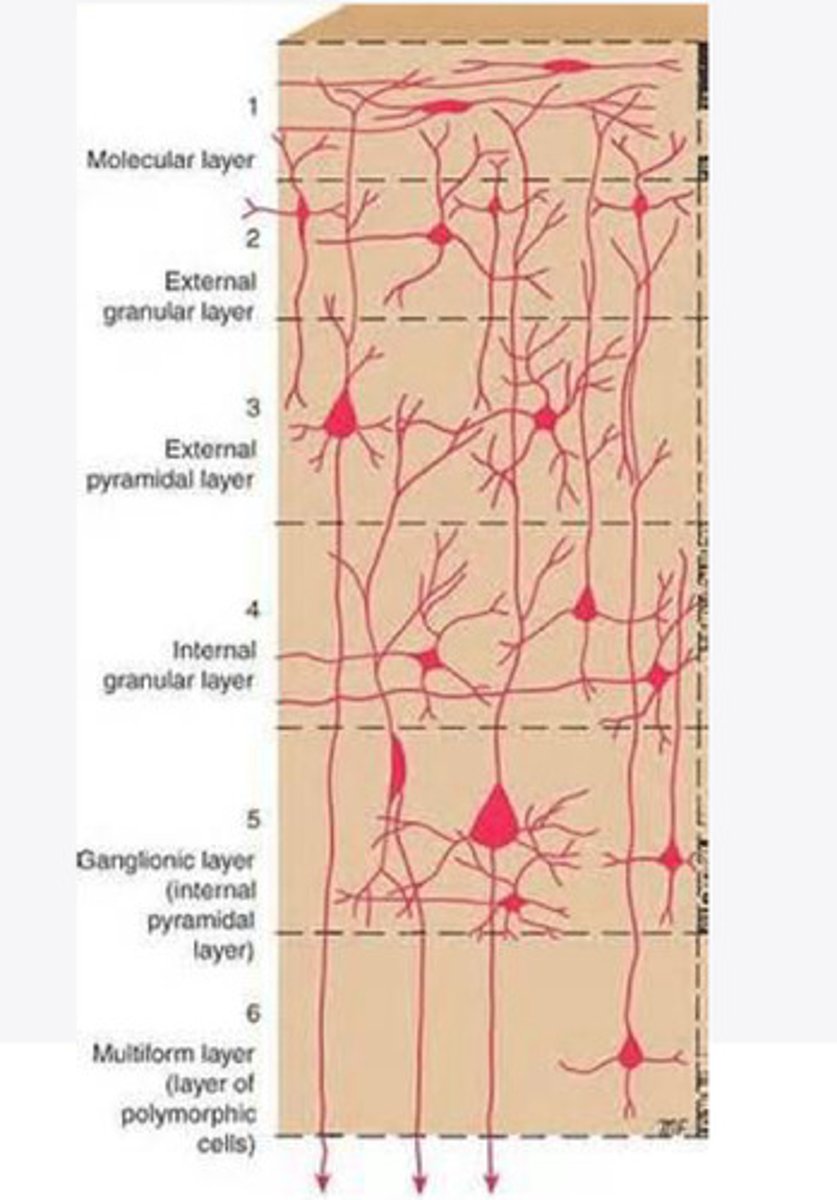
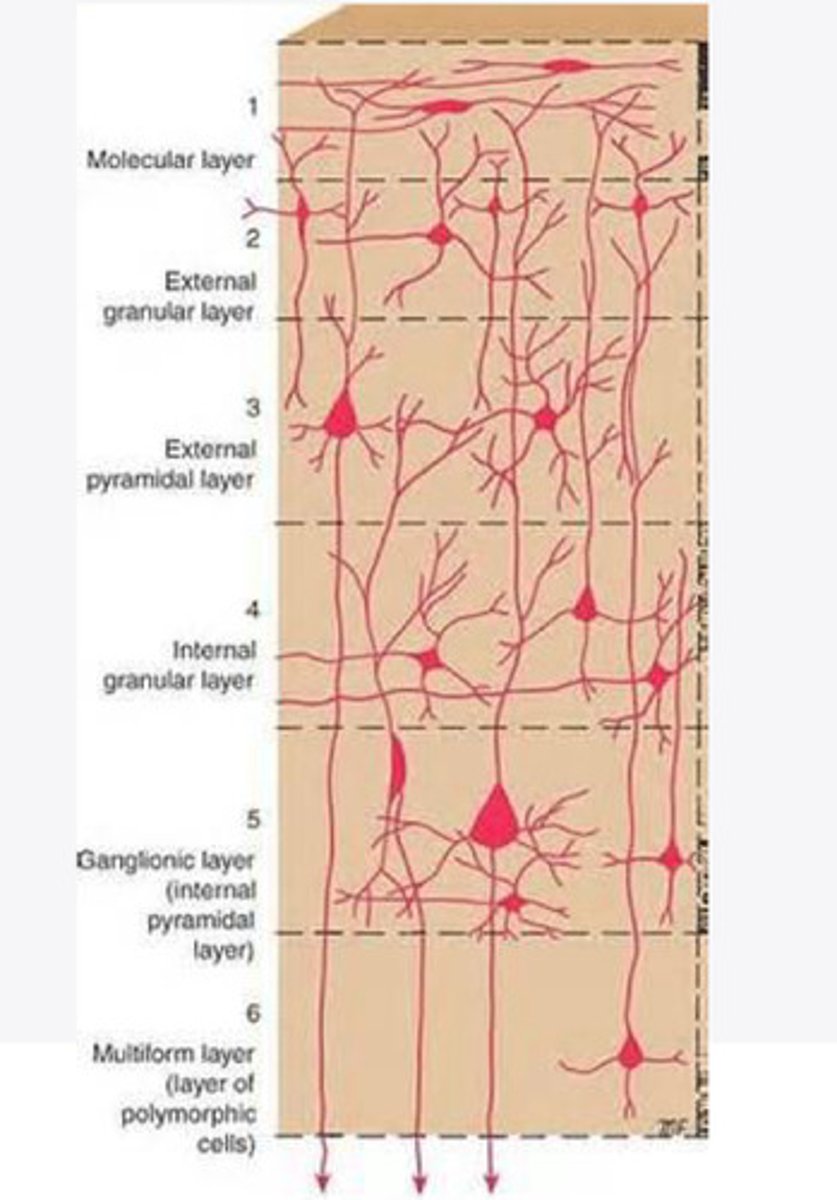
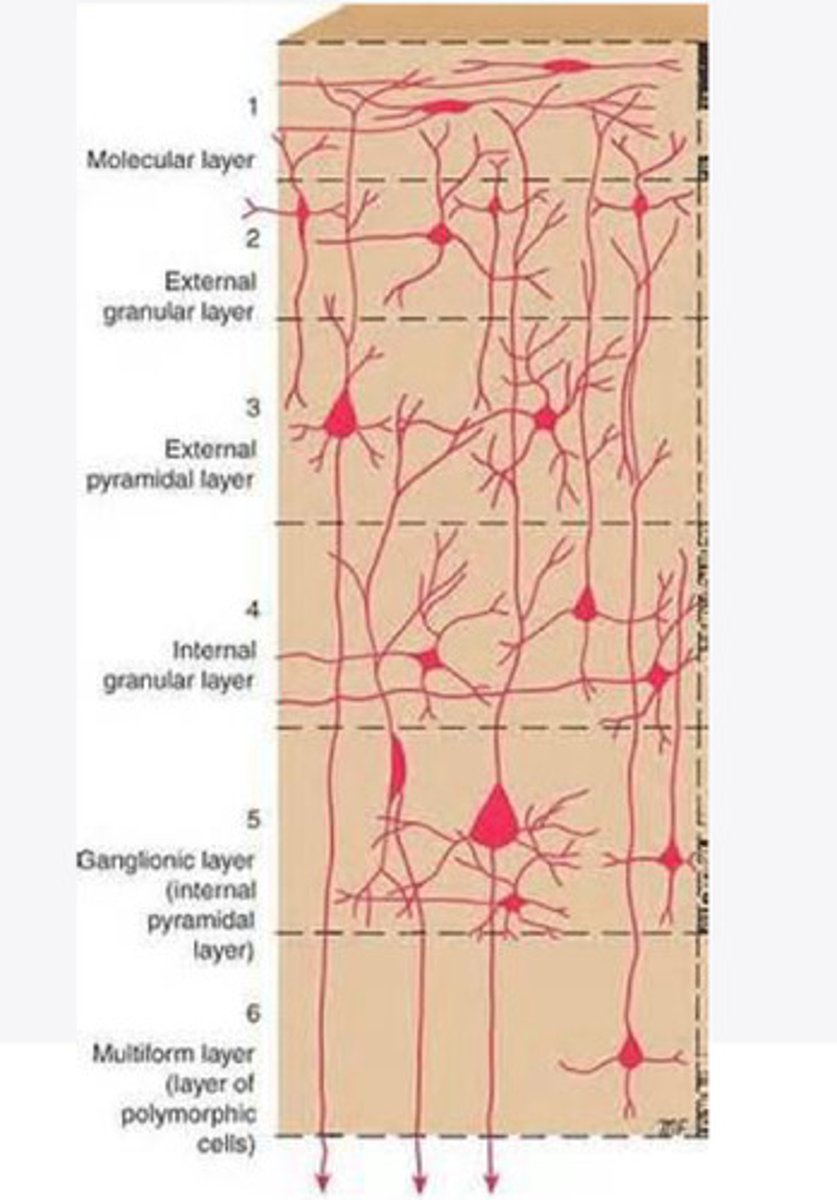
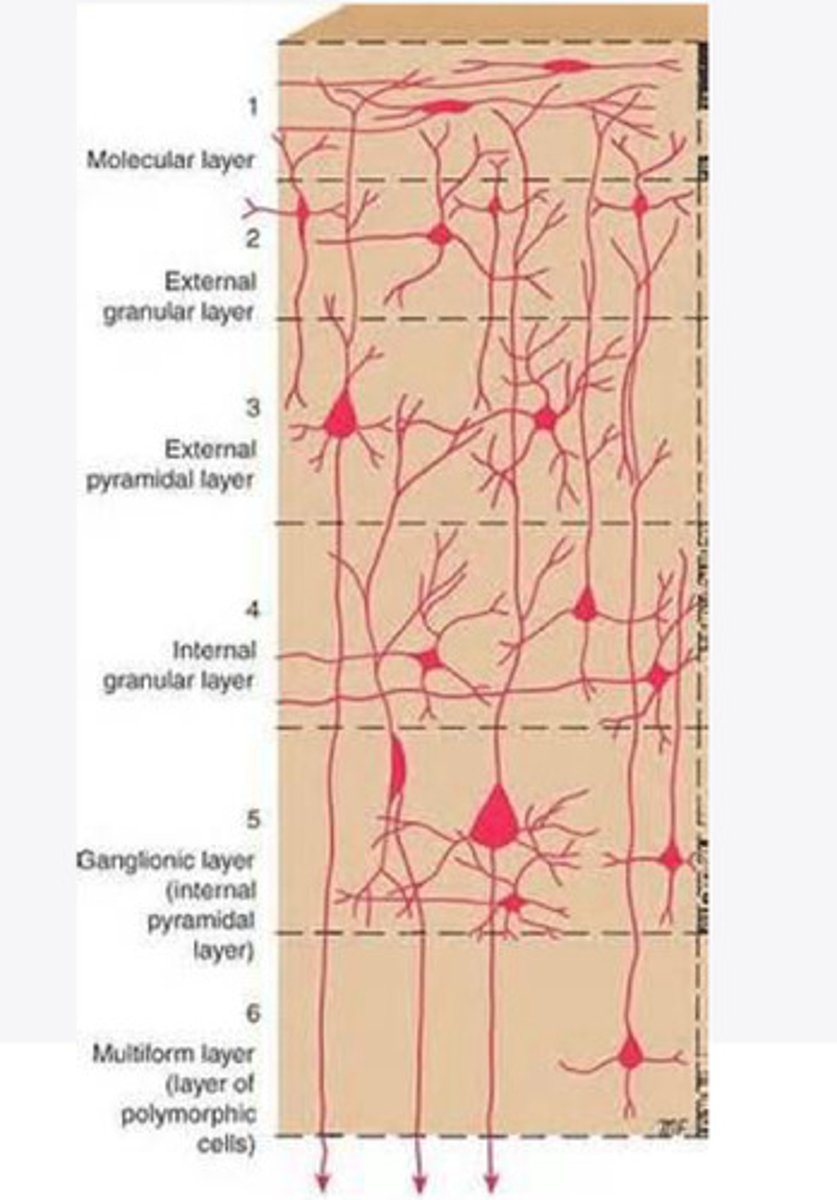
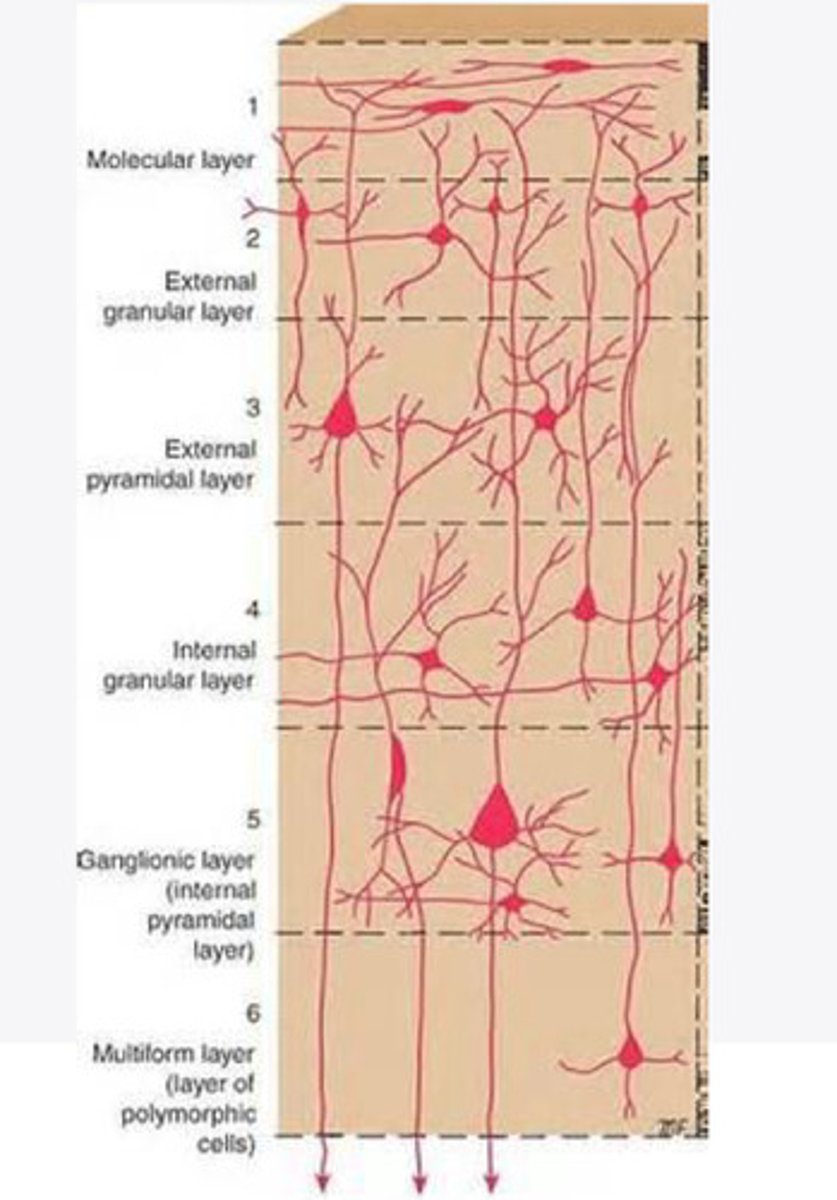
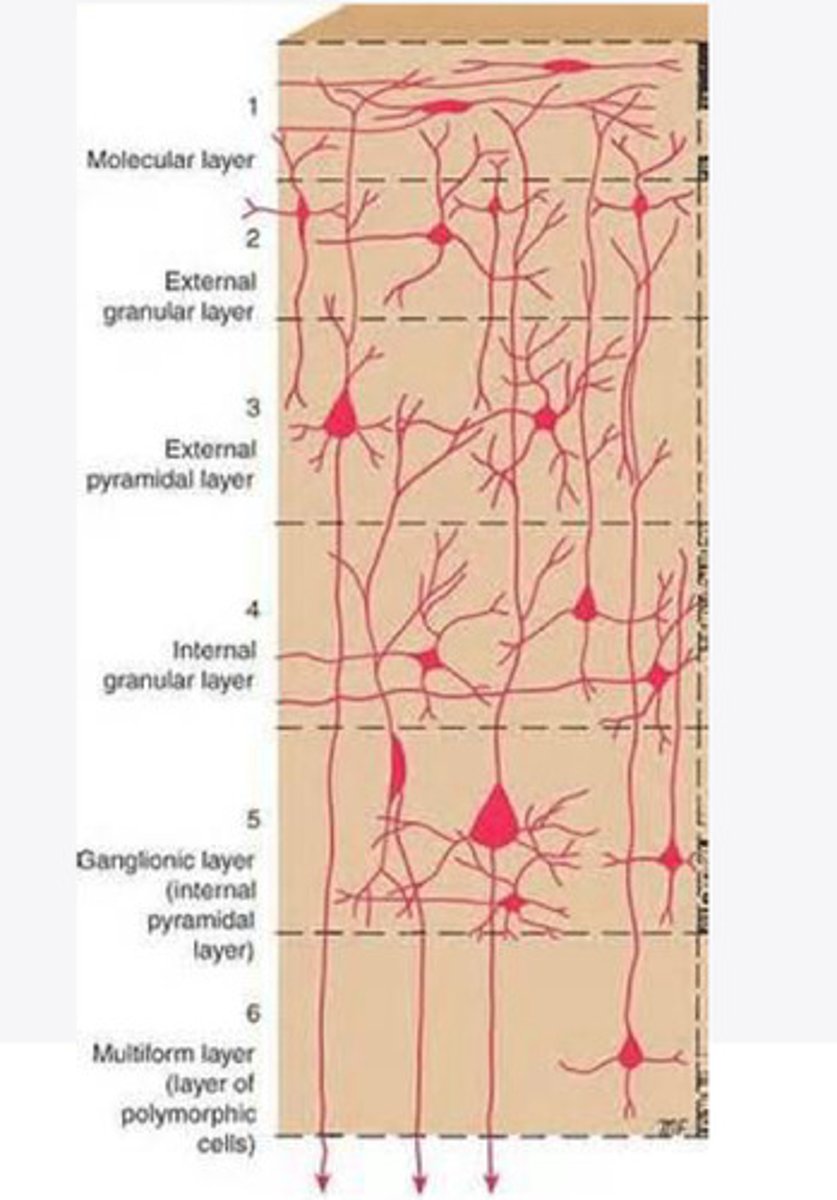
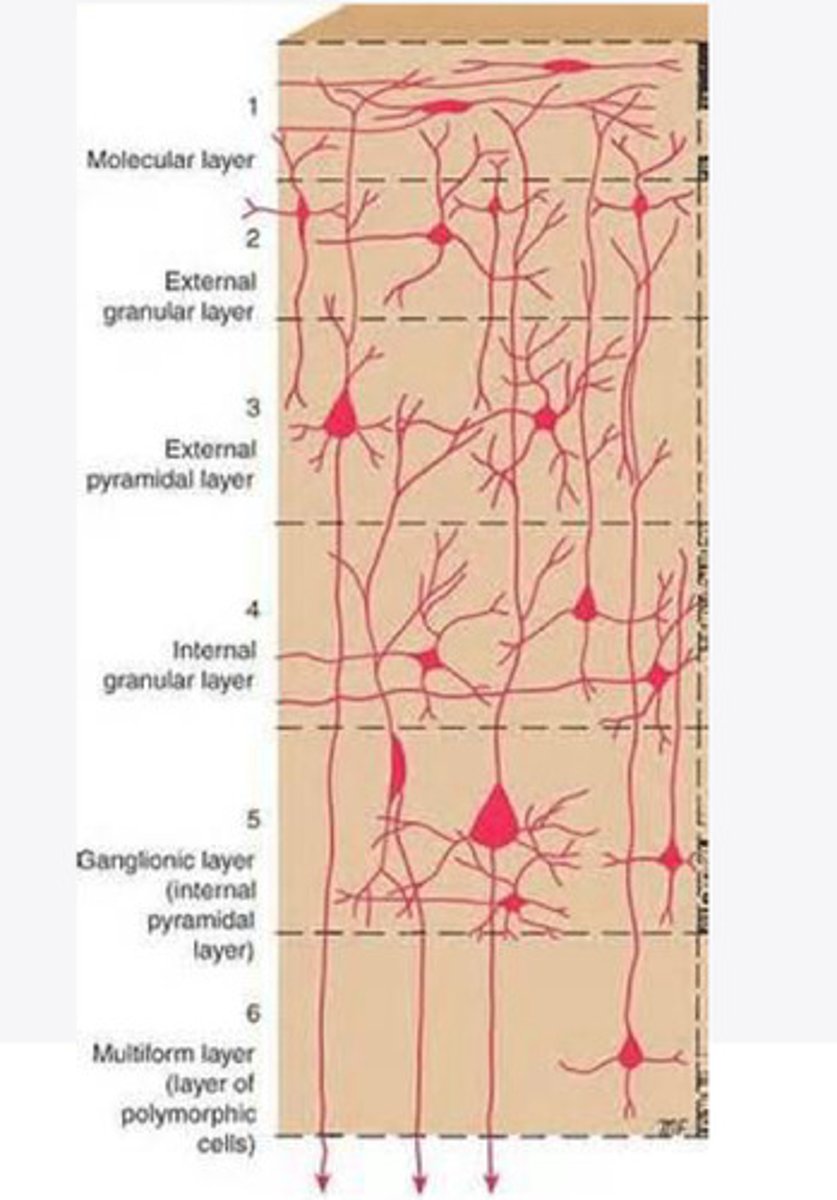
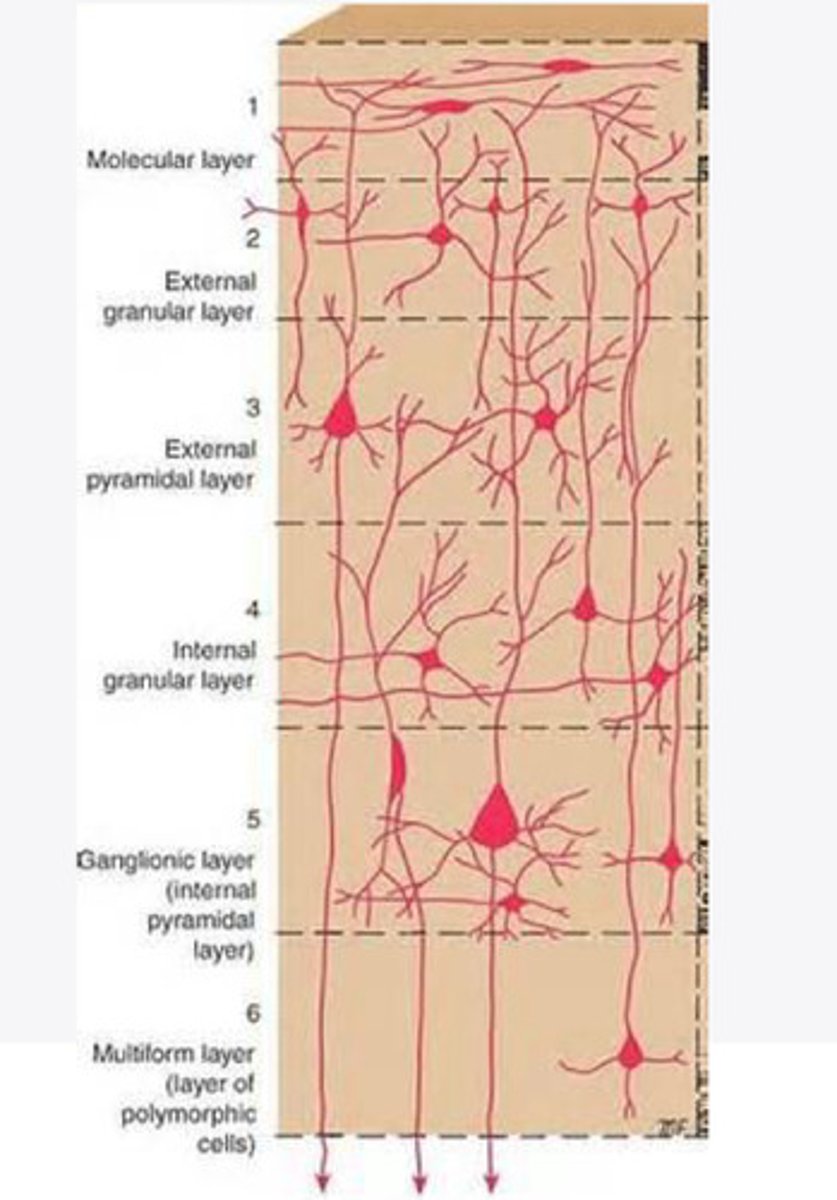
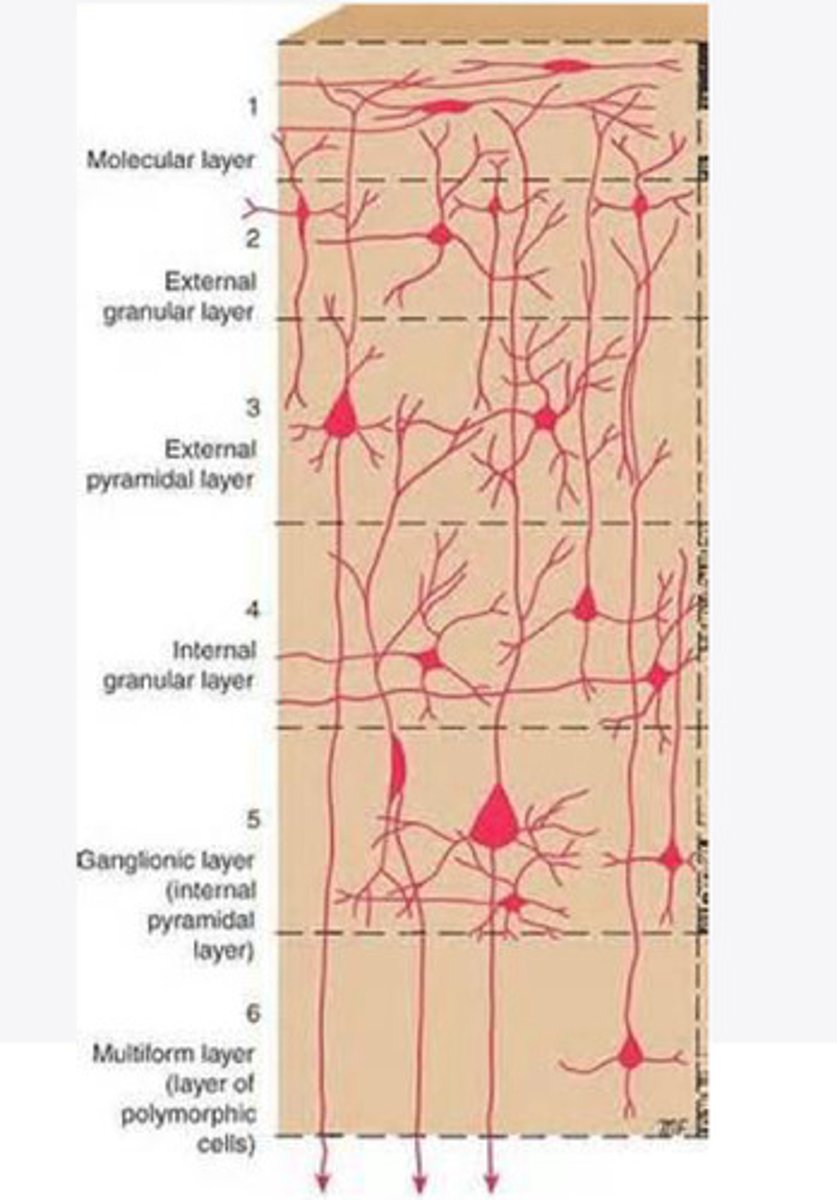
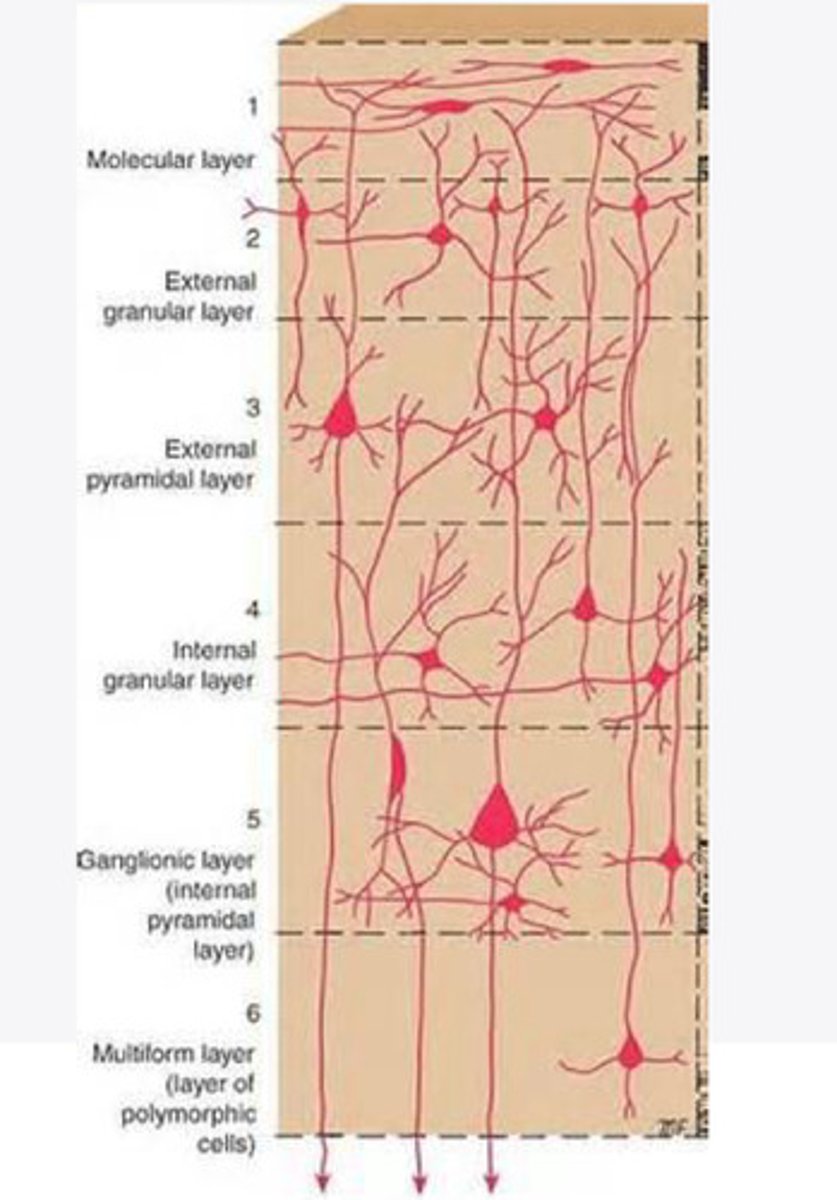
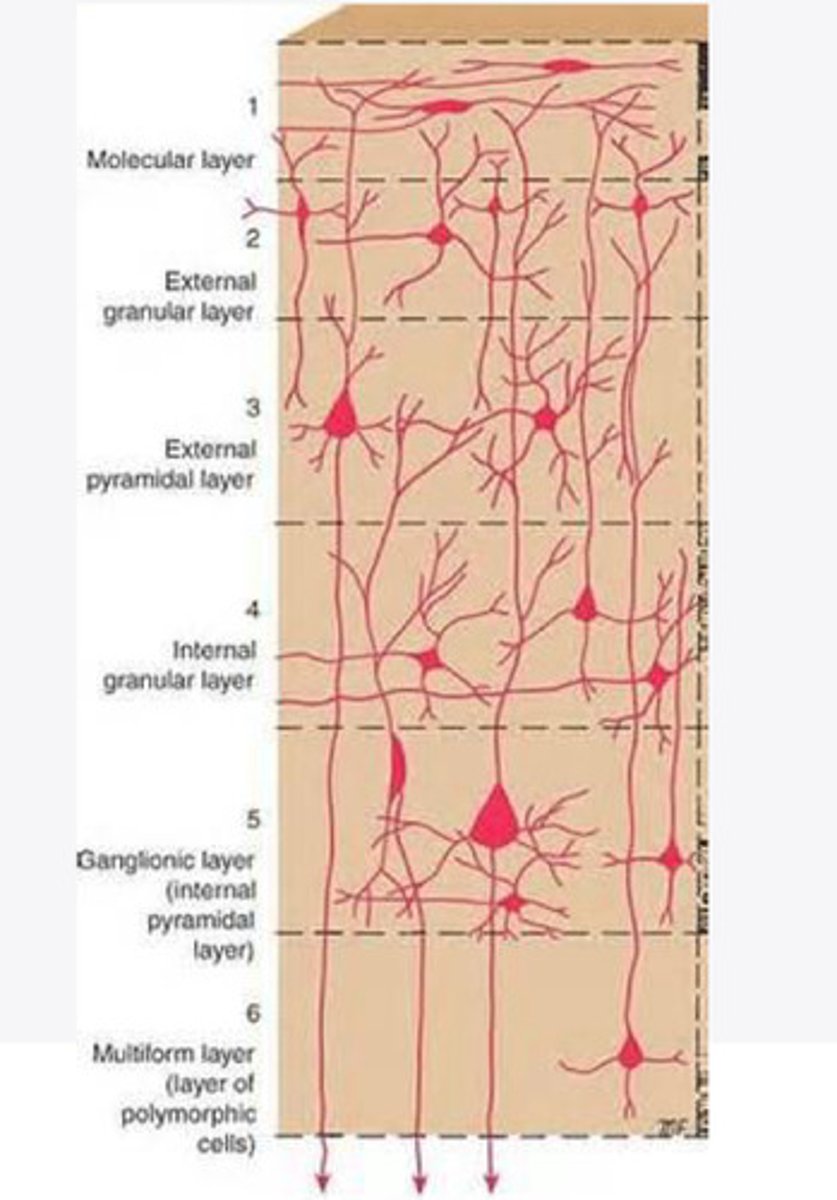
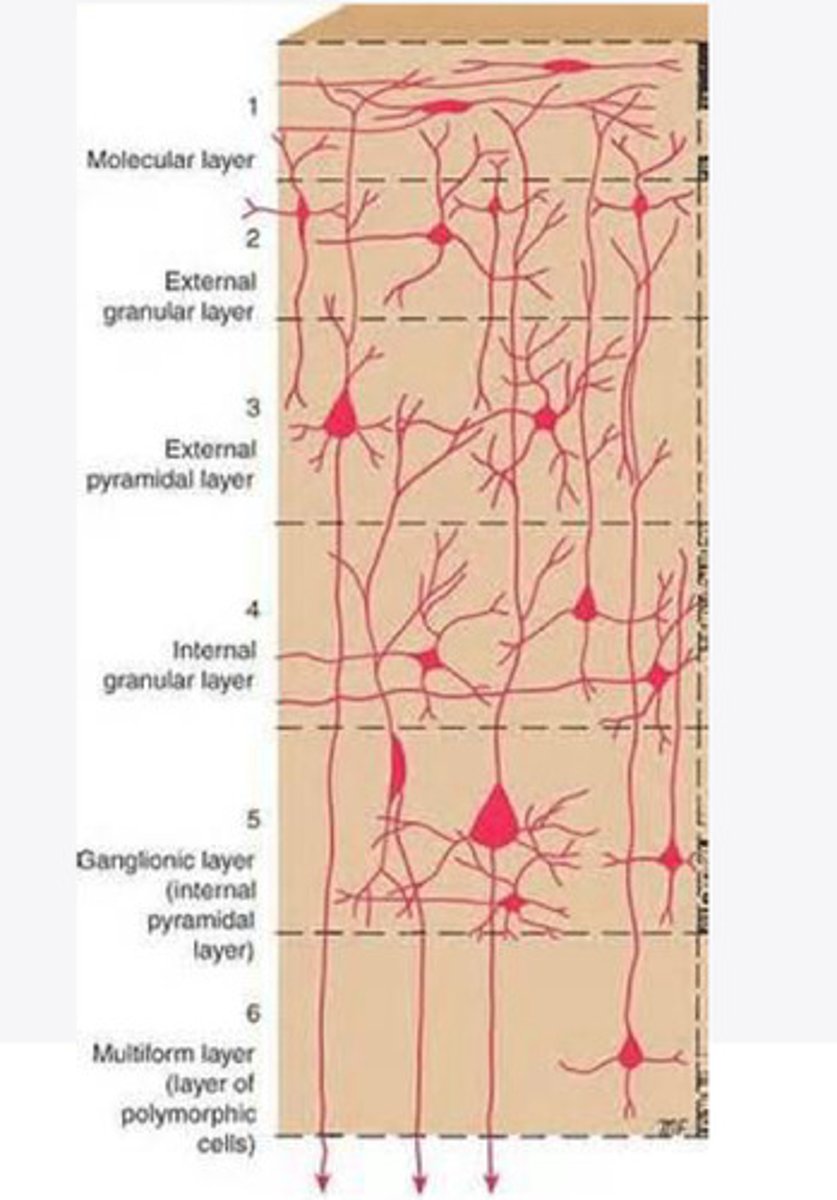
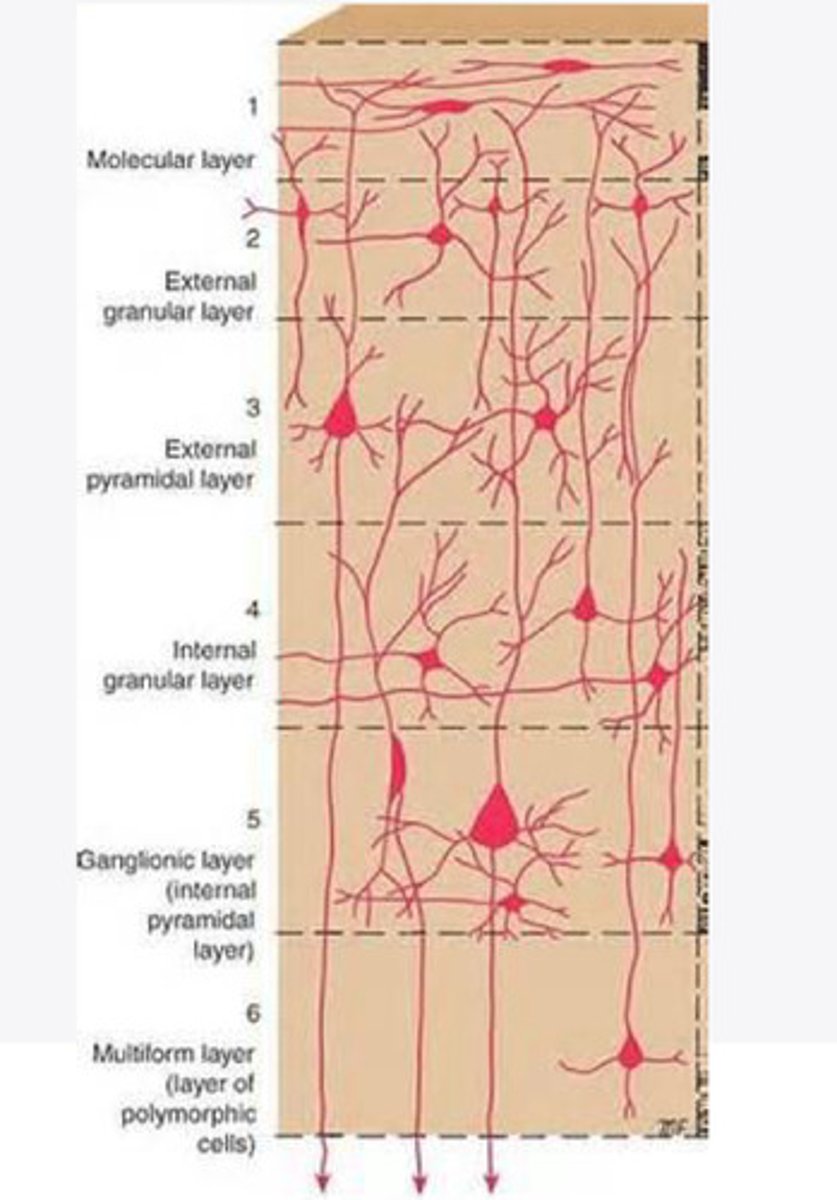
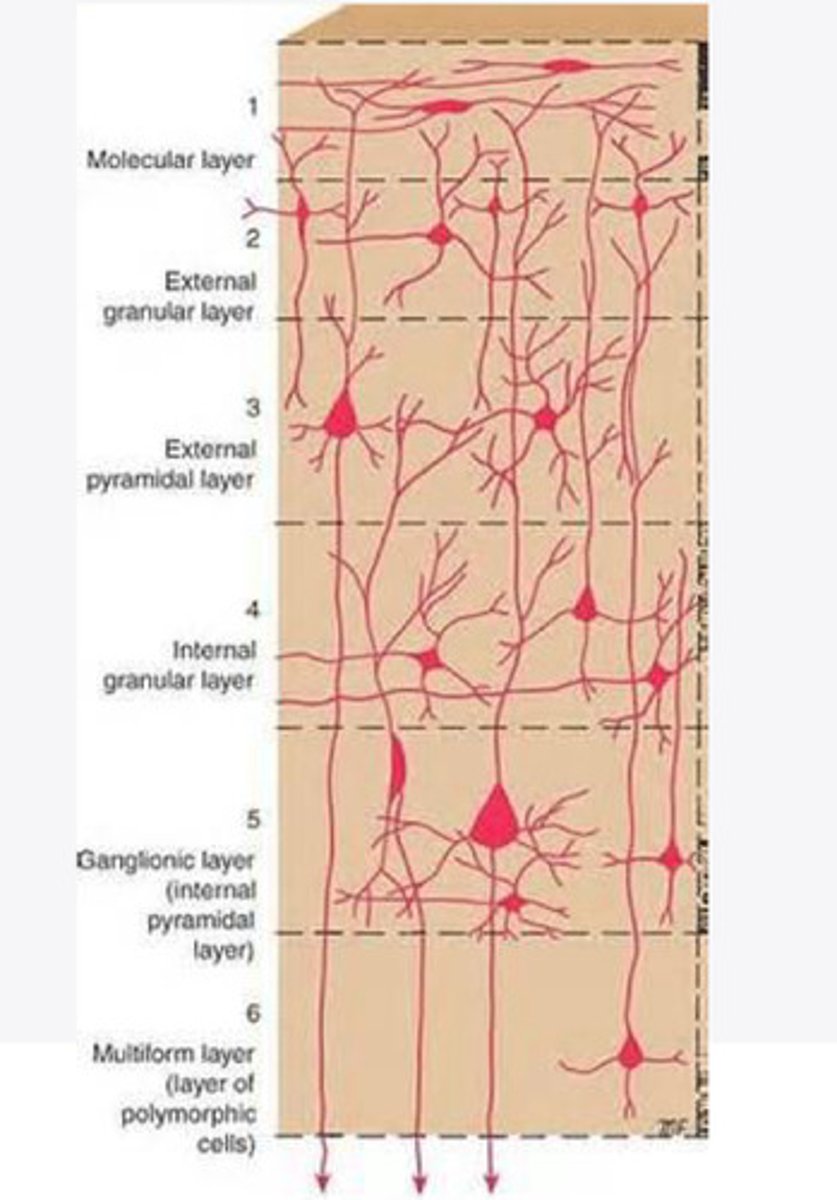
Layers of the cortex of the brain pic
stellate cells
These cells of the cortex RECEIVE impulses from other areas. There are numerous dendrites
in the regions of cortex associated with signal input
Where are stellate cells heavily concentrated in the cortex of the brain?
pyramidal cells
These cells of the cortex SEND impulses to other areas. Have 1 apical and 2 basal dendrites with a large axon
in regions of the cortex associated with sending output
Where are pyramidal cells heavily concentrated in the cortex of the brain?
2 and 4
What are the layers of the cortex that are associated with input?
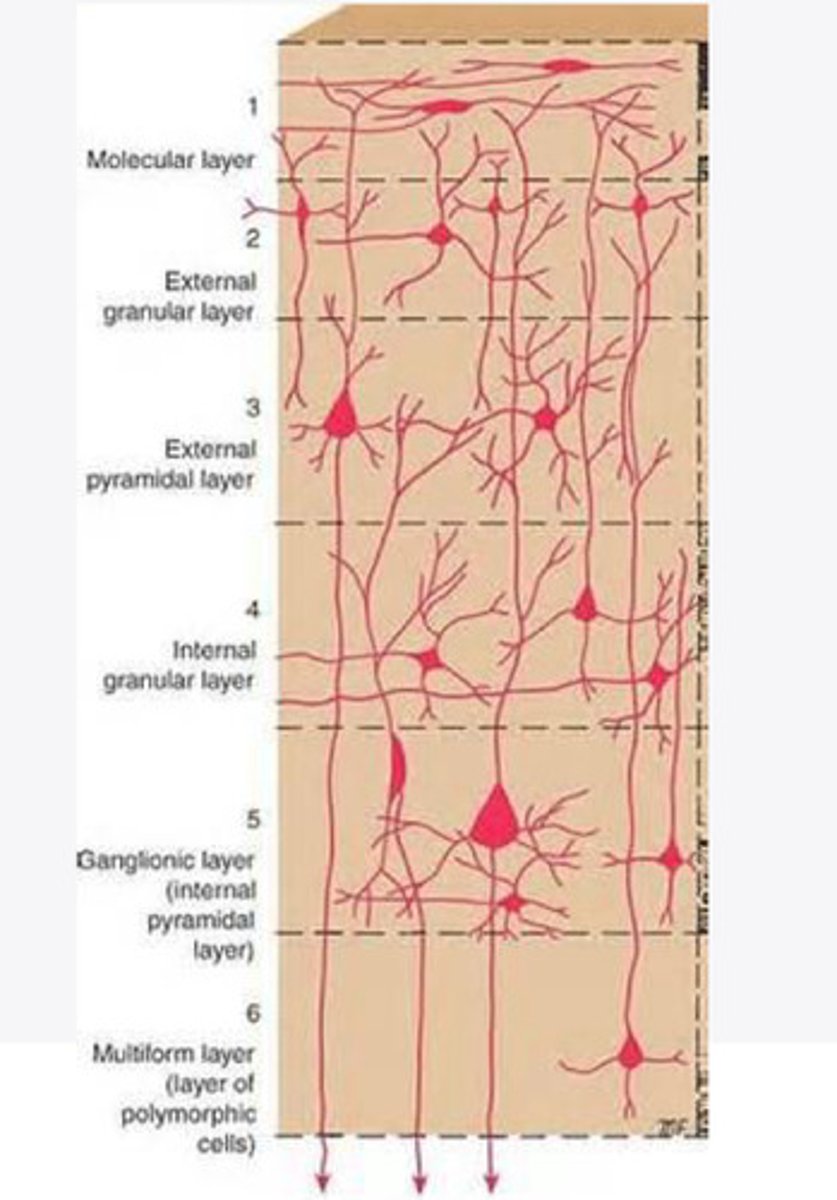
3 and 5
What are the layers of the cortex that are associated with output?

association fibers
fibers in the white matter of the brain that connect one part of a hemisphere to another area of the SAME hemisphere
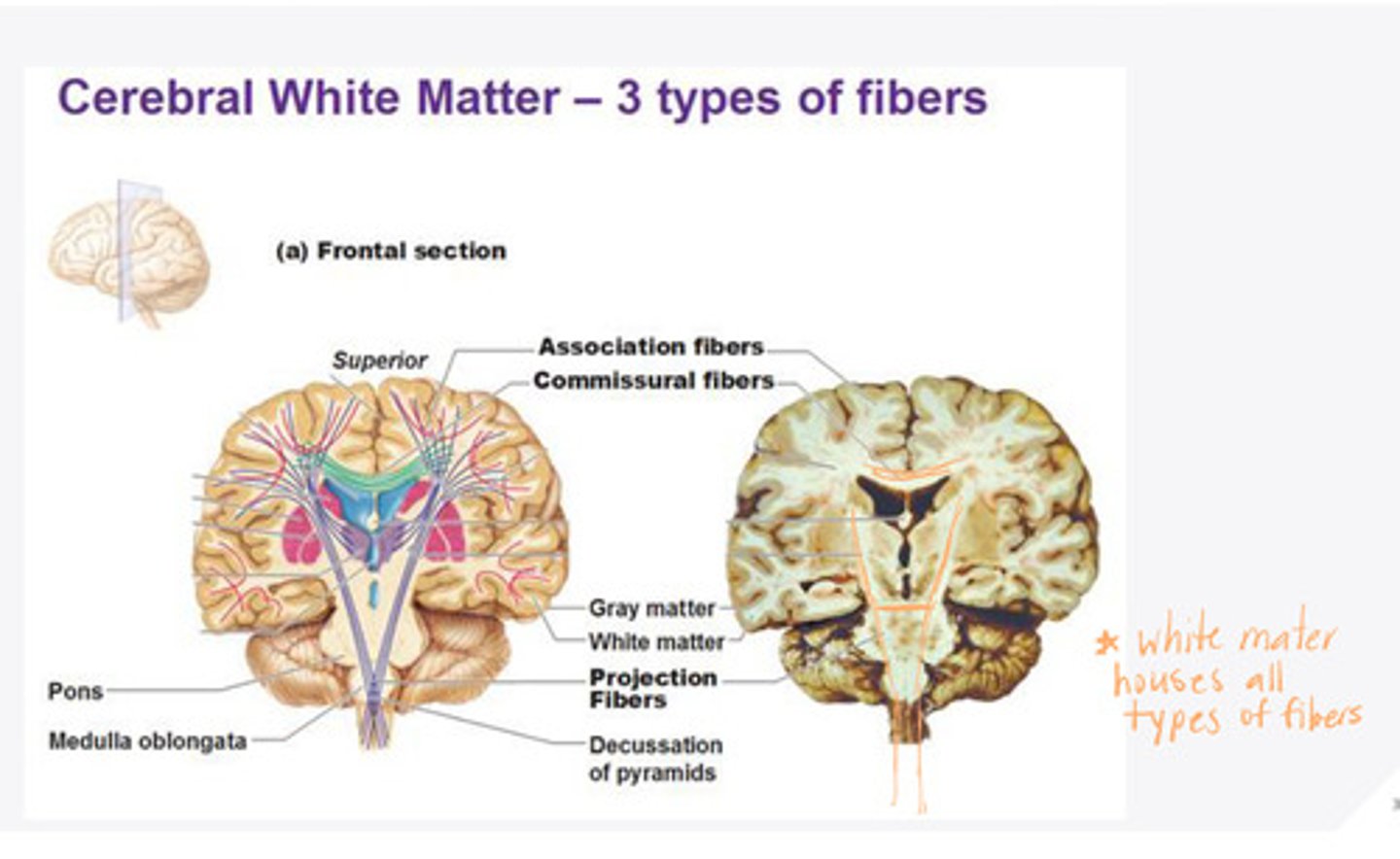
commissural fibers
fibers in the white matter of the brain that connect one part of the cortex to another part of the cortex in the OTHER hemisphere
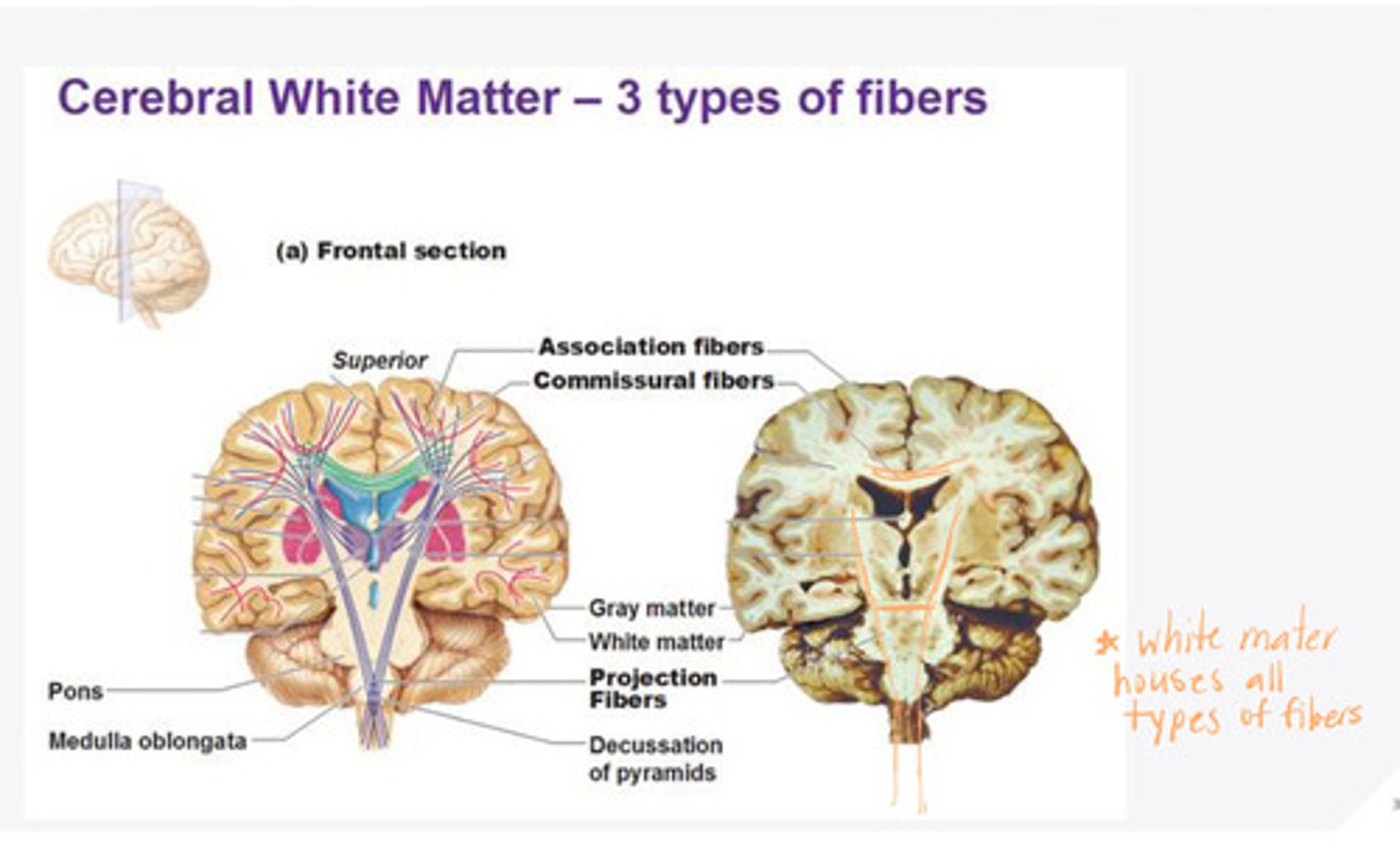
occipitofrontal tract, occipitoparital tract, occipitotemporal tract
**vision comes INTO the occipital and information is sent to be analyzed in many other regions
What are the 3 examples given for commissural fibers?
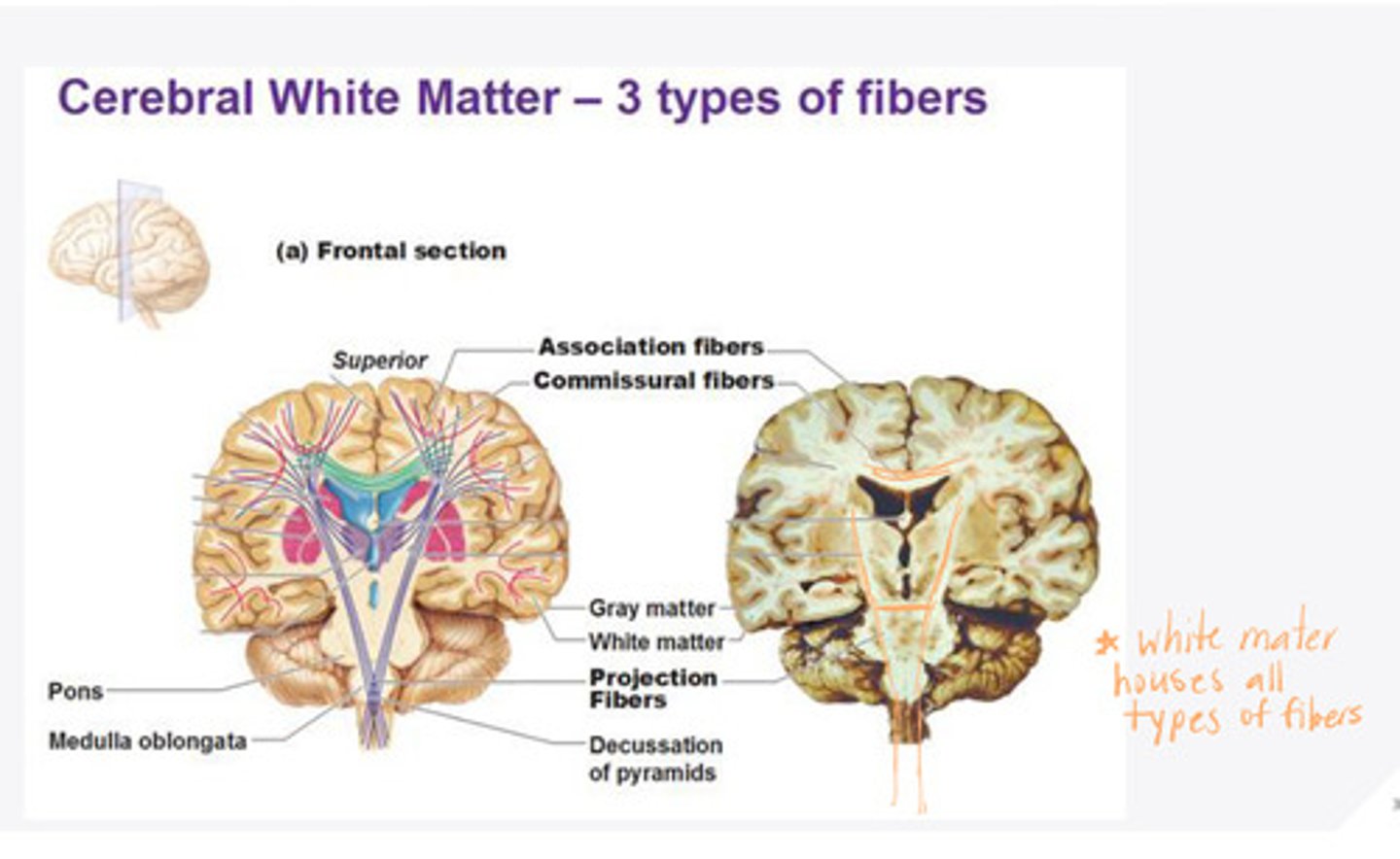
projection fibers
Fibers in the white matter of the brain that connect cortex to thalamus, brainstem, and spinal cord
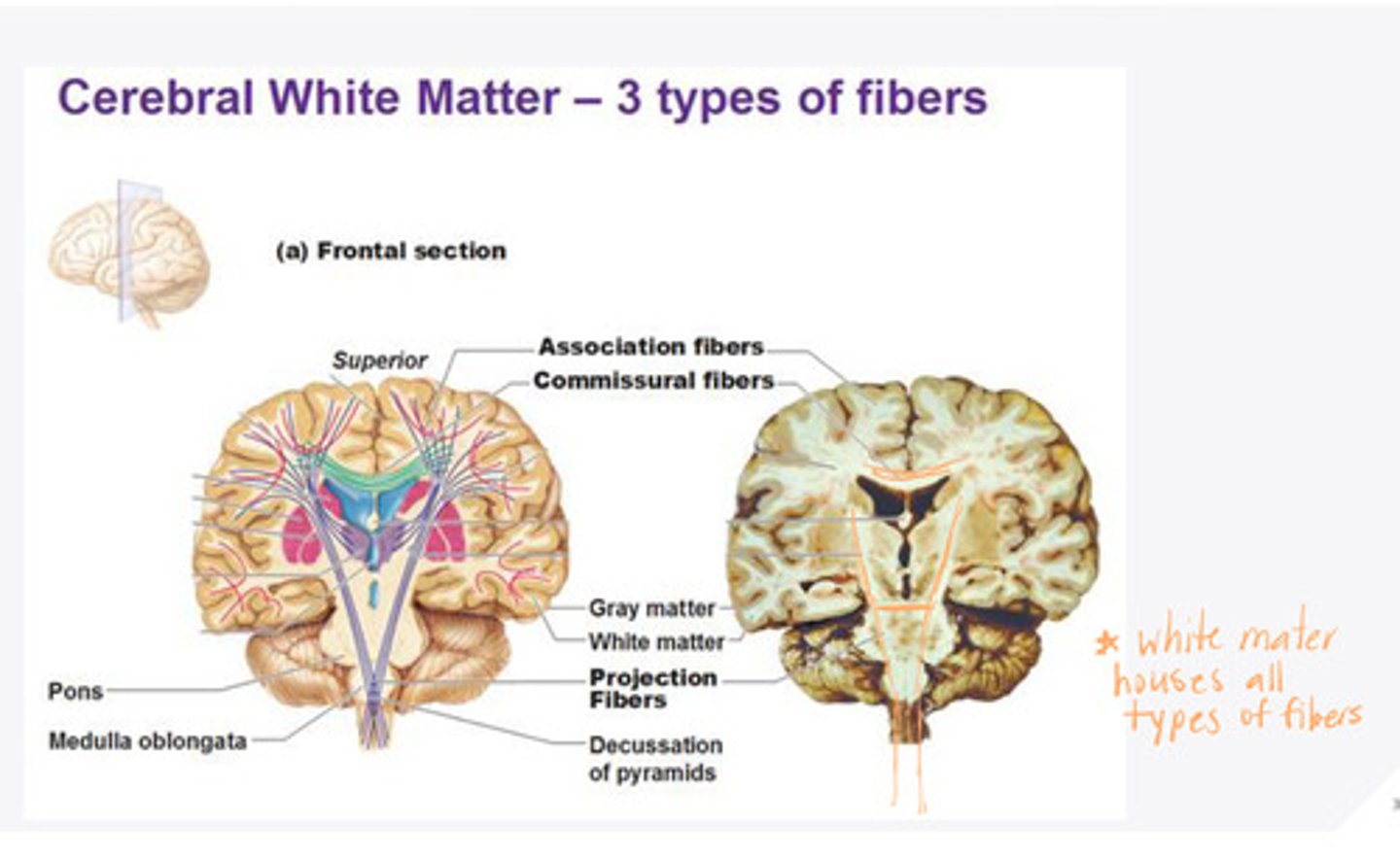
-geniculocortical
-thalamic radiations
What are the examples of corticopedal (afferent) projection fibers in the white matter of the brain?
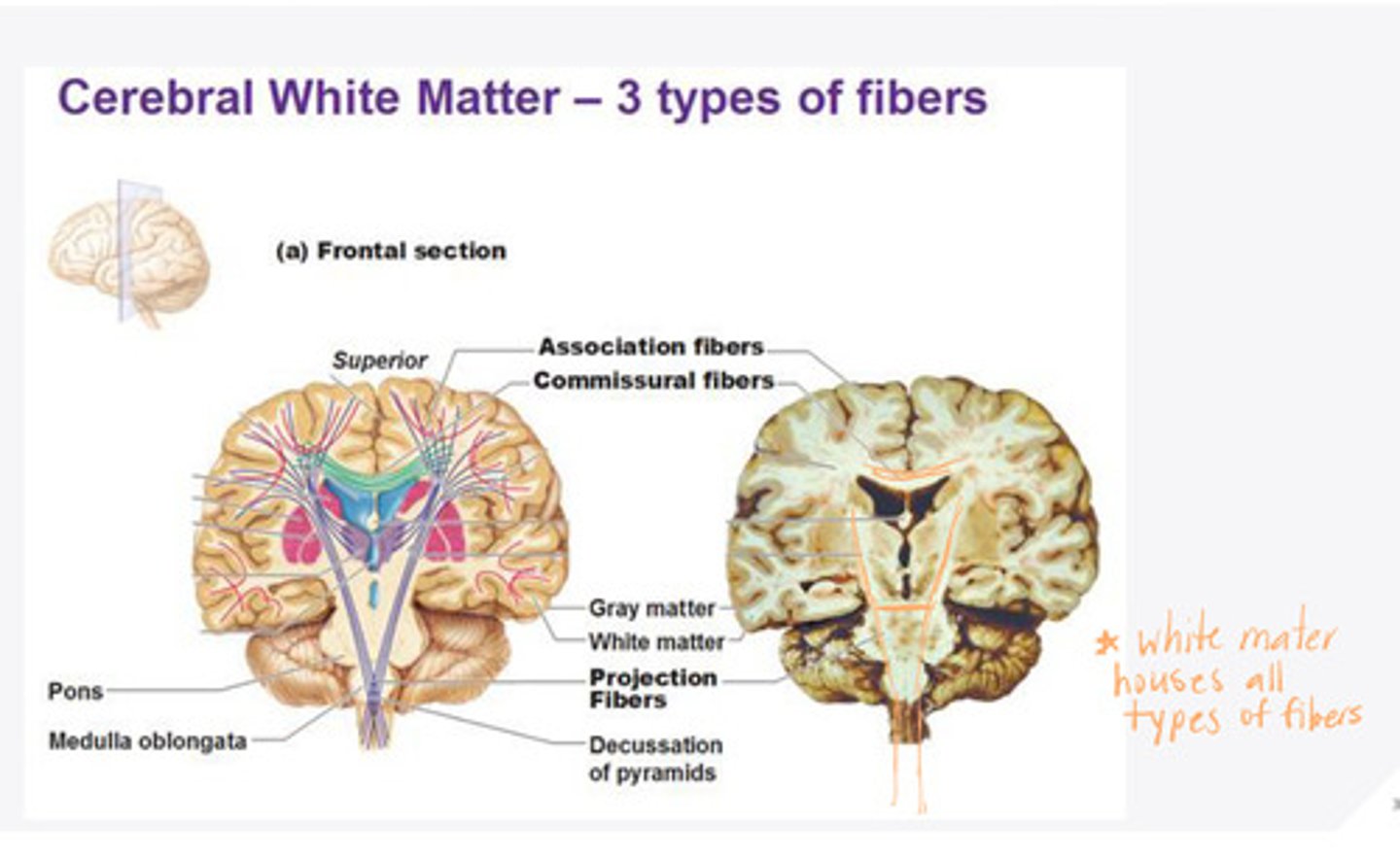
-corticobulbar
-corticospinal
What are the examples of corticofugal (efferent) projection fibers in the white matter of the brain?
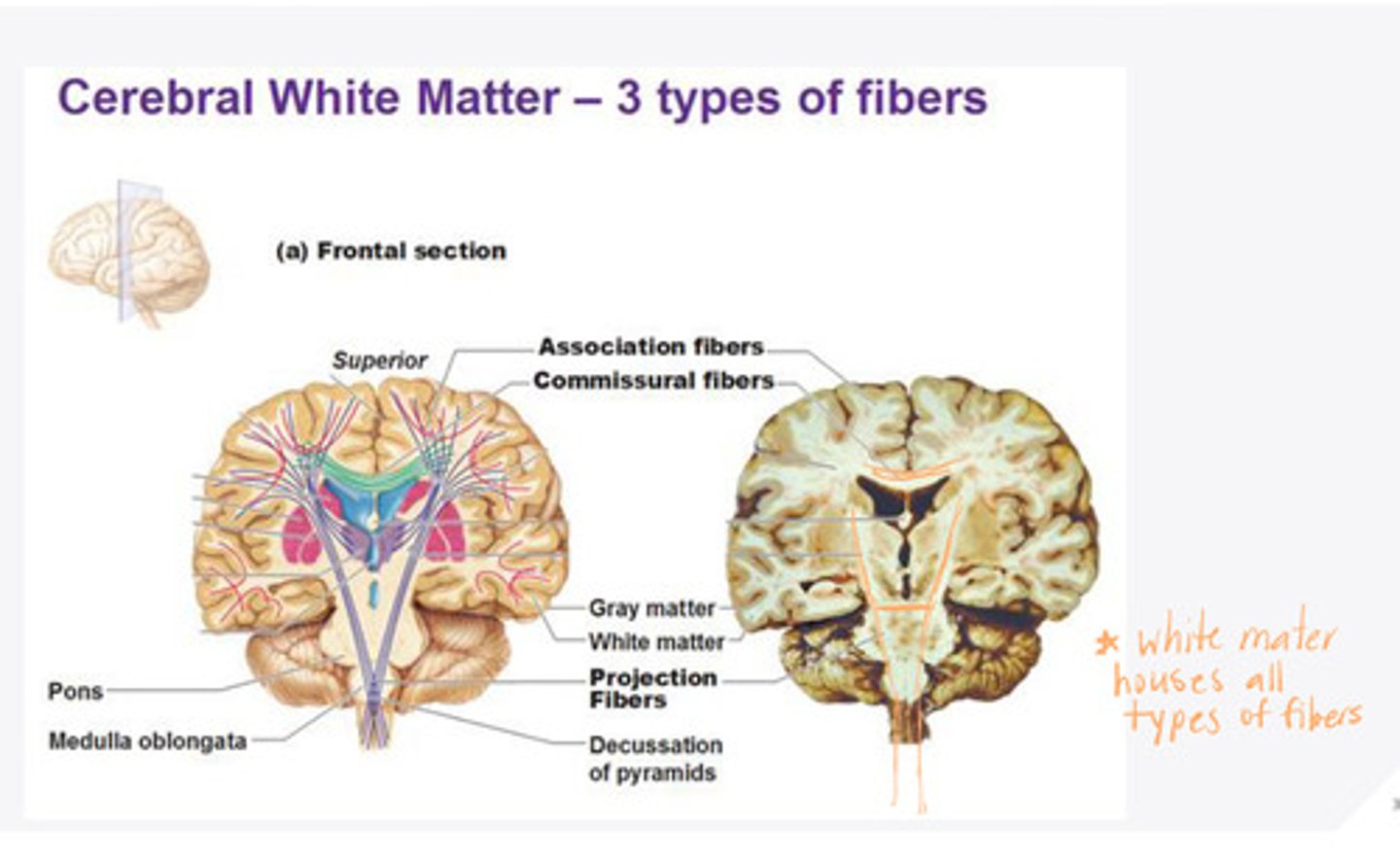
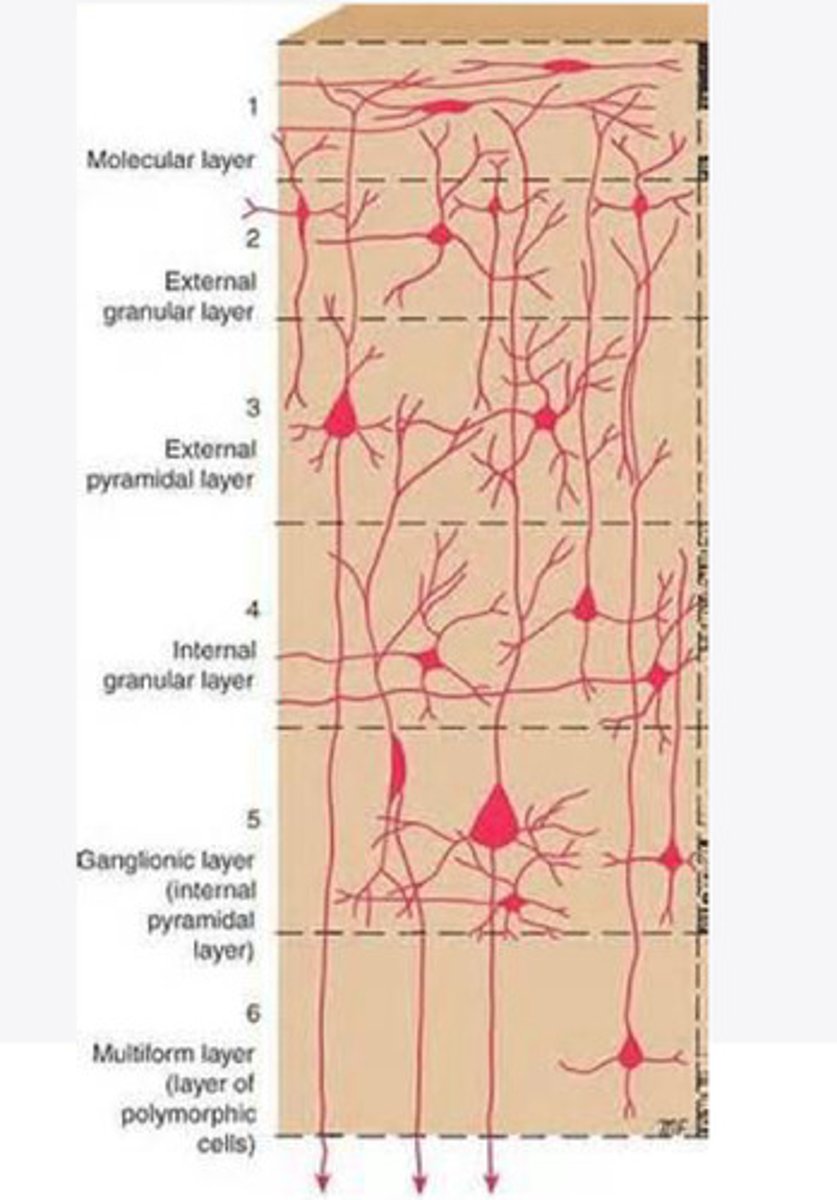
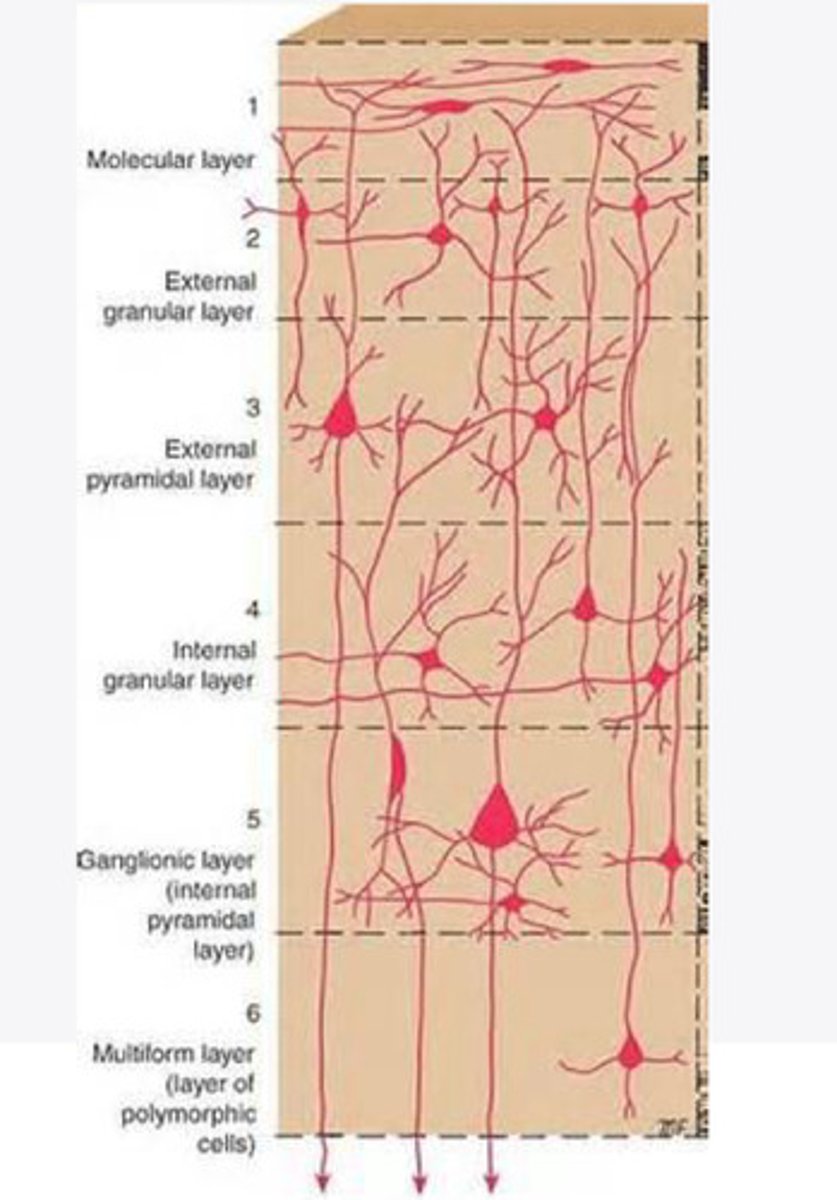
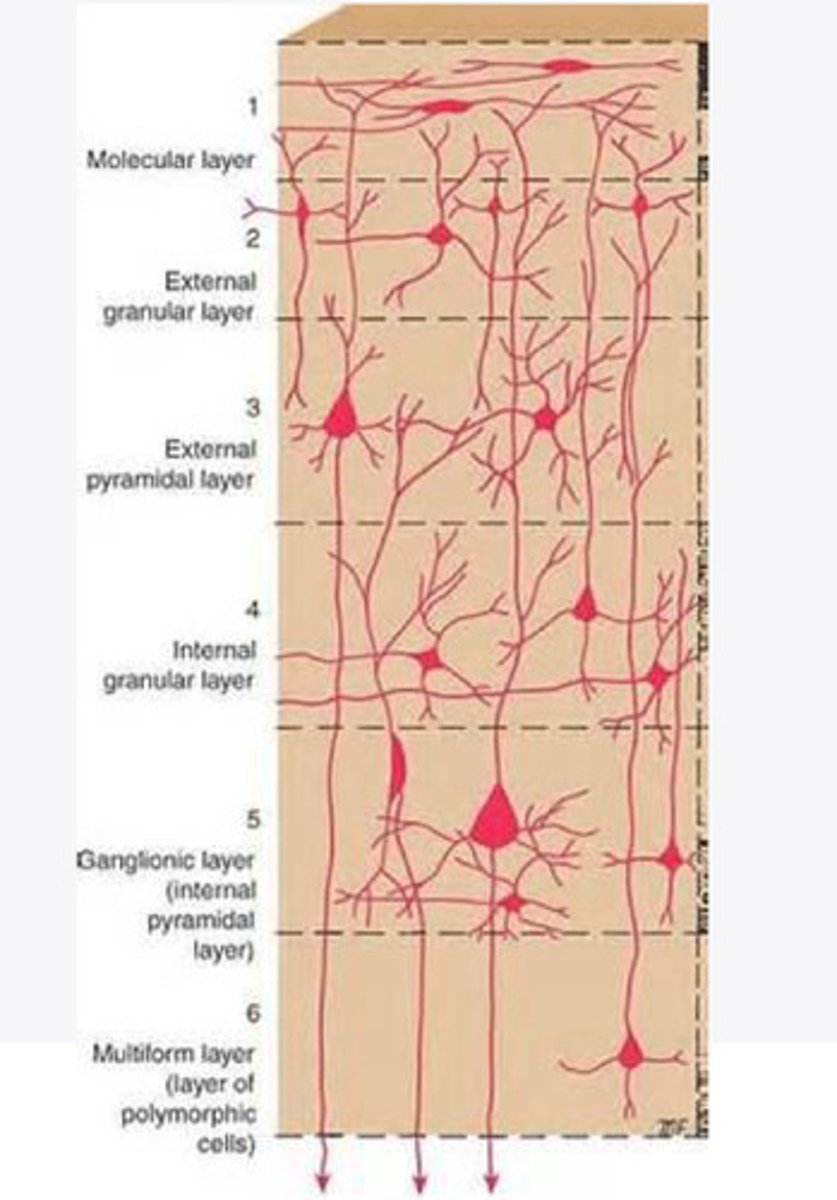
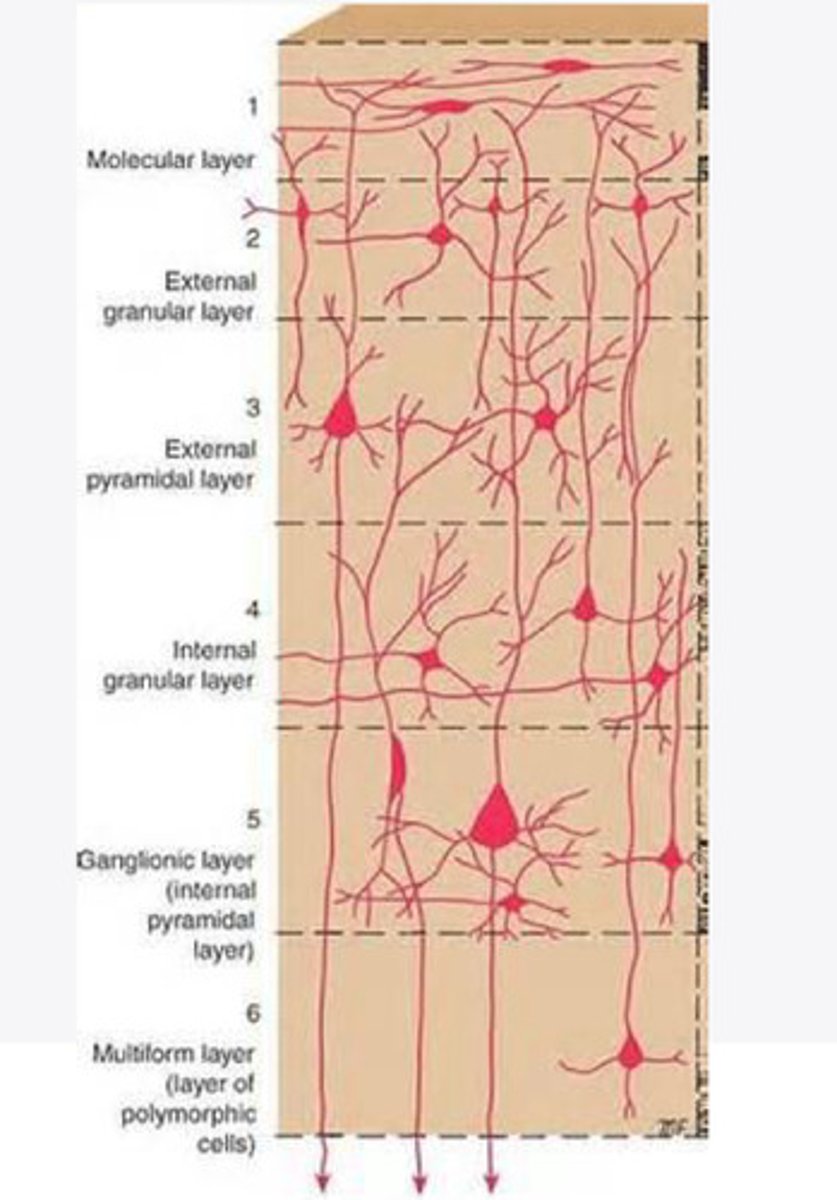
molecular layer
What is the name of Layer 1 of the cortex of the brain?
very few cells
Does Layer 1 of the cortex have a lot or few cells?
receives dendrites from internal layers so it may actually function as a coordinating center where layers can communicate action
What does Layer 1 of the cortex do?
1
Every layer sends densities to Layer ____?
1
What layer serves as the "water cooler" of the brain?
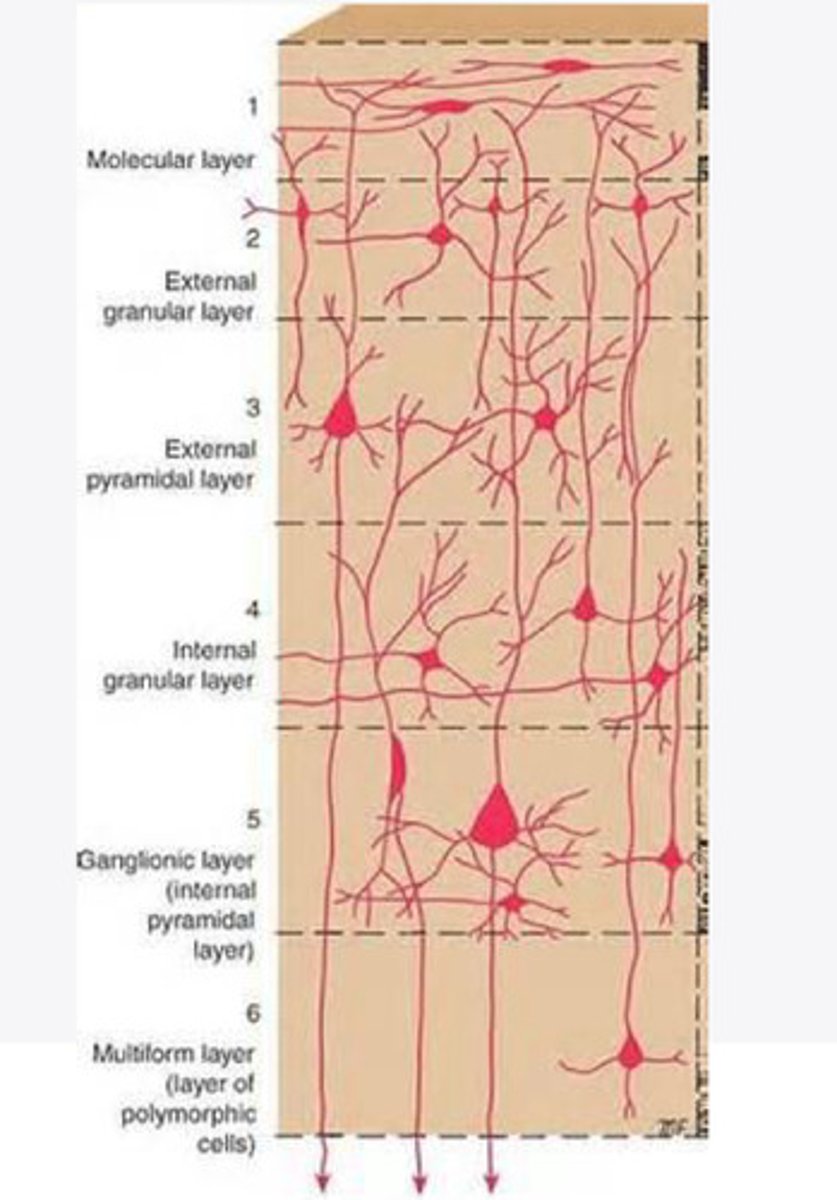
external granular layer
What is the name for layer 2 of the cortex of the brain?
receives input from other cortical regions
What is the function of Layer 2 of the Cortex of the brain?
Stellate
What type of cells (stellate/pyramidal) would be most concentrated in Layer 2?
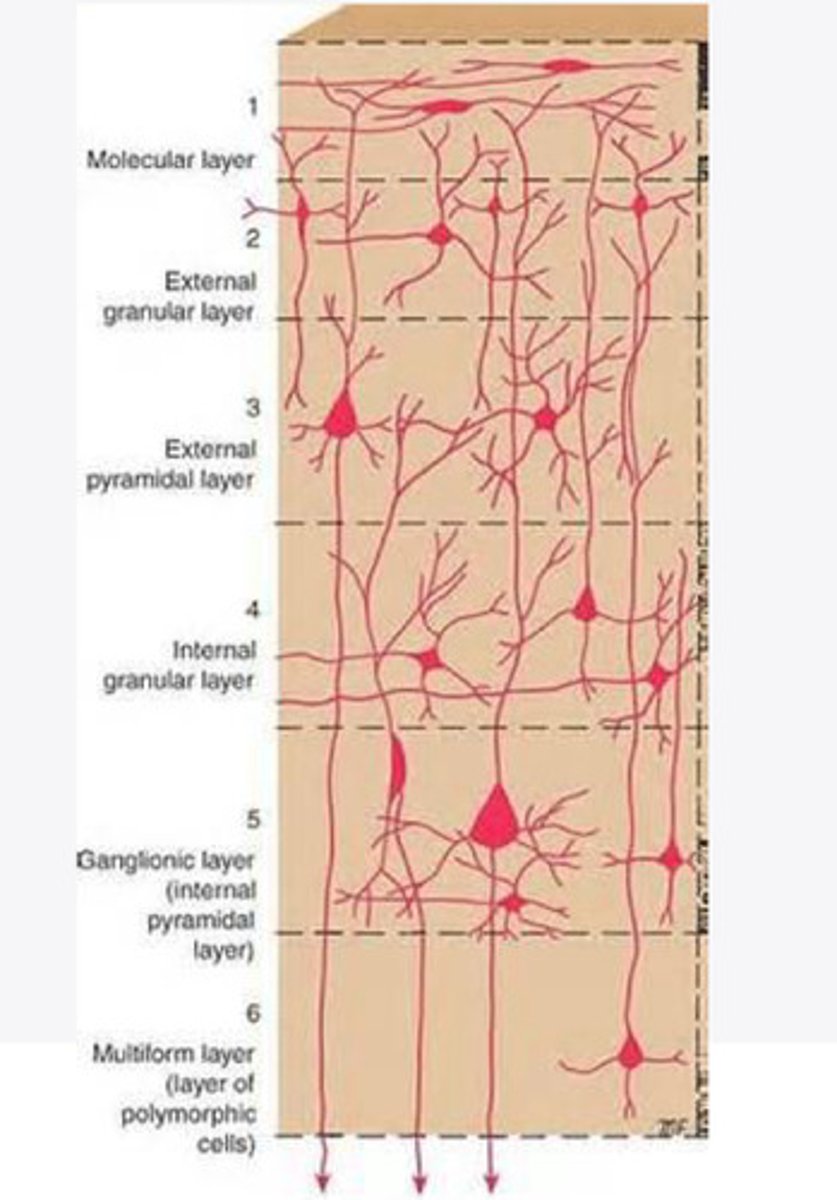
external pyramidal layer
What is the name for layer 3 of the cortex of the brain?
sends output to the other cortical layers
What is the function of Layer 3 of the cortex of the brain?
pyramidal
What type of cells (stellate/pyramidal) would be most concentrated in Layer 3 of the brain?
Layers 2 and 3
What layers are associated with association and commissural fibers?
Layer 3 - axons of cell bodies
Layer 2 - synapse into target areas in Layer 2
What part of the axons is in Layer 2/ in layer 3?
Layer 3 - external pyramidal layer
All axonal cel bodies for association and commissural fibers lie within what layer of the Cortex of the brain?
internal granular
** or called the striate cortex because it is so thick that you can see a line through this layer even in unstrained brain slides
What is the name for the 4th layer of the cortex of the brain?
receives input from the thalamus, geniculocortical layer, and other brainstem areas
What is the function for the 4th layer of the Cortex of the brain?
very thick within the vision, auditory, and somatosensory areas
Is Layer 4 thick or thin within SENSORY areas of the cortex?
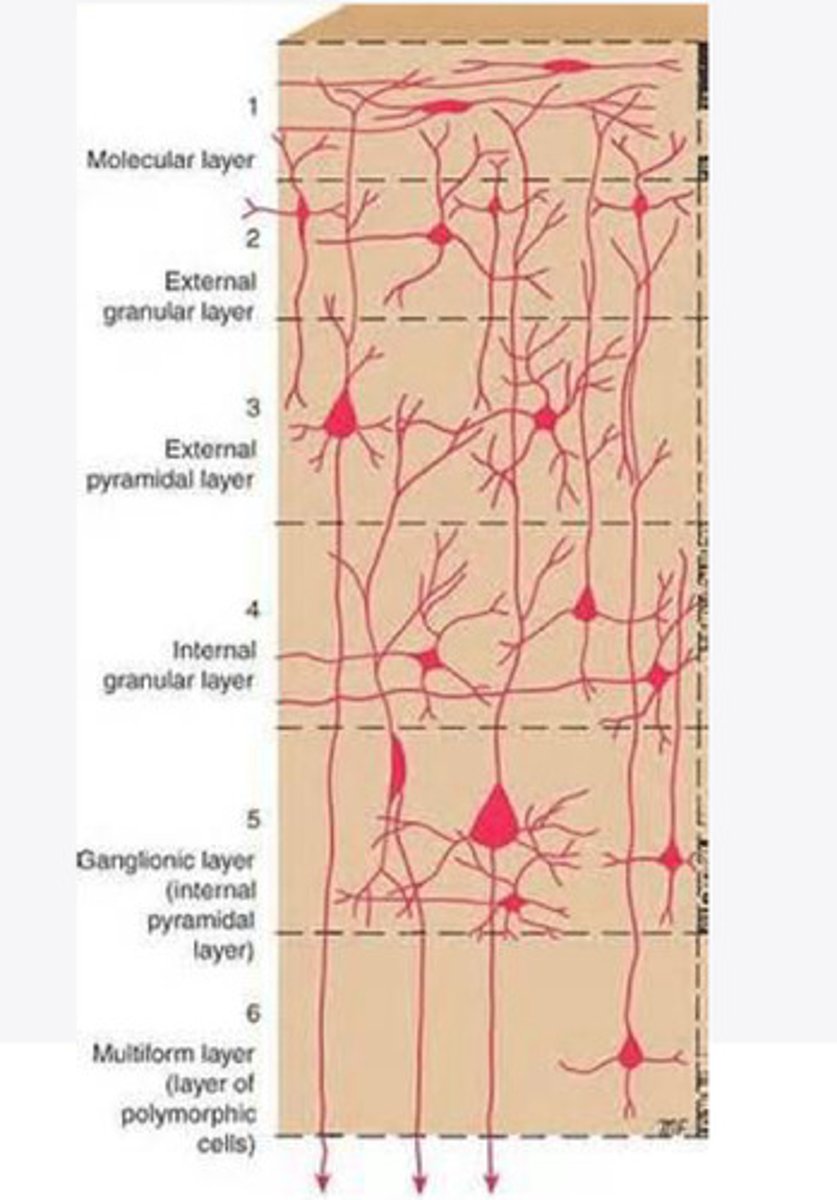
Internal pyramidal
What is the name for Layer 5 of the cortex of the brain?
sends axons to the brainstem (corticobulbar) and spinal cord (corticospinal)
What is the function of Layer 5 of the cortex of the brain?
in motor areas of the cortex?
Where is layer 5 very thick in the brain?
the frontal lobe -- very motor heavy
What lobe of the brain will have a thick layer 5 of the cortex of the brain?
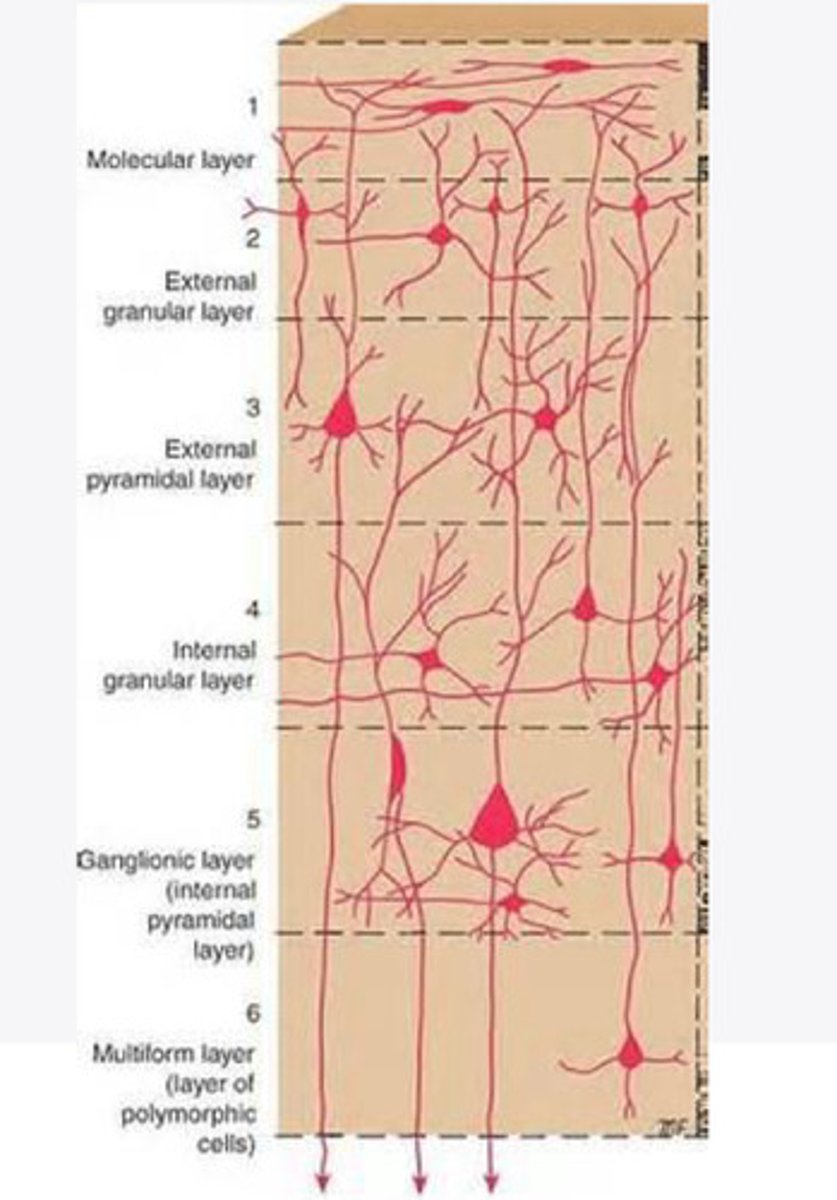
the multiform layer
What is the name of layer 6 of the cortex of the brain?
-sends axons back to the thalamus through corticogeniculate fibers
-modulates what information the thalamus sends to the cortex to control the strength of the signal received and modulate what you pay attention to
What is the function of layer 6 of the cortex of the brain?
no
Is layer 6 a motor layer?
without knowledge?
What are a priori decisions?
Yes, Layer 6 allows the cortex to make these decisions with corticogeniculate fibers
Can Layer 6 of the cortex of the brain make a priori decisions?
Symptoms experienced by TBI
Damage to Layer 6 of the cortex of the brain can play a role in what symptoms?
cerebral cortex on the basis of histological sections
What did Brodmann study?
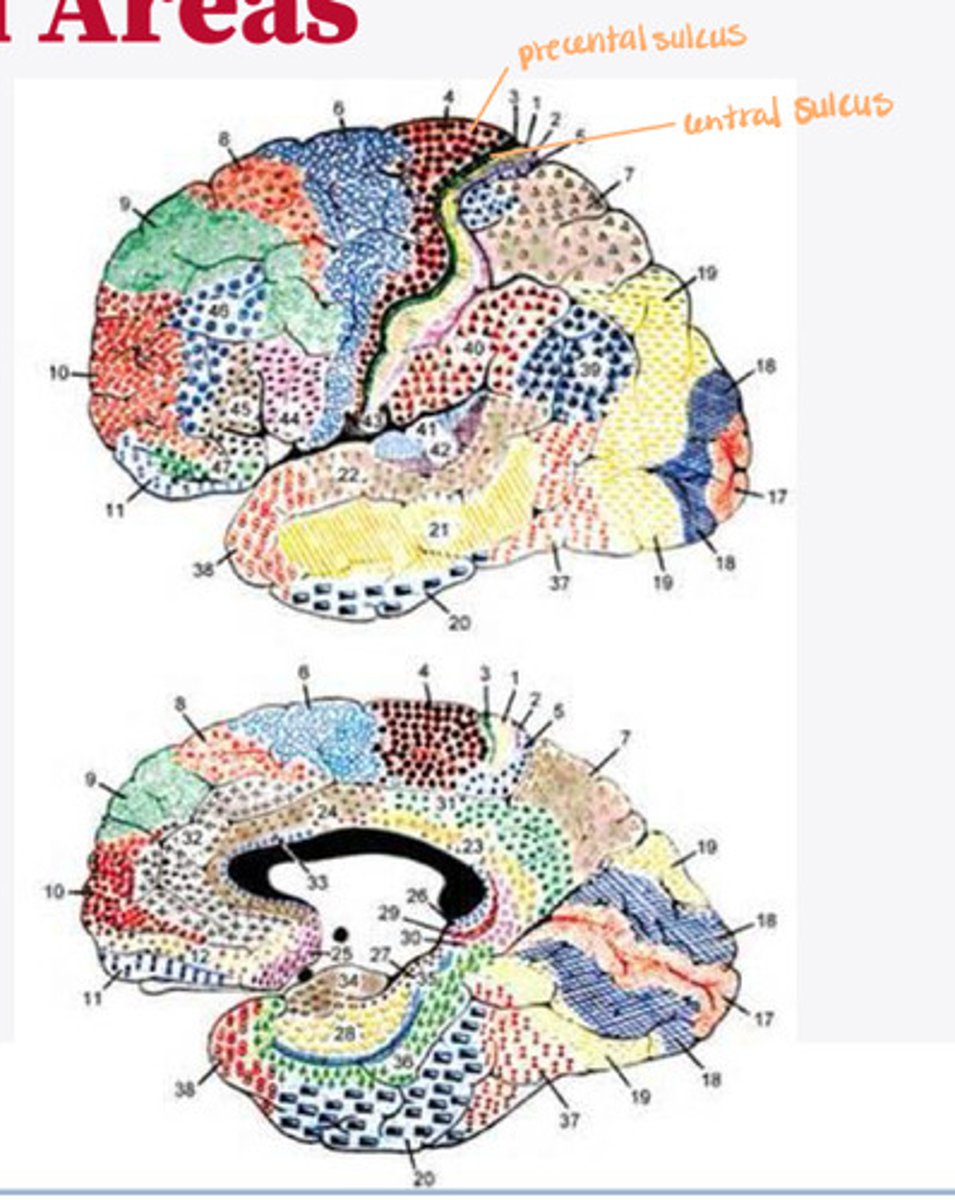
52 distinct regions of the cortex based on the thickness of cell layers alone
What did Brodmann find?
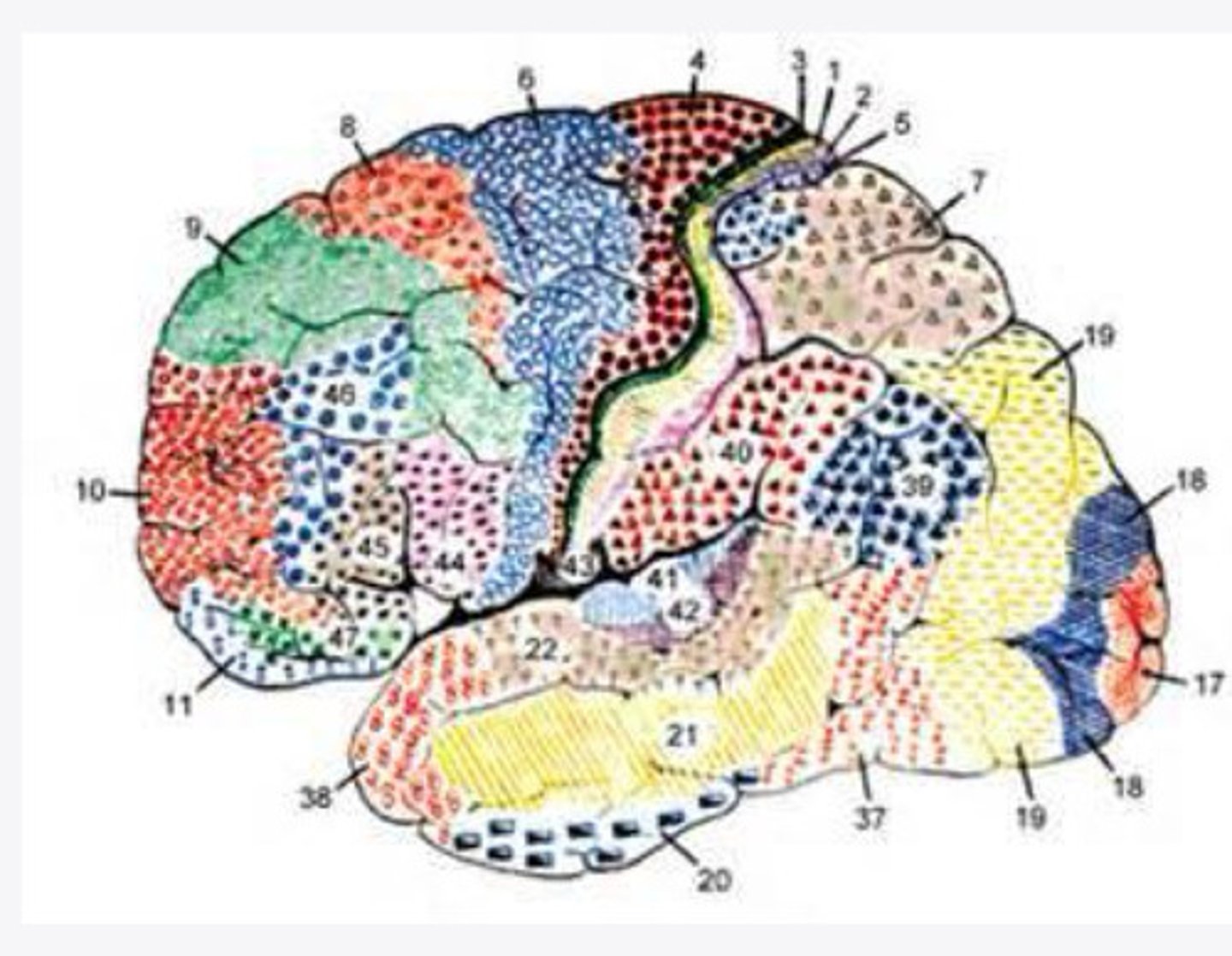
2-5
What layers of the cortex of the brain did Brodmann find were variable in histological sections?
function
In the 52 Brodmann areas, structure lens itself to ______
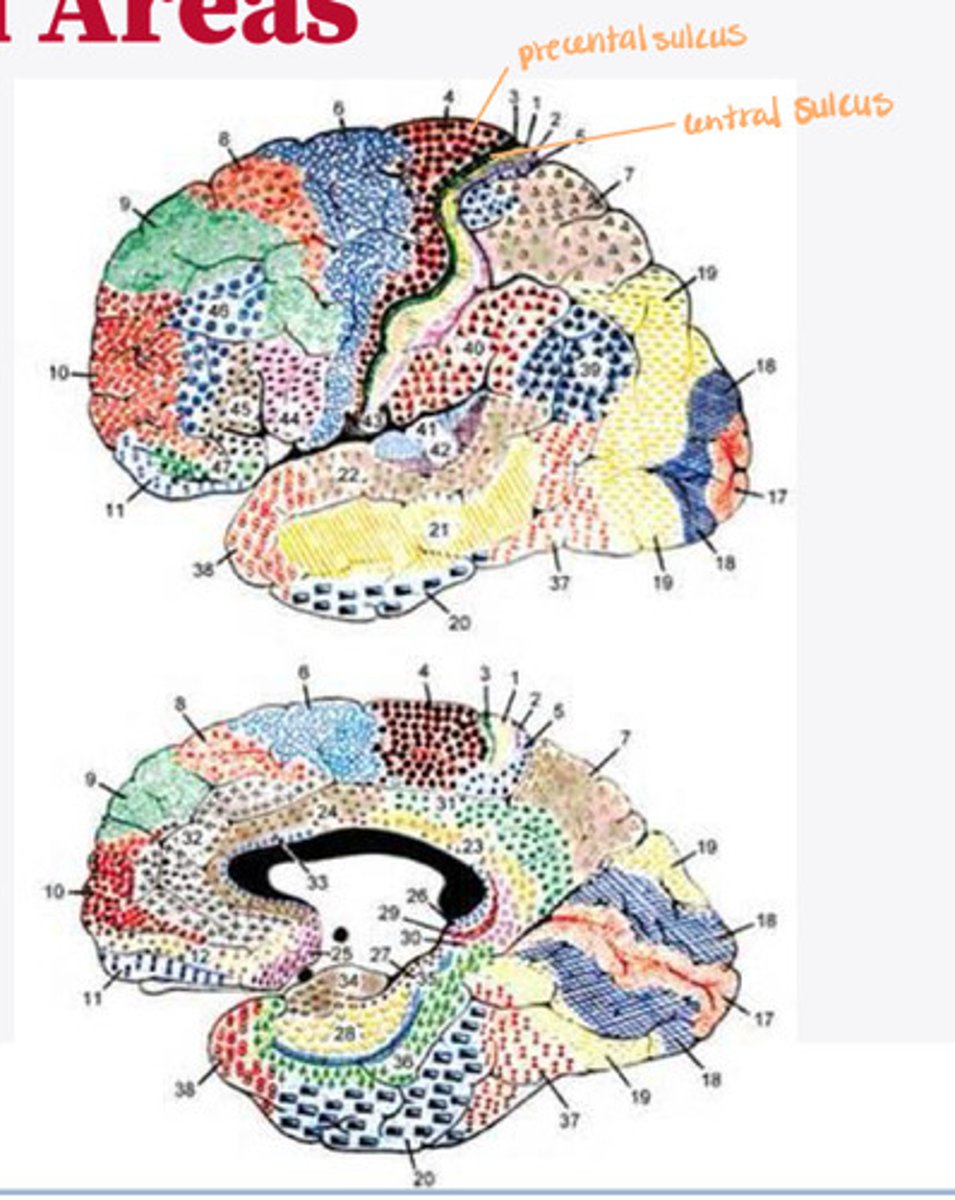
4, 6, 8, 44/45
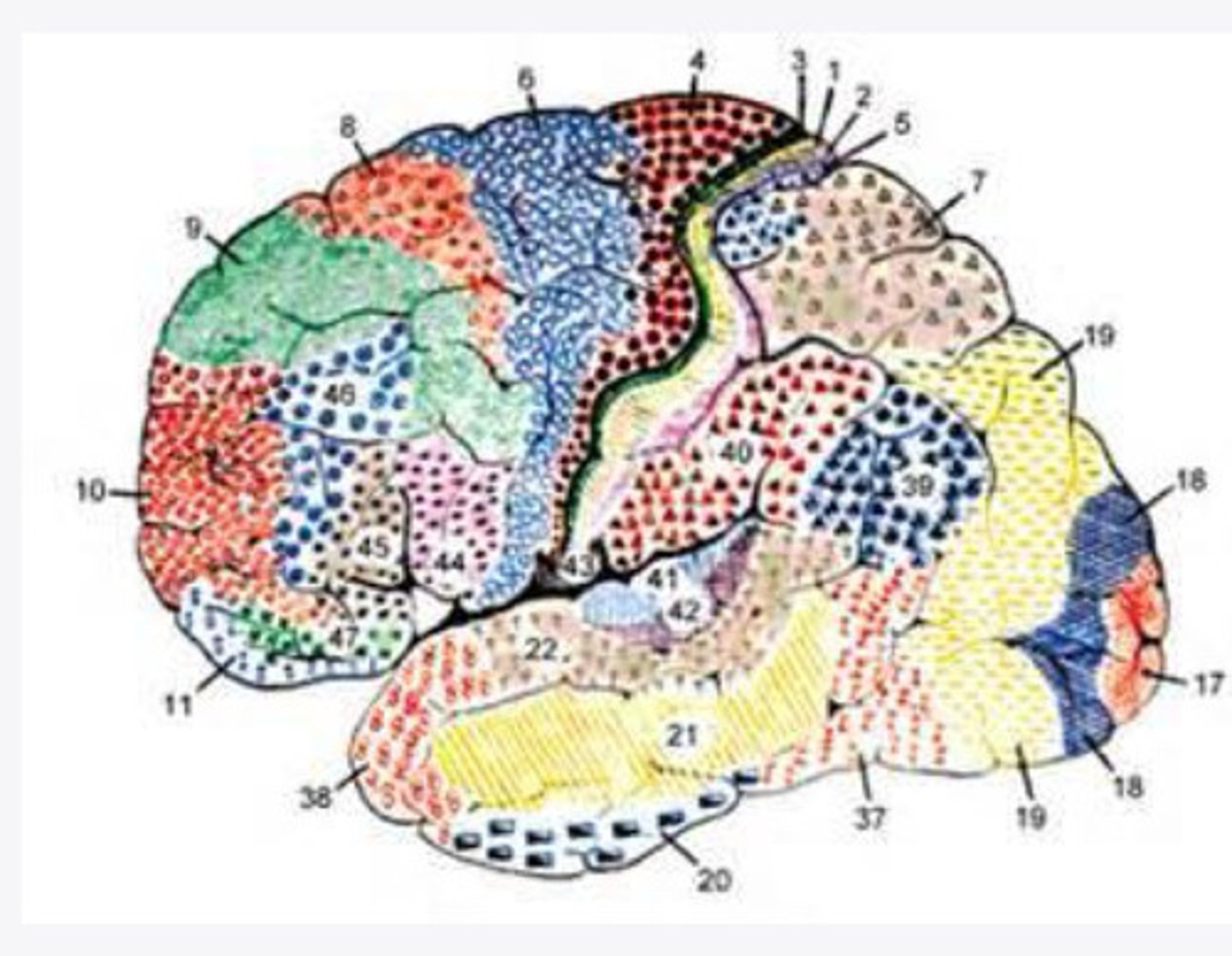
What are the important Brodmann areas of the frontal lobe?
motor movements
What is the function of Brodmann area 4?
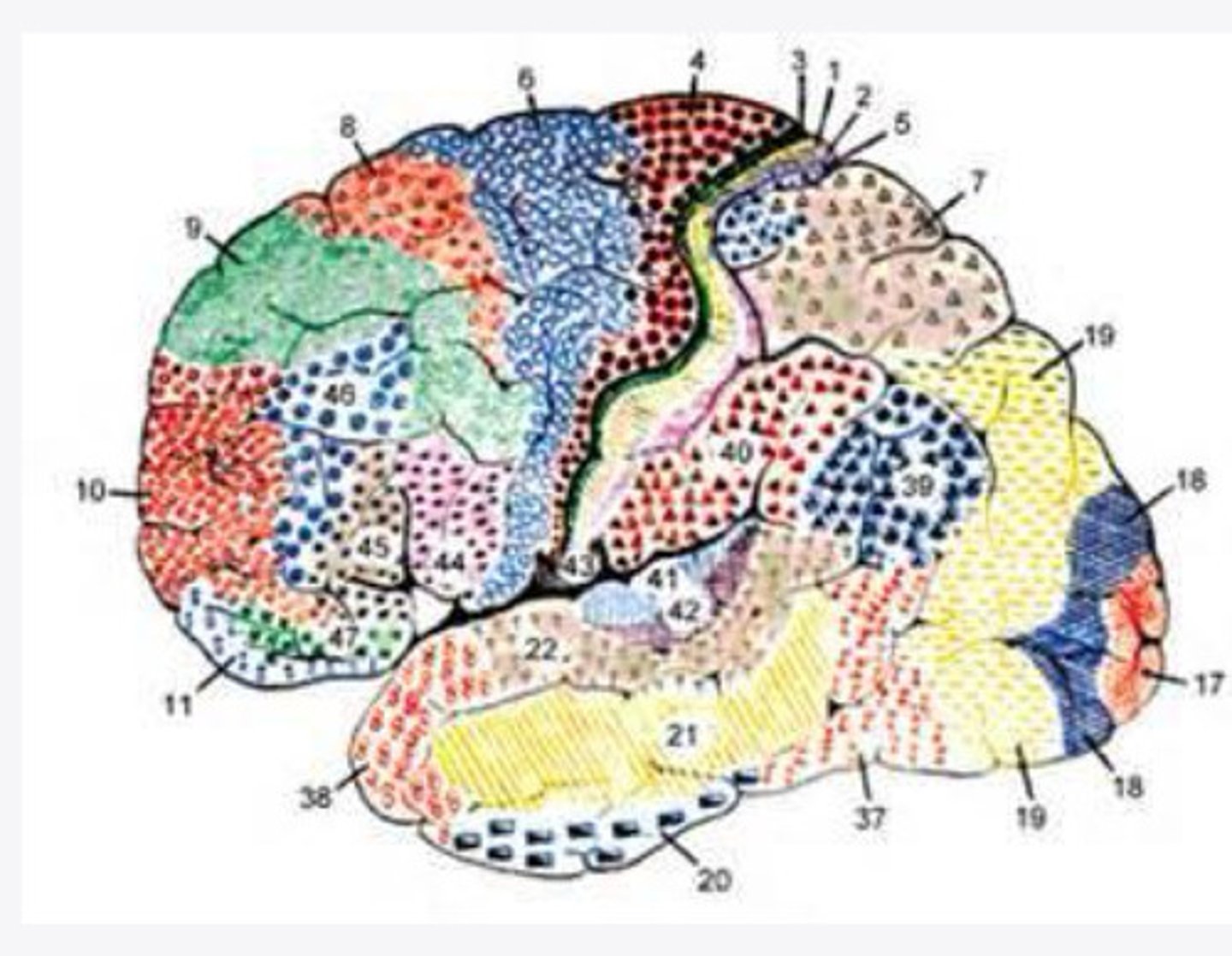
2 and 5
What layers of the cortex are thick in Brodmann area 4?
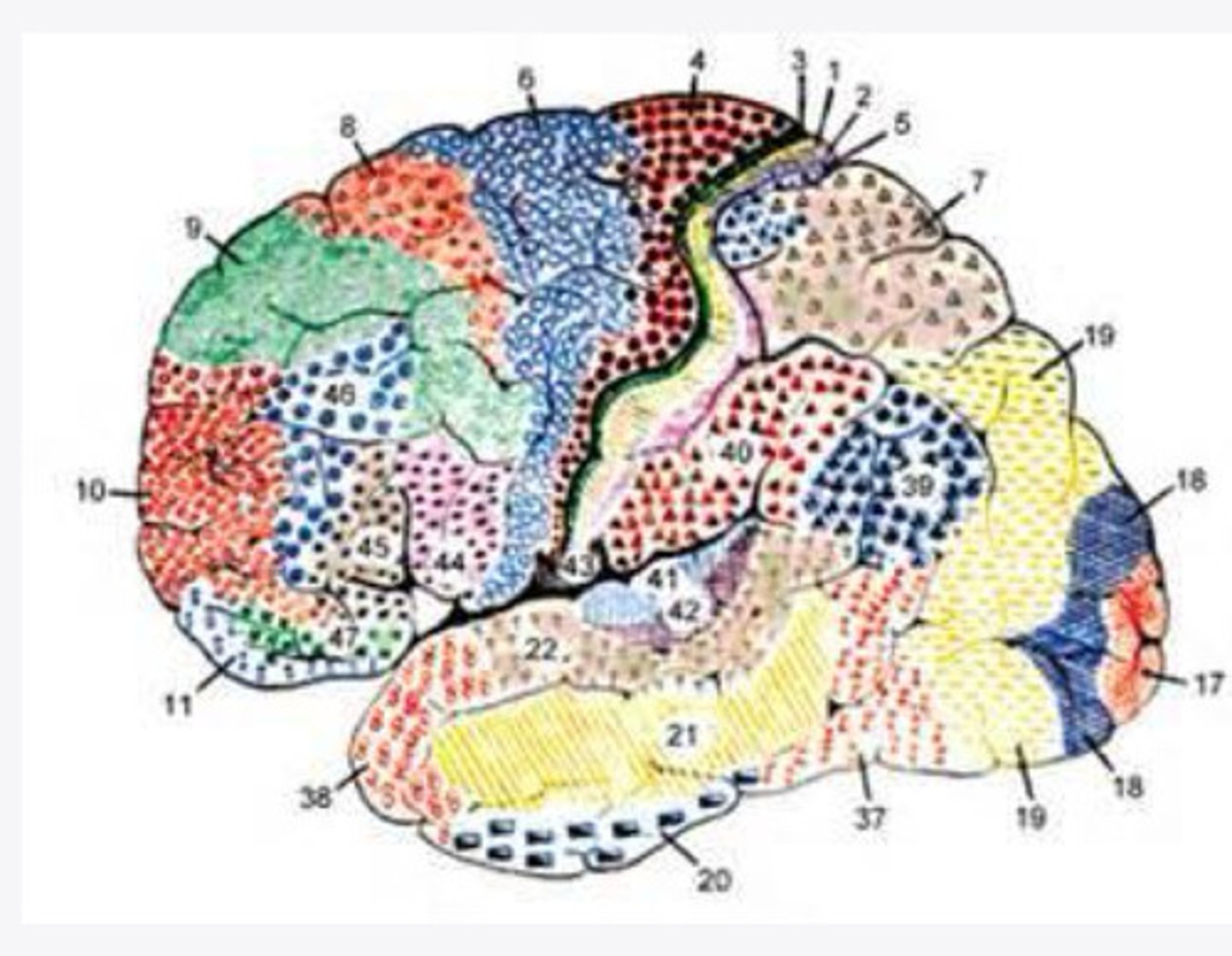
helps coordinate activity in the motor cortex (opposing muscle groups)
What is the function of Brodmann area 6?
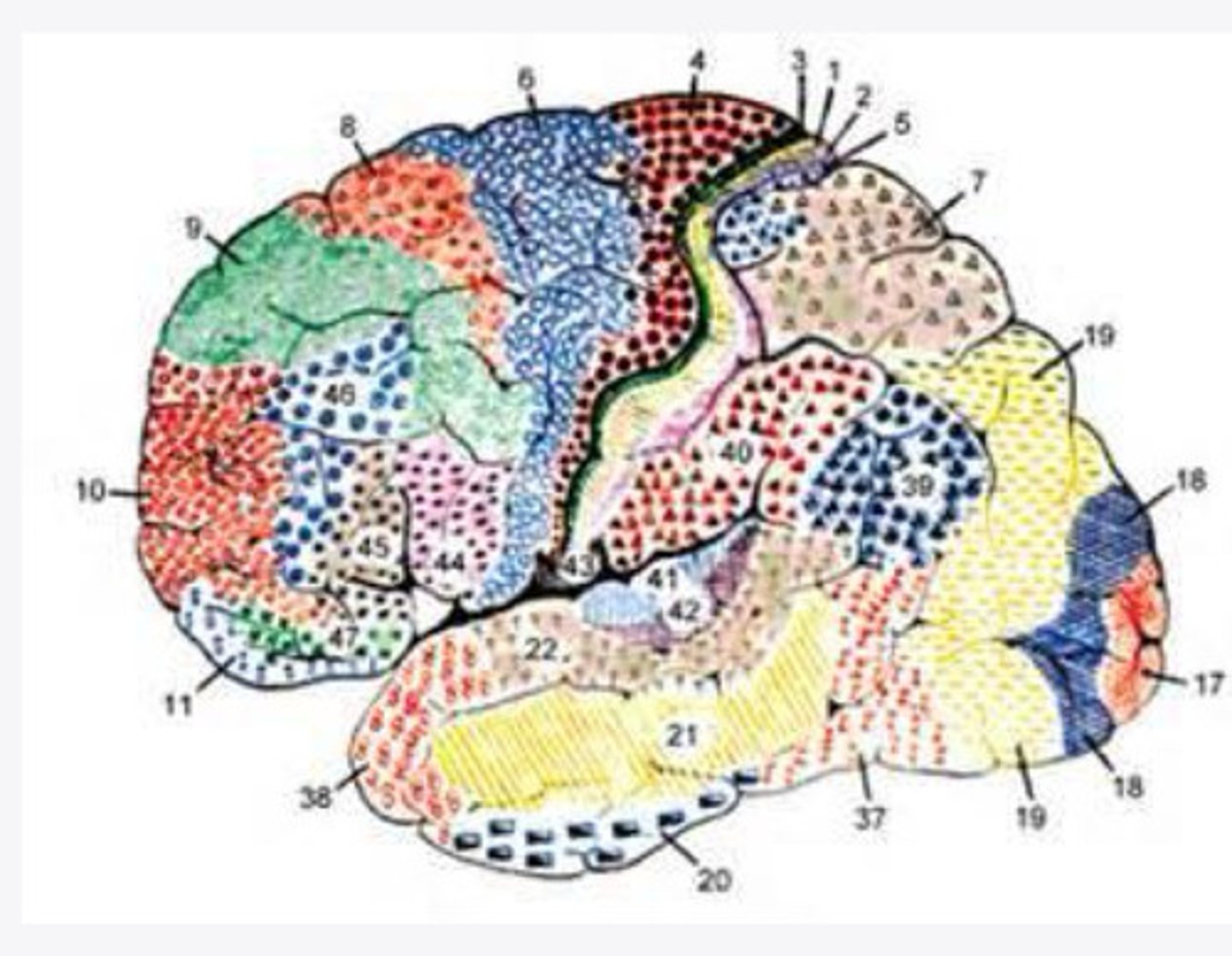
2 and 3
What layers of the cortex are thick in Brodmann area 6?