synapses
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
rectifying transmission
one way transmission
non rectifying transmission
two way transmission
electrical synapse
two neurons connected by specialised proteins creating gap junction
non rectifying
fast transmission
often attenuated
connexons and electrical synapse
2 connexons per synapse
6 connexins per connexon - 12 connexins per synapse
pore diameter is 1-2nm
not flexible
drosophila escape reflex
relies on innexin (invertebrate form of connexin)
electrical synapses with motor neurons
gap junctions
chemical synapses
very flexible
more plasticity than motor neurons
primary method for communication
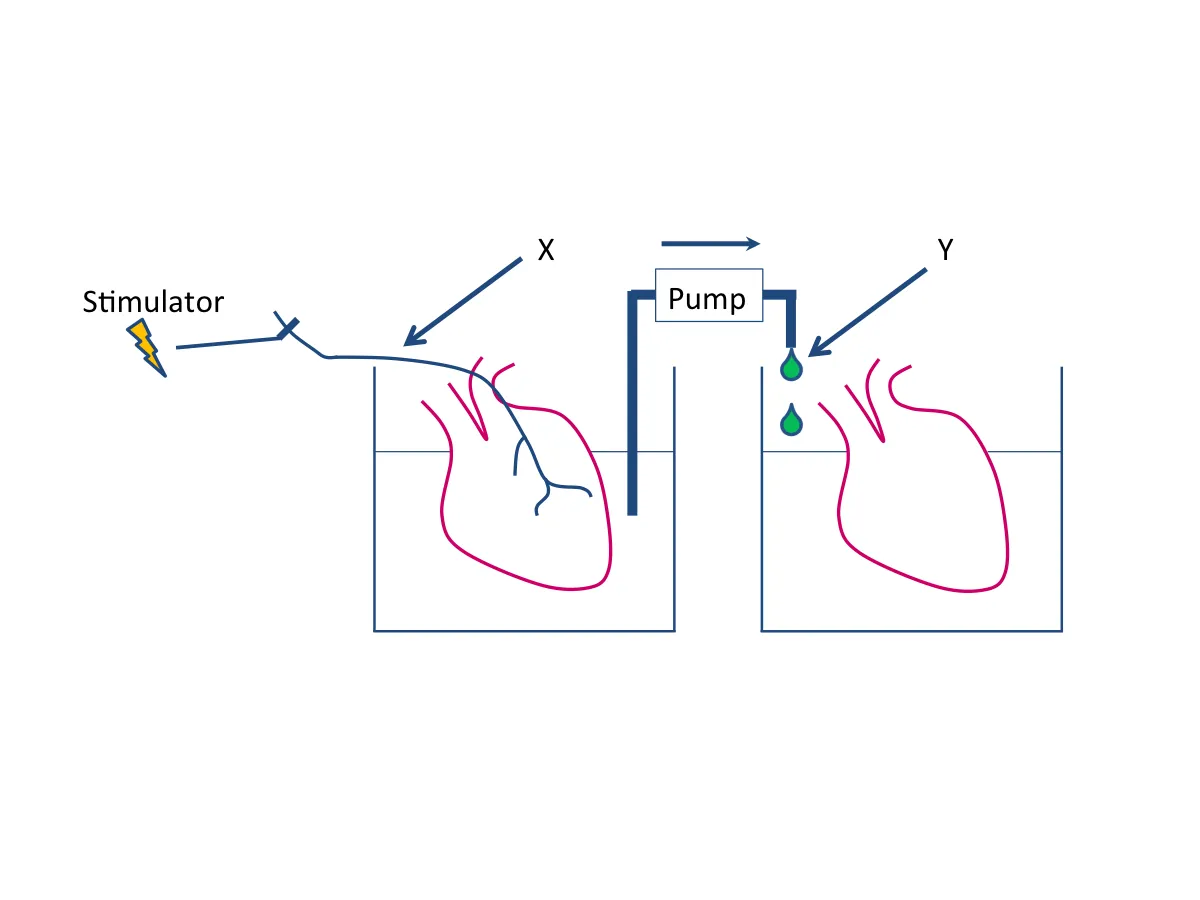
electrical stimulation of vagus nerve effect
slower heart rate
effect of vagus substance in otto loewi experiment
vagus substance released by heart with vagus nerve slows down heart without vagus nerve
acetylcholine neurotransmitter released by vagus nerve influences contraction
active zones of chemical synapses
creates dark areas on EM morphology
where neurotransmitter is released
calcium voltage gated channels are found here
why are there many mitochondria in chemical synapses
lots of energy required for neurotransmitter release in vesicles
brain uses up to 30% of energy bc of this
SNARE proteins
synaptobrevin, snap-25 and syntaxin
where is synaptobrevin found
in the vesciles
wher
purpose of snare proteins
snare proteins bind to eachother
draw vesicles close to membrane
neurotransmitter release into presynaptic cleft
what destroy snare proteins and why
tetanus toxins to stop them from releasing GABA or glycine
spontaneous release
no calcium
still some neurotransmitter being released
smaller size change in post synaptic membrane
miniature end plate potential
evoked release
by action potential
calcium enters cell
many vesicles fusing with postsynaptic membrane
end plate poltential
miniature endplate potential
many small miniature end plate potentials
stepwise variation
due to release of one or few quanta
quantum
amount of neurotransmitter per vesicle
quantal current
EPP current / 1 quantum current
how many quanta per action potential
200
clathrin
involved in vesicle recycling
binds to vesicles and forms interactions with other clathrin molecules
hexagon and pentagon conformations
drags vesicles away from membrane
constants in vesicle recycling
vesicle size (Determined by clathrin)
number of