BIOL 2010 - Control of transcription in prokaryotes
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
types of expression
constitutive - always on
regulated genes - can be turned on/off in response to changes in environment
operons
genes encoding for proteins in the same pathway are located adjacent to one anther and controlled as a single unit that is transcribed into a polycistronic RNA
polycistronic RNA is RNA with no introns and is specific to prokaryotes
LAC OPERON
lac z - beta galactosidase breaks down lactose
lac y - permease encodes the transporter that allows lactose in
lac a -transacetylase is involved in acetylating pyranosides so that they cant enter cells and become toxic
consensus sequence gives directionality to RNA pol
down/up mutations decrease or increase the affinity of the promoter to the RNA pol to increase or decrease the expression of the gene
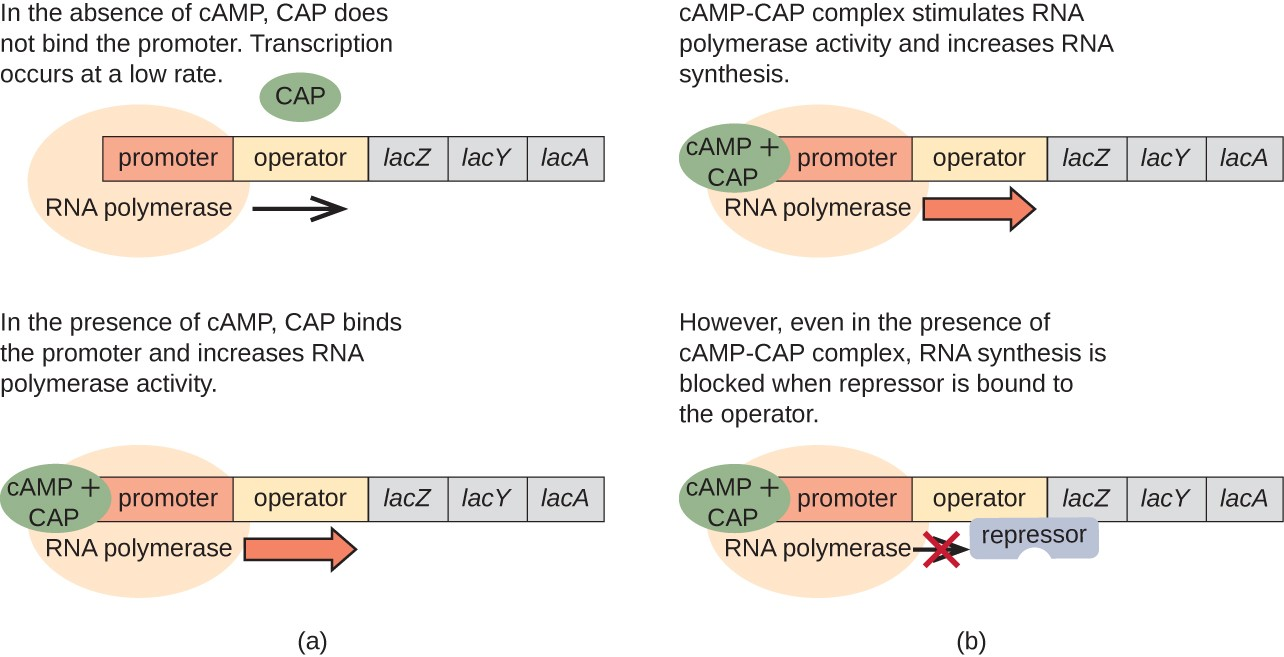
lacI repressor is constitutively expressed but when lactose is present it binds to the lactose repressor
the lac repressor is a tetramer made of 2 dimers
the lac operon has 3 operator sites and in order to repress transcription O1 must be bound with either O2 or O3
in order for the repressor to be bound to 2 regions the DNA must loop in different ways —> this looping of DNA physically prevents RNA polymerase from binding to DNA
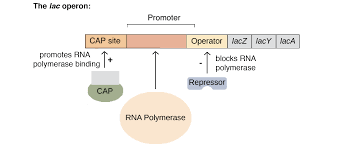
catabolite activating protein acts as a transcriptional activator
NOTE: IPTG mimics allolactose
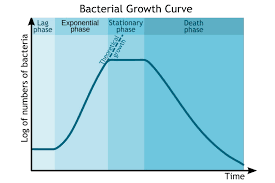
bacterial growth curve
lag phase: cells are getting used to the environment producing diff proteins so theres no oncrease
log phase: use sigma 70 to exponentially increase
stationary phase: plateau in rate of growth —> the death and division rate is equal
death/decline phase: the bacteria run out of resource
regulon
a group of genes that are regulated as a unit
its different from an operon because a regulon could be multiple operons and some individual genes
transcription factors
negative regulation: transcriptional repressors that bind at an operator site within the promoter region
positive regulator: transcriptional activators which interacts with the RNA polymerase binding close by and increases affinity
CAP site
some promoters have low affinity
cap increases affinity of RNA for promoter site
CAP functions when glucose is unavailable
when glucose is low there’s an increase in cAMP which causes the activation of CAP —> lac operon turns on so lactose can be used instead of glucose
when glucose and lactose are high the lac operon is turned on but not producing much protein as glucose is the preferred substrate