PHOrgChem (Lecture) | Module 6 (Part 2: ALIPHATIC, AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS AND ALKYL HALIDES ONLY)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
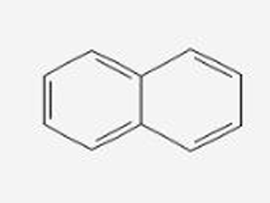
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, consisting two fused benzene rings and it is best known for its strong odor
Strong Odor
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Naphtalene is best known for its?
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: This contains 10 delocalized pi electrons, following the Huckel’s Rule
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Less aromatic than benzene because the delocalization is spread over two ring making it likely reactive
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS:
Melting Point: ~80°C
Boiling Point: ~218°C
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Sublimates easily (solid to vapor) due to weak intermolecular forces.
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Slightly soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents (benzene, ether). TWO-FUSED BENZENE RINGS
Naphtalene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Uses and applications → mothballs are insect repellent, they are a precursor to phthalic anhydride which is used in plastics and dyes, they are also used in glue, fuels, and lubricants as a hydrogen donor-solvent and in organic semiconductors
Naphtalene
Anthracene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS:
Melting Point: ~218°C
Boiling point: ~340°C
Anthracene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Slightly soluble in water but dissolves well in organic solvents like benzene and chloroform.
Anthracene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a chemical formula of C14H10
Anthracene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: It consists of three-fused benzene rings in a linear arrangement
Anthracene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: It is aromatic due to its conjugated pi electron system following the huckel’s rule, this delocalization provides stability but makes it less reactive than non-aromatic compounds. THREE-FUSED BENZENE RINGS
Anthracene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Uses and application → Organic semiconductors, dyes and pigments, scintillators for radiation detection, and precursor to anthraquinone which is used in dyes
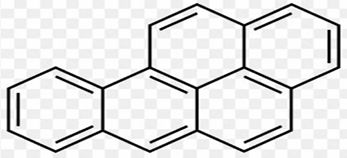
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS:
Melting Point: ~179°C
Boiling Point: ~495°C
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Insoluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents (benzene, toluene, chloroform). FIVE-FUSED BENZENE RINGS
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a chemical formula of C20H12
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: It consists of five fused benzene rings making it highly conjugated and aromatic.
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Like any other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, this follows Hückel’s rule. This extensive pi conjugation makes it thermodynamically stable. However, it may region or the group structure, making areas form high electron density, making some positions chemically reactive.
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Uses and application → used in research to study cancer mechanisms and as an indicator of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution in environmental studies
Benzo [a] Pyrene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS:
Coronene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS:
Melting Point: ~438°C
Boiling Point: Decomposes before boiling
Coronene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Insoluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents (benzene, toluene). SIX-FUSED BENZENE RINGS
Coronene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a structure resembling a benzenoid.
Coronene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: It is considered a "super benzene" due to its six fused benzene rings forming a hexagonal shape.
Coronene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: It follows Hückel’s rule and is highly aromatic with strong pi electron delocalization, making it very stable. Its planar and symmetrical structure contributes to strong pi–pi stacking interactions, which affect its solid-state properties.
Coronene
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: Uses and applications → organic semiconductors, in graphene related materials used in carbon nanotechnology, used in fluorescent, dyes, and UV-blocking materials, used as polymer additives for heat resistance. These compounds can instate the wide applications of aromatics in science industry
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Benzene ring (salicylate structure)
Benzene ring increases stability by delocalizing electron, allowing effective enzyme inhibition, which reducing inflammation and pain.
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Benzene ring (hydroxy & amide substitutions)
Benzene ring enhances lipophilicity, allowing it to cross biological membranes easily
The stable structure prevents rapid degradation it the body
Ibuprofen
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Benzene ring (with carboxyl and isobutyl groups)
Aromaticity of benzene ring stabilizes non-polar interaction with COX enzyme, enhancing anti inflammatory effects which improve drug metabolism and distribution
Diazepam (Valium)
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Benzodiazepine fused ring system
The presence of Benzodiazepine fused ring enhances the binding to GABAA receptors, increasing sedative effects, improves lipid solubility, ensuring faster CNS penetration.
Chlorpromazine
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Phenothiazine core (three-ring system)
The presence of Phenothiazine enhances stability and receptor binding to dopamine D2 receptors and maintains effectiveness for longer duration
Morphine
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Phenanthrene core (three fused benzene rings)
Phenanthrene core provides a rigid structure for opioid receptor binding, which increase stability and bioavailability in the body
Tamoxifen
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Triphenylethylene structure
The presence of triphenylethylene structure, an aromatic ring structure interacts with estrogen receptors blocking estrogen driven cancer growth which enhances metabolic stability
Losartan
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Biphenyl system
Hypertensive drug
The presence of the biphenyl system improves the receptor activity for angiotensin receptors and enhances bioavailability and drug effectiveness.
Sildenafil (Viagra)
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Pyrazolopyrimidine system ●
The presence of pyrazolopyrimidine system enhances binding receptors to phosphodiesterase 5, increasing vasodilation, provide stability and longer lasting effects
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
WHAT DRUG?
AROMATIC RING: Trifluoromethyl benzene system
The presence of the trifluoromethyl benzene system enhances lipophilicity, allowing it to cross the blood-brain barrier and stabilize the drug’s interaction with serotonin transporters.
Stability
HOW DOES AROMATICITY AFFECTS DRUG EFFECTIVENESS: Aromatic delocalization prevents rapid degradation
Lipophocity
HOW DOES AROMATICITY AFFECTS DRUG EFFECTIVENESS: Enhances absorption and Blood Brain Barrier crossing and receptor binding. The electron pi-pi stacking and hydrophobic interactions improves drug target interactions
Alkyl Halides
Organic compounds where a halogen replaces a hydrogen in alkane
Alkyl Halides
Organic compounds where a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces a hydrogen in an alkane
Alkyl Halides
Higher boiling points than corresponding alkanes.
Insoluble
ALKYL HALIDES: ________ in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Alkyl Halides
Undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Alkyl Halides
Participate in elimination reactions.
Halothane
An inhalation anesthetic containing alkyl halides which contributes to its stability and volatility, making it effective as an inhaled anesthetic.