Chapter 14 Brain & Cranial Nerves Review
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
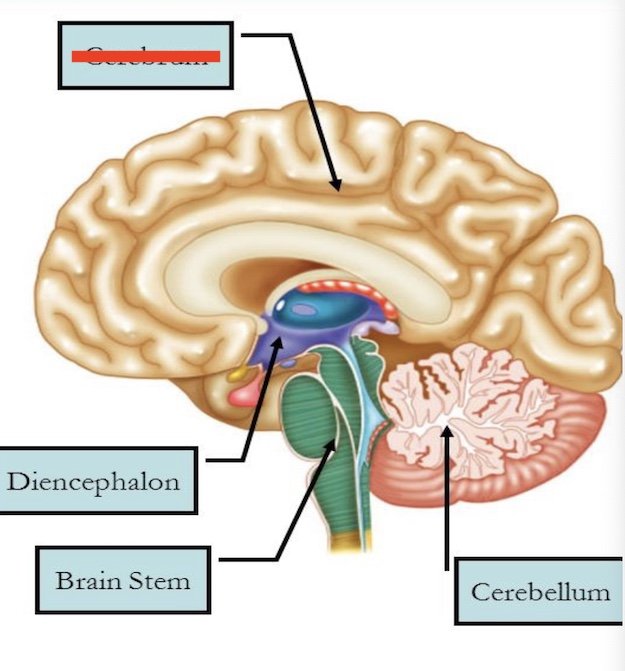
14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
Cerebrum
Controls thinking, movement, emotion, language

14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
Cerebellum
Muscle movement, balance, posture
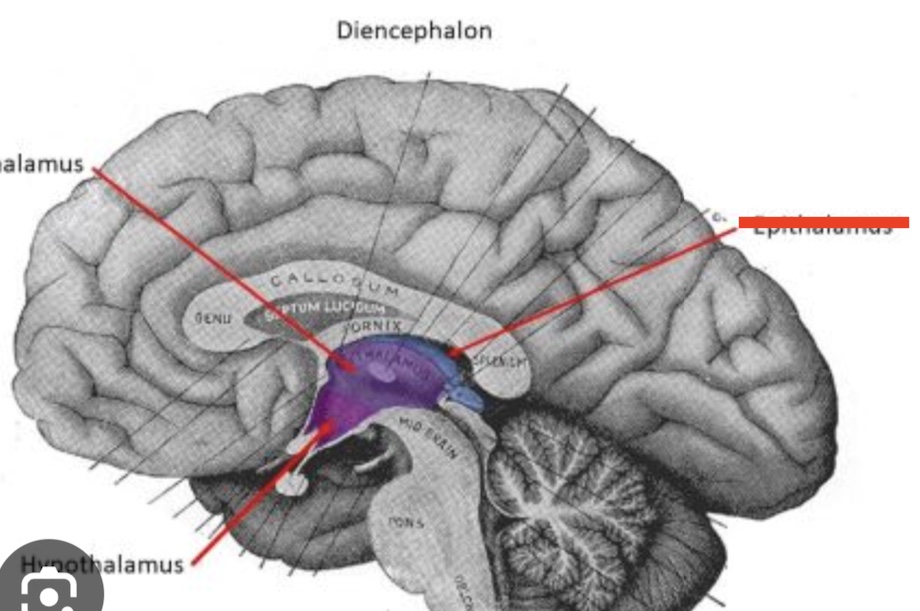
14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
Hypothalamus
Regulates hunger, thirst, temperature, hormones
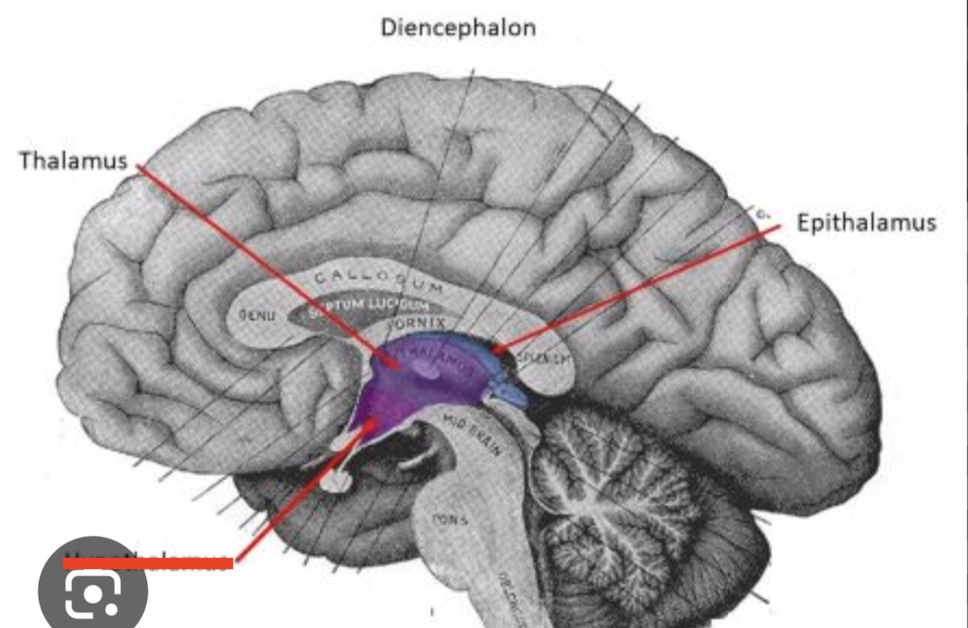
14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
epithalamus
contains pineal gland for melatonin
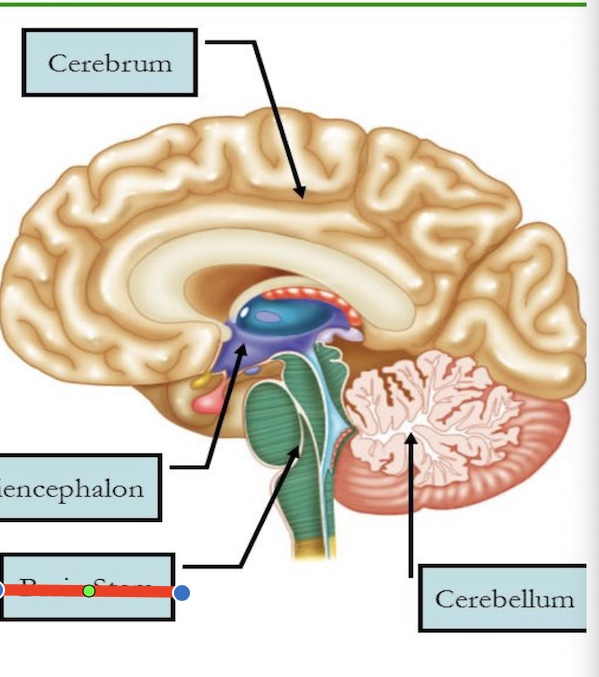
14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
Brainstem
Controls breathing, heart rate
14.1 What does the forebrain become?
Telencephalon / Diencephalon
14.1 What does the midbrain become?
Stays a midbrain
14.1 What does the hindbrain become
Metencephalon
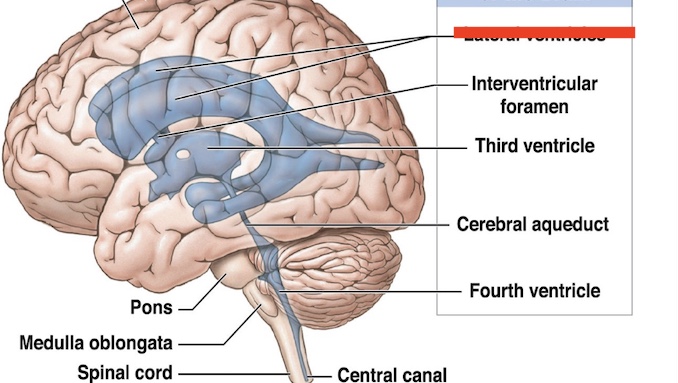
14.1 What ventricle is this? What is the function?
Lateral Ventricle
Produce circulate CSF
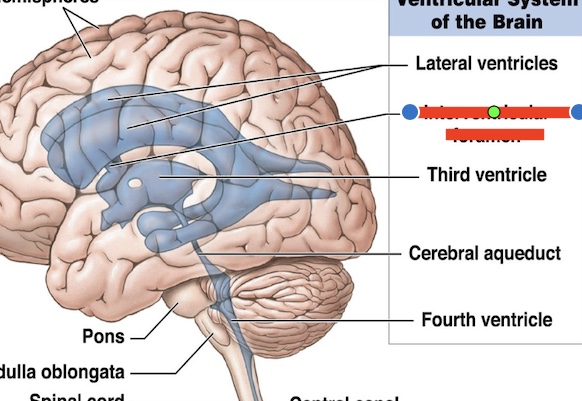
14.1 What is this? What is its function?
Interventricular foramen
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
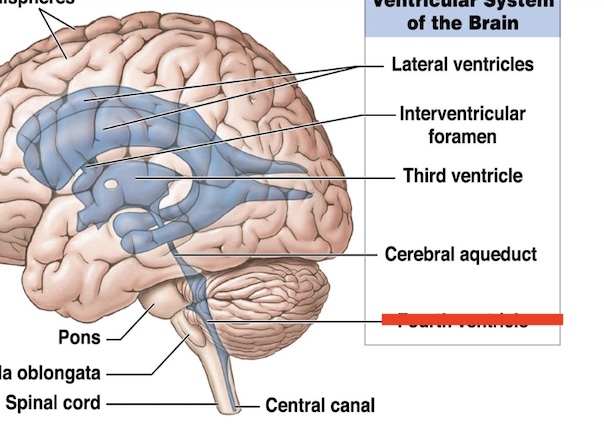
14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
fourth ventricle
Circulates CSF into spinal cord
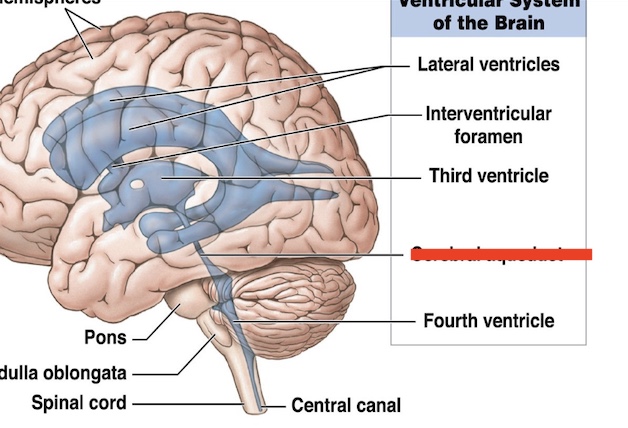
14.1 What is marked? What is the function?
Cerebral aqueduct
connects 3rd ventricle to 4th
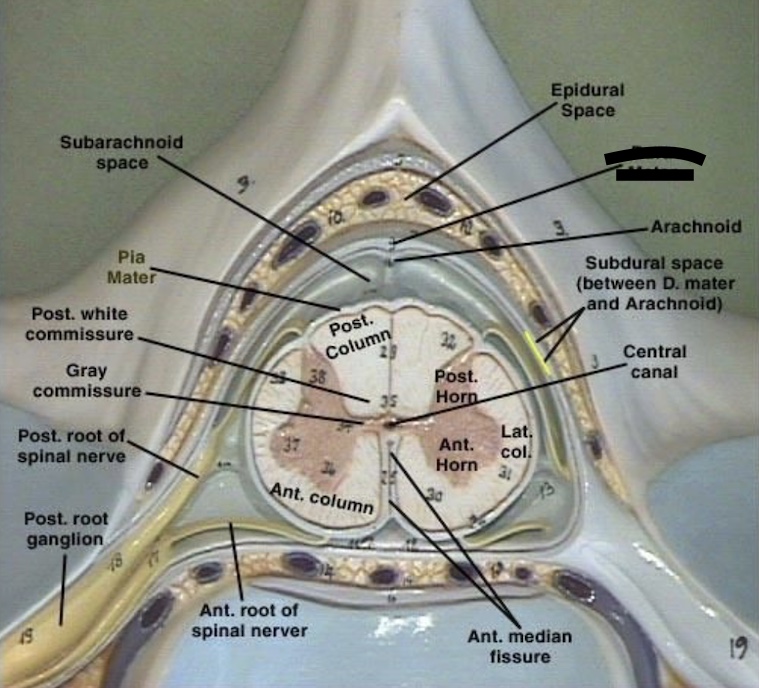
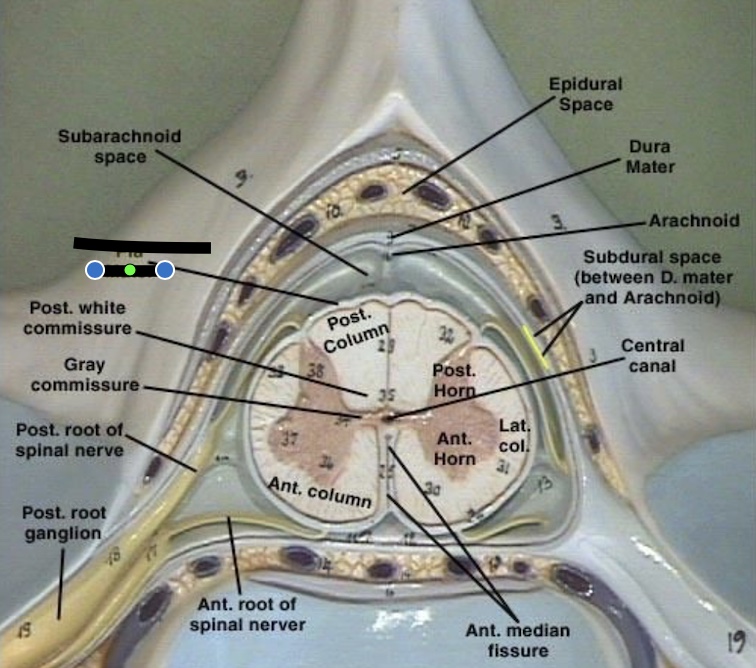
14.2 What layer is this?
Dura matter
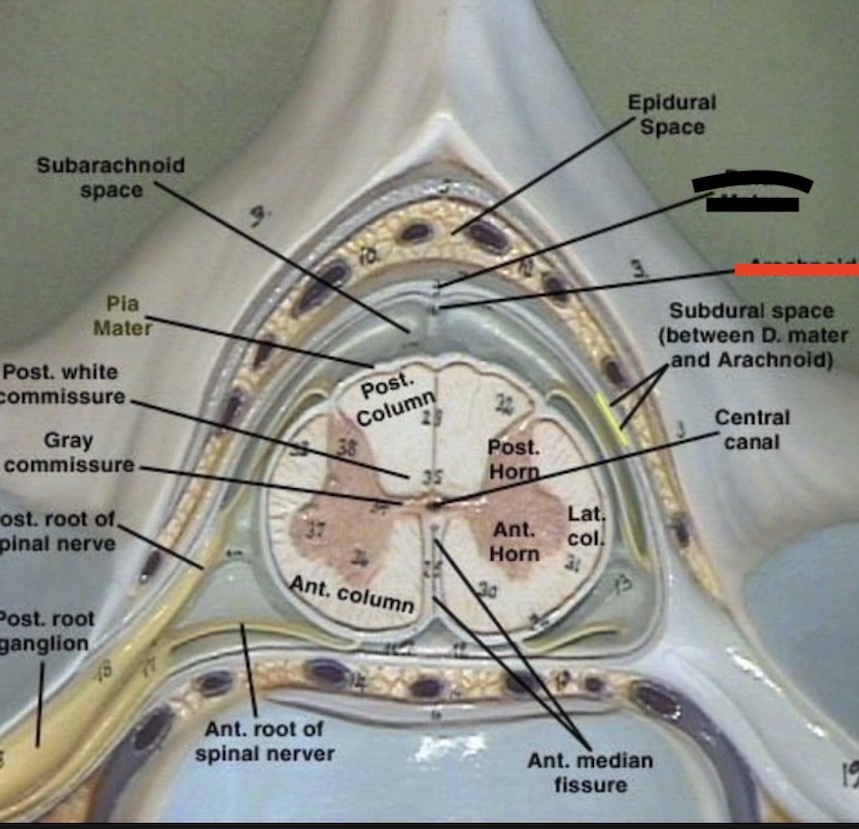
14.2 What layer is this? ( In red )
Arachnoid matter
14.2 What layer is this?
Pia matter
14.2 function of cerebrospinal fluid? Where is it formed?
Surrounds cushions brain / spinal cord
Shock Absorber / circulates nutrients
Choroid plexus
14.3 give some classifications of the medulla oblongata compared to spinal cord?
Wider
Mixed gray / white matter
Cranial nerves (9,10,11,12)
Regulate heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, vomiting.
14.3 give some classifications of the spinal cord compared to the medulla oblongata?
Cylindrical / Elongated
White matter on outside, gray inside
No Cranial nerves, only spinal
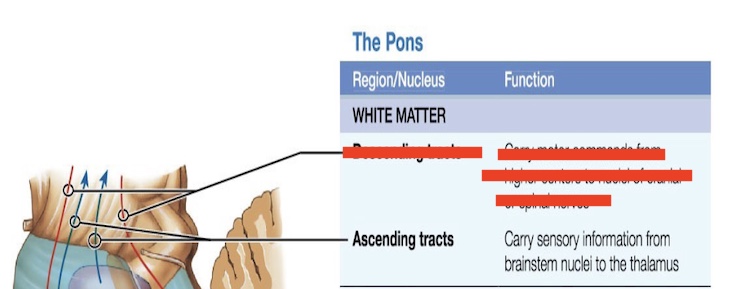
14.4 What is this in the pons? Function?
Descending tract
Carries signals DOWN the brain
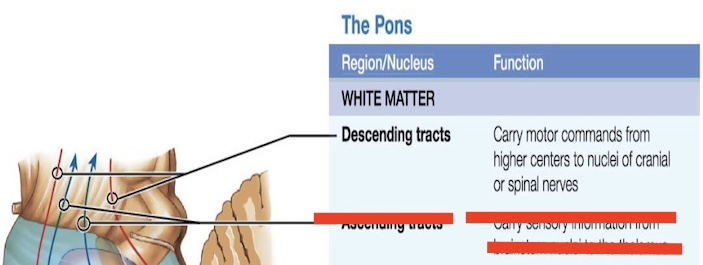
14.4 What is this in the pons? Function?
Ascending tact
Carries signals UP to the brain
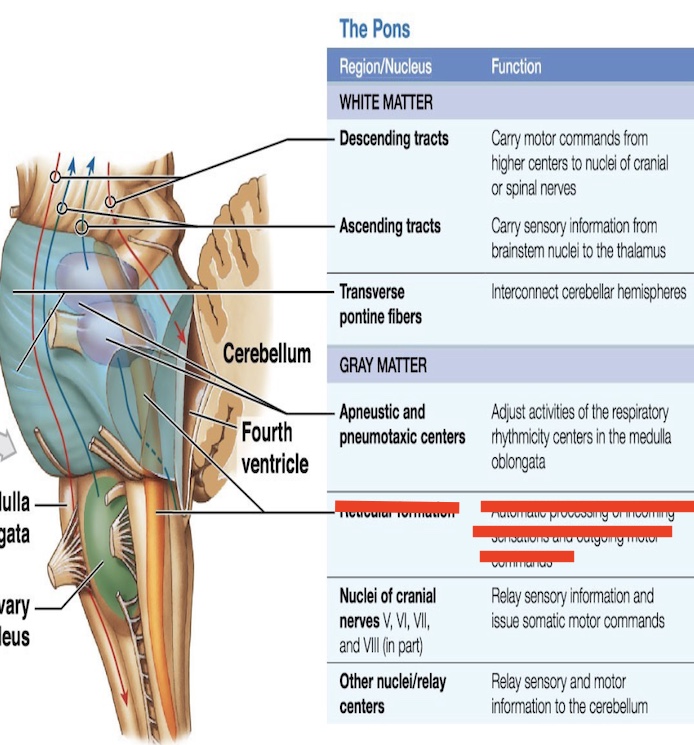
14.4 What is this in the pons? Function?
Reticular forman
Controls alertness, sleep, posture
14.4 What nerves are present in the pons
trigeminal
abducens
facial
vestibulocochlear
14.4 Function of tectum in midbrain
superior colliculi - controls reflexes for vision
inferior colliculi - controls reflexes for hearing
14.4 function of cerebral peduncles in midbrain
carrys messages from brain to body
14.4 function of substantia nigra in midbrain
helps control movement
makes dopamine
14.4 function of red nucleus in midbrain
helps with motor coordination
14.4 cranial nerves in the midbrain
oculomotor - moves eyes
trochlear - moves ONE eye muscle superior oblique
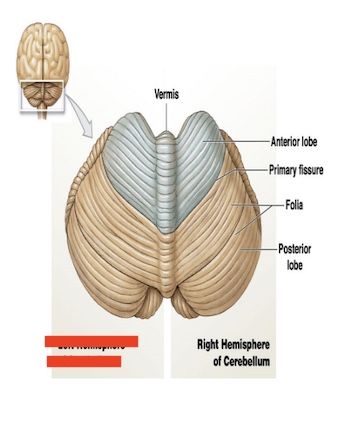
14.6 what is this in the cerebellum? what is its function?
Left hemisphere of cerebellum
control LEFT side of body
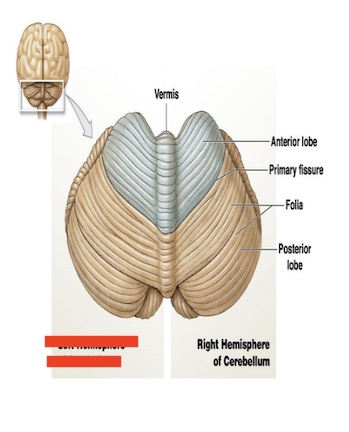
14.6 what is this in the cerebellum? what is its function?
Right side hemisphere
Controls right side of the body
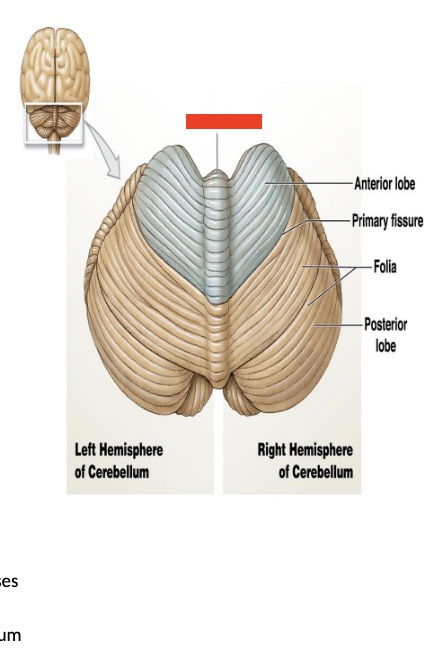
14.6 what is this in the cerebellum? what is its function?
Vermis
seperates the two hemispheres
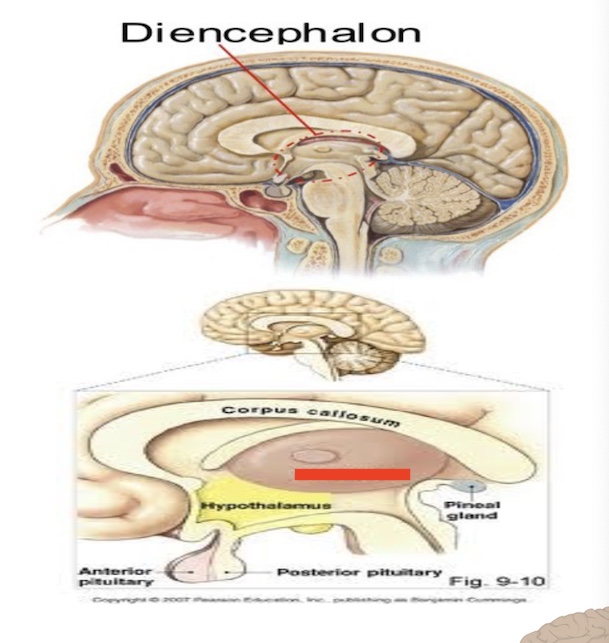
14.7 what part of the diencephalon is this? Function?
Thalamus
Relay, processes sensory info
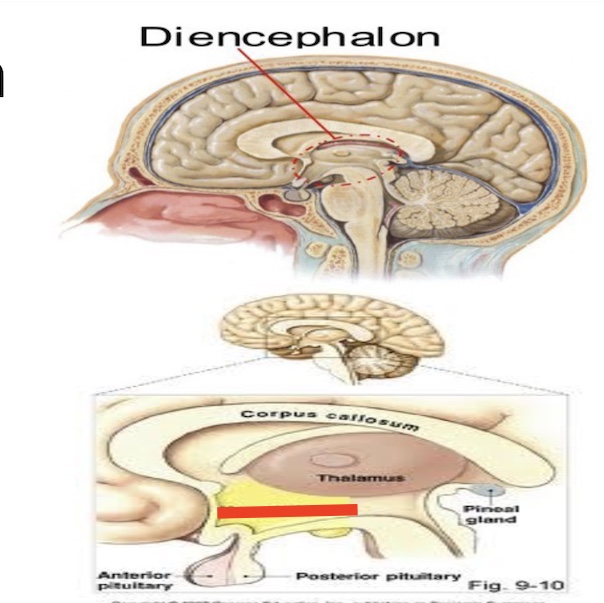
14.7 what part of the diencephalon is this? Function?
Hypothalamus
controls emotions, hormone function, produce hormones that affect pituitarity gland
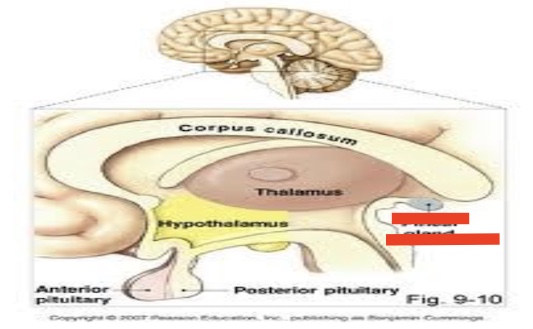
14.7 what part of the diencephalon is this? Function?
Pineal gland
secretes melatonin
14.8 What is the function of the hippocampus in the limbic system?
stores forms memories
14.8 function of amygdala
controls emotions
fear aggression
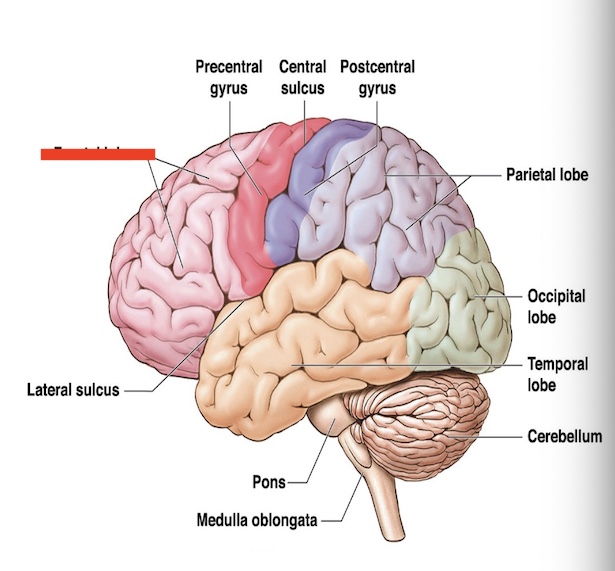
14.9 what part of the cerebrum is this? what is the function?
Frontal lobe
problem solving, decision making, mood
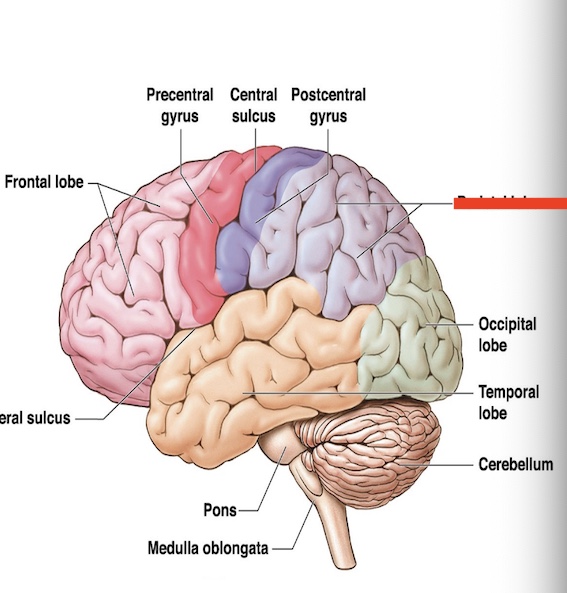
14.9 what part of the cerebrum is this? what is the function?
Parietal lobe
temperature, pain, awareness
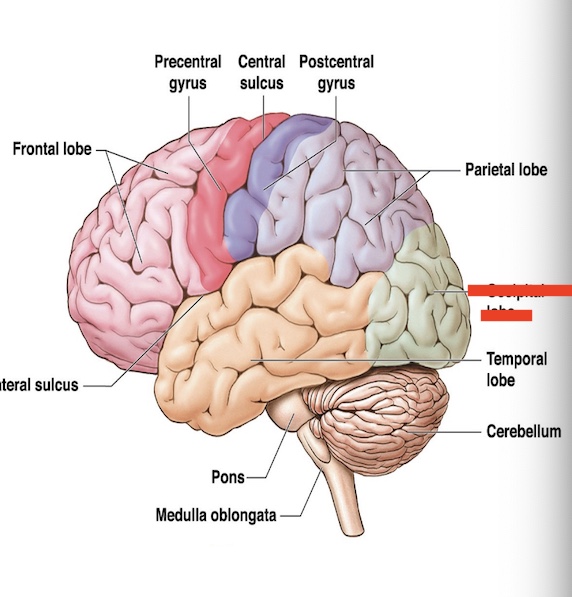
14.9 what part of the cerebrum is this? what is the function?
Occipital lobe
Vision
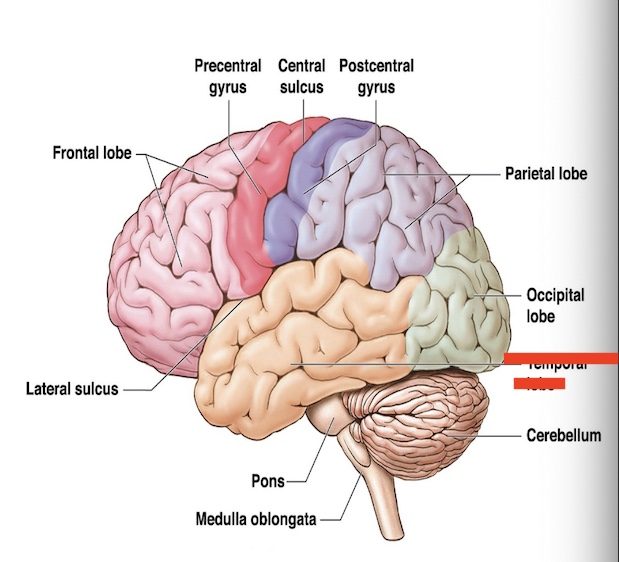
14.9 what part of the cerebrum is this? what is the function?
Temporal lobe
Memory

14.9 Function of lateral sulcus
separates frontal lobe from temporal lobe
14.10
14.10 What type of response is pupillary light reflex? what is the stimulus? what is the response to the light?
type of stimulus - somatic response
stimulus - light shinning in eye
response - pupil constricts, to protect eye from bright light
Optic nerve and oculomotor nerve
14.10 What type of response is corneal reflex? what is the stimulus? what is the response to the touch?
type of stimulus - somatic response
stimulus - something touching the eye
response- blinking of eyelids
Trigeminal / facial nerve
What is your left cerebral hemisphere in control of specifically?
Reading
writing
math
speech
language
decision making
What is your right cerebral hemisphere in control of?
analyzes sensory info
touch, smell, sight, taste
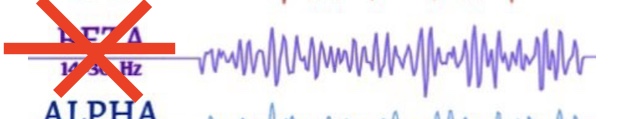
What brain wave is this? Where is it present?
Beta waves
Seen in adults who are concentrating or who are stressed

What brain wave is this? Where is it present?
Alpha waves
Seen is healthy awake adults at rest with eyes closed

What brain wave is this? Where is it present? What can it mean in adults?
Theta waves
seen in children and frustrated adults
Brain disorder in adults

What brain wave is this? Where is it present?
Delta waves
In sleep for infants
In awake adults with brain damage