Genetics & Inheritance Task
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Genetics & Inheritance Task
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
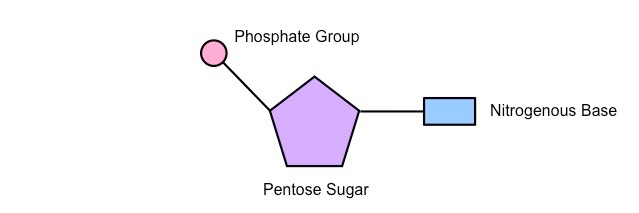
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. It consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What is a nucleotide
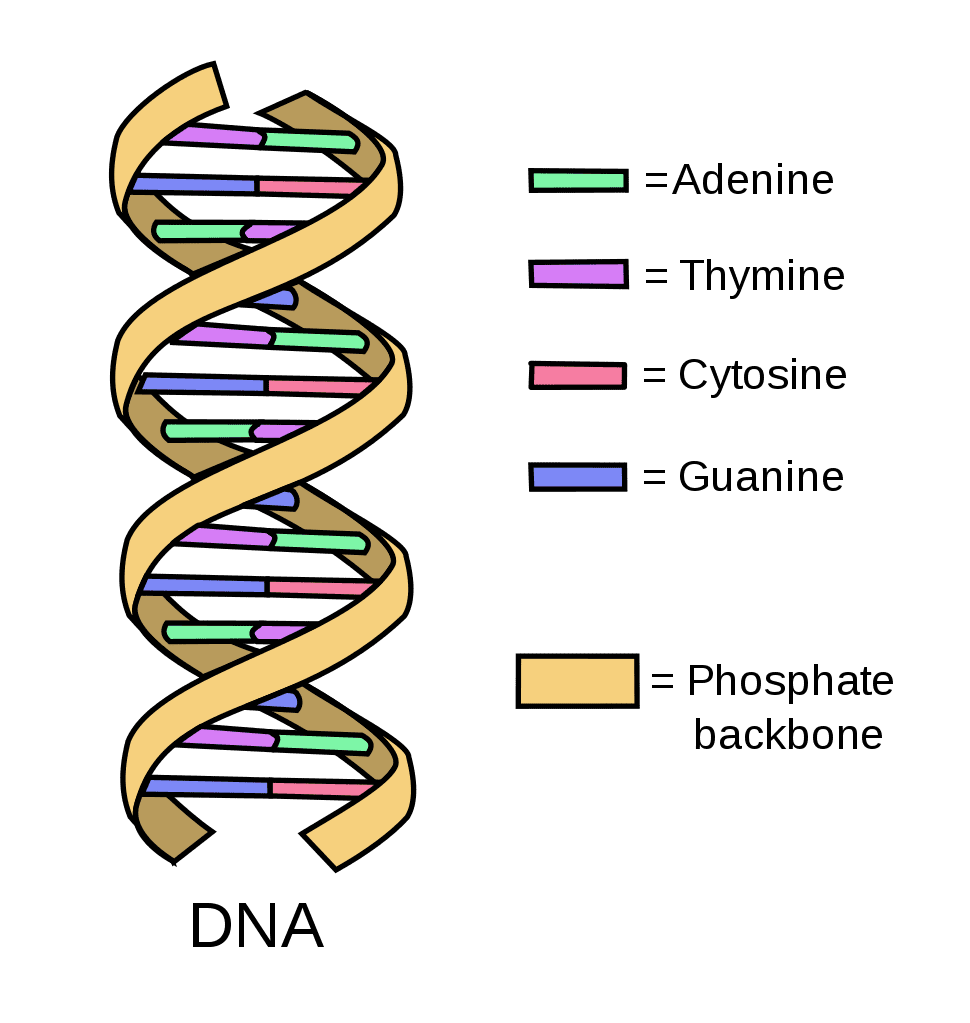
The basic building blocks in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
What are the basic building blocks of dna
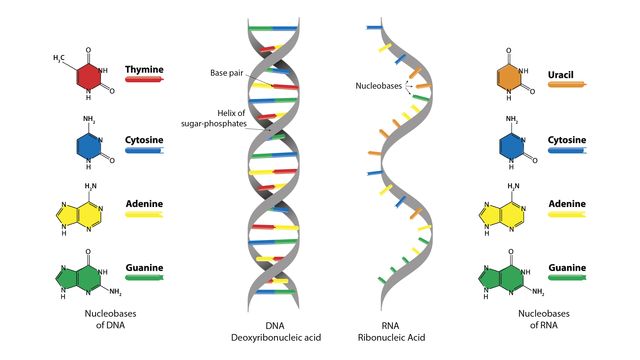
RNA is a single stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of molecules.
what is rna
RNA is used for carrying genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is translated into proteins.
What is RNA used for?
DNA ia a double stranded molecule, what has a long chain of nucleotides, and that carries genetic information.
What is dna
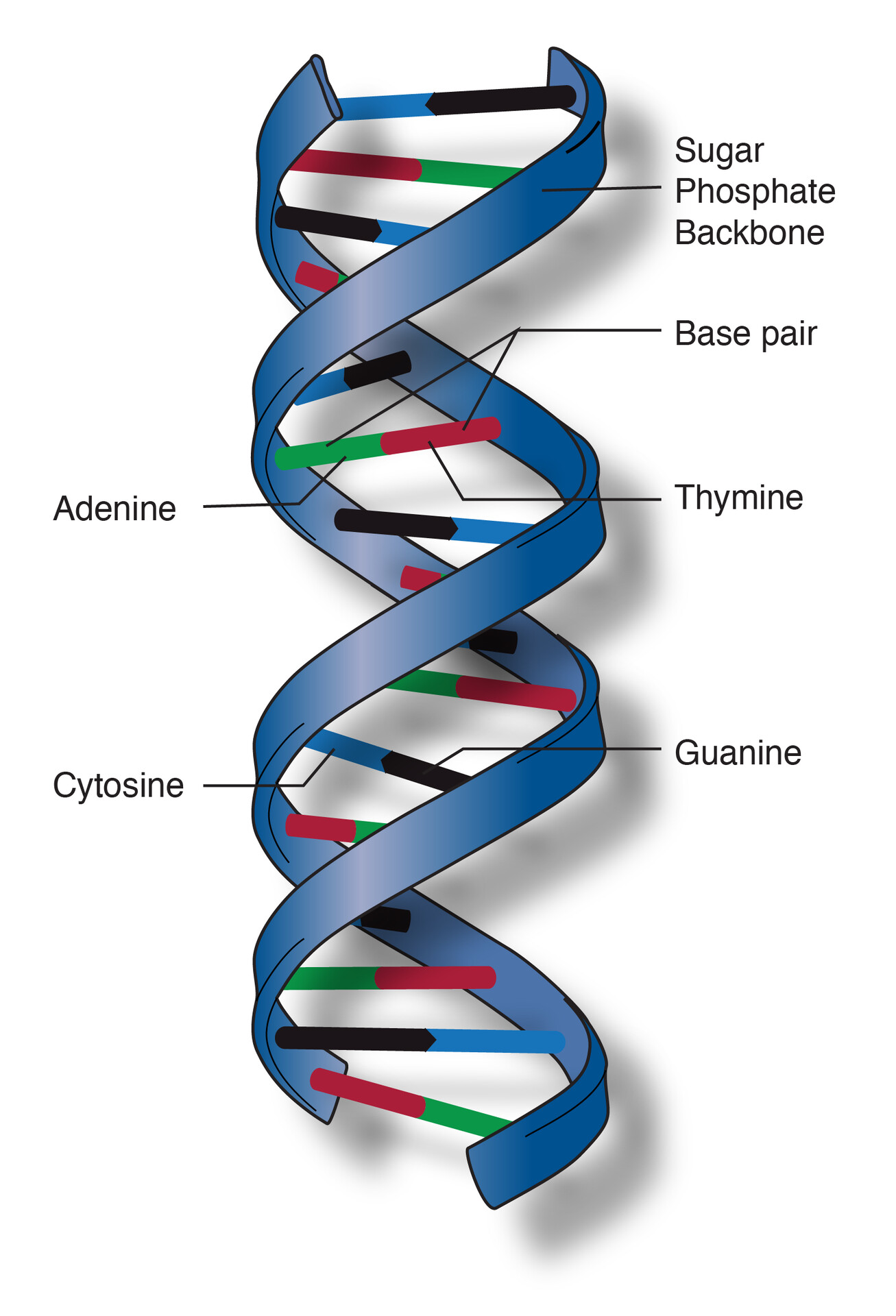
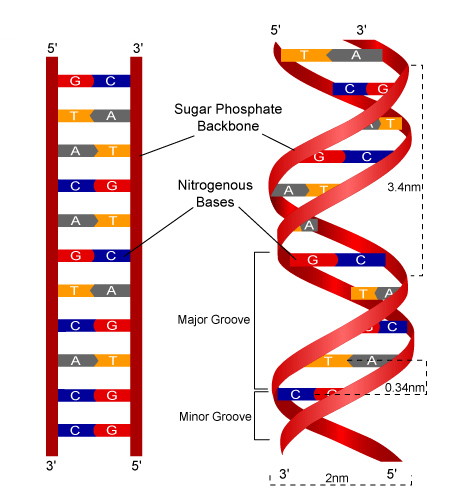
A double helix consists of two chains that twist around each other like a deformed ladder. The rungs connected to the chain are base pairs.
Describe a double helix
DNA molecules are made up of two long chains of nucleotides that form a double helix structure with complimentary base pairings connecting the two.
describe the structure and composition of dna molecules in terms of nucleotides and double helix
Phosphate groups are part of the building blocks (nucleotides) in DNA and RNA. They help form the backbone of the DNA or RNA strand, linking the other parts of the nucleotide together. Phosphate groups are made up of phosphorus and oxygen atoms, and they are important for the overall structure of DNA and RNA.
What are the phosphate groups
Thymine, adenine, guanine, cytosine
what is a nitrogenous base
Deoxyribose sugar is a type of sugar found in DNA. It helps make up the structure of DNA by connecting to phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases. It’s similar to the sugar in RNA but is missing one oxygen atom.
Identify the structure of a nucleotide in terms of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Thymine, adenine
Guanine, cytosine
4 nitrogen bases in DNA
Uracil, adenine
Guanine, cytosine
4 nitrogen bases in RNA
Adenine always pairs with thymine/uracil
Cytosine always pairs with guanine
Complimentary base pairing rule
The four nitrogen bases consist of guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine, with thymine being replaced with uracil in RNA. G and C always pair, and A and T always pair.
Identify the four nitrogen bases and describe the complementary base pairing rule
DNA is a molecule that contains genetic informations. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic, is a very large molecule that contains instructions for building proteins.
what is DNA
Splitting of a cell to form new cells. Cell division allows organism to grow , repair damage, and reproduce.
What is cell division
The parent cell is the cell that divides to form daughter cells.
Parent cell
Daughter cells are the new cells formed by cell division.
Daughter cell
In cell division, DNA replicates itself by the parent cell that divides to form 2 daughter cells.
Identify that DNA copies itself during cell division
made up of more than one cell and are extremely complex
what is a multicellular organism
when one parent cell divides to form two daughter cells (mitosis)
when one parent cell divides to form 4 daughter cells (meiosis)
what is cell division
Vital to keep the organisms alive and to help them grow through cell division
Identify the role of cell division in growth, repair, and reproduction in multicellular organis
a molecule that condenses during cell division
most humen cells contain only 46
sex cells contain 23
what are chromosomes
a double helix formed by nucleotides that is connected by base pairs C-G, A-T
What is the DNA structure
What are the two types of cell reproduction and what do they do
during cell division, the DNA on chromosomes is replicated from the parent cell, which splits into two daughter cells
what is genetic transfer
during cell division, the DNA on chromosomes is replicated from the parent cell, which splits into two daughter cells
Identify that information is transferred as DNA on chromosomes when cells reproduce.
An asexual process in which one parent cell produces two identical daughter cells
What is Mitosis
Mitosis diagram
produces daughter cells and is the cell replication method used form normal growth, tissue repair, generation of tissues, and asexual reproduction
Identify the role of mitosis during the production of new cells for growth and repair.
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes with variation
What is meisos
gametes are sex cells (sperm and egg) that contain half the number of chromosomes a human cell has
what are gametes
Allows for sexual reproduction by making daughter cells with only half the amount of chromosomes as the parent cell
Identify the role of meiosis during the production of gametes (sex cells).
Different form of the same gene
what are alleles
When 2 alleles are the same (RR, rr)
what is homozygous
When 2 alleles are different (Rr)
what is heterozygous
A gene that is observed in the outwards appearance of a heterozygous gene (RR, Rr)
Capital letter = Dominant gene
what is a dominant gene
A trait that doesn’t appear when gene is heterozygous and only seen when homozygous (rr)
Lower case = recessive
what is a recessive gene
Eye colour
Skin colour
Dimples
Hair colour
Attached/ not attached earlobe
State some inherited traits.
Genetic information carried by an individuals and it is also the combination of alleles
what is a genotype
observable characteristics of the way the genotype is expressed
what is a phenotype
Genotype is the combination of alleles while the phenotype is what that code displays
State the difference between genotype and phenotype
The manipulation and genetic modification of genes using technology
define genetic modification
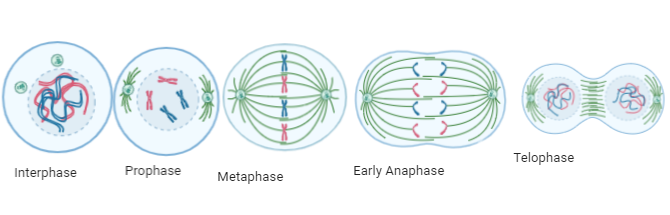
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Stages of Mitosis
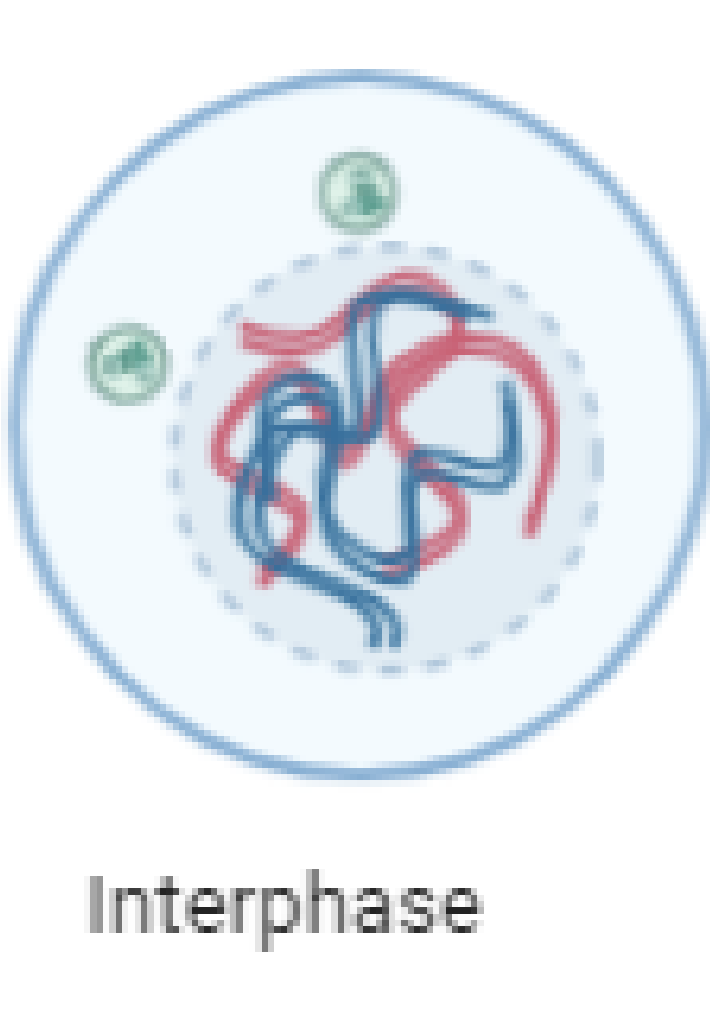
Chromosomes replicate to have 2 chromatids
What is the interphase (draw diagram)
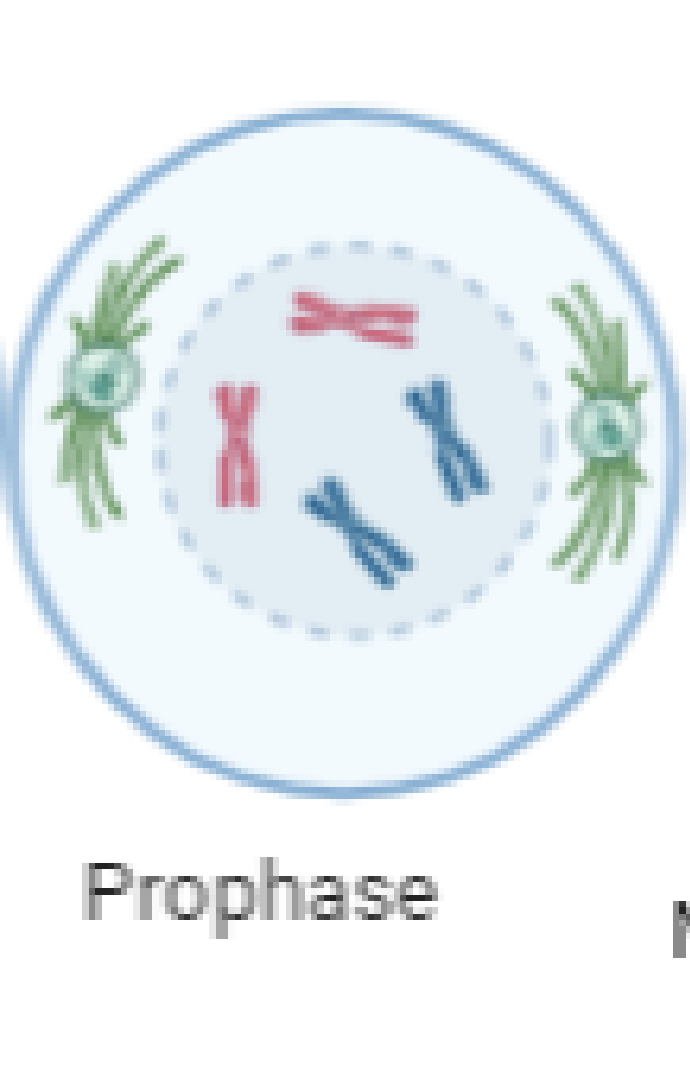
Replicated chromosomes and their chromatids become visible
What is the prophase (draw diagram)
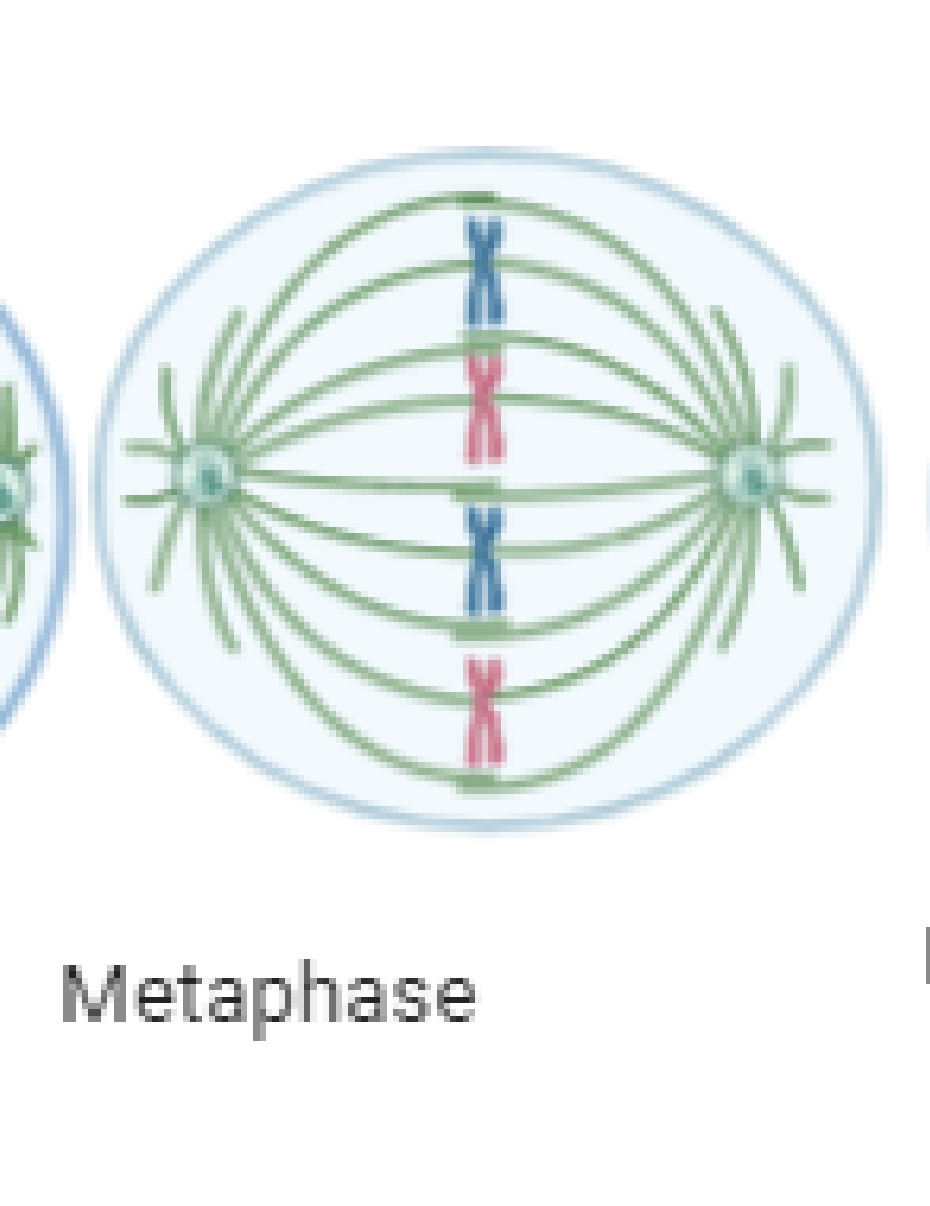
Replicated chromosomes line up along the equator
What is the metaphase (draw diagram)
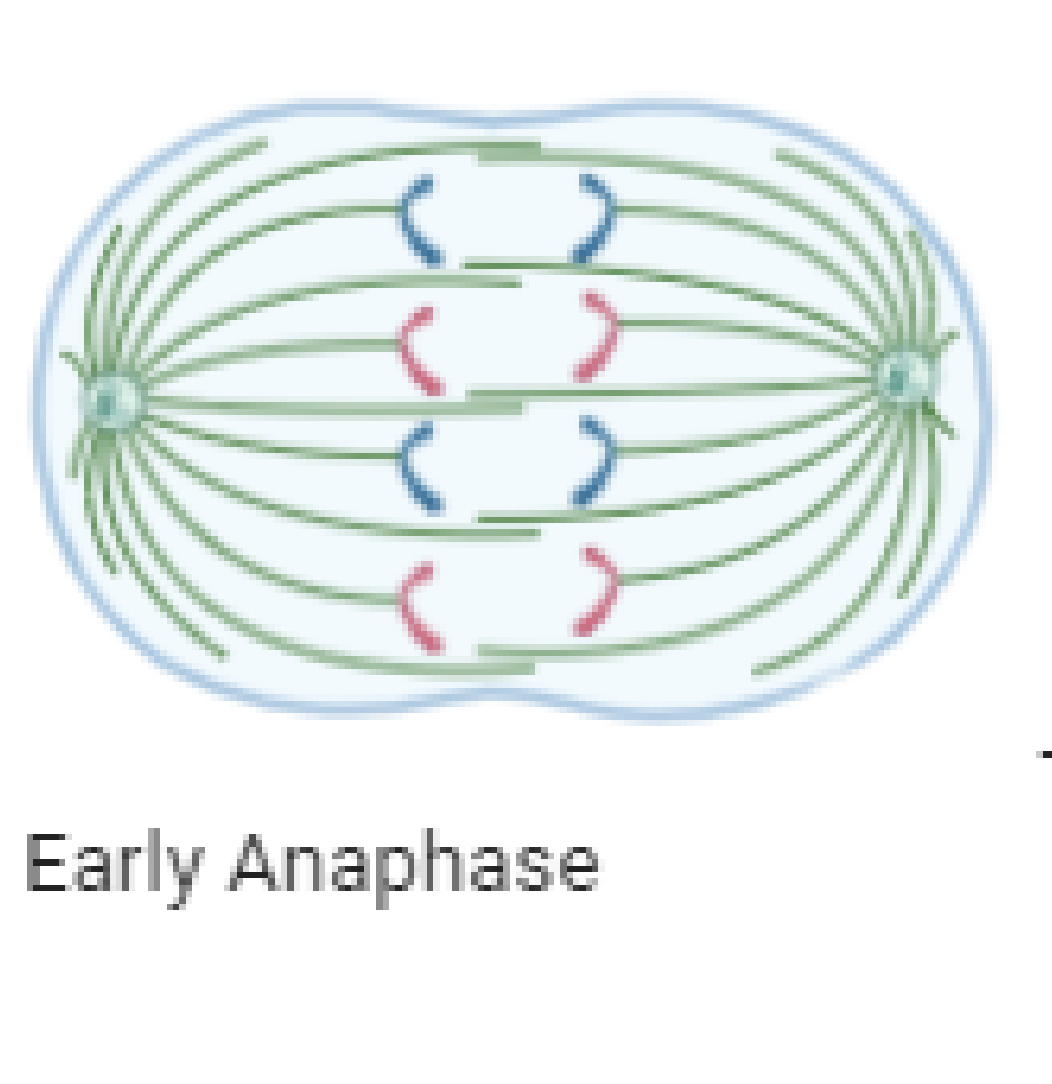
Chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell
What is the anaphase (draw diagram)
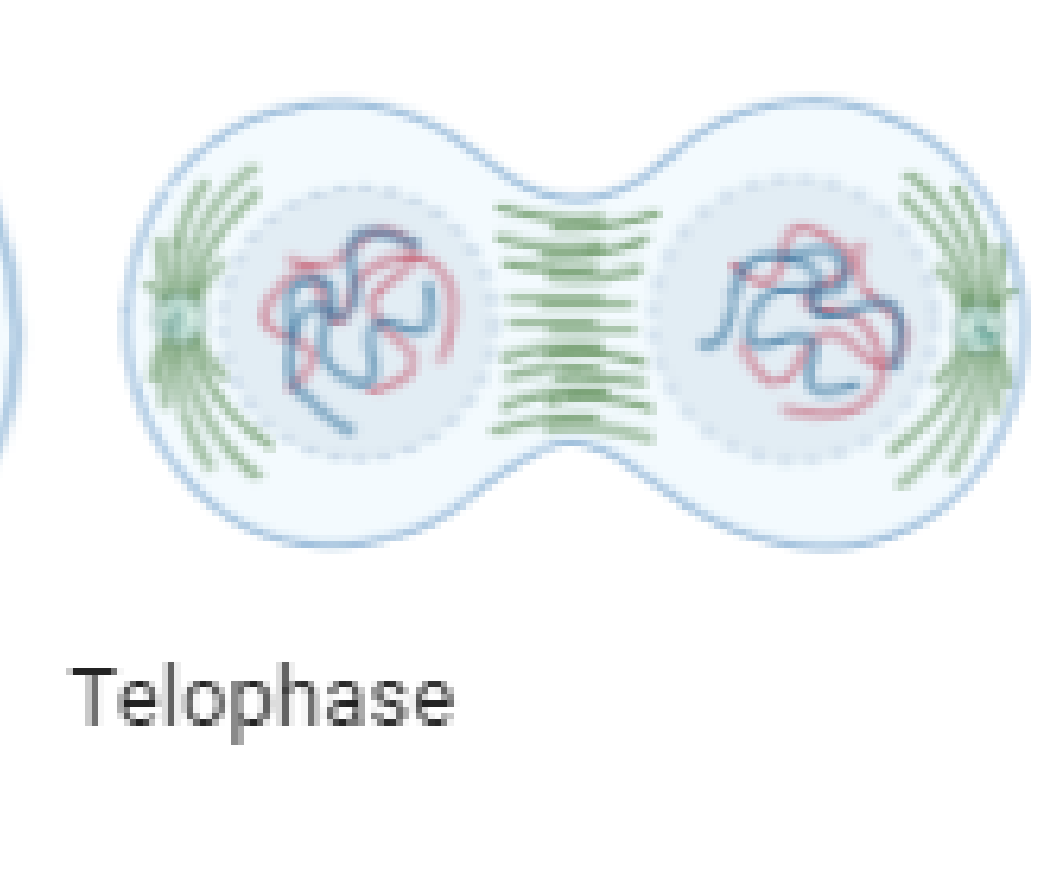
Two nuclei form, each with the same number come chromosomes
What is the telophase (draw diagram)
Cell membranes form, making two daughter cells, each with a nucleus
What is the cytokinesis (draw diagram)
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Stages of Meiosis
Replicated chromosomes form homozygous pairs, attached to spindle fibres and lined up in the middle.
What is the metaphase 1 (draw diagram)
One replicated chromosome of each pair moves to each pole
What is the anaphase 1 (draw diagram)
Two cells are formed, each replicated with 1 chromosome
What is the telophase 1 (draw diagram)
Chromosomes line up along the equator attached to spindle fibres
What is the metaphase 2 (draw diagram)
Chromatids separate and move to poles
What is the anaphase 2 (draw diagram)
4 cells result with half the amount of chromosomes as the parent cell. They are gametes
What is the telophase 2 (draw diagram)
The production of new living organisms by combining genetic information from two different sexes.
What is sexual reproduction
Offspring are produced by a single parent without fertilization or genetic exchange
What is asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves combining genetic information from 2 genders, where as asexual reproduction is without fertilization or genetic exchange
Explain the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction
A gene that is observed in the outwards appearance of a heterozygous gene (RR, Rr)
Capital letter = Dominant gene
Dominant allele
A trait that doesn’t appear when gene is heterozygous and only seen when homozygous (rr)
Lower case = recessive
Recessive allele
A dominant allele can be seen whenever it is in a genotype, whereas a recessive allele can only be seen when the gene is homozygous
Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles
Used to identify changes in DNA sequences of chromosome structure
what is gene testing
Early detection of diseases
Personalised treatment
Understanding inherited traits
Advantages in precision medicine
Advantages of gene testing
Incomplete understanding of complex traits
Psychological impact
False negatives and false positives
Overdiagnosis and over medicalisation
disadvantages of gene testing
Explains how traits are inherited through genes, which are passed from parent to child
Explain gene theory
To develop new products, methods, and organisms intended to improve human health and scociety
What is biotechnology
Research into diseases
Cures for diseases
Medical advancements
Environmental sustainability
advantages of biotechnology
Loss of biodiversity
False hope in finding medical cures
Health risks
Disadvantages of biotechnology
Replication is doubling the DNA and making a copy. It occurs in the nucleus through mitosis and meiosis
What is replication and where does it happen