Muscarinic antagonists
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What neurotransmitter acts on muscarinic receptors?
Acetylcholine
What are muscarinic receptors?
GPCRs activated by acetylcholine.
What are the subtypes of muscarinic receptors?
- M1 (neural)
- M2 (Cardiac)
- M3 (Glandular/smooth muscle)
- M4 and M5 (CNS)
What do muscarinic receptors signal via?
- M1 uses IP3/Ca2+
- M2 uses cAMP
- M3 uses IP3/Ca2+
- M4 uses cAMP
- M5 uses IP3/Ca2+
What effects do muscarinic agonists have on the body?
- Reduce heart rate (bradychardia).
- Vasodilation so redcued blood pressure.
- Contraction of smooth muscle in the gut and bronchi. NO contraction of vascular smooth muscle.
- Pupil constriction of eyes.
- Increased secretion of enzymes and hormones from glands.
Are muscarinic antagonists selective?
Not selective
What are examples of muscarinic antagonists?
Based on acetylcholine:
Ipratropium
Tiotropium
Hyoscine
What effects do muscarinic antagonists have on the body?
- Increased heart rate (tachychardia).
- Relaxation of smooth muscle
- Pupils dilate.
- Secretion of enzymes and hormones is inhibited.
What are clinical uses of muscarinic antagonists?
- Asthma and COPD, ipratropium.
- Motion sickness, hyoscine hydrobromide.
What are side effects of muscarinic antagonists e.g., ipratropium?
-Dry mouth and skin.
- Palpitations, arrhythmias, tachycardia.
- Urinary urgency and retention.
What are the clinical uses of muscarinic agonists?
- Glaucoma treatment, Pilocarpine.
- Dry eyes and mouth.
- Urinary retention treatment - Bethanechol.
How do muscarinic antagonists e.g., Ipratropium and Tiotropium, work?
They block muscarinic receptors which inhibit acetylcholine binding to them preventing contraction of smooth muscle leading to bronchodilation reducing asthma and COPD symptoms.
What is an example of a LAMA?
Tiotropium (Spiriva)
What are issues with muscarinic antagonists?
- They are non-selective so there are lots of side effects e.g., dry mouth, constipation.
- They have lots of cautions like glaucoma and prostatic hyperplasia.
What are counselling points of using muscarinic antagonists?
- Should be carried with patient at all times.
- Use regularly
- Use a mouth peice as can be harmful if it makes contact with the eyes.
What can affect agonist activity to muscarinic receptors?
- Charged Nitrogen group.
- Substituents on charged nitrogen.
- Changing the length of the molecule.
- Substitution of group at the α and β position.
- Presence of hydrogen bond acceptor.
- Ester substituents
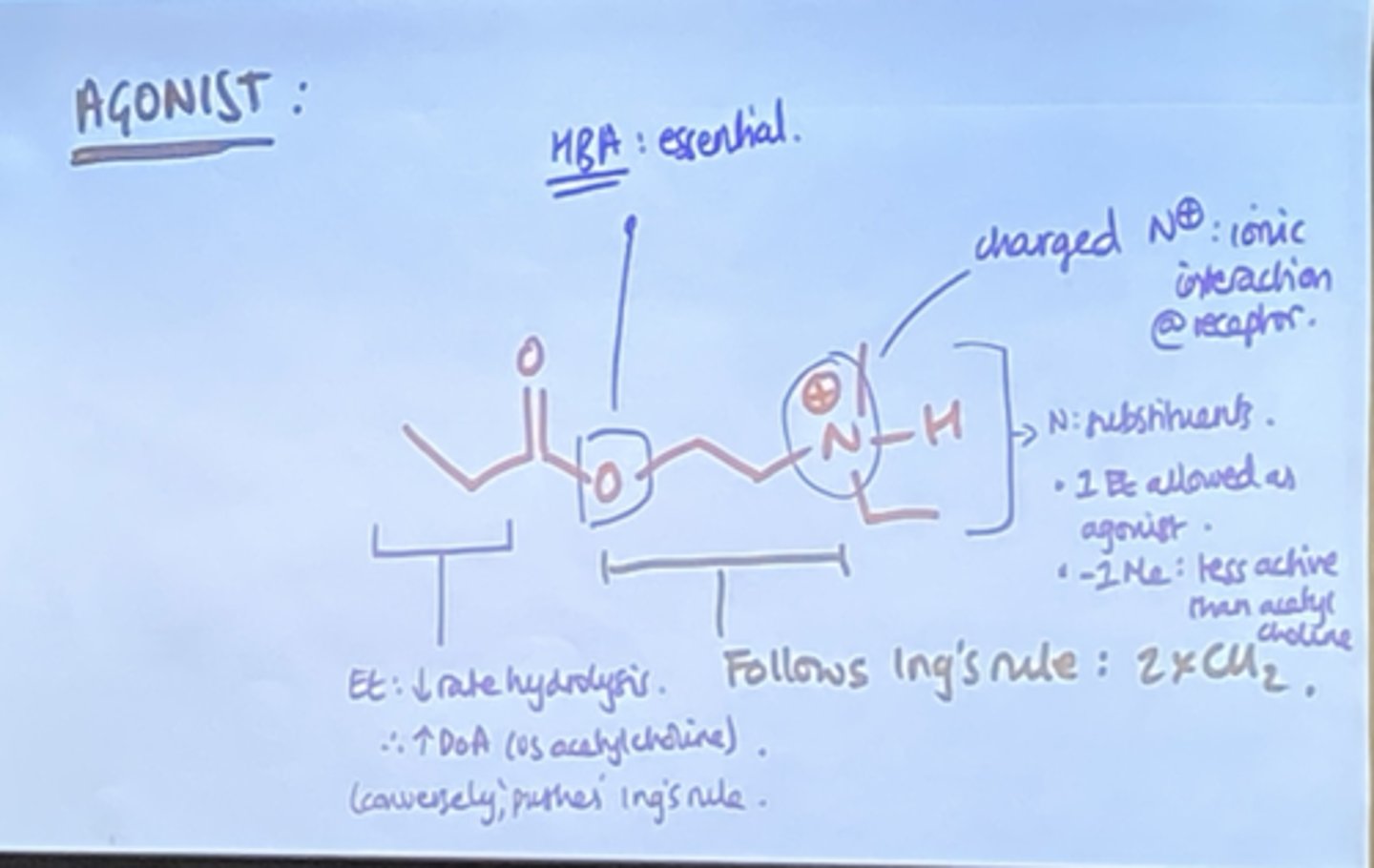
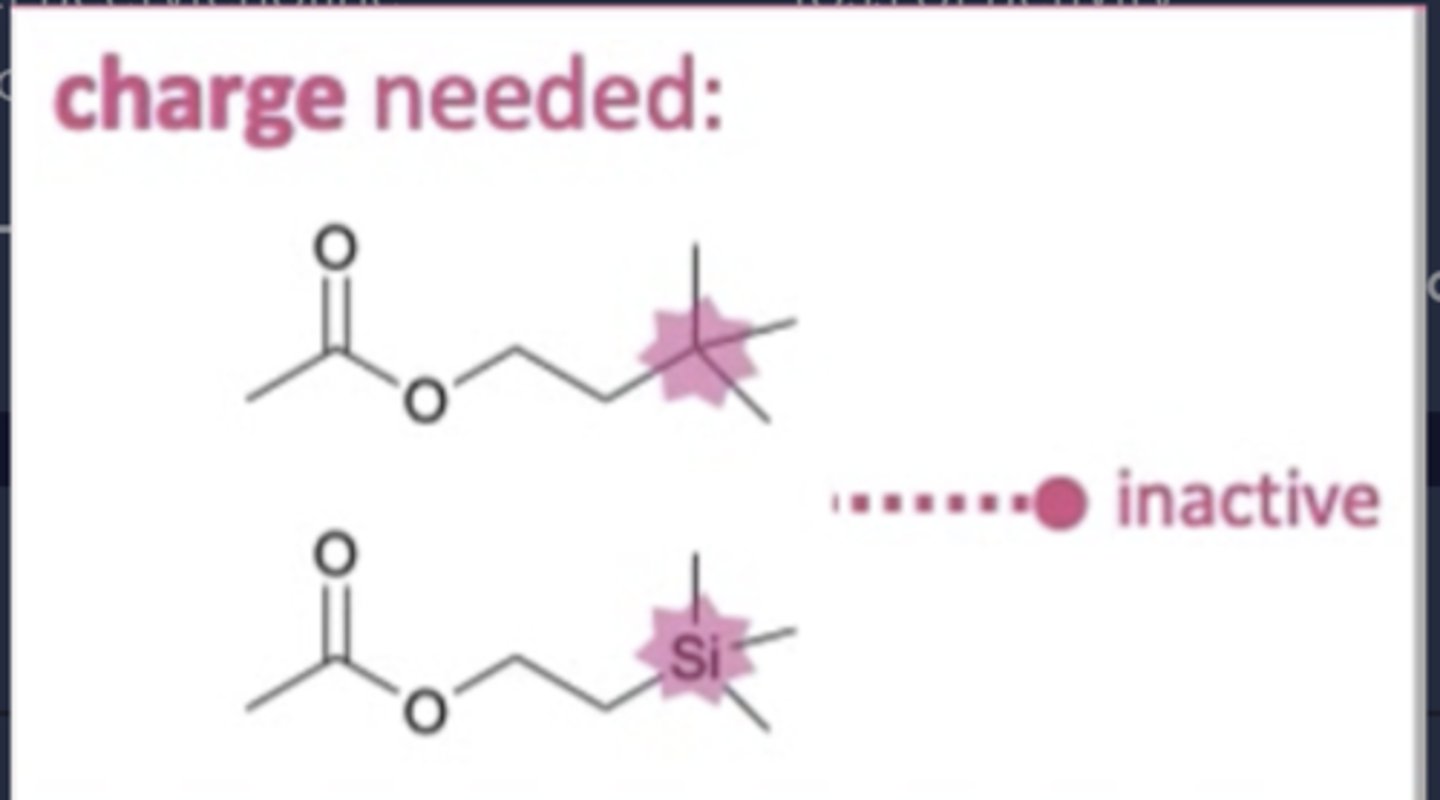
How does the presence of a charged nitrogen group affect agonist activity to muscarinic receptors?
- Essential to agonist activity.
- Allows ionic interaction with muscarinic receptor.
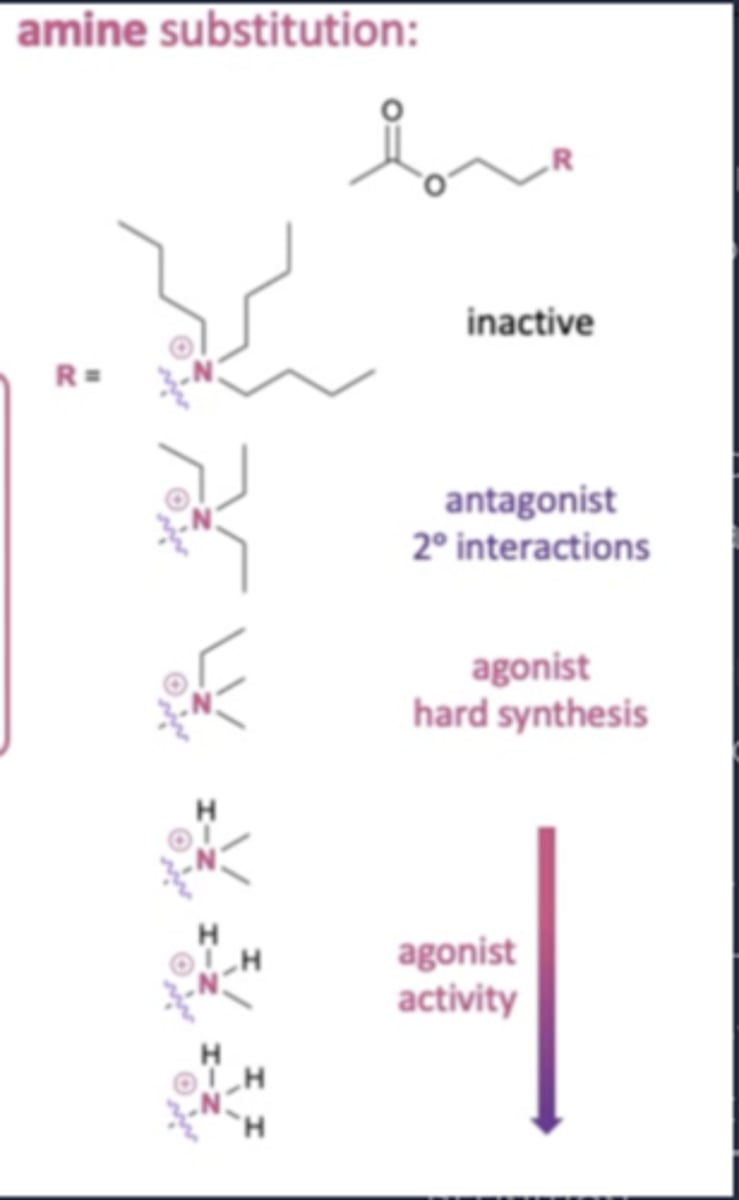
How does changing the substituents on the charged nitrogen affect agonist activity?
- Increasing length of substituents too much leads to a loss of activity.
- Agonist activity increases with removal of alkyl groups.
What is Ing's rule of 5?
A molecule must have no more than 5 atoms between the N-atom and terminal H-atom in order to exhibit muscarinic agonist activity.
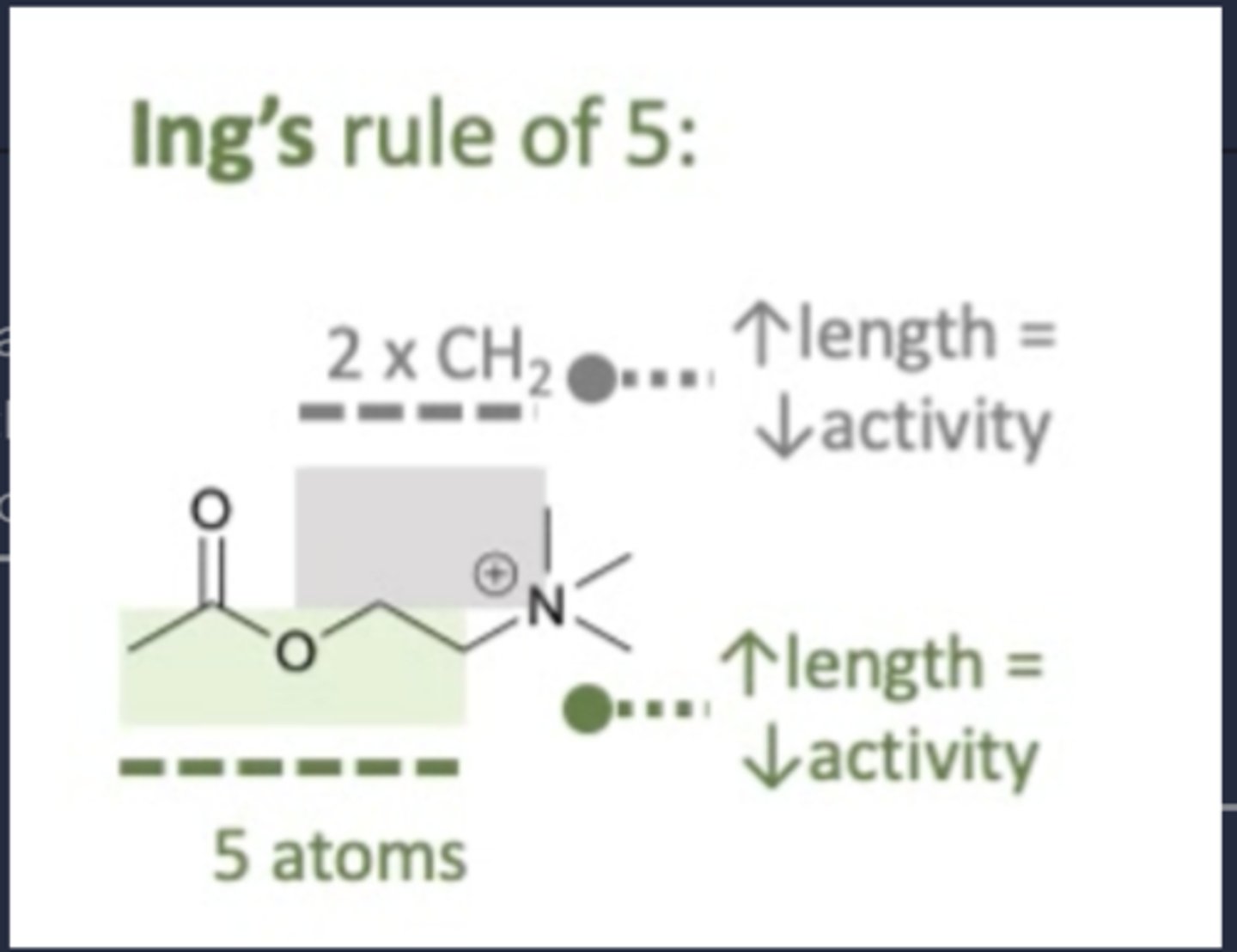
How does changing the length affect acetylcholine selectivity to muscarinic receptors? (agonist)
- Increasing the length of the molecule decreases the selectivity to the receptor as it breaks Ing's rule of 5.
- Allows molecule to fir into T-shaped receptor.
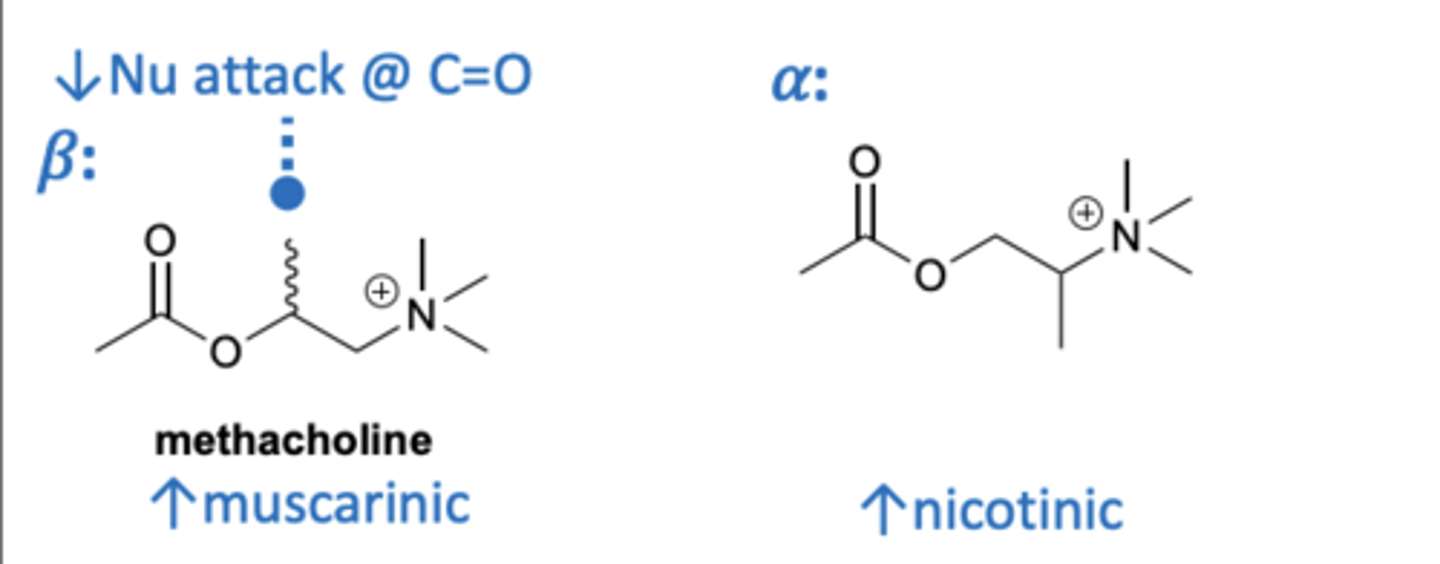
How does substitution of group at the α and β affect acetylcholine selectivity to muscarinic receptors? (agonist)
- Substituting a molecule at the β position increases muscarinic selectivity by reducing chances of nucleophilic attack of the carbonyl.
- Substituting a molecule at α position increases nicotinic selectivity.
What groups can increase antagonist activity to muscarinic receptors?
- Charged Nitrogen atom.
- Alkyl groups on charged nitrogen.
- Hydrogen bond acceptor (oxygen).
- Obey's Ing's rule of 5.
- 2 aromatic compounds
How does a charged nitrogen increase antagonist activity?
- Essential to antagonist activity.
- Allows essential ionic interaction with muscarinic receptor.
How does alkyl groups on charged nitrogen increase antagonist activity?
- Increases size of molecule.
- The bulkier the group the better.
How does the hydrogen bond acceptor increase antagonist activity?
- Essential to activity
- Must be a lone oxygen e.g., ester or epoxide.
- Allows hydrogen bond with muscarinic receptor.
How does obeying Ing's rule increase antagonist activity?
- Essential to activity.
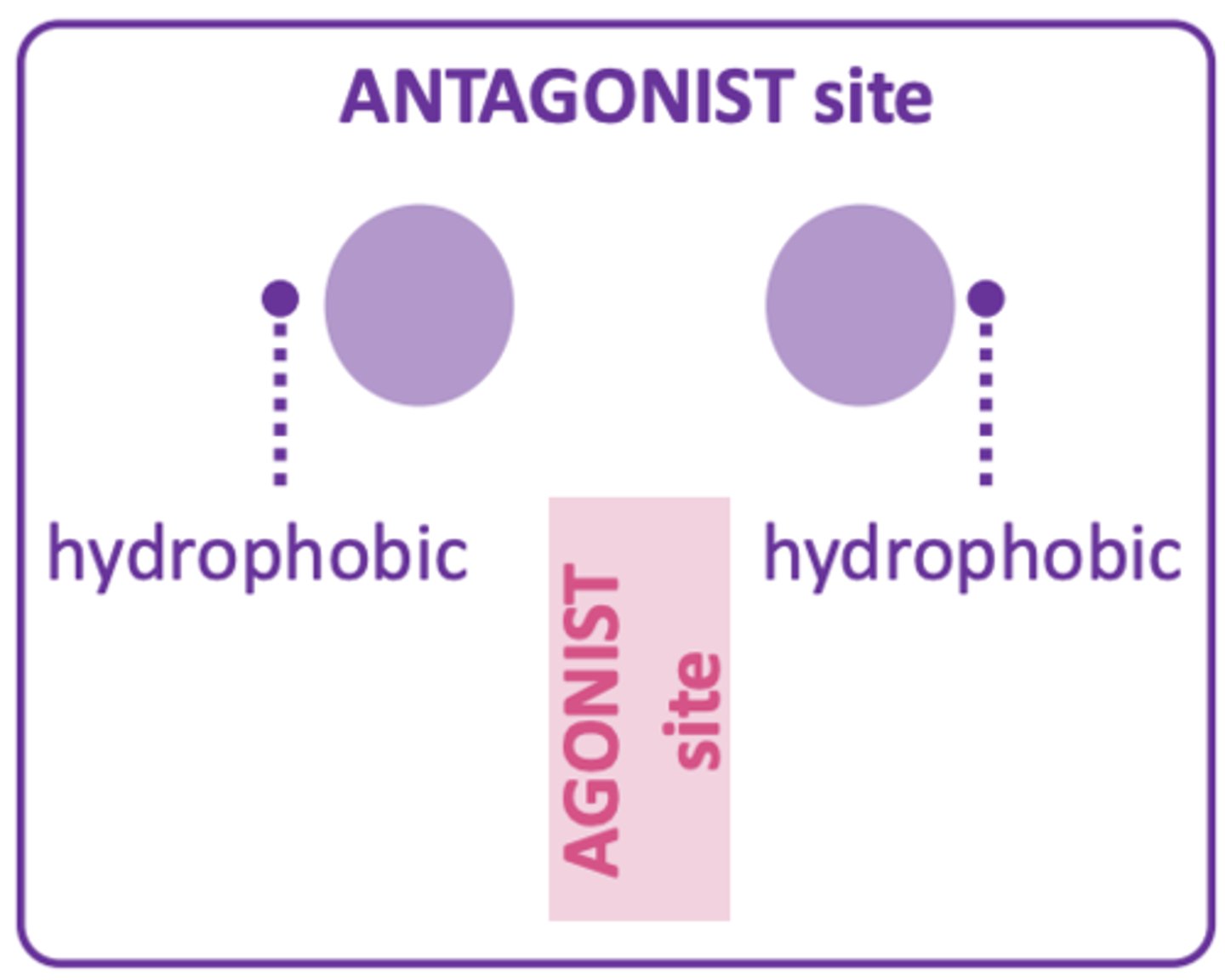
- Allows molecule to fit into the T-shaped receptor between hydrophobic pockets.

How does having 2 aromatic groups increase antagonist activity?
- Not essential to have 2 aromatics but increases activity if there are large groups.
- Allows molecule to fit into the hydrophobic pockets of antagonist site.
- Activity decreases if groups are bigger or smaller than 2 aromatics.