Internet marketing
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Stockholm university
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
Explains why people choose to adopt technology or not
Relies on two fundamental variables to explain resultant behaviour:
“Perceived usefulness”
“Perceived ease of use”
Social contagion
Explains social influence on decision making
If an increasing number of people start using a particular technology, it will be harder for those not using the technology to resist adopting it
Two main types:
Social contact - having close friendships with other individuals/groups
Vicarious learning - individuals learn from observation
Uses and gratifications theory (UGT)
Individuals actively seek out media to satisfy needs or desires
Someone looking for entertainment will choose media platforms that deliver that experience
Classifies gratification into four categories:
Diversion: seeking entertainment, escape or emotional release
Personal relationships: seeking information useful for the maintenance of personal relationship
Personal identity: watching similar others and seeking validation through this
Surveillance: satisfying curiosity about what happens around them
Social information processing theory (SIP)
Explains how individuals make decisions and form attitudes in social context
Online relationships can become as strong or stronger than face-to-face ones: called this term “hyperpersonal communication”, and is the result of four effects:
Information exchanged is of shared interest; receiver develops a sense of similarity with sender
Receiver controls the image he wishes to portray; disclosing socially desirable traits
Communication is time-delayed; sender can reflect upon and edit messages
Pre-existing impressions; if A has the impression that B is friendly, A is likely to send a friendly message
In-game advertising (IGA) and Advergaming
Placing products or brands within the context of a game
Ads on side of the football pitch
Advergaming is a hybrid between advertising and gaming
Aim to entertain and engage players to create emotional connection between the brand and the player
Games are frequently played many times - allows the player to be exposed and interact with the brand for a long time
Has strong positive effect on WOM
Theoretical models: Advergaming & IGA
Social cognitive theory
Learning by observing others
Limited-capacity model of motivated mediated message processing
Once an individual is oversaturated with stimuli, information can no longer be successfully processed or recalled
Attention is divided into primary task (playing the game) and secondary task (paying attention to the commercial message)
If the game is perceived difficult then all cognitive resources go to the primary task, leaving not enough resources available for the secondary task
Flow
A mental stage where an individual i fully immersed in a task, feeling in complete control
Flow distract from brands in the game, leading to low brand recall
Gamification
A process of applying game-like elements to non-game activites to make it more engaging, fun and motivating
Duolingo
Relies on two strategies:
Include rewards for completing tasks
Competition with friends to get users engaged and motivated
Mobile device-based websites
Ease of use is more important for mobile devices in relation to traditional websites
CCT stages
Pre-consumption stage
Purchasing stage
Core consumption stage
Remembered consumption stage
Online purchasing decision (steps)
Five stages
Awareness of need
Search for more information
Evaluation of alternatives
Actual purchase decision
Post-purchase contact with firm
Consumer behavior online
Once firms have an understanding of who is online, they need to focus on how consumers behave online
Clickstream behavior
Refers to the path a user takes while clicking through a website/app, until a final decision to purchase - or not
Attention and shelf space in e-commerce
In e-commerce, shelf space is an “unlimited” resource
Shelf space disappears as a limiting factor
But “attention costs” remain in e-commerce
Subcultures of consumption
Groups with a communal commitment to a particular brand, product or other consumption activity
Tribes or brand communities
Brand community
A community based on a structures set of social relations amongst admirers of a brand
Tribes
A community based on a structured set of social relations and shared behaviors, also expressed or experienced through the consumption of shared products of symbolic meaning
Tribes are broader
Bound together through social connectedness
Service dominant logic
Theory argues that modern consumption i no longer focused on tangible resources and goods.
Focus has been replaced by the on the co-creation of value through service
The interaction between producer and consumer
Linking value
The “social links” a product or brand creates between individual tribe members at a communal level
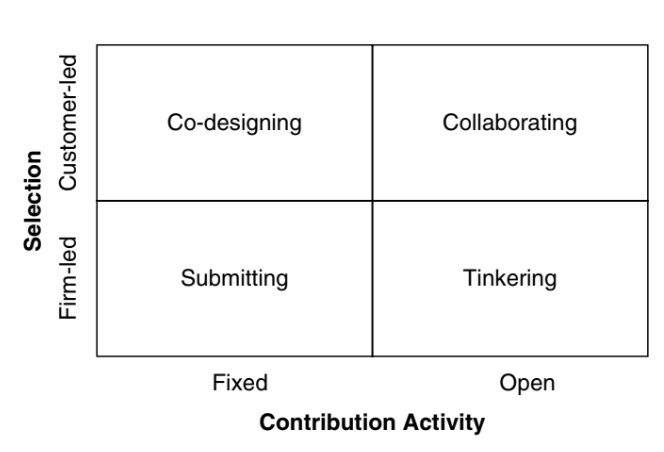
Commercial co-creation
Collaborating
Customers regulate the production of value
Contributor have the power to make change to the basic structure of the product
Tinkering
Allows consumers to use products in a fairly open way and customise the core product, but the organisation still remains in close control of the core product
Google maps
Co-designing
Allows a group of customers to contribute to products, with the final contribution being selected again in an open fashion by all customers
Submitting
Design contests where the organisation decides on the final winner
Co-creation
When a company and its customers work together to create value
Leads to increased brand loyalty and more fulfilling consumer-brand relationships
Customers achieve psychological satisfaction through being creatively engaged in the creation process
Anti-consumption
Anti-consumption society
Groups who try to remove themselves from a consumption society by actively reducing consumption to only essential consumption
Can also be expressed through actively consumption of competing brands
Selective consumption
Consuming certain products linked with causes they support, not consuming products that oppose their personal values
Conservation
Members reduce consumption often of specific products based on personal values
Rejection of brand hegemony
Groups create a community resulting from frustration from major brands
Creating their own brand or boycott
Critiques of co-creation
Asking consumers to create products: double exploitation of consumers
Asking consumers to provide free labour to create the products
Brand personality
Aakers framework consists of five dimensions
Sincerity
Excitement
Competence
Sophistication
Ruggedness
Brands with strong personality = increasing consumer brand loyalty
The more a consumer perceive a brand to be “person-like”, the more they are likely to remain loyal
Easier and cheaper to create brand personality through social media
Brand relationships
People relate to brands in similar ways as to other humans
Soft-sell appeals are focused on building positive affects towards the product and brand, and therefore more likely to create positive attitudes towards the ad
Associating them with higher purchase intention
When a brand is perceived as “human-like” the brand is seen as anthropomorphic - has a positive effect on brand relationships
Anthropomorphic marketing
Brand or product assume human-like characteristics
The characters in ToyStory are personifications of toys
A technique that attempts to connect emotional feelings to products or brands
Desired outcome is that the audience transfers perceived attributes to the brand
Elaboration likelihood model (ELM)
Explains how people are persuaded - how peoples attitudes can be changed
Two main ways:
Peripheral route: understated cues to subtly shift or associate attitudes towards a product/brand
A popular influencer uses a certain product - viewers may feel more positively towards it
Central route: persuaded by carefully thinking about the message’s content
Someone watches a detailed YouTube review of a laptop, thinking hard about the features and value before deciding if they like it
Used to research persuasiveness in social media
Cultivation theory
Perspective to why influencers and exposure to social media messages may be effective as a persuasive tool
Long-term, repeated exposure to media (social media or influencers) can shape how people see reality (first-order effects) and even influence their values and beliefs (second-order effects)
E-commerce & E-business
Related but not interchangeable terms
E-commerce:
Involves an external change of value
Is about who the company does business with
Example: selling products online or buying supplies from a vendor
E-business:
An internal digital process within a firm
Is about how a company runs
Example: a company tracking its inventory or managing payroll online
Eight unique features of e-commerce technology
Ubiquity: its available everywhere and at all times
Global reach
Universal standards: shared by all nations around the world
Social technology: user-generated content, creators, and social networks
Personalization & customization: can target their marketing message to a specific individual by adjusting message to a persons name, and changing the delivered product or service based on a users preference or prior behavior
Information density: information is more plentiful, less expensive and of higher quality
Interactivity
Richness: offer more information richness than traditional media
The internet key technology concepts
Internet defined as network that:
Uses IP addressing
Supports TCP/IP
Three important concepts:
Packet switching
TCP/IP communications protocol
Client/server computing
Packet switching
A method of slicing digital messages comprised of bits into packet, sending the packets along different communication paths as they become available, and then reassembling the packets once they arrive at their destination
The codes travel from computer to computer (router) until they reach their destination
Routing algorithm: to ensure the packets take the best available path

Transmission control protocol/Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
Protocols were developed to ensure all devices follow so they can communicate properly
To provide high-speed communication network links
TCP establishes connections among sending and receiving computers and handles assembly and reassembly of packets
IP provides the internets addressing scheme and is responsible for delivery of packets
TCP/IP architecture and protocol suite
IP is divided into four separate layers:
Network interface layer
Internet layer
Transport layer
Application layer
IP addresses
Every device connected to the internet has an address - otherwise it cannot send or receive TCP packets
Can be expressed as 32-bit or 128-bit
An IP address can be represented by a domain name, using a domain name system (DNS)
The web and hypertext
Text formatted with embedded links
Links connect documents to one another, and to other objects such as sounds, video etc
Uses hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) and URLs to locate resources on the web
Example URL: https://cloud.timeedit.net/su/web
HTTP is the internet protocol used to transfer web pages
When opening a website, the browser sends an HTTP request to a server
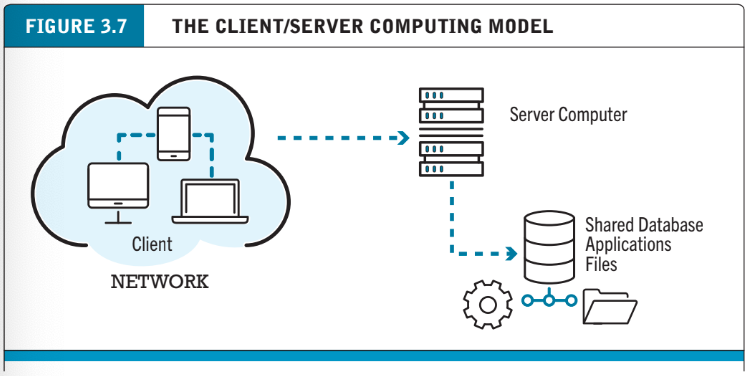
Client/server computing
A model of computing in which client devices are connected in a network together with one or more servers
Without it, the web would not exist
The internet is a giant example of client/server computing
Cloud computing
Using the internet to access computing resources like storage, software, or processing power
Three types of clouds:
Public cloud: shared with others, managed by big providers like Google or Microsoft, you only pay for what you use
Private cloud: used by just one organisation, more security and control
Hybrid cloud: a mix of both, often used by large firms
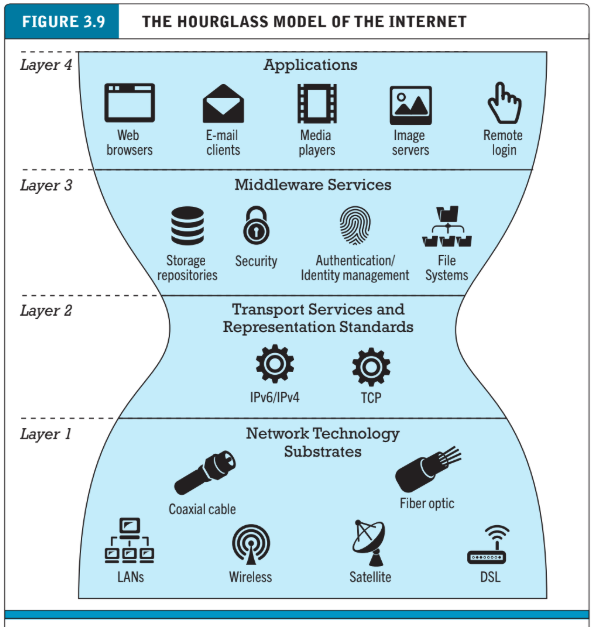
Internet infrastructure
The internet has four layers:
Network technology substrate layer
Composed of telecommunications networks and protocols
Transport service and representation standards layer
Houses the TCP/IP protocol
Applications layer
Client applications such as web, e-mail, audio or video playback
Middleware services layer
Glue that ties the applications layer to the others
Includes security, authentication, addresses, storage repositories
Eight key elements of a business model
Value proposition
Revenue model
Market opportunity
Competitive environment
Competitive advantage
Market strategy
Organizational development
Management team
Value proposition
Defines how a companys products or service fulfills the needs of customers
“Why should the customer buy from you?”
Successful e-commerce value proposition:
Personalization/customization
Reduction of product search, price discovery costs
Products get from the seller to buyer efficiently
Revenue model
Describes how a business will earn revenue, generate profit
“How will you earn money?”
Major types of revenue model:
Advertising revenue model
Subscription revenue model
Transaction fee revenue model
Sales revenue model
Affiliate revenue model
Freemium strategy
Market opportunity
“What marketspace do you intend to serve and what is its size?”
Realistic market opportunity:
Defines by revenue potential in each market niche in which company hopes to compete
Typically focuses on one or a few market segments
Competitive environment
“Who else occupies your intended marketspace?”
Other companies selling similar products in the same marketspace
Both indirect (different industries but product can substitute for one another) and direct (sell very similar products in the same market) competitors
Influenced by:
Number and size of active competitors
Each competitors market share
Competitors profitability
Competitors pricing
Competitive advantage
When they can product a superior product and/or sell a lower price than competitors
Important concepts:
Asymmetries: whenever one participant has more resources than others
First-mover advantage: being the first (pioneer), they sometimes lack complementary resources
Complementary resources: resources not directly involved in production but required for success - marketing, management, assets, reputation etc
Unfair competitive advantage: one develops an advantage that other businesses cannot purchase - built loyalty, trust, reliability etc
Leverage: a business uses its advantages to achieve more advantage in other markets
Perfect markets: no competitive advantages or asymmetries
Market strategy
“How do you plan to promote your products or services to attract your target audience?”
A plan that details how a company intends to enter market and attract customers
Need to be properly marketed to potential customers
Organizational development
“What types of organizational structures within the firm are necessary to carry out the business plan?”
How firms will organize the work that needs to be accomplished
Divided into functional departments:
Production
Shipping
Marketing
Customer support
Finance
Management team
Employees of the business responsible for making the business model work
“What kind of backgrounds should the company leaders have?”
A strong management team:
Can make the business model work
Can give credibility to outside investors
Has market-specific knowledge
Has experience in implementing business plans
B2C business models
Online business attempt to reach individual consumers
E-tailer
Community provider
Content provider
Portal
Transaction broker
Market creator
Service provider
B2C models: E-tailor
Online version of traditional retailer
A business that enables customers to shop and purchase via a website and/or mobile app
Revenue model: sales
Variations:
Virtual merchant
“Bricks-and-clicks”
Catalog merchant
Manufacturer-direct
Low barriers to enter - competitive sector
B2C models: Community provider
Provide online environment (social network) where people with similar interests can transact, share content and communicate
Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter etc
Revenue models:
Hybrid: combining advertisement, subscription, sales, transaction fees etc
Value proposition is to create fast, convenient, one-stop platform where users can communicate and share information
B2C models: Content provider
Distributes digital content on the web such as news, information, music, photos and video
Dominated by traditional publishers
Revenue models:
Advertising, subscription, sales
Key to success: owning the content
B2C models: Portal
Offers various services, “everything” in one place such as search tools, news e-mail etc
Yahoo, MSN, AOL
Sells nothing themselves
Revenue models:
Advertising, referral fees for steering customers to other sites, transaction fees, subscriptions
Variations:
Horizontal/general: include all users of the internet
Vertical/specialized: focused on a particular subject matter or market segment
Search: focuses on offering search and advertising services, Google
B2C models: Transaction broker
Process online transactions for consumers
Primary value proposition - saving time and money
Revenue model: transaction fees
Industries using this model:
Financial services
Travel services: generate commissions from travel bookings
Job placement services
B2C models: Market creator
Builds a digital environment (market) where buyers and sellers can meet, display and search for products and services etc
Does not execute the transaction for the customer (unlike transaction broker)
eBay
Uber
Airbnb
Revenue model: transaction fees, fees to merchants for access
B2C models: Service provider
Offers online services
Google, Google maps, Gmail
Value proposition
Valuable, convenient, time-saving, low-cost alternatives to traditional services
Revenue models:
sales, subscription fees, advertising
Virtual merchants
Single-channel e-commerce firms that generate almost all revenue from online sales
Amazon
No physical stores
Challenges:
Building business and brand name quickly - to cover costs of operations
Low barriers to entry - invites many competitors
Costs to build and maintain e-commerce presence
Steep learning curve
Omni-channel merchants (Brick-and-Clicks)
Network of physical stores as primary retail channel but also online operations
Walmart
Advantages such as brand name, national customer base, warehouses and trained staff
Acquiring customers is less expensive because of their brand names
Challenges:
High cost of physical buildings and staff
Coordinate prices across channels
Building credible e-commerce presence
Hiring new skilled staff
Manufacturer-direct (DTC)
Single or multi-channel manufacturers who sell directly to consumers online without invention of retailers
Apple, Dell, Sony
Challenges:
Channel conflict
Switching from supply-push model (products made prior) to demand-pull model (products built when order)
Catalog merchants
Established companies that primarily sell through printed catalogs but have also moved into online sells
Challenges
High costs for printing and mailing catalogs
Adapting to the new technology
Has become less revelant
How e-commerce changes business
E-commerce changes industry structure by changing:
Rivalry among existing competitors
Barriers to entry
Threat of new substitute products
Strength of suppliers
Bargaining power of buyers
Improves each part of the value chain: easier and cheaper to share information
Businesses can:
Buy and sell more efficiently
Skip middlemen
Use data to operate faster and better
Serve customers more personally
Wider audience
E-commerce helps improve:
Production
Customer service
Coordination and outsourcing
B2B marketing
B2B marketing has not grown as quick as B2C, because they are different markets
B2B firms sell low volumes of very valuable and complex products to a small number of purchases
LinkedIn most common social network for B2B
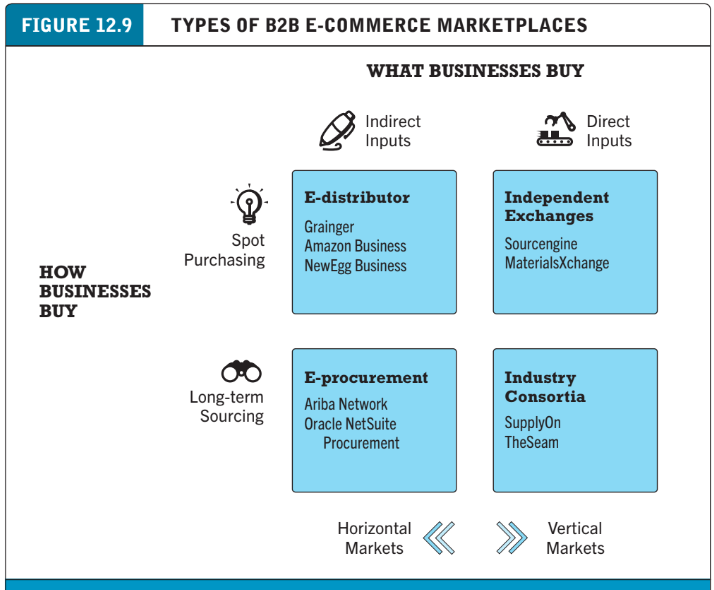
B2B marketplaces
What businesses buy:
Direct goods (used in production - raw materials)
Indirect goods (used for operations - office suppliers)
How businesses buy:
Spot purchases (one-time buys, often urgent)
Long-term sourcing (ongoing supplier relationships with contracts)
Types of marketplace:
E-distributors
E-procurement
Exchanges
Industry consortia
Private industrial networks
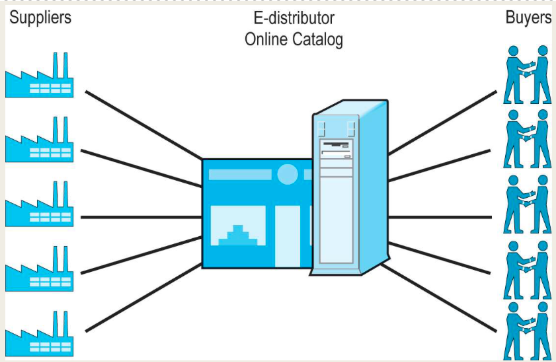
B2B models: E-distributors
Provides an online catalog of products from many different manufacturers that are available to purchase by individual businesses
Most common type of net marketplace
Middlemen between manufacturer and businesses
Helping companies buy indirect goods quickly and easily
Revenue model: sales
Operate in horizontal markets
One-to-many market
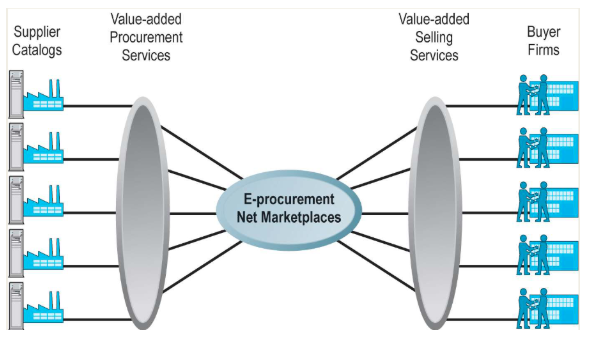
B2B models: E-procurement net marketplaces
Establishes digital markets for trade between companies
Helps businesses use technology to buy goods and services more easily and efficiently
Connect hundreds of suppliers of indirect goods
They create horizontal markets
Revenue model: transaction fees, licensing consultation services and software, network fees
Many-to-many market
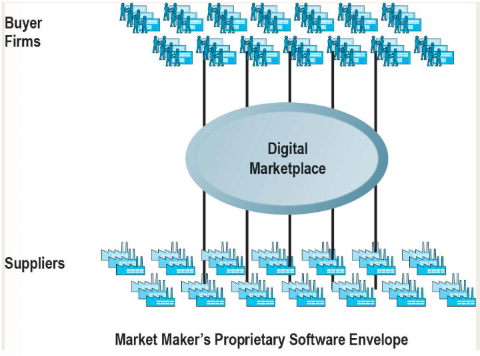
B2B model: Exchanges
An independent digital marketplace where a large number of suppliers meet a limited number of very large companies in a sector
Steel business
Creates mostly vertical markets
Revenue model: fee or commission on the transaction
Benefits include lower prices, reduced search costs and access to global purchasing environments
Has had trouble attracting suppliers due to increased transparency
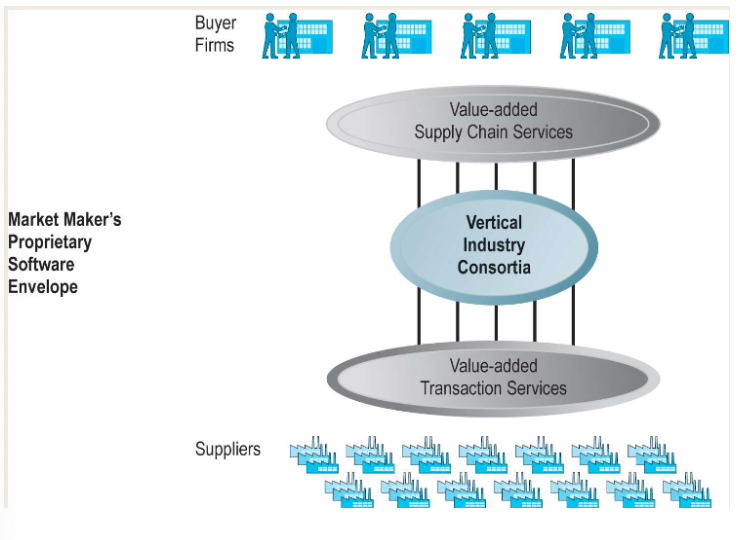
B2B models: Industry consortia
Industrial sector-owned vertical marketplace that serve specific industries with products e.g., automobile industry
Can also be horizontal, i.e., offers products of a special kind to a large number of companies
Goal is long-term purchasing and improve supply chain coordination
Revenue model: fee or commission
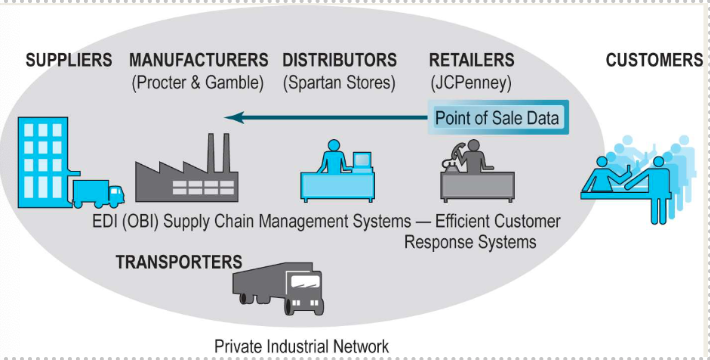
B2B models: Private industrial networks
A digital network designed to coordinate the flow of communications and supply chains among firms engaged in business together
Full control of supply chain coordination
Example: Walmart, Procter & Gamble
Business strategies
Differentiation
Ways producers can make their products or services unique and different to distinguish them from competitors
Commoditization
Where there are no differences among products or services, and the only basis of choosing is price
The opposite of differentiation
Strategy of cost competition
Offering products and services at lower cost than competitors
Short-lived and tricky
Scope strategy
Competing in all markets around the globe
Focus/market niche strategy
Competing within a narrow market or product segment
Customer intimacy
Focuses on developing strong ties with customers in order to increase switching costs – and therefore enhance a firm’s competitive advantage
Procurement process and supply chains
B2B e-commerce is about changing the procurement process (how firms purchase the goods they need to produce goods for consumers)
Can be done by contrast purchasing or spot purchasing
In the procurement process, firms purchase goods from a set of suppliers, which in turn purchase their inputs from their own suppliers
Seven steps in the procurement process
Trends in supply chain management
Supply chain management (SCM)
A wide variety of activities that firms use to coordinate the key players in their procurement process
Major trends in SCM
Continual efforts to improve process
Trends include: Just-in-time and lean production, supply chain simplification, adaptive supply chains, sustainable supply chains, electronic data interchange, supply chain management (SCM) systems.
App marketing
Apps reach web services “without” browsers
Most efficient are in-app ads
Faster access to content
Has influenced the design of traditional web pages
Four revenue models
Payment for download
In-app purchase
Subscription
Advertising
E-mail marketing
High response rates and low cost
Ability to track and measure response, personalise content and tailor offers, drive traffic to websites for more interaction etc.
Three main challenges
Spam
Anti-spam software: software tools used to control spam that eliminate many e-mails from users inboxes
Poorly targeted purchased e-mail lists
Key figures of e-mail marketing
Delivery rate: measures how many emails reach
Opening rate: measures how many emails are opened by recipients
Click rate: number of clicks on a link in the email
Disadvantages of e-mail marketing
Difficult to get the email through firewall etc.
Important to avoid certain keywords
Important to examine how the mail fits the e-mail software
Difficult to create creative design of email
Hard to get consumers over time to get involved in the mail
Resource-intensive to personalise the email
Widespread spam distribution
Big Data
Big data
Huge sets of data that are too massive to be processed and analysed using traditional data tools
Petabyte, exabyte range
Web traffic, e-mail, social media, content
Traditional DBMS (database management systems) unable to process Internet of Things
Hadoop
Open-source software framework used to store and process big data
Processes any type of data, even unstructured
Distributed processing
CRM (Customer relationship management)
A repository of customer information that records all the contacts that a customer has with a firm
Customer information builds up over time in a customer profile
One-to-one marketing is another name
Business-consumer relations are built up at individual level
Increases the opportunity to focus on the most valuable customers
CRM-data
Customer profiles can contain the following information:
Personal data and profile data; contact details etc
Transaction data; log of purchases
Communication data; log targeted campaigns and response to them
Other online marketing strategies
Customer retention strategies
One-to-one marketing (personalisation)
Behavioural targeting (interest-based targeting)
Retargeting
Customisation and customer co-production
Customer service
FAQ
Real-time customer service chat systems
Automated response systems
One-to-one marketing (personalisation)
Personalising marketing efforts for each individual customer
Involves tailoring messages, offers, or products to meet the unique needs or preferences of individual customers
Behavioral targeting (interest-based advertising)
Involves using online and offline data about behaviour of consumers to adjust the advertising messages delivered to them
If you are visiting a jewelry site, you would be shown jewelry ads
Retargeting (remarketing)
Showing the same or similar ads to individuals across multiple websites or apps
Is a popular tactic because of its perceived effectiveness
Customisation and customer co-production
Changing the product, not just the marketing message, according to user preferences
Customer co-production takes the customisation one step further by allowing the customer to interactively create the product
Affiliate marketing
Commissions paid by advertisers to affiliate websites for referring potential customers to their website
Pay-for-performance: the affiliate only gets paid if users click on a link or purchase a product
Marketing/sales via a third-party company
Big players have their own affiliate systems while smaller ones use affiliate networks to place the ads
Traditional affiliates
Comparison sites
Review pages
Blogs
Viral marketing
Represent WOM online
Primarily two forms
Forwarded email
Discussions on social media
Viral marketing encompasses consumer-to-consumer discussion of products by electronic means - can be used synonymously with eWOM (199)
Disadvantages
High-risk marketing that requires careful preparation while there is no guarantee that the desired distribution will be achieved
Social marketing
Marketing and advertising via social media sites like Facebook
Encourage consumers to become fans and engage and enter conversations
Strengthen brand by increasing share of online conversation
Social sign-on
Information is transmitted when users on social networks connect to commercial pages on the network
Collaborative shopping
Sharing buying experiences with others
Network notification
Consumers can express pleasure/dissatisfaction with the company’s products
Traditional online marketing and advertising tools
Marketing and advertising tools for attracting e-commerce consumers:
Search engine marketing and advertising
Search engine marketing (SEM) (largest share)
Search engine optimisation (SEO)
Display ad marketing
E-mail marketing
Affiliate marketing
Viral marketing
Keyword advertising
Keyword advertising benefits advertisers as they only pay when the ad is clicked
Benefit consumers when the ads are only linked to relevant keywords. No pop-up
More keywords are purchased with increased click-through cost
Display ad marketing
Banner ads
Rich media ads
Video ads
Sponsorships
Native advertising
Advertisers pay for ads on third-party site
Effectiveness is measured by how many impressions your ads are served
Display advertising issues
Ad fraud
Viewability
Ad blocking
Advantage/disadvantages of display ads
Direct response
Increases brand awareness
Can often be cheaper than printed media ads
May damage the brand depending on the placement of the ad
Uncertainty about which ad formats give the best results
How well does online advertising work?
ROI (Return on Investment) in the ad campaign is what counts
Difficult of cross-platform attribution
Highest click-through rates:
Search engine ads
Permission e-mail campaigns
Putting the recipient’s name in the subject line can double the click-through rate
Most powerful marketing campaigns use multiple channels, including online, catalog, TV, radio, newspapers, stores
Digital rights management (DRM)
A combination of technical and legal means to protect digital content from unlimited reproduction and distribution without permission
Can prevent users from purchasing and making copies for widespread distribution
Downside of social marketing
Loss of control
Where ads appear in terms of other content
Ads placed near content that does not represent the values of the brand
What people say
Posts
Comments
Inaccurate or embarrassing material
In contrast, TV ads maintain near complete control
Why is local mobile attrative to marketers?
Mobile users more active and in a closer proximity to merchant, more ready to purchase than desktop users
Over 80% of US consumers use mobile devices to search for local products, services
Faces some challenges:
Privacy concerns, find it “creepy”
Website as marketing platform
Major tool for establishing the initial relationship with the customer
The website performs four important functions:
Establishing brand identity and consumer expectations
Informing and educating the consumer
Shaping the customer experience
Anchoring the brand in an ocean of marketing messages from different sources
Persuasiveness
Elaboration likelihood model
Heuristic-systematic model
Integrated model of persuasion
Heuristic-systematic model
Suggests that information is processed in one of two ways: either by following relatively simple decision rules (heuristics) or by engaging with the message content in a systematic form.
Integrated model of persuasion
An additional processing path to the heuristic (peripheral) and systematic (central)
After a message is evaluated a judgement evaluation stage completes the information processing
Persuasion knowledge
Explains the coping mechanisms employed by consumers in response to marketers' persuasion tactics
The central premise of the model is that consumers, being constantly exposed to multiple persuasion attempts, over time develop certain coping strategies and become better able to repond to such attempts and learn to adapt their behaviour accordingly.
Functional triad
How technology can be designed to influence people’s attitudes or behaviours
Create engaging, effective experiences that users are more likely to stick with
At the centre of the framework are seven design principles:
Simplification
Sign-posting
Self-relevance
Self-supervision
Support
Suggestion
Socialisation
Credibility
Four types
Presumed credibility
Reputed credibility
Surface credibility
Experienced credibility
Perceived similarity
People are more influenced by messages that come from people like them — especially those they identify with or look up to.
Three theories help explain why:
Source attractiveness model
Social influence theory
Reference group theory