Raman Spectroscopy
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Scattering of light by vibrating molecules
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Elastic scattering
Leave the molecule in the same state, same wavelength - more abundant.
Rayleigh Scattering
Inelastic scattering
leave the molecule in a different quantum state, different wavelength - less abundant.
Raman Scattering
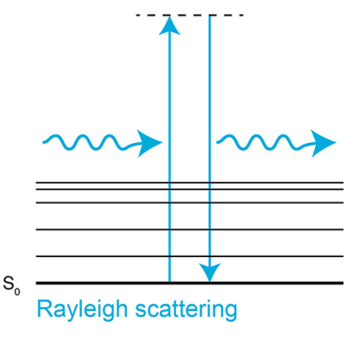
Rayleigh Scattering
elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation
Depends on the wavelength (I = 1/λ4)
Isotropic
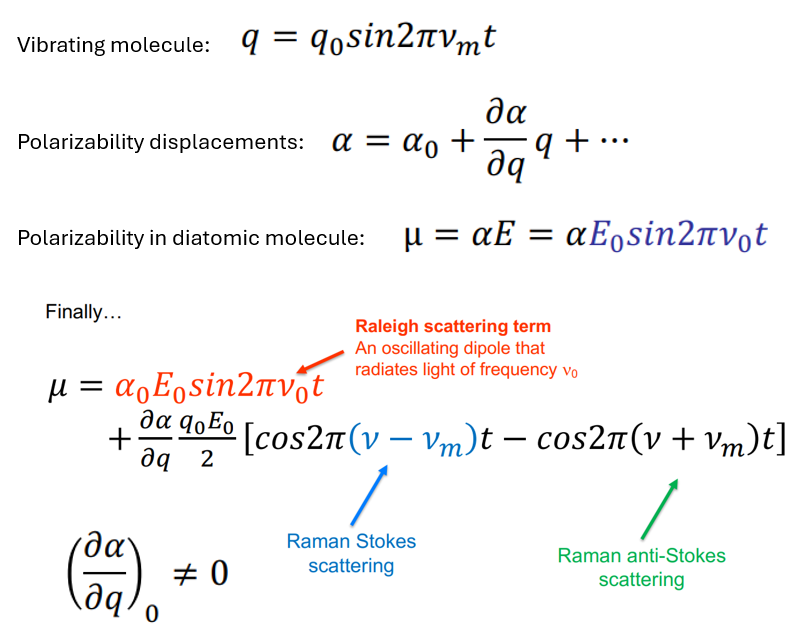
Raman Scattering
Inelastic scatter, shifted frequency (vs=v0±vmolecule)
correspond either to rotational, vibrational or electronic frequencies
Scattering events
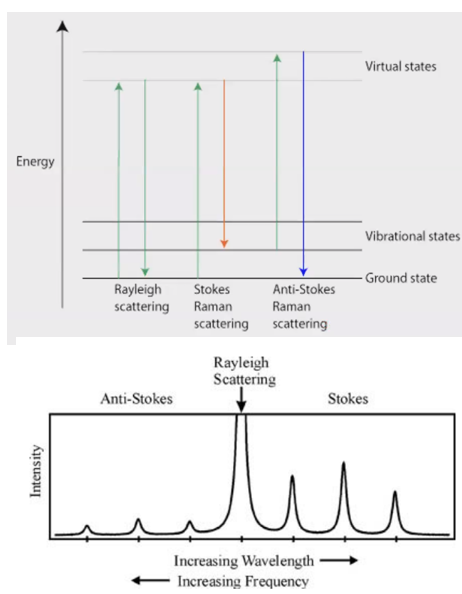
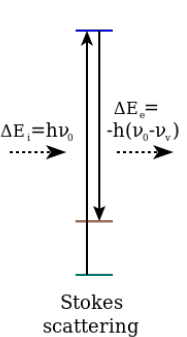
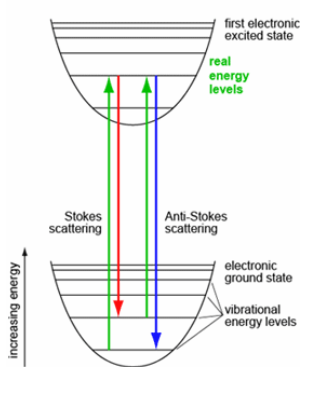
Stokes
Material absorbs energy and the emitted photon has a lower energy (higher wavelength) then incident photon.
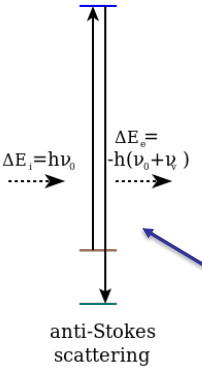
Anti-stokes
Material loses energy and the emitted photon has a higher energy (lower wavelength) than the incident photon.
Molecular Vibrations
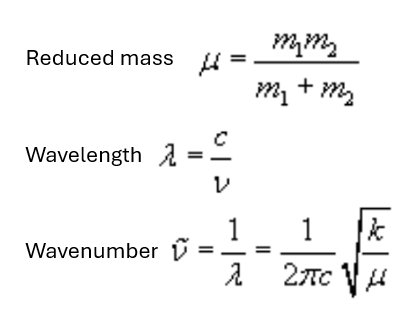
Intensity: Temperature Dependence
Stokes more favoured over anti stokes
The ratio of anti-Stokes to Stokes intensities will increase with temperature - more molecules in vibrationally excited state

Raman Scattering Theory
If a diatomic molecule is irradiated by this light, an electric dipole moment µ is induced.
where α is polarizability - proportionality constant
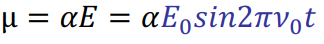
Polarizability
Tensor - ease of distortion of a collection of electric charges (how easily can electrons be moved in response to external field)
Polarizability decreases with increasing electron density, increasing bond strength and decreasing bond length.
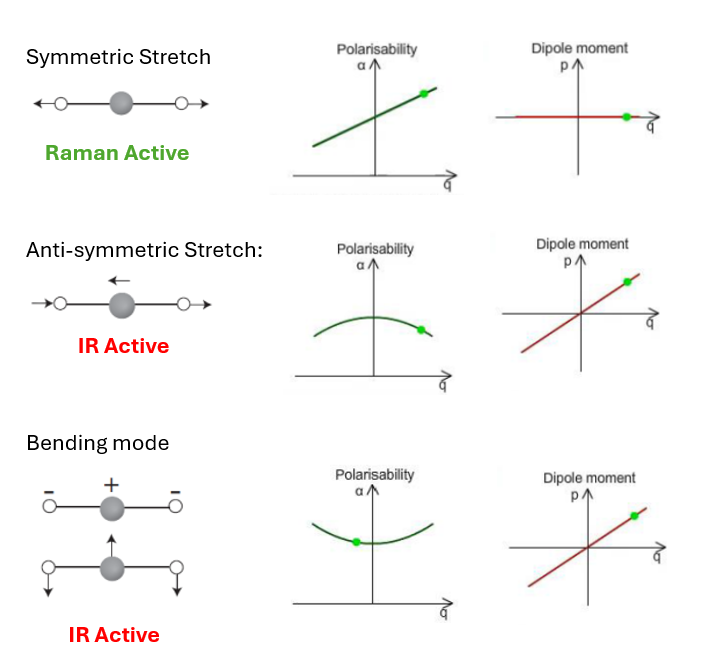
Raman active condition
A molecular rotation or vibration must cause some change in a component of the molecular polarizability - magnitude/direction change in polarizability ellipsoid.
Polarizability Proof
Example CO2
Example H2O
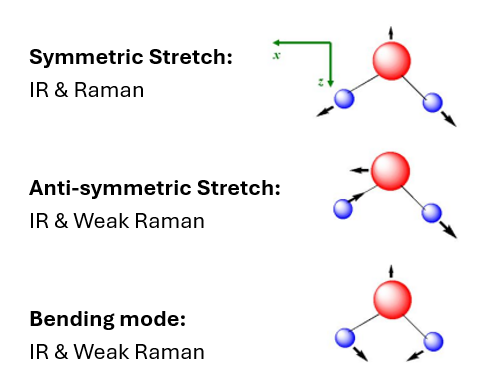
Rule of mutual exclusion
If a molecule has a centre of symmetry, then IR active vibrations are Raman incative and vice versa.
Spectra: Features
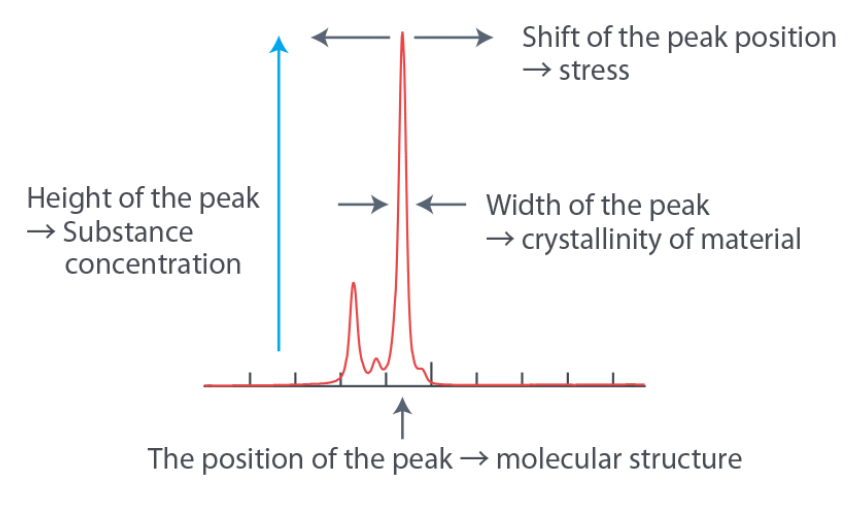
Spectra: Effect of applied force
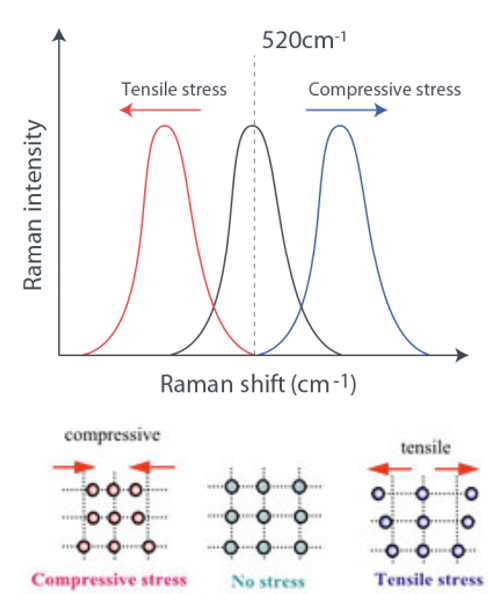
Polarised Raman spectroscopy
Polarised Raman spectroscopy probes information about molecular orientation and symmetry of the bond vibrations.

Resonance Raman spectroscopy
In resonance Raman the excitation wavelength is carefully chosen to overlap with (or be very close to) an electronic transition - real energy level.
High fluorescence background
Laser wavelength selection
Conventionally: 785nm
short-wavelength: high fluorecence, high intensity
long-wavelength: low fluorescence, weak signal
Raman Pros and Cons
Pros:
no sample prep
non-destructive
no vacuum required
short time scale
Cons:
cant use metals or alloys
Raman effect is very weak (Low sensitivity)
fluorescence noise