Psychology Review: Chapter 10
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the theories of emotion
Discrete emotions theory
James-Lange theory
Somatic Marker theory
Cannon-Bard theory
Two-factor theory (schacter and singer)
What is the discrete emotions theory?
Emotions are a product of evolution
A small amount of distinct emotions create more complex versions
Rooted in
Biological roots
Evolutionary functions
Emotional reactions often occur before thoughts
Seen via the fact that the limbic system was created before other organs
Emotions are innate and occur naturally
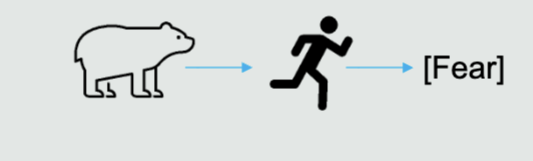
What is the James-Lange theory?
Emotions result from interpretations of bodily reactions to stimuli
Ones’ observations determines psychological state
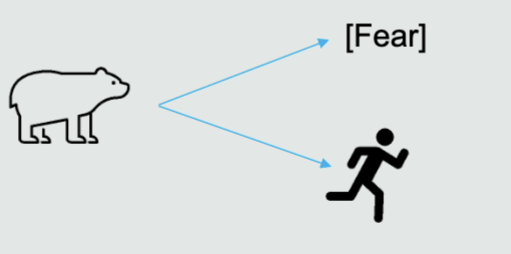
What is somatic marker theory?
The unconscious use of autonomic responses to determine the source of influence
"trusting" your gut
What is cannon-bard theory
Believes that James-Lange is too dispersed
Thinks that emotion and bodily response to stimuli happen simultaneously
Involves the thalamus, hypothalamus, and amygdala
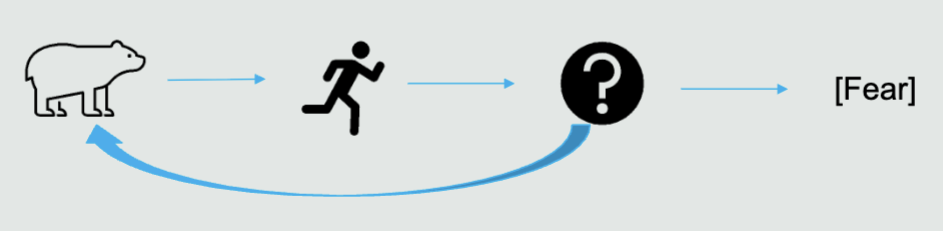
What is the two-factor theory
Emotion is produced by two psychological events
Emotions are a cognitive label
2 states
Undifferentiated physiological arousal (alertness)
Attribution of arousal (labeling)
Identifying why some behaviors occur
Emotions are the explanations we create for our state of arousal
Potential limitation for the study: pool was all males (involved adrenaline injection and emotion reflection)
How do we nonverbally express our emotions
Gestures
Personal Space
What are the types of gestures
Illustrators: highlights or accentuates speech
Manipulators: one body part touches another
i.e. twirling hair or biting nails give off the impression that they are scared
Emblems: conveyance of conventional meanings
i.e. thumbs up = got it!
What is the significance of personal space
Physical distance = emotional distance
Exception: Intimidation
4 implicit rules to personal space?
Public (12ft+)
Social (4-12ft)
Personal (1.5-4ft)
Intimate (0-1.5ft)
Significance of lying and deception
Nonverbal cues are not always more telling than verbal cues
Overreliance on nonverbal cues
Poor=no better "than" chance (54%)
Accuracy and validity for non and verbal cues are around the same
People create mistakes (i.e. custom officials, police officers, etc.)
What are the methods to detecting deception
Polygraph test
Controlled Question Test (CQT) and Guilty Knowledge Test (GKT)
Integrity testing
“Truth serum”
Brain scanning
Utility of verbal vs. non-verbal cues
Describe polygraph testing
Predicts the existence of physiological indicators of lying
Types
Controlled Question Test
Guilty Knowledge Test
Describe CQT and its issues
How its done
Controlled Questions
Is used to detect the "baseline
Irrelevant: unrelated to the crime
Relevant: directly related to the crime in question
Issues
Design: will be asked irrelevant and relevant questions
High rates of false positives
Biased against innocent suspects
Confuses physiological arousal with attempting deception
High amount of false negatives, because they made their baseline for physiological baseline high, so that when they lie it won't be flagged
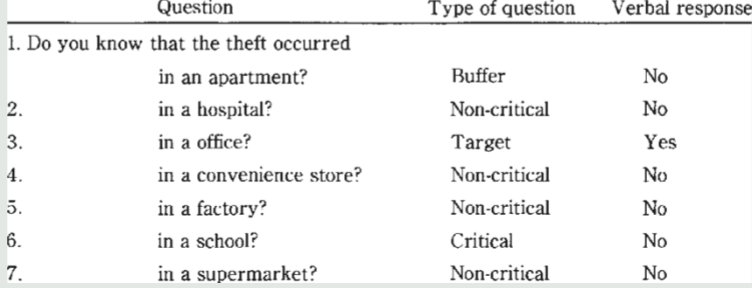
Describe GKT and its issues
Idea: only true suspect would react to pertinent knowledge of the crime
Observes physiological responses to non-public knowledge about crime
Via multiple-choice questions
Put in table of example questions
Has fewer false-positives, but more false-negatives occur
Alternative lie detection methods
Reasoning for the creation of these methods are due to the limitations in only looking at physiological arousal
Brain scans (EEG and fMRI)
EEG: when, but not where
fMRI: where
However is not well supported
"Truth Serums"
Barbiturates (Sedative-hypnotics): depressant so it causes relaxation and sleepiness
Lowers the threshold for response, as both true and false information are discussed
Integrity tests
Assesses a worker’s tendency to steal or cheat
Limitation: records a high rate of false-positives
What are display rules?
societal guidelines or norms for how and when to express emotions
i.e. in western cultures more parents teach boys not to cry, while its okay for girls
different cultures may be associated with different “nonverbal accents”
i.e. some cultures show different emotions, despite being in the same circumstance
can be affected by immigration (i.e. diff between asian americans and native-born asians)
What is the significance of the mere exposure effect
Definition: repeated exposure to stimulus makes us like it more
contradicts popular wisdom (“familiarity breeds contempt")
Why?
people usually seek things they enjoy
another hypothesis: repeated exposure reinforces the idea that the stimulus is correct, so it has a positive evaluation
Ex..
faces: we like the image in the mirror compared to what appear in a photograph
advertising: repeated exposure to ads make us want it more
What is facial feedback hypothesis
Definition: changes in the blood vessels in the face send temperature information to the brain, which alters our emotions
Argued that emotions arise from behavioral and physiological reactions (akin to James-Lange)
Differed: purely biochemical and not cognitive(no thinking)
Why are we unable to affective forecast moods
Definition: ability to predict our own happiness and others’
Durability bias: overestimation of the impact events will have on a person's mood
Ex. Belief that getting that promotion would maintain our happiness over an extended period of time, instead our feelings will fade as we become more acclimated to it
Drives the hedonic treadmill: continuously chasing the high of pleasure, but ultimately losing it
i.e. getting the promotion, but then it levels out as your realize the increase in work
What is the significance of drive reduction theory
Drive to minimize negative feelings and seek pleasure
Drive is unpleasant
Desire for satisfaction reduces tension and causes pleasure
The strength of the drive serves as an evolutionary function (i.e. thirst vs. hunger)
Affected by physiological arousal (alertness)
Influences how much "energy" we're willing to perform the functions necessary to complete this drive
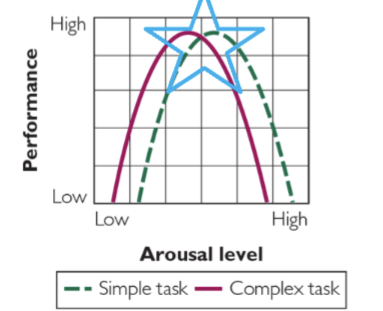
Yerkes-Dodson Law
Define motivation
The drive the propels us in a direction (toward or away)
Based on needs and wants

Elaborate on the Yerkes-Dodson Law
The existence of an optimal point of arousal for best performance
Ex. Think about if you pulled an all-nighter, then you aren't "alert" enough to perform the degree you hope to
What are the incentive theories
meant to explain
"why do we continue to have drive, despite already achieving something"
i.e. music artists keep putting out music, even though they might have already gotten successful from their first album
intrinsic
extrinsic
Explain intrinsic motivation
Intrinsic (internal) motivation
Positive feeling/goals that we give to ourselves
There is something inherently good about it
Half-marathons: some people inherently enjoy it/find pleasure from it
Explain extrinsic motivation
Ex. Runners (first inherent) but were offered 1500 per mile which made it extrinsic
However, once the motivator went away runners no longer wanted to do it as their motivation was no longer intrinsic
What are types of eating disorders
Obesity
Bulimia nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa
Discuss the different types of obesity
Biological perspective:
Leptin resistance
body tells you that you feel full
neurotransmitters
Biological set-point
genetically determined weight range for when a person's body naturally functions best
Serotonin sensitivity
how good someone feels when eating certain foods
Bodies have individual differences, which impact when they feel full
Food can be used as a coping mechanism (contributes to weight gain);
Portion distortion (everything in America is bigger, so on average people eat more calories)
Describe the specific types of eating disorders
Bulimia nervosa: binge, then purge pattern
High intake in one sitting, then a feeling to get rid of the rate (vomiting, exercise, and laxatives)
Anorexia nervosa: excessive calorie restriction
Social (western are heavily associated with eating disorders) and biological factors occur
Discovered via twin studies
What are some other motivations in daily life
Libido (sex drive)
Testosterone
Serotonin (high levels = low levels of sexual desire)
DRD4 gene (protein related to dopamine transmission)
variations correlate to reports of sexual desire and arousal
Cultural Norms
Are hookups okay?
Sexual Orientation
Corpus Callosum thickness
Study looked at males who identify are straight and gay
Fetal exposure to testosterone
Maternal Immune responses
Cultural acknowledgement and acceptance
What are the influences on interpersonal attraction?
Proximity (near becomes dear)
Similarity (birds of a feather flock together)
People feel more comfortable around others that are similar to themselves
Reciprocity (all give and no take does not a good relationship make)
Equal effort>One-sided relationship
Physical Attraction
What are the types of love (stages)
Passionate Love: powerful, and overwhelming longing
Think: Romeo and Juliet
Strong emotional experience, where both sides are ignorant to the issues
Companionate love: deep friendship and fondness
Passionate love transforms into deep fondness
Instead of a burning flame it becomes softer and more reliable
What is the significance of Maslow's hierarchy of needs
Created by Abraham Maslow
The desire to satisfy primary needs before secondary needs
Primary: basic biological needs
Secondary: psychological desire
What does supercilious mean?
the feeling of being superior to others
Facial expressions associated with contempt, of which communicate the sense that others are “beneath us”
What is the difference between the pan am smile and the duchenne
Pan am: obviously fake smiles, where only the mouth moves but not the eyes
Duchenne smile: a genuine smile displayed when people experience positive emotions in the presence of others
Describe the Broaden and Build Theory
happiness leads us to feeling more openly
ex. doctors who received a small bag of candy made more accurate diagnoses of liver disease than did other doctor
broader thinking can permit people to find more unique solutions to problem
Elaborate positive psychology
a discipline that emphasize human strengths such as resilience, coping, life satisfaction, love, kindness, and happiness
it focuses on helping people find ways to enhance positive emotions like happiness and fulfillment
Explain defensive pessimism
it is a strategy of anticipating failure and then compensating for this expectation by mentally over-preparing for potential negative outcomes
used as solution for many anxious people
helps certain people improve their performance, because it encourages them to work harder
Limitations: pessimism can decrease life satisfaction, and irritate others due to its focus on worst-case scenarios
What is the ventromedial
it is the lower middle part of the rats’ hypothalamus
it seems to let rats know when to stop eating
Describe glucostatic theory
the belief that when our blood glucose levels drop, hunger creates a drive to eat in order to restore the proper level of glucose
via this theory homeostasis is achieved as the balance of energy we take in and expend
people gain weight when there is a an imbalance in energy taken in and burned