ANSC 1401 LAB Final Exam
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
stunning
what is the first step in the harvest process?
to decrease contamination
what is the reason for tying off both ends of the gastrointestinal tract?
fisting
what step is unique to lamb and goat harvest?
Fecal, Milk, Ingesta
what does the acronym FMI stand for?
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)
what is the regulating agency which oversees the process of harvesting animals here at Texas Tech University and at other processing plants in the United States?
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
stimulates follicular growth and recruitment
luteinizing hormone (LH)
causes the follicle to mature and ovulation
gonadtropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
causes a surge of LH and can treat cystic ovaries
estrogen
causes estrus, development of female sex characteristics and reproductive tract, and uterine contractions
progesterone
maintains pregnancy, inhibits uterine contractions, and inhibits estrus
testosterone
regulates spermatocytogenesis, influences male sexual behavior, and develops secondary sex characteristics
oxytocin
milk let down and smooth muscle contractions
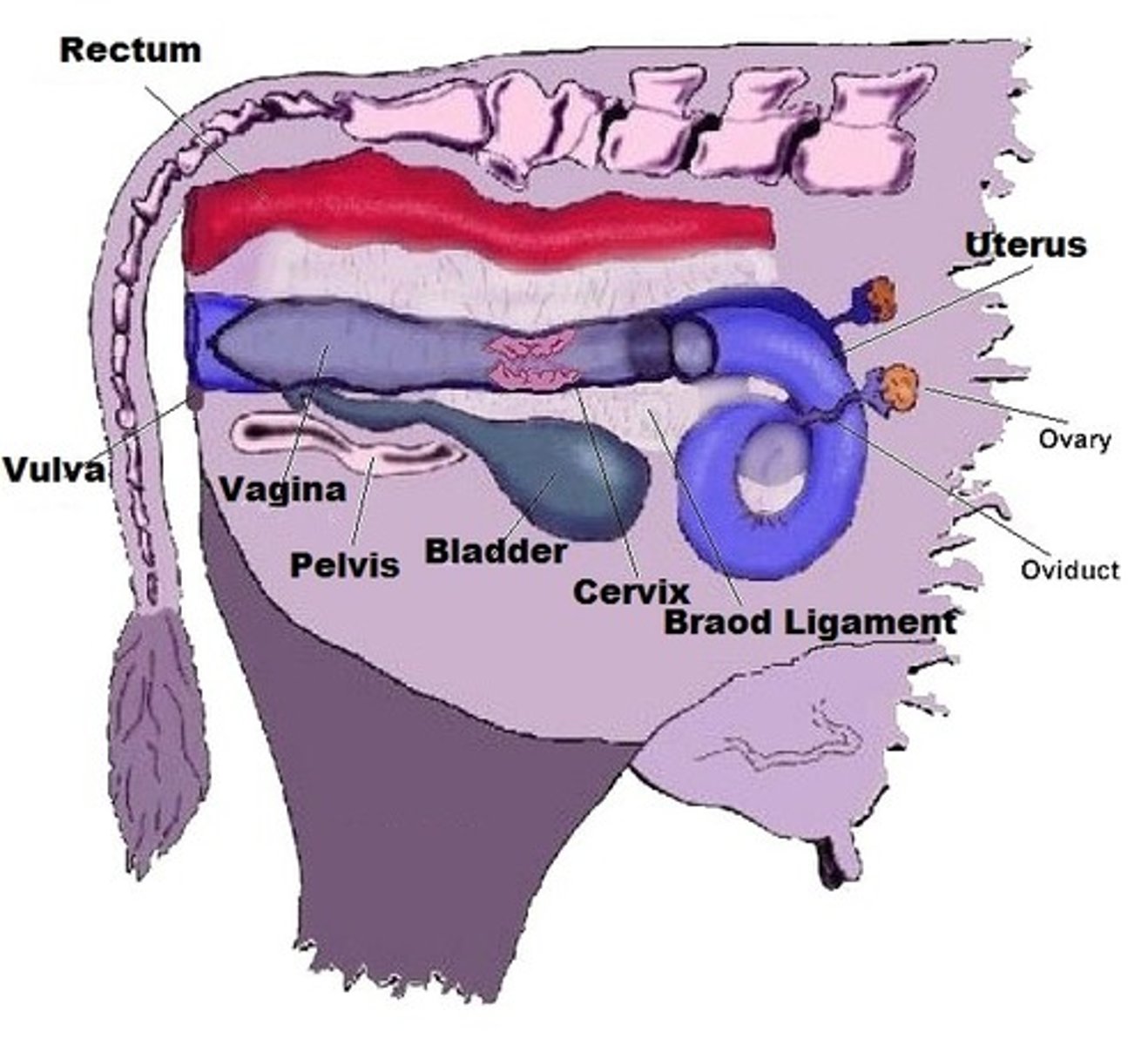
oviduct
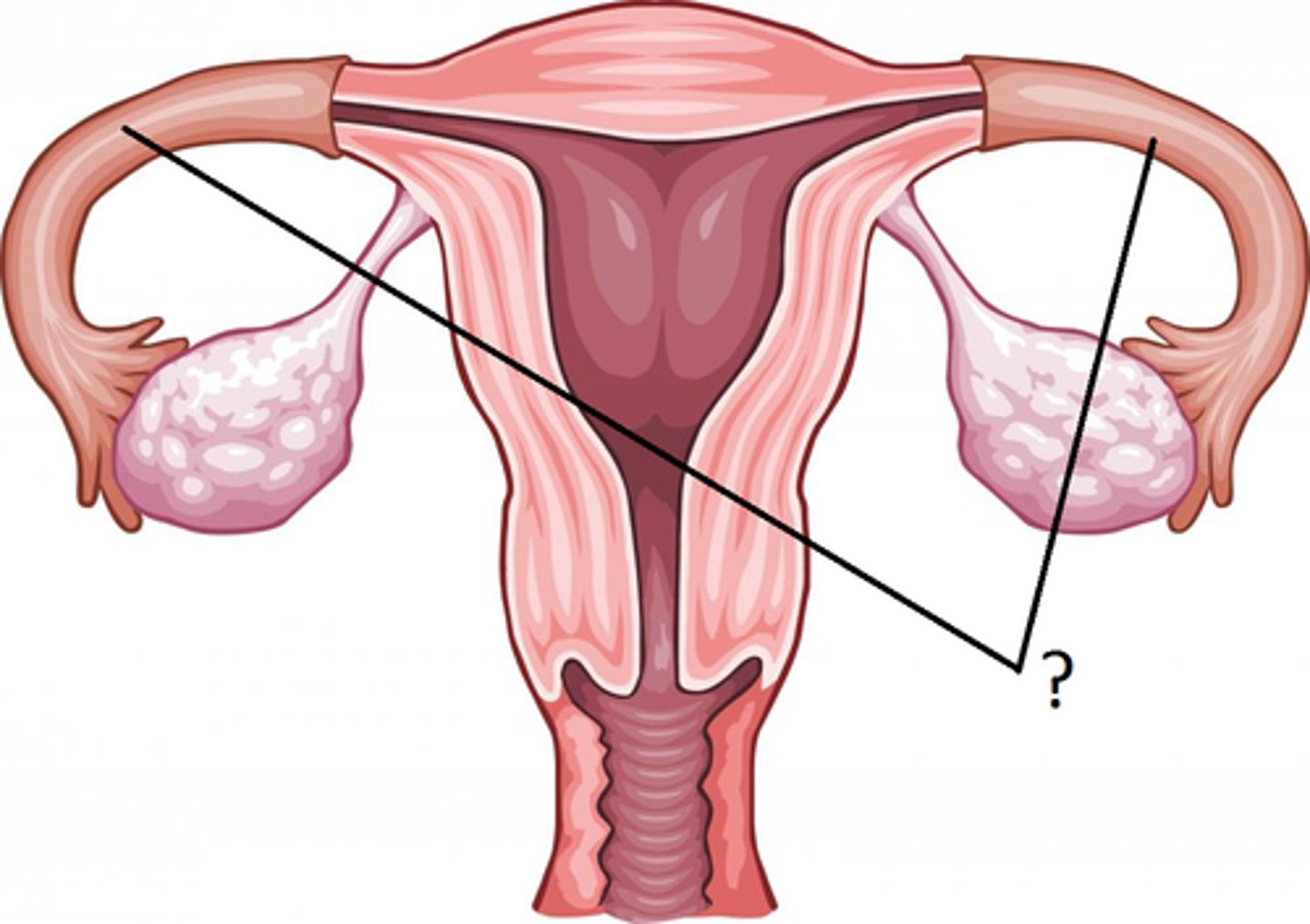
oviducts
(fallopian or uterine tubes) paired structure that connect the ovaries and the uterus; transport ova and sperm
vagina
copulatory organ and birth canal; site of sperm deposition in cow, ewe & doe; contains many mucosal glands (lubrication), made of highly elastic muscle and connective tissue
broad ligament
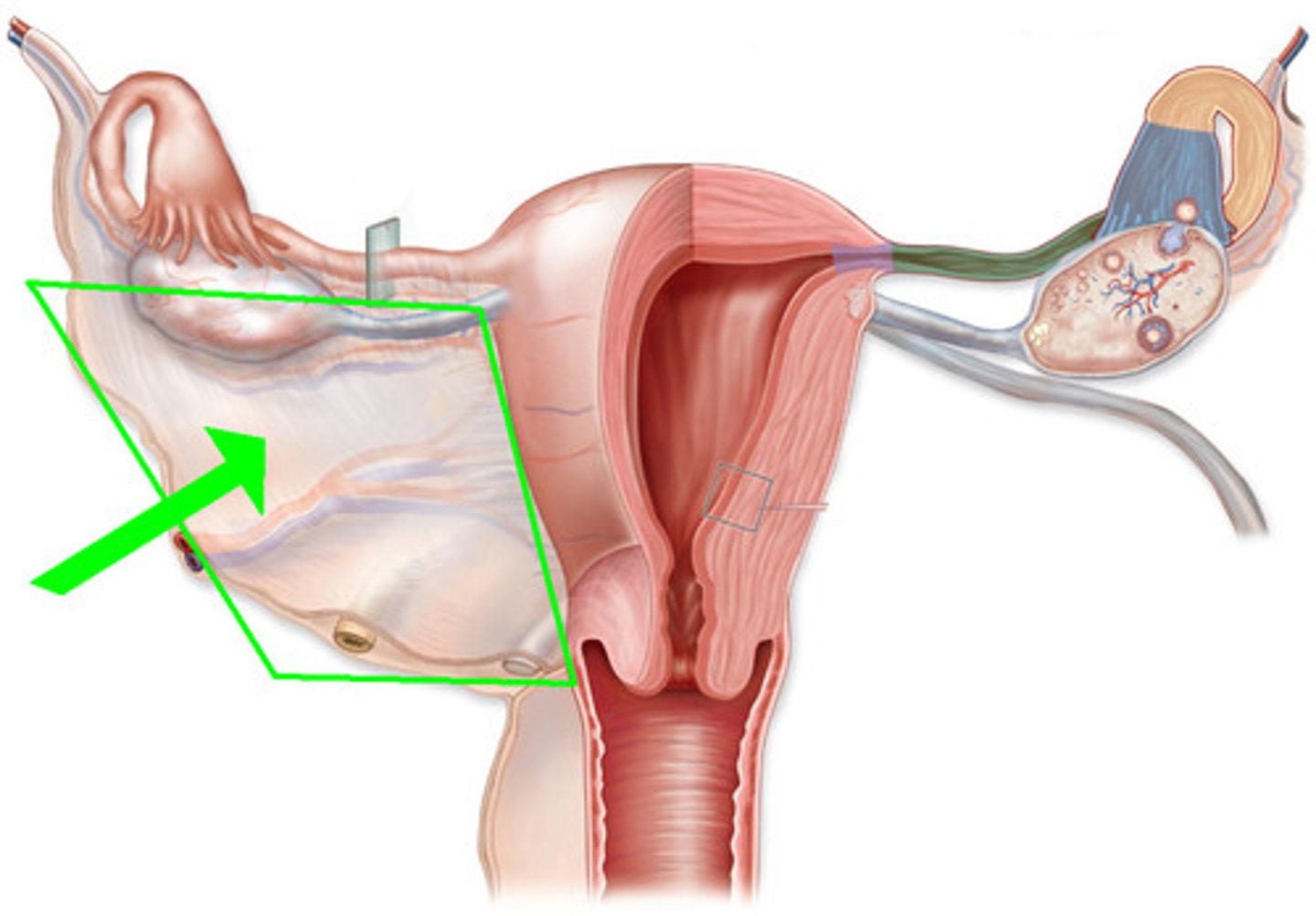
uterus
uterus
site of placental attachment; produces hormones
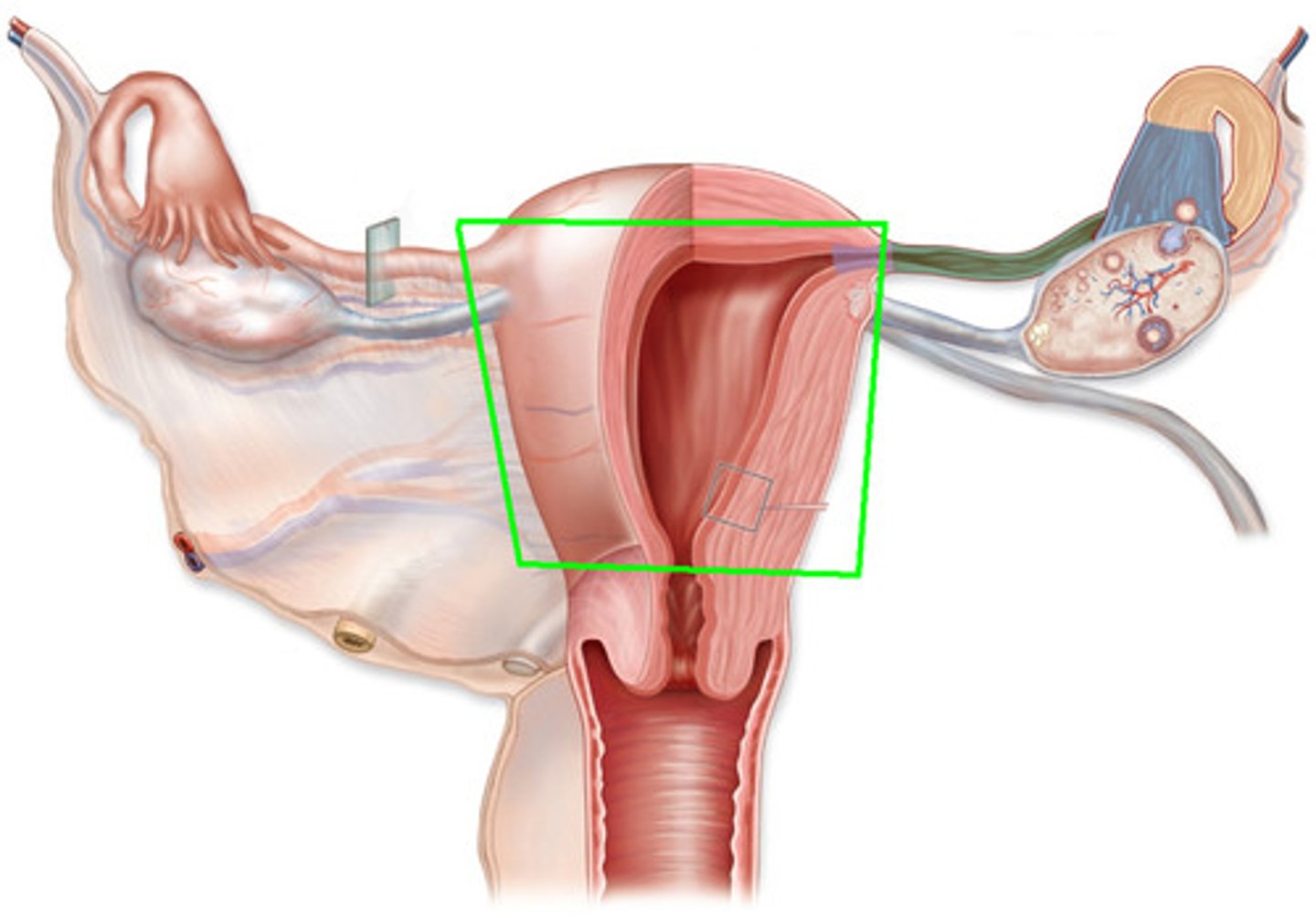
vulva
vestibule
common pathway of reproductive and urinary tract; terminal portion of the vagina, site of the urethral opening
uterine horn
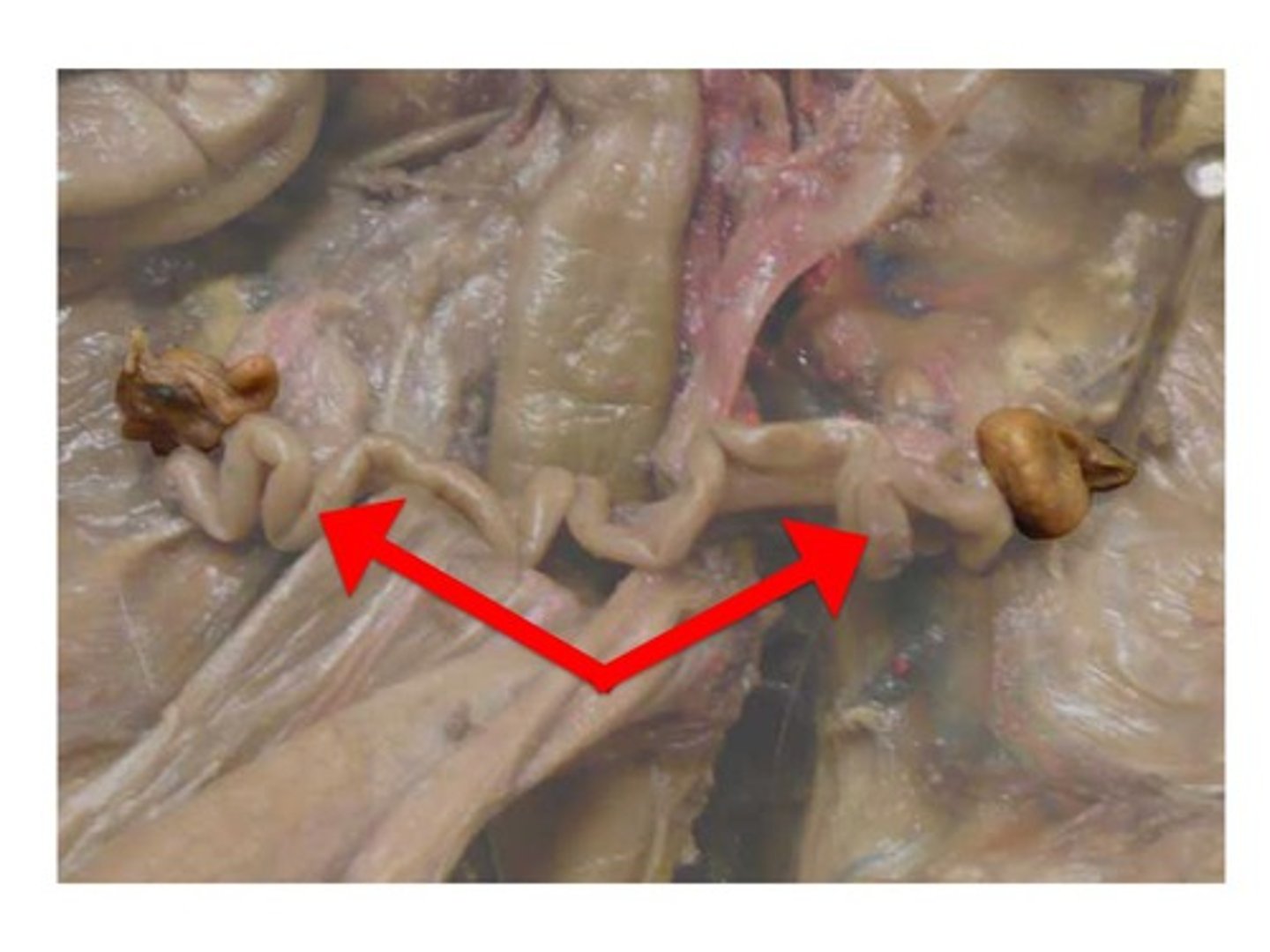
cervix
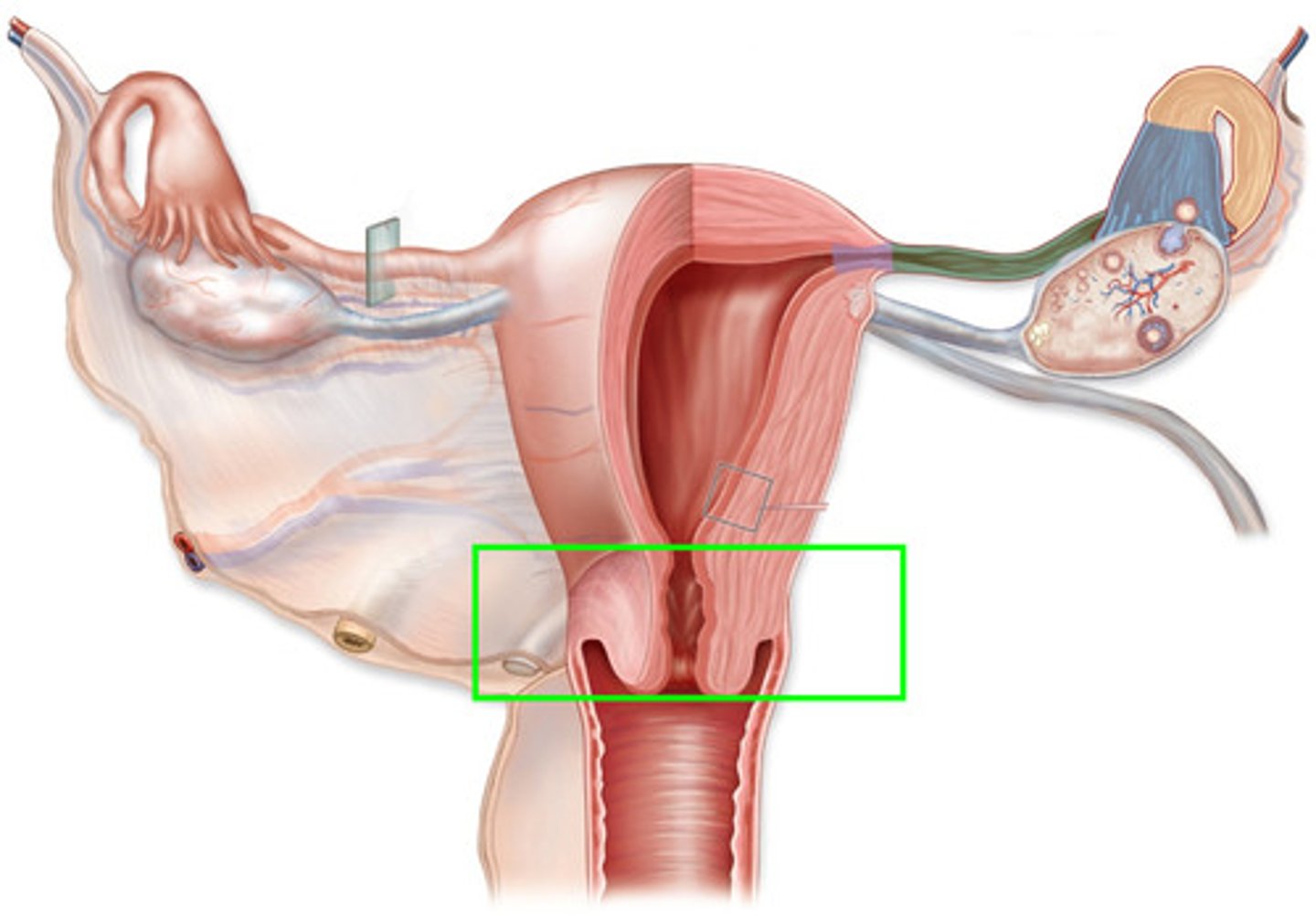
cervix
separates the vagina from the uterus; site of semen deposition in the mare and sow; functions: prevents contamination of the uterus, serves as a sperm reservoir and produces cervical mucous
bicornate uterus
2 horns, no body, 1 cervix, 1 vagina (cattle, sheep, goats, swine, dogs)
bipartite uterus
2 horns, 1 body, 1 cervix, 1 vagina (horses)
ovary
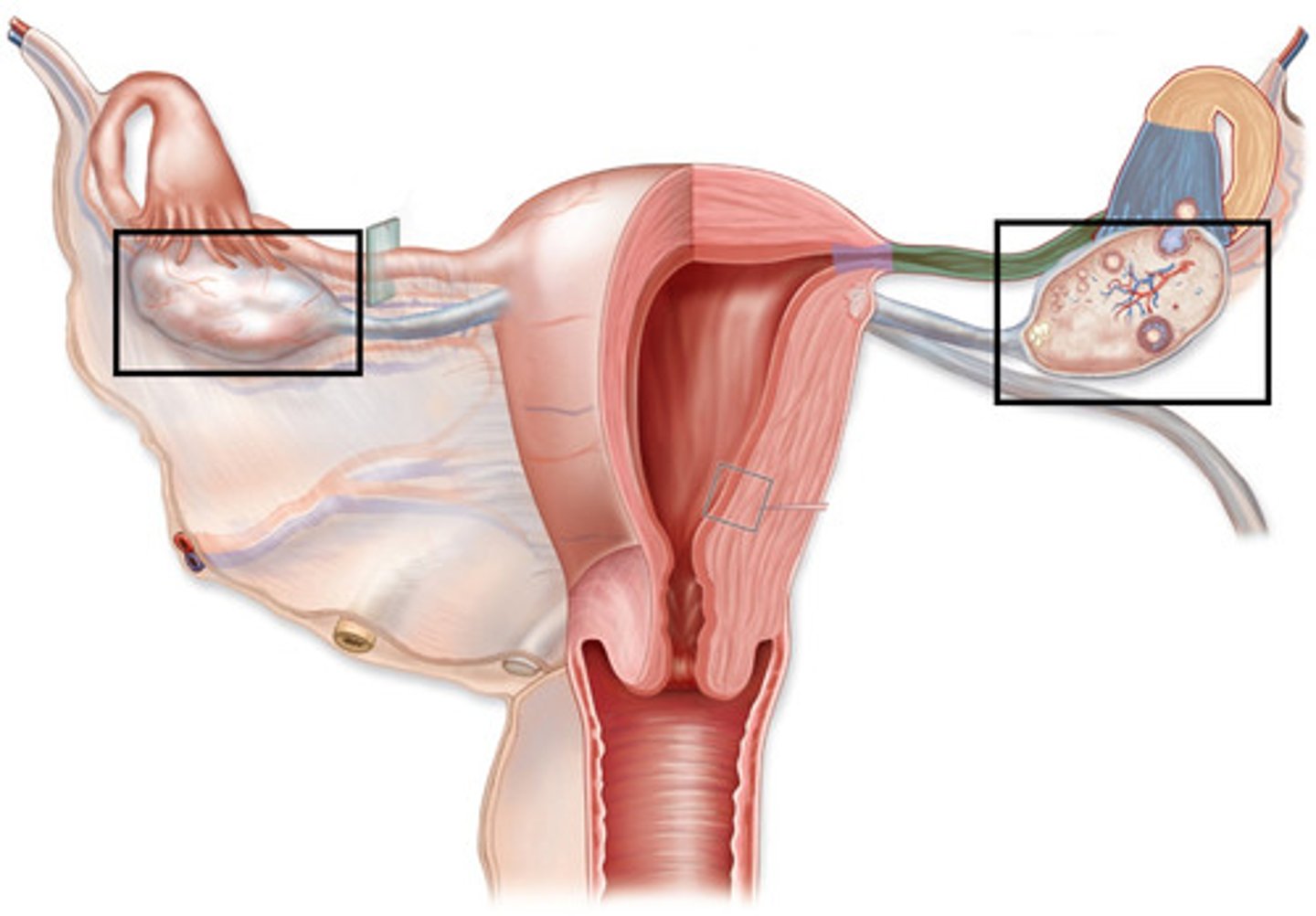
ovaries
primary sex organs in the female, produces female gametes, produces hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
corpus luteum
structure formed after follicle ruptures at ovulation; produces progesterone
clitoris
erectile tissue located just inside the vulva; contains sensory nerves and increases sexual excitement in the female during copulation
fimbria
finger-like projections that catch the oocyte
infundibulum
funnel portion connected to the fimbria
AI junction
where is the site of fertilization?
estrogen
(ovary, follicle, placenta)
estrus, uterine contractions, secondary sex characteristics; growth of female reproductive tract, induction of behavioral estrus, induction of uterine contractions; promotes growth in domestic animals
progesterone
(ovary, corpus luteum, placenta)
maintenance of pregnancy; inhibits uterine contractions, inhibition of estrus, secondary sex characteristics, growth of female reproductive tract; stimulates endometrial secretion
FSH
female:
(anterior pituitary) stimulates follicle growth; stimulates estrogen production (in conjunction with LH)
LH
female:
(anterior pituitary) maturation of follicle, ovulation, corpus luteum (CL) formation; progesterone production
FSH
male:
(anterior pituitary) stimulates formations of immature sperm to mature sperm
LH
male:
(anterior pituitary) testosterone production
testosterone
(testis) formation of immature sperm; male sexual behavior, secondary sex characteristics; maintains accessory sex organs
oxytocin
(hypothalamus) stimulates uterine contractions during sperm and egg transport and parturition; induces milk let-down, expulsion of retained placenta; aids delivery of young when labor is extended
muscling (REA), fat thickness, carcass weight, KPH
what factors go into calculating yield grades in cattle?
genetics
what is the most important factor which determines marbling?
live weight x 1.1
what is the method to calculate a benchmark Ribeye Area for cattle?
live weight x 0.02
what is the method to calculate a benchmark Ribeye Area for sheep?
BF x 10 + .4
what is the yield grade formula for sheep?
2, 3
which two yield grades do most of the cattle harvested fall into?
left atrium
what is the chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs?
A
what is not a function of the liver in all species?
A. stores bile
B. none of the above
C. produces bile
D. produces enzymes
E. filters toxins
lungs
what does the right ventricle pump blood directly to?
valves
what structures prevent back flow in the heart?
left ventricle
which chamber of the heart has to use more pressure to pump blood? (which side has to work harder)
maillard reaction
what is the chemical reaction called that creates the "meaty" flavor in meat products?
non-enzymatic browning reaction
what is another name for the maillard reaction?
grain fed beef
in the United States, what is the preferred meat flavor?
heat
what causes meat to develop its cooked flavor?
true
true or false:
breed of cattle has an impact on meat flavor
false
true or false:
there are 6 basic tastes
cellulose
what is the most abundant organic molecule on the planet?
mouth
where does digestion begin?
make the feed cheaper
what is NOT a reason to further process feed stuffs?
horses
who utilizes in post-gastric fermentation in order to digest higher fiber feed stuffs?
false
true or false:
mastication is an example of chemical digestion
ruminants and non-ruminants
who contains one true stomach?
non-ruminant
who would consume a diet consisting strictly of meat?
true
true or false:
the cecum is larger and more complex in omnivores compared to carnivores
cattle
who utilizes in pre-gastric fermentation in order to digest higher fiber feed stuffs?
no!
can ruminants and non-ruminants digest cellulose? can humans?
non-ruminants
monogastric/one-stomach (simple stomach)
ruminants
complex stomach (multiple compartments)
digestion
a process, in which large insoluble molecules are broken down into simpler compounds; preparing food for absorption
absorption
the passage of the digested nutrients through the mucous membrane into the blood stream
mechanical, chemical and microbial
what are the 3 types of digestion process?
mechanical
digestion process:
mastication, muscular contraction of GIT; digestion in the mouth
chemical
digestion process:
enzymatic digestion, stomach HCl and bile acids; digestion in the stomach
microbial
digestion process:
bacteria and protozoa
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
what are the 3 sections of the small intestine?
small intestine
site of final stages of chemical enzymatic digestion; where almost all nutrients are absorbed
duodenum
section of the small intestine:
major site on nutrient digestion; regulates the rate of stomach emptying via hormonal pathway (pancreatic juice, bile, intestinal enzymes)
jejunum
section of the small intestine:
main site for nutrient absorption; amino acids, short peptides, fatty acids, sugars (monosaccharides), etc
ileum
section of small intestine:
absorption (B12, bile salts, and nutrients)
pancreas
an important organ because of its many digestive and regulatory secretions
exocrine function
neutralize acids (bicarbonate), break down macromolecules (enzymes)
bile salts
produced in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, emulsify fats; aid in fat digestion and absorption
cecum (appendix)
section of large intestine:
bacterial fermentation of high fiber ingredients (especially in monogastric herbivores); some B-vitamin and vitamin K synthesis, last point of digestion
ileocecal valve
junction of small intestine and large intestine
colon
section of large intestine:
water absorption
rectum
section of large intestine:
formation and storage of feces
anus
section of large intestine:
sphincter that controls the release of waste from the body
ruminants
animals that regurgitate ingesta and remasticate their feed (rumination); a four compartment stomach; cud-chewing, even toed, hooved animals (naturally consume grasses, forbs, and/or browse)
reticulum
functions:
(honeycomb)
-plays a crucial role in stomach contractions
-responsible for regurgitation and eructation
-catches foreign heavy objects
-controls digesta passing to the omasum
rumen
what is the reticulum connected to? (Hardware Disease)
rumen (paunch)
what is the largest stomach compartment of ruminants?
-storage and soaking
-rumination and microbial fermentation
rumination
process of bringing feed from the rumen back up to the mouth to be re-chewed
4 step process: regurgitation, remastication, resalvation, reswallowing
omasum
function: absorbs water, helps with grinding feed particles (many piles)
abomasum
(true stomach)
function: digest feed fractions not fermented in the rumen, digest bacterial cell proteins produced in the rumen; very similar to the stomach of monogastric animals
maintenance, growth, reproduction and production/work
what functions do animals require nutrients for?
nutrient
any food component that aids in the support of life (available via microbial digestion)
water, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, minerals, vitamins
what are the 6 nutrients?
feeds/feedstuffs
any material included in a diet or ration because of its nutritional properties
ex: cereal grains, by-product feeds, forages and roughages, protein feeds, mineral and vitamin supplements, feed additives
roughage
-any feed ingredient with less/equal than 20% crude fiber
-low level of nutrient density
-typically low in dry matter digestibility
-bulky feeds, high in fiber and low in energy relative to concentrates