17 Endocrine
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
hypothalamus
this gland produces ADH, oxytocin, & releasing and inhibiting hormones
located in third ventricle
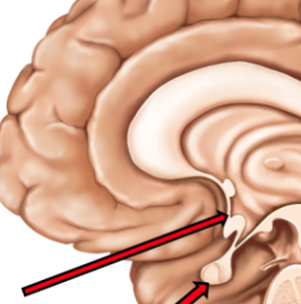
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormone conserves water by targeting distal tubules of nephrons
slows urine formation
hyposecretion: diabetes insipidus
diabetes insipidus
Due to hyposecretion of ADH resulting in polyuria & polydipsia due to body’s inability to regulate fluid balance
Oxytocin (pitocin)
delivery of baby by stimulating smooth muscle contraction of uterus
works in conjunction w/t prolactin, stimulate contraction within breast
Males: movement of sperm through reproductive tract
Posterior pituitary
Stores oxytocin & ADH
called neurohypophysis (composed of neurons)
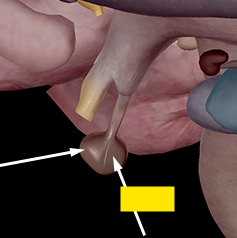
growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRO), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH)
What hormones does the anterior pituitary gland produce? (7)
anterior pituitary
Also called the adenohypophysis (gland below thalamus)
produces: growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, interstitial cell stimulating hormone
sella turcica, sphenoid
the pituitary gland sits in the ____ ____ which is located in the _______ bone
tropic hormones
hormones that target another endocrine gland to secrete hormones
mineralocorticoid
hormones from the adrenal cortex that regulate composition & concentration of electrolytes (ions) in body fluids
Ex: aldosterone
glucocorticoid
group of hormones released from the adrenal cortex, helps regulate glucose levels
includes cortisol & corticosterone
growth hormone (GH)
Hormone produced by anterior pituitary responsible for growth & protein synthesis
Targets: general + epiphyseal discs
hyposecretion: dwarfism & Simmond’s disease
hypersecretion: giantism & acromegaly
prolactin (PRO)
Produced by anterior pituitary responsible for formation of milk
targets mammary glands
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Hormone produced by anterior pituitary for thyroid stimulation
targets thyroid gland
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
hormone produced by anterior pituitary that stimulates adrenal cortex
targets adrenal cortex
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
hormone produced by anterior pituitary responsible for oogenesis & estrogen production in females or spermatogenesis in males
stimulates maturation of follicle & oocyte
targets ovarian follicles or seminiferous tubules
hyposecretion: infertility
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
hormone produced by anterior pituitary responsible for ovulation, formation of corpus luteum, & secretion of progesterone
peaks at day 14 causing ovulation
interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH)
hormone produced by anterior pituitary that promotes testosterone production
targets interstitial cells of testes
thyroid
gland also known as “shield” in Latin, produces T3, T4, & calcitonin
follicular cells, thyroglobulin
_____ _____ of the thyroid is responsible for the production of T3 & T4
_____ is the pink colloid and precursor of T3/T4
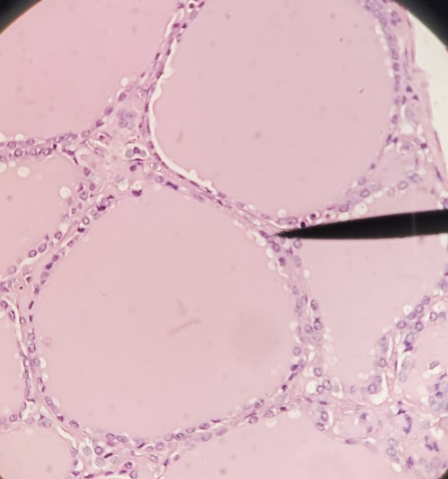
parafollicular cells
thyroid cells that are responsible for secreting calcitonin
triiodothyronine & thyroxin (T3, T4)
Hormones produced by the thyroid that are responsible for metabolism & development
Target: general
w/o it, neural connections can’t be made
newborns tested for this, given synthroid
hyposecretion: cretinism & myxedema
hypersecretion: grave’s disease
calcitonin
Hormone produced by thyroid gland responsible for Ca deposition, stimulates osteoblast to pull calcium into bones
target: bone
parathyroids
posterior of thyroid usually 4 nodules, releases PTH
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Hormone that raises blood Ca
withdraws Ca from bone via osteoclasts
Targets: bone, kidney, intestine
hyposecretion: tetany
hypersecretion: osteitis, fibrosa, cystica
adrenal medulla
Highly vascularized portion of the adrenal gland, core of gland
release catecholamines epinephrine (adrenaline) & norepinephrine
epinephrine (adrenalin)
Hormone secreted by adrenal medulla, same function as sympathetic nervous system (flight/fight)
target: general
hypersecretion: hypertension
urinary, reproductive, digestive
Epinephrine inhibits what 3 systems?
adrenal cortex
outer portion of adrenal gland responsible for secreting cortisol, cortisone, aldosterone, and sex hormones (androgens)
Cortisol, cortisone
Hormones released by the adrenal cortex functions in stress and anti-inflammatory responses; considered glucocorticoids
target: general
hyposecretion: Addison’s disease
hypersecretion: Cushing’s disease
aldosterone
a mineralocorticoid, conserves NaCl and water
targets kidney tubules
hyposecretion: Addison’s
hypersecretion: cushing’s
70-100 mg/dL
At what concentrations is blood glucose maintained at?
estrogen, androgen
Sex hormones produced by the adrenal cortex
hypersecretion of one of these hormones in females may lead to varying degrees of precocity & virilism; while this is a secondary site of production in males it is the primary site for females
pancreatic islets
Also known as islet of Langerhans, produces insulin and glucagon
ascinus
cells in the pancreas, surrounding islet of Langerhans that secrete digestive enzymes
insulin
hormone produced by beta cells of pancreatic islets, function in sugar transport, storage, & usage
target: general
hyposecretion: diabetes mellitus
glucagon
produced by alpha cells of pancreatic islets, function is to raise blood sugar
target: general
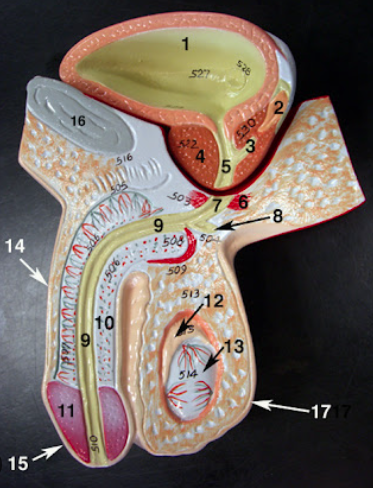
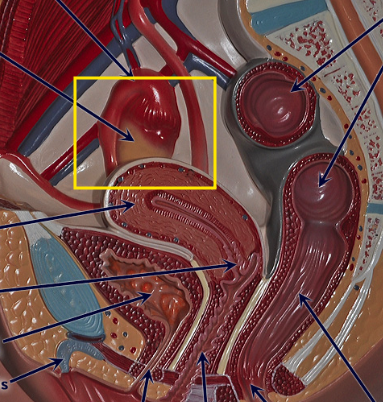
testes
gonads, responsible for production of testosterone
#13
testosterone
hormone produced primarily in the testes, promotes maleness
target: general
hyposecretion: infertility
ovaries
gonads that produce estrogen & progesterone
estrogen
hormone produced in the ovaries that promote femaleness + secondary sex characteristics
target: general
hyposecretion: infertility
lack of linked to osteoporosis
progesterone
hormone produced by the ovaries that maintain pregnancy; levels increase after ovulation
target: uterus
hyposecretion: infertility
thymus
gland is located in the chest, creates thymosin
thymosin
hormone secreted by the thymus responsible for immunity
target: lymphoid tissue
hyposecretion: immune failure
hormon
Derived from Greek, meaning to excite
hormones can also be inhibitory
pineal
Gland that secretes melatonin
melatonin
hormone produced by the pineal gland causes drowsiness & inhibit early sex development
targets: sex organs
hormonal, humoral, nervous
What are the 3 forms of endocrine stimulation (mode of secretion)?
hormonal stimulation
stimulation, the release of another hormone triggers release of the hormone
Ex: thyroid stimulating hormone from anterior pituitary triggers thyroid hormone in the thyroid
humoral stimulation
changes in level of nutrient or ion in the blood triggers release of the hormone
Ex: insulin, glucagon, ADH
nervous system stimulation
stimulation by the nervous system triggers release of the hormone
Ex: epinephrine & norepinephrine
direct gene activation
steroid (fat soluble) hormones enter target cells & bind to intracellular receptors & can influence gene expression
liver, kidney
Hormones are quickly broken down in the ____ & ____
Permeability, protein synthesis, enzyme activation/ suppression, secretion, mitosis
Typically effects (mechanisms) of hormones include: (5)
reproduction, development, stress, fluid/ electrolyte balance, metabolism
Significant things controlled by hormones include: (5)
goiter
caused by iodine deficiency, abnormal growth of the thyroid gland (capture more iodine)
non toxic vs toxic (cancerous)
amino acid/ protein and steroids
What are the 2 general chemical groups of hormones?
some are simply altered (adrenalin & thyroxin), short (ADH), or long (insulin) chains
complex rings made from cholesterol, includes all sex hormones + products of adrenal cortex
Hormone receptor complex
In a lipid soluble hormone a _____ _____ _____ is formed when the unbound hormone binds with intracellular receptors
Hormone response element
For lipid soluble hormones, once the HRC binds with a DNA sequence called _______ _______ ______ it stimulates mRNA synthesis resulting in a new protein
signal transduction pathway
biochemical events initiated when water soluble hormone binds to plasma membrane receptor
the hormone is considered the first messenger
second messenger
an intracellular chemical that modifies activity within a cell after a first messenger binds to plasma membrane
Ex: cAMP, DAG, Ca2+
adenylate cyclase & phospholipase C
What are the 2 most common signal transduction pathways?
G protein
specific protein that when activated by membrane receptor, relays signal to another membrane protein & alters the activity of that protein
Both signal transduction pathways go through this
cAMP
When adenylate cyclase & G protein binds together, increases the formation of ______ which activates protein kinase
protein kinase
an enzyme that adds phosphates to other molecules (phosphorylation), results in activation or inhibition
PIP2
Binding of G protein & phospholipase C results in splitting of _____
splitting of ____ results in two secondary messengers DAG & IP3
DAG
second messenger that remains in the membrane, similar action to cAMP where it activates protein kinase which phosphorylates other molecules
IP3
second messenger that diffuses into cytosol, causes an incr in intracellular Ca2+ [] which acts as a third messenger
Diabetes mellitus
An endocrine disorder that affects 5% of those in the US, 3rd cause of death
Starving in the land of plenty
syndrome: glucosuria, hyperglycemia, polyphagia, ketoacidosis
complications: retinopathy, nephropathy, atherosclerotic coronary & peripheral arterial disease, peripheral & autonomic neuropathies
Type 1 diabetes (IDDM)
most serious of the diabetes mellitus with juvenile onset
5-10% of total
prone to ketosis, microangiopathy, gangrene, blindness, impotence
could be autoimmune
insulin injections vital
ketosis
Occurs when fats & proteins are burned anaerobically producing ketones, making the blood acidic > denaturing of proteins
cholesterol of cell membrane taken out, resulting in rigid membrane
type 2 diabetes (NIDDM)
Onset typically more mature, causes can be genetic or obesity
80% are obese
atherosclerosis: saturated fats no good but unsaturated fats good
treatment: diet, exercise, oral hypoglycemics
gestational diabetes (GDM)
may occur during pregnancy, “warning shot”
80% become NIDDM within 20 years unless they get their fat% in check
breast feeding helps shed some fat
aerobic exercise
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
Responses that occurs in stress reactions, same responses despite different stressors
tachycardia, hyperventilation, sweating, hyperglycemia, hypertension, high adrenalin + cortisol
stressors typically extremes
alarm and resistance reaction
What are the two types of response mechanisms to stress monitored by the hypothalamus?
alarm reaction
reaction in response to stress, involves sympathetic nervous system & adrenal medulla
SNS speeds things up
Adrenalin prolongs SNS responses
lasts seconds to minutes
resistance reaction
Slower & more prolonged stress response involving cortisol & aldosterone
body is supported for increased activity over a period of time
response & hormones can suppress pain
exhaustion stage
Occurs following prolong stress & body can’t continue to work in high stress capacity
cortisol levels may be depleted
hypokalemia (low potassium) may lead to cell death
organ fatigue & failure
aldosterone gets rid of further potassium
health, age, sex, nationality, past experiences
What factors influence stress reaction? (5)