CSC405 Final Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Last updated 9:33 PM on 12/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Cars drive 60 km/h over a 1 km long bridge. A car thus requires 1 minute to cross the bridge. Cars stay separated by about 100 m, so 1 car enters and another exits the bridge every 6 seconds. What is the execution time?
1 Minute
2
New cards
Behind a car's simple items like steering wheel, gas pedal, and brake pedal are complex mechanical/computerized details. This is an example of what?
Abstraction
3
New cards
The hex number F represents what decimal number?
15
4
New cards
An integrated circuit is often referred to as what?
chip
5
New cards
101011101010101000 Is an example of what kind of language?
Machine Language
6
New cards
add $2, $4, $6 is an example of what kind of language?
Assembly Language
7
New cards
Kilobyte is how many bytes?
1000
8
New cards
Megabyte is how many bytes?
1,000,000
9
New cards
Gigabyte is how many bytes?
1,000,000,000
10
New cards
Terabyte is how many bytes?
1,000,000,000,000
11
New cards
temp = v[k]; is an example of what kind of language?
High level language
12
New cards
Which term refers to software that provides services that are commonly useful, including operating systems, compilers, loaders, and assemblers?
Systems software
13
New cards
A device through which the user gives information to the computer is called
Input device
14
New cards
A device through which the computer gives information to the user is called
Output device
15
New cards
The part of the computer that performs arithmetic operations and makes decisions is called
CPU
16
New cards
The part of the computer being used to store data being used by programs is called
Main Memory
17
New cards
The part of the computer used for long-term, non-volatile storage is called
Secondary Memory
18
New cards
What is the biggest change in microprocessing in the last 20 years?
Multi-processing
19
New cards
A computer designed for use by an individual, usually incorporating a graphics display, a keyboard, and a mouse, is called what?
PC
20
New cards
A computer inside another device running one or more predetermine application or software is called
Embedded Computer
21
New cards
A computer used to run large programs for multiple users on a network is called
Server
22
New cards
What was the firs general purpose, electronic computer?
ENIAC
23
New cards
Which term refers to a program that translates a program written in a high-level language language into a low-level language like assembly or machine language?
Compiler
24
New cards
Which term refers to a class of computers with the highest performance and cost? They are configured as servers and typically cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.
Supercomputer
25
New cards
A desktop computer is not a personal mobile device, true or false?
True
26
New cards
Which term, which is just one simple metric used in measuring performance, is the number of tasks completed per unit of time?
Throughput
27
New cards
Clock speeds have not increased in the last several years. Why?
Powerwall
28
New cards
Java is an example of which type of language?
High-Level Language
29
New cards
Cars drive 30 mph over a 1 mile long bridge. A car thus requires 2 minutes to cross the bridge. Cars stay separated by about one-tenth of a mile, so 1 car enters and another exits the bridge every 12 seconds. What is the execution time?
2 Minutes
30
New cards
"A sister and brother are hanging clothes to dry. They both hang clothes simultaneously to make the job go faster." is an example of what Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Performance via Paralellism
31
New cards
A brother and sister are washing and drying dishes. The sister is drying each dish immediately after the brother washes it." is an example of what Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Performance Via Pipelining
32
New cards
"A mom expects her son will be hungry after a long airplane flight, so she cooks dinner just in case." is an example of which Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Performance Via Prediction
33
New cards
"A drummer's stick breaks, but he quickly grabs another one and continues playing the song." is an example of which Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Dependability via Redundancy
34
New cards
Cars drive 30 mph over a 1 mile long bridge. A car thus requires 2 minutes to cross the bridge. Cars stay separated by about one-tenth of a mile, so 1 car enters and another exits the bridge every 12 seconds. What is the throughput?
5 Cars per Minute
35
New cards
"A customer talks to a phone agent. If there's a problem, he talks to the agent's supervisor" is an example of which Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Hierarchy of Memories
36
New cards
"A house architect first designs a house with 5 rooms, then designs room details like closets, windows, and flooring." is an example of which Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Abstraction to simplify design
37
New cards
"A College student rents a flat closer to campus than her weekend beach spot" is an example of which Great Idea of Computer Architecture?
Make the common case fast
38
New cards
Convert 21 to binary
10101
39
New cards
Convert 10111 to Decimal
23
40
New cards
Translate 101010 into decimal
42
41
New cards
The hex code 1F represents what decimal number?
31
42
New cards
What is the sum of the binary codes 1011 and 1101?
11000
43
New cards
In assembly language programming, which of the following is used to assign a name to a memory address?
Label
44
New cards
Which section of a MIPS assembly program contains the assembly program instructions?
.text
45
New cards
Which section of a MIPS assembly program contains program data?
.data
46
New cards
Is 'avoiding errors' a valid reason to choose assembly programming?
No
47
New cards
In assembly language programming, what starts with a dot and is used to give information to the assembler without being directly translated into machine language instructions?
Assembler Directives
48
New cards
What is a type of assembly language instruction that isn't actually recognized by the CPU hardware, but is instead translated by the assembler into one or more CPU instructions?
Pseudoinstruction
49
New cards
A short segment of MIPS/SPIM code is shown below that is supposed to print a string. Note that 4 is the SPIM system call code for printing a string.
li ____, 4
la $a0, str
syscall
What should be used to fill in the blank to complete the segment of code?
li ____, 4
la $a0, str
syscall
What should be used to fill in the blank to complete the segment of code?
$v0
50
New cards
A short segment of MIPS/SPIM code is shown below that is supposed to exit the program. Note that 10 is the SPIM system call code for exiting the program.
li ____, 10
syscall
What should be used to fill in the blank to complete the segment of code?
li ____, 10
syscall
What should be used to fill in the blank to complete the segment of code?
$v0
51
New cards
What is the difference between a flip-flop and a latch?
The flip-flop change on a clock edge, while a latch changes when input changes.
52
New cards
What type of device contains logic circuitry that can be configured programmatically to implement desired combinational and sequential logic?
FPGA
53
New cards
True or false: SRAM is faster than DRAM, but more expensive. ?
True
54
New cards
What type of device takes an n-bit binary input and has 2n outputs, such that each binary input corresponds to exactly one of the outputs?
Decoder
55
New cards
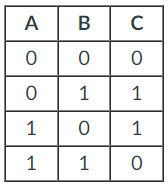
Give a Boolean algebra expression that represents the truth table below.
(~A*B) + (A*~B)
56
New cards
Consider an SR latch with outputs Q and ~Q.
Assume the output is currently Q=0 and ~Q=1.
What would happen if the input S is asserted?
Assume the output is currently Q=0 and ~Q=1.
What would happen if the input S is asserted?
Q and ~Q are toggled.
57
New cards
Consider an SR latch with outputs Q and ~Q.
Assume the output is currently Q=0 and ~Q=1.
What would happen if the input R is asserted?
Assume the output is currently Q=0 and ~Q=1.
What would happen if the input R is asserted?
Nothing changes.
58
New cards
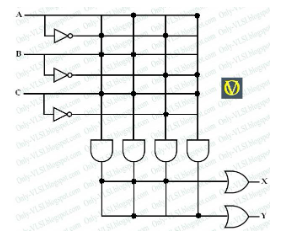
What is the Boolean expression that corresponds to the output Y?
Y = (A · B · C) + (A · ~B · C)
59
New cards
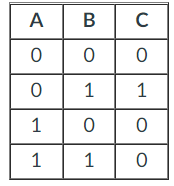
Give a Boolean algebra expression that represents the truth table below.
C = ~A · B
60
New cards
True or false: RISC processors have instructions that take many clock cycles to execute
False
61
New cards
Both instructions and data can be stored in memory and encoded as binary numbers. True or false?
True
62
New cards
Given b=2, c=5, d=1. What is the final value of a after the following instructions have executed?
add t, d, c
add a, t, c
add t, d, c
add a, t, c
11
63
New cards
Given b=2, c=5, and d=1. What is the final value of b after the following statement has executed?
add b, c, d
add b, c, d
6
64
New cards
Give a MIPS add instruction that would compute the following:
z = x + y
z = x + y
add z x y
65
New cards
Write a total of exactly 3 add and subtract instructions in MIPS assembly that would calculate the following:
a = b + c - d + e
a = b + c - d + e
add a b c
sub a a d
add a a e
sub a a d
add a a e
66
New cards
Which term is used for the natural unit of a computer? It typically refers to the size of data that the architecture is designed to handle per instruction.
Word
67
New cards
True or false: $one is a valid MIPS register?
False
68
New cards
True or false, $zero is a valid MIPS register?
True
69
New cards
In the MIPS architecture, how many bits is each register?
32
70
New cards
Convert the following binary number into hexadecimal:
1001 1011 0001 0011
1001 1011 0001 0011
9B13
71
New cards
True or false: 'jump 2500' is a valid MIPS instruction?
False
72
New cards
In the MIPS architecture, how many bytes is each word?
4
73
New cards
Assume $s3=5000 and words addressed from 5000 to 5002 have the data shown:
5000: 99
5001: 77
5002: 323
What value will be put in $t0 by the following instruction?
lw $t0 1($s3)
5000: 99
5001: 77
5002: 323
What value will be put in $t0 by the following instruction?
lw $t0 1($s3)
77
74
New cards
Assume $s3=900, $t0=77, and memory locations 900, 904, and 908 have the values 10, 15, 20 respectively. What would those memory locations have after the following instruction executes?
sw $t0 4($s3)
sw $t0 4($s3)
10, 77, 20
75
New cards
Assume that an int takes up 4 bytes of memory on a computer architecture that has 4-byte words. Also, like MIPS, this architecture addresses each byte of memory.
Assume that we have an array of 5 int values:
int values[5];
If the values array has a base address of 2000, then what is the address of values[1]?
Assume that we have an array of 5 int values:
int values[5];
If the values array has a base address of 2000, then what is the address of values[1]?
2004
76
New cards
Assume $s0=3. What value would be stored in $t2 after the following instruction has executed?
12
77
New cards
Assume $s0=10, $s1=50, and $s2=30. Given this code:
bne $s3, $s4, Else
add $s0, $s1, $s2
j Exit
Else: sub $s0, $s1, $s2
Exit:
What value would be stored in $s0 after this code has executed?
bne $s3, $s4, Else
add $s0, $s1, $s2
j Exit
Else: sub $s0, $s1, $s2
Exit:
What value would be stored in $s0 after this code has executed?
20
78
New cards
Consider the following high-level loop:
int i=10;
do {
i+=5;
} while(i
int i=10;
do {
i+=5;
} while(i
main:
.text
li $t0, 10
li $t1, 50
loop:
add $t0 $t0 5
ble $t0 $t1 loop
jr $ra
.text
li $t0, 10
li $t1, 50
loop:
add $t0 $t0 5
ble $t0 $t1 loop
jr $ra
79
New cards
What is the name of the register that contains the address of the instruction currently being executed?
Program counter or PC
80
New cards
What is the common name for the area of memory where local variables and function parameters are stored?
Stack
81
New cards
What term is used for the segment of memory that contains a function's saved registers, local variables, and parameters?
Activation Record
82
New cards
What happens if memory is dynamically allocated on the heap and never deallocated?
Memory Leak
83
New cards
C++ programmers have to explicitly deallocate dynamic memory on the heap, while Java automatically deallocates memory on the heap through garbage collection. True or false?
True
84
New cards
Consider << to be a bitwise left shift operator. What is 13<
52
85
New cards
Consider >> to be a bitwise right shift operator. What is 13>>2?
Give your answer in decimal.
Give your answer in decimal.
3
86
New cards
Consider the addition of two binary numbers: 1 + 1
Which of the following is a true statement about the result of the addition?
Which of the following is a true statement about the result of the addition?
The result is 10, 1 is the carry and 0 is the sum
87
New cards
What situation occurs when the result of an operation contains more bits than can be represented by the architecture?
Overflow
88
New cards
Convert 0.5 to binary.
0.1
89
New cards
Convert 2.375 to binary.
10.011
90
New cards
Assume -1.5 is represented using the 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point standard. What would the content of the 'Sign' field in the binary value? Your answer should consist of exactly 1 bit.
1
91
New cards
Assume -1.5 is represented using the 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point standard. What would be the first 8 bits of the 'Mantissa' field be in the binary value? Your answer should consist of exactly 8 bits. If applicable, include leading zeroes in your answer. Also, be sure to drop the digit before the point.
1000 0000
92
New cards
Assume -1.5 is represented using the 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point standard. What would the content of the 'Exponent' field in the binary value? Your answer should consist of exactly 8 bits. If applicable, include leading zeroes in your answer. Also, be sure to account for bias on the exponent.
0111 1111
93
New cards
Assume 10.375 is represented using the 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point standard. What would the content of the 'Exponent' field in the binary value? Your answer should consist of exactly 8 bits. If applicable, include leading zeroes in your answer. Also, be sure to account for bias on the exponent.
1000 0010
94
New cards
Assume 10.375 is represented using the 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point standard. What would be the first 8 bits of the 'Mantissa' field be in the binary value? Your answer should consist of exactly 8 bits. If applicable, include leading zeroes in your answer. Also, be sure to drop the digit before the point.
0100 1100
95
New cards
Which of the following best characterizes a rising clock edge?
Clock signal changing from 0 to 1
96
New cards
What term refers to the ALU, registers, buses that carry data between the ALU and registers, and simple components that are connected to the ALU?
Datapath
97
New cards
Assume we have the 4-bit binary value 1000. If the value is sign-extended to 8-bits, what is the result?
1111 1000
98
New cards
The outputs of what type of logic component are determined solely on its current inputs?
Combinational
99
New cards
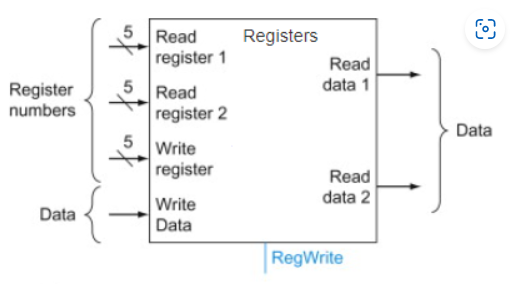
Consider the MIPS register file. The register file always writes data to the register whose number is input to the "Write register' input. True or false?
False
100
New cards
Assume that the Program Counter contains the address 1000. Assuming no branch or jump instruction is executed, the Program Counter will be updated to what address next?
1004