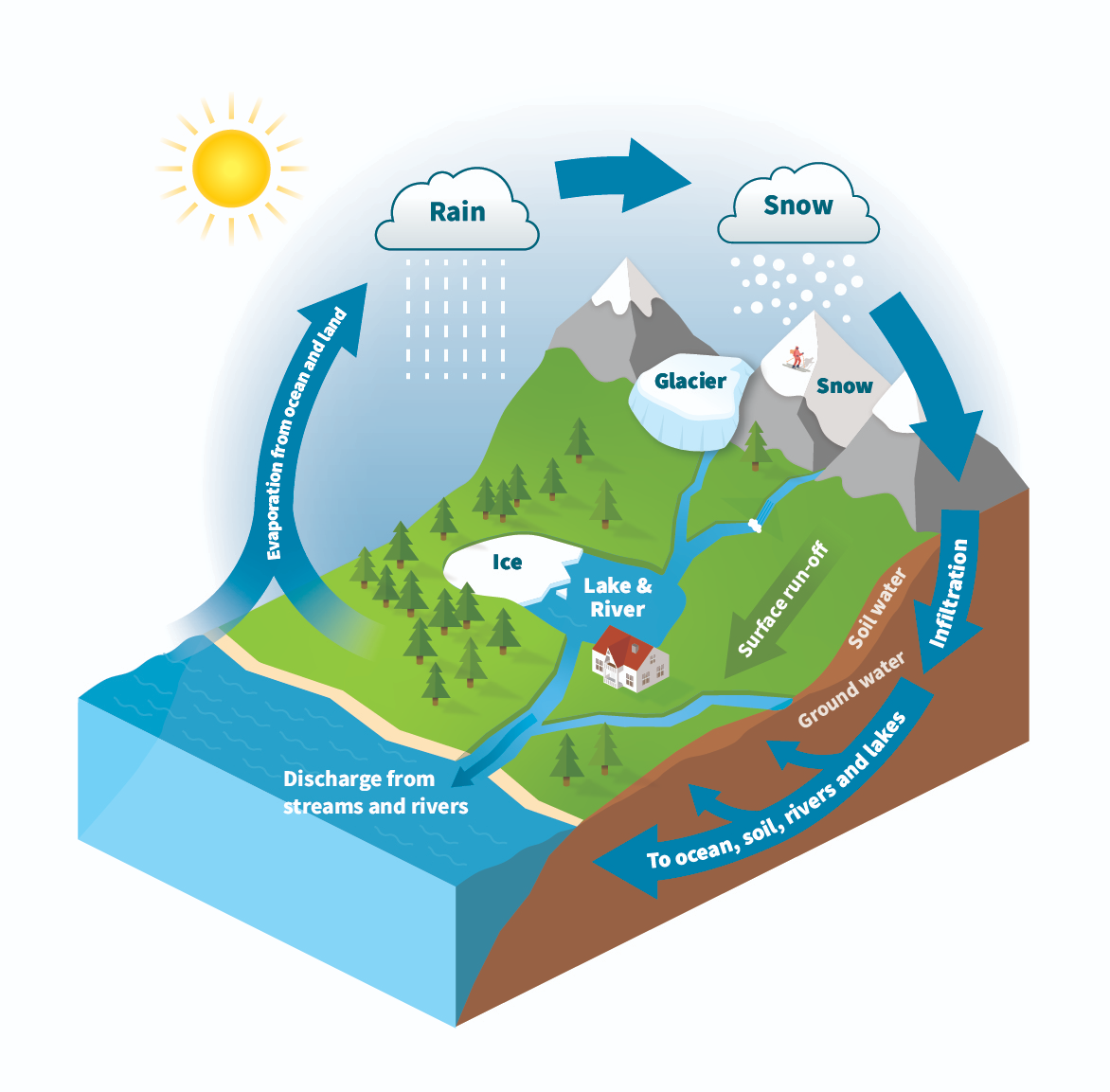
Water cycle - intro
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What are ice shelves?
Platforms of ice formed where glaciers and ice sheets move out into oceans.
What is currently happening to sea ice?
It is in decline.
What percentage of our fresh water is in glaciers?
79%
What can water in the cryosphere be described as?
Solid, or ice.
What are ice bergs?
Chunks of ice that break off glaciers or ice shelves.
What is the size of the Greenland ice sheet?
1.2 million km²
Which two ice sheets contain over 99% of the world’s freshwater ice?
The Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets.
How do ice sheets maintain equilibrium?
By gaining the snow they lose.
Where does the term Cryosphere originate from?
The Greek term for cold: krios.
What do glaciers form as they melt?
U-shaped valleys
What state is water in the atmosphere mainly stored as?
Water vapour.
What states can water in the atmosphere be stored in?
Solid, liquid or gas.
What processes take place in water in the atmosphere?
Evaporation, condensation and sublimation.
What percentage of the earth’s atmosphere is made up of water vapour?
<1%
Water vapour is considered to be what kind of pollutant?
A greenhouse gas.
What percentage of the earth’s water is contained in the atmosphere?
0.0001% (approx.)
How does water move from the biosphere to the atmosphere?
One product of respiration is water vapour, which rises into the atmosphere.
What do the salts in ocean water do to its freezing point?
Lower it.
What is the ocean’s average freezing point?
-2°C
What is the ocean’s average salinity level?
3.5%
What is seawater’s average density?
1025 kg/m³
What is the average pH of seawater?
8.1
What is the most abundant salt component in seawater?
Chloride.
What percentage of the earth’s water is in oceans?
97%
What is the average depth of the ocean?
3682 m
What percentage of the earth’s surface is water?
72%
What percentage of the earth’s oceans is approximated to have been explored?
5%
What percentage of Earth’s water do rivers make up?
0.0002%
What is the Amazon river’s discharge per second?
209,000 m³/s
What is the deepest that groundwater has been found?
18km
What percentage of the Earth’s water is extracted for human consumption?
3%
Freshwater is considered what type of resource?
A finite resource.
What is another name for water stored in aquifers?
Fossil water.
What percentage of freshwater is ground water?
30%
What is latent heat?
‘Hidden’ heat energy.
Which way does condensation transfer water between stores?
Atmospheric store → terrestrial + oceanic stores
Which way does evaporation transfer water between stores?
Terrestrial + oceanic stores → atmospheric store
How does evaporation work in terms of latent heat and water stores?
Latent heat of vapourisation absorbed from the environment
Water moves from surface stores to atmosphere as water vapour
Surface water stores decrease
Atmospheric water storage increases
How does condensation work in terms of latent heat and water stores?
Latent heat of condensation released into atmosphere
Water vapour forms clouds / precipitation
Atmospheric storage decreases
Surface and ice stores increase
How do melting and freezing work in terms of latent heat and water stores?
Latent heat of fusion absorbed in melting or lost in freezing
Melting of ice increases liquid water stores
Freezing increases cryospheric stores
What factors effect the rate of evaporation?
Amount of solar energy
Water availability
Air humidity (more humid = less space to gain water)
Air temperature - warm air is less dense
Transpiration / number of plants
What is the process of condensation?
At dew point temperature, water molecules in the air need something to condense on
These are called condensation nuclei or condensation surfaces
If the surface is below freezing, the water sublimates
This forms hoar frost
What process directly causes all precipitation?
Condensation.
How does precipitation occur if air temperature is reduced but volume remains constant?
Dew
Hoar frost
Fog
How does precipitation form if the volume of air increases but heat is not added?
Adiabatic cooling:
Rainfall- relief, frontal or convectional
What is adiabatic cooling?
Adiabatic cooling is the process by which the temperature of a gas decreases as it rises and expands, without any heat being added or removed from the system.
How does adiabatic cooling work?
As air rises, pressure decreases
The air parcel expands in the lower pressure environment
Expansion requires energy, which comes from the air parcel’s internal energy
As a result, temperature drops, even though no heat is exchanged with the surroundings
Adiabatic cooling causes cloud formation
How does convectional rainfall occur?
A surface heats up
Water evaporates
Parcel of hot air rises
Temperature drops
Relative humidity increases as temperature drops
Condensation leads to precipitation
How does frontal rainfall occur?
Cold front meets warm air
Warm air rises and cools, as it is less dense
Water in the air condenses to form clouds
Condensation leads to precipitation
How does relief rainfall form?
Warm, moist air is forced to rise over high areas
The air cools and condenses, forming clouds
Precipitation occurs
The air sinks and becomes warmer and drier
How does rain form generally?
Water vapour condenses and falls as a liquid.
How does sleet form generally?
Precipitation starts as snow, falls through warm air and melts partially.
How does snow form generally?
A cloud freezes, the water droplets crystallise and fall as snowflakes.
How does hail form generally?
Storm updraft causes water to move upwards and solidify in droplets, which become hailstones.
When was the most recent glacial period?
2.58 million years ago
What is quarternary glaciation?
The current glacial cycle.
What part of a glacial cycle are we in now?
An interglacial period.
What defines an interglacial period?
Ablation exceeds accumulation, thus more ice melts than freezes.
How does the hydrological cycle function in an interglacial period?
It functions normally.
How does the hydrological cycle function in a glacial period?
It does not function properly, as ice is held in the cryosphere.
What defines a glacial period?
Accumulation exceeds ablation, thus more ice forms than is melted.
How many glacial cycles have there been over the past 740000 years?
8.
What is another name for a glacial period?
An ice age.
Define a drainage basin.
An area of land drained by a river.
Define evapotranspiration.
The overall transfer of water from land to the atmosphere.
Define groundwater flow.
Movement of water in bedrock beneath the earth’s surface.
Define infiltration.
Water on the surface of the ground entering the soil.
Define interception storage.
Precipitation that is caught and temporarily held by vegetation.
Define water balance.
The relationship between water inputs, outputs and storage in a system.
Define overland flow.
The movement of water across the ground’s surface.
Define percolation.
The downward movement of water through soil and rock layers.
Define runoff.
The total volume of water that reaches a river.
Define saturated.
Soil where the pores are full of water.
Define stem flow.
A process where precipitation is caught by the leaves or branches of a plant, and flows down the stem or trunk.
Define a storm and rainfall event.
A period of precipitation from a single storm system.
Define throughfall.
Precipitation that drips through leaves and branches.
Define throughflow.
The lateral movement of water through soil.
Define transpiration.
The loss of water vapour from plants through pores in the leaves.
Define precipitation.
Water lost from the atmosphere that falls to the land.
Define condensation.
Water vapour forming liquid droplets.
What is ablation?
Ice melting.
What is accumulation?
The formation of ice.
The Hydrological cycle: