OOP Midterms
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Object-oriented programming
a computer programming model that organizes software design around data, or objects rather than functions and logic.
Object
a data field that has unique attributes and behavior.
Benefits of OOP
Reusability, scalability, and efficiency
Data Modeling
First step in OOP
collect all of the objects a programmer wants to manipulate and identify how they relate to each other
Example of OOP
The object is a human being, who is described by properties like name and address.
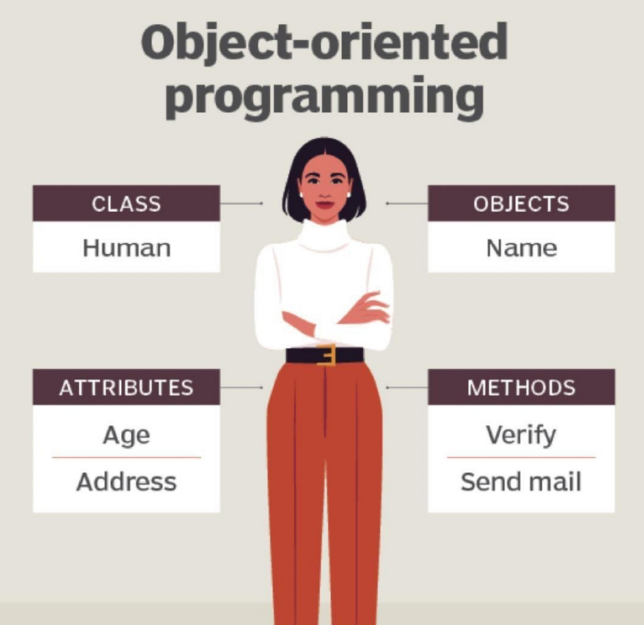
Classes
are user-defined data types that act as the blueprint for individual objects, attributes, and methods
Objects
are instances of a class created with specifically defined data.
when class is defined initially, the description is the only _____ that is defined.
Methods
are functions that objects can perform.
they are defined inside a class that describe the behaviors of an object.
Instance Methods
subroutines contained in an object
Attributes
represent the state of an object
they are the characteristics that distinguish classes.
Encapsulation
states that all important information is contained inside an object and only select information is exposed.
the implementation and state of each object are privately held inside a defined class.
Abstraction
objects only reveal internal mechanisms that are relevant for the use of other objects, hiding any unnecessary implementation code.
Inhertiance
classes can reuse code and properties from other classes
relationships and subclasses between objects can be assigned, enabling developers to reuse common logic while still maintaining a unique hierarchy.
Polymorphism
objects are designed to share behaviors, and they can take on more than one form.
The program determines which meaning or usage is necessary for each execution of that object from a parent class, reducing the need to duplicate code.
enables different types of objects to pass through the same interface.
Syntax
set of rules that define how words and punctation are organized in a programming language
Coupling
is the degree to which software elements are connected to one another.
if a class has its attribute change, then any other coupled class also changes.
Association
is the connection between one or more classes.
can be one to one, many to many, one to many or many to one
Advantages of OOP
Modularity
Reusability
Flexibility and Extensibility
Encapsulation
Abstraction
Modularity
breaking down a complex system intro smaller, manageable units (classes and objects).
Each class represents a specific functionality, making it easier to understand, maintain, and update the codebase.
Reusability
OOP facilities code ______ through inheritance and polymorphism.
inheritance allows a subclass to inherit properties and behaviors from a superclass, reducing code duplication
Polymorphism enables objects to be treated as instances of their superclass, enhancing flexibility and extensibility,
Flexibility and Extensibility
provides ____ and ___ by allowing developers to add new features or modify existing ones without affecting the entire codebase.
Encapsulation
is the key principle of OOP that encapsulates data (attributes) and methods (functions) with a single unit (class).
Abstraction
focuses on hiding complex implementation details and exposing only essential features to users.
Simula
the first object-oriented programming language
Pure OOP languages
Ruby
Scala
JADE
Emerald
Primarily for OOP Languages
Java
Python
C++
Languages that pair with OOP
Visual Basic.NET
PHP
JavaScript
Benefits of OOP
Modularity
Reusability
Productivity
Easily upgradable and scalable
Interface Descriptions
Security
Flexibility
Code maintenance
Lower cost
Encapsulation
is a fundamental OOP principle that combines data and methods class
it allows implementation details to be hidden while exposing a public interface for interaction.
Example of Encapsulation

How encapsulation is implemented
by declaring instance variables as private, restricting direct access.
public getter methods retrieve variable values, while setter methods modify them, enabling controlled access.
Encapsulation
is defined as the wrapping up of data under a single unit.
the variables or data of class are hidden from any other class and can be accessed only through any member function of its own class.
Private class
can hide its members or methods from the end user, using abstraction to hide implementation details, by combining data hiding and abstraction.
How to achieve encapsulation?
by declaring all the variables in the class as private and writing public methods in the class to set and get values of variables.
Inheritance
a mechanism in java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features (fields & methods) of another class.
Reasons on why we need Java Inheritance
Code Reusability
Method Overriding
Abstraction
Class
is a set of objects which shares common characteristics/behavior and common properties/attributes.
a blueprint or prototype from which objects are created.
Super Class/Parent Class
the class whose features are inherited is known as a superclass. (or base class/parent class)
Sub Class/Child Class
the class that inherits the other class is known as a subclass (or a derived class, extended class or child class).
has its own fields and methods on addition to the superclass fields and methods.
Reusability
inheritance supports the concept of “______”
when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class.
How to use inheritance in Java?
the extends keyword is used for ______ in java.
Using the extends keyword indicates you are derived from an existing class.
Subclass
During inheritance only the object of the _____ is created, not the superclass.
Types of Inheritance
Single Inheritance
Multilevel Inheritance
Hierarchical Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance
Single Inheritance
a sub-class is derived from only one super class.
it inherits the properties and behavior of a single-parent class
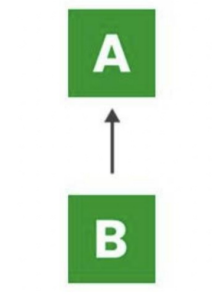
Multilevel Inheritance
a derived class will be inheriting a base class, and as well as the derived class also acts as the base class for other classes.

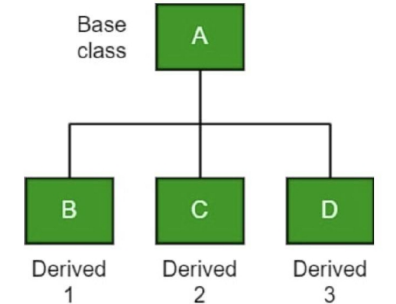
Hierarchical Inheritance
one class serves as a superclass for more than one subclass.
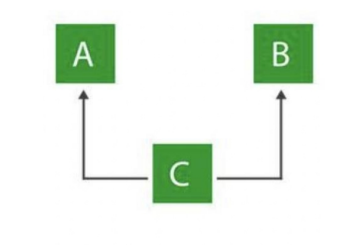
Multiple Inheritance (Through Interfaces)
one class can have more than one superclass and inherit features from all parent classes.
note: java does not support ______ inheritances with classes. this is only achievable through interfaces.
Hybrid Inheritance
is a mix of two or more of the above types of inheritance.
java does not support multiple inheritances with classes, ______ inheritance involving multiple inheritance is also not possible with classes.
it can be achieved through a combination of multilevel inheritance and hierarchical inheritance with classes, hierarchical and single inheritance with classes.
IS-A
is a way of saying: this object is a type of that object.

Sub-classes
in _____ we can inherit members as is, replace them, hide them, or supplement them with new members
Inherited Fields
The _____ ____ _can be used directly, just like any other fields.
New fields
We can declare ____ ____ in the subclass that are not in the superclass.
Inherited Methods
The _____ methods can be used directly as they are.
Instance Method
We can write a new _____ ____ in the subclass that has the same signature as the one in the superclass, thus overriding it.
Static method
W can write a new ____ ___ in the subclass the same signature as the one in the superclass, thus hiding it.
New methods
We can declare ____ ___ in the subclass that are not in the superclass.
Subclass Constructor
We can write a _____ ____ that invokes the constructor of the superclass, either, implicitly or by using the keyword super.
Advantages of Inheritance in Java
Code Reusability
Abstraction
Class Hierarchy
Polymorphism
Disadvantages of Inheritance in Java
Complexity
can make the code more complex and harder to understand.
Tight Coupling
creates a tight coupling between the superclass and subclass, making it difficult to make changes to the superclass without affecting the subclass.
Default Superclass
every class has one and only one direct ________ (single inheritance). In the absence of any other explicit _______, every class is implicitly a subclass of the Object class.
Super class can only be one
can have any number of subclasses but only one superclass.
Inheriting Constructors
inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass.
Private member inheritance
a subclass does not inherit the private members of its parent class.
however, if the superclass has public or protected methods (getters and setters) for accessing its private fields, these can also be used by the subclass.
Polymorphism
means ‘having many forms’
refers to the ability of a message to be displayed in more than one form
it allows objects to behave differently based on their specific class type.
Types of Java Polymorphism
Complie-Time Polymorphism
Runtime Polymorphism
Compile-Time Polymorphism
also known as static polymorphism
is achieved by function overloading or operator overloading. (but java doesnt support operator overloading.
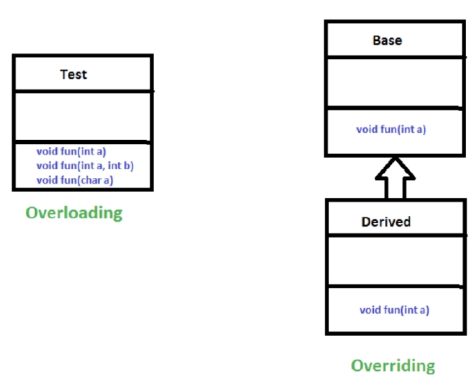
Method Overloading
when there are multiple functions with the same name but different parameters then these functions are said to be overloaded.
functions can be overloaded by changes in the number of arguments or/and a change in the type of arguments.
Subtypes of Compile-time Polymorphism
Function overloading
Operator overloading
Template
Function Overloading
a feature in c++ and java where multiple functions can have the same name but with different parameter lists. the compiler will decide which function to call based on the number and types of arguments passed to the function.
Operator Overloading
a feature in c++ where the operators such as +, -. *, etc. can be given additional meanings when applied to user-defined data types.
Template
is a powerful feature in C++ that allows us to write generic functions and classes.
is a blueprint for creating a family of functions or classes.
Runtime Polymorphism
is known as dynamic method dispatch
a process in which a function call to the overridden method is resolved at runtime.
this can be done method overriding
Subtype of Run-Time Polymorphism
Virtual Functions
Virtual Functions
allows an object of a derived class to behave as if it were an object of the base class.
the derived class can override the _____ ____ of the base class to provide its own implementation.
the function call is resolved at runtime, depending on the actual type of object.
Advantages of Polymorphism

Disadvantages of Polymorphism

Subtyping vs Subclassing
OOP relies heavily on concepts of subtyping and subclassing.
Understanding these concepts is crucial for effectively writing reusable and maintainable code.
Subclassing
is a specific mechanism in OOP languages like Java that implements subtyping through inheritance.
inherits the attributes and methods of its superclass, establishing an “is-a” relationship
Subtyping
is a broader concept that deals with relationships between types.
it’s about the ability of one type to be substituted for another type in certain context.
is primarily achieved through inheritance and interfaces
Benefits of Subtyping with Interfaces

Subclassing
is a specific implementation of subtyping through class hierarchies
involves creating a new class that inherits attributes and behaviors from an existing class, known as a superclass.
Key Characteristics of Subclassing

Subtyping without Subclassing

Polymorphism via Interfaces

Abstraction
is the process of hiding the implementation details and only showing the essential functionality or features to the user.
this helps simplify the system by focusing on what the object does rather than how it does it.
How is abstraction achieved in Java?
by interfaces and abstract classes.
Abstract Class
is a class that is declared with an abstract keyword.
may or may not have all abstract methods. some of them can be concrete methods
can have parameterized constructors and the default constructor is always present in an abstract class.
Abstract Method
is a method that is declared without implementation
must always be redefined in the subclass, thus making overriding compulsory or making the subclass itself abstract.
Class
any ____ that contains one or more abstract methods must also be declared with an abstract keyword.
Instantiated
There can be no object of an abstract class. That is, an abstract class can not be directly ______ with the new operator.
Algorithm to Implement Abstraction

Advantages of Abstraction
simplifies complex systems by hiding implementation details.
increases code reusability and maintainability
enhances security by exposing only essential features
improves modularity and separation of concerns.
provides a clear and user-friendly interface.
Disadvantages of Abstraction
it can add unnecessary complexity if overused.
may reduce flexibility in implementation.
makes debugging and understanding the system harder for unfamiliar users.
overhead from abstraction layers can affect performance.
Why do we use abstract?
it is used to simplify the complexity and make easier for both user and end users. we can use abstraction to hide details and show necessary parts.