Chapter 15: The Special Senses
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
olfactory neurons
15.1: Olfaction
olfactory receptor cells
found in the olfactory epithelium
bipolar
olfactory epithelium
15.1: Olfaction
pseudostratified columnar epithelium tissue located in the nasal cavity that plays a crucial role in the sense of smell
airborne molecules
15.1: Olfaction
what enters the nasal cavity and gets dissolved in the fluid covering the olfactory epithelium?
papillae
15.2: Taste
projections on the surface of the tongue, often mistaken for taste buds
filiform papillae
15.2: Taste
a major type of papillae that is filament-shaped
has no taste buds
most numerous papillae
provide a rough surface on the tongue
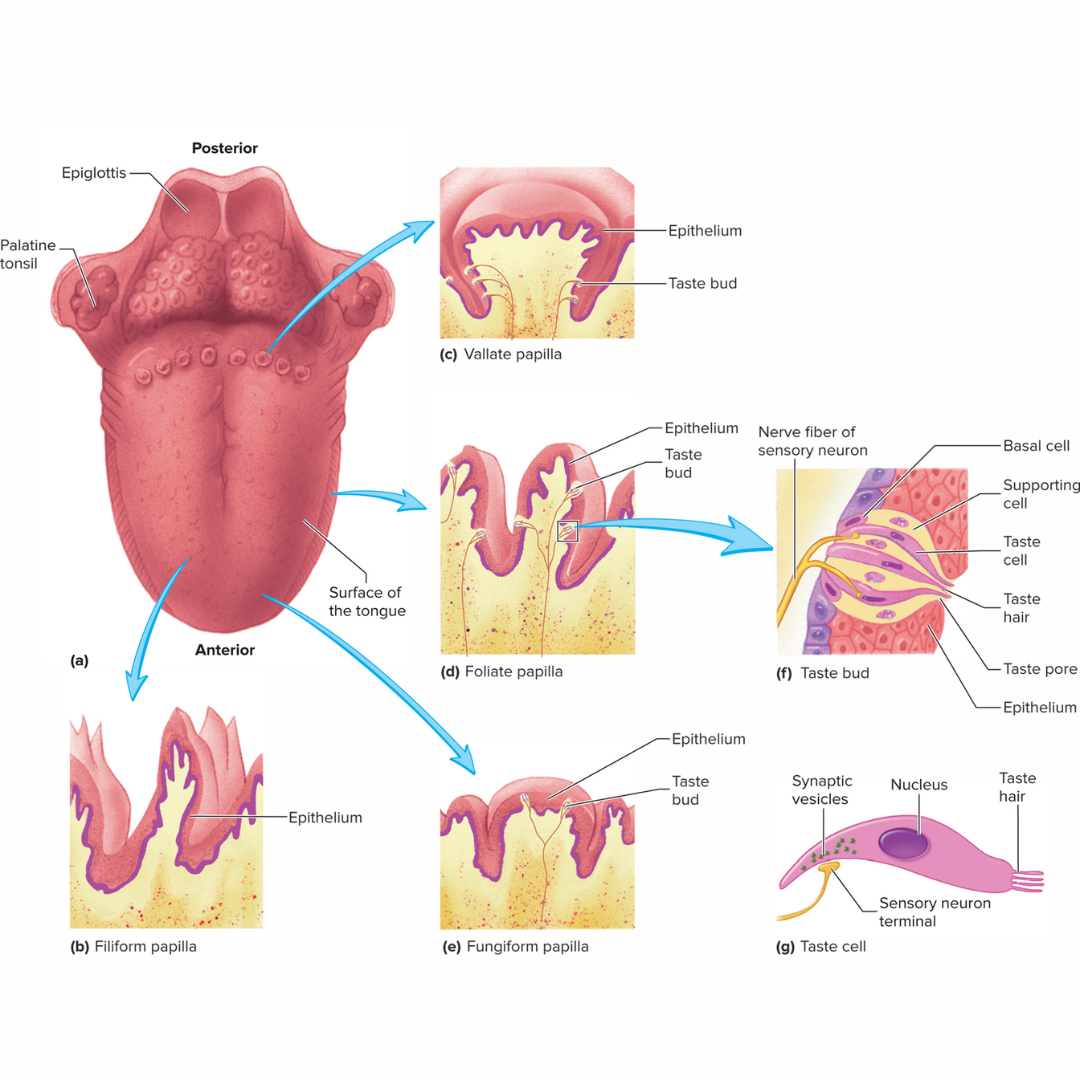
vallate papillae
15.2: Taste
a major type of papillae that means “surrounded by a wall”
largest, but least numerous
8-12 of the form a V-shaped raw along the border between the anterior and posterior parts of the tongue
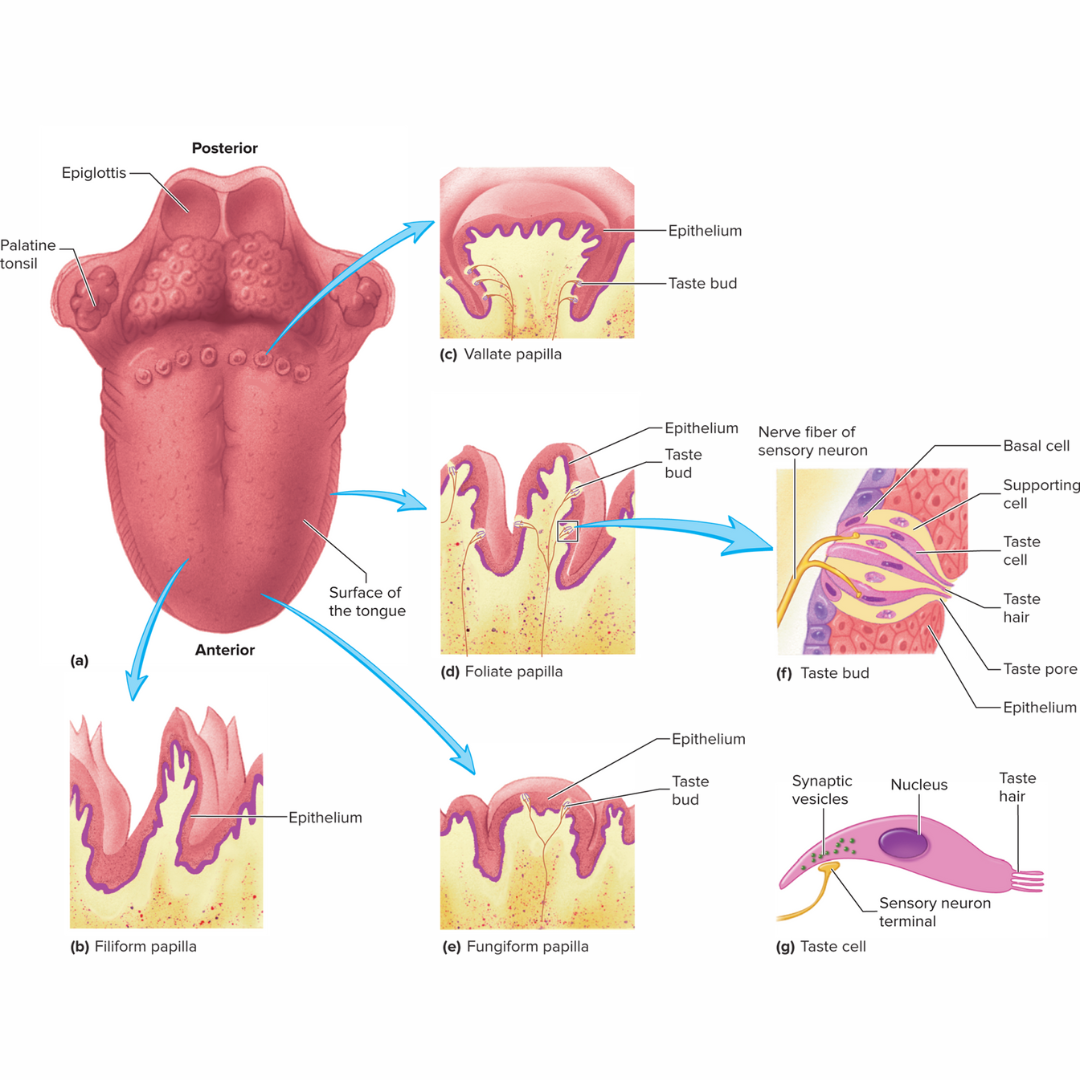
foliate
15.2: Taste
a major type of papillae that is leaf-shaped
distributed in folds on the sides of the tongue
contain the most sensitive taste buds
located posteriorly
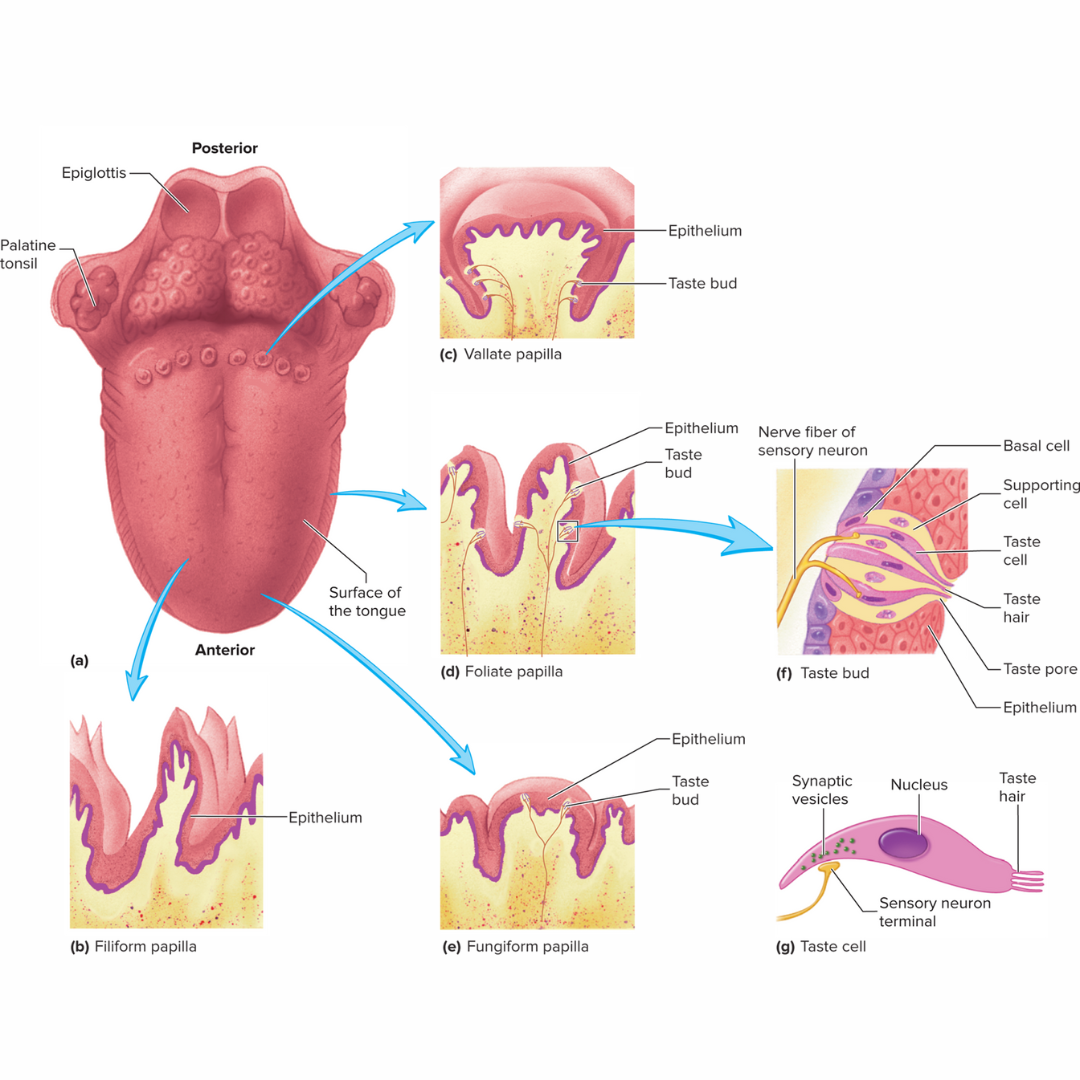
fungiform
15.2: Taste
a major type of papillae that is mushroom-shaped
scattered irregularly over the superior surface of the tongue
appear as small, red dots interspersed among the far more numerous filiform papillae
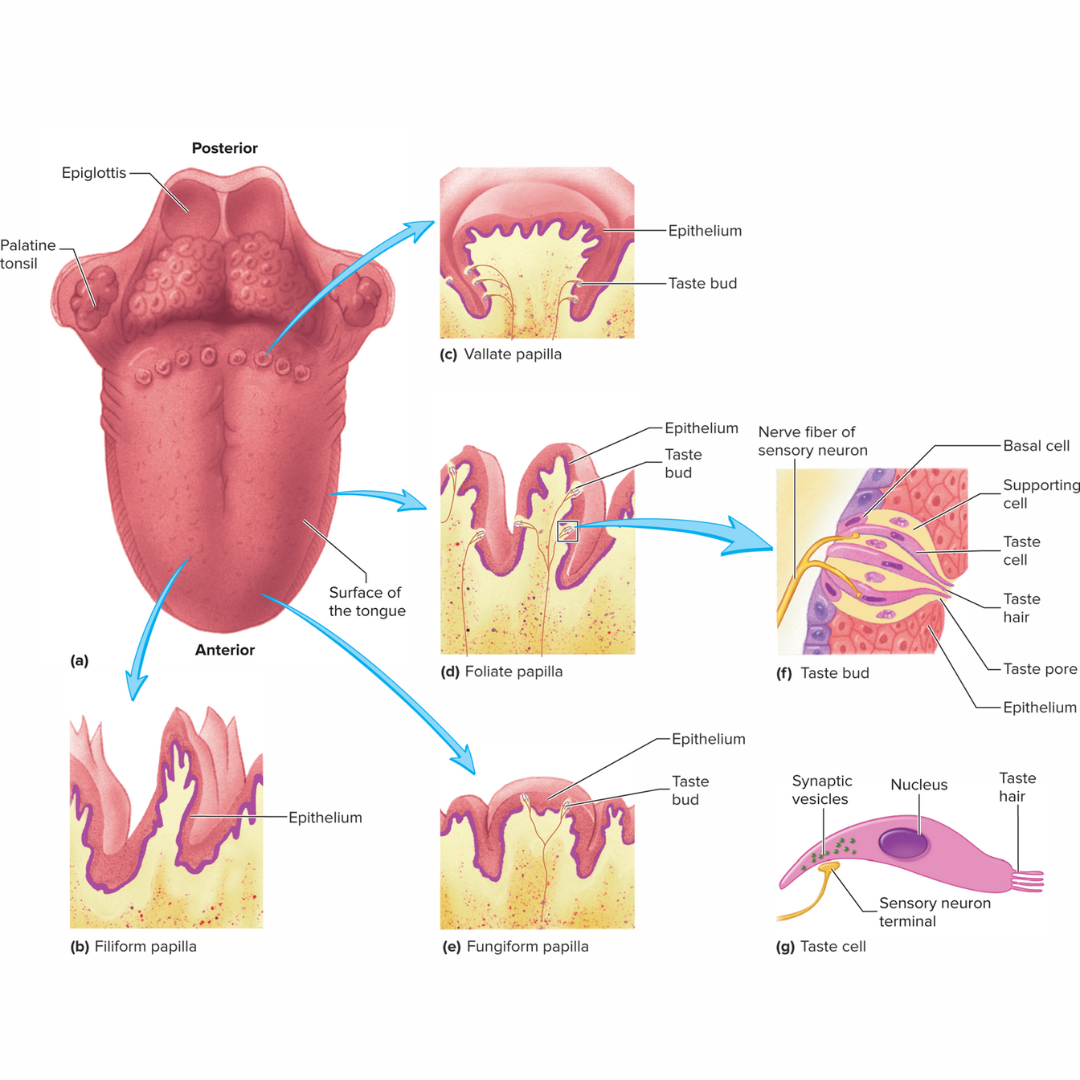
taste buds
15.2: Taste
sensory structures that detect taste
oval structures embedded in the epithelium of the tongue and mouth
consist of basal cells, supporting cells, and taste cells
each one has about 50 taste cells
tastants
15.2: Taste
substances that, when dissolved in saliva, enter the taste pores and stimulate the taste cells
There are five major classes: salt, sour, sweet, bitter, and umami
eyebrows
15.3: Visual System: Accessory Structures
short hairs on the bony ridge above the eyes
prevent perspiration from running down the forehead and into the eyes
shades eyes from sunlight
eyelids
15.3: Visual System: Accessory Structures
The movable fold of skin in front of the eyeball
also called palpebrae
protects the eyes from foreign objects
eyelashes
15.3: Visual System: Accessory Structures
Hair at the margins of the eyelids
ciliary glands are modified sweat glands that open into the follicles to keep these lubricated
a sty forms when one of these glands is inflamed
conjunctiva
15.3: Visual System: Accessory Structures
a thin, transparent mucous membrane covering the anterior surface of the eyeball and lining the lids
when this is inflamed, caused by an infection or irritation, it’s called pink eye
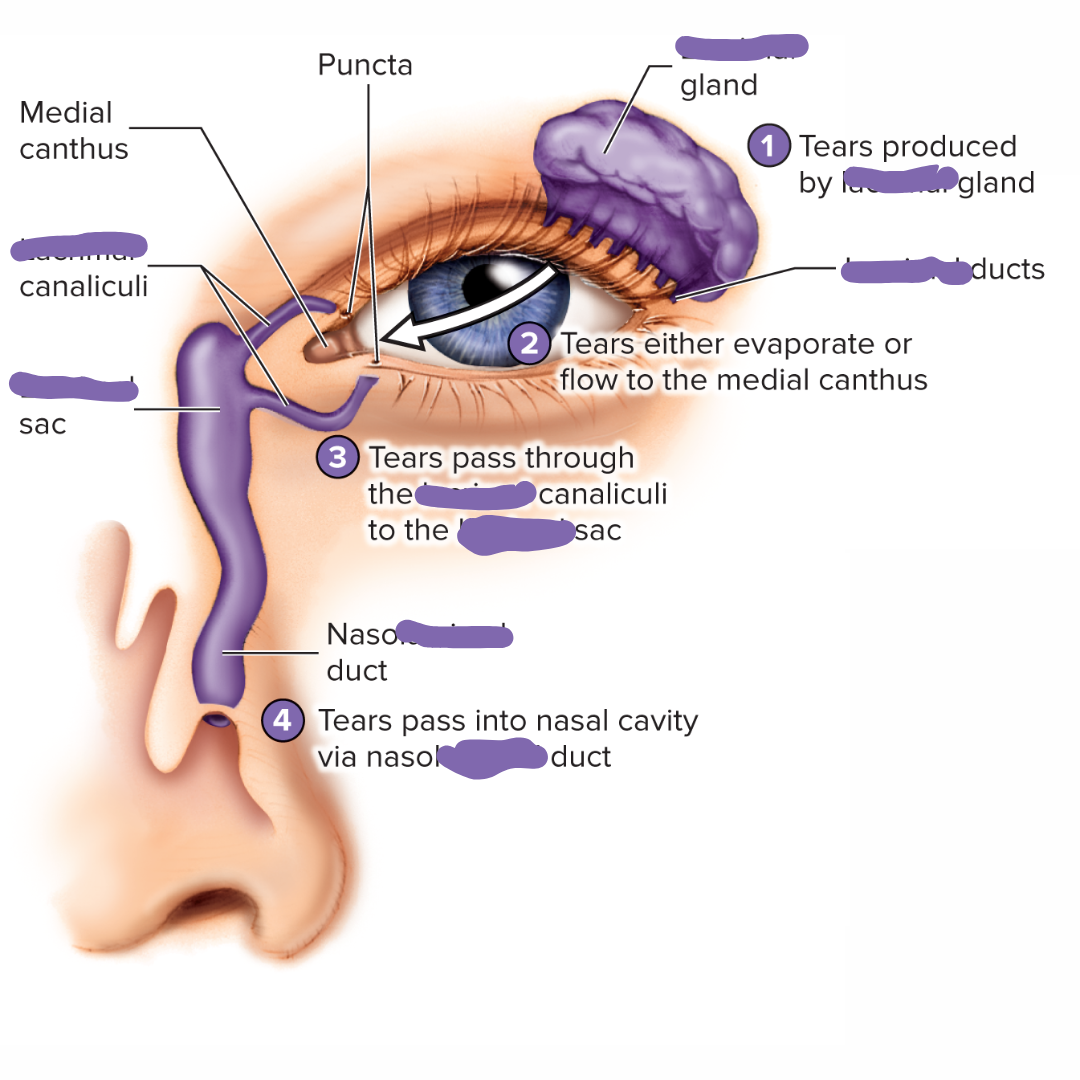
lacrimal apparatus
15.3: Visual System: Accessory Structures
consists of a “tear” gland in the superolateral corner of the orbit of the eye and a duct system that extends from the eye to the nasal cavity.
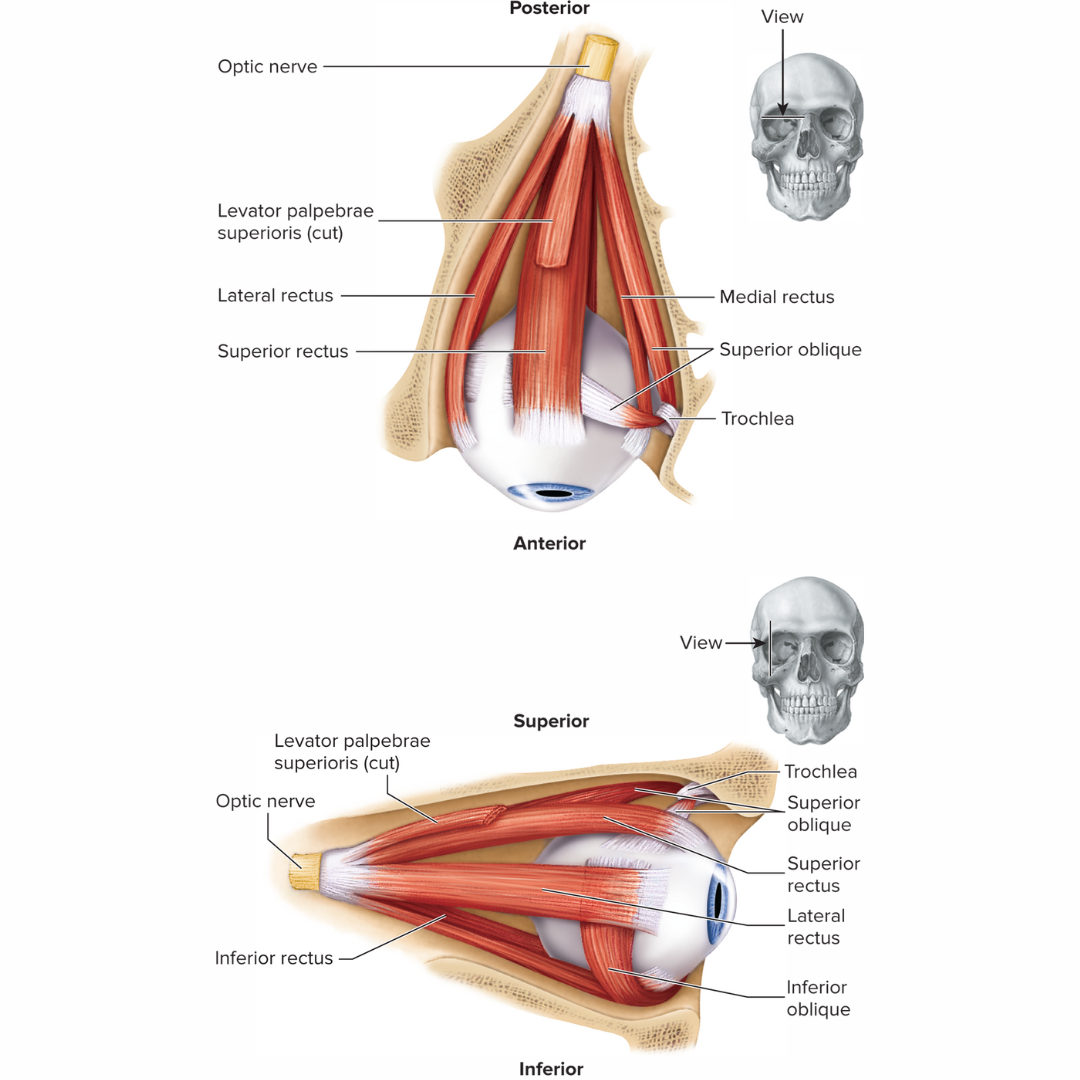
extrinsic eye muscles
15.3: Visual System: Accessory Structures
muscles located outside the structure (eye) being moved
the eye has six of these
four of these run more or less straight anteroposteriorly
two are positioned at an angle to the globe of the eye
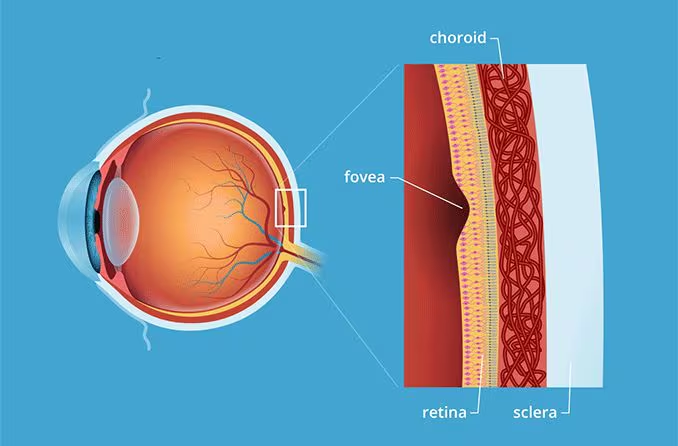
distant vision
when the ciliary muscles are relaxed
fovea centralis
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
the area of greatest visual acuity
anterior chamber
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
Chamber of the eye between the cornea and the iris (separator)
filled with aqueous humor
posterior chamber
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
Chamber of the eye between the iris (separator) and the lens
filled with aqueous humor
vitreous chamber
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
larger chamber of the eye
completely surrounded by the retina
filled with a transparent, jelly-like substance called [term part] humor that holds the lens and retina in place
fibrous tunic
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
outer layer of the eye
consists of the sclera and the cornea
sclera: a tough white outer layer that protects the eye
cornea: the transparent, anterior part of the eye that allows light to enter (avascular)
firm, opaque tissue layer
vascular tunic
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
middle layer of the eye
consists of the choroid, ciliary body, and iris
choroid: A vascular layer that nourishes the retina and contains blood vessels.
ciliary body: A ring-shaped structure that produces aqueous humor and contains the ciliary muscles that control lens shape
iris:The colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light entering the pupi
contains many blood vessels
nervous tunic
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
the inner layer of the eye
consists of the retina
retina: The light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye where images are formed.
retina
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
the nervous tunic of the eyeball
consists of:
outer pigmented layer: composed of pigmented simple cuboidal epithelium
inner neural layer: responds to light with numerous photoreceptor cells (120 million rods and 6-7 million cones), and numerous relay neurons
covers the inner surface of the eyeball posterior to the ciliary body
rods
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
photoreceptor in the retina of the eye
responsible for noncolor vision in low-intensity light.
cones
15.3: Visual System: Anatomy
photoreceptor in the retina of the eye
responsible for color vision
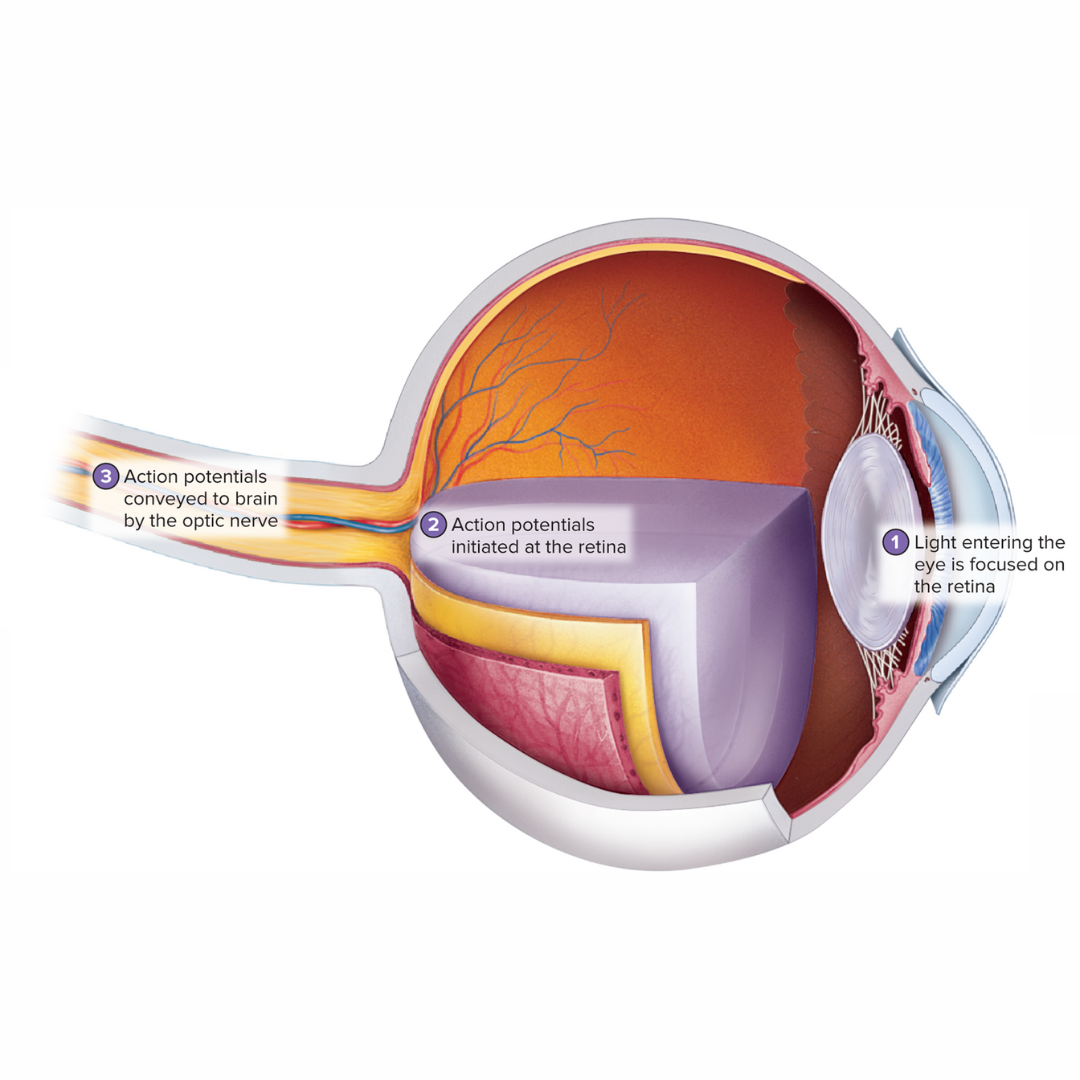
process of vision
15.3: Visual System: Functions
as light passes through the pupil of the iris, it is focused on the retina by the cornea, lens, and humors
the light striking the retina is converted into action potentials
the optic nerve conveys these action potentials to the brain
external ear
15.4: Hearing and Balance
consists of the auricle and the external acoustic meatus
middle ear
15.4: Hearing and Balance
connects the external and inner ears
tympanic membrane
15.4: Hearing and Balance
the structure in the middle ear that is stretched across the external acoustic meatus
the auditory ossicles
15.4: Hearing and Balance
the three structures (malleus, incus, and stapes) that transmit vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window
malleus
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Largest of the three auditory ossicles
attached to the tympanic membrane
the hammer
incus
15.4: Hearing and Balance
middle of the three ossicles in the middle ear.
the anvil
stapes
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Smallest of the three auditory ossicles
attached to the oval window
the stirrup
oval window
15.4: Hearing and Balance
membranous structure to which the stapes attaches
transmits vibrations to the inner ear
mastoid air cells
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Spaces within the mastoid process of the temporal bone that are connected to the middle ear by ducts.
auditory tube
15.4: Hearing and Balance
the structure that connects the middle ear to the pharynx
equalizes pressure between the middle ear and outside air
inner ear
15.4: Hearing and Balance
a canal system within the temporal bone that contains perilymph and the membranous labyrinth
a bony labyrinth
bony labyrinth
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Part of the inner ear
contains the membranous labyrinth that forms the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
membranous labyrinth
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Membranous structure within the inner ear consisting of the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
endolymph
15.4: Hearing and Balance
the fluid found within the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear
high concentration of K+ and a low concentration of Na+
perilymph
15.4: Hearing and Balance
the fluid that fills the space between the membranous labyrinth and the bony labyrinth in the inner ear
low concentration of K+ and a high concentration of Na+
vestibule
15.4: Hearing and Balance
middle region of the inner ear containing the utricle and saccule
involved in balance
semicircular canals
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Canal in the petrous portion of the temporal bone that contains sensory organs that detect kinetic or dynamic equilibrium
Three [term] are within each inner ear.
cochlea
15.4: Hearing and Balance
a fluid-filled, spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear
crucial for hearing, converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound
divided into three regions by the vestibular and basilar membranes
scala vestibuli
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Division of the cochlea lying above the spiral lamina and vestibular membrane
contains perilymph
scala tympani
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Division of the spiral canal of the cochlea lying below the spiral lamina and basilar membrane.
contains perilymph
round window
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Membranous structure separating the scala tympani of the inner ear from the middle ear
cochlear duct
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Interior of the membranous labyrinth of the cochlea
filled with endolymph
contains the spiral organ
also called cochlear canal or scala media
spiral organ
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Organ of Corti
rests on the basilar membrane and consists of the hair cells that detect sound.
found within the cochlear duct
action potential
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Fill-the-blank
In the spiral organ (organ of Corti), sound vibrations cause basilar membrane movement, which in turn stimulates hair cells and their stereocilia. This mechanical stimulation leads to the opening of ion channels, resulting in an influx of ions and the generation of a(n) [term].
utricle and saccule
15.4: Hearing and Balance
Part of the membranous labyrinth
contains a sensory structure, the macula, that detects static equilibrium.