HGAP Unit 5 Vocab
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Agriculture
Planting and harvesting domesticated plants and raising domesticated animals for food.
Domesticated Plant
A deliberately planted, protected, cared for plant that is used by humans and is genetically distinct from its wild ancestors.
Domesticated Animal
An animal that depends on people for food and shelter and is different from its wild ancestors in looks, behavior as a result of close contact with humans.
Farmers
People who raise crops and livestock to sell in the market at a profit rather than raising them for their own consumption.
Physical Geography for Agriculture
3 of the most important elements for agriculture are soil, topography, and climate.
Nutrients
Found in topsoil, which is created of decomposing matter. They are components of topsoil (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) that are necessary for plants to survive, grow, and reproduce.
Topography
The arrangement of shapes on Earth's surface. Ex: Mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.
Climate
The average weather over a 30 year period.
Weather
The daily outdoor conditions that differ every day.
Tropical Wet Climates
A climate located along the equator that experiences rain every day of the year.
Tropical Wet and Dry Climates
A climate located along the equator that has a dry season with little to no rain, usually in the winter; often has monsoons.
Monsoon
A seasonal shift of winds that can cause a rainy season or a very dry season.
Monsoon Rains
Long periods of heavy rains caused by onshore winds from a monsoon.
Arid
A dry climate that gets less than 10 inches of rain annually.
Semiarid
A climate that gets 10-20 inches of rain annually and long periods of drought. They can support farming. Also known as a steppe climate.
Moderate Climates
Climates found north and south of the equator with an average temperature of 75°F
Humid Subtropical Climates
Climates found on the eastern side of continents. They have long summers and mild winters.
Marine West Coast Climates
Found along western coasts, closer to the poles. Breezes that carry contrasting air temperatures cause a moderate climate. Long summers and cool winters.
Mediterranean Climate
A climate located around the Mediterranean Sea with mild winters and clear skies and abundant sunshine.
Mediterranean Agriculture
Continental Climates
A climate with a large temperature range and moderate precipitation. It is found in the interior of continents, north of the moderate climate zones only in the northern hemisphere.
Continentality
Remoteness from oceans
Humid Continental Climates
A climate with a wide temperature range, moderate precipitation, and 4 distinct seasons; experiences warm to hot summers, moderate to abundant rainfall (20-50 inches) and cold winters with snow.
Humid Cold Climates
Found in the north of continental climates with year round cold temperatures.
Intensive Farming Practices
Agriculture that requires high levels of labor and financial capital to own a farm. Farmers need to put in a lot of effort to get the maximum return from their farm.
Subsistence Agriculture
Small local food production for consumption with a lot of effort from family members.
Commercial Agriculture
The large-scale production of crops and livestock with machinery and farming techniques to sell on the market instead of personal consumption.
Market Gardening
The practice of growing a diverse range of crops on a small scale for local markets, typically in moderate climates that support year-round production or through controlled environments like greenhouses.
Truck Farm
A larger type of market gardening. It has more land, less crop diversity, and more national/global markets. They usually concentrate on a single product and work together with other farmers to get their product in the markets.
Plantation
A large farm that requires a lot of investments for the production of a single tropical/subtropical crop for the global marketplace. Farmers don't own the land, they are owned by a wealthy landowner/corporation. A type of intensive agricultural system.
Mixed Crop/Livestock Agriculture
A diverse type of agriculture that produces cereal grains, root crops, and herd livestock. An intensive agriculture system.
Cereal Grains
Seeds that come from a wide variety of grasses around the world. Ex: corn, wheat, barley, etc.
Root Crops
Vegetables that form below the ground and are needed to be dug out. They are mostly used to feed the family. Ex: Potatoes, yams, etc.
Cash Crops
Crops raised to sell for a profit through exports. Ex: cotten, hemp, coffee, etc.
Peasants
Farmers with small farms who own their fields, rely on family labor, and produce cereal crops for themselves and for markets. They raise livestock to help with farming.
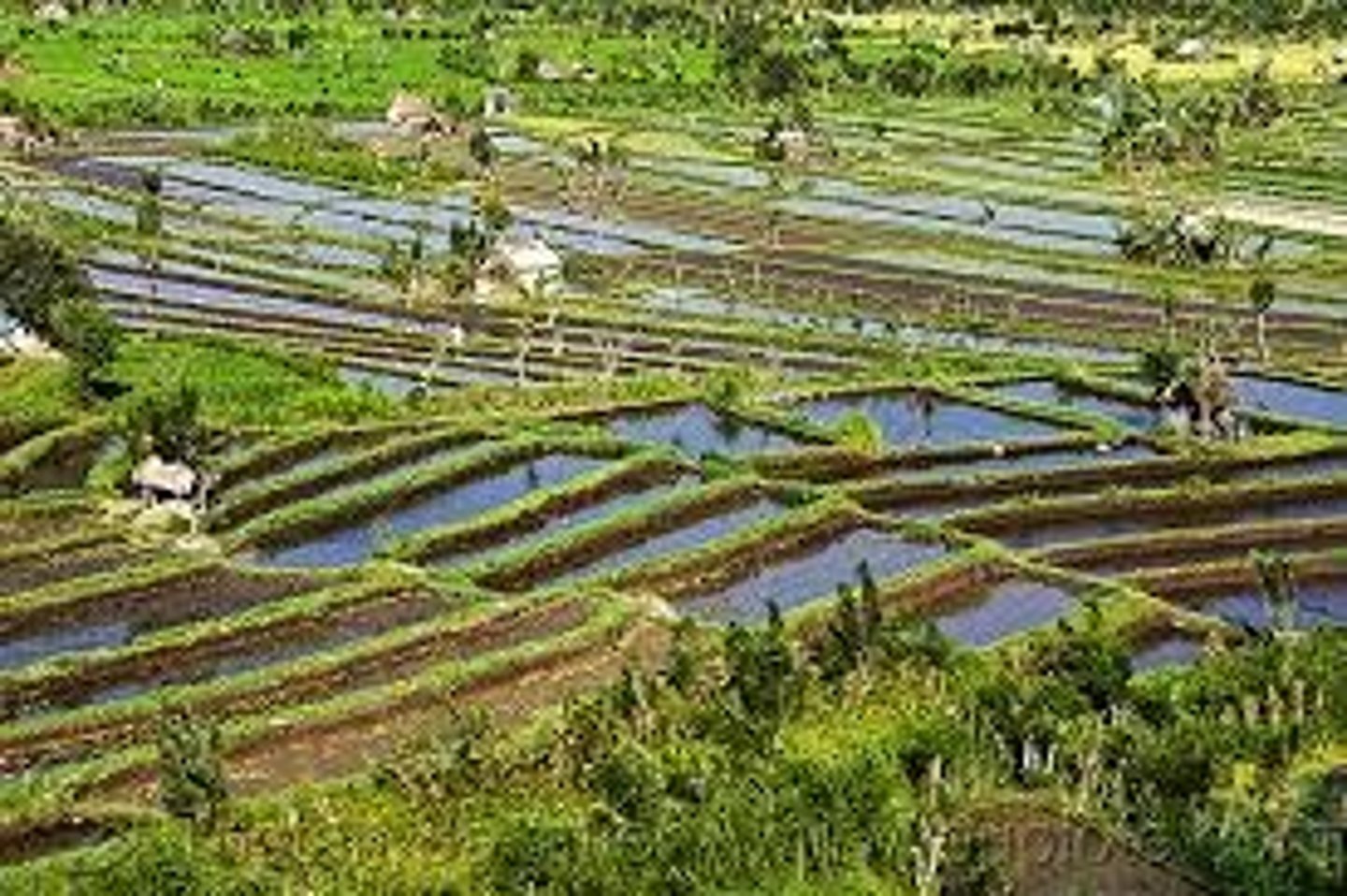
Paddy Rice Farming
Intensive agriculture system. Wet rice growing using small fields bordered by long walls. The fields are called paddies and are flooded with a few inches of water for the growing season.

Grain Farming
An intensive mechanized farming system that produces cereal grains. It takes place on large units of land and machinery, pesticides, fertilizer, and genetically engineered seeds allow farmers to operate the land. Grain regions are often called belts.
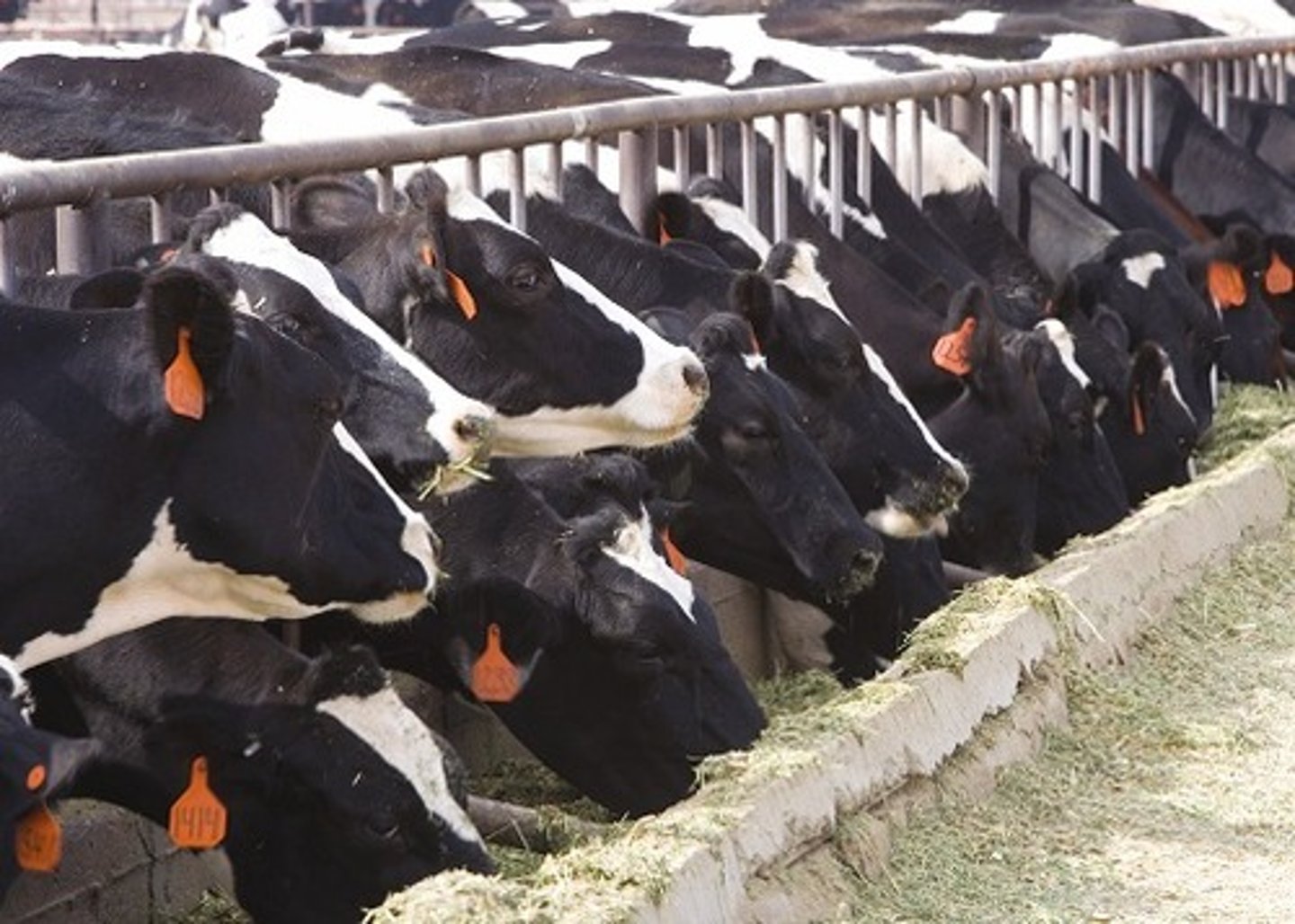
Livestock Fattening
An intensive system of animal feeding using feedlots to limit movement and weight loss to fatten livestock for slaughter. Slaughterhouses depend on immigrant labor for butchering and packing.
Feedlots
Fenced enclosures to limit movement to fatten livestock.
Dairying
A intensive farming system that breeds, raises, and utilizes livestock (usually cows) to produce milk and various dairy products.
Extensive Farming Practices
An agriculture system that requires little investment and labor to successfully raise crops and animals. They rely on natural fertility and climate conditions.
Shifting Cultivation
A type of extensive agriculture. Cultivating in a plot of land until it becomes less productive. The farmer then goes to another land that has been prepared by slash-and-burn agriculture.
Slash and Burn
Cutting plots in forests and burning the cuttings to clear the ground and release nutrients, and planting in the ash of the cleared plot. Also known as swidden agriculture.
Intercropping
The practice of planting multiple crops in the same clearing. It allows taller crops to protect fragile ones.
Nomadic Herding
An extensive agriculture system of breeding domesticated herd animals by moving them to open pasturelands with mobility and move their animals with transhumance. The nomads usually herd for subsistence due to unpredictable environments.
Tundra
A flat arctic region of Europe, Asia, and North America where the subsoil is permanently frozen.
Livestock Ranching
A type of extensive agriculture using large pieces of land to raise large herds of livestock. They need large pieces of land in order to move around to find food, due to the limited grasslands in arid regions.
Rural Area
An area located outside of towns and cities.
Rural Settlement
A small group of people living outside of an urban area
Agricultural Landscape
Areas used for agricultural production. They can tell us about agricultural practices in specific areas.
Grain Elevator
Large storage facility for grain. Usually used for grain farming.
Suitcase Farms
A farm in the grain belt that is not owned by a farm family. Corporations hire migratory crews who live elsewhere.
Silo
A round tower structure that stores food for the livestock. Used in dairy farming.
Settlement Patterns
The way people organize themselves on the land.
Clustered Settlements
Farmers grouped together with a farmstead for defense and communal ties. Farmers journey out of the village everyday to work on the fields. Also known as farm villages.
Farmstead
The center of the farm operations, which includes the farmhouse, barns, sheds, livestock pens, and the family garden. Used in clustered settlements.
Dispersed Settlements
When families/people live further apart because they want space, or because of things like peace and colonization.
Linear Settlements
Where buildings are arranged in a line along a road/river because legal systems dictated that property lines must be rectangular. Ex: Long lot settlement pattern
Survey Methods
The methods used by surveyors to lay out property lines.
Cadastral
Systematic documentation of property ownership, shape, use, and boundaries.
Metes and Bounds
A survey system that uses natural features to mark boundaries. They have a more irregular outline than rectangular surveying.
Long-Lot Settlements
A survey method that divides the land into rectangles that provides each farmer with fertile land, water, and access to transportation.
Domestication
The process where humans selectively breed for unique plants and animals to create a genetically distinct species.
First Agricultural Revolution
The period where the early domestication and diffusion of plants and animals and the cultivation of seed crops led to the development of agriculture.
Teosinte
A wild grass in Mexico that produced 1 inch long corn.
Mesoamerica
The region in the Americas that includes the diverse civilizations in Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Belize, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica.
Fertile Crescent
An area in Southwest Asia that includes the Tigris and Euphrates river, which were the earliest center for domestication of seed plants.
Indus River Valley
Area along the Indus River that flows from Tibet to Pakistan. It is the site of the earliest domestication of plants and herd animals.
Columbian Exchange
The interaction and transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, disease, and ideas between the Americas, West Africa, and the Old World during the 15th and 16th centuries.
Second Agricultural Revolution
The period between 1600-1930 where methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of farm produce improved.
Seed Drill
An invention that allowed seeds to be organized when planting.
Mechanical Reaper
A machine used to harvest grain crops mechanically; patented by Cyrus McCormick in 1831.
Scythe
A tool used for hand cutting grain.
Agrichemicals
Chemical compounds obtained from petroleum and natural gas for use in agriculture. Includes fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides.
Synthetic Fertilizer
Industrially manufactured nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, made from petroleum by-products; contains higher concentrations of nutrients for plants than natural fertilizers.
Pesticide
Used to kill or repel animals that damage crops
Herbicide
A pesticide used to kill weeds.
Nutrient Pollution
When fertilizer seep down into groundwater or are carried into nearby waterways as runoff.
Runoff
The flow of rain or irrigation water over land.
The Green Revolution
The US supported development of high-seed varieties that increased the productivity of cereal crops and accompanying agricultural technologies for transfer to developing countries.
Crossbreeding
Mixing different species/varieties of plants/animals to produce a hybrid.
Hybrid
The offspring of two plants or animals of different species or varieties.
Double-Cropping
Planting another crop on the same plot of land as soon as the first crop has been harvested.
Multicropping
Planting 2 or 3 crops per year on the same land.
Cassava
A root vegetable native to South America that diffused to Africa during the Columbian Exchange.
Sorghum
An African grain plant similar to corn.
Endemic
Native to or characteristic of a certain environment.
Environmental Contamination
The chemical residue that builds up due to fertilizers and pesticides.
Soil Salinization
The concentration of dissolved salts in the soil due to poor drainage from irrigation.
Capital Expenditures
Assets that cost money, such as land, machinery, synthetic fertilizers, etc.
Bid-Rent Theory
Explains how the demand for/price of land decreases as its distance from the central business district increases.
Central Business District
A dense cluster of offices and shops located at a city's most accessible point, usually its center.
Large-Scale Commercial Operation
A large-scale farm oriented towards producing crops for sale on the market.
Monocropping
Producing one crop on extensive tracts of land.
Agricultural Cooperative
A organization where farmers pool their resources in certain areas of activity.
Family Farm
A farming operation owned by a family/family corporation that sells its products to some defined market, directly or through a cooperative.
Commodity
A primary product that can be brought. Ex: Chicken, rice, etc.
Commodity Chain
Series of links showing the processes involving a commodity's place of production, distribution, and consumption.
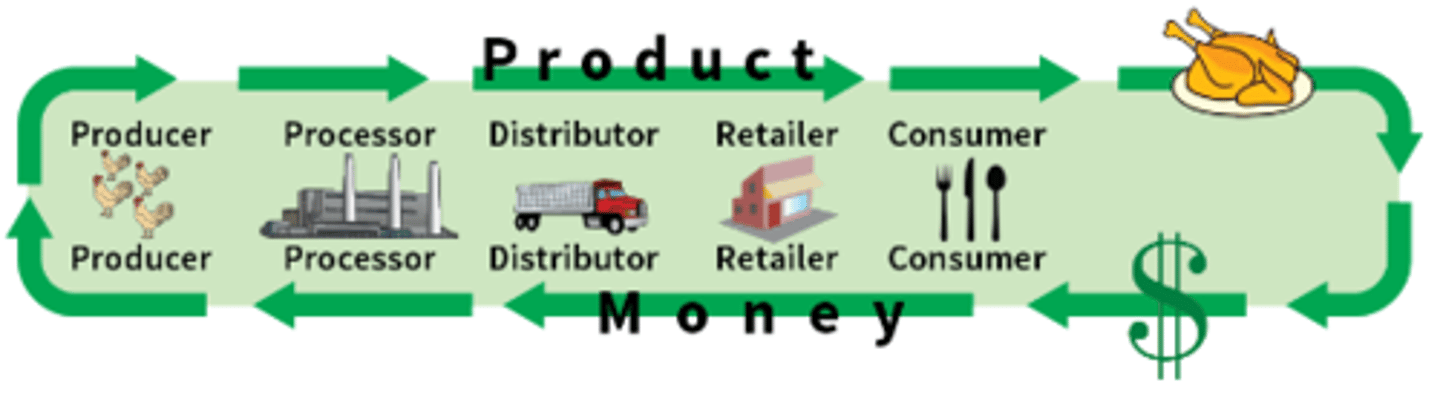
Agribusiness
A large corporation that provides a variety of goods and services to support the agricultural industry.
Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation
Cages that only allow the livestock to grow.
