Diffraction, Polarization, and Relativity in Physics 250
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is diffraction?
Diffraction is the bending of light waves around obstacles and the spreading out of waves when they pass through narrow openings.
What scientific technique is used to study atomic structures?
X-ray diffraction is used to study atomic structures by shining X-rays on materials.
Who discovered the double helix structure of DNA?
James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the double helix structure of DNA in 1953.
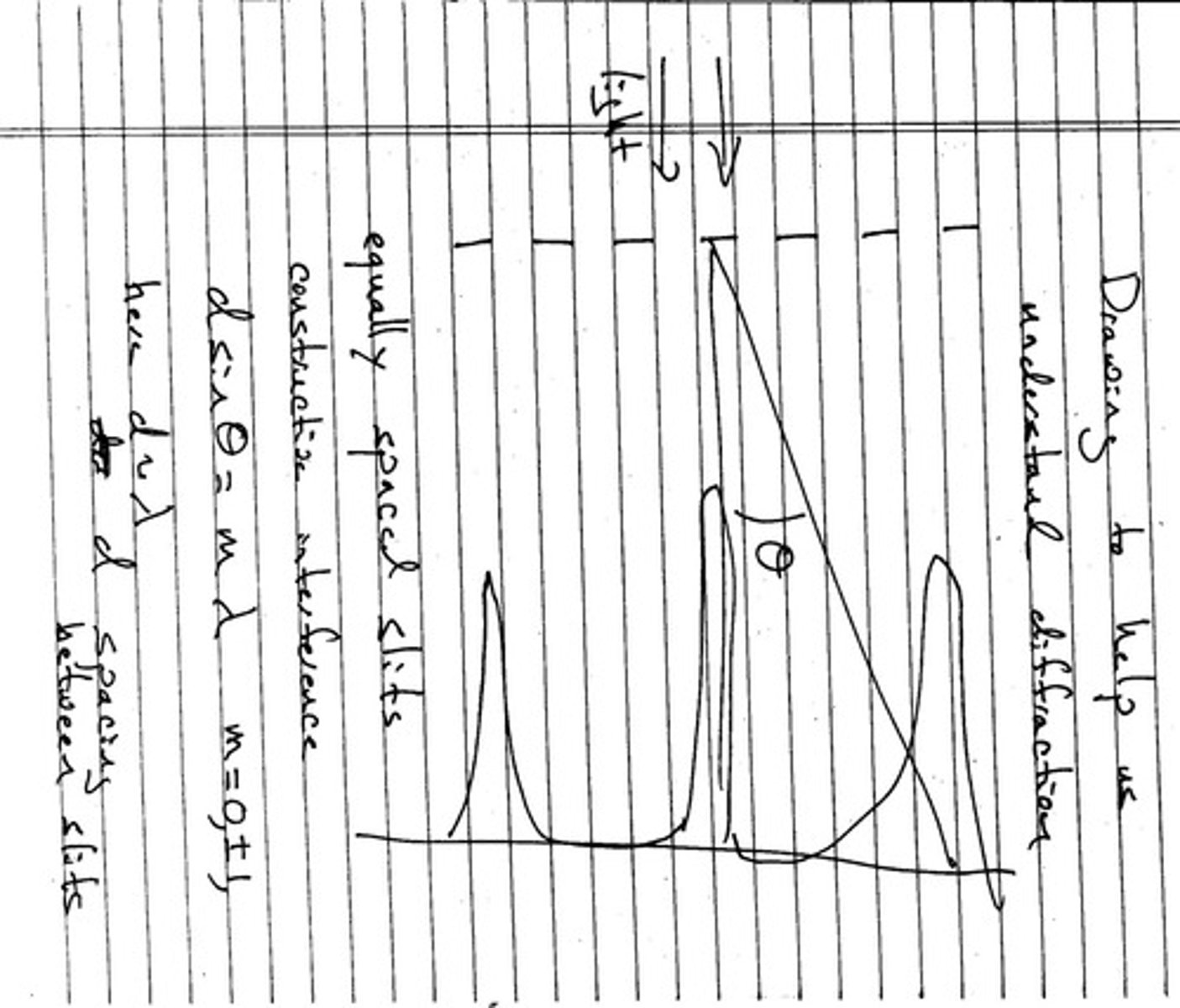
What is the spacing of a diffraction grating with 1000 lines per millimeter?
The spacing d is 1 x 10^-6 meters.
What is Brewster's angle?
Brewster's angle is the angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection.
What happens to light at Brewster's angle?
At Brewster's angle, p-polarized light is transmitted more readily, while s-polarized light is reflected.
What are Fresnel's equations used for?
Fresnel's equations describe how light behaves when it encounters a boundary between two different media, specifically the reflection and transmission coefficients.
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
What is the principle of special relativity?
The principles of special relativity state that the laws of physics are the same in all inertial reference frames and that the speed of light is constant in a vacuum.
What is the consequence of time dilation in special relativity?
Time dilation means that time is measured differently for observers in different inertial frames, particularly those moving relative to each other.
What does the equivalence principle state?
The equivalence principle states that no experiment can distinguish between a uniform gravitational field and an accelerating frame of reference.
How does gravity affect the path of light?
Gravity changes the path of light but does not affect its speed.
What is the effect of gravity on clocks according to general relativity?
Clocks run faster in weaker gravitational fields and slower in stronger gravitational fields.
What is the significance of the Michelson-Morley experiment?
The Michelson-Morley experiment failed to detect the ether and demonstrated that the speed of light is constant, leading to the development of special relativity.
What is the relationship between mass and energy in relativity?
The relationship is expressed in Einstein's equation E = mc², indicating that mass can be converted into energy.
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection occurs when a wave traveling in a medium hits a boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing it to reflect entirely back into the medium.
What is the role of atomic clocks in GPS technology?
Atomic clocks in GPS satellites account for time dilation effects due to both special and general relativity to provide accurate positioning.

What is the difference in clock rates between satellites and clocks on Earth?
Clocks in satellites run faster due to weaker gravity (general relativity) and slower due to their relative motion (special relativity), resulting in a net difference.
What is the significance of the term 'inertial reference frame'?
An inertial reference frame is one in which an object either remains at rest or moves at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
What is the formula for the transmission coefficient?
The transmission coefficient T is given by T = 1 - R, where R is the reflection coefficient.
What is the significance of the term 'non-inertial frame'?
A non-inertial frame is one that is accelerating, meaning that the laws of physics may appear different compared to an inertial frame.
What is the impact of the speed of light on modern physics?
The constancy of the speed of light has led to the development of theories such as special relativity and has profound implications for our understanding of space and time.