Lab 4: PLANT CELLS, VEGETATIVE ORGAN STRUCTURES, AND PATTERNS OF GROWTH
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
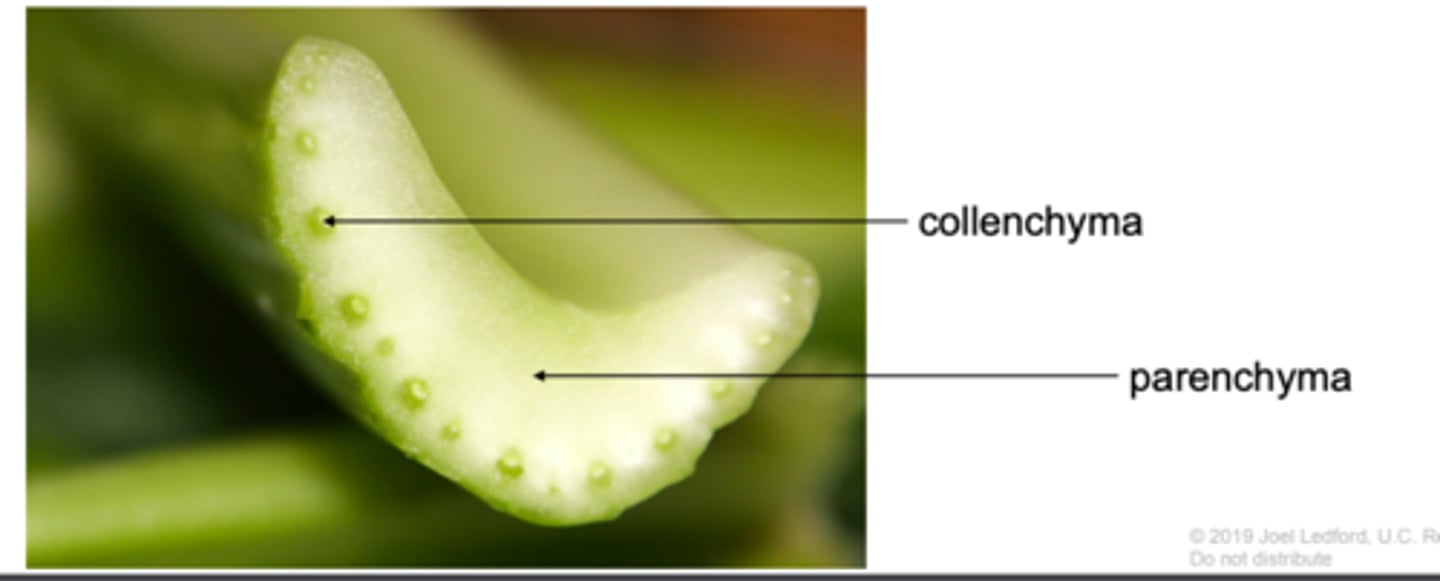
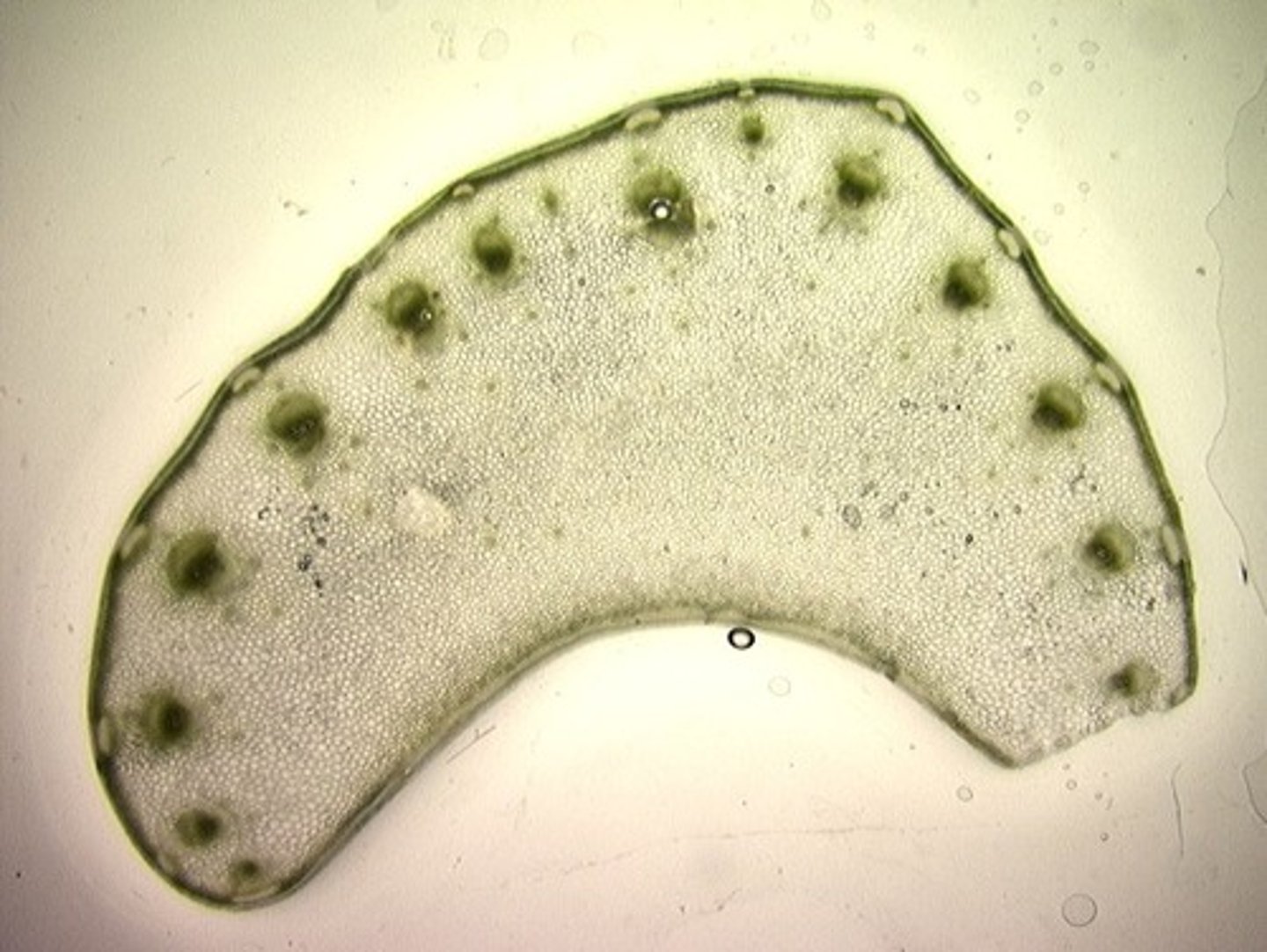
celery petiole
parenchyma cells celery

Epidermal cell in celery
outer layer of cells on the celery stalk
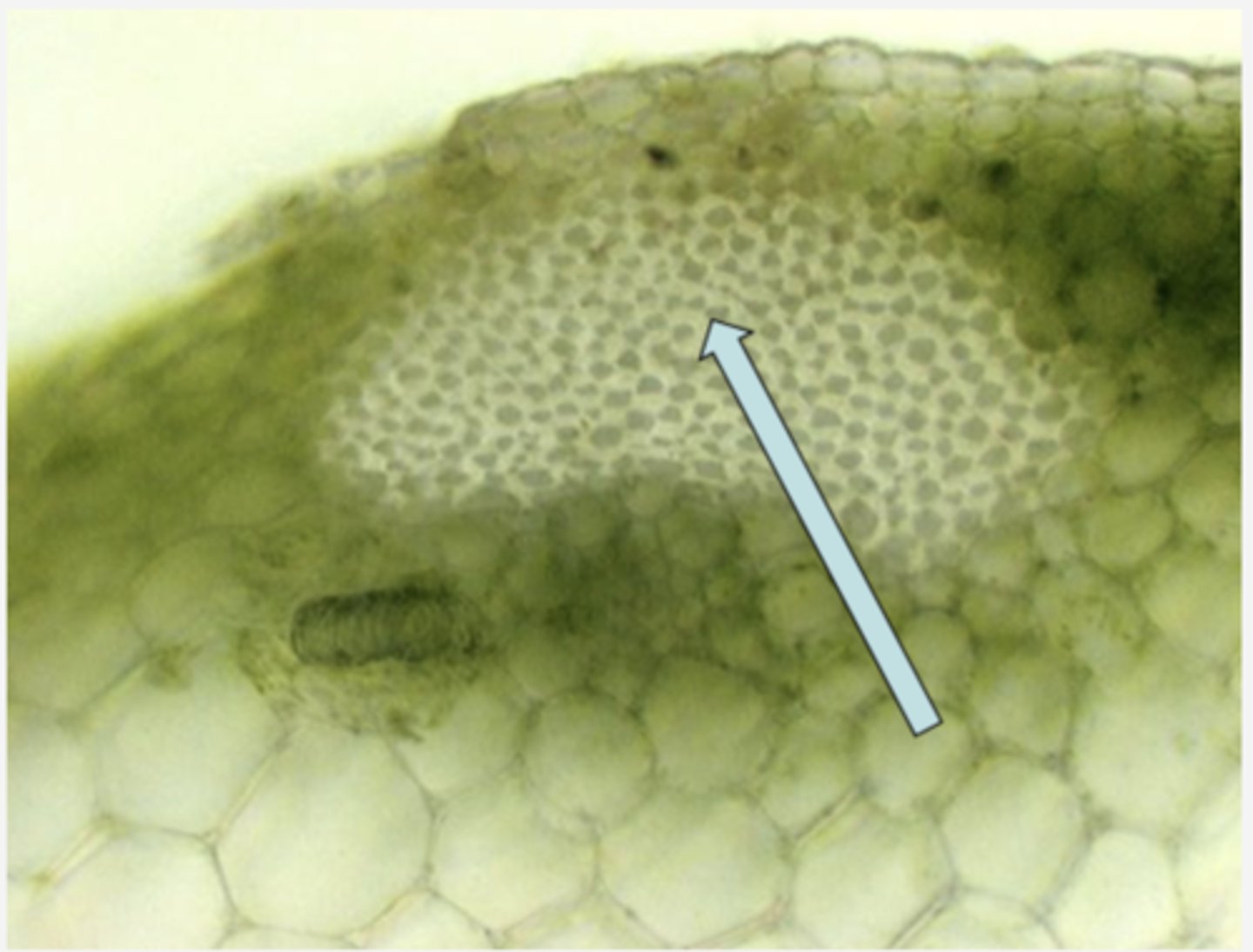
Vascular bundle celery
collenchyma cell celery
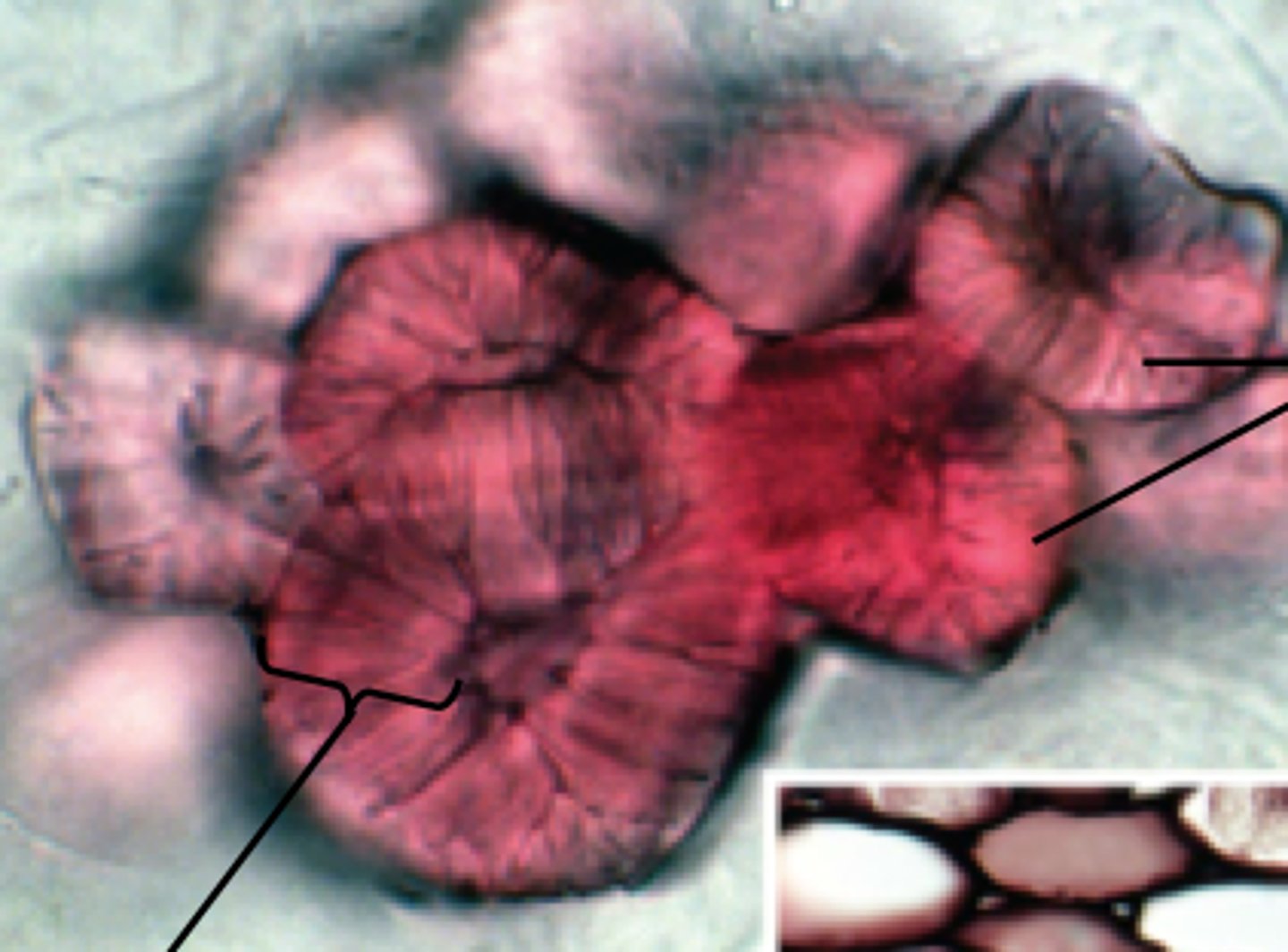
pear sclereids
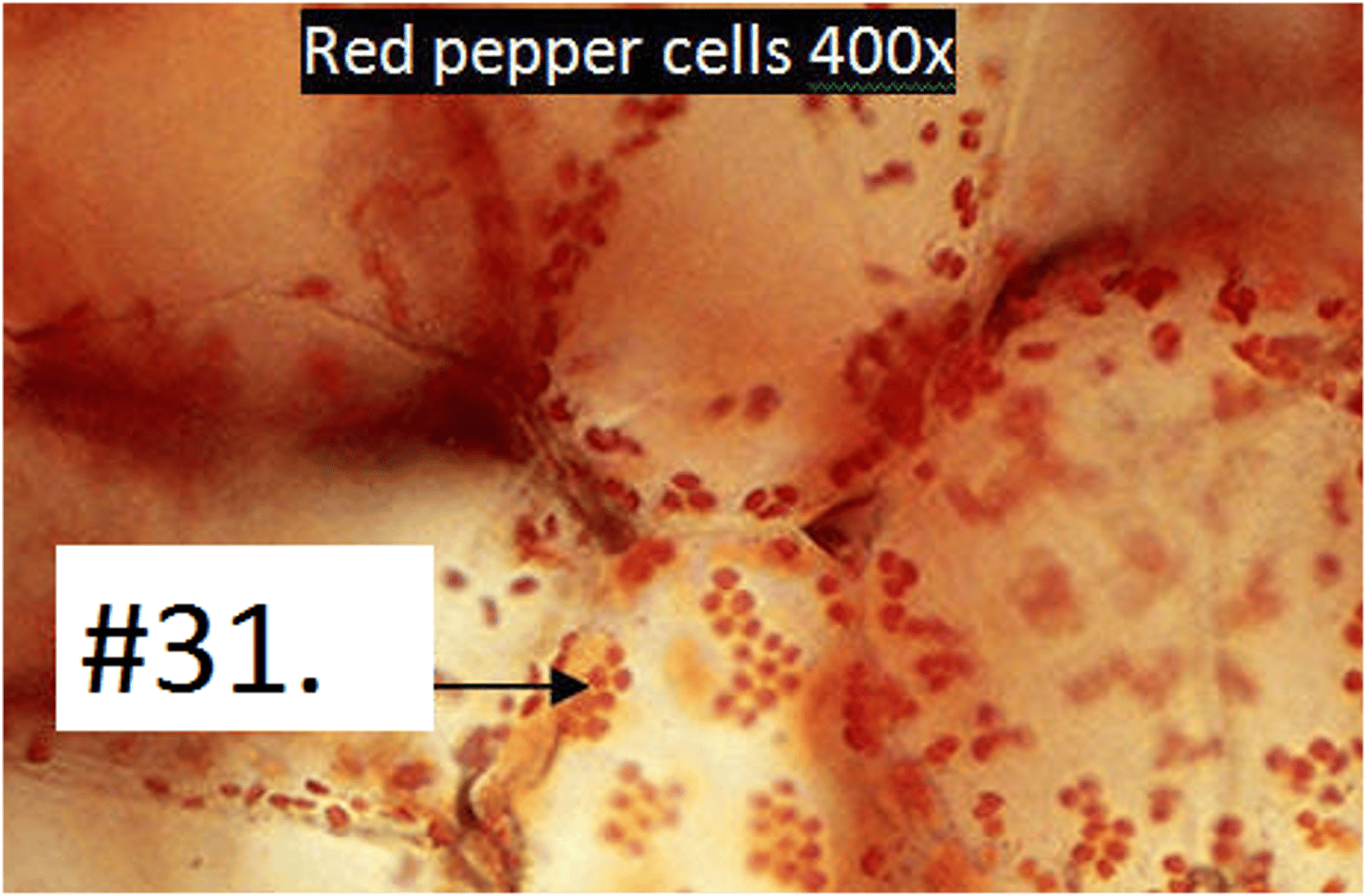
red pepper chromoplasts
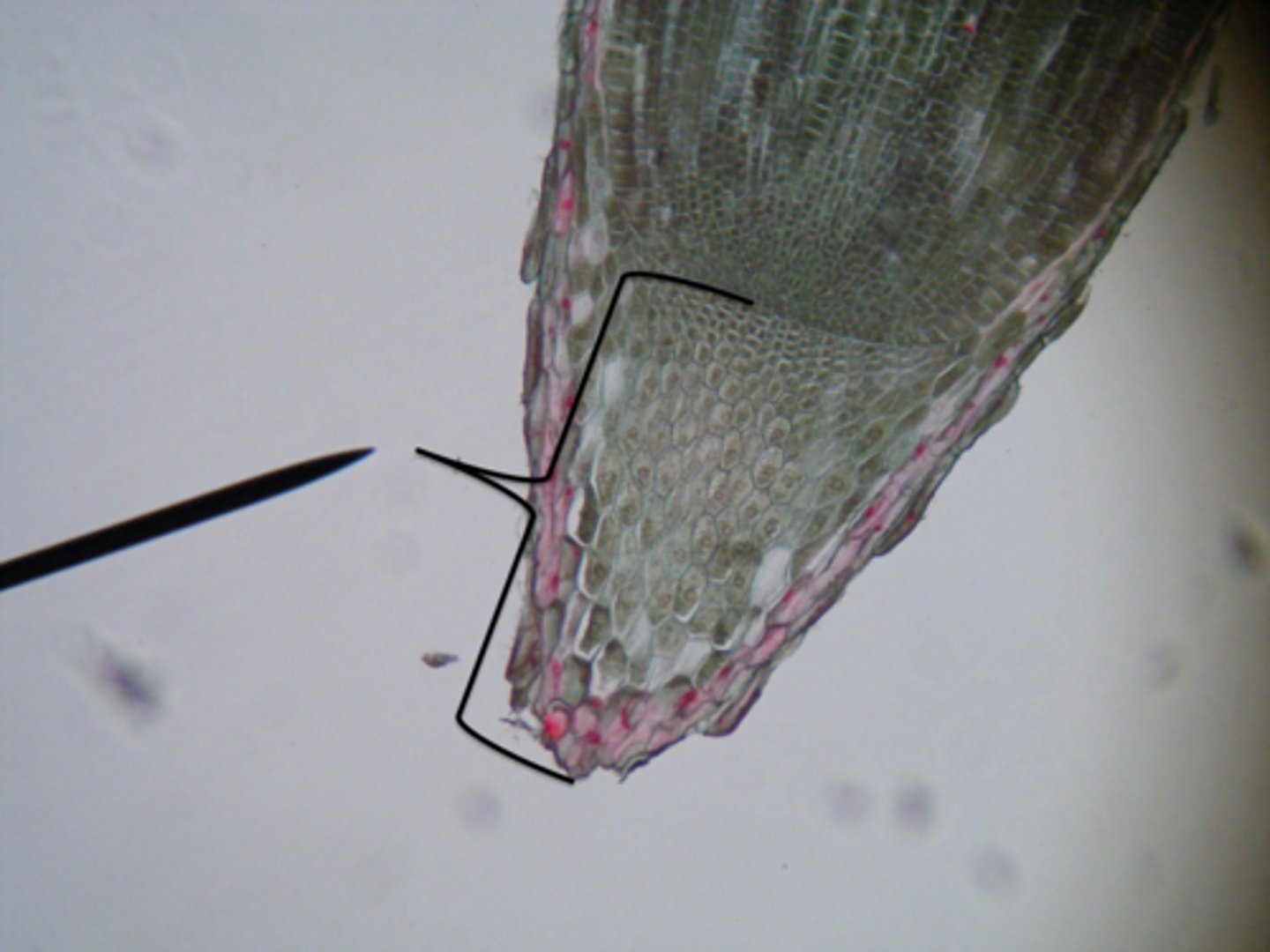
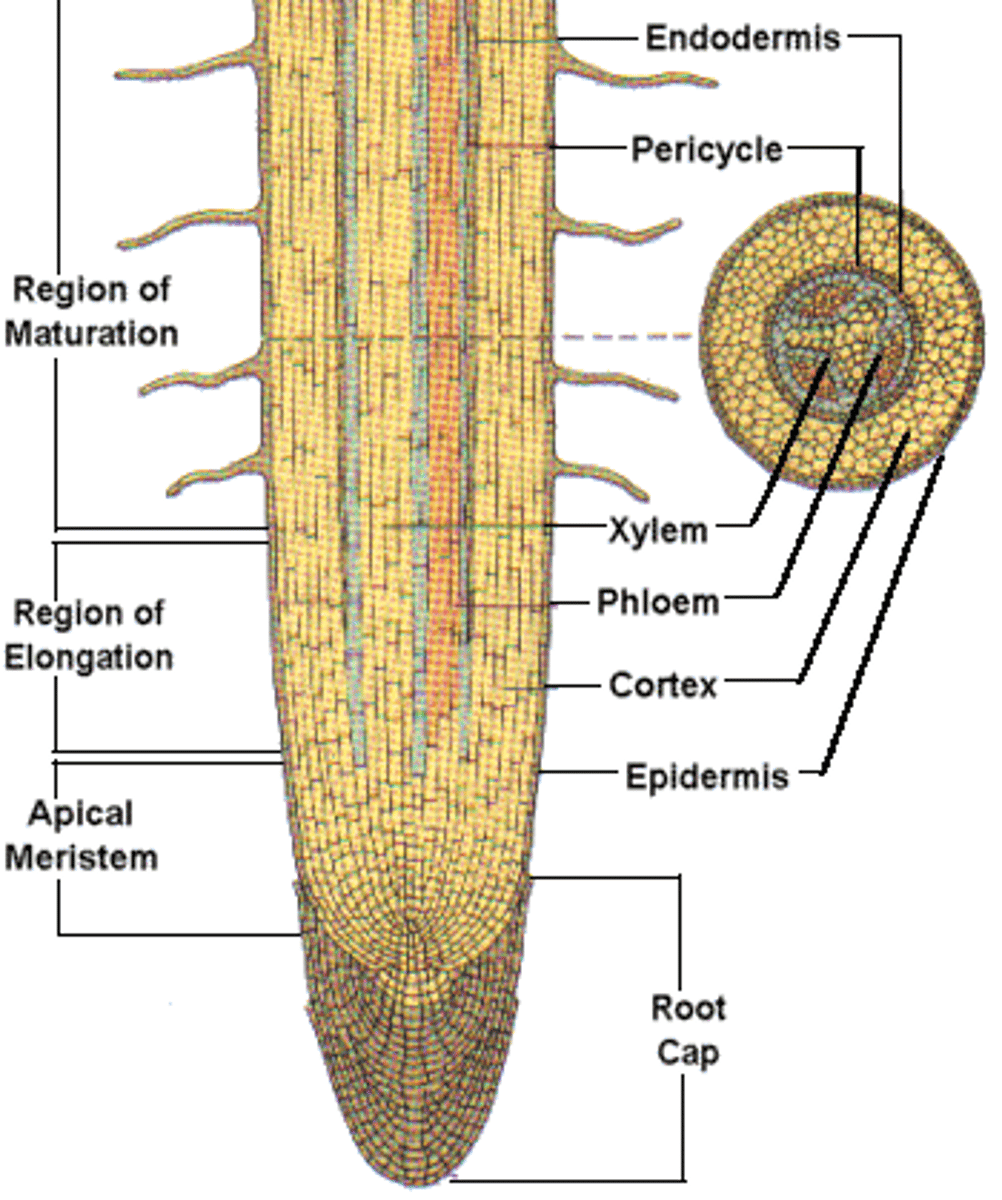
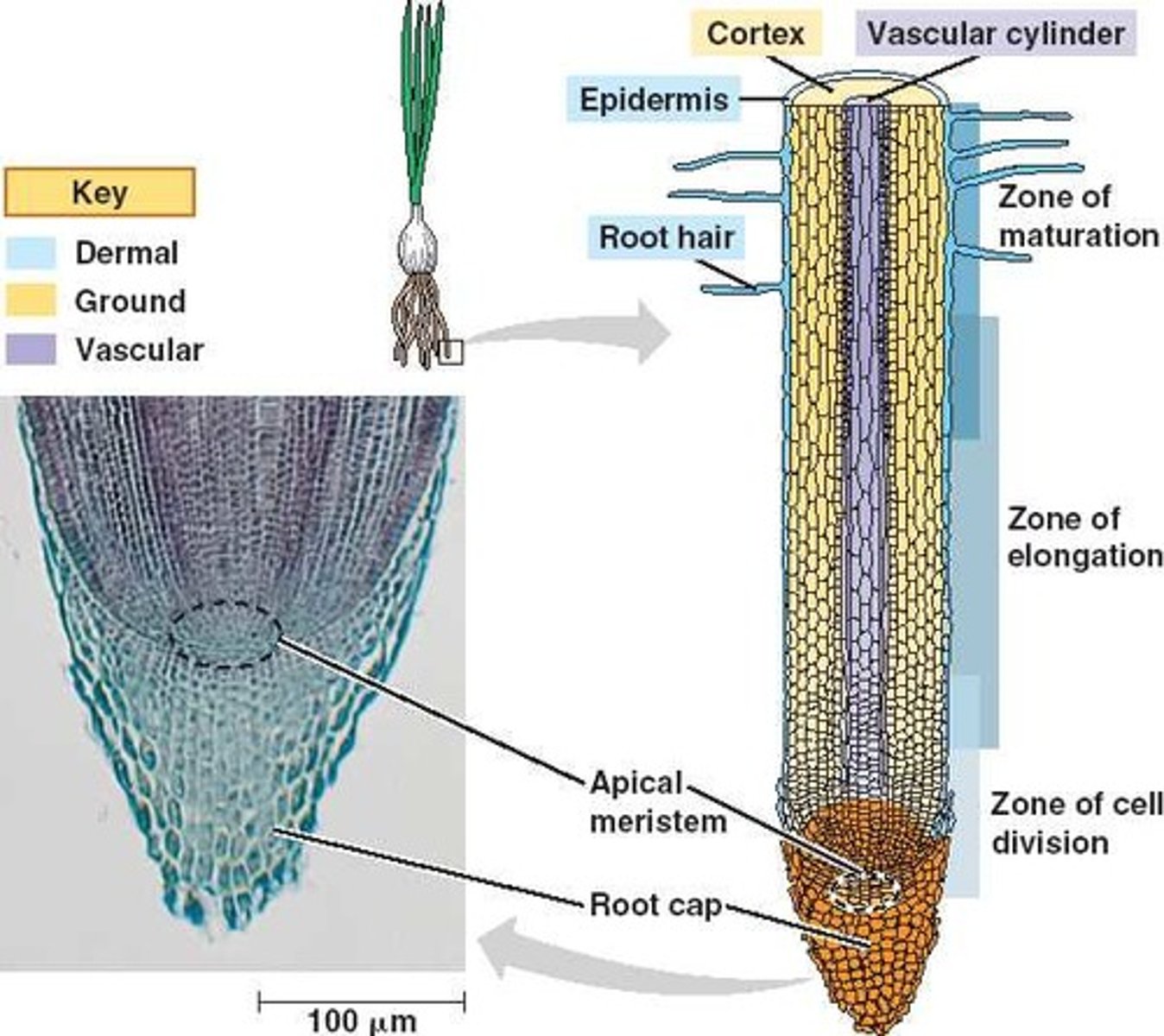
root cap
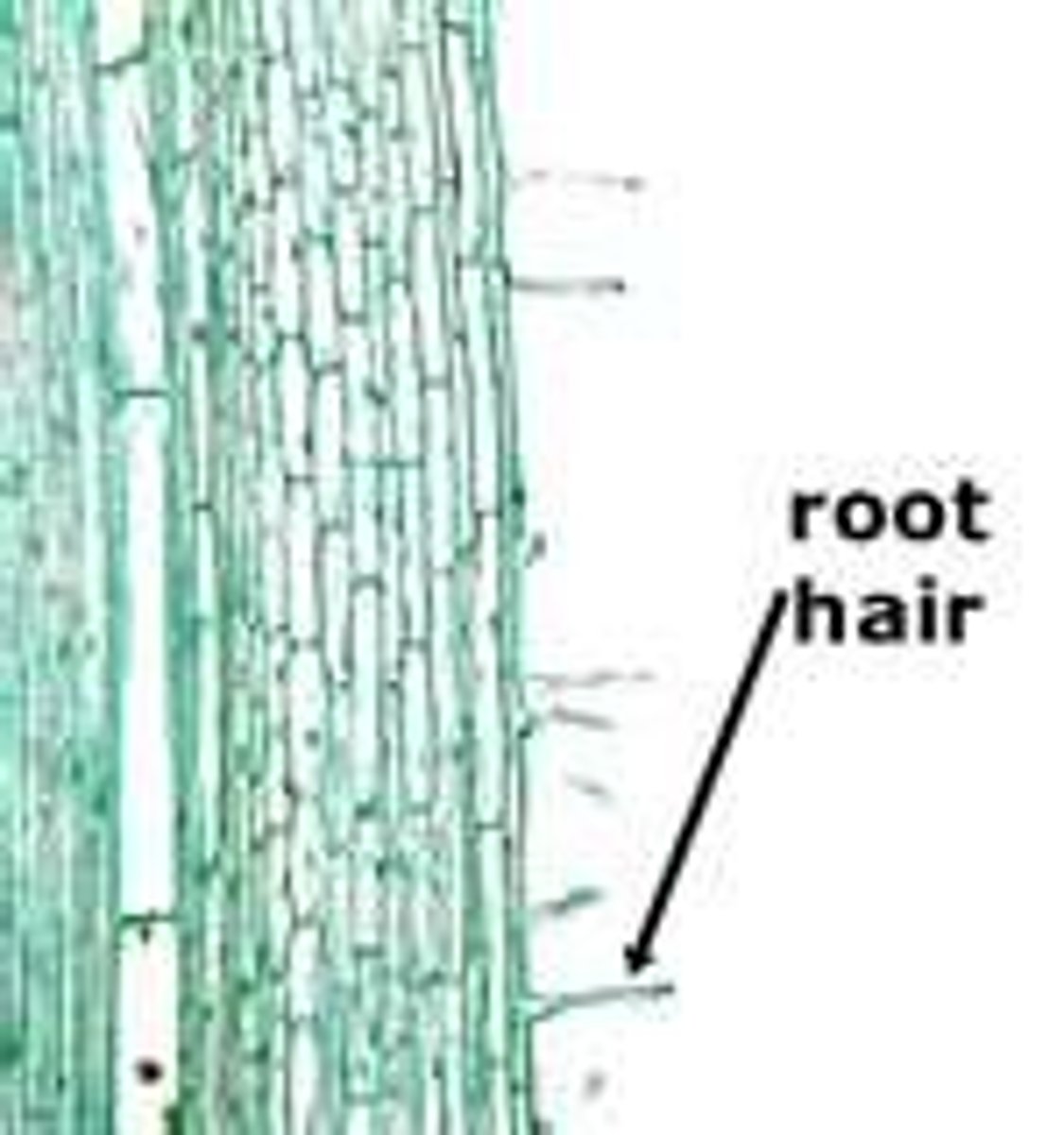
root hair
ranunculus
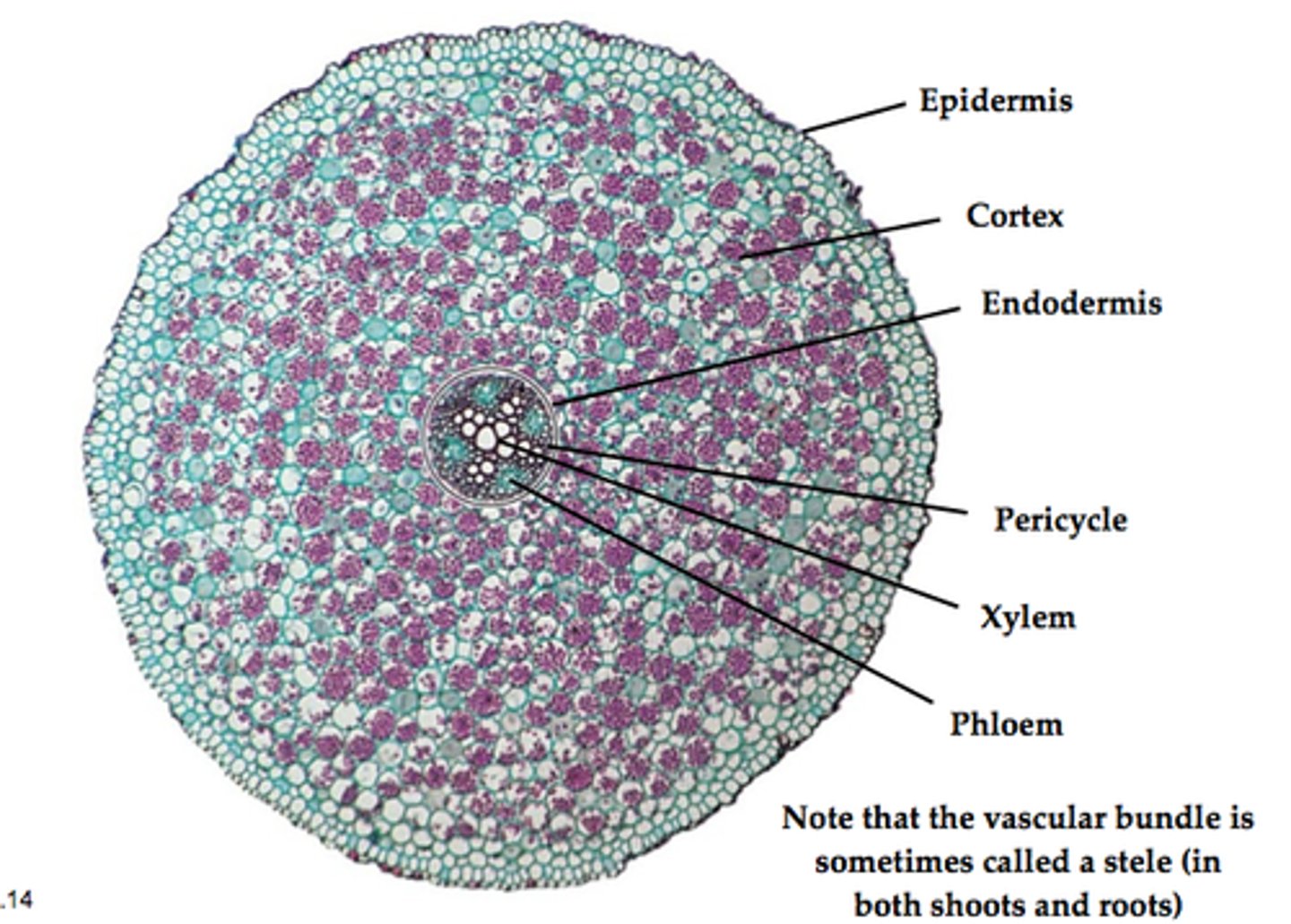
Zea
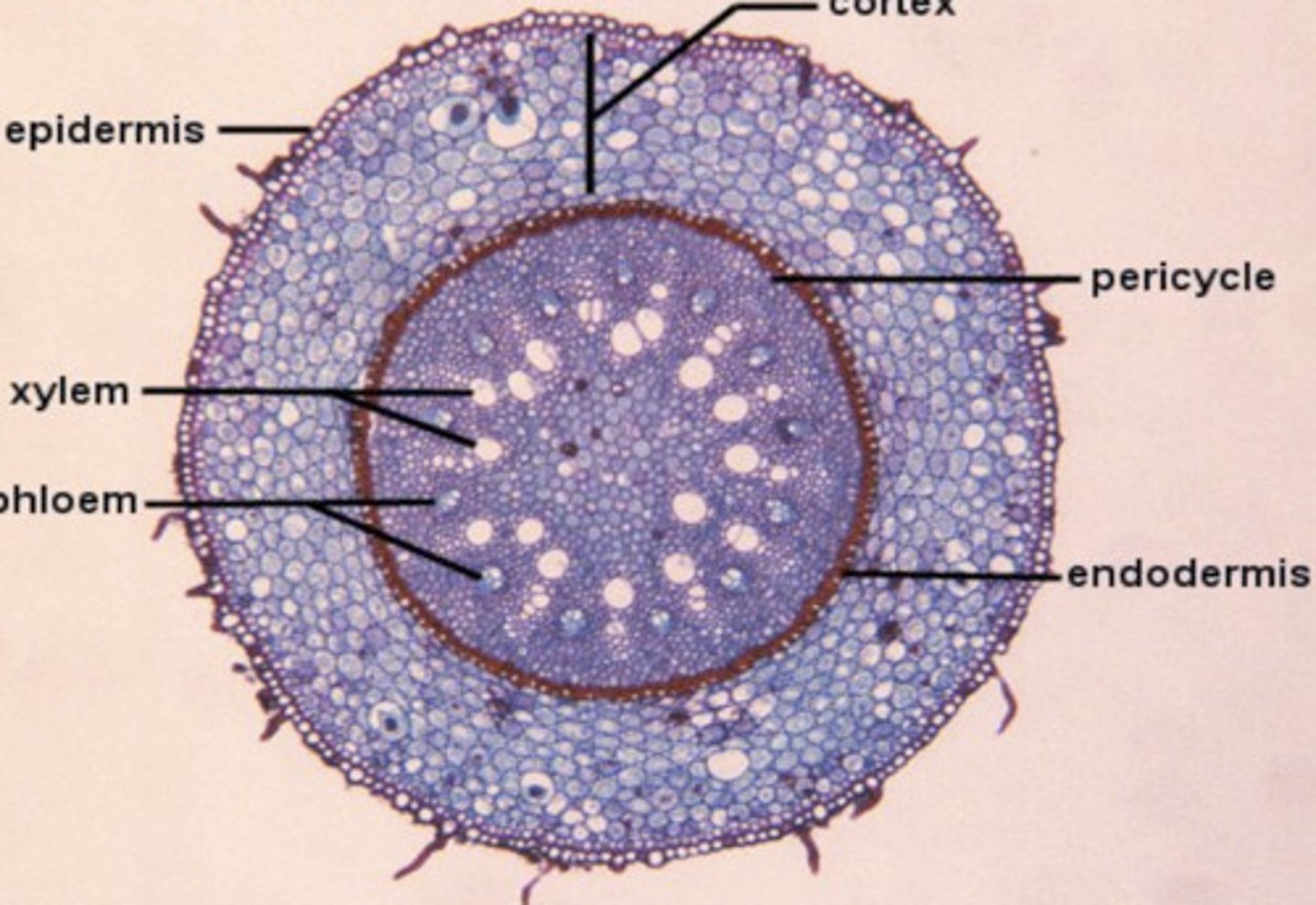
Medicago stem
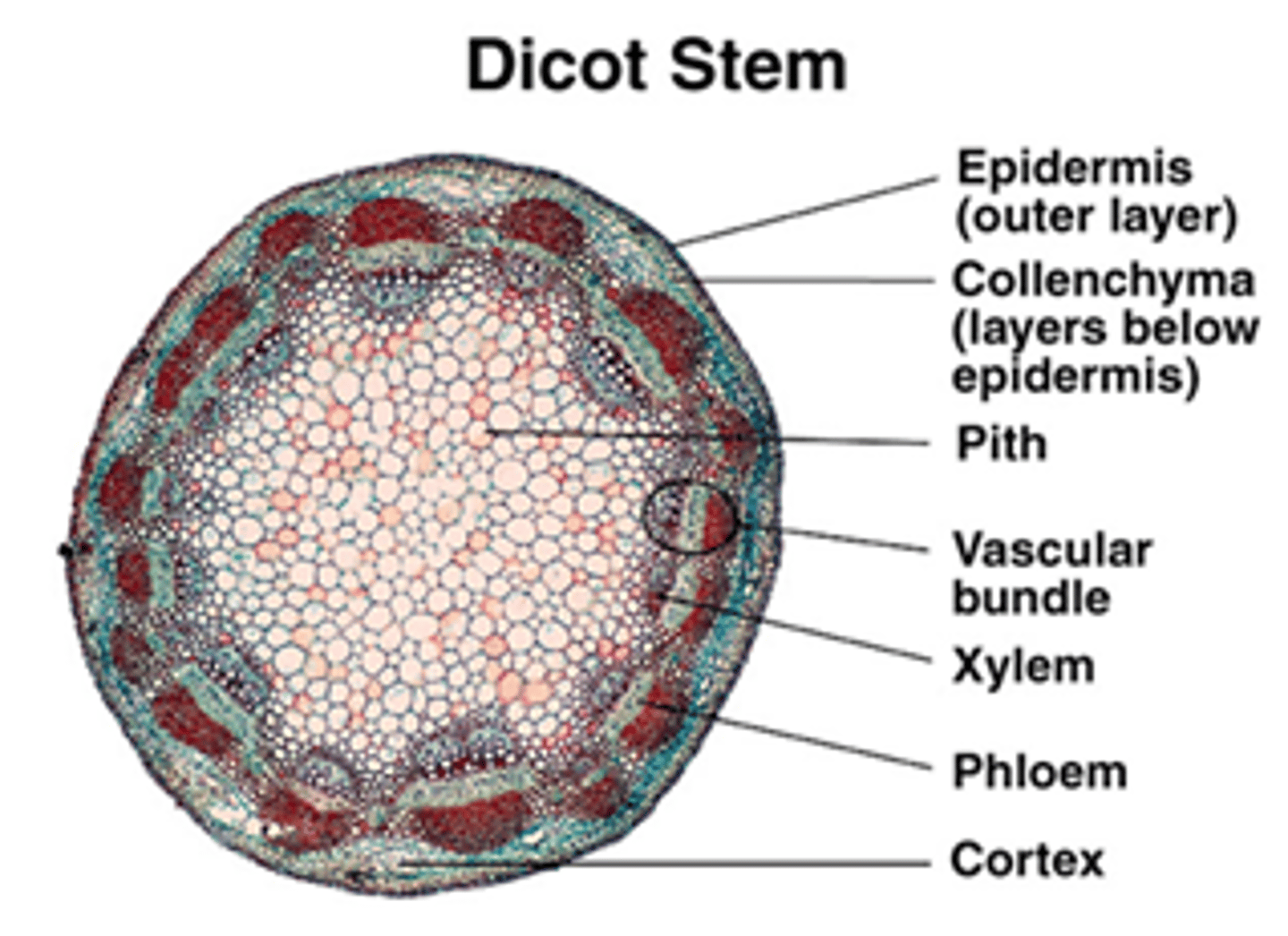
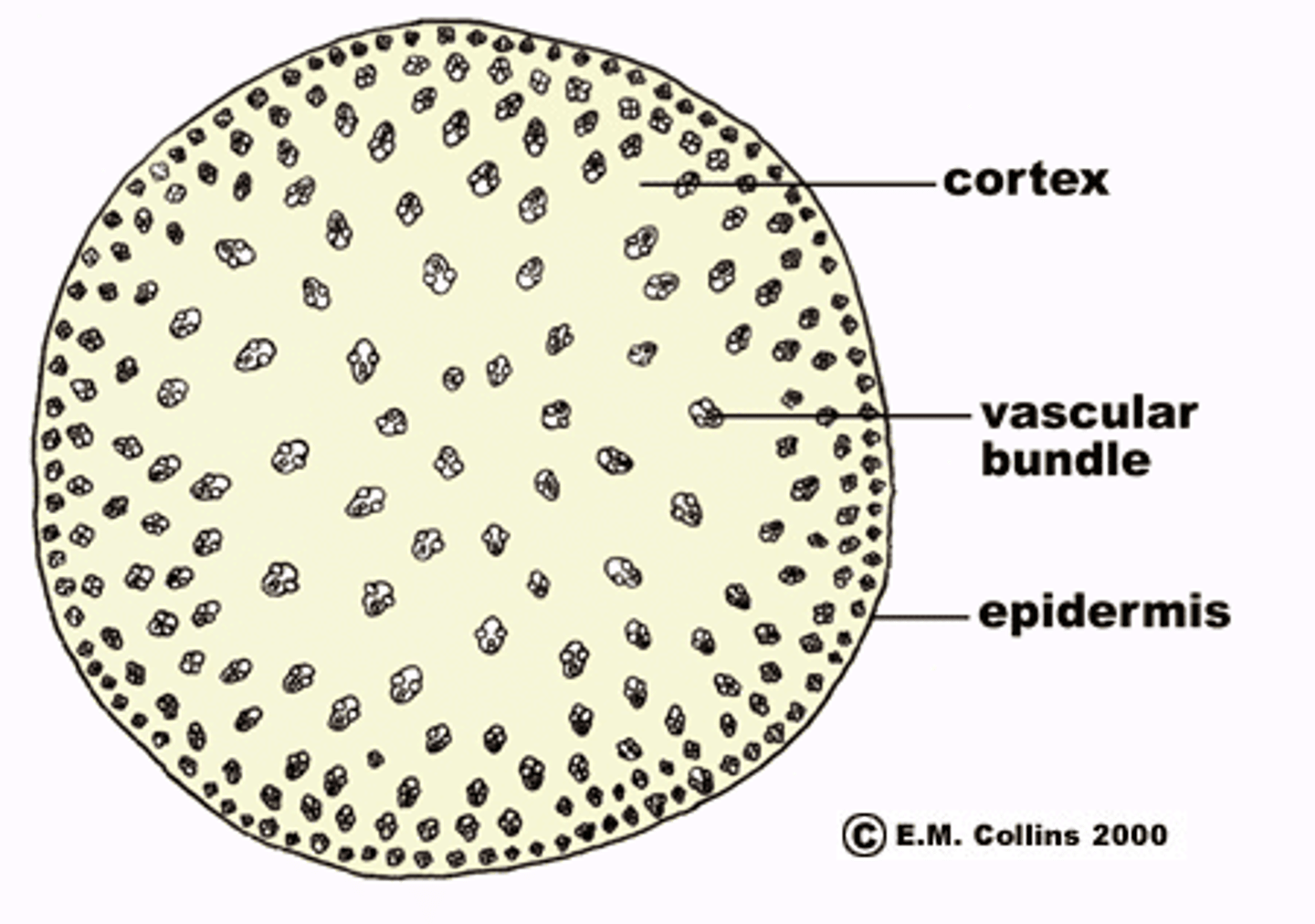
Zea mays stem
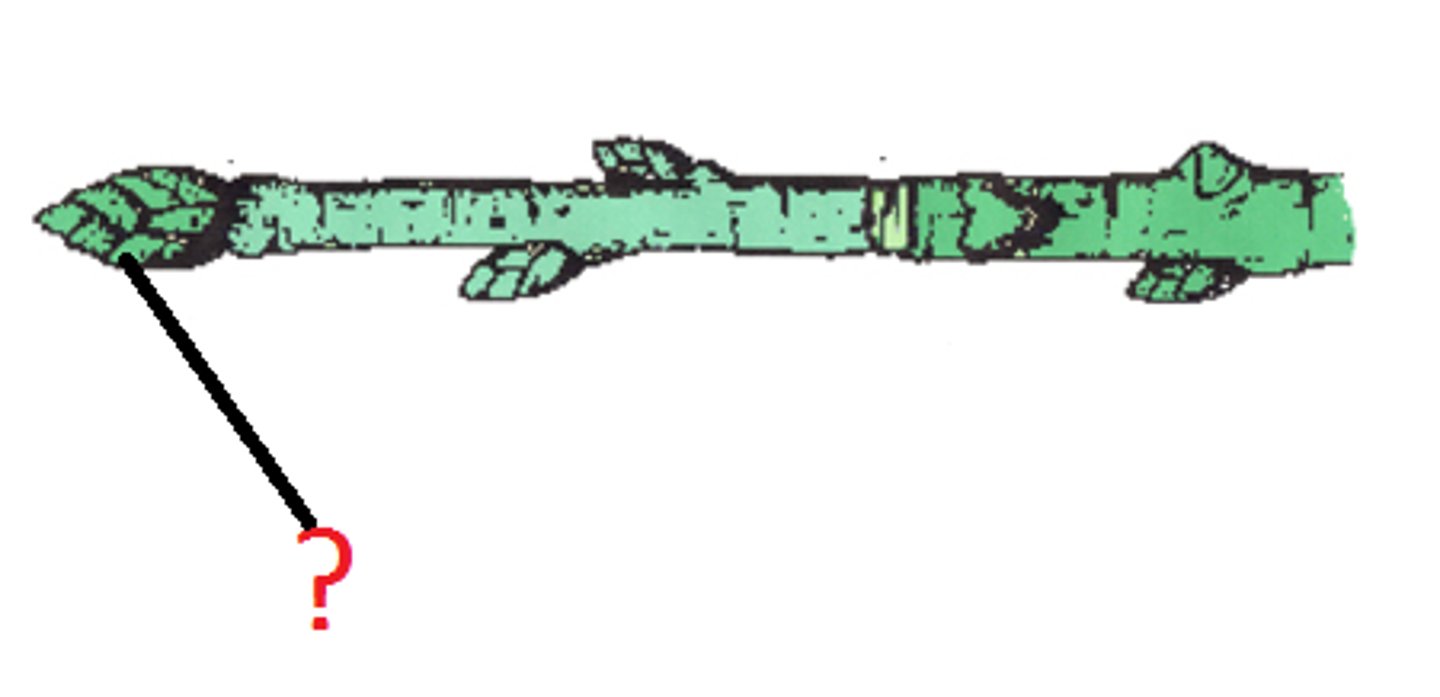
woody twigs
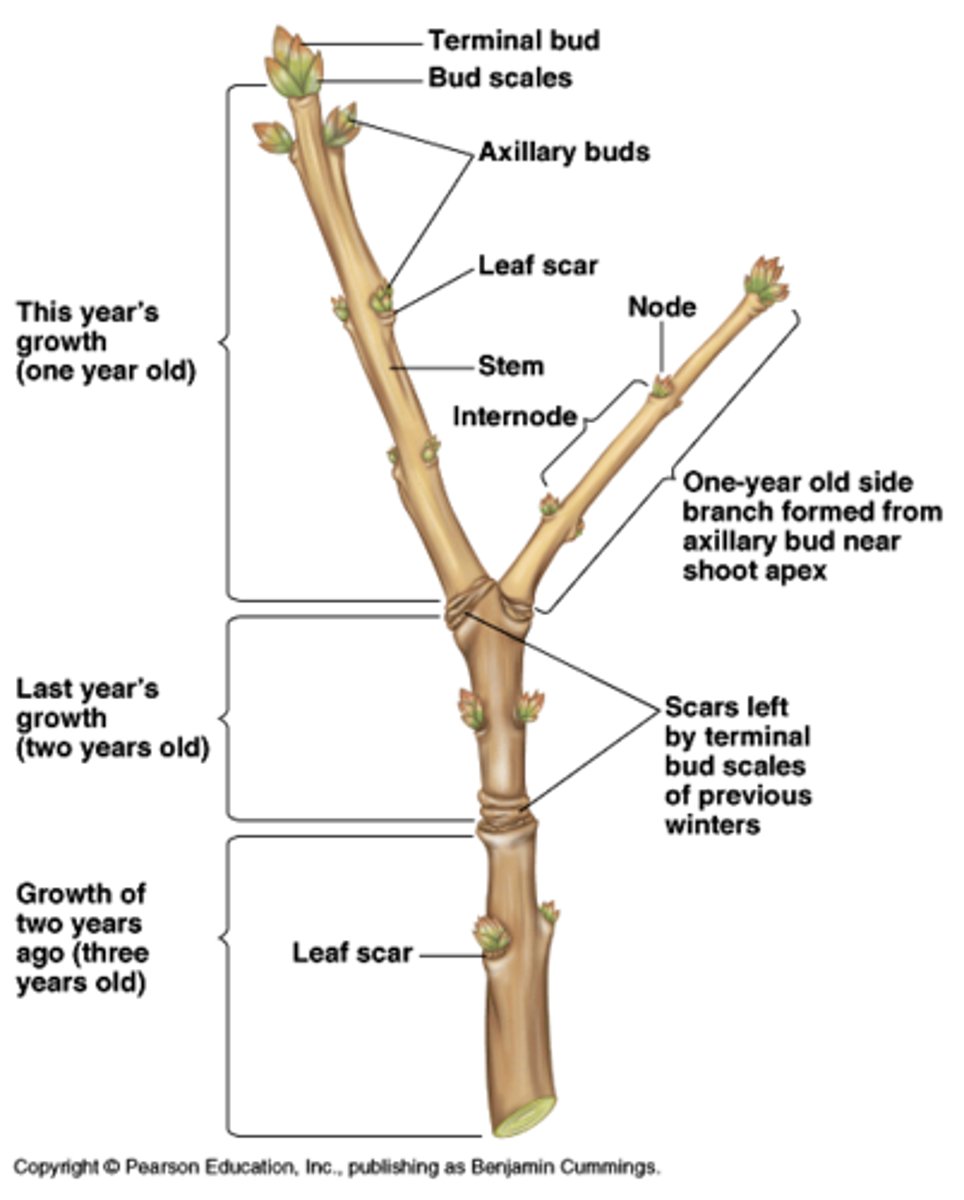
terminal bud
bud scale scars
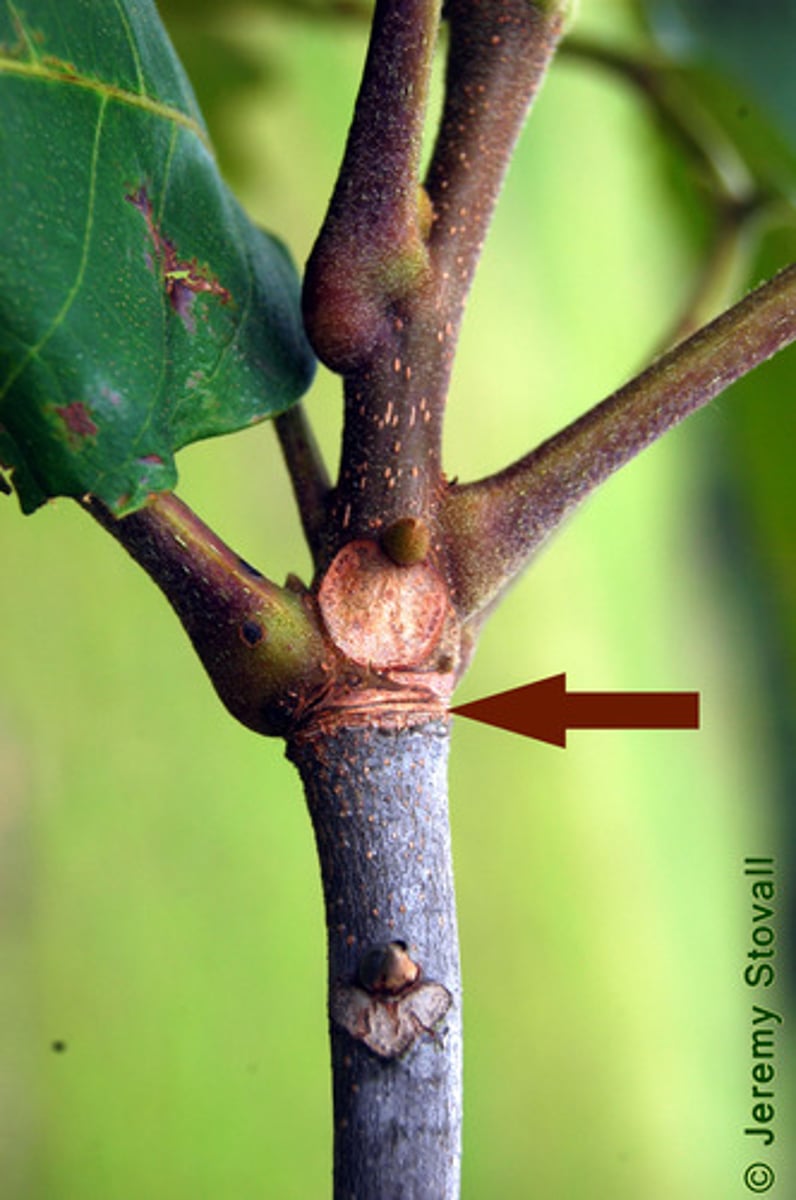

leaf scars
Show where leaves were attached
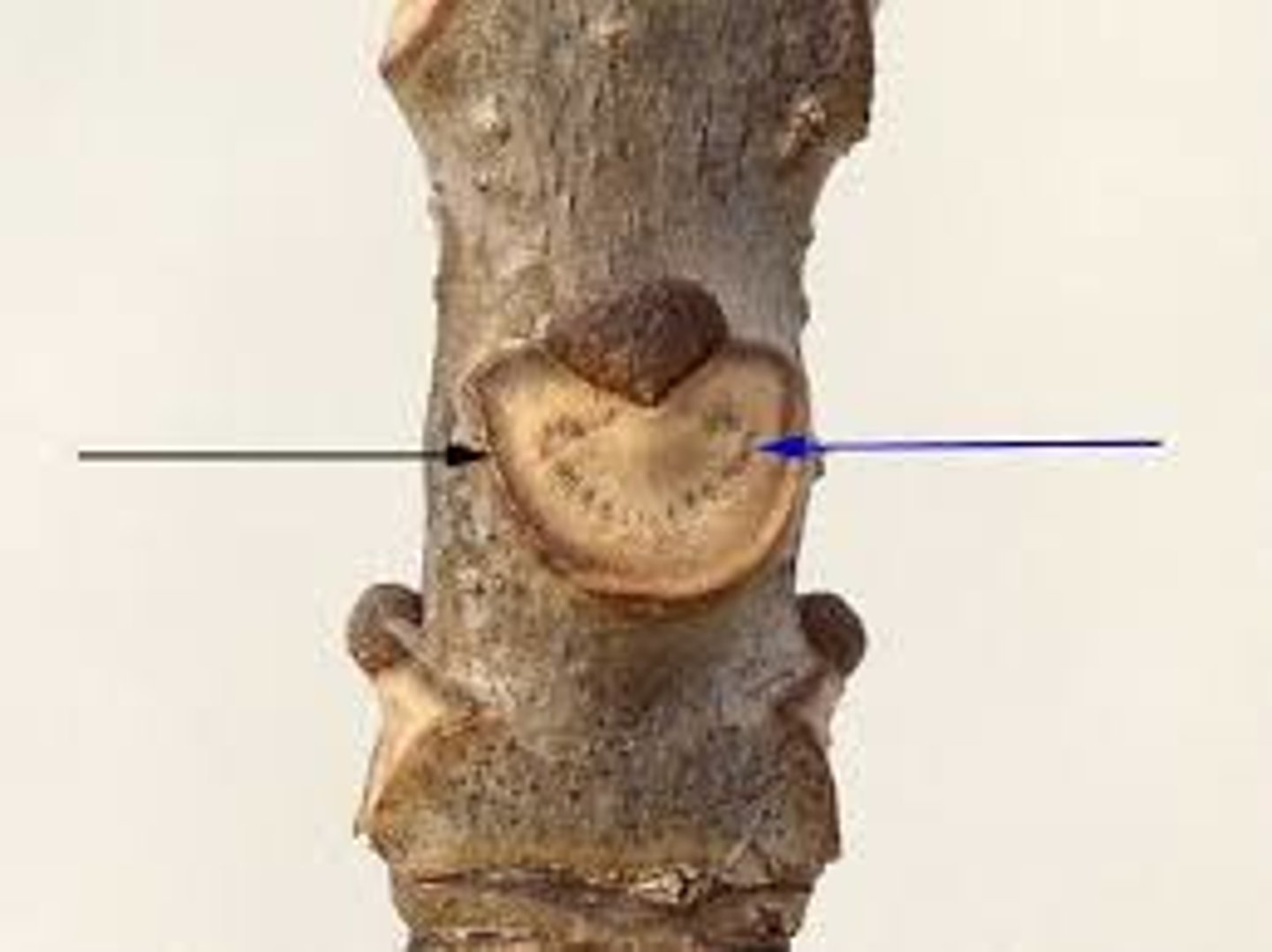

axillary bud
Lenticels
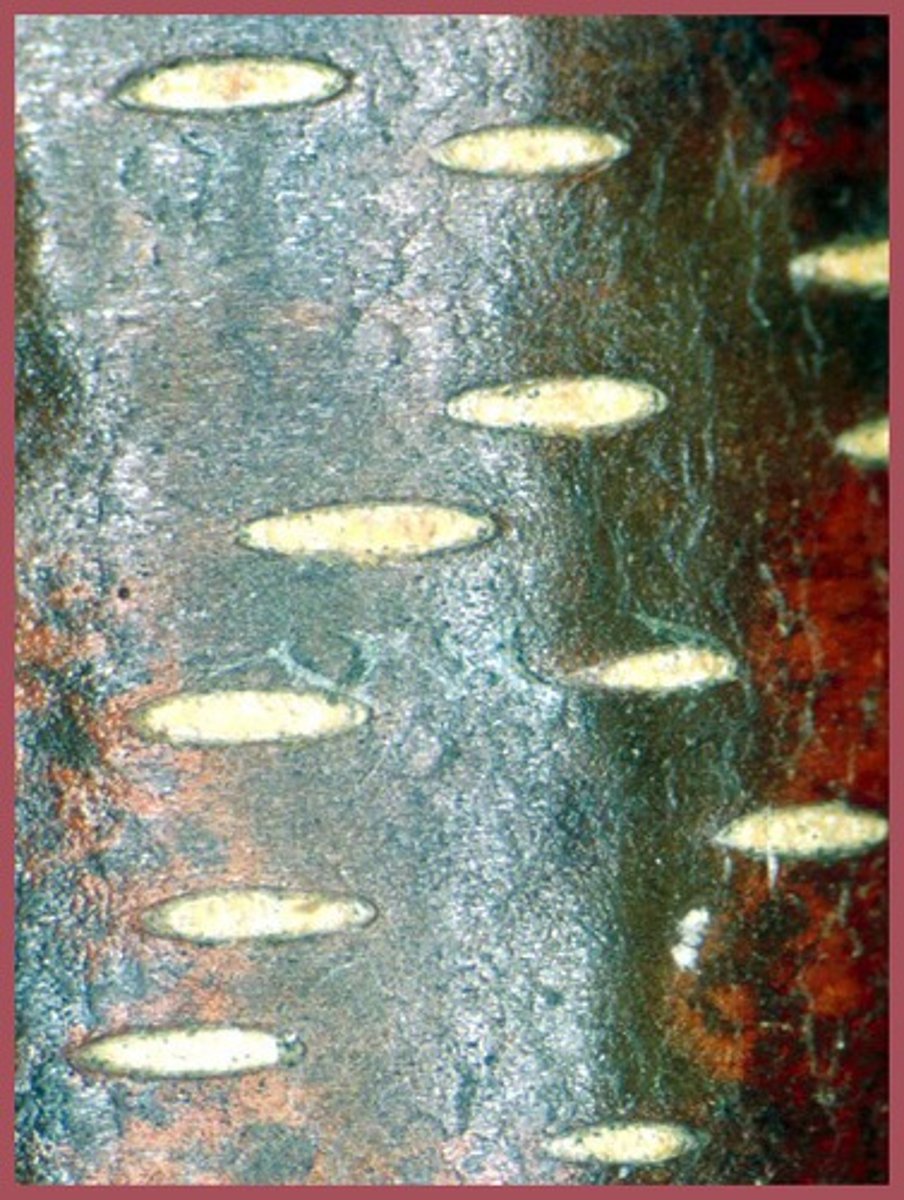

ligustrum leaf
Allium cepa
onion
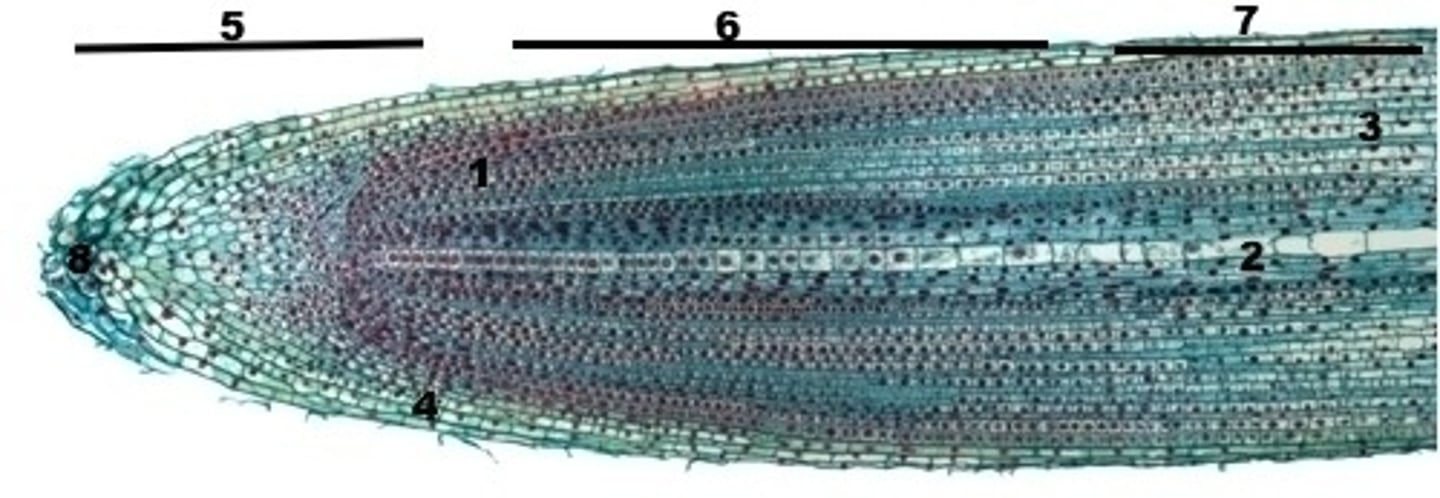
root cap onion
tough covering of the root tip that protects the meristem
root hairs onion
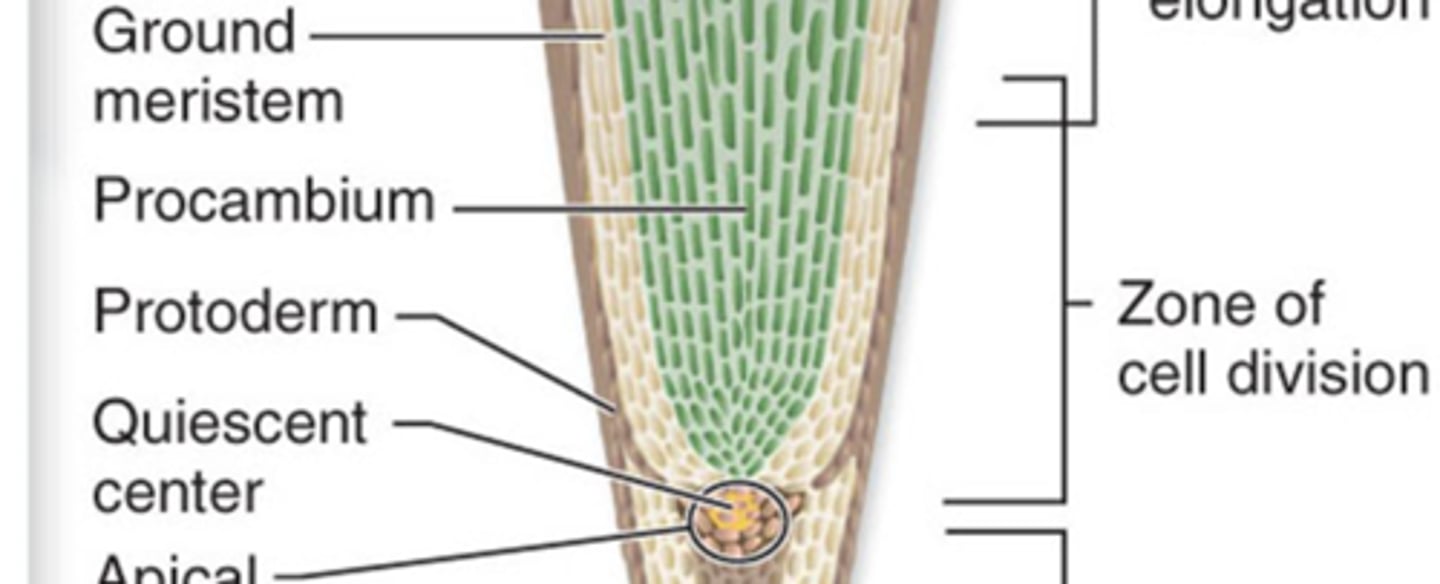
apical meristem
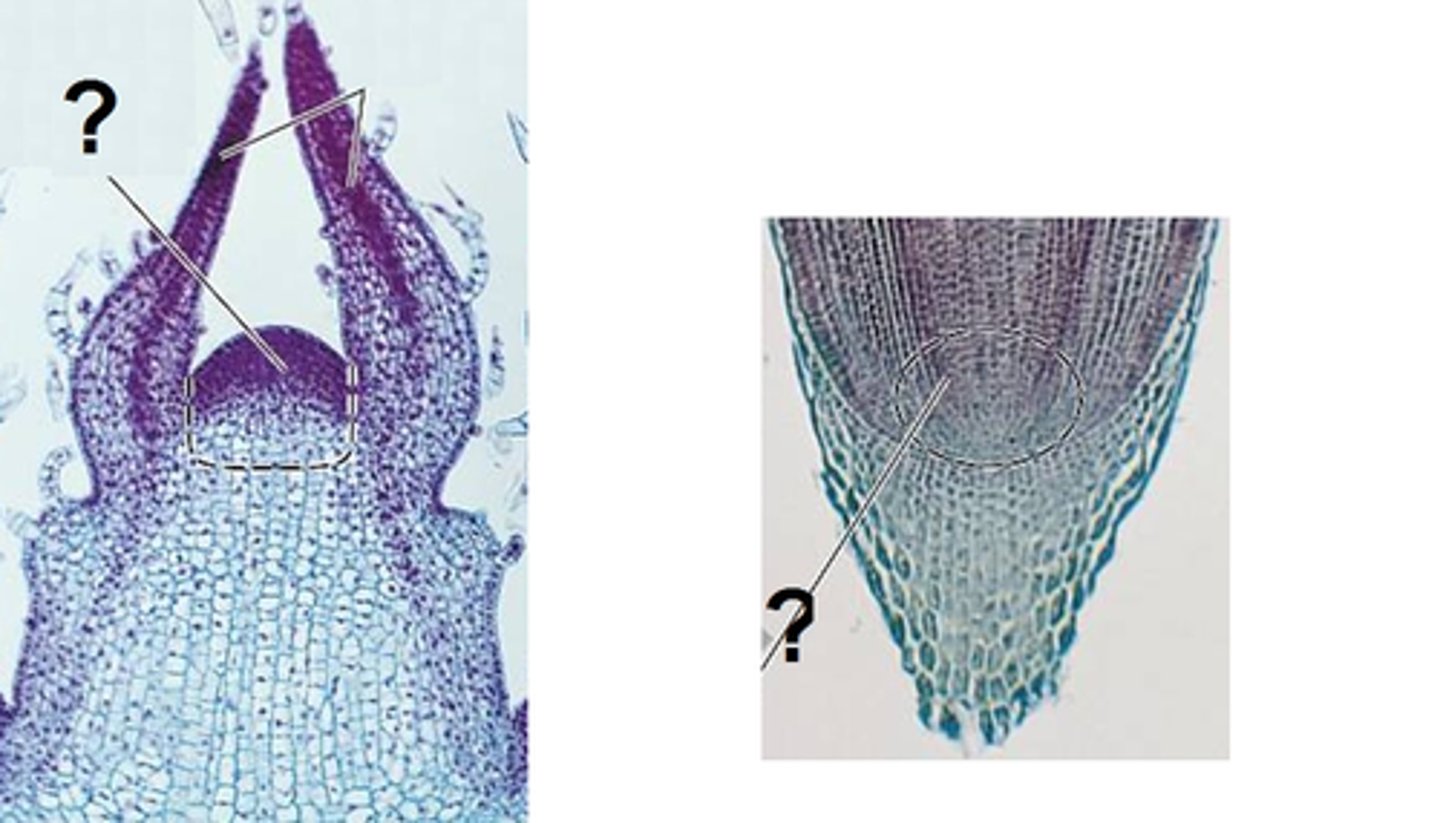
quiescent center
The initial region in the apical meristem of roots that has reached a state of relative inactivity.
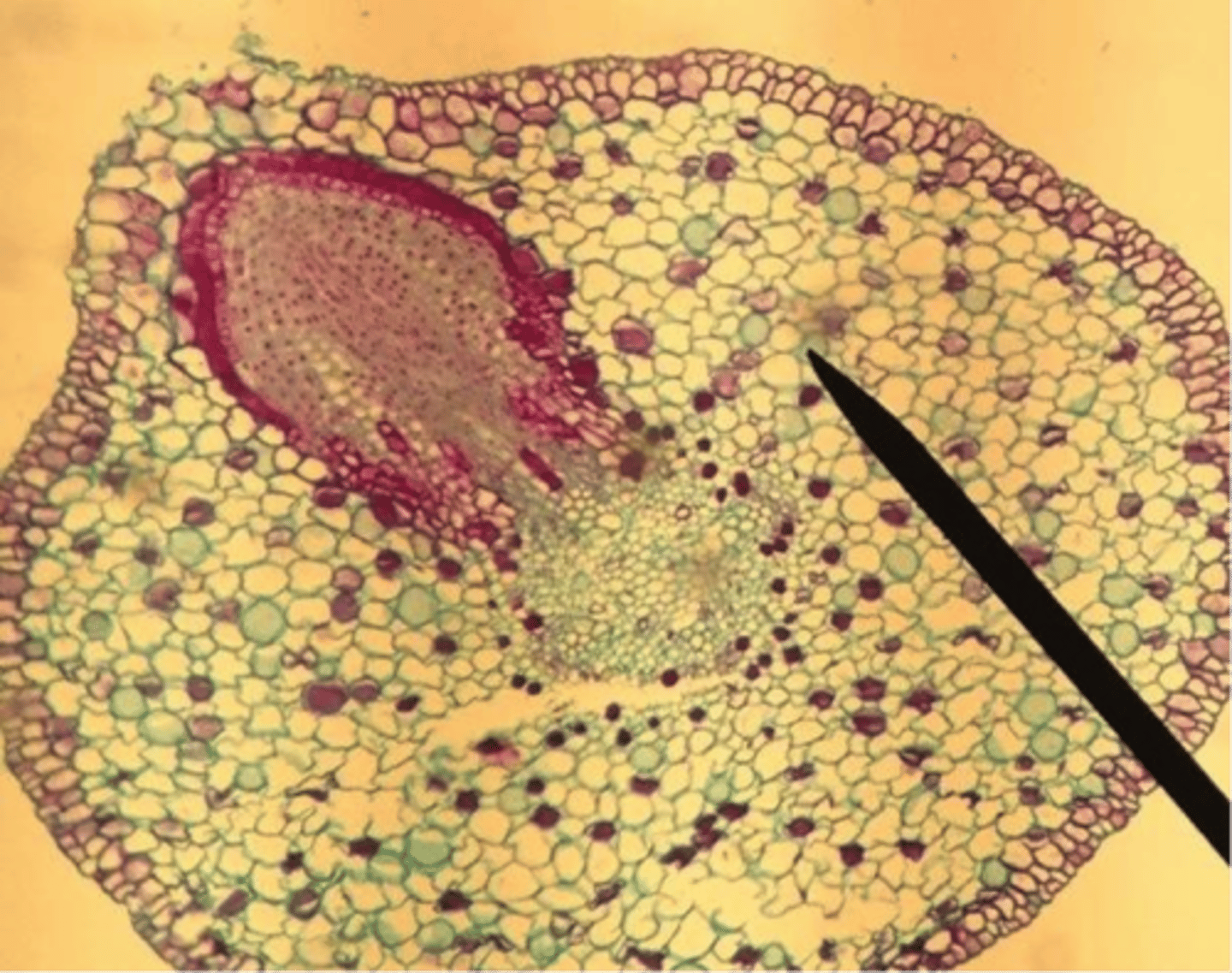
Salix lateral root
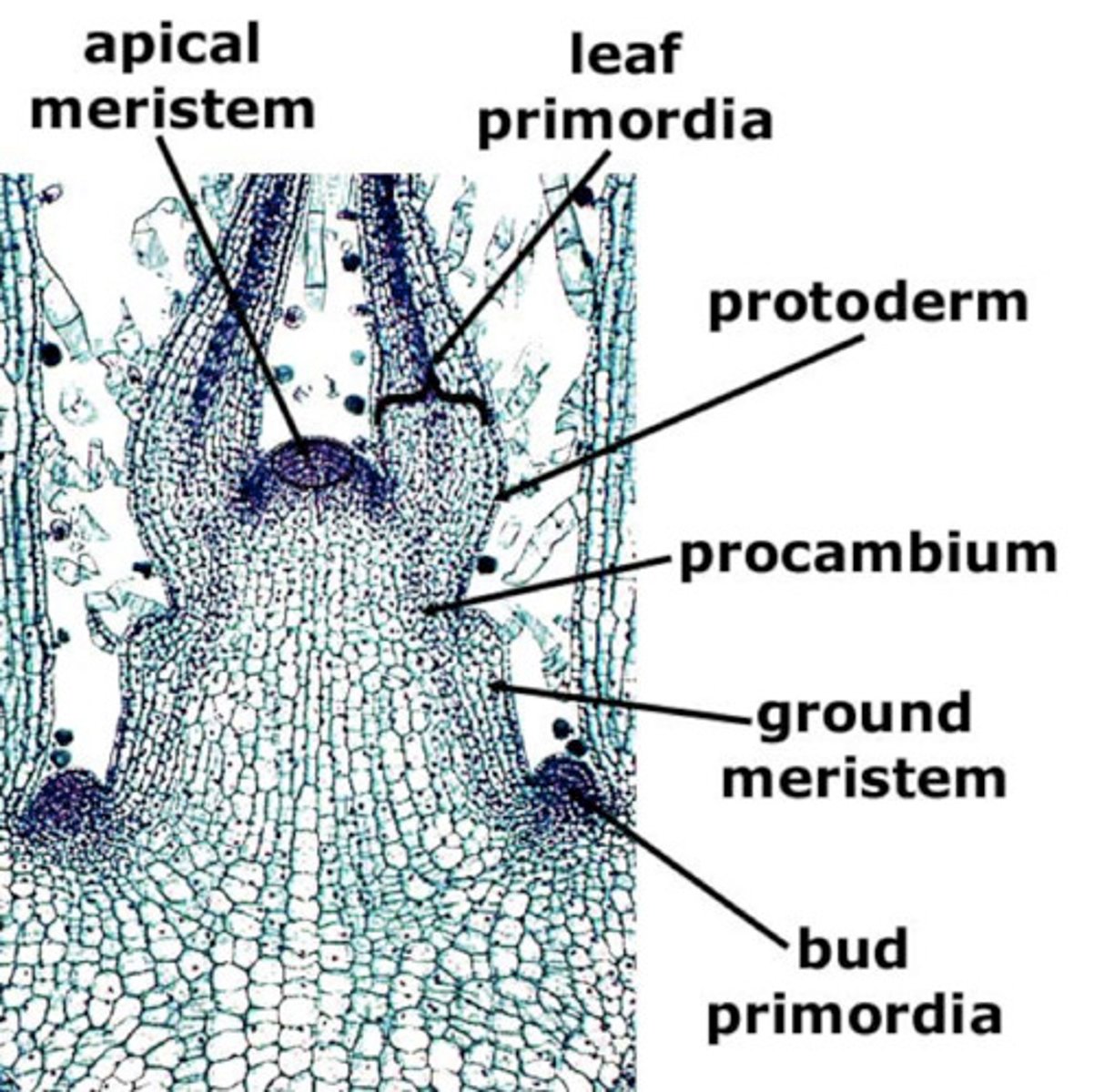
Coleus
Tilia
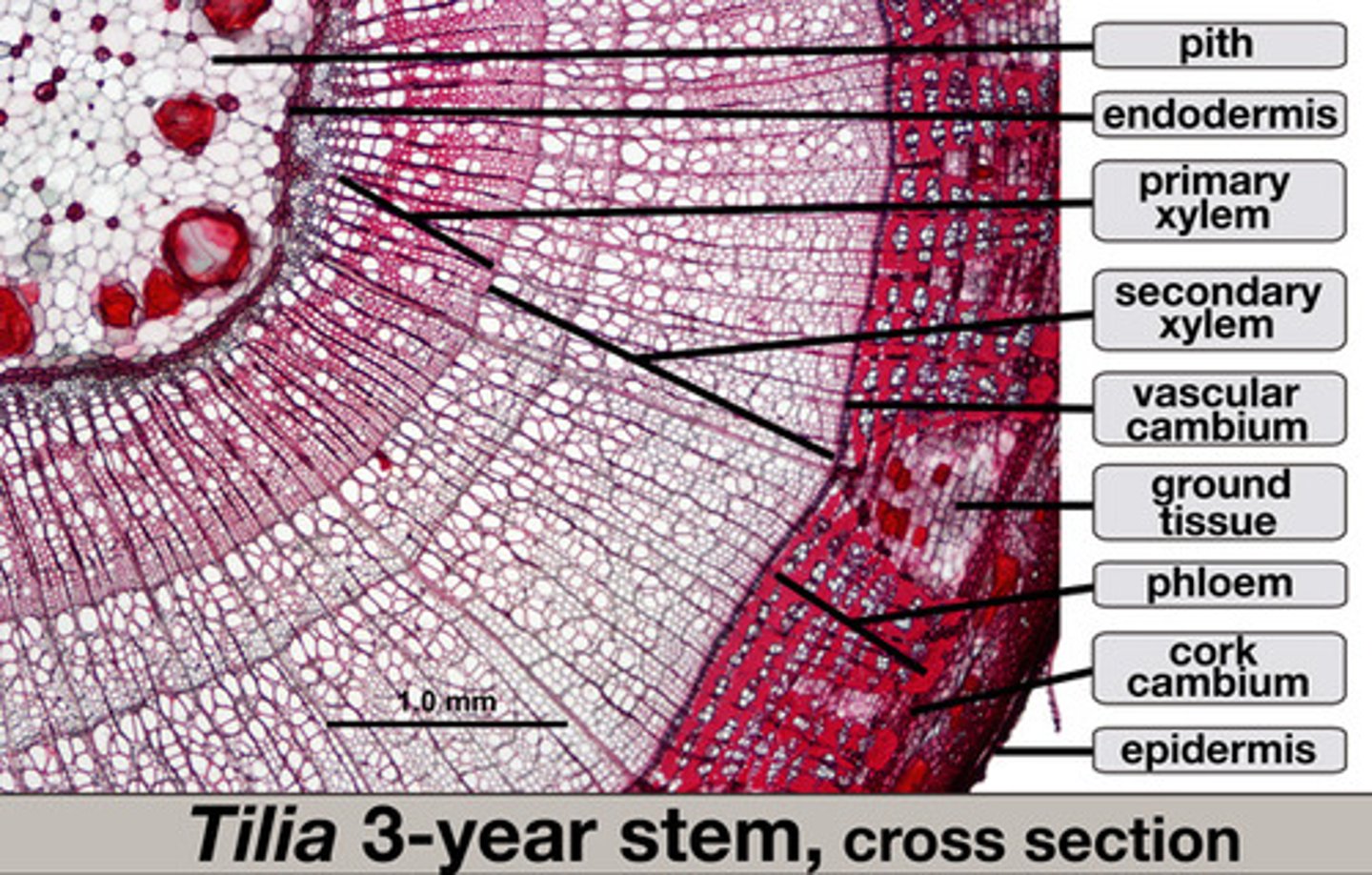
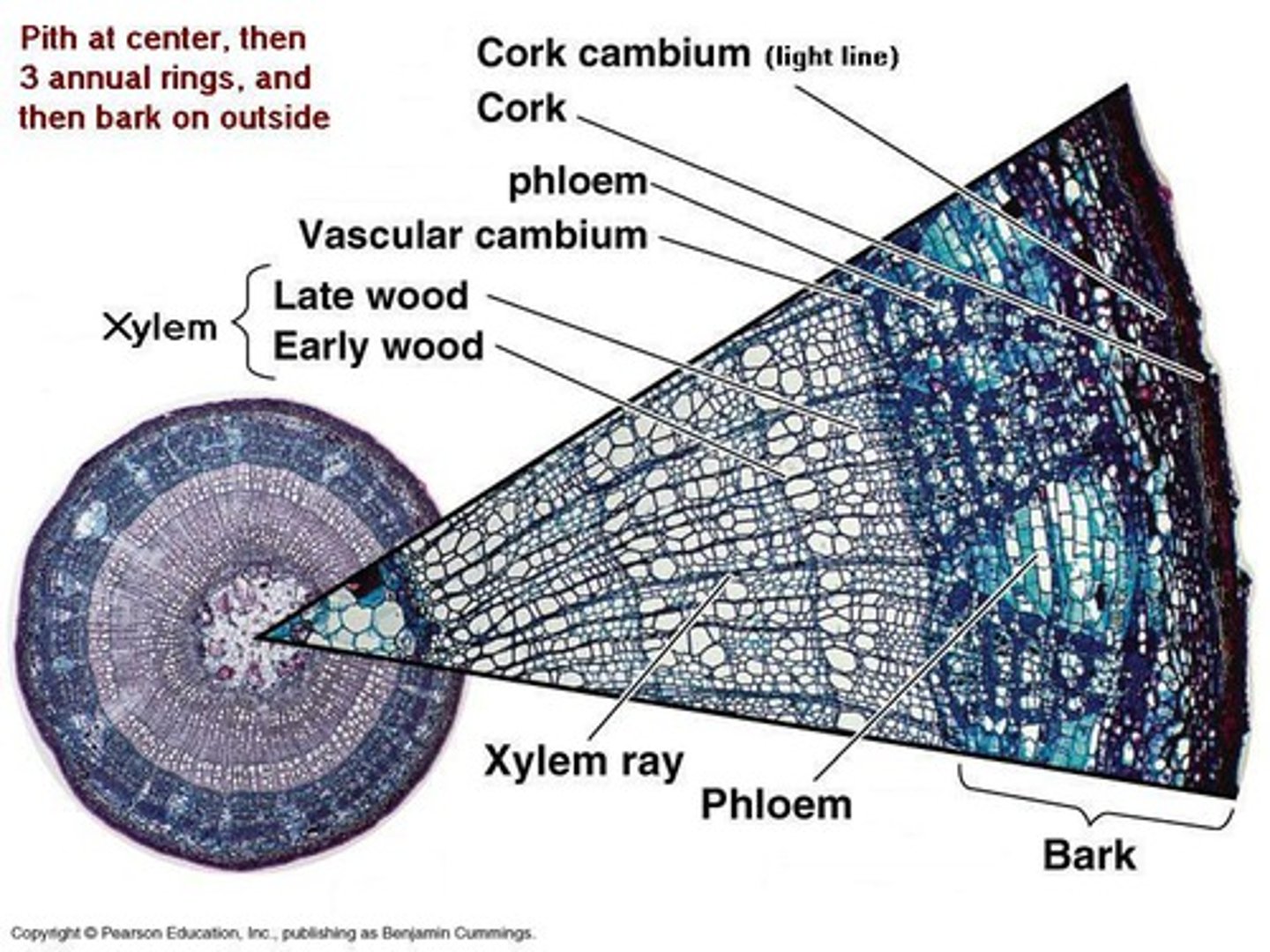
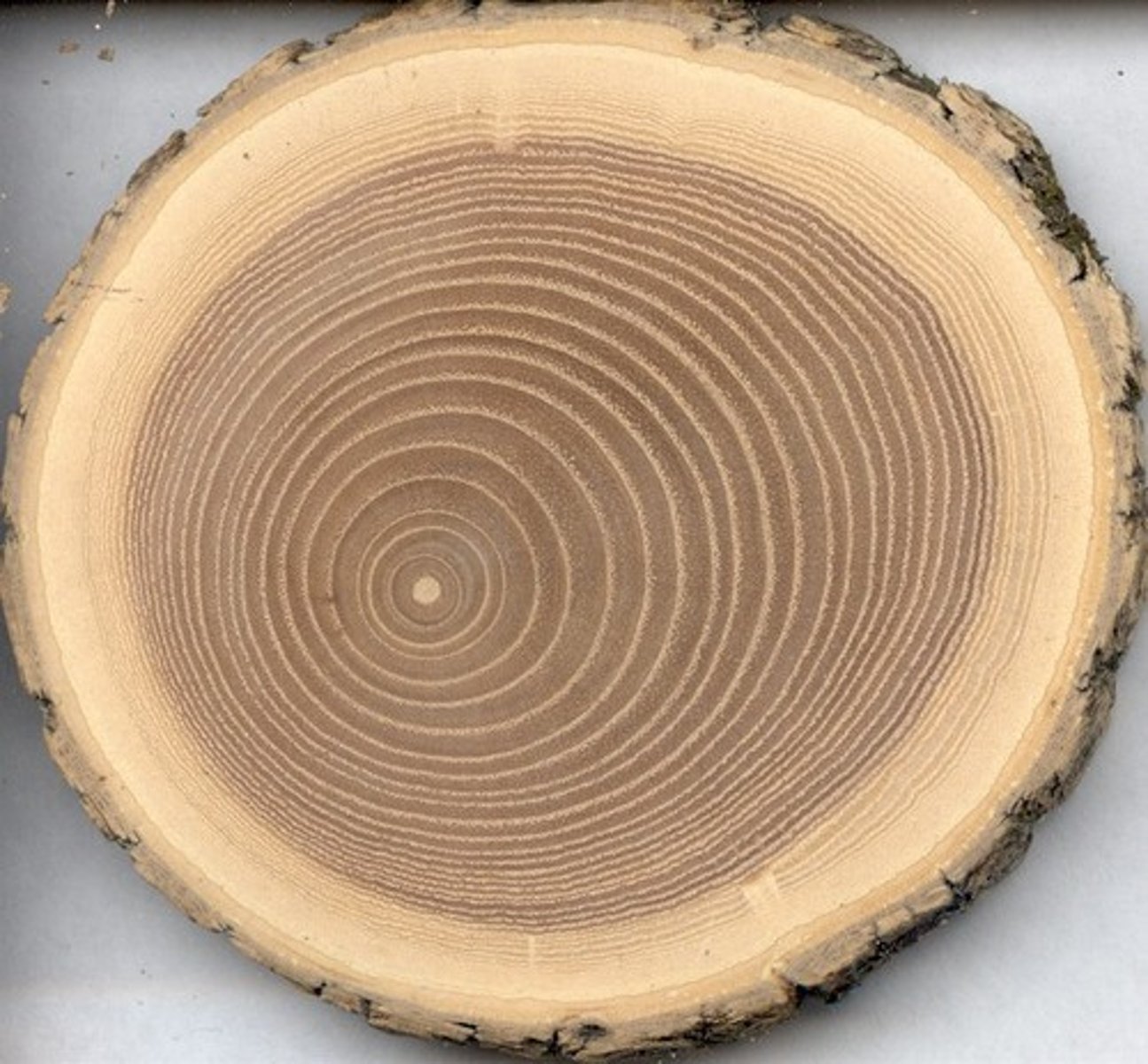
annual rings
Rings or layers of wood which represent one growth period of a tree. In cross section the rings may indicate the age of the tree.

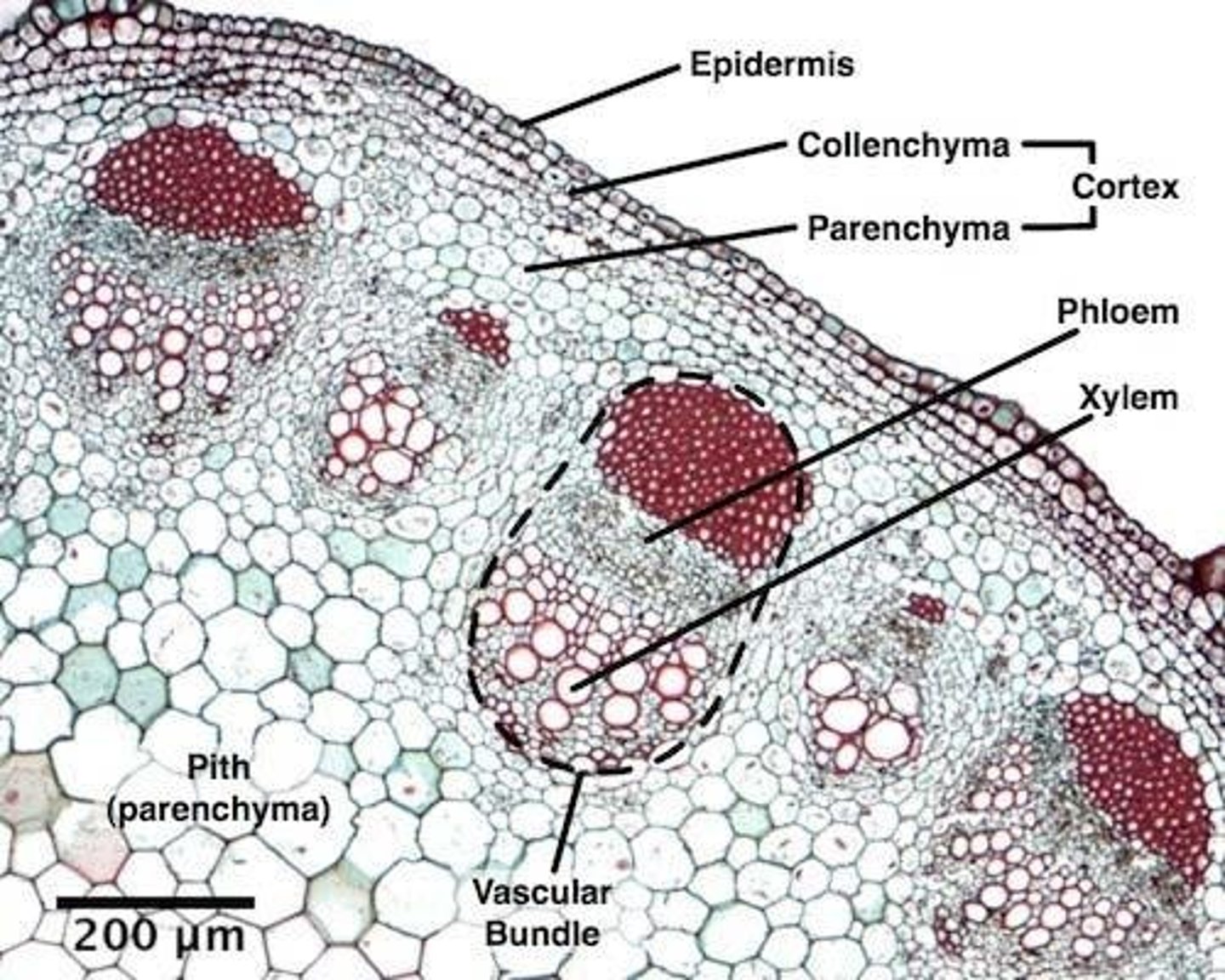
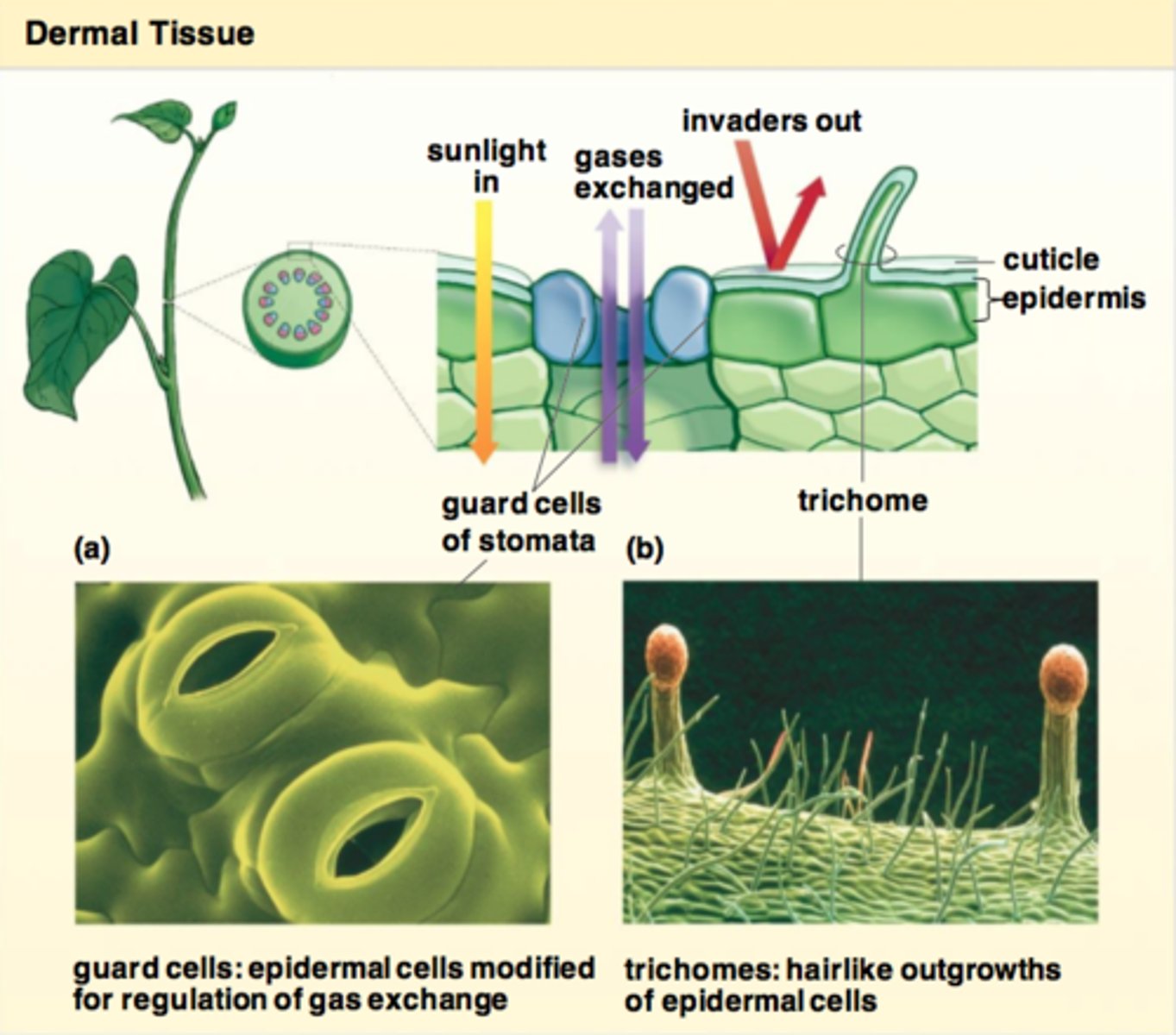
dermal tissue system
The outer protective covering of plants.
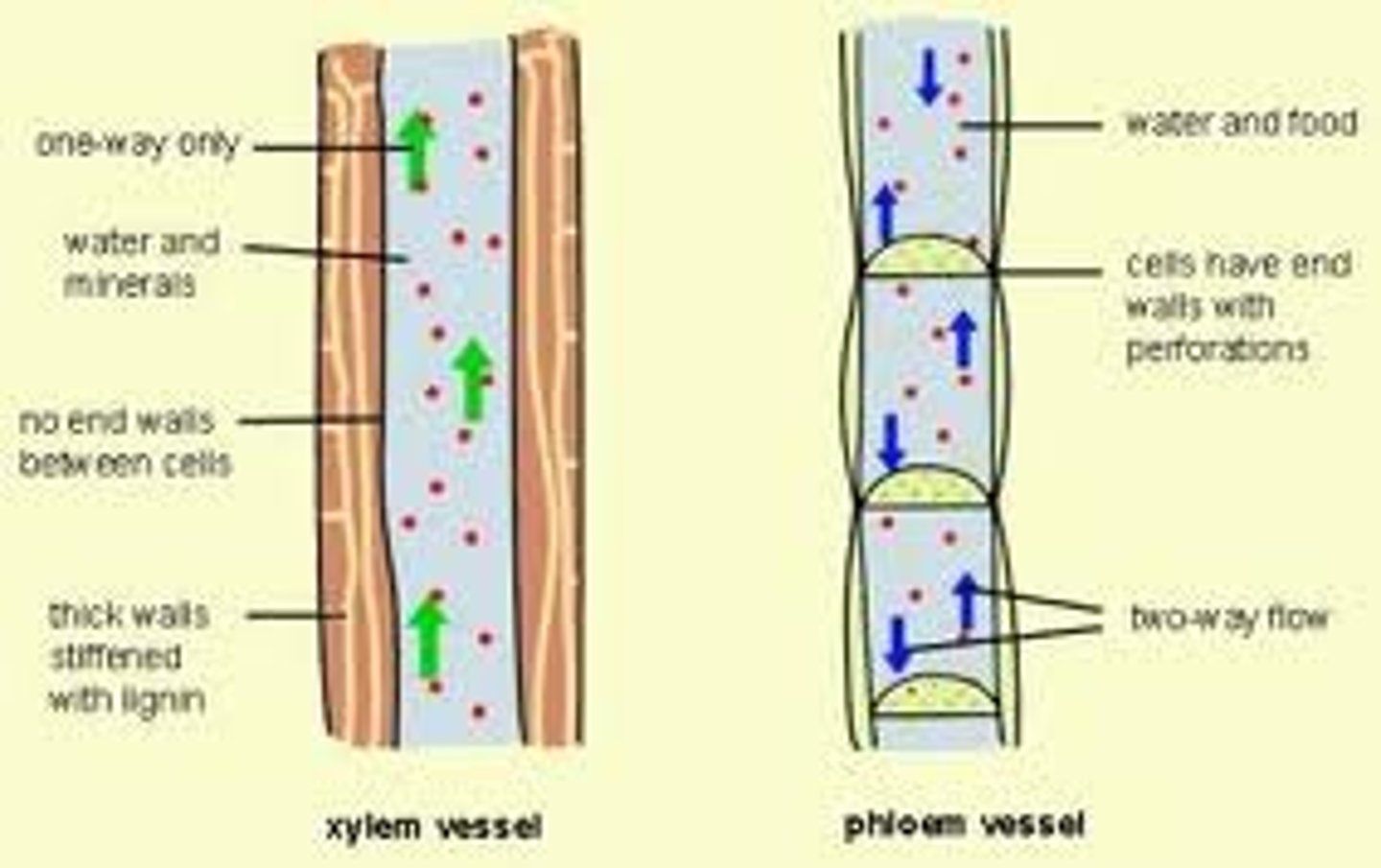
vascular tissue system
A system formed by xylem and phloem throughout a vascular plant, serving as a transport system for water and nutrients, respectively.
ground tissue system
Plant tissues that are neither vascular nor dermal, fulfilling a variety of functions, such as storage, photosynthesis, and support.
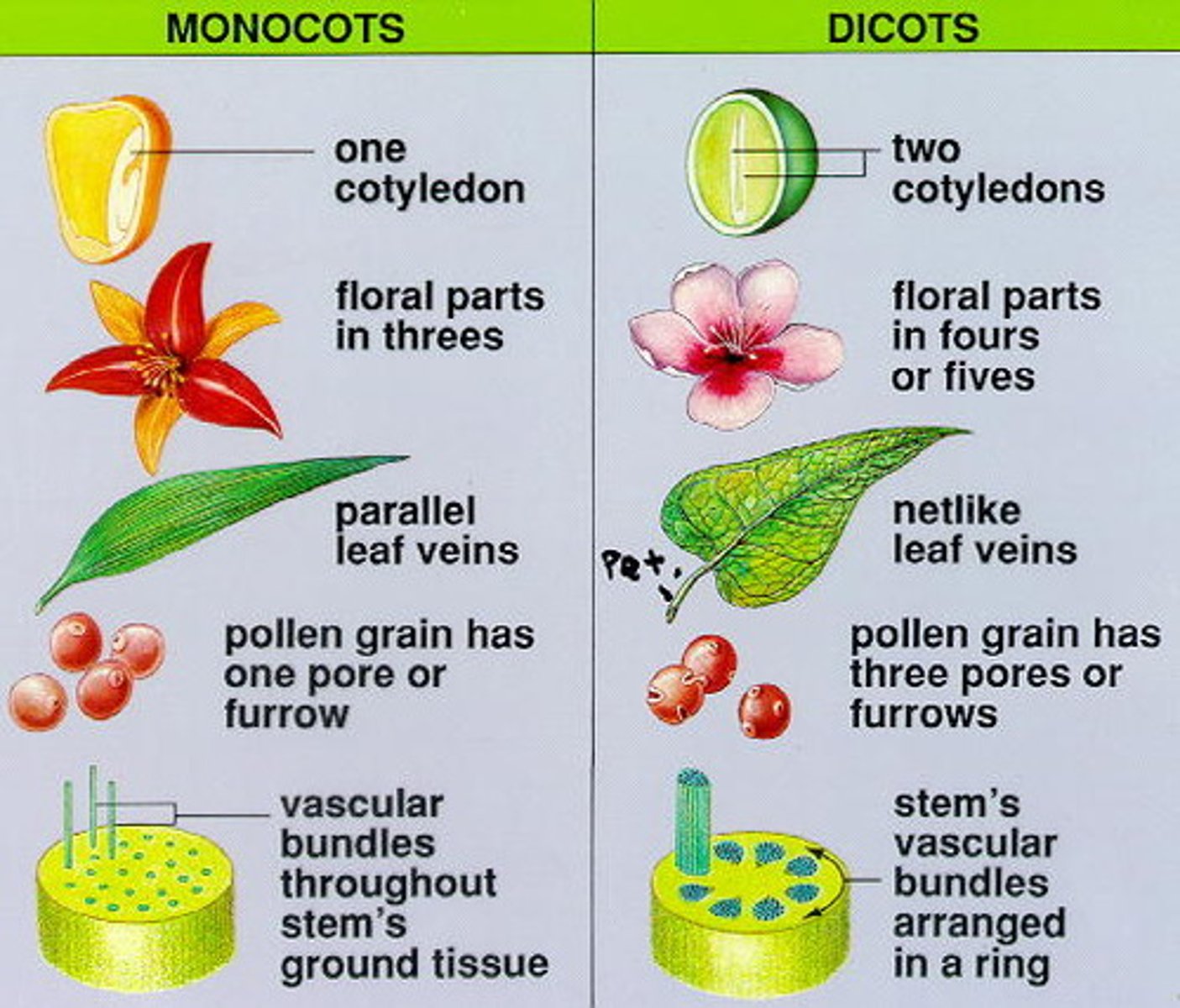
Monocots
Flowering plant whose embryos have one cotyledon
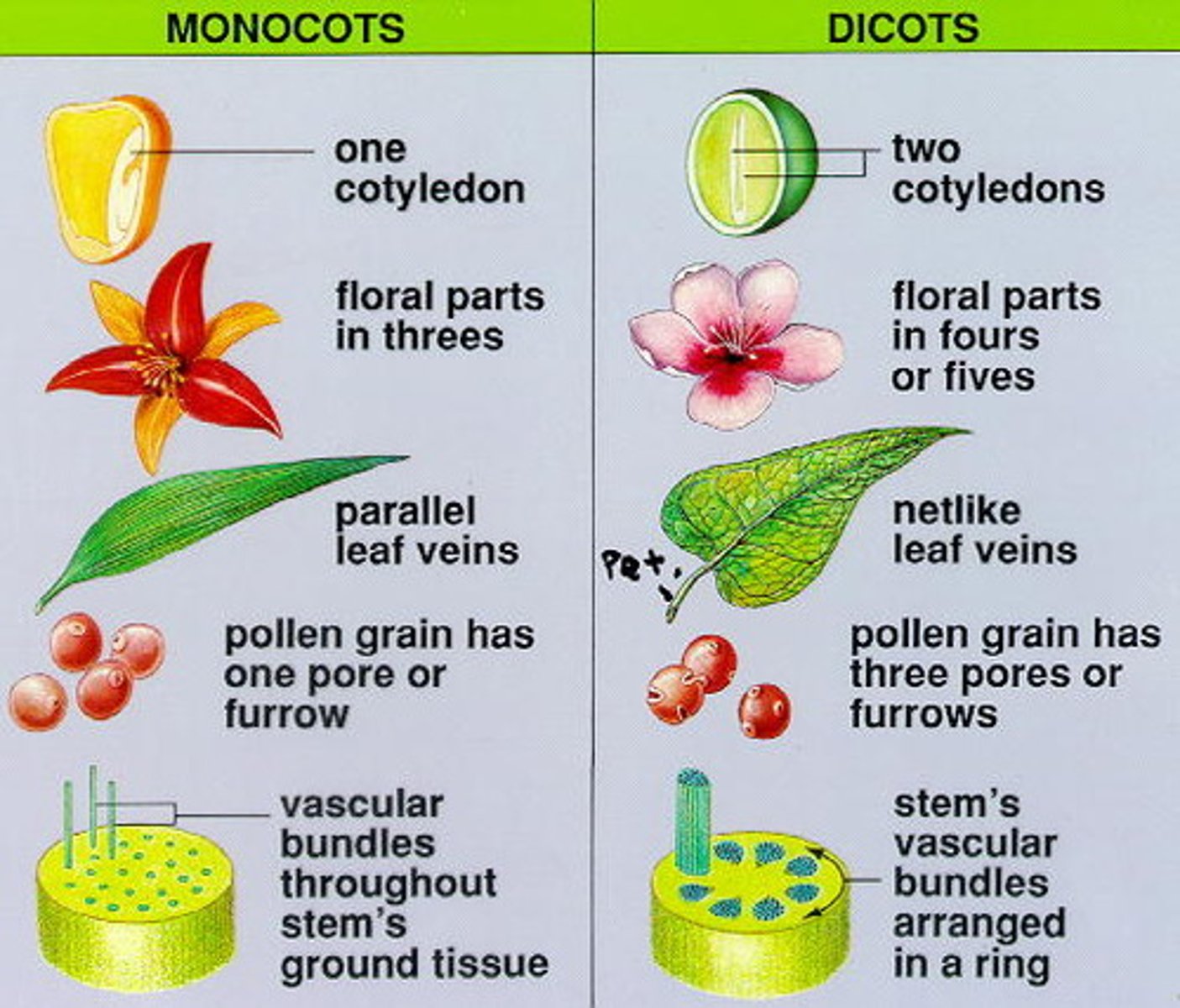
Eudicots
two cotyledons
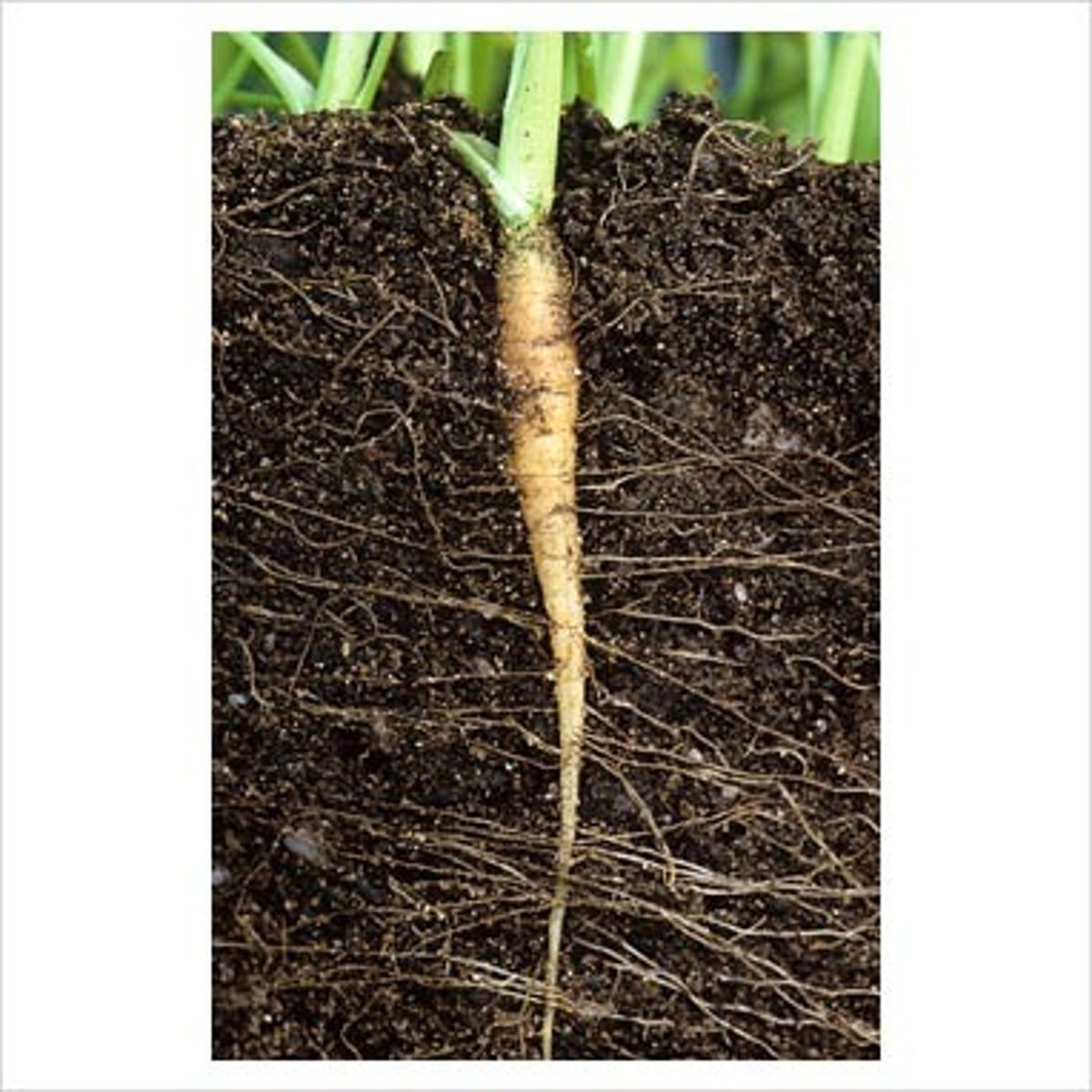
Tap roots
seen in most eudicots that have one large primary root that normally functions as a storage system with smaller lateral roots extending off the primary root (e.g. carrots)

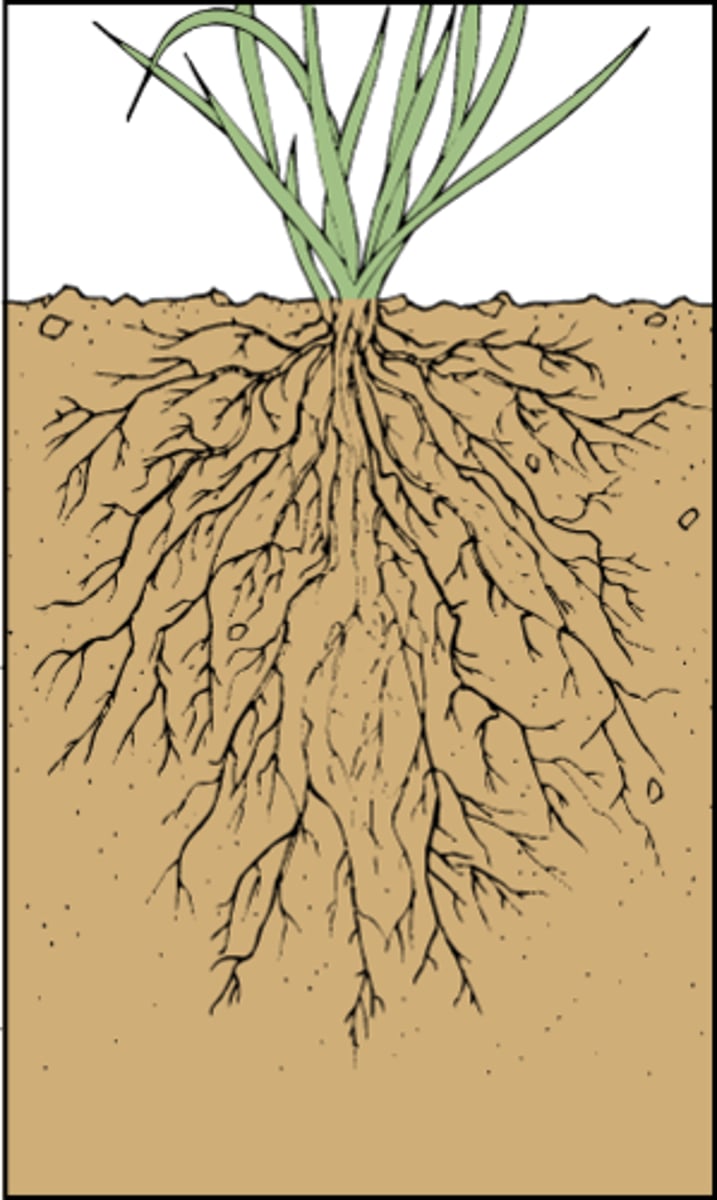
Fibrous roots
part of a root system in which roots branch to such an extent that no single root grows larger than the rest
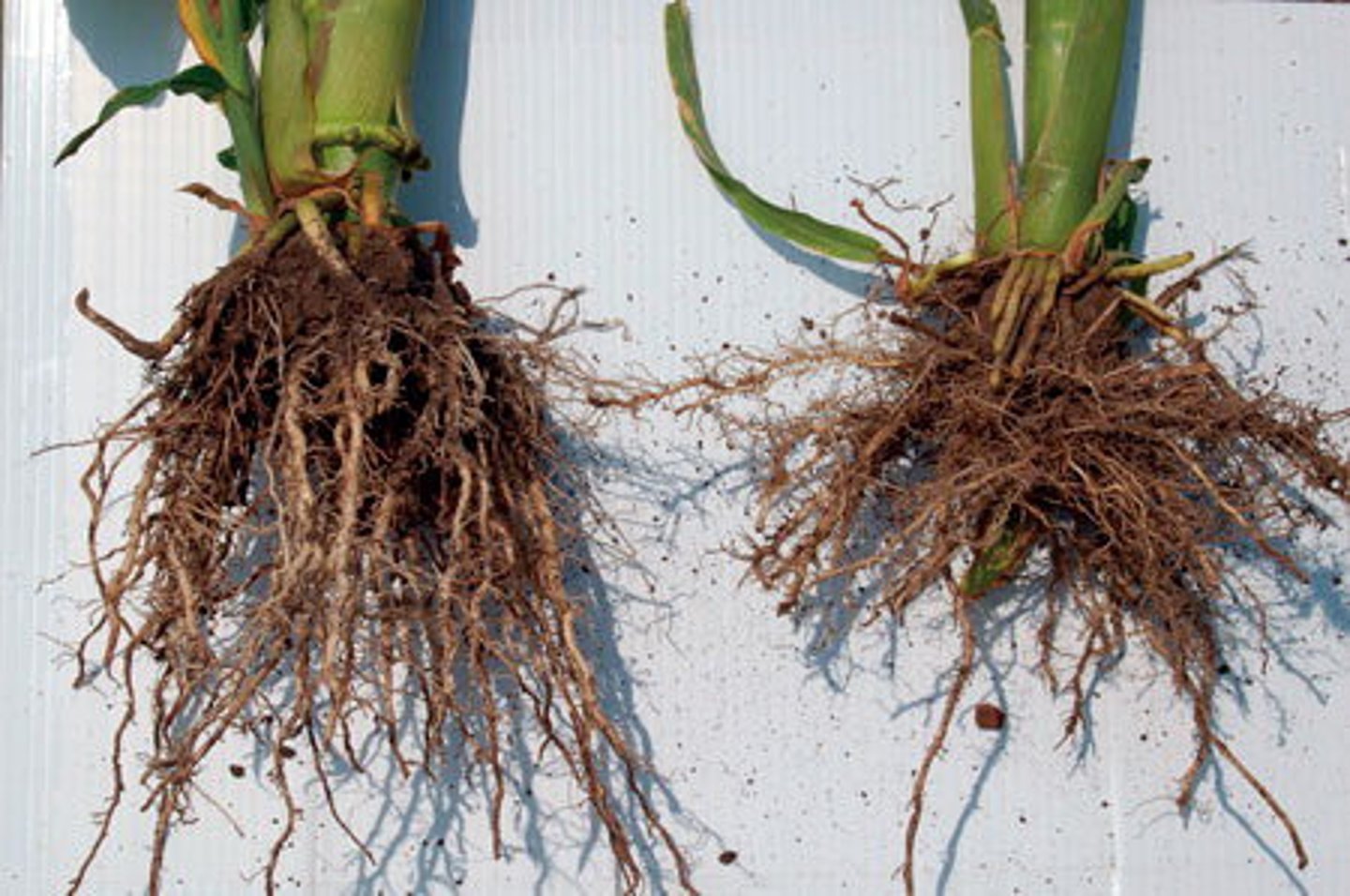

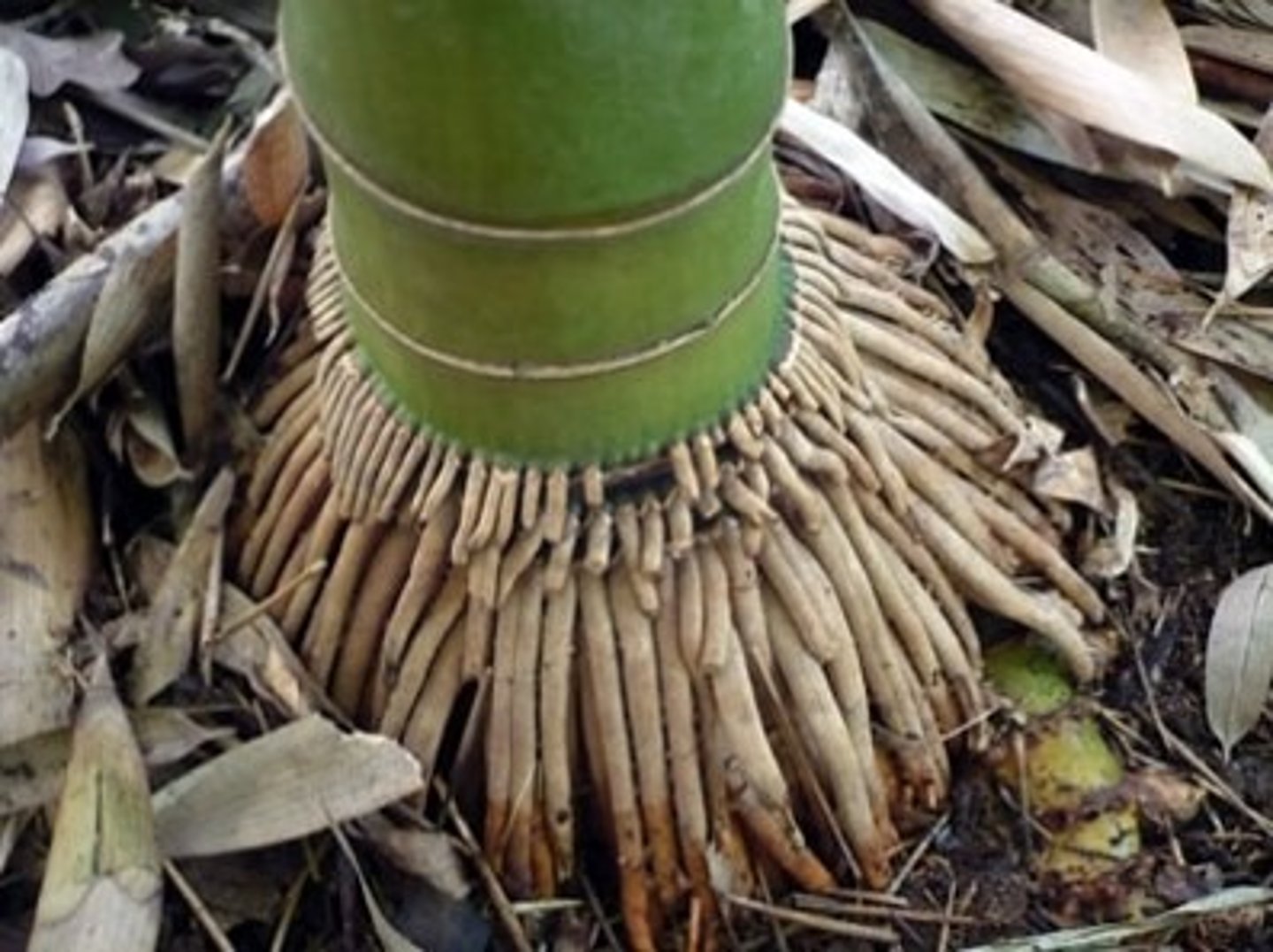
prop root (adventitious root)

Parenchyma cell
used to store nutrients and are involved with photosynthesis and other metabolic processes
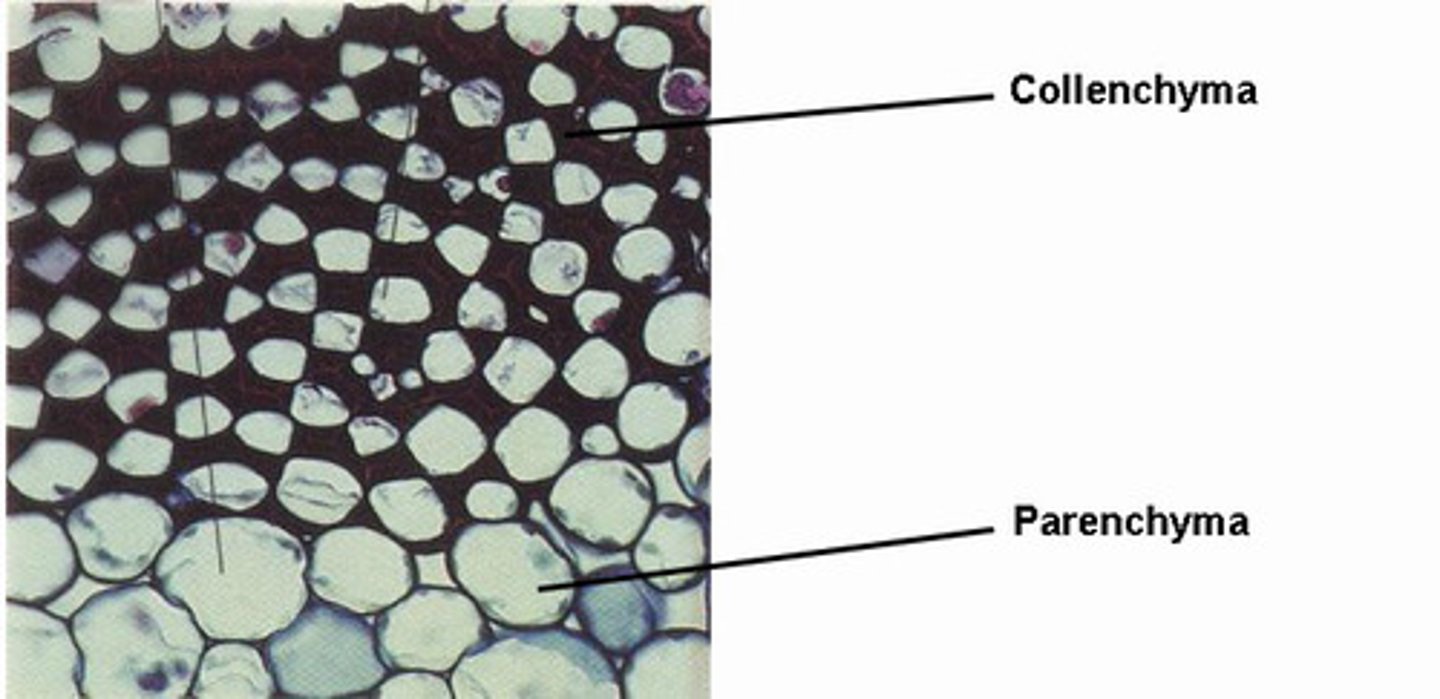
Collenchyma cells
provide strength and flexibility to stems and other structures
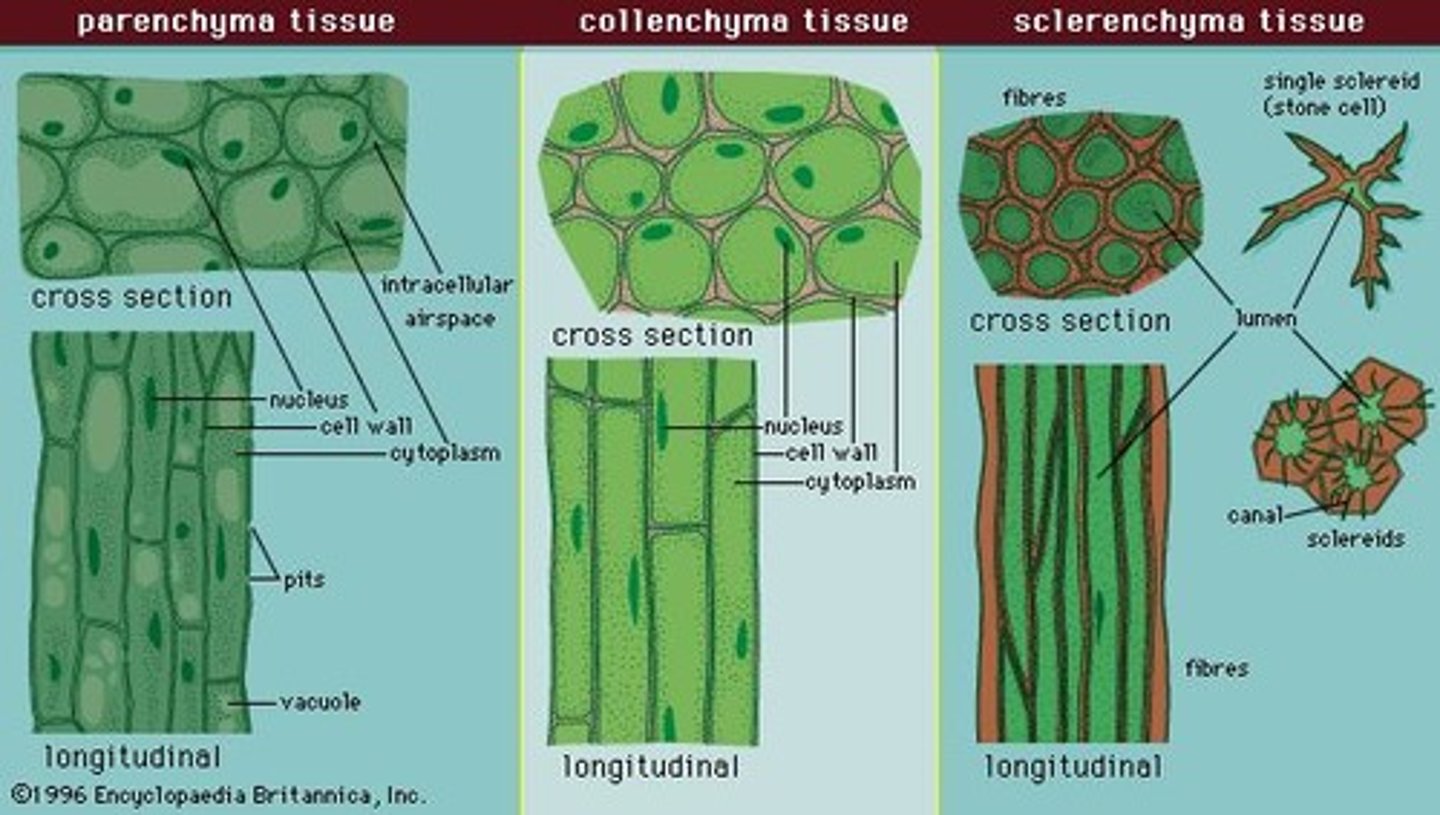
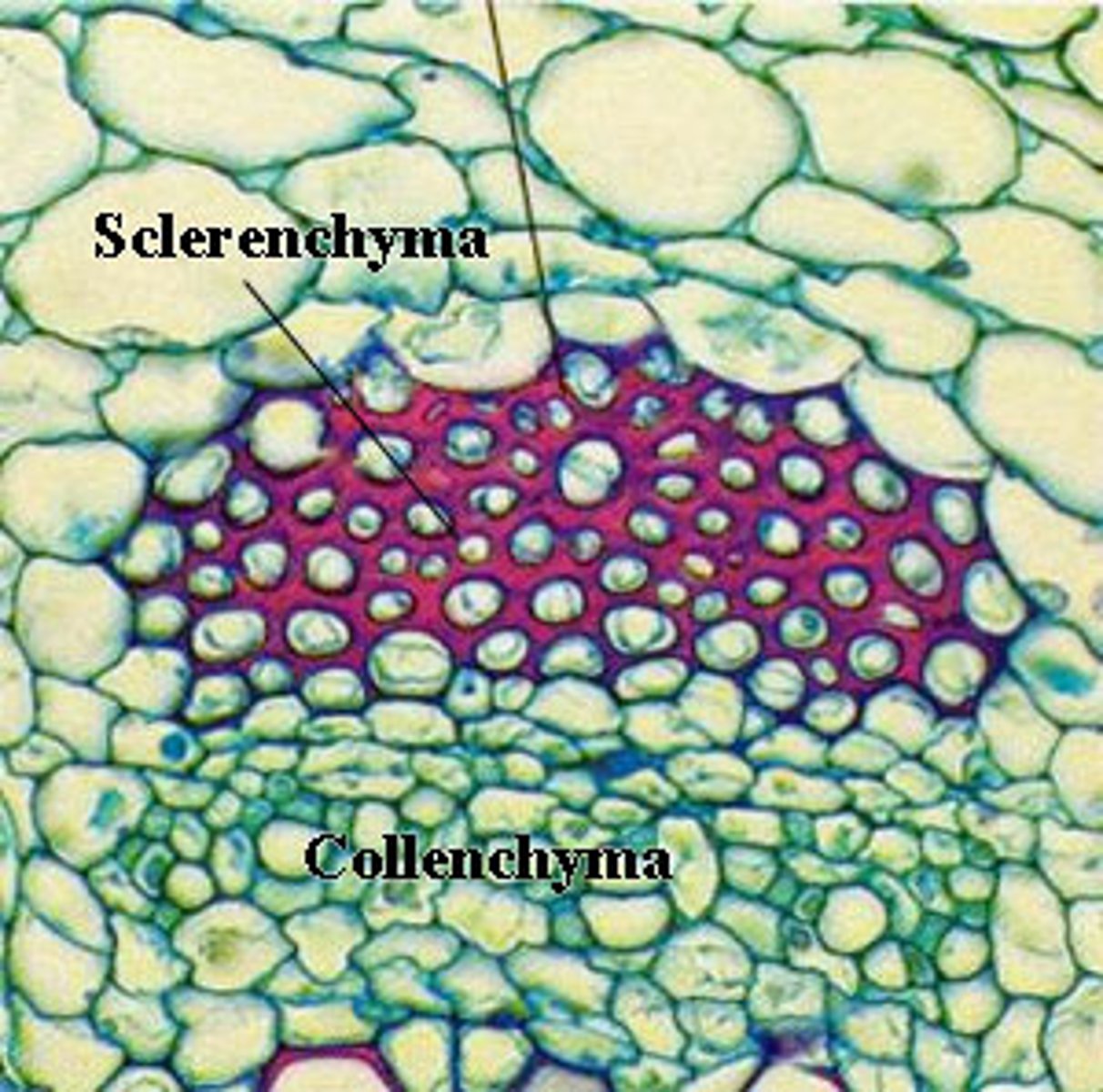
Sclerenchyma cells
protects seeds and support the plants
Simple leaf
leaf with a single blade, i.e. grass, maple leaves, oak leaves

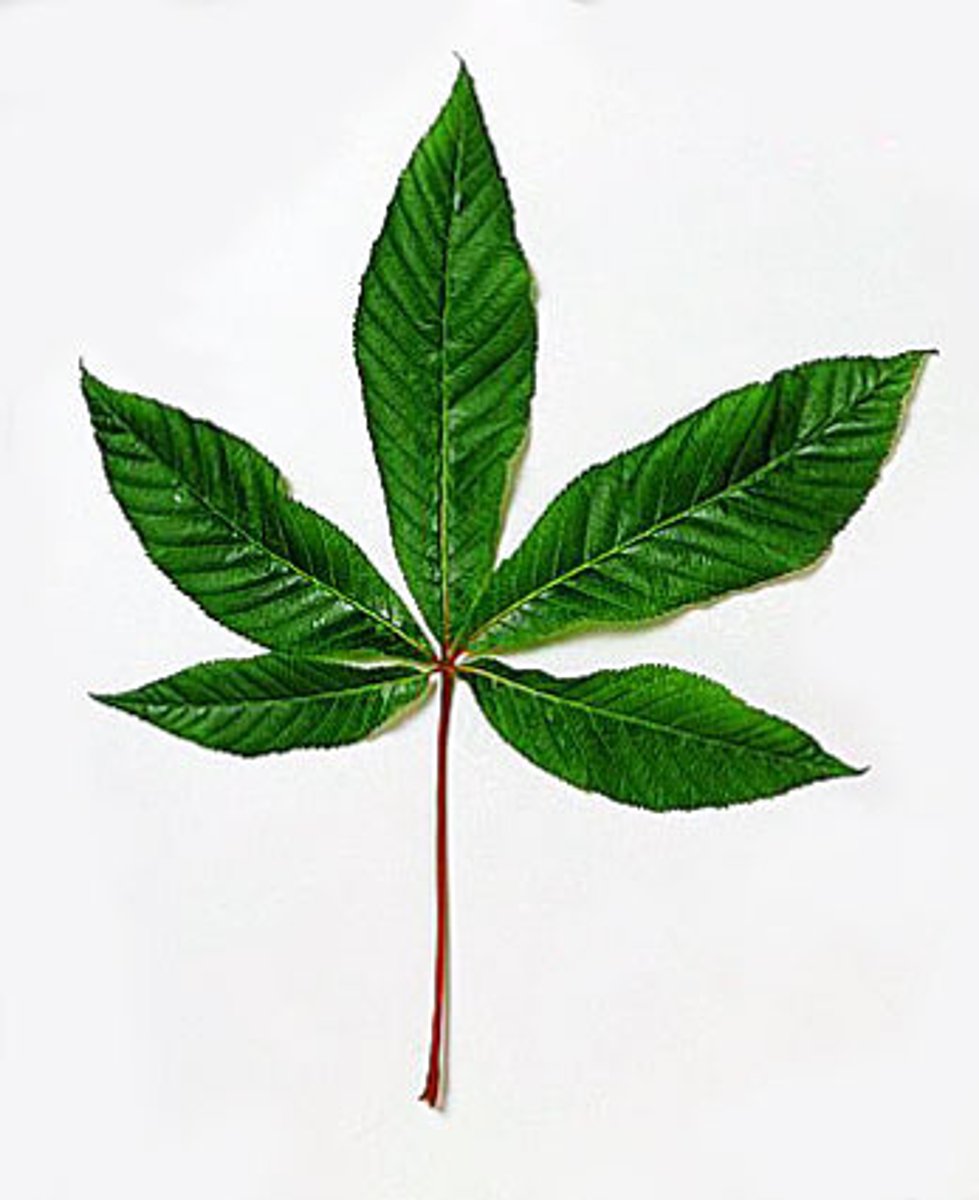
Compound leaf
a type of leaf in which the blade is divided into leaflets

Primary growth
Growth produced by apical meristems, which lengthen stems and roots.
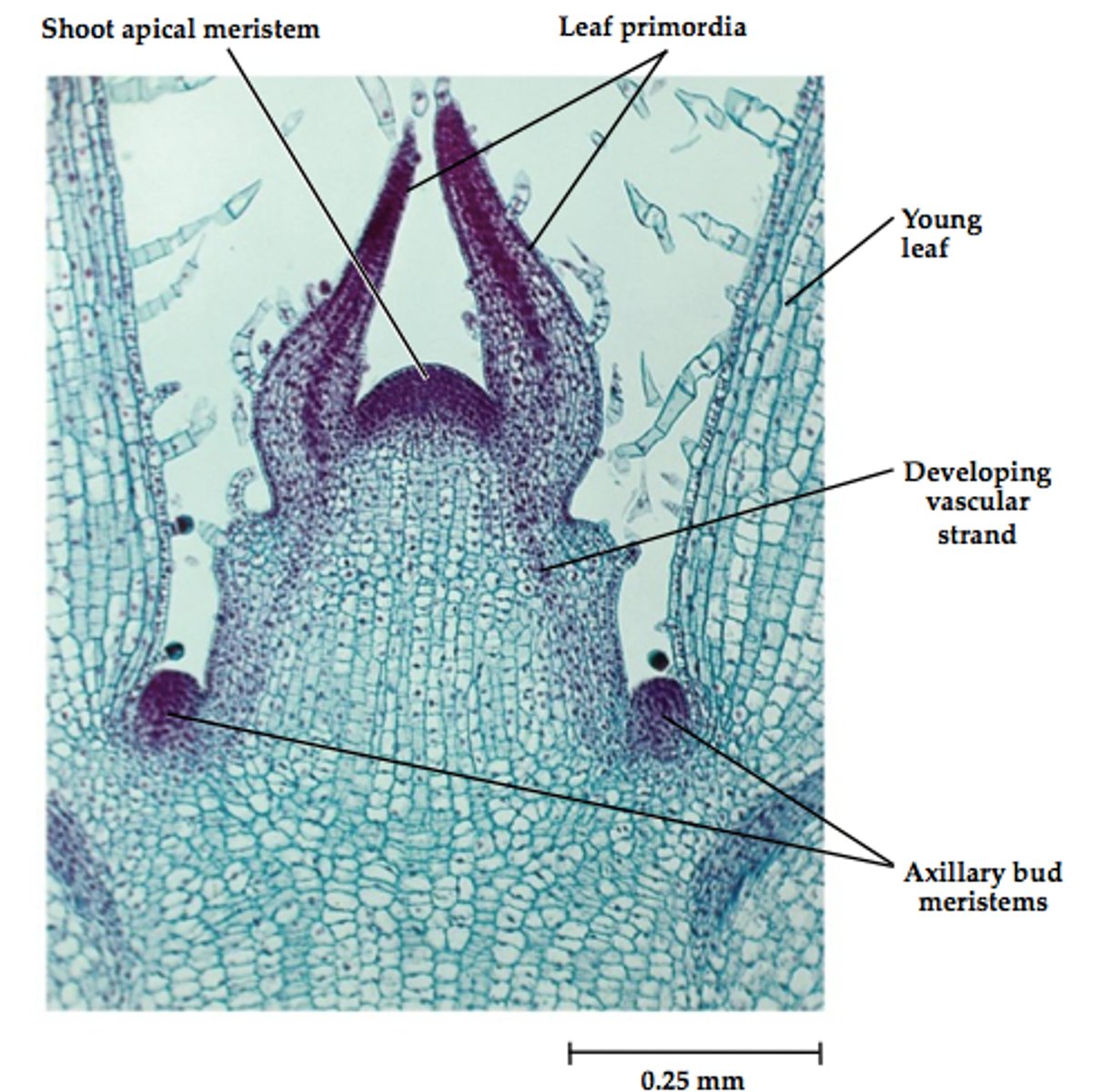
Secondary growth
the pattern of plant growth in which stems increase in width