Monitoring II: Oxygenation and Ventilation
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What is the goal of oxygen monitoring?
Ensure adequate oxygen delivery
When does hypoxemia begin?
SaO2 < 90% or PaO2 < 60mmHg
What are the consequences of hypoxemia?
End-organ hypoxia, dysfunction, cell death, organ failure
What is SaO2?
Saturation of arterial hemoglobin with O2
What is P50?
Partial pressure where SaO2 is 50% (typically 26 or 27 mmHg)
How do you find the delivery of oxygen to tissues (DO2)?
Cardiac output (L/min) x CaO2
97% of oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, yet that value is determined by another factor which is what?
Gas oxygen that is present
At what point in partial pressure of oxygen is there a very little increase in SaO2?
80mmHg
SaO2 is a value that is difficult to directly calculate, how do we get a value for it during surgery?
SpO2 (pulse oximetry) is used to calculate SaO2
What do pulse oximeters detect?
Estimate SaO2 by detecting % hemoglobin in either oxyhemoglobin or deoxyhemoglobin state
What can SpO2 tell you?
Percent Hb saturated with O2
Existence of peripheral perfusion
Pulse rate; rhythm
Information regarding Resp and CV systems
What is required for pulse oximeters to be accurate?
Must detect pulsatility
What does deoxyhemoglobin absorb more of?
Red light cause deoxygenated blood to be less red
What does oxyhemoglobin absorb?
More IR light causing oxygenated blood to be brighter red
What should SpO2 be in a healthy patient breathing room air?
96-99%
What should SpO2 be in an anesthetized patient?
>95%
If SpO2 is <90% what are causes of hypoxemia?
Hypoventilation, low inspired oxygen concentration, V/Q mismatch, R-L shunt, diffusion impairment
What can cause a falsely low SpO2?
Any movement
When do we use pulse oximetry?
Unsure of oxygenation status (check before GA)
Every moderate-heavily sedate patient
Every anesthetized patient
Every patient recovering from general anesthesia
Why would you need to move the lingual clip during anesthesia?
The clip can occlude blood flow
What is ventilation?
Mechanical process that causes the movement of gas between atmosphere and respo system conducting airways and alveoli via respiratory muscles
How do we maintain normal levels of blood oxygen, CO2, and pH?
Ventilation
What does hyperventilation do to CO2?
Reduces it
What does hypoventilation do to CO2?
Increases it
What is Ve?
Ventilation = Tidal volume x RR
What controls ventilation?
Respiratory center in medulla controlling RR, ventilatory rhythm, breath size
What influences ventilation?
Acid-base status and partial pressure of O2 and CO2
What has the most impact on ventilation?
CO2 levels
What are sources of CO2?
Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration
What happens to our ability to breath while anesthetized?
We lose the ability to sense CO2 levels
What does the partial pressure of CO2 tell you?
Effective ventilation both how well CO2 is being eliminated (mechanical) and the ventilatory drive from brainstem (stimulatory)
What are the major effects of anesthetics on ventilation?
Altered static lung volumes
Respiratory depression
What does muscle relaxation due to anesthesia cause?
Decreased primary and accessory respiratory muscles function and decreased tidal volume
What does a smaller functional residual capacity (FRC) mean?
Decreases gas exchanges efficiency
Decrease time to desaturation
What is the normal PaCO2?
37mmHg
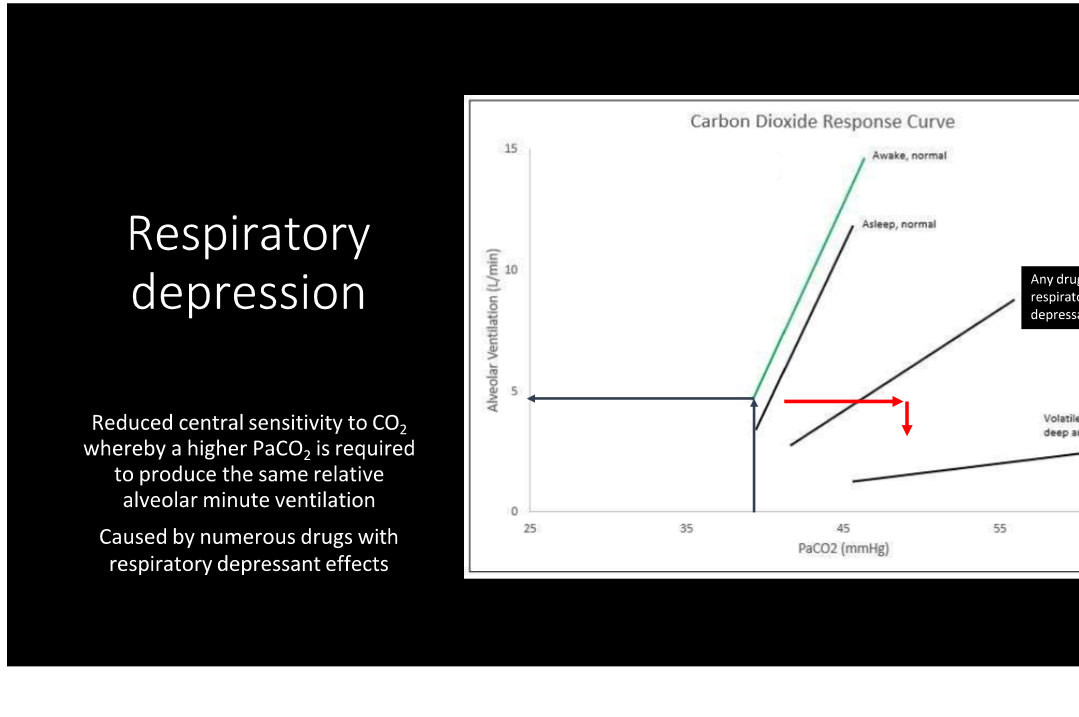
Describe what is happening here
When people have anesthetics on board, the brain needs a higher PaCO2 in order to stimulate the body to breath at the same rate when awake. This is additive between a premedication like an opioid and a volatile anesthetic like isoflurane
T/F every patient will hypoventilate?
True
What are the results of respiratory depressents?
Decreased sensitivity of central chemoreceptors to CO2
Results in ventilatory response relationship shifting right and down
Reduces RR, Vt, or both
Increases PaCO2, and PvCO2
What are some respiratory depressants?
Opioids, ketamine, propofol, alfaxalone, volatile anesthetics, benzodiazepines (except acepromazine in small animals)
What benzodiazepine does not cause a respiratory depressant effect in small animal only?
Acepromazine
For every 10 increase in PACO2, what happens to pH?
Drops by 0.7
What is capnography?
Measures CO2 from expired breaths
What does capnography directly measure?
End-Tidal gas sampled at end of expiration which reflects PCO2
What happens to End-Tidal CO2 if the heart arrests?
It decreases
What is the benefit of capnogrpahy?
Gives you information on ventilation status of the patient
Assess cardiovascular system
Assess patency of airway
When is ETCO2 highest during the waveform of ETCO2?
Phase 3 during the alveolar plateau
What are the two types of capnographs?
Mainstream and side stream
What does a mainstream capnogrpah mean?
Sensor is present at the level of the Y piece
What is the downside of mainstream capnographs?
It is large and bulky
What is the most accurate capnograph type?
Mainstream
What is a tolerated EtCO2 in healthy patients?
55-60 mmHg
When is it dangerous for EtCO2 to be 55-60?
If they already are acidotic or there brain mass messing something else up
What do you do if the patient is hypoventilating?
Turn down inhalant or give IPPV (intermittent positive pressure ventilation)
What is required for IPPV?
Requires endotracheal intubation w/ inflated cuff
What are indications for IPPV?
Hypoventilation / apnea
Management of anesthetic depth
Disrupted thoracic wall/diaphragm, loss of pleural pressure
Neuromuscular blocking agents
How do you do an IPPV?
Close pop-off valve
Squeeze re-breathing bag over 1-1.5 seconds
Release pop-off valve
Repeat as needed to maintain appropriate EtCO2
T/F giving an extra breath once a minute does not help?
True
What is peak inspiratory pressure (PIP)?
Maximum pressure achieved within anesthetic circuit while administering a positive pressure breath. This estimates the pressure in thoracic cavity
What value is very important to monitor when giving an IPPV?
PIP (peak inspiratory pressure)
What happens when you give IPPV?
You introduce positive pressure to the thoracic cavity. This causes external compression of low-pressure venous vessels causing reduced venous return (preload) during inspiration reducing CO an and BP
What are the types of pulse ox sensors?
Reflectance and transmittance
How does the transmittance work?
Red light and infrared light shine through the tissue and are read on the other side. Wavelength absorption of each estimates the SpO2
How do reflectance probes work?
Shine red light and infrared light into tissue and it reflects back on the SAM side. Wavelength absorption estimates the SpO2
What happens during systole?
Peripheral blood levels increase causing more oxygenated blood in the system
What happens to the venous blood during a cardiac cycle?
Stays relatively constant
What are the most common cause of pulse ox inaccuracies?
Clip induced tissue compression
Vasoconstriction/poor peripheral perfusion
Movement
Skin pigment
What causes vasoconstriction/poor peripheral perfusion leading to a false pulse ox?
Hypothermia, iatrogenic drugs like dex or vasopressors
What is functional residual capacity?
Volume of gas left over after a normal tidal volume expiration
What are the systemic effects of hypoventilation?
Acid-base imbalance (acidosis)
Cardiovascular dilation and negative inotropy
Higher CNS depression and increased cerebral blood flow
Respiratory system
What are the acid-base effects of hypoventilation?
Respiratory acidosis which leads to increased K levels
What are the cardiovascular effects of hypoventilation?
Peripheral vasodilation and negative inotropy
Sympathetic nervous system stimulation
Increase catecholamines (arrythmia risk)
What are the CNS effects of hypoventiliation?
Depression at higher levels
Increased cerebral blood flow
Cerebral edema if prolonged elevation
What are the respiratory effects of hypoventilation?
Pulmonary vascular constriction
What is really bad for patients with a brain tumor?
Hypoventilation because cerebral blood flow and pressure increases
What is CO2 levels during phase 1?
None
What are CO2 levels during phase 2?
Beginning of expiration so increases
What does peak CO2 at the end of phase III correlate with?
PaCO2

Bronchospasm and rebreathing/air trapping (shark fin)
Dead space has not emptied before next inspiration
Increasing level of baseline PeCO2 due to air trapping
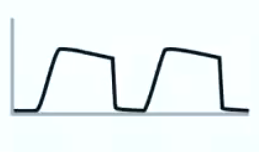
Emphysema
Arterial CO2 represented by early peak, not end tidal, due to hypercompliance and poor gas exchange
Also seen with a pneumothorax with air leak

Sudden loss of waveform
Critical event needing emergency intervention
ET tube disconnected, dislodged, kinked, or obstructed
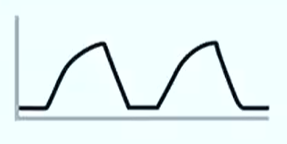
Mechanical airway obstruction
Fixed mechanical obstruction affecting both inspiration and expiration
alpha and beta angle are both above 90 degrees
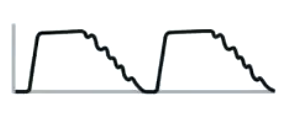
Cardiogenic oscillation
Pulsation from heart to parenchyma causing small volume changes
Sign of cardiomegaly

Downtrending ETCO2
Decrease waveform due to
Shock/low CO
Pulmonary embolism
Hyperventilation
What is the VT for IPPV in dogs and cats?
8-12
What is the RR for dogs on IPPV?
8-20
What is the RR for cats with IPPV?
10-20
What is the inspiratory time for dogs and cats for IPPV?
1-1.5 seconds
What is the peak inspiratory pressure for dogs on IPPV?
8-12
What is the peak inspiratory pressure for cats on IPPV?
5-8
What is the EtCO2 for dogs and cats on IPPV?
45-55
What should the peak inspiratory pressure be for puppies and kittens?
5-8
What should peak inspiratory pressure be for adult horses?
20-30