Neurons & Glia
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Electrical current results from movement of ____ across a membrane
Electrical current results from movement of ions across a membrane
How is RMP negative? What makes it that way?
Unequal distribution of ions (Na +, K +, Cl - ) across cell membrane
Greater permeability to K + than Na +
Large anions inside cell
Na + /K + electrogenic pump (3 Na + out, 2 K + in) (Inside made negative relative to outside)
Resting membrane potential generally between _____ mV
Resting membrane potential generally between -60 to -80 mV
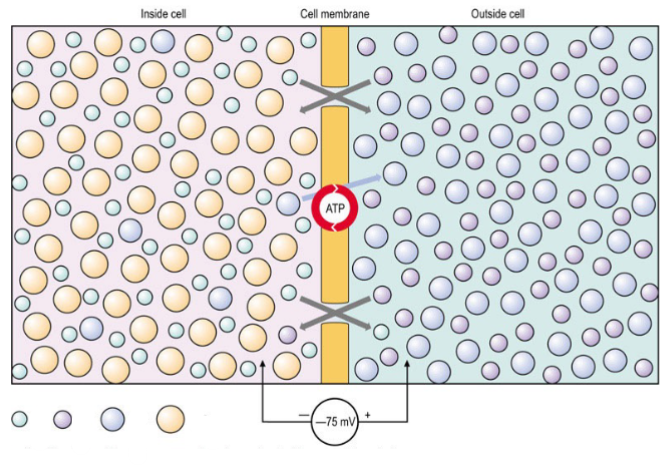
What does each colour represent
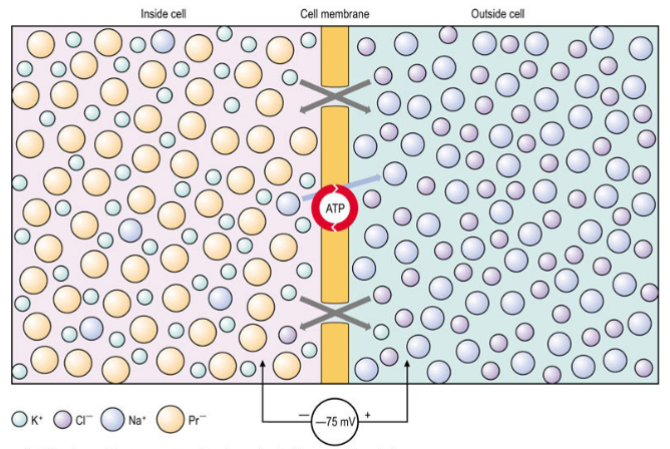

Fill in numbers
What two types of gradients influence ion movement across the membrane?
Concentration gradient → ions move from high to low concentration.
Electrical gradient → ions are attracted or repelled by the membrane potential.
What happens when K⁺ moves along its concentration gradient? What direction does it go?
K⁺ tends to diffuse out of the cell because intracellular [K⁺] is higher than extracellular [K⁺].
Why doesn’t K⁺ keep diffusing out of cells forever?
As K⁺ leaves, the inside of the cell becomes more negative, creating an electrical gradient pulling K⁺ back in. When this electrical force balances the concentration force, equilibrium potential is reached.
What is the equilibrium potential?
It’s the membrane potential at which there is no net movement of a specific ion, because the concentration and electrical gradients are equal and opposite.
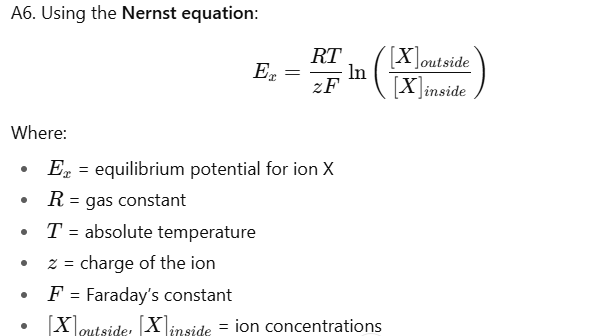
How can the equilibrium potential for an ion be calculated?
Sub in any ion (e.g. K+) for X
Which ion is the main determinant of the resting membrane potential?
K⁺ (potassium), because the membrane is most permeable to K⁺ at rest.
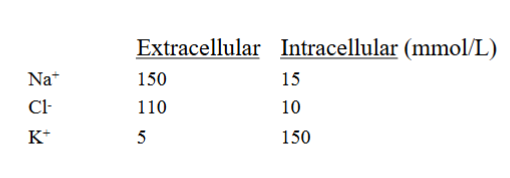
Equilibrium potential (voltage inside cell) of Cl-
-70mV
Equilibrium potential (voltage inside cell) of K+
-80mV
Equilibrium potential (voltage inside cell) of Na+
+50mV
Permeability constant (cm/s) of water

Permeability constant (cm/s) of Cl-

Permeability constant (cm/s) of K+

Permeability constant (cm/s) of Na+

Which ion is being pumped against its concentration gradient in the Na+ /K+ electrogenic pump
Both
Ion channels are composed of ……
Protein subunits (typically 4 or 5 subunits)
3 types of ion channels
Voltage gated
Ligand gated
Mechanosensitive
Give examples of what mechanosensitive ion channels might be used for
Touch
Hearing
How does a voltage gated channel work
Something that changes the balance of charges in the cell triggers the tertiary structure
Threshold
The change required to activate voltage sensitive ion channels
What triggers the opening of voltage-gated Na⁺ channels?
Depolarisation of the membrane, usually when it reaches threshold.
What is the approximate threshold potential for opening Na⁺ channels relative to RMP
+15 mV relative to resting membrane potential (RMP).
What is the role of the Na⁺ channel activation gate?
It opens rapidly once threshold is reached, allowing Na⁺ to rush into the cell.
What is the role of the inactivation gate in Na⁺ channels?
It closes shortly after depolarisation, stopping further Na⁺ influx, and is responsible for the refractory period.
What are the two types of refractory period?
Absolute refractory period → no new action potential can be initiated (Na⁺ channels are inactivated).
Relative refractory period → a stronger-than-normal stimulus is needed (some Na⁺ channels recover, but K⁺ efflux makes threshold harder to reach).
By how much does Na⁺ conductance increase during an action potential?
Up to 5000 times.
What is the function of voltage-gated K⁺ channels?
They open during depolarisation (slower than Na⁺ channels) and mediate repolarisation by allowing K⁺ efflux.
How do Na⁺ and K⁺ channels work together to produce an action potential?
Na⁺ influx via voltage-gated Na⁺ channels → rapid depolarisation (upstroke).
K⁺ efflux via voltage-gated K⁺ channels → repolarisation and return to RMP.
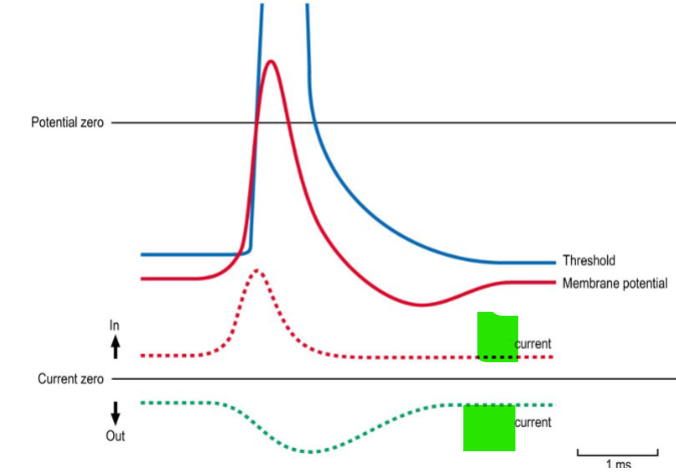
Which ion is represented by each dotted line
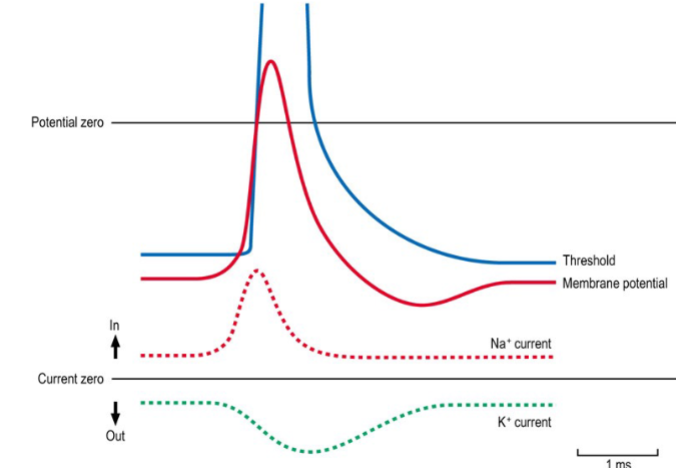
What are local circuits in the context of action potentials?
Local circuits are small currents that spread to adjacent regions of the membrane when an area depolarises during an action potential
How do local circuits contribute to AP propagation?
The depolarising current from an active region causes adjacent membrane areas to reach threshold, triggering new action potentials.
Why does an action potential propagate in only one direction?
Because the region just behind the active site is in a refractory period (Na⁺ channels inactivated), preventing it from being re-excited immediately.
What ensures that AP propagation is continuous along the axon?
Sequential depolarisation of adjacent areas via local circuits ensures the AP moves smoothly along the axon.
How does Saltatory conduction work
On myelinated axons Na+ influx depolarises the cell for up to 3mm along axon (distance between nodes of Ranvier)
Current flows through extracellular fluid and axoplasm from node to node
What produces myelin
Glia (Glial cells)
In the PNS: Schwann cells
In the CNS: Oligodendrocytes
Myelin sheaths are made of multiple concentric layers of membrane wrapped around an axon.
These layers are rich in _______, which is highly insulating
Myelin sheaths are made of multiple concentric layers of membrane wrapped around an axon.
These layers are rich in sphingomyelin, which is highly insulating
Nodes of Ranvier interval lengths
1-3mm intervals
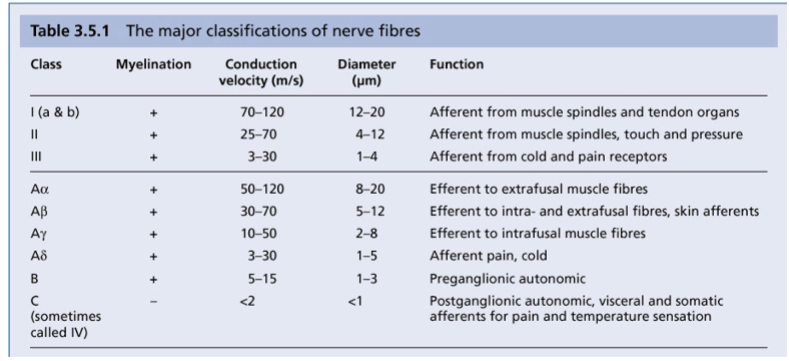
How are nerves generally classified
A (a, b, g, d)
B
C
How are sensory nerves classified
I (A, B), II, III, IV
Fill in the functions of each nerve fibre group
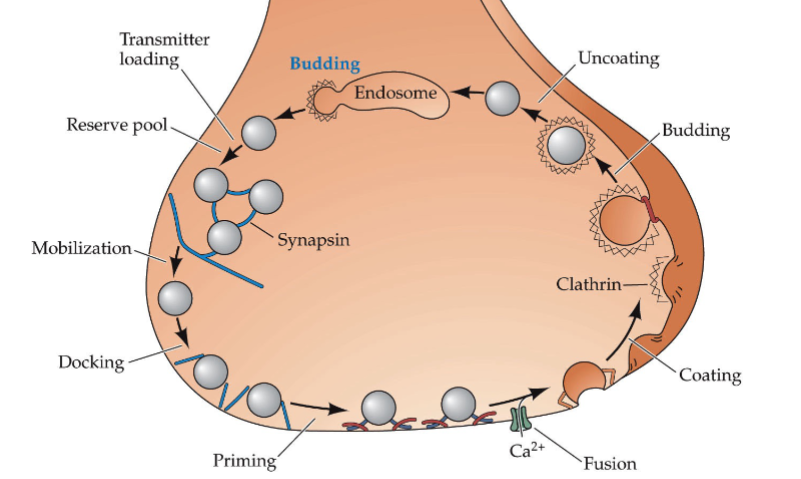
How does an AP lead to exocytosis at an axon terminal (synapse)
AP propagation to axon terminal
Activation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Ca2+ activates Ca2+-calmodulin- dependent protein kinase II
Primes vesicles for mobilisation → docking to release sites on presynaptic membrane → membrane fusion
Exocytosis
The most common type of neurotransmission goes from what part of the presynaptic neuron to what part of the postsynaptic neuron
Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron synapses on the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron
This is axodendritic
In ionotropic receptors, how are protein subunits arranged
Arranged around a pore
How does the speed & duration of action of ionotropic receptors compare to metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic
• Fast activation
• Short duration of action
Metabotropic
• Slow activation
• Long duration of action
What is a post-synaptic potential (PSP)?
A PSP is a change in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron caused by neurotransmitter binding to receptors.
What happens when an excitatory neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane?
It causes depolarisation, making the inside of the neuron less negative.
What is an Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential (EPSP)?
An EPSP is a graded depolarisation that favors generation of an action potential but is not itself an action potential
Do EPSPs propagate along the axon like action potentials?
No — EPSPs are local, graded responses and do not propagate.
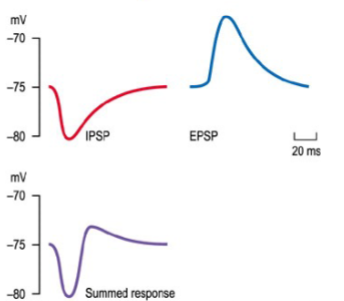
What is an Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential (IPSP)?
An IPSP is a graded hyperpolarisation that reduces the likelihood of an action potential.
Can PSPs be summed to influence action potential generation?
Yes, EPSPs and IPSPs can summate (spatially or temporally) to determine whether the postsynaptic neuron reaches threshold for firing an action potential.
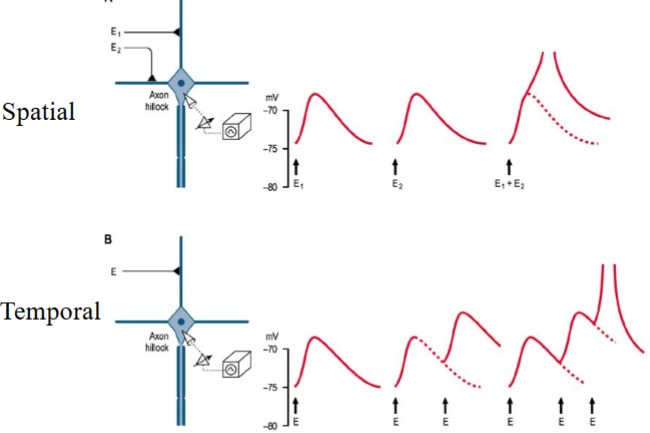
What are 2 types of summation
Spatial: Multiple presynaptic neurons fire at the same time onto the same postsynaptic neuron.
Temporal: A single presynaptic neuron fires rapidly in succession.
(Spatial all ends on the Same Space. Temporal goes loads of Times)
Glia function
Protectors and support cells of neurons
Heighten the functional capacity of neurons
(glia = greek for glue)
Name some types of glia (6)
Schwann cells
Oligodendrocytes
Astrocytes
Ependymal cells
Radial glia
Microglia
Which glia control the extracellular environment around neurons
Astrocytes
Ependymal cells
Which glia play a part in brain development
Radial glia
Which glia have an immune function
Microglia
How does the no. of glia compare to the no. of neurons
10-50x more glia than neurones
Glia can be split into 2 groups - what are they
Microglia & macroglia (all groups other than microglia)
Microglia role
CNS immune cells
They are Phagocytes - activated by infection and injury
What are microglia derived from
derived from macrophages outside of CNS
What are macroglia derived from
neural stem cells
What are the main general functions of macroglia?
Macroglia provide:
Structural support for neurons
Insulation of axons (myelination)
Blood-brain barrier support
Neuronal nourishment by releasing growth factors (neurotrophins e.g. GDNF)
Guidance for neuronal migration and axon outgrowth
Support for synaptogenesis
Promotion of efficient neuronal signalling
How do macroglia promote efficient signaling between neurons?
Clearing neurotransmitters from synapses (e.g., glutamate)
Responding to neuronal signals by releasing glial factors that modulate synaptic activity
What specific role do astrocytes play in synaptogenesis?
Astrocytes:
Regulate synapse number
Regulate synapse function
Regulate synapse stability
Can Schwann cells perform similar functions to astrocytes?
Yes, Schwann cells in the PNS can perform similar functions & release similar factors
What role do glia play in synaptogenesis
Synapse formation:
Extracellular protein signals from astrocytes trigger synapse formation in CNS
Neurones migrate during development but synapse formation only occurs when astrocytes (or other macroglia) are present
Schwann cells in the periphery trigger neuromuscular junction formation
Synapse maintenance:
Macroglia are also necessary for synapse maintenance
For these reasons Macroglia have a crucial role in the anatomical development of the brain
Do adult neural stem cells also depend on astrocytes for synapse formation?
Yes, adult hippocampal stem cells require astrocytes for forming functional synapses.
Give an example of a neurotrophin released by macroglia.
GDNF (Glial cell line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor)
How do glial cells sense synaptic activity?
Glial cells detect neuronal activity by monitoring calcium transient currents in their processes
What do glial cells release in response to neuronal activity?
They release gliotransmitters, which can modulate synaptic function and neuronal signalling.