RS lab
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
nasal cavity/oral cavity
breathing through nose, breathing through mouth
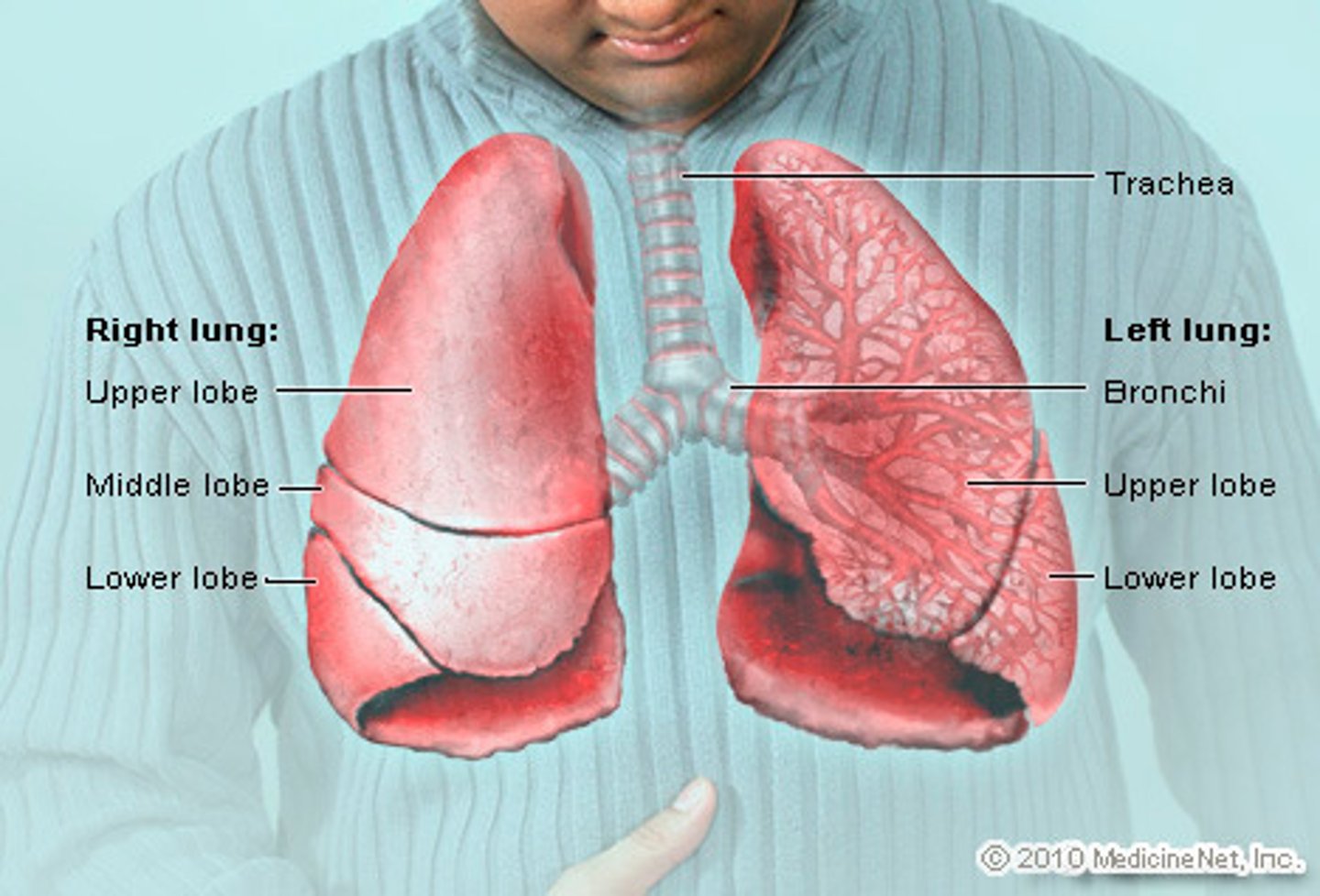
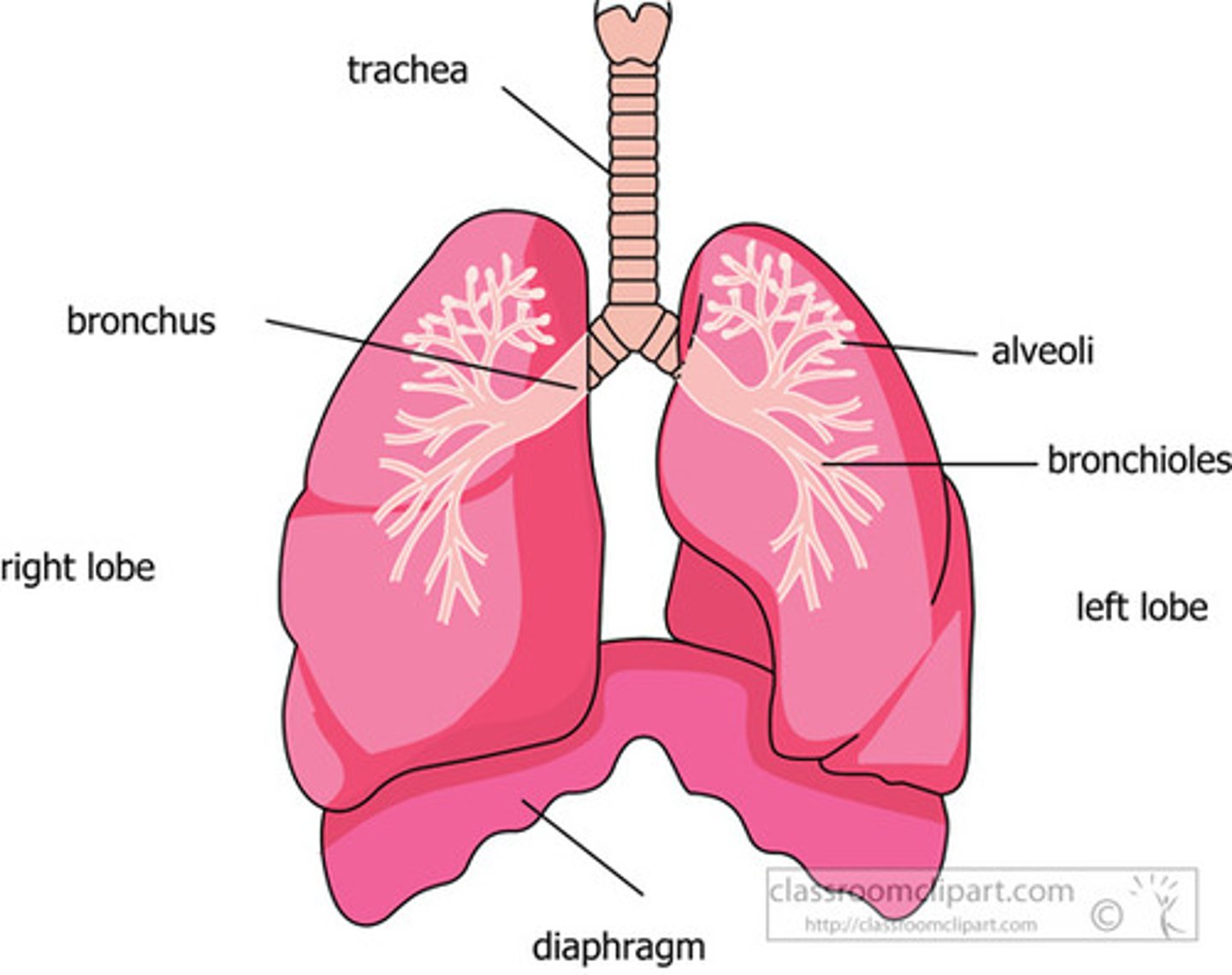
lungs r/l
sitting in thoracic cavity surround heart above diaphragm
apex- top of lung
base- bottom of lung
cardiac notch- - in left lung only; accommodates heart (slightly more left in thoracic cavity)
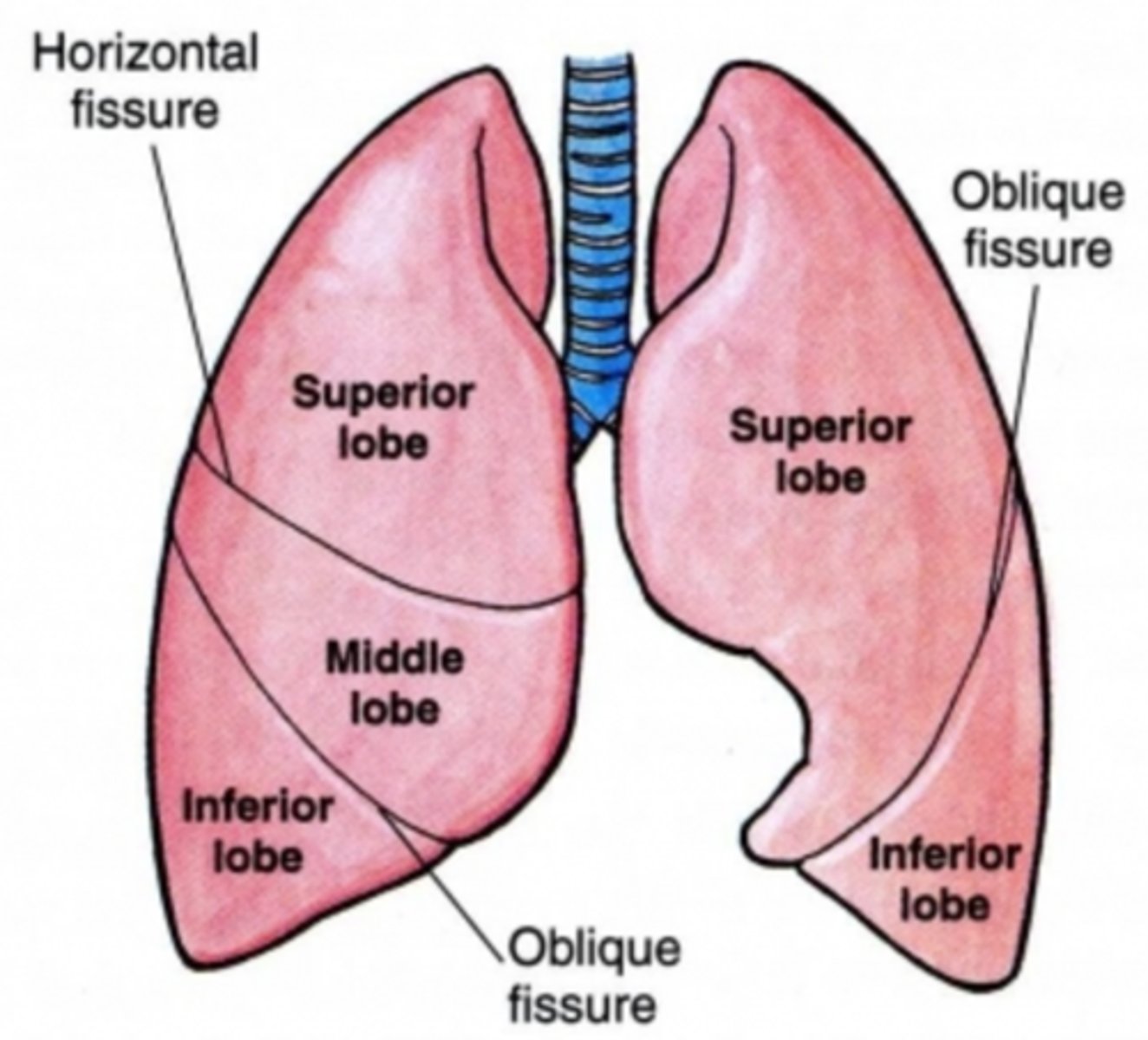
lung lobes
3 right, 2 left (no middle lobe)
surfaces: costal surface (facing chest well)
mediastna surface (facing heart)
hilum- area where airway and blood vessels go in and out of lung
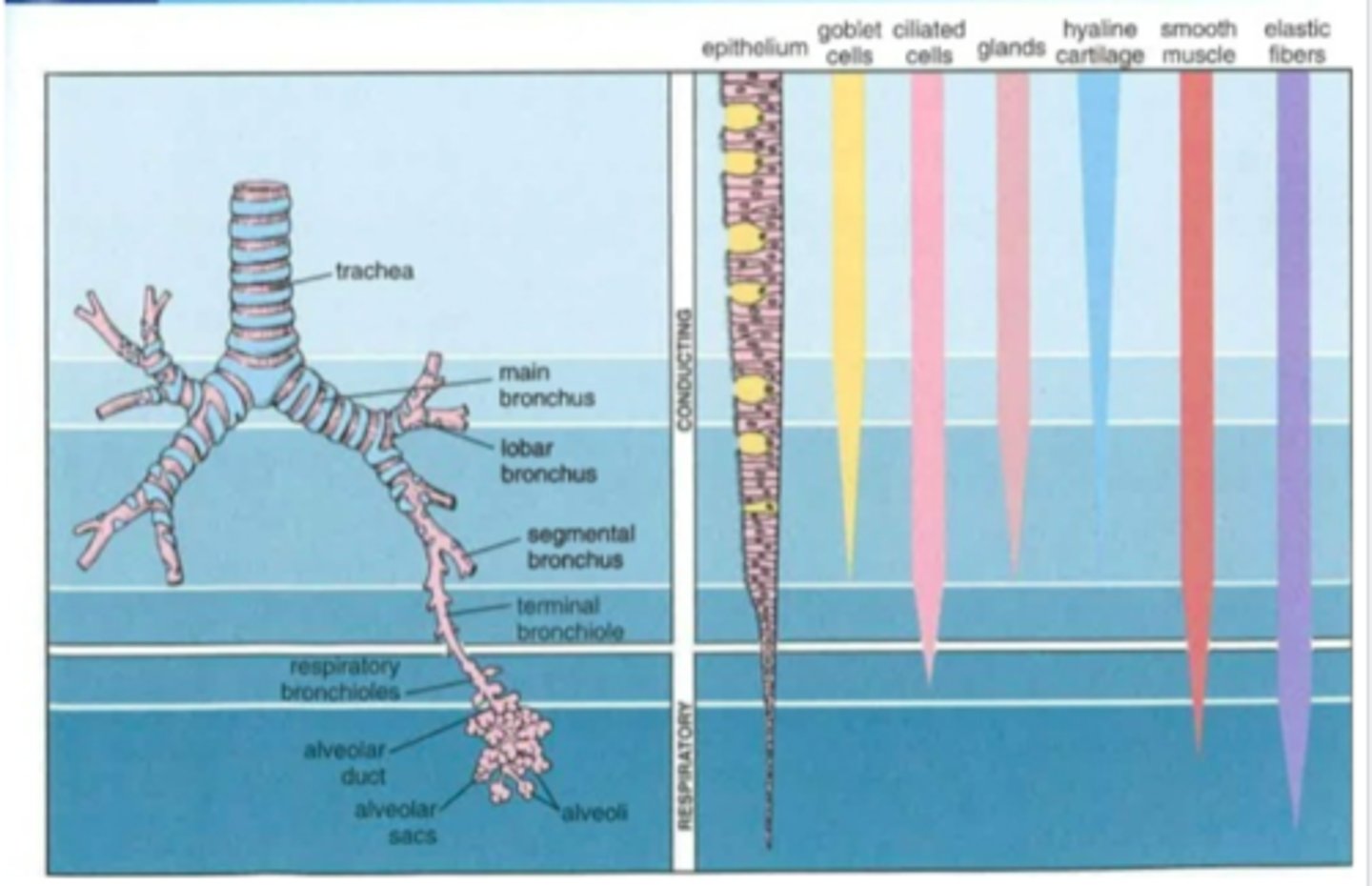
Airways
passage connecting atmosphere and alveoli
3 zones
- upper airways - no gas exchange (alveoli absent), nasal cavity /pharynx/larynx
- conducting zone - gas exchange (alveoli absent); trachea/bronchi/bronchioles/serveral more divisions of bronchioles/ terminal bronchioles
- respiratory zone- gas exchange (alveoli present); respiratory bronchioles/alveolar ducts/alveolar sacs/alveoli
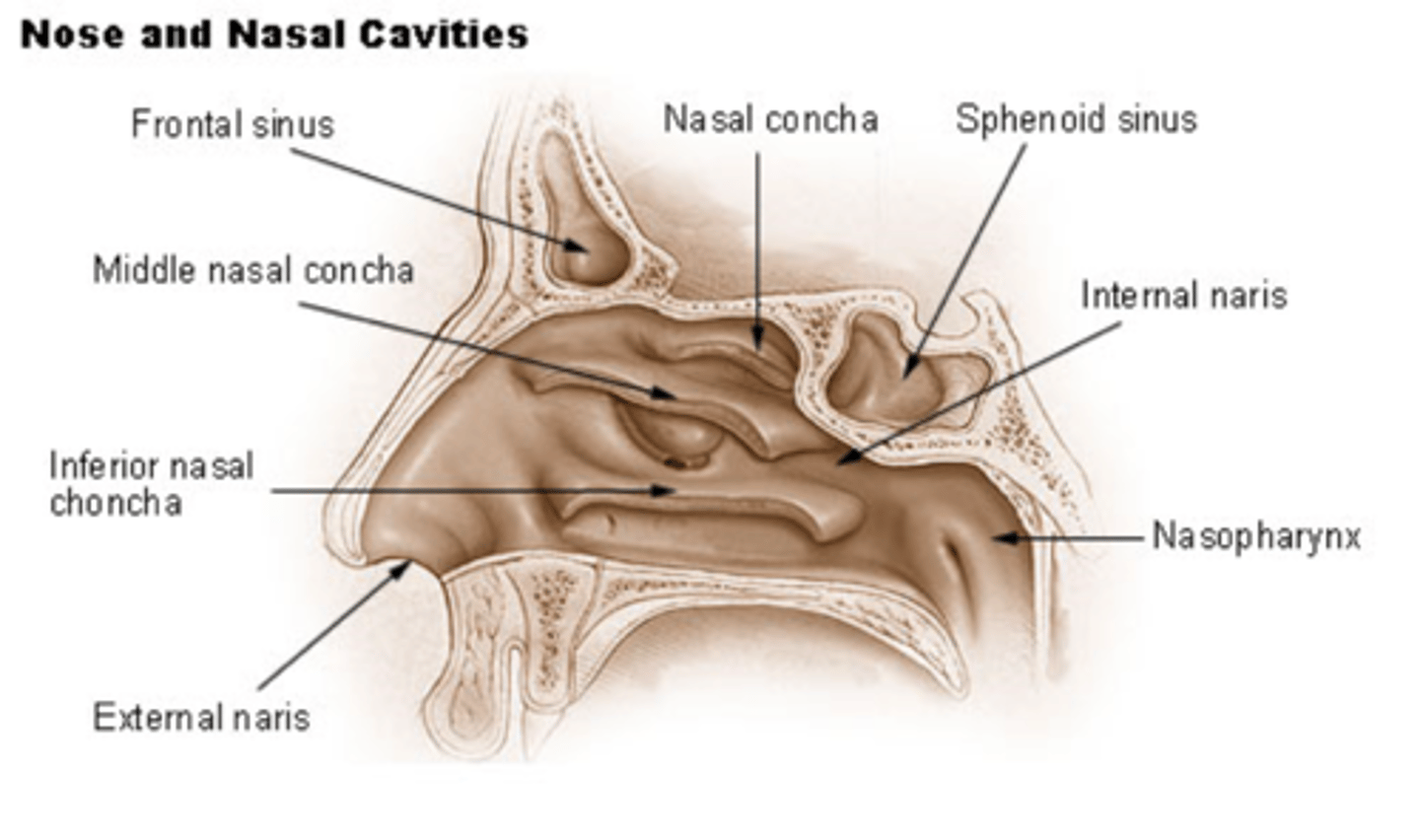
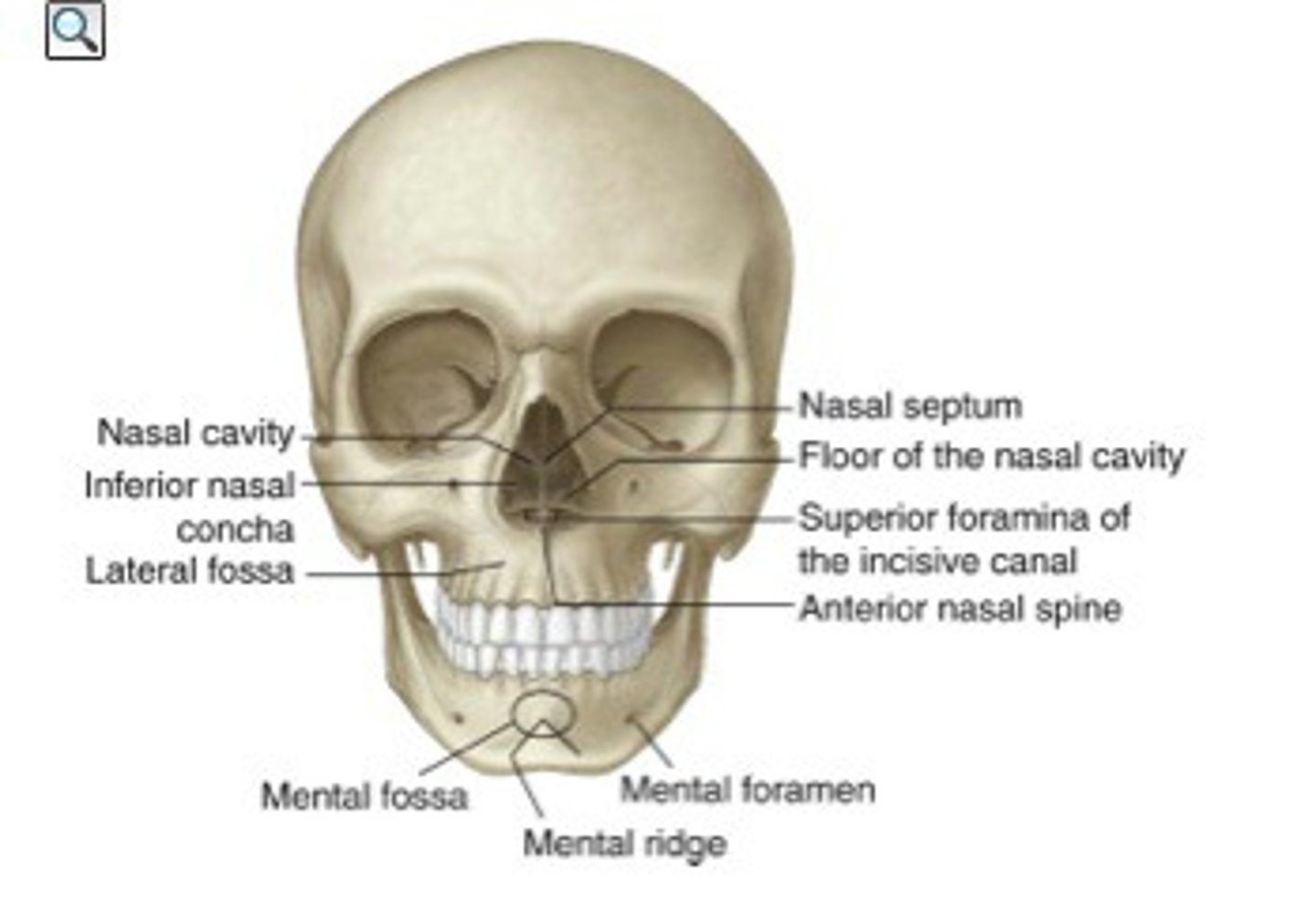
nasal cavity/septum
cavity: inner area of nose
septum: composed of bone (upper portion: ethmoid/lower portion: vomer) covered in a membrane; divides nasal cavity into R and L
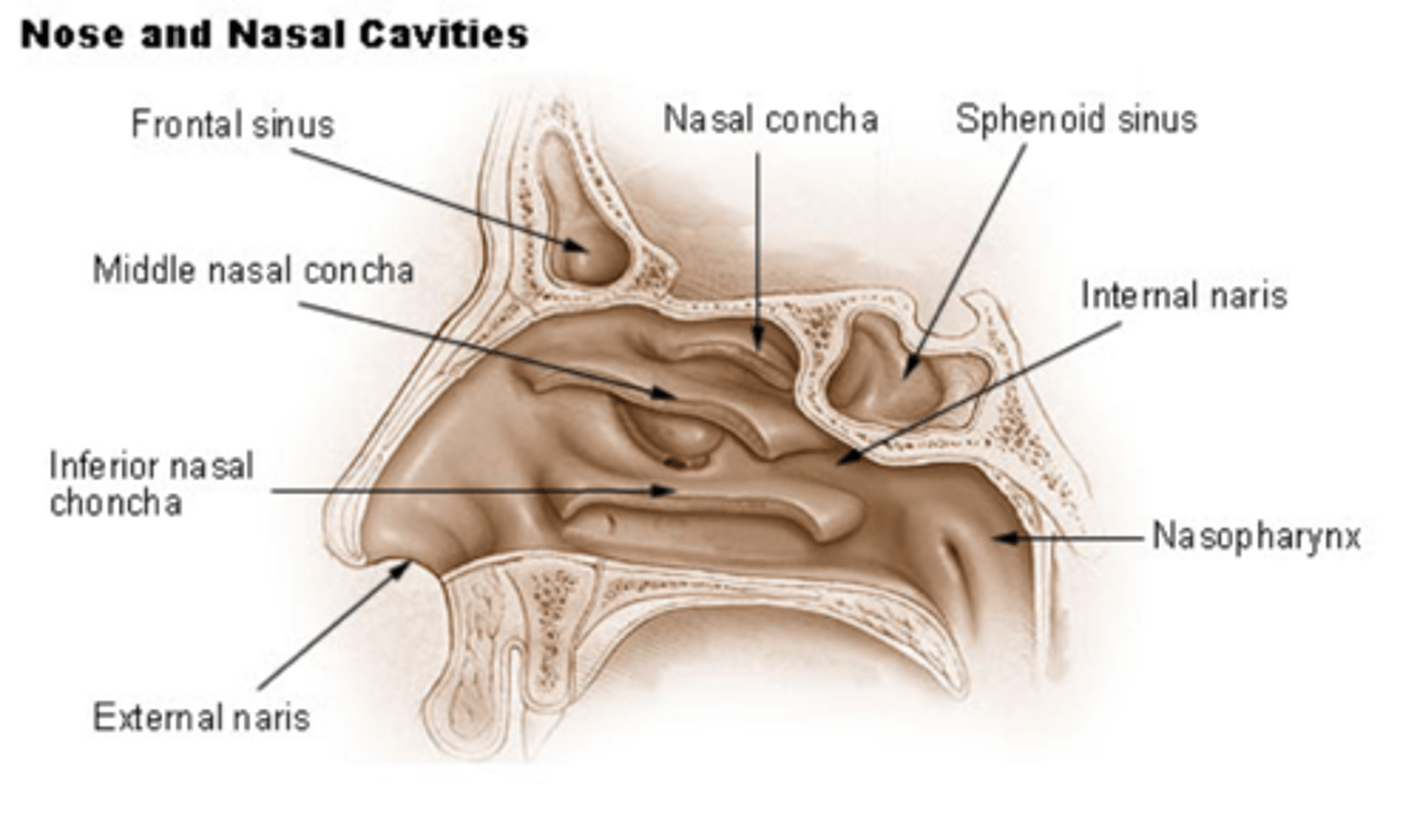
naris
external (entrance) and internal ( exit) to nasal cavity
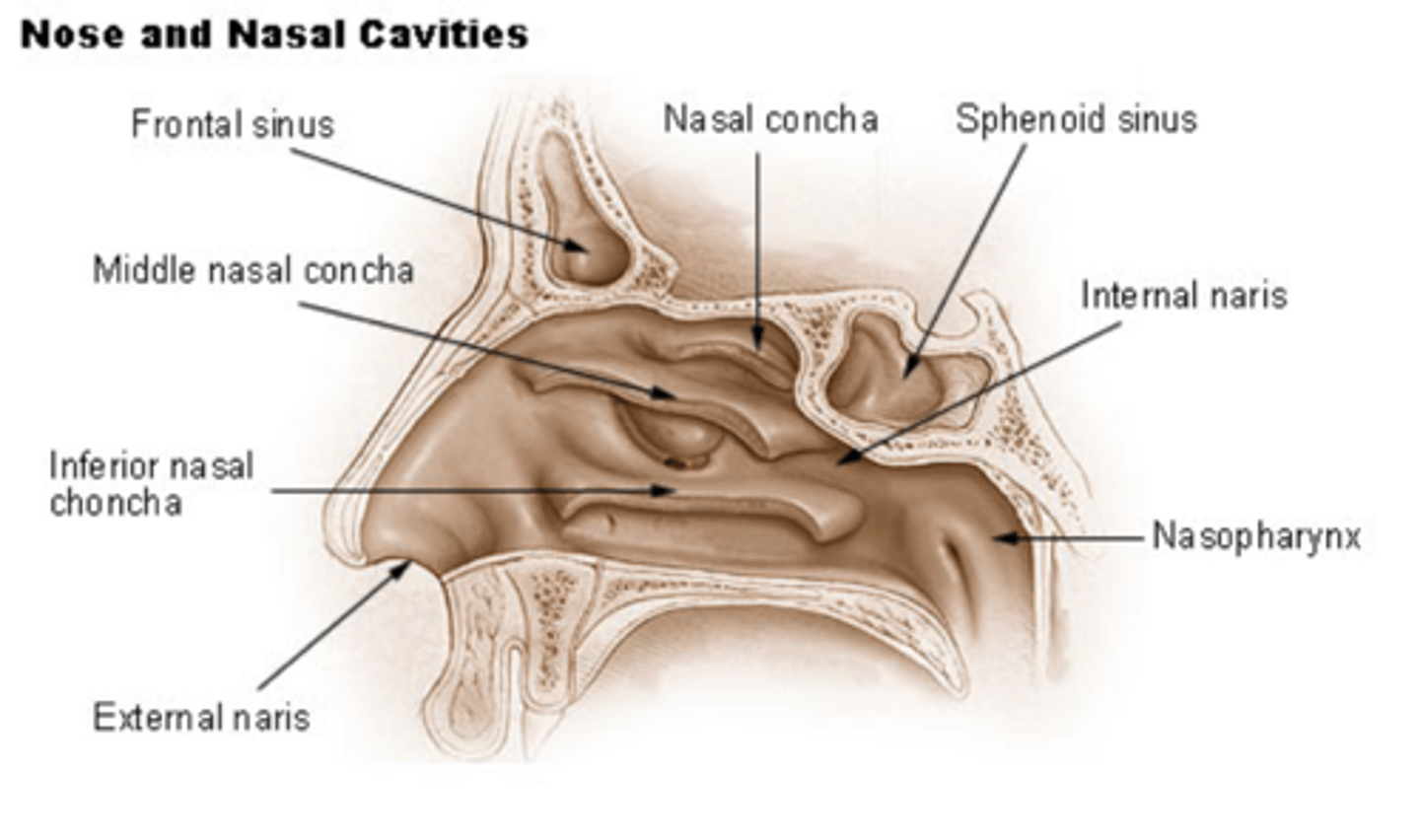
turbinate/meatus
composed of bone (conchae) covered in membrane
form shelves projecting into nasal cavity
meatus (passageway) is created under each corresponding turbinate
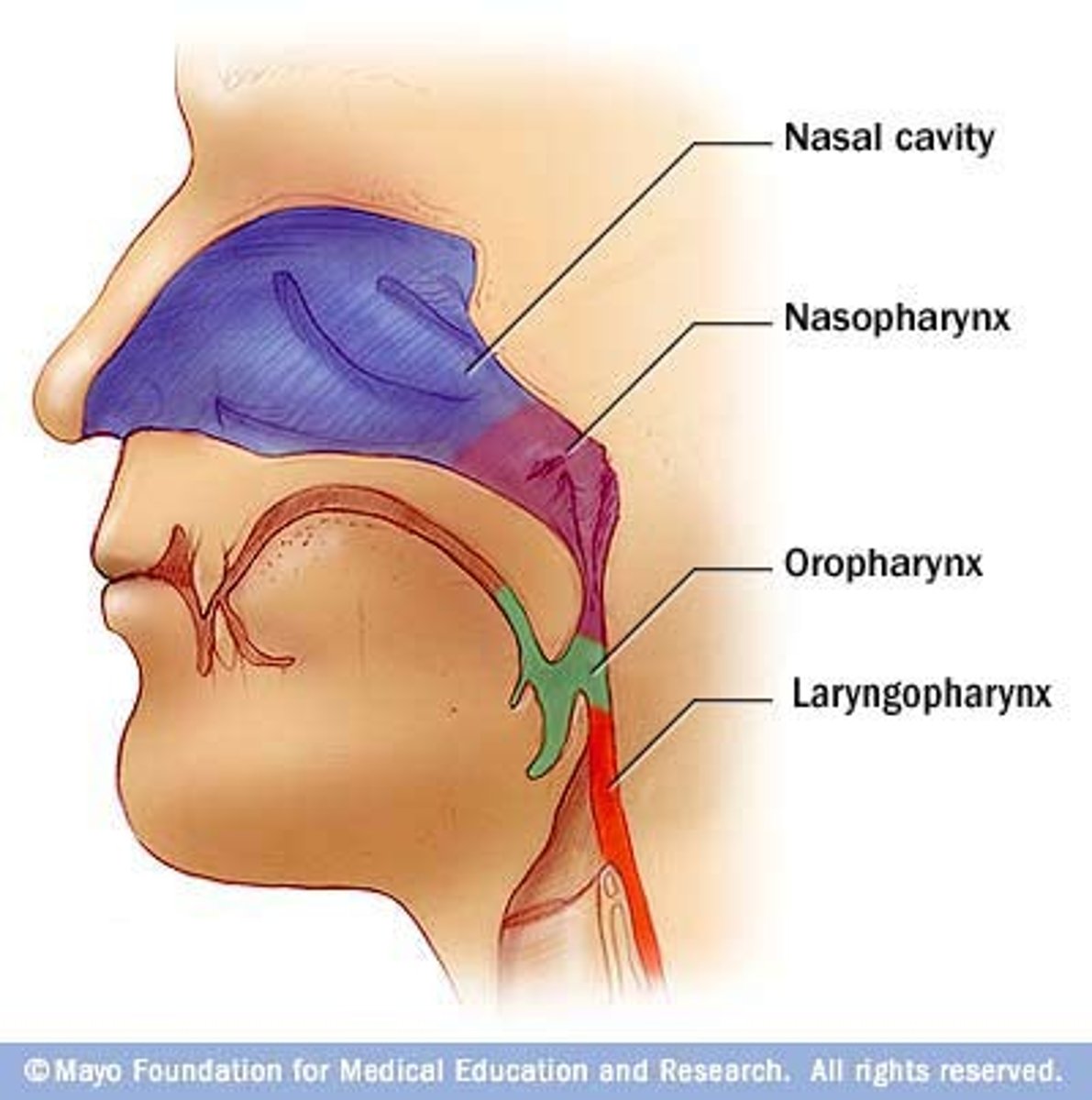
pharynx
3 parts
1. nasal phraynx: end of internal naris -> tip of uvula
2. oral pharynx: tip of uvula -> tip of epiglottis
3. laryngral pharynx: tip of epiglottis -> start of lrynx
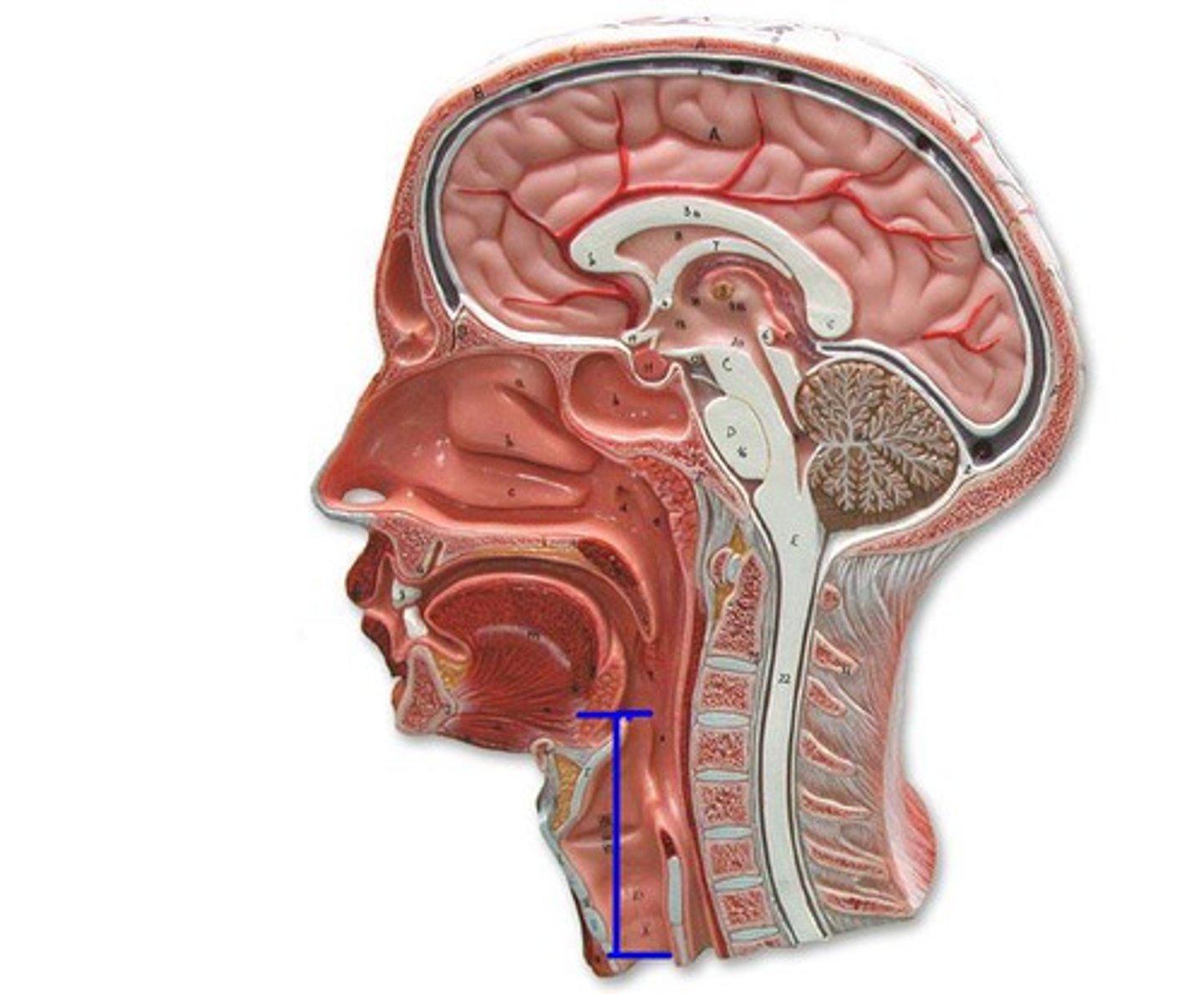
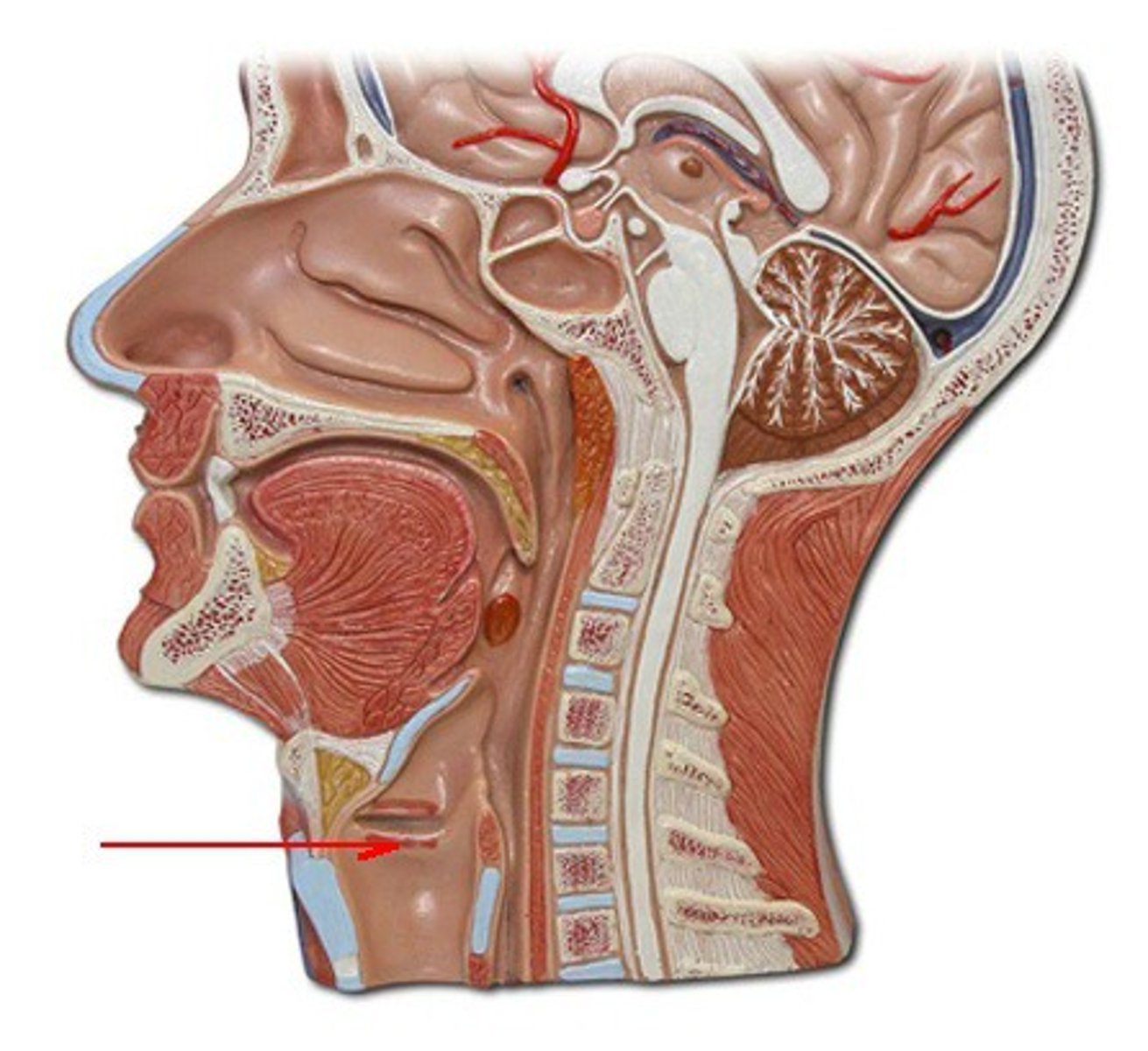
Larynx
starts below laryngeal pharynx
- sound production
- composed of 1 bone, cartilages, and ligaments/membranes
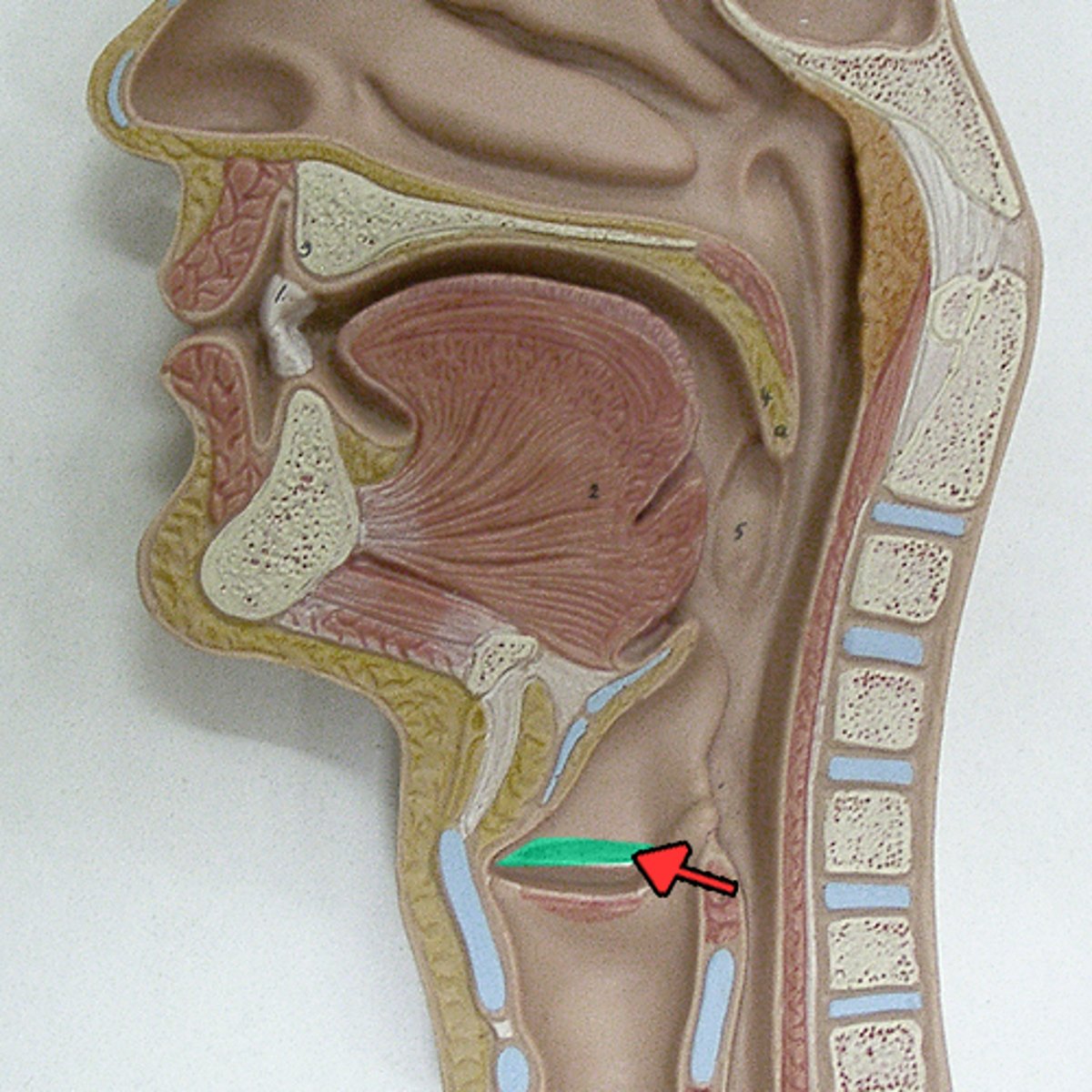
glottis
Opening between vocal cords; passageway going past vocal and vestibular folds
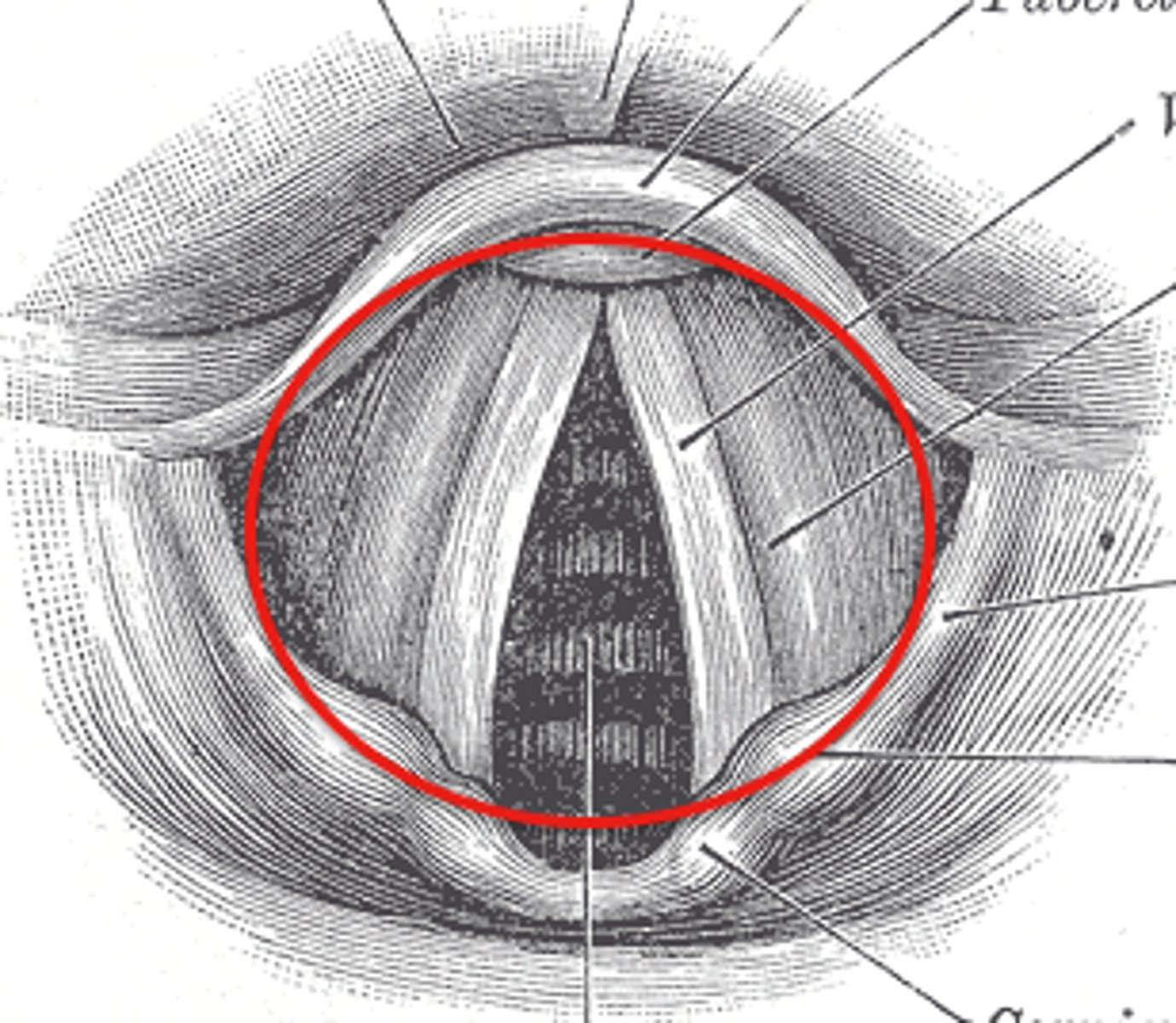
vocal folds
inferior, vibrate for sound production
vestibular folds
superior, modify air cuurrents to assist with sound production
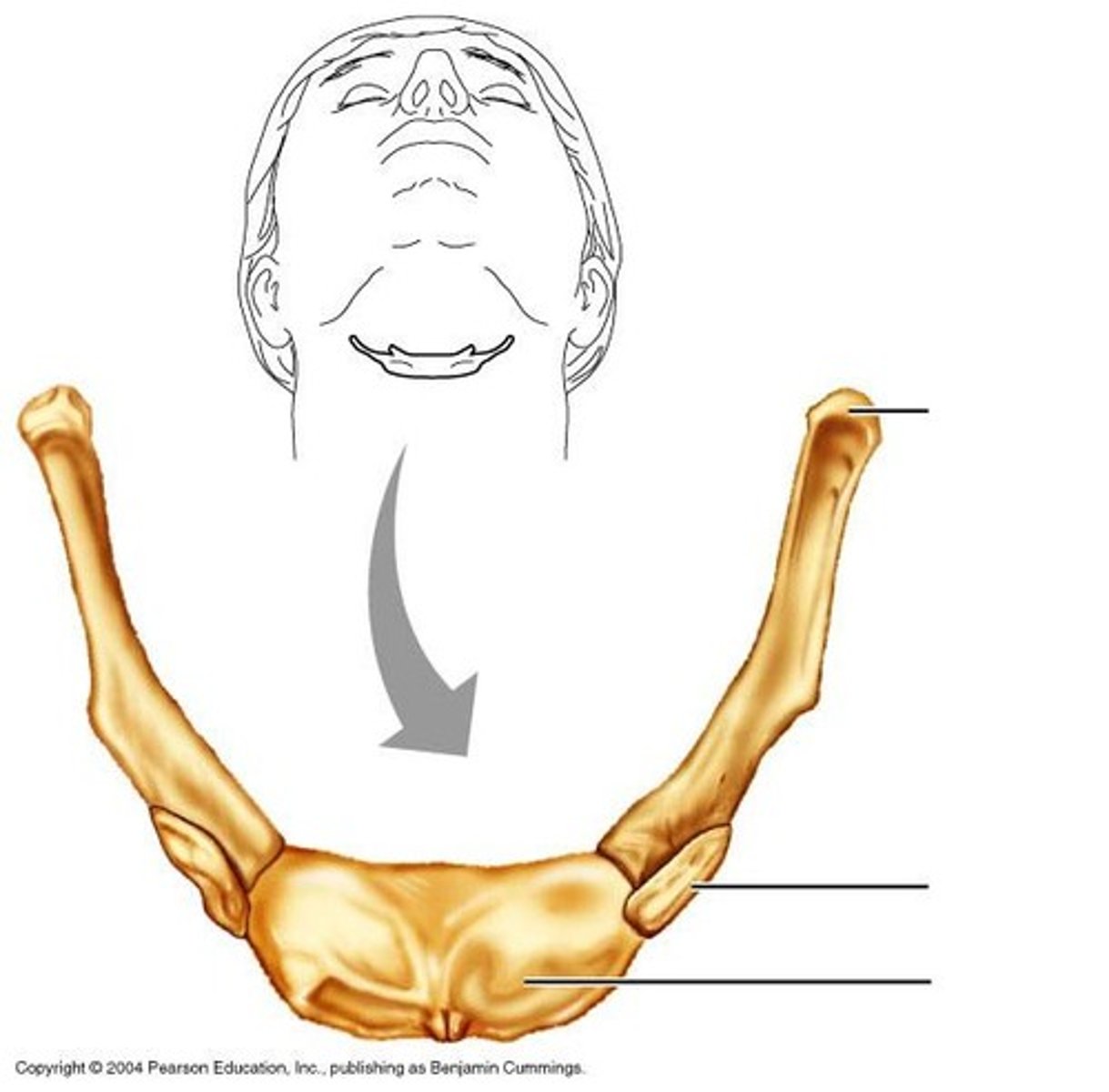
hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
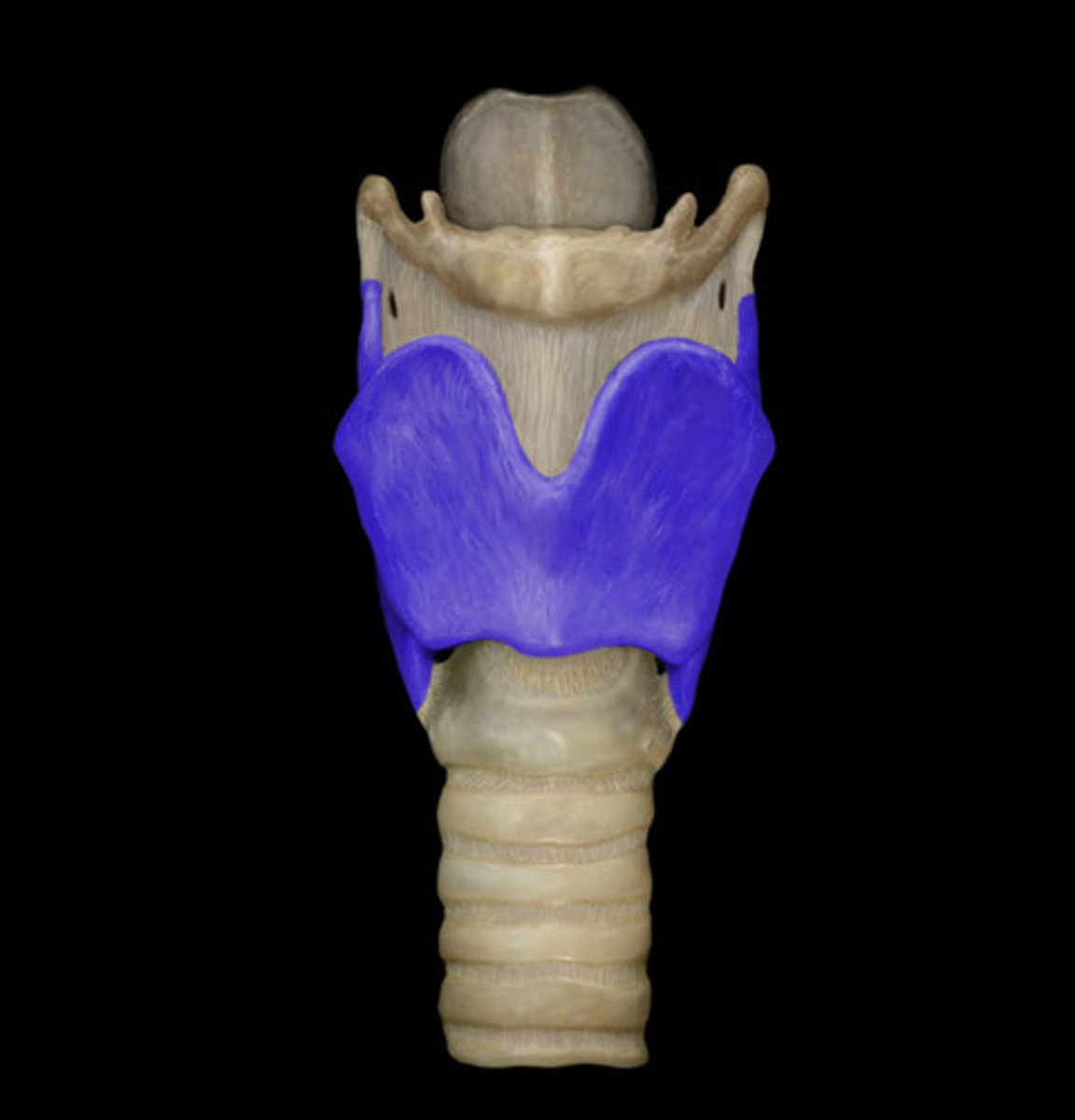
thyroid cartilage
below hyoid bone, anterior of thyroid cartilage has (thyroid notch) and a bump (laryngeal prominence)
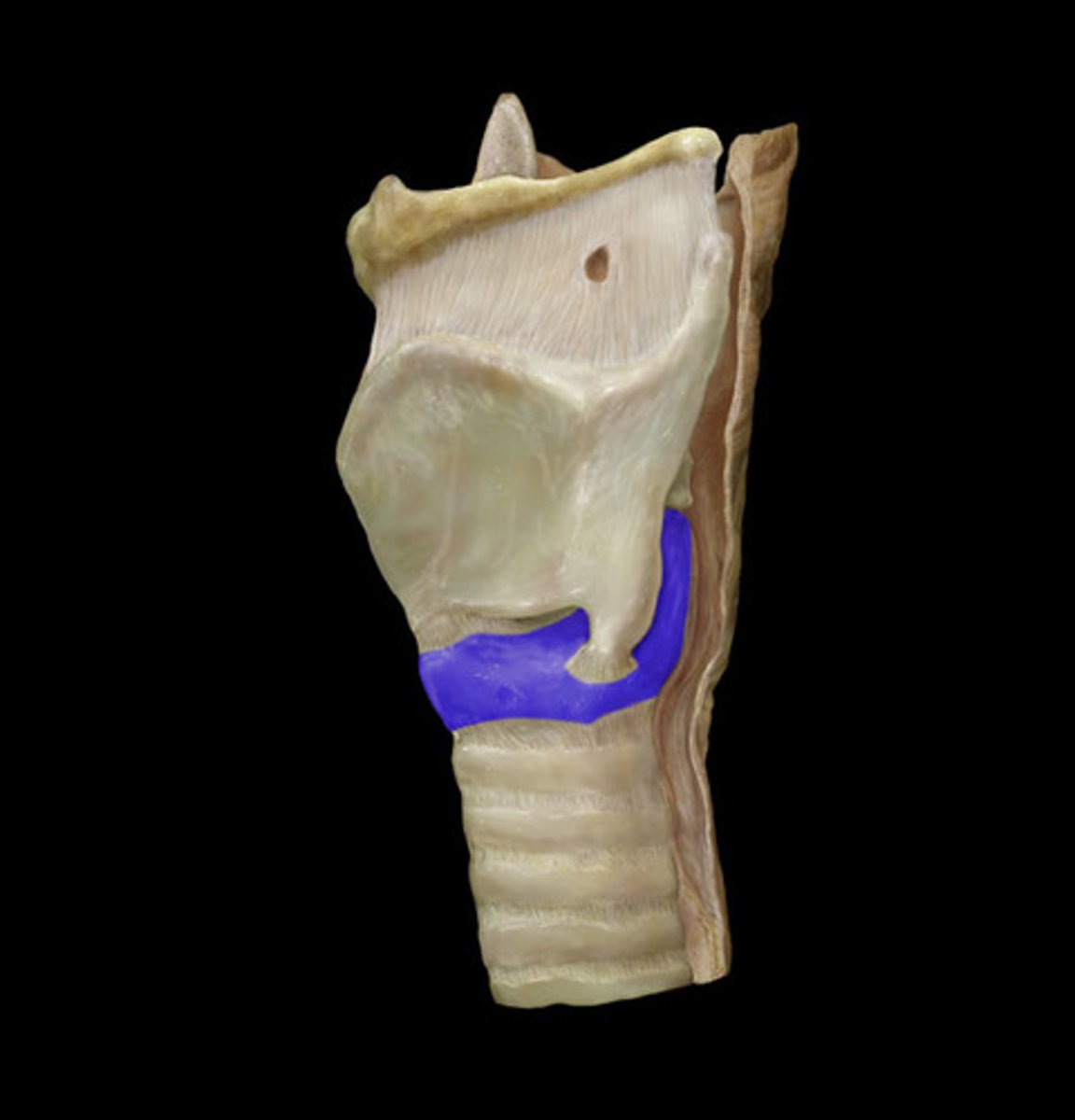
cricoid cartilage
below thyroid cartilage; completes a full circle ( ring), thyroid cartilage does not
last part of larynx
thyrohyoid membrane
connect hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage
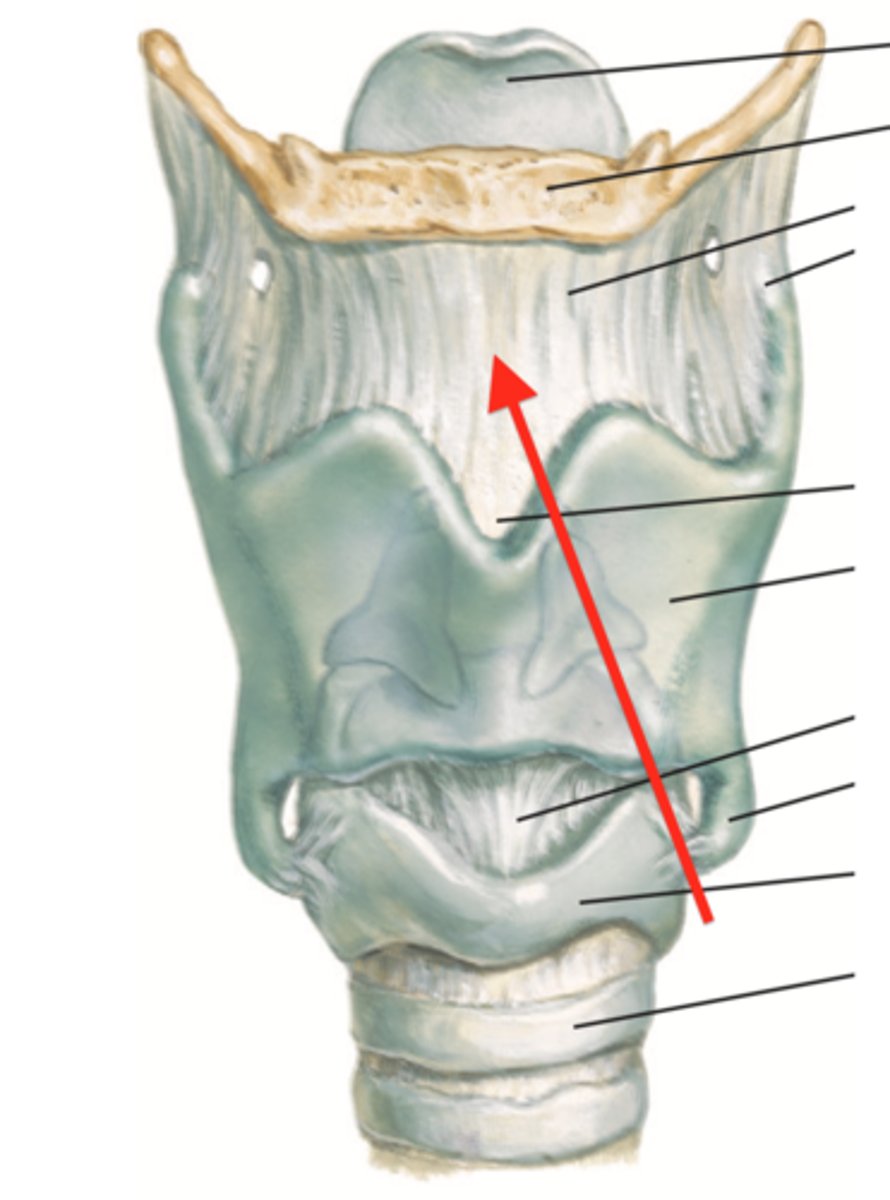
cricothyroid ligament
connect thyroud cartilage and cricoid cartilage
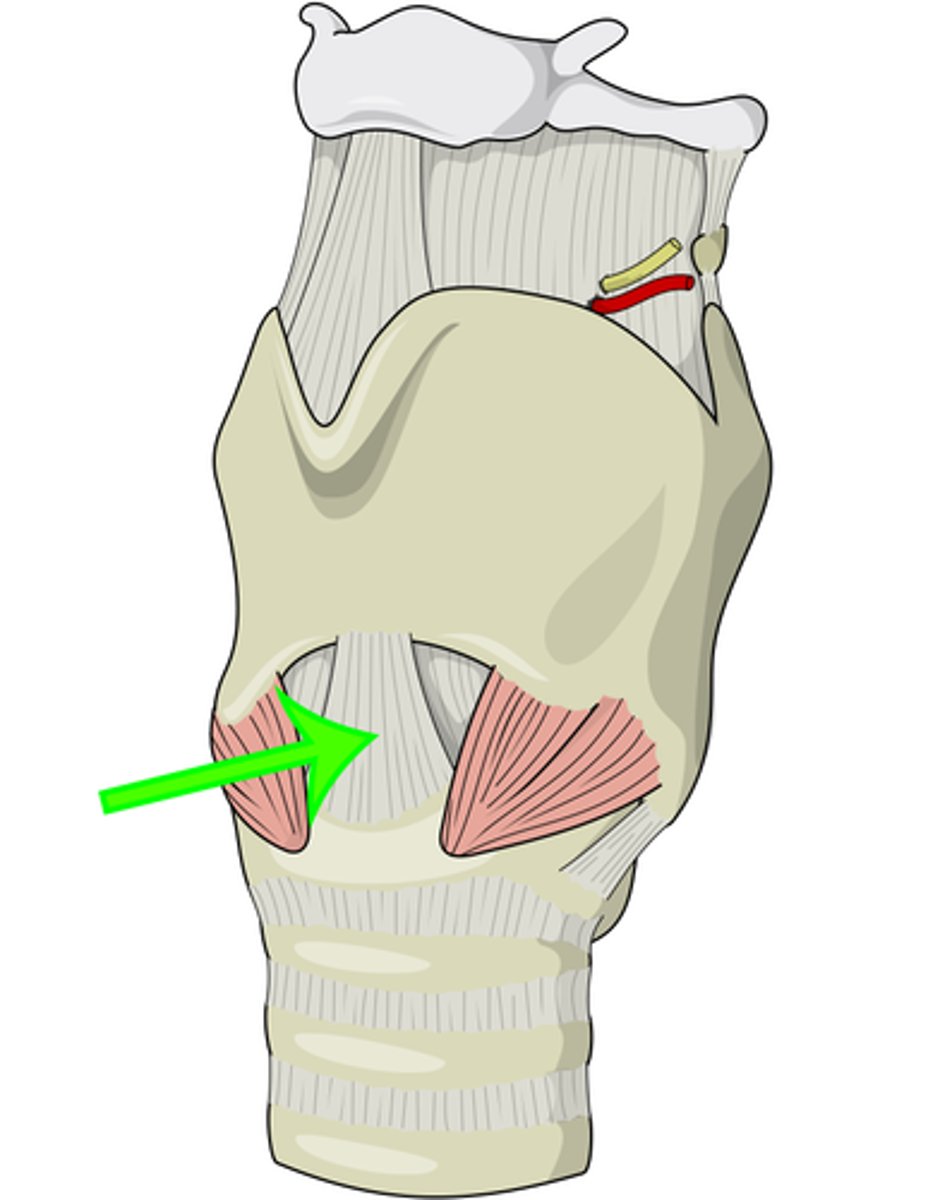
arytenoid cartilage
helps move vocal folds for sound production
bottom part of triangle shapr
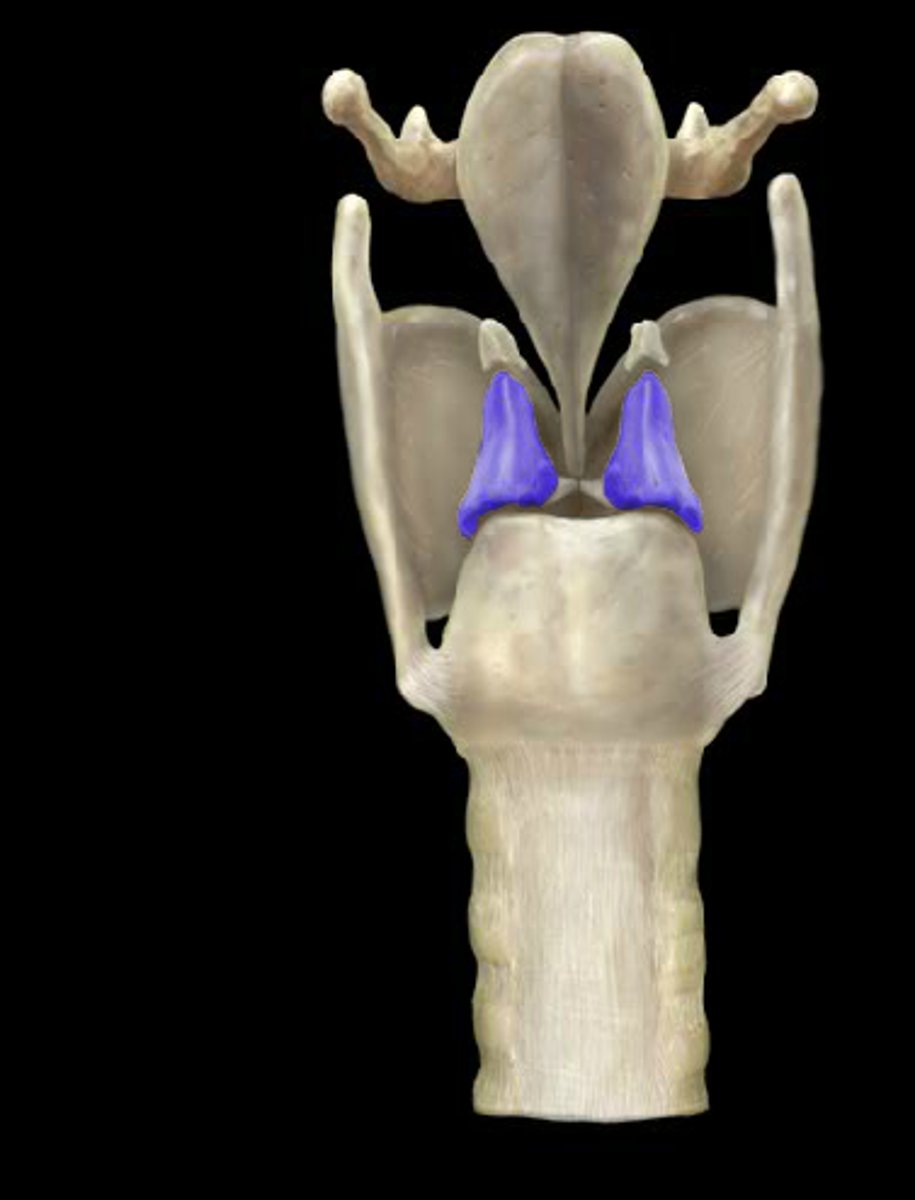
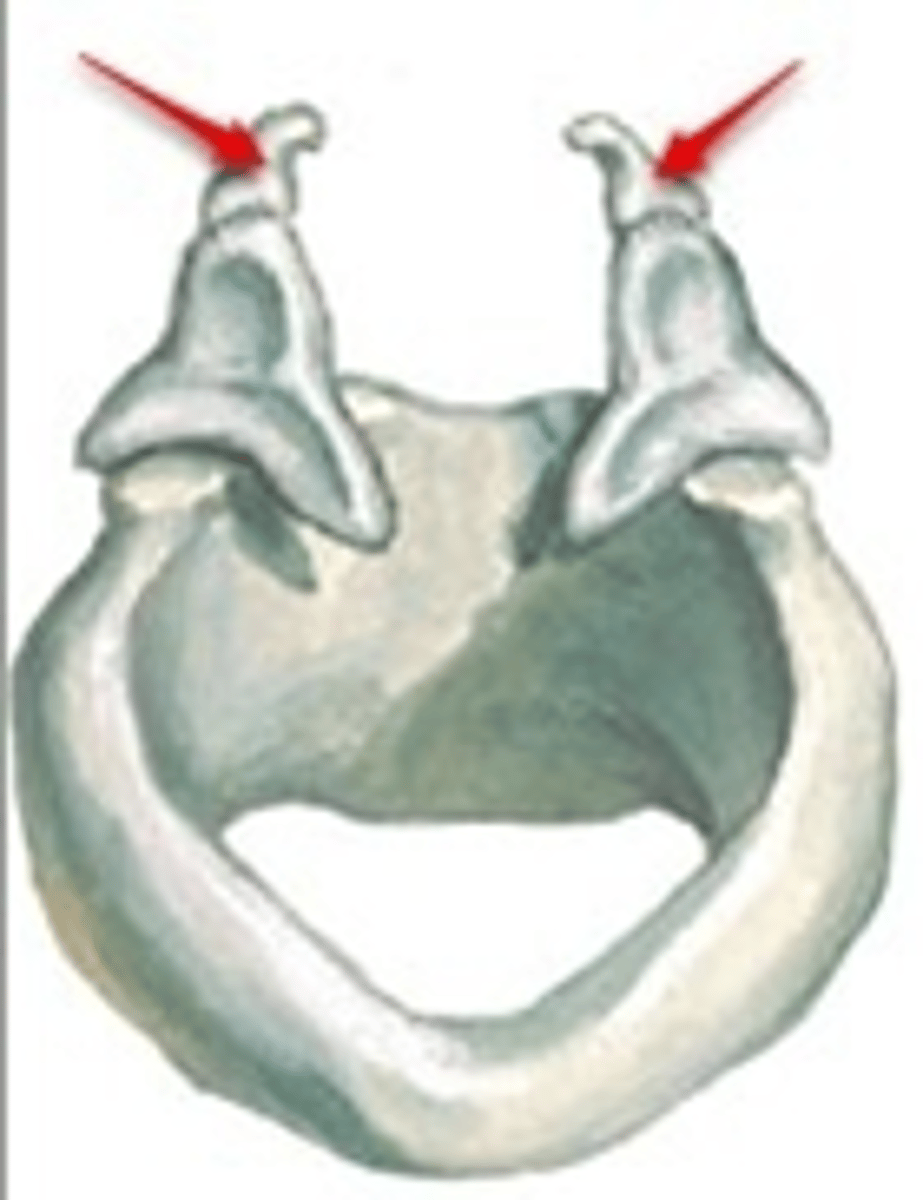
corniculate cartilage
a pair of horn-like pieces of elastic cartilage located at the apex of each arytenoid cartilage

trachea
starts below cricoid cartilage, series of cartilaginous rings covering tissue
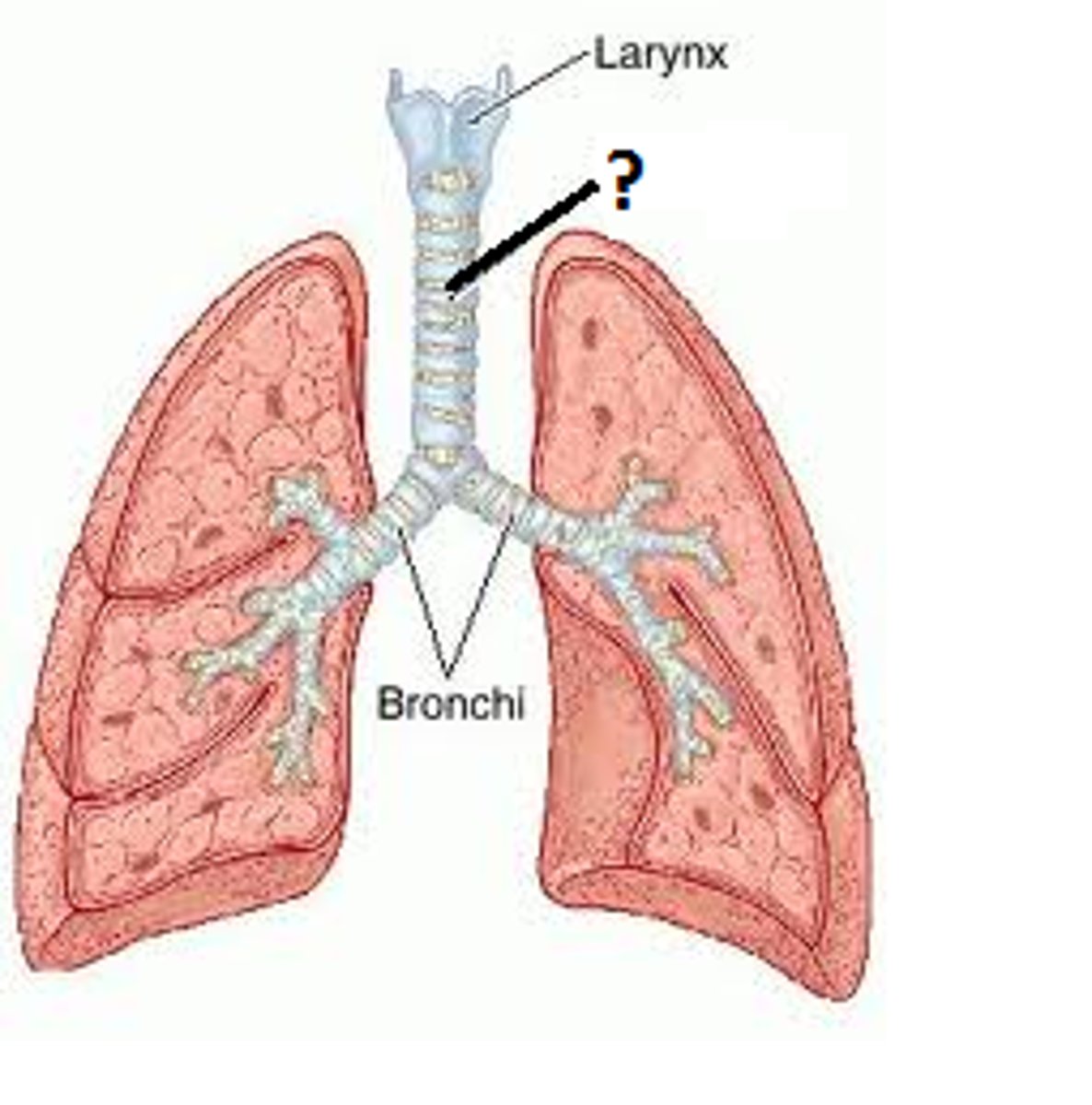
bronchi -> bronchiole divisions
trachea -> main bronchi -> lobar bronchi -> segmental bronchi -> bronchioles
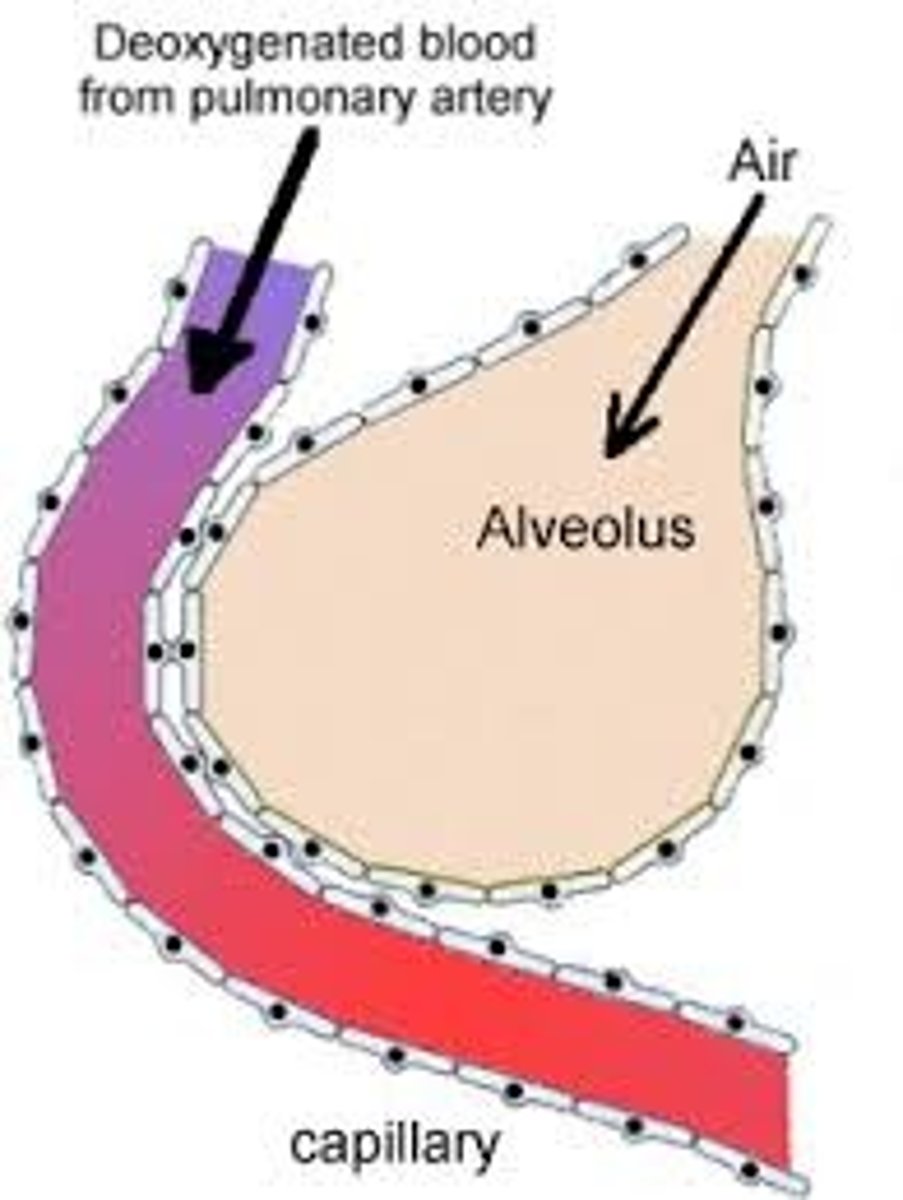
external respiration
where airways and pulmonary circulation meet for gas exchange
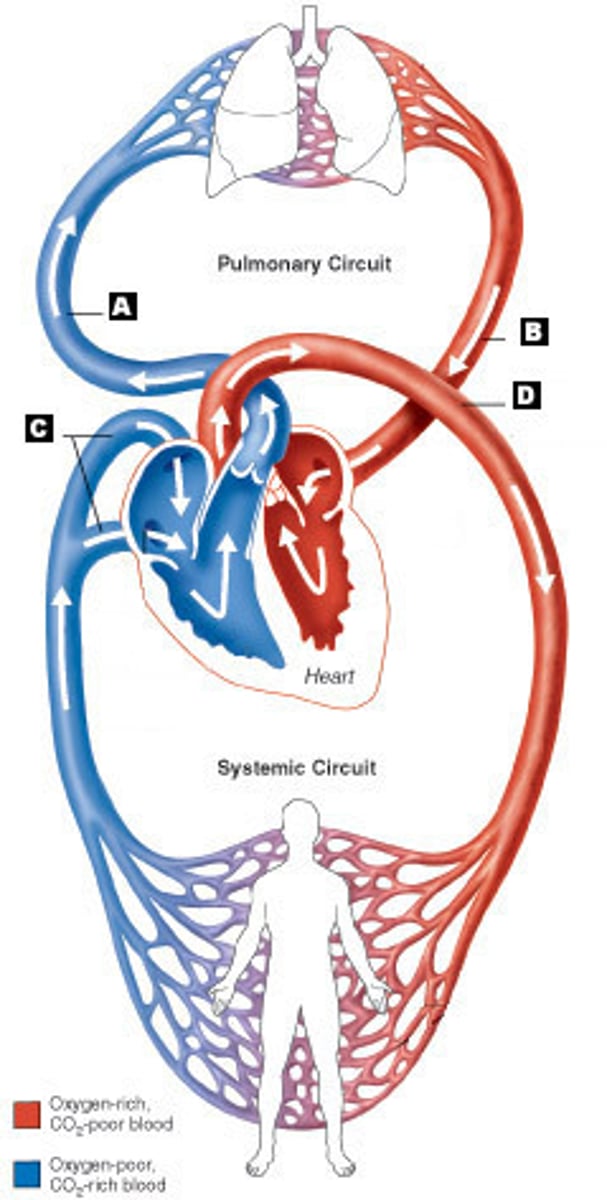
pulmonary circulation
Overall pathway: right ventricle - pulmonary trunk - pulmonary arteries - pulmonary arteriole - pulmonary capillaries - pulmonary venule - pulmonary veins - left atrium. • Pulmonary vessels are an exception to usual colour of artery being red and vein being blue
pleura
tissue laters mainly between lung and chest wall
visceral pleura: layer attached to lungs costal surface
parietal pleura: layer attached to inner surface of chest wall
intrapleual space: between visceral and parietal pleura, thin fluid filled cavity (lubricate lung movement with breathing and creates subatmospheric pressure)
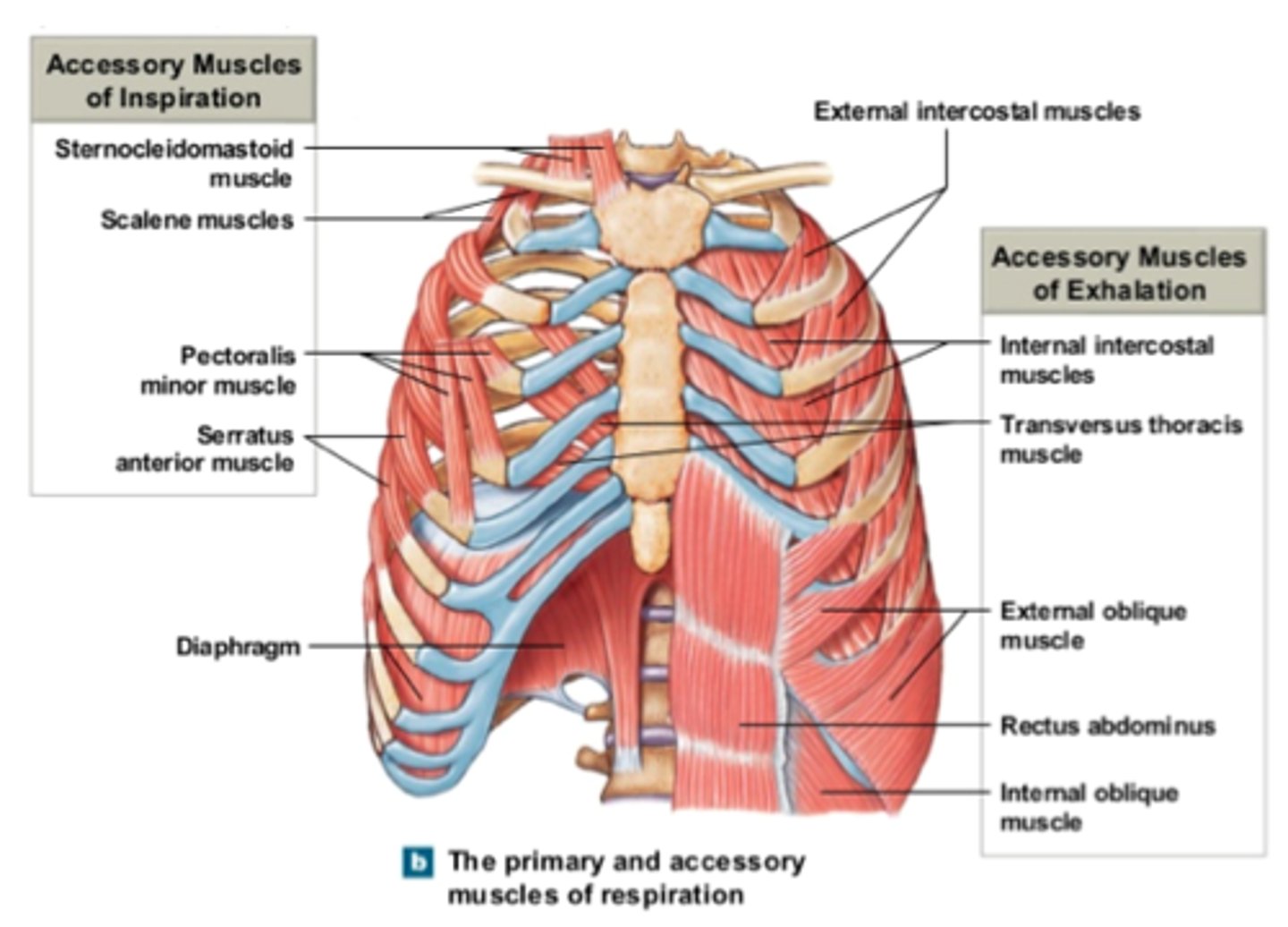
respiratory muscles
scalenes: vertebrae to first 2 ribs
Sternocleidomastoid : skull mastoid process to sternum and clavicle.
Pectoralis minor: scapula to ribs. I
ntercostals: between ribs; internal and external layers.
Diaphragm: attach to pleura at base of lungs
Abdominals: arranged in layers; fiber directions can be used to help identify
- Rectus abdominus - vertical.
- Transverse abdominus - horizontal.
- External oblique - "V" shape (down and to centre)
- Internal oblique - inverted "V" shape (up and to centre).