BISC 202 chromosomes and genetic information (W9-10)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms

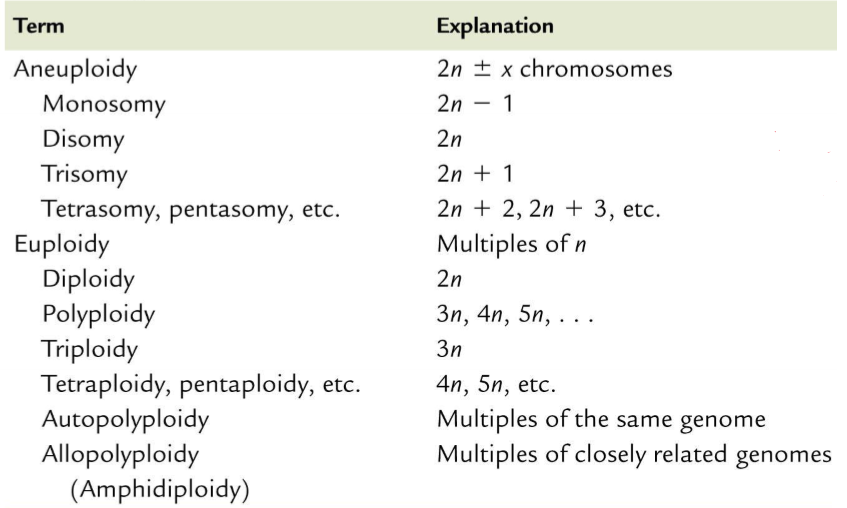
what are the two types of mutations affecting the number of chromosomes?
euploidy and aneuploidy
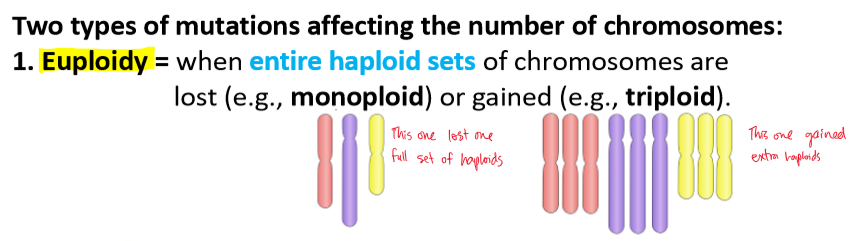
euploidy
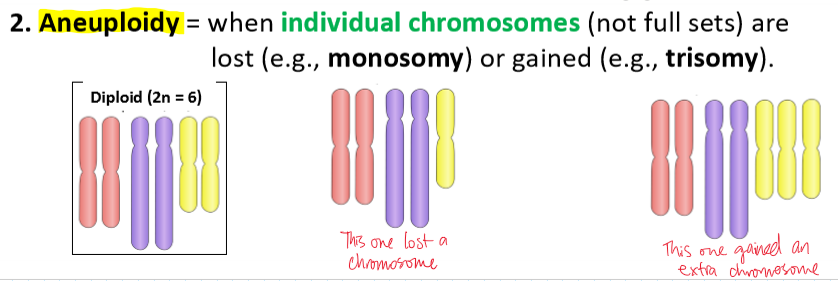
aneuploidy
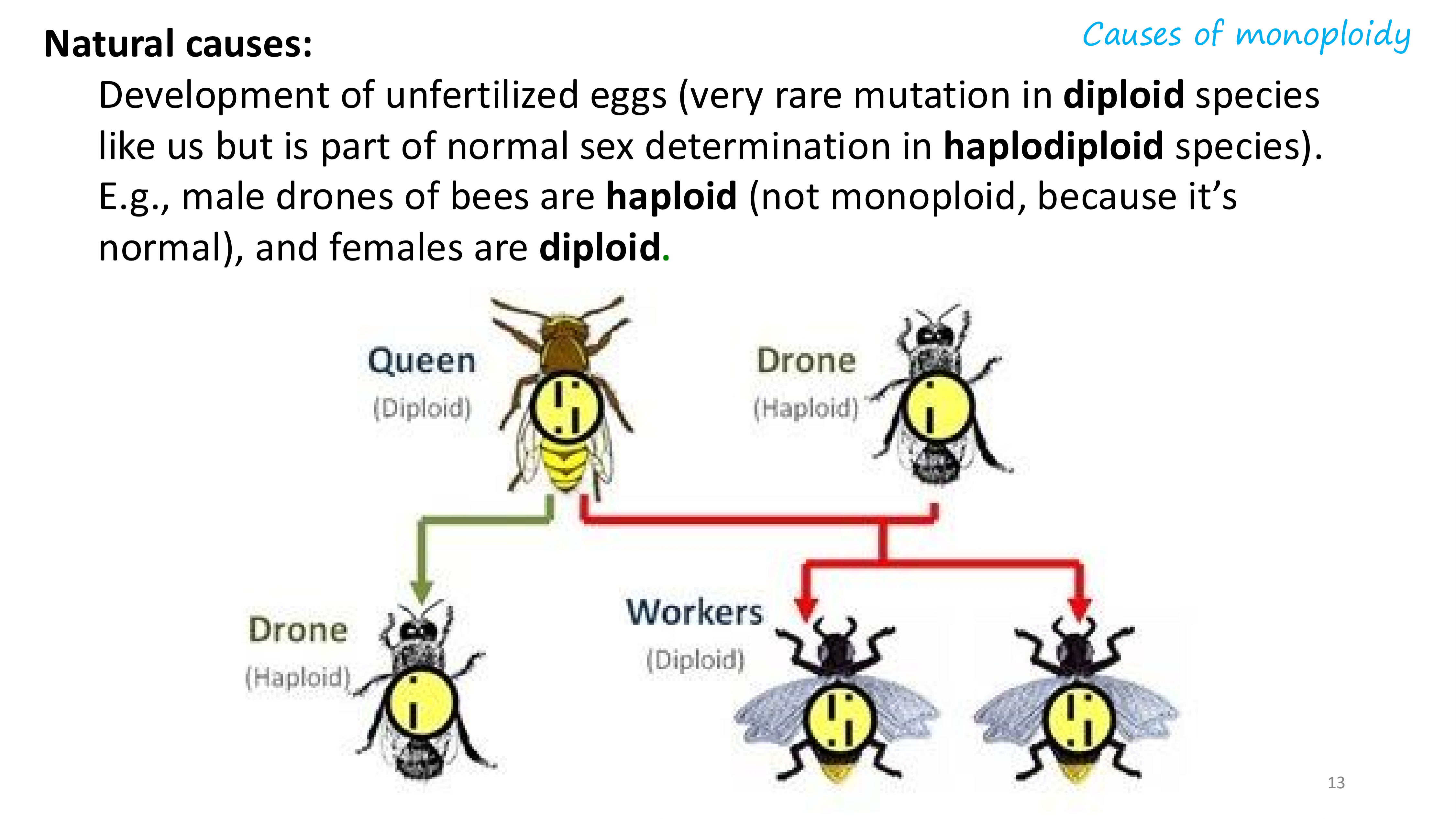
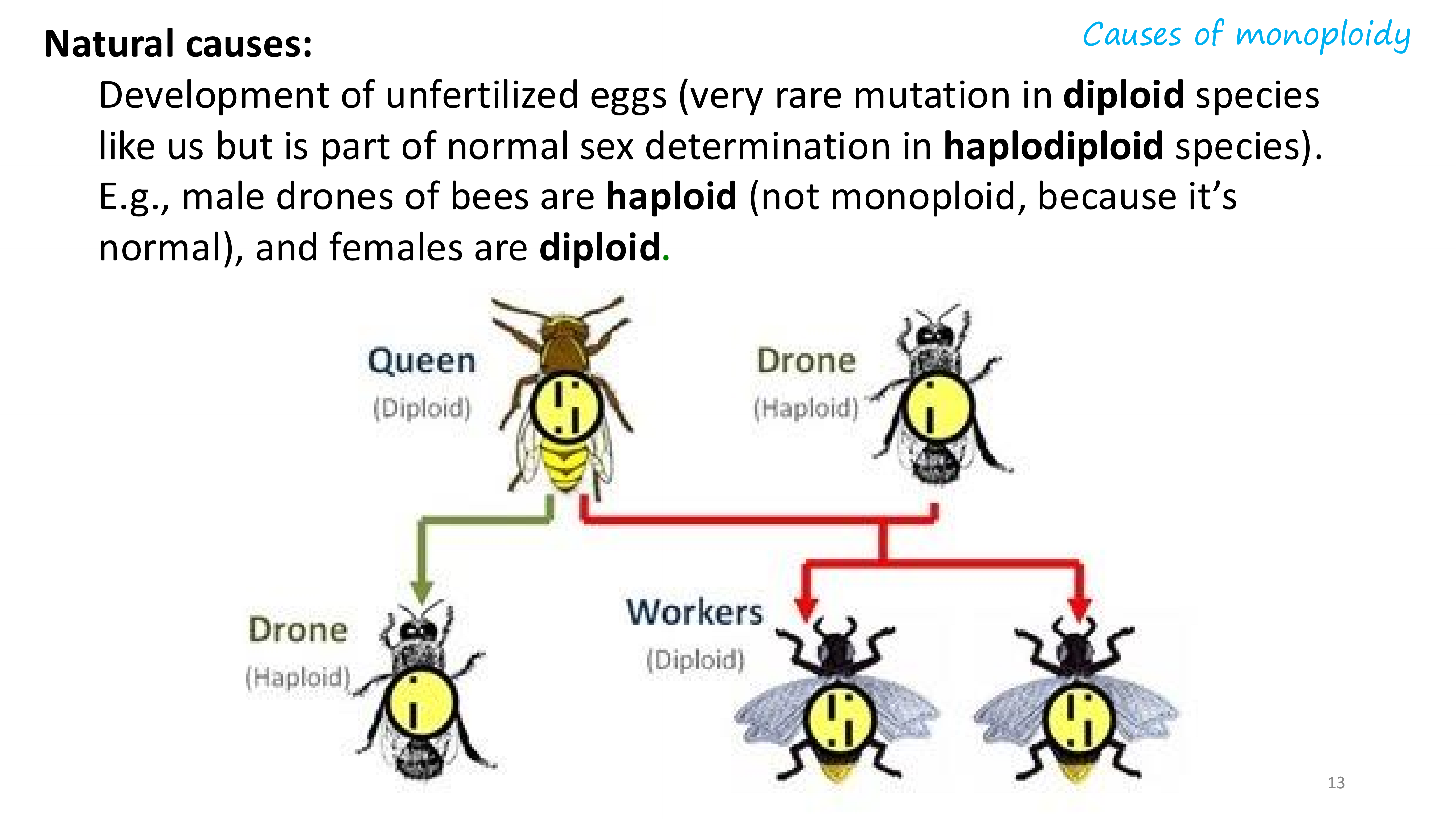
natural causes of monoploidy
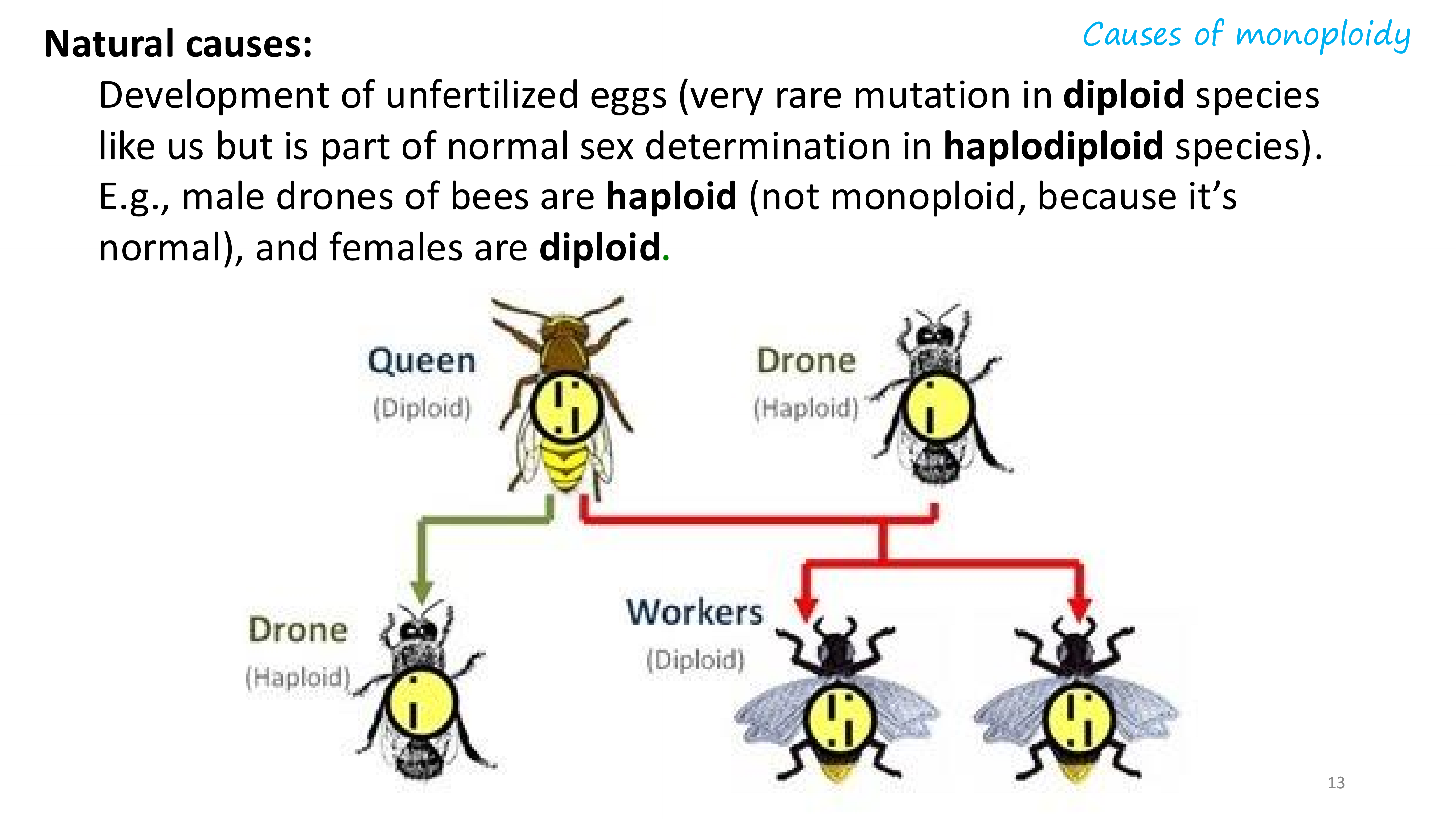
artificial causes of monoploidy
effects of monoploidy on survival and phenotype
effects of monoploidy on reproduction

why are monoploids almost always sterile
unless the gamete is lucky enough to get every chromosome (during meiosis I) it will be missing one or more chromosomes, and the resulting offspring will usually not survive
which events can contribute to the formation of a tetraploid cell?

how do tetraploids compare to normal diploids, in plants?
tetraploids are fertile and have larger size/yields
types of polyploidy with >2n
autopolyploid and allo(amphi)polyploid
autopolyploid
a polyploid created by the multiplication of one basic set of chromosomes (in one species)
allo(amphi)polyploid
an individual that has 2 or more sets of genetically distinct chromosomes, made by hybridization of two different species
effects of allopolyploidy examples

allotetraploid
mix of the DNA of two different species
triploidy
when the odd number of chromosome sets (one extra set of chromosomes as in 3n) is present
how would you make triploid plant?
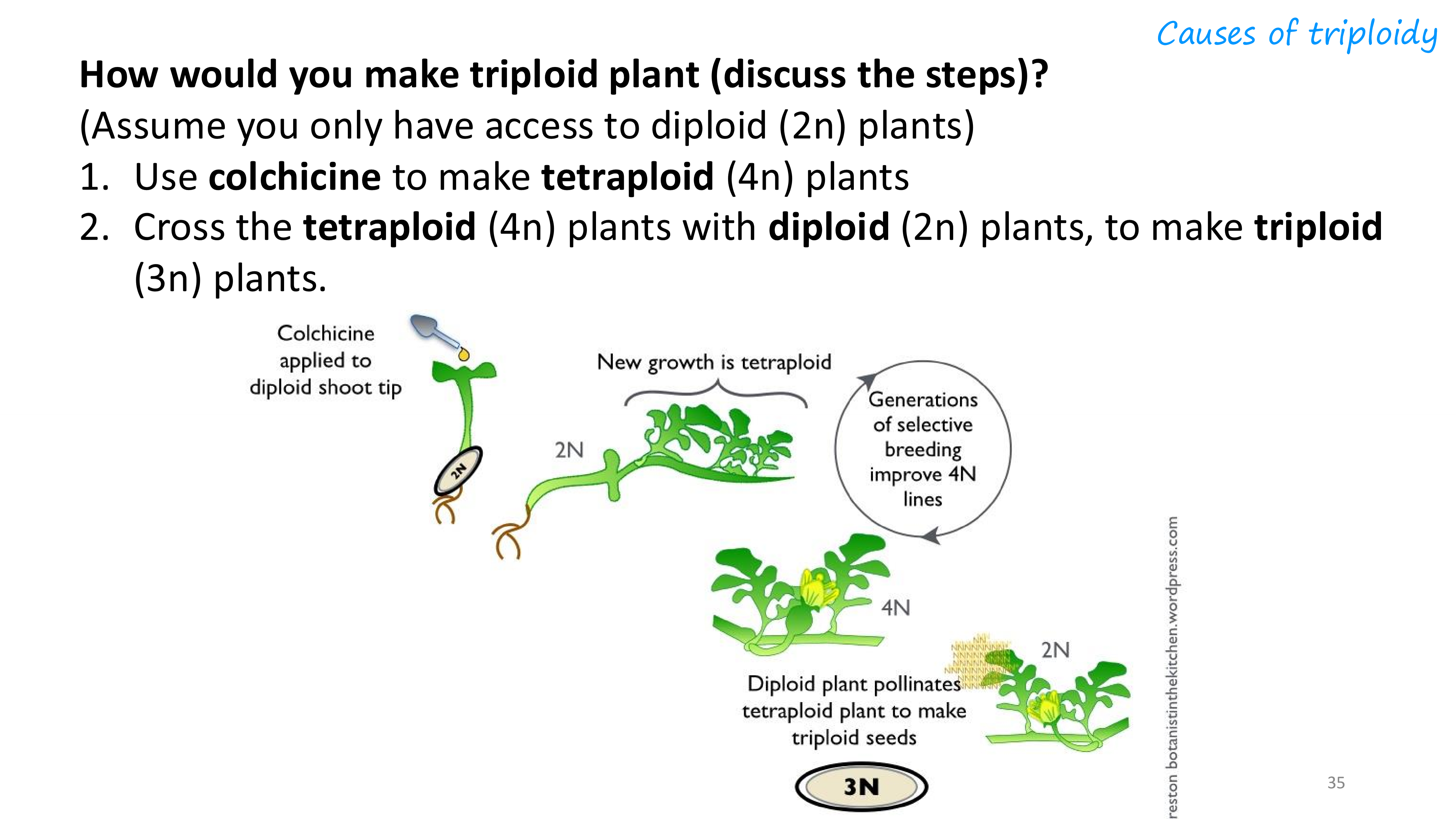
why would agricultural scientists make a triploid plant?
the triploid plant can be hardier and have higher yield than the diploid plants
triploid plants are sterile and can’t make viable offspring
imagine we took a diploid plant species and made a monoploid, an autotriploid, and an autotetraploid
order them from lowest to highest Darwinian fitness, if released in the wild

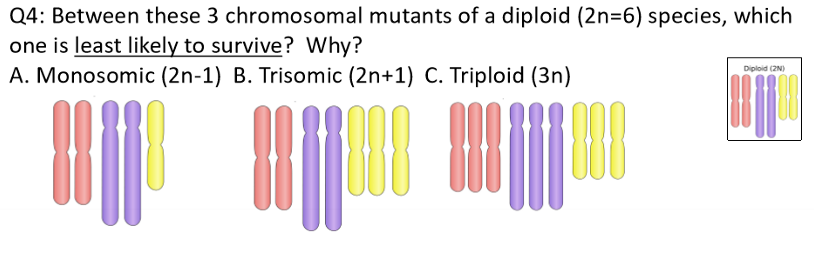
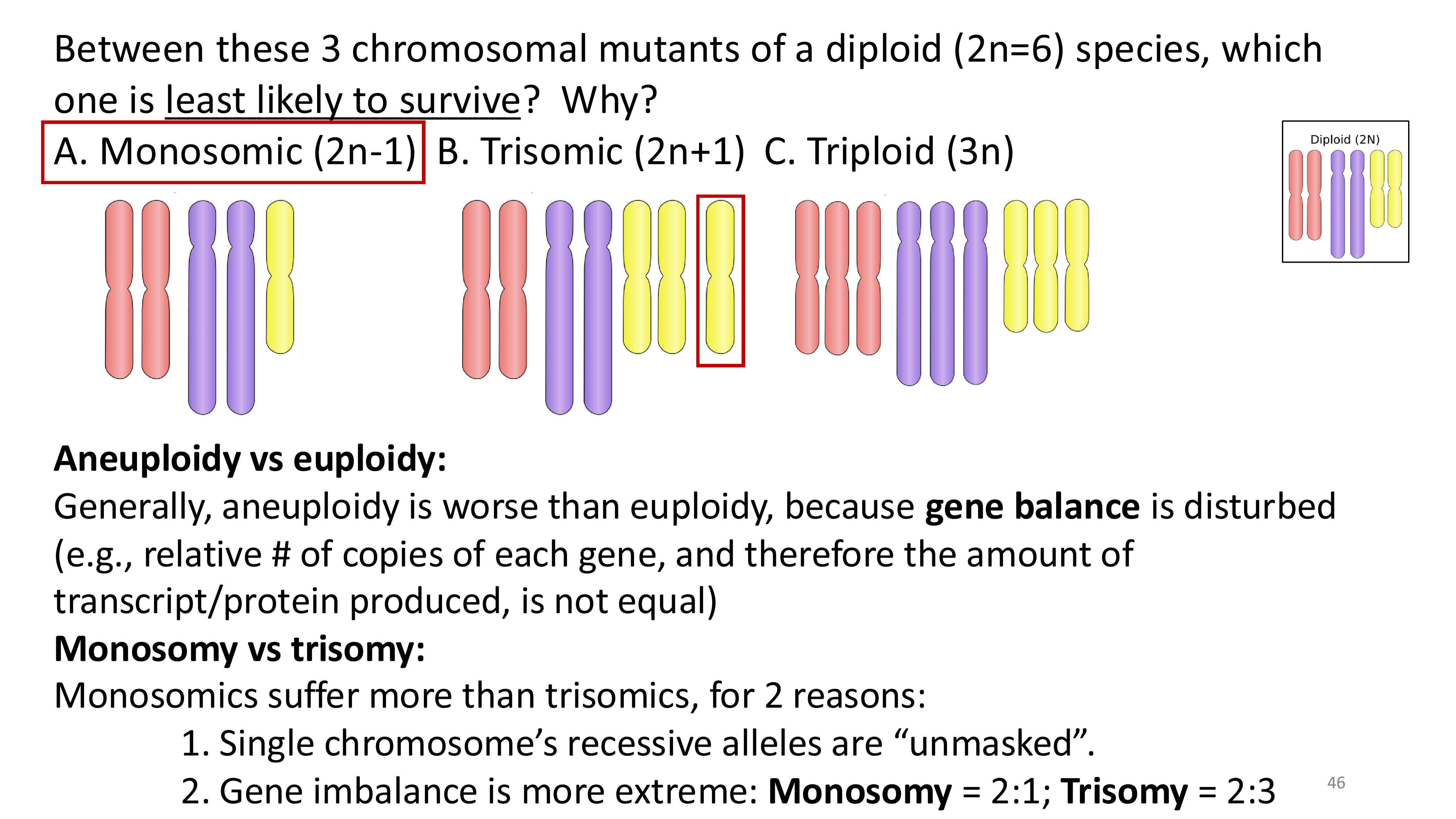
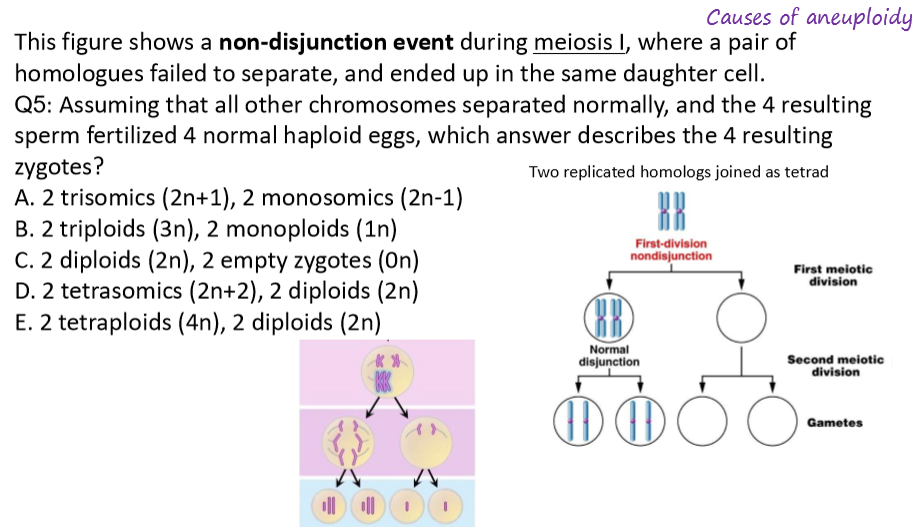
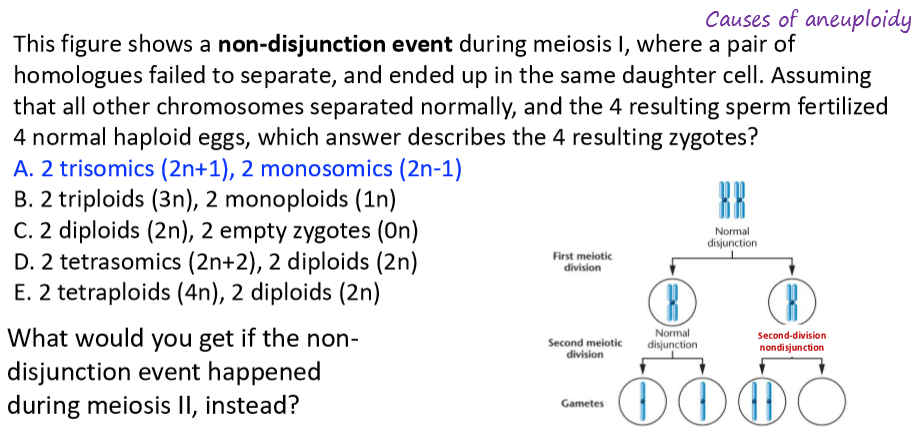
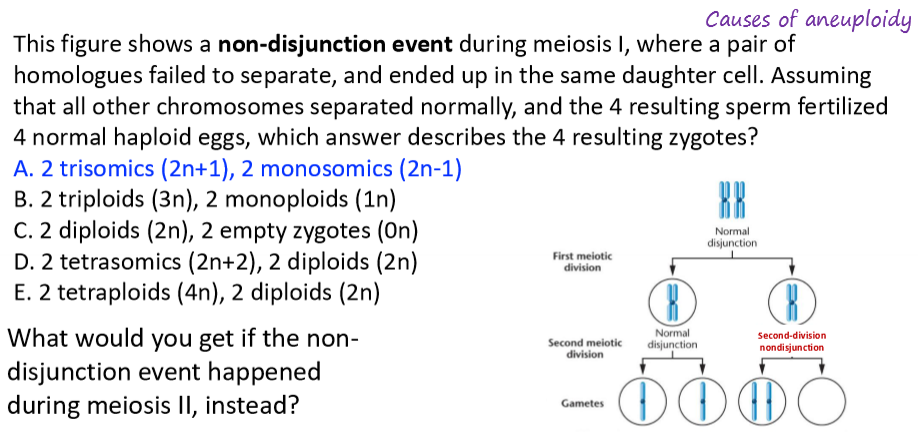

why do non-disjunction events happen?
before birth, oocytes are all formed, and arrested in meiosis I. Meiosis resumes for each oocyte just before ovulation…decades later
if a microtubule breaks/detaches during that wait, non-disjunction occurs and aneuploidy is seen in offspring
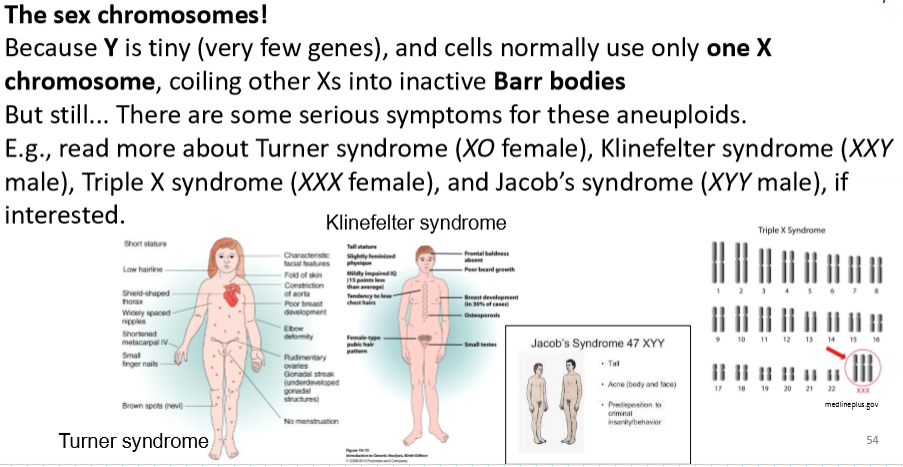
Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21, but why don’t we hear more about monosomy 21, or other trisomies and monosomies?
most of the other aneuploids don’t survive long enough to be born
most animals have a very delicate gene balance and many recessive lethal alleles, so most aneuploids are lost before birth
chromosome 21’s small size and gene compliment is why people with trisomy 21 are more likely to survive
for which chromosome pair is aneuploidy less lethal?
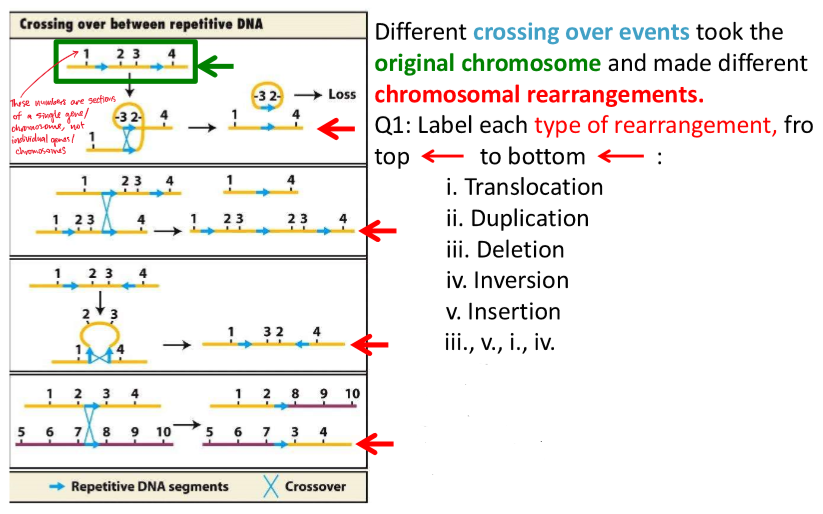
iii., ii., iv., i.
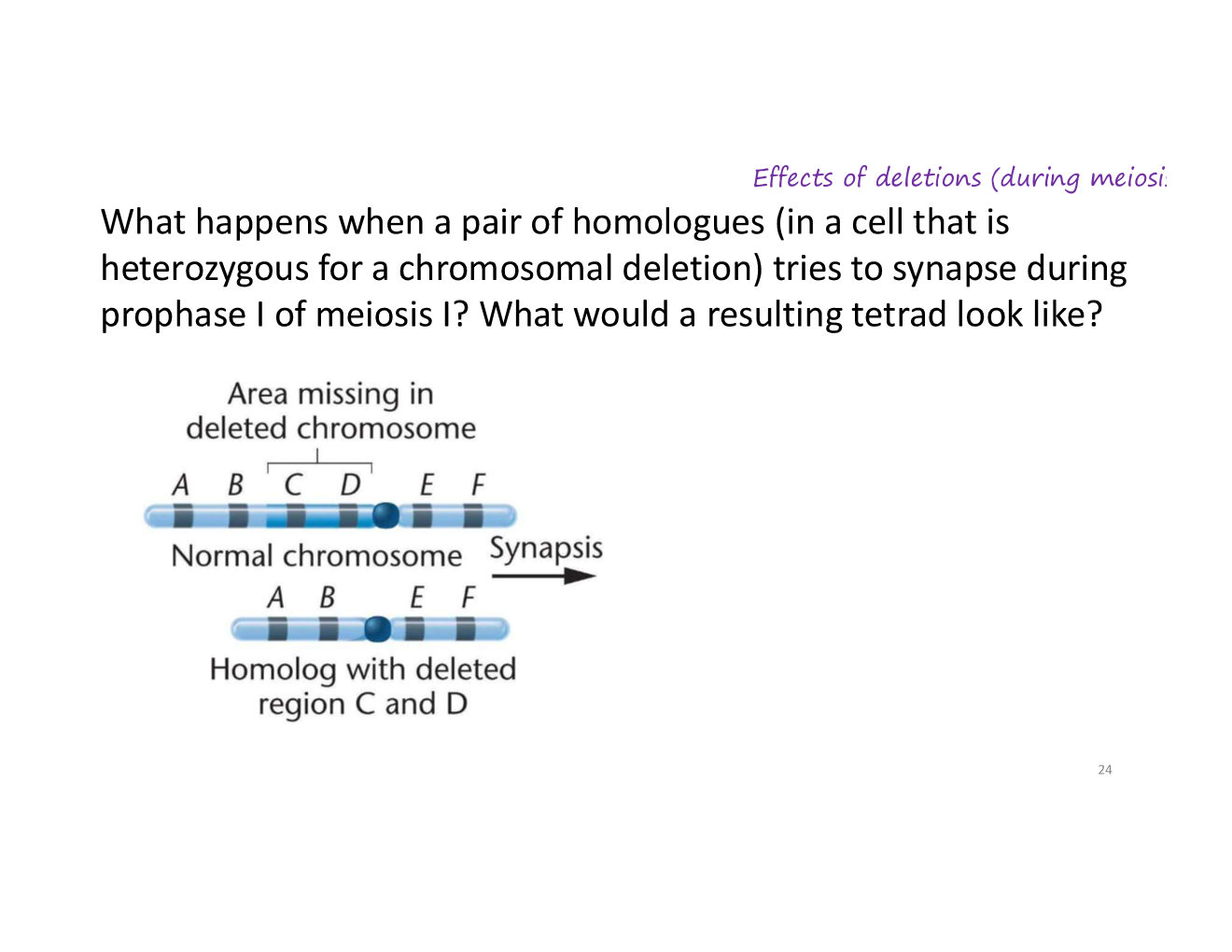
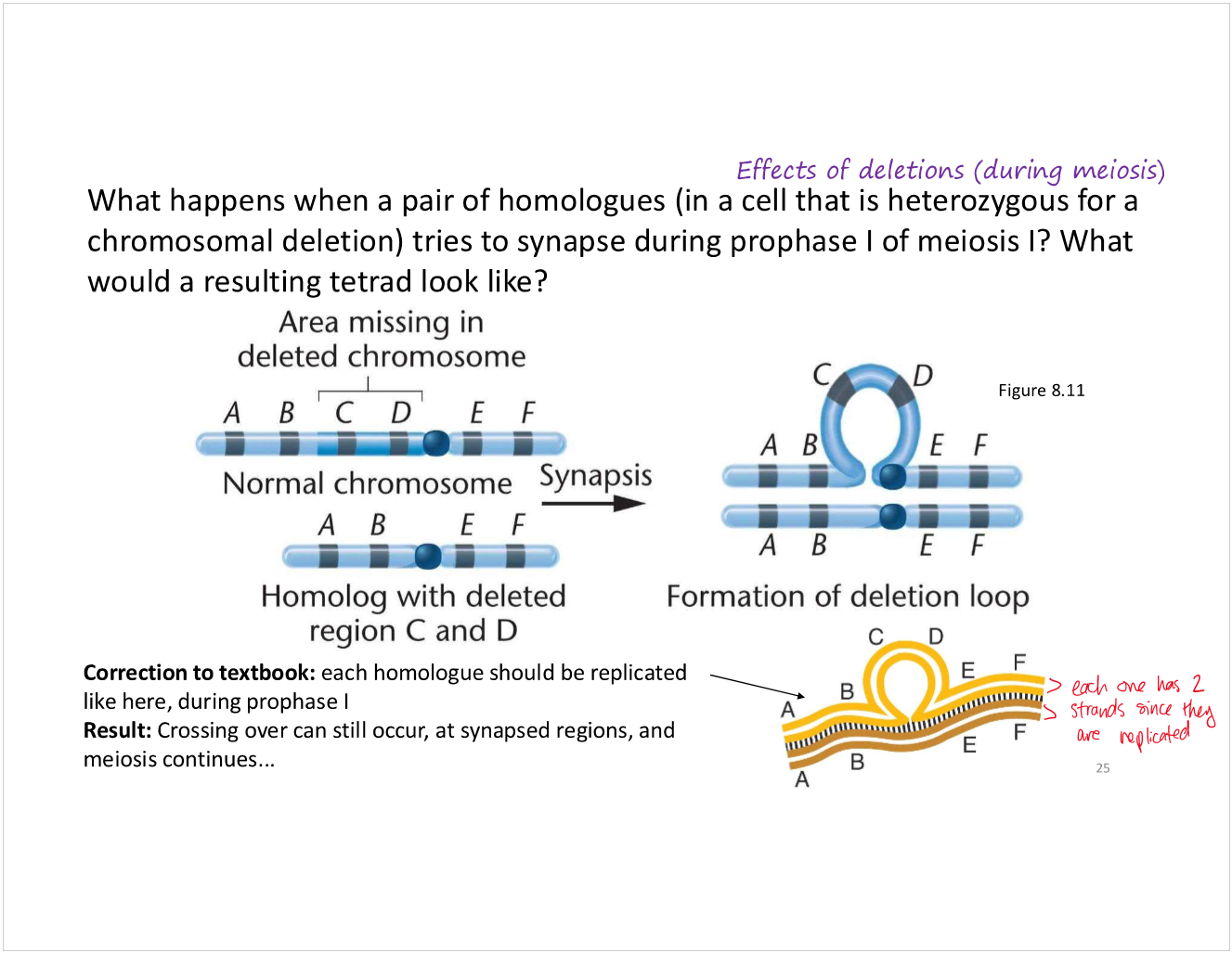
deletions
when a portion of DNA is lost from the chromosome (e.g., 2 and 3)
note: the numbers indicate major chromosomal segments that each contain many genes
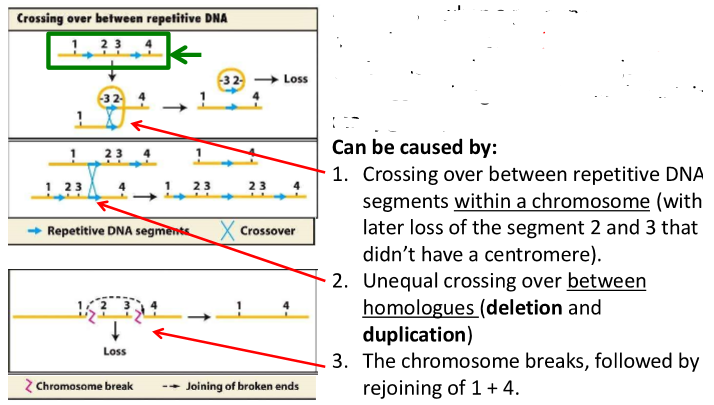
what can deletions be caused by?
these chromosomes are homologous
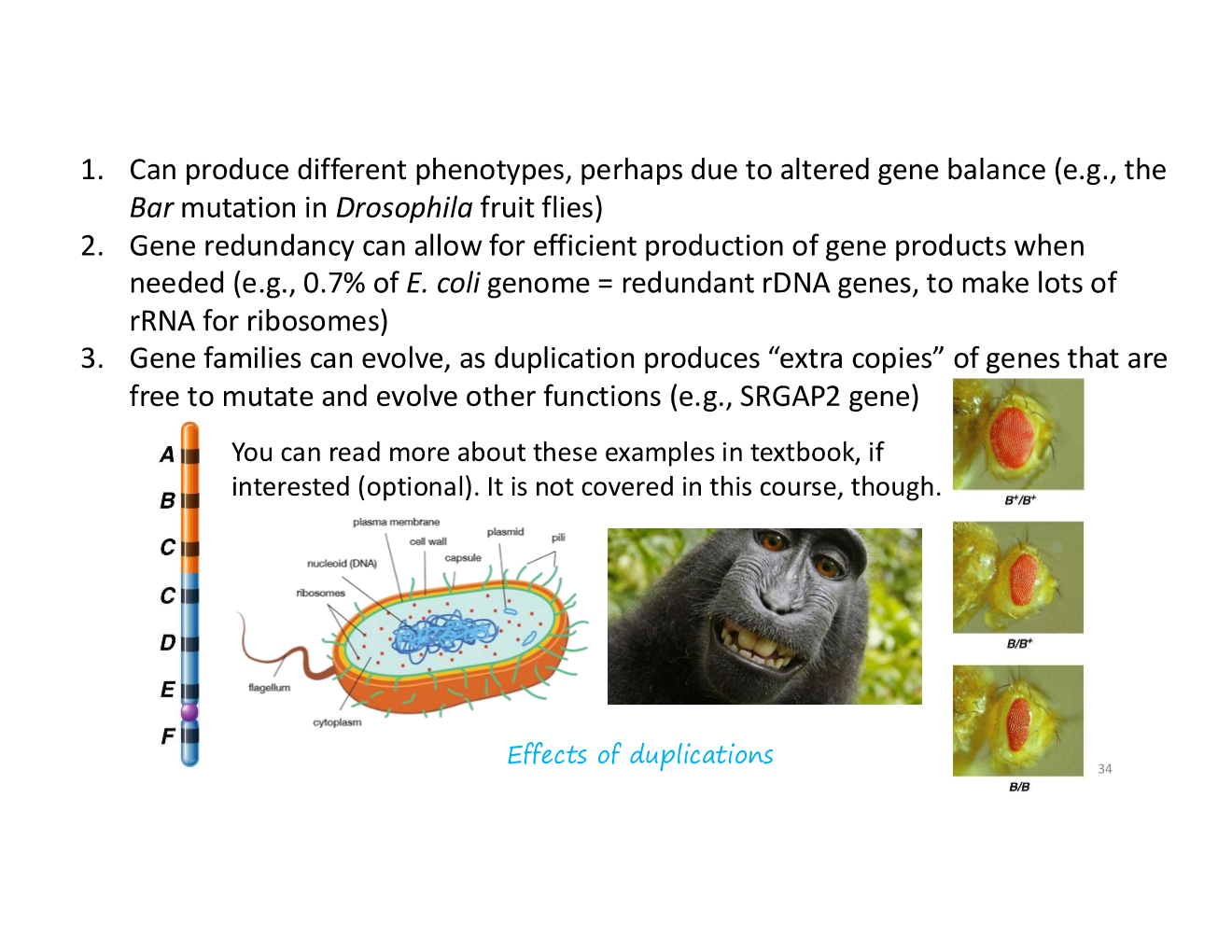
duplication
when a portion of DNA is present more than once in a chromosome
what can duplications be caused by?
these chromosomes are homologous
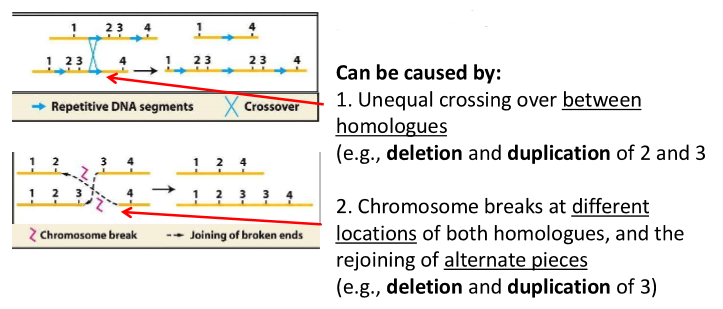
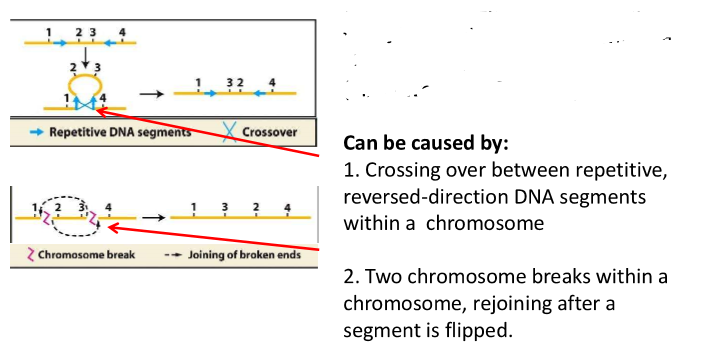
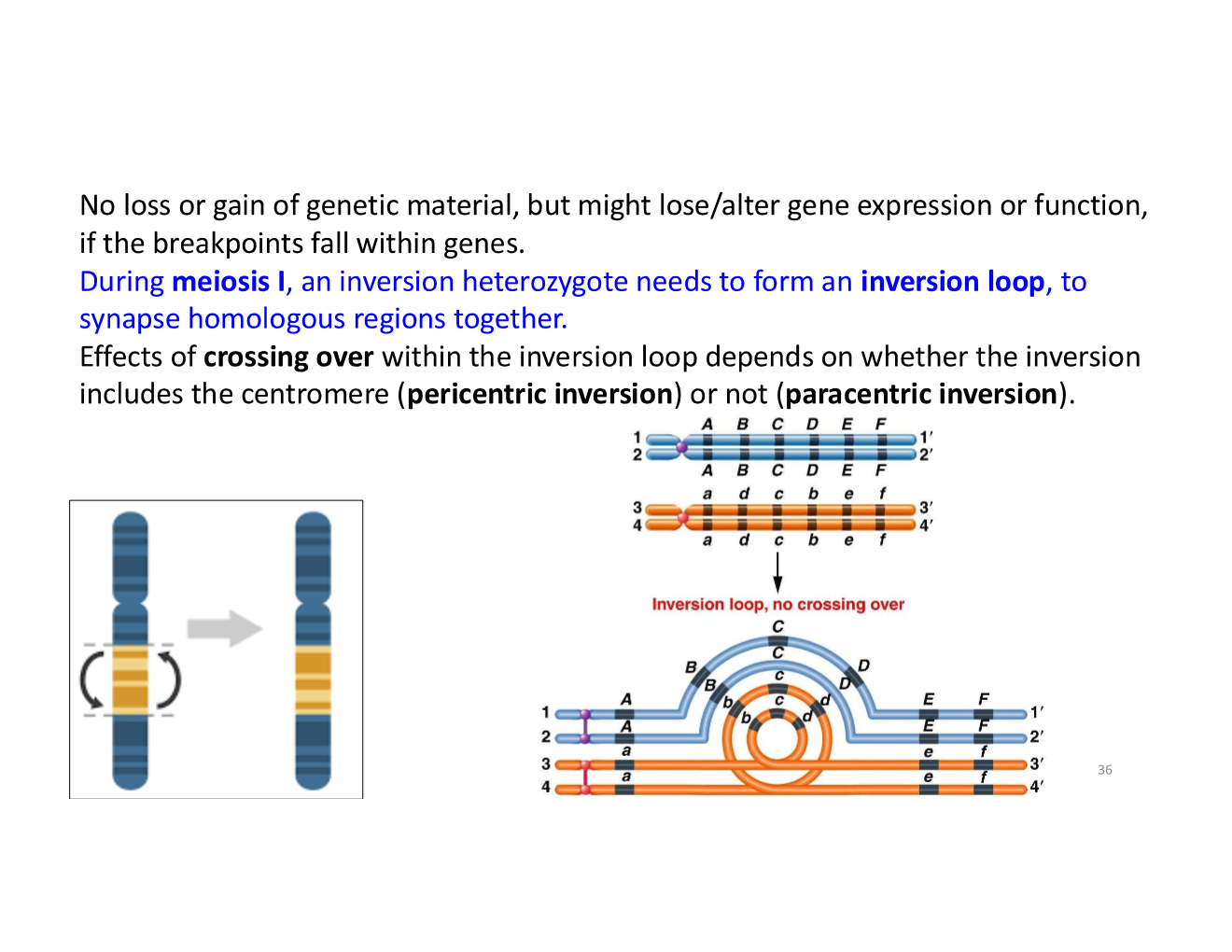
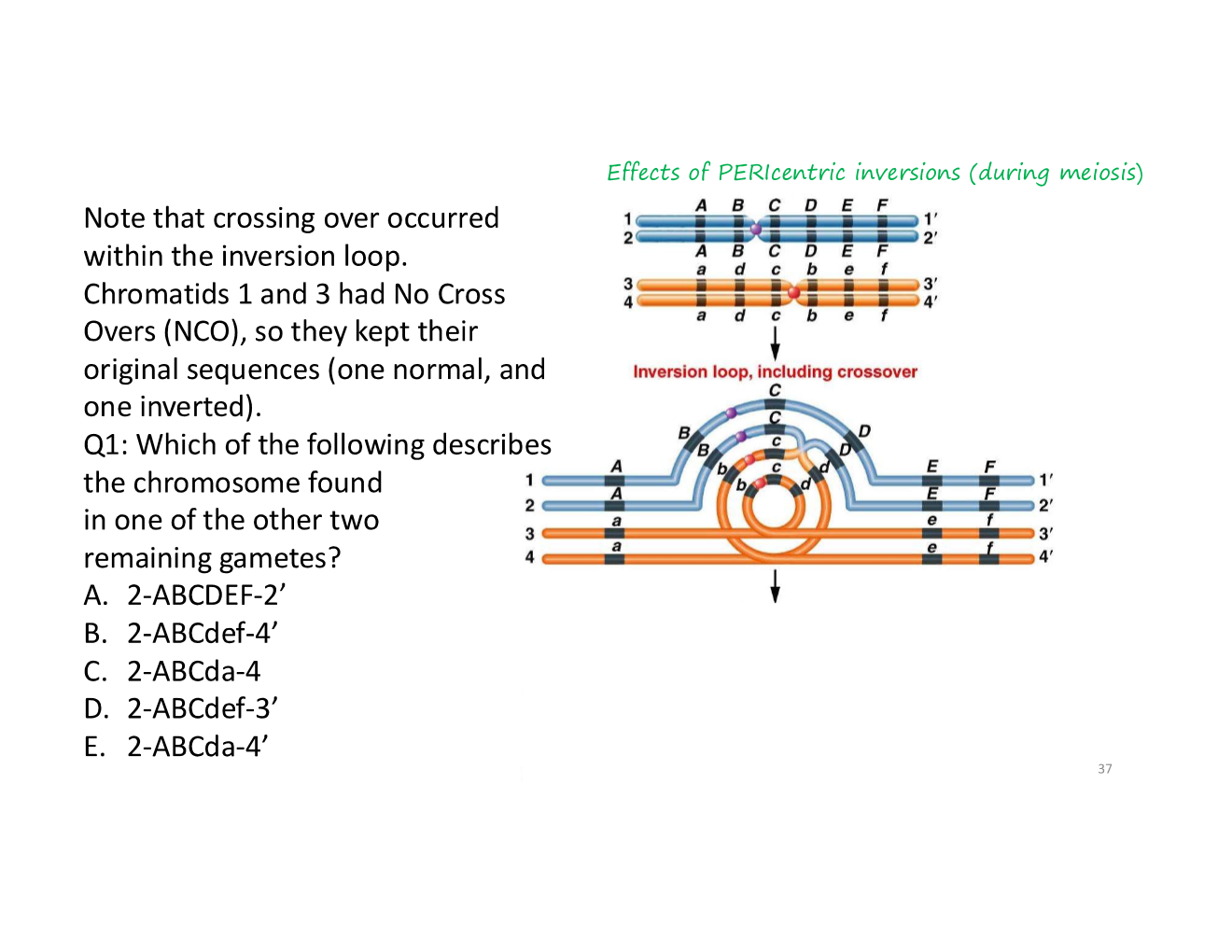
inversion
when a portion of DNA is turned around 180 degrees, within a chromosome
e.g., inversion of 2 and 3
what can inversion be caused by?
these chromosomes are homologous
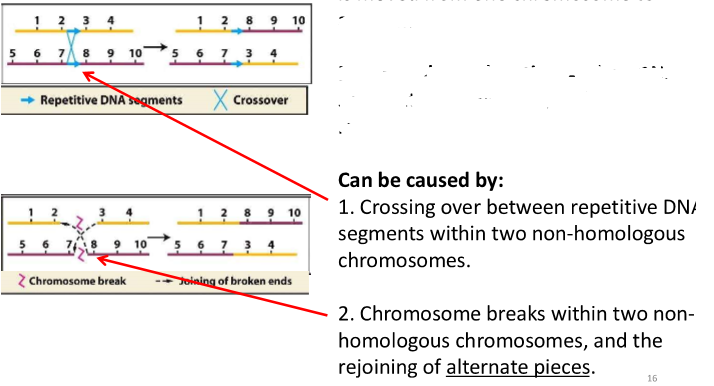
translocation
when a portion of DNA is moved from one chromosome to another
reciprocal translation is when DNA segments are swapped, and no DNA is lost
what can translocation be caused by?

E

effects of duplications
inversions summary
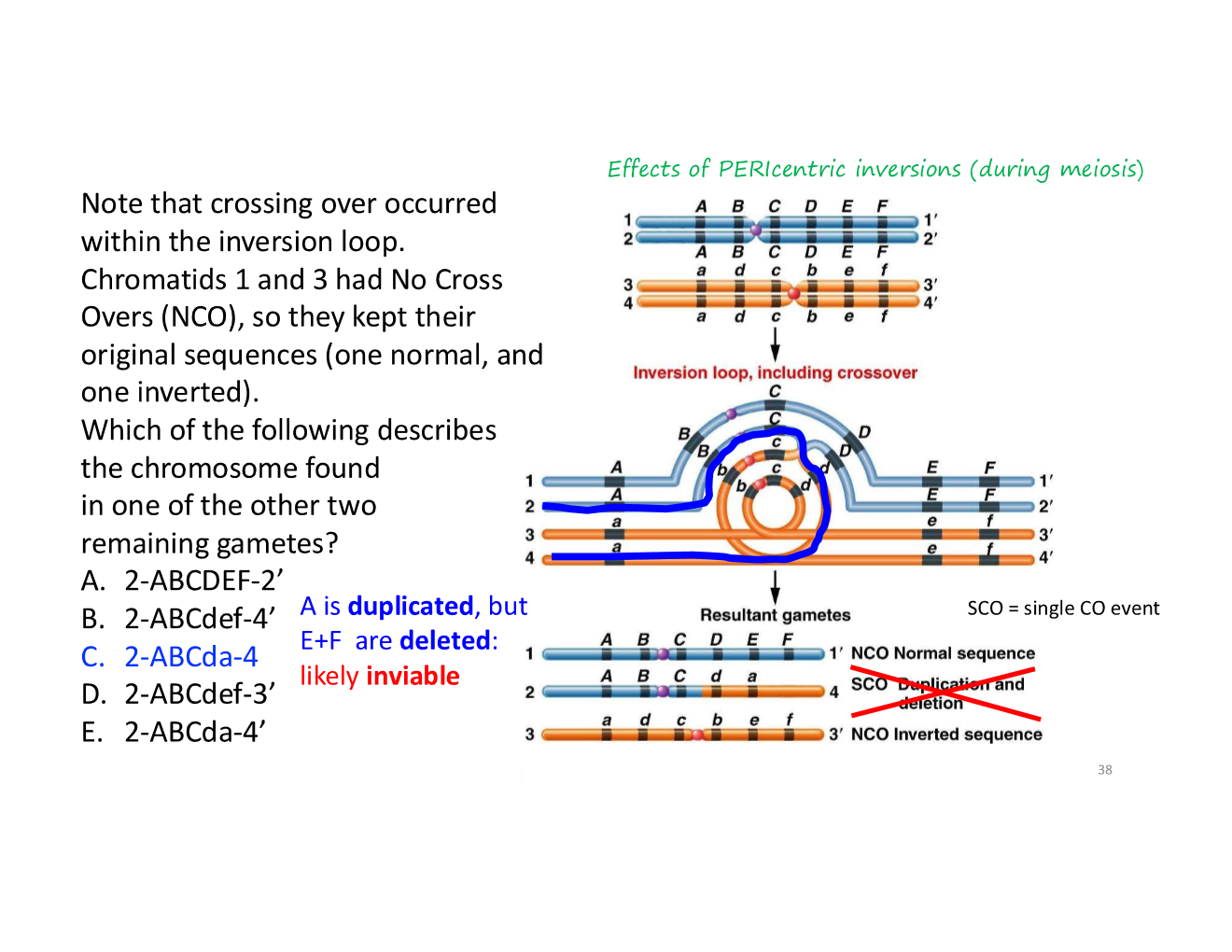
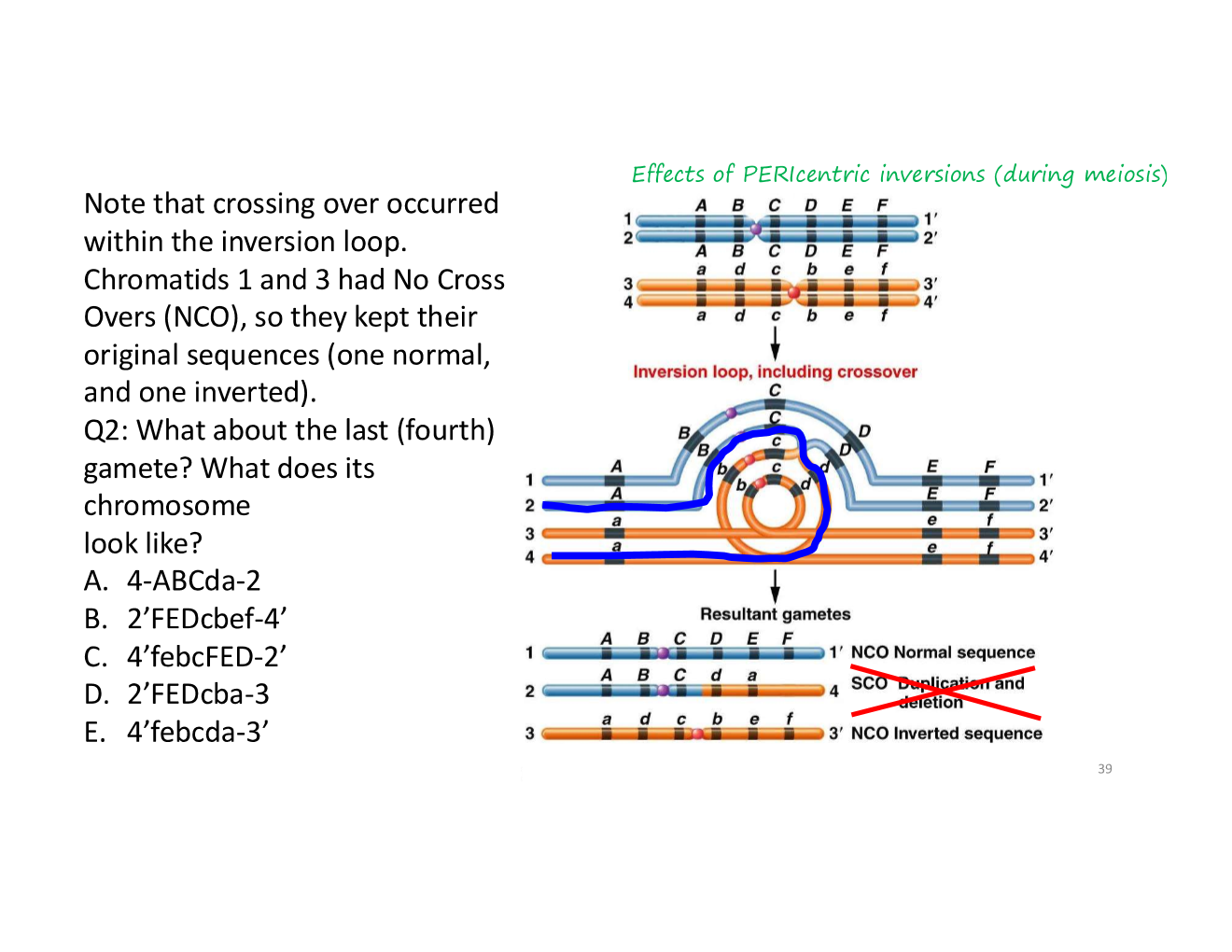
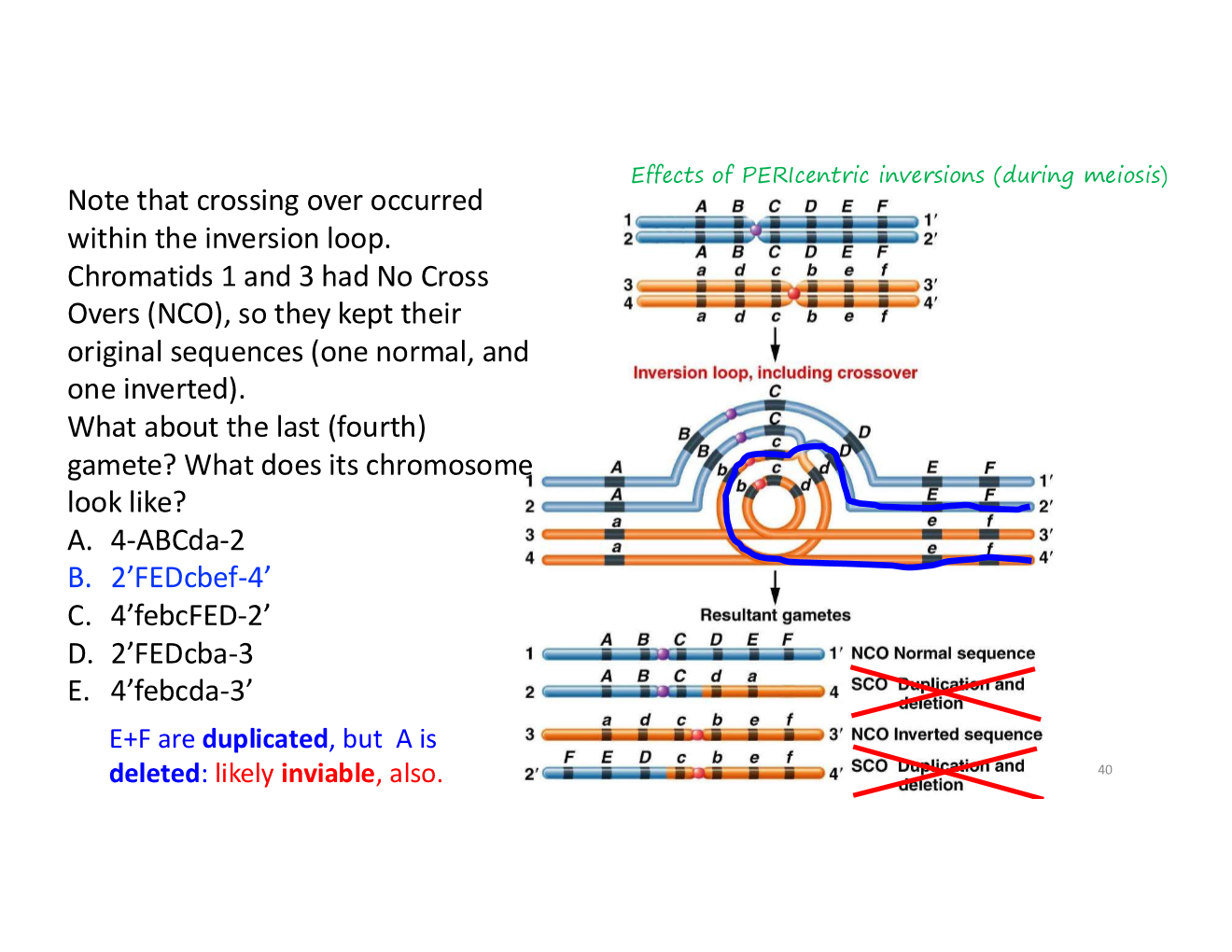
acentric
has no centromere
will likely create inviable offspring
dicentric
has 2 centromeres
dicentric chromosomes will be pulled in two directions and break at a random point
will likely create inviable offspring
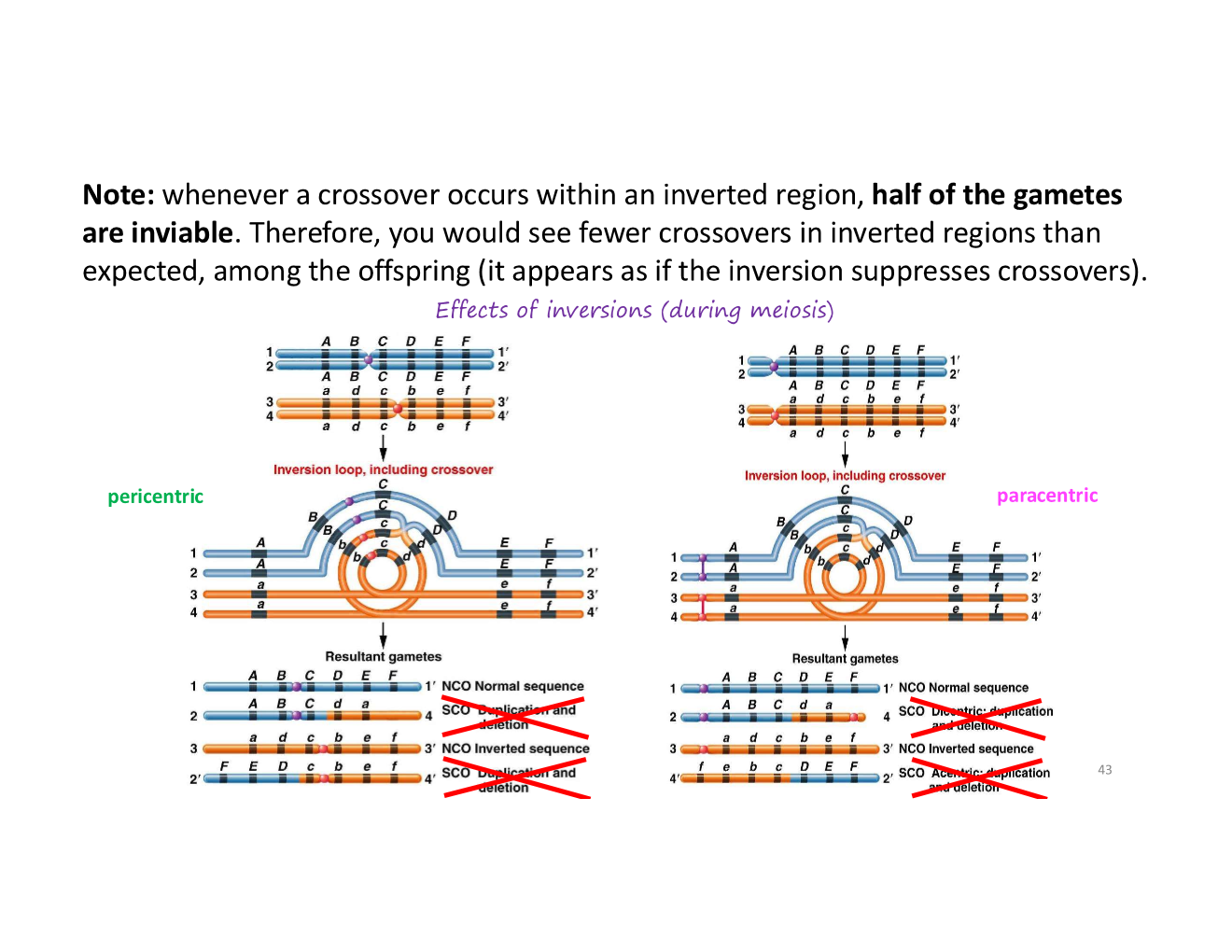
what happens when a crossover occurs within an inverted region