DRRR - Definition of Terms
DRR
The concept and practice of reducing disaster risks through systematic efforts to analyze and manage causal factors of disasters
★ reduced exposure to hazards
★ lessened vulnerability of people and property
★ wise management of land and environment, &
★ improved preparedness for adverse events
Philippine Disaster Reduction and Management Act of 2010
the establishment of Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (LDRRM) Office in every province, city, and municipality.
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
DRR
The concept and practice of reducing disaster risks through systematic efforts to analyze and manage causal factors of disasters
★ reduced exposure to hazards
★ lessened vulnerability of people and property
★ wise management of land and environment, &
★ improved preparedness for adverse events
Philippine Disaster Reduction and Management Act of 2010
the establishment of Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (LDRRM) Office in every province, city, and municipality.
DRRM
The application of disaster risk reduction policies and strategies, to prevent new disaster risks.
PRE-EVENT | Prevention
The outright avoidance of adverse impacts of hazards and related disasters. Can be in the form of proper land use or using suitable engineering design.
PRE-EVENT | Mitigation
Lessening or limitation of the adverse impacts of hazards and related disasters.
PRE-EVENT | Adaptation
The adjustment in natural or human systems in response to actual or expected climatic stimuli or their effects. Addresses the concerns of climate change and is sourced from UNFCCC
PRE-EVENT | Preparedness
The knowledge and capacities developed by governments, professional response and recovery organizations, communities and individuals to effectively anticipate, respond to, and recover from the impact of likely, imminent, or current hazard events.
Action is carried out within the context of disaster risk management and aims to build the capacities needed to efficiently manage all types of emergencies
POST-EVENT | Response
The provisions of emergency services and public assistance during or immediately after a disaster in order to save lives. Predominantly focused on immediate and short-term needs, and is sometimes called, “Disaster Relief.”
POST-EVENT | Recovery
The restoration, and improvement where the appropriate use of facilities, livelihoods, and living conditions of disaster affected communities.
This task of rehabilitation and reconstruction begins soon after the emergency phase has ended and should be based on pre-existing strategies.
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | Disasters are influenced by development.
An example of this would be illegal logging, which makes an area prone to landslide.
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | The existence of policies and laws in disaster risk reduction does not guarantee zero casualty if there is no actual implementation in communities.
Government can’t act alone, it needs the cooperation of the community in reinforcing the rules
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | Disaster risk management starts at the level of community
The community is directly affected by the disaster, they need to work together and cooperate in employing DRRM
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | Disaster risk reduction is not limited to a single activity
In solving and mitigating the risks of disasters, there are several steps to be done.
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | Time is an essential component of disaster risk reduction at the national, provincial, and community level.
Sufficient time is needed for planning, orientation, and training.
PRINCIPLES OF DRR| As part of the decentralized development process, there should be the transfer of the planning and management of DRR to various sectors in the society down to the community level.
Community-based Practices For Managing Disaster Risks
1. Having a LDRRMF that should not be lower than 5% of the estimated revenue from regular sources to support various task in disaster risk reduction.
2. Reinforcement of traditional community values through disaster education programs that includes self-help, resourcefulness and cooperation.
3.A Training institute to establish risk reduction and management by training public and private individuals, whether at the local or national level.
4. Development of disaster risk reduction modules to be integrated in the secondary school curriculum.
5. Other disaster preparedness activities related to disaster education.
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | Seminars and Workshops on Natural Hazards awareness
Educate public school teachers in their awareness and preparedness for natural hazards.
PRINCIPLES OF DRRR | Joining organization such as the Red Cross Youth
A way for the youth to get involvement in community-based disaster risk reduction and management activities.
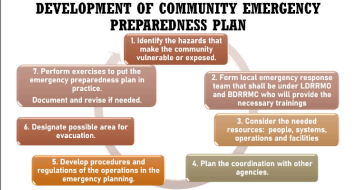
Development of a Community Preparedness Plan
Early Warning Systems
Essential component of emergency preparedness planning

Emergency Kit
Also known as a “Survival Kit,” a portable set that contains the needed items to survive a disaster.

The items a basic emergency supply kit should have.
Paradigm Shift | Reactive
Top-down and centralized disaster management
Considers disasters as merely a function of physical hazards
Lessens the impacts and upgrades the management we used to practice
Focus on Disaster Response and Anticipation
Paradigm Shift | Proactive
Starts with the community, assess, and scales up to the main agency
Reflections of people’s vulnerability
Integrates approach of social and human development to reduce disaster risks
Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act of 2010 (RA 10121)
- aims at having a system for disaster risk reduction and management
- includes the creation of frameworks, establishments, institutions and allocation of resources and funds
Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA)
- implemented due to the event that happened in the Indian Ocean, a tsunami
- Implemented by the Philippines in 2009
- a response to growing concerns worldwide as the increasing effects of disasters on humans and national development.
Policies (Section 2)
It is the involvement of all sectors, stakeholders, and organizations (e.g., civil society and volunteer organizations) at all levels in disaster risk reduction and management;
Integration of disaster risk reduction and climate change in policies, socioeconomic development planning, budgeting, and governance;
Strengthening LGUs and communities and building their resilience in preparation and mitigation of disasters in their localities; and
Provision of disaster relief and emergency rehabilitation programs to affected communities
National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Framework (Section 3)
- It describes the government's approach to DRRM to be multi-sectoral, inter-agency, and community-based,
- gives emphasis to the community with the focus on the vulnerable and marginal groups
- deals with the root causes of disasters
National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council (NDRRMC)
- head agency that is composed of government agencies, LGUs, CSOs and private Sectors.
- tasked to create the framework to serve as the main guide of the country's move toward disaster risk reduction
- oversees the implementation of policies, procedures, plans, programs, and other disaster risk reduction measures.
Regional Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council (RDRRMC)
- serves as the support of the LDRRMCs in terms of its management, coordination, and assessment of its plans and programs at the regional level
Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council (LDRRMC)
- Supervises the provinces, cities, and municipalities
- Its main responsibility is management, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of the LDRRMPs and budget allocation in their designated localities.
Measures (Section 4)
- includes provision for this section, such as services, programs, and projects, to help reduce the effects of disasters on the lives of the people and their properties.
Among these are the following,
★ Risk Assessment
★ Knowledge Management
★ Programs and Training Institutes
★ Funding (NDRRMF & LDRRMF)
Measures (Section 4) | Risk Assessment
Involves the process of determining the possible hazards and vulnerable groups in a community that should be considered in planning the measures for prevention, preparation, and recovery as response to disasters.
Office of Civil Defense (OCD) in Risk Assessment
Handles the Risk Assessment at a National Level
Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Office (LDRRMOs) in Risk Assessment
Handles the Risk Assessment at a Local Level
Measures (Section 4) | Knowledge Management
Involves securing information on a disaster that includes existing scientific information, socio-economic data, records of previous disasters, and maps.
Also involves sharing of information among various government agencies and respective areas in the community (LDRRMOs) for awareness
Measures (Section 4) | Public Awareness and Training Institutes
In this measure, these institutions are required to do the following for ___________
OCD (Office of Civil Defense) - Required to develop national standards for the programs related to DRRM. Also entrusted to establish training institutes.
LDRRMOs - Implementation of these policies, programs, plans, as well as information dissemination on DRRM.
DRRM is also incorporated in the school curriculum
Measures (Section 4) | Funding
Institutions that handle the funding at every level,
National Level - National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Fund (NDRRMF), covers personal training, purchase of facilities, and capital expenses.
Local Level - Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Fund (LDRRMF), covers programs and procurement of equipment and supplies.
30% Quick Response Fund
State of Calamity (Section 16)
Impact of natural and man-made hazards on an area may result in a state of calamity.
Large areas = President with the recommendation of NDRRMC
For Individual places = Local Sanggunian with accordance in the recommendation of LDRRMC
Coordination During Disaster Response (Relief Operations - State of Calamity)
- LDRRMCs directly supervise the response and recovery measures to an area declared under a state of calamity. The specific DRRMCS are directly engaged depending on the extent of the area affected, which as follows:
City/Municipal DRRMCs - for at least two affected barangays
Provincial DRRMC - for at least two affected cities/municipalities
Regional DRRMC - for at least two affected provinces
NDRRMC - for at least two affected regions in the country
Coordination During Disaster Response (Policies for Assistance - State of Calamity)
- Price ceiling on basic necessities are set.
- Overpricing and hoarding of basic goods, medicines, and petroleum products are prohibited.
- Affected people can avail loans without government financing institution.
Violations (Section 19)
- Negligence of responsibilities leading to harm such as death, damages in properties, and improper use of fund.
- Illegal representation and intentional use of wrong information in soliciting donations
- Deterring distribution of relief goods as well as their purchasing or reselling, seizing, redirecting delivery, replacement
- Receiving and consumption of relief goods not designated for the affected area, and its discarding
- Tampering of relief goods like alternating labels, repacking, and falsely claiming of its donors
Penalties (Section 20)
- A fine from PHP 50,000 to PHP 500,000
- Imprisonment from 6-12 years
- Permanent disqualification of the government officer
- Penalty given to involved persons in non-government organizations like corporations, partnerships, and associations