Microconomics - Chapter 6: Elasticity: The Responsiveness of Demand and Supply
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Elasticity
A measure of how much one economic variable responds to changes in another economic variable. (based on percentage changes in the variables)
formula for price elasticity of demand
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
True or False: price elasticity of demand is a negative number
True
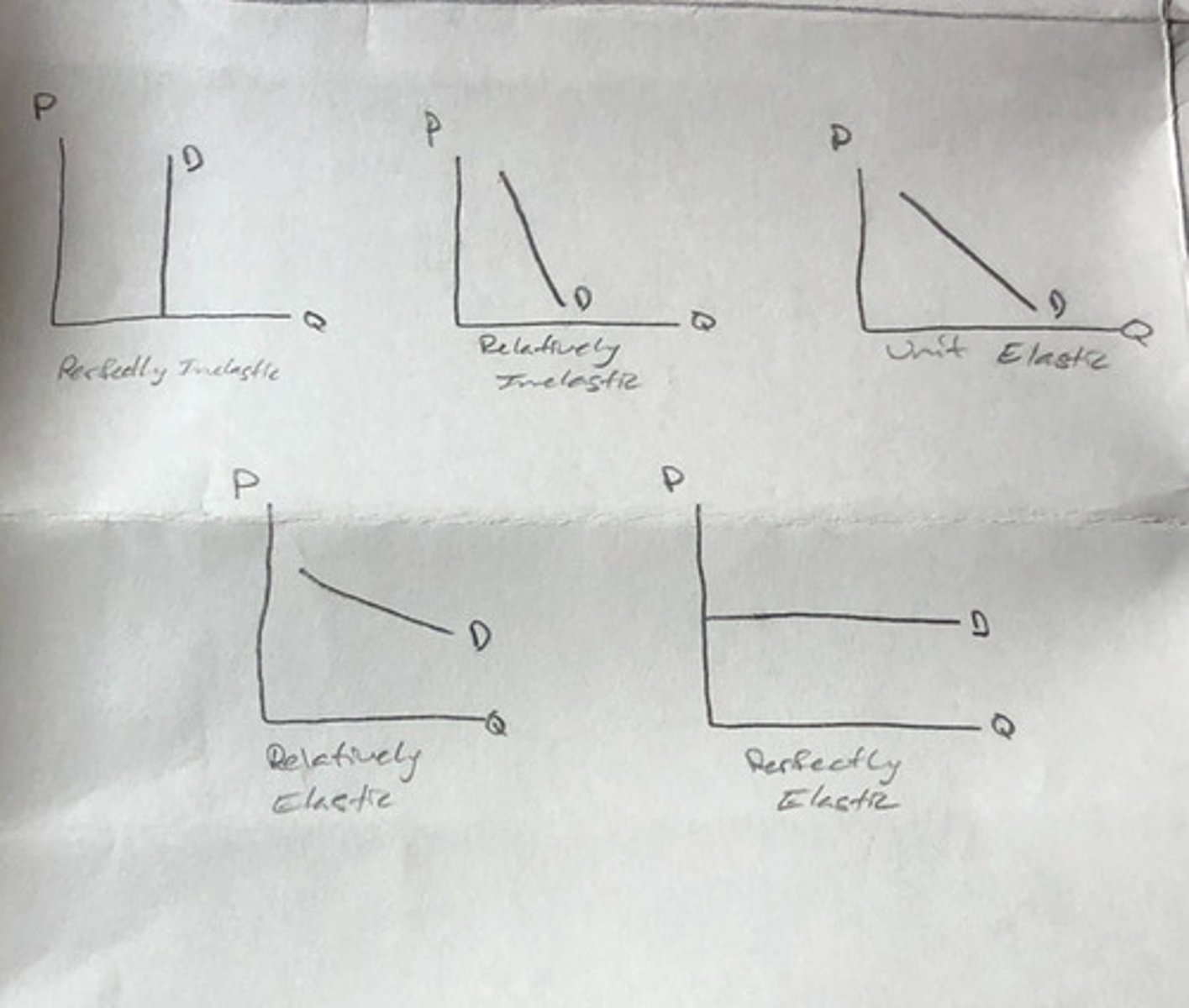
we say demand is elastic if its price elasticity of demand is _________ (in absolute value) than 1.
larger/greater
we say demand is inelastic if its price elasticity of demand is _________ (in absolute value) than 1.
smaller/less
we say demand is unit-elastic if its price elasticity of demand is _________ (in absolute value) to 1.
equal
midpoint formula for percentage changes (avoids the confusion of whether we are going from A to B or from B to A)
percentage change = (A-B)/(A+B/2)x100
Price elasticity of demand becomes:
Price elasticity of demand = [(Q2-Q1)/(Q1+Q2/2)]/[(p2-p1)/(p1+p2/2)]
-This first term is the percentage change in quantity, using the midpoint formula.
-The second term is the percentage change in price, using the midpoint formula.
steps to finding price elasticity of demand
1) find avg Q & p (A+B/2)
2) then find the percentage change in Q & p (A-B)/(what you found in step 1) x 100 {since its a percentage}
3) then divide (Percentage change in quantity demanded)/(Percentage change in price) which gives you the Price elasticity of demand
remember to look at answer in abs value (positive)
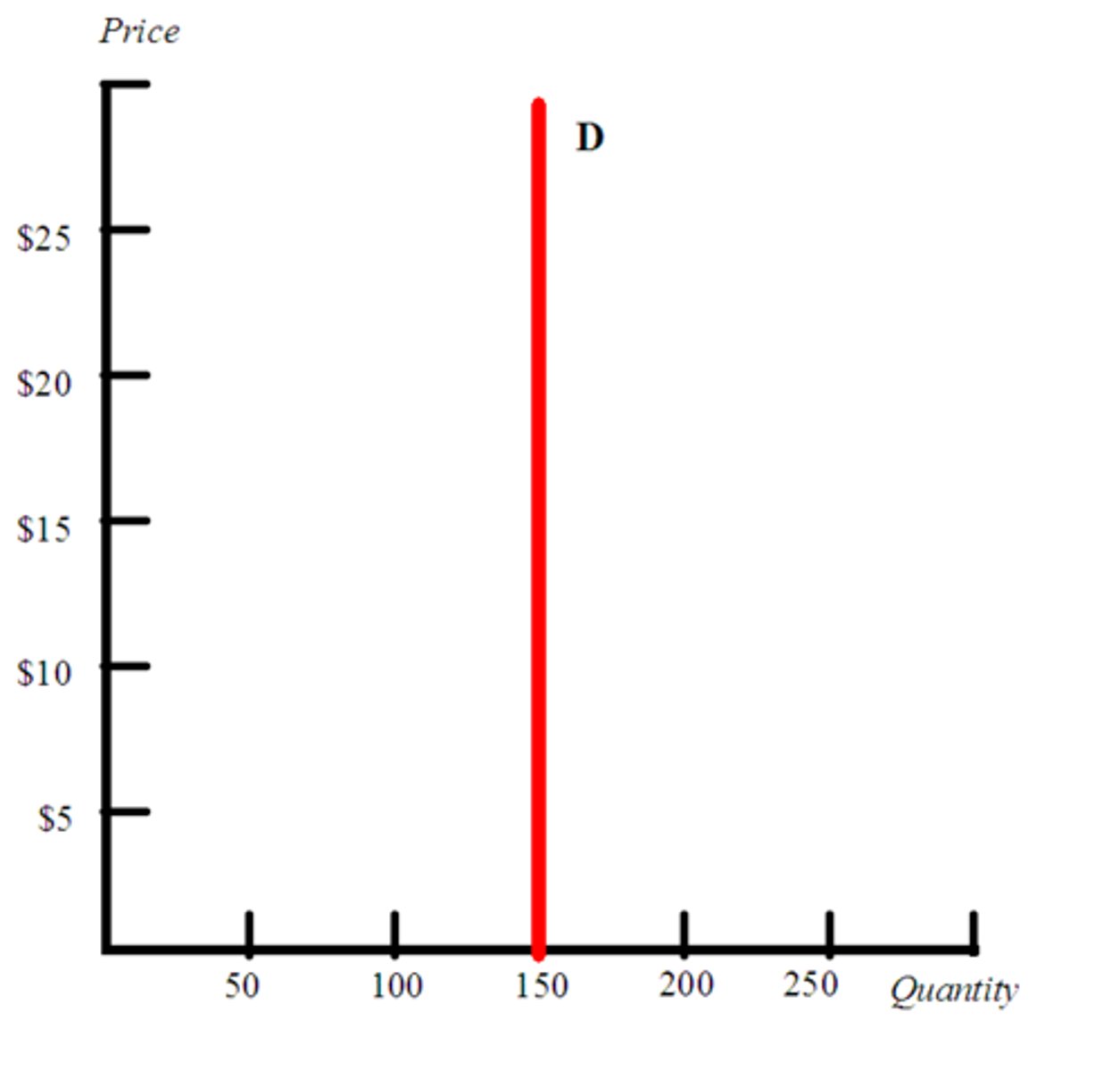
perfectly inelastic demand
the case where the quantity demanded is completely unresponsive to price and the price elasticity of demand equals zero
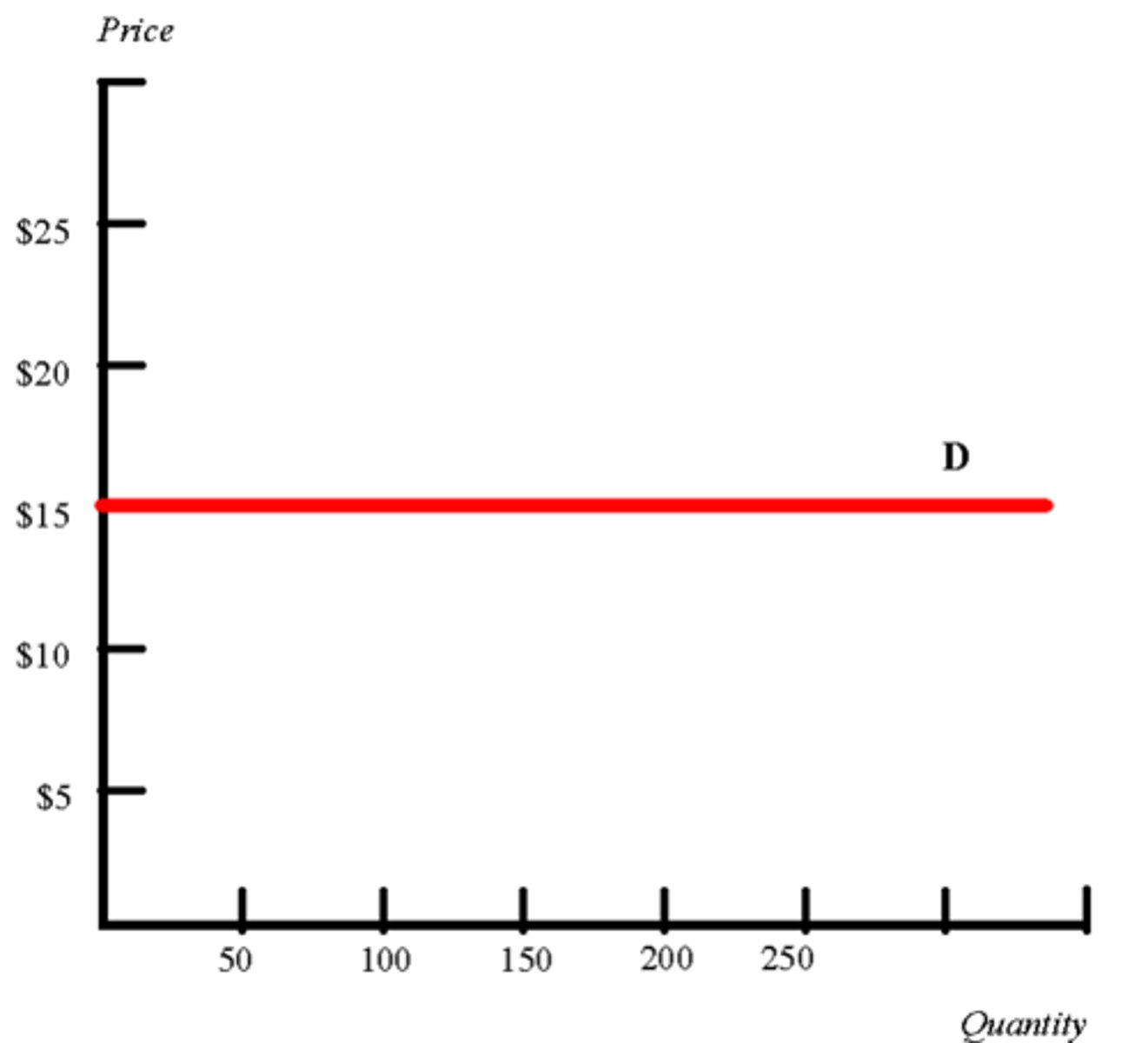
perfectly elastic demand
the case where the quantity demanded is infinitely responsive to price and the price elasticity of demand equals infinity
unit elastic demand
demand is unit elastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price, so the price elasticity is equal to 1 in absolute value
Total Revenue (TR)
The total amount of funds a seller receives from selling a good or service, calculated by price x quantity.
If demand is elastic then an increase in price _________ revenue
reduces
If demand is elastic then an decrease in price _________ revenue
increases
If demand is inelastic then an increase in price _________ revenue
increases
If demand is inelastic then an decrease in price _________ revenue
reduces/decreases
If demand is unit then an increase/decrease in price _____ ___ ______ revenue
does not affect
cross-price elasticity of demand
the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good divided by the percentage change in the price of another good
It measures the strength of substitute or complement relationships between goods.
If the products are substitutes then the cross price elasticity of demand will be
positive
ex: two brands of smartphones
If the products are compliments then the cross price elasticity of demand will be
negative
ex: iphones and apps downloaded from stores
If the products are unrelated then the cross price elasticity of demand will be
zero
ex: iphones and peanut butter
income elasticity of demand
a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in income, measured by the percentage change in the quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income
if the income elasticity of demand is positive but less than 1 then the good is
normal and a necessity
ex: bread
if the income elasticity of demand is positve but greater than 1 then the good is
normal and a luxury
ex: caviar
if the income elasticity of demand is negative then the good is
inferior
ex: high-fat meat
price elasticity of supply
the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to a change in price, measured by dividing the percentage change in the quantity supplied of a product by the percentage change in the product's price
its similar to price elasticity of demand so the same sort of calculation methods apply (midpoint formula, etc.)
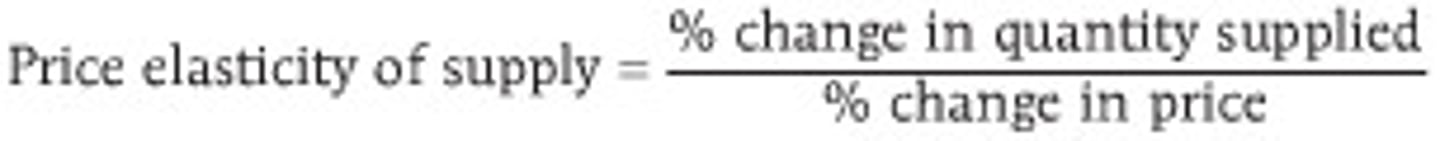
If supply is elastic then the value of price elasticity is _______ than 1
greater

If supply is inelastic then the value of price elasticity is _______ than 1
less
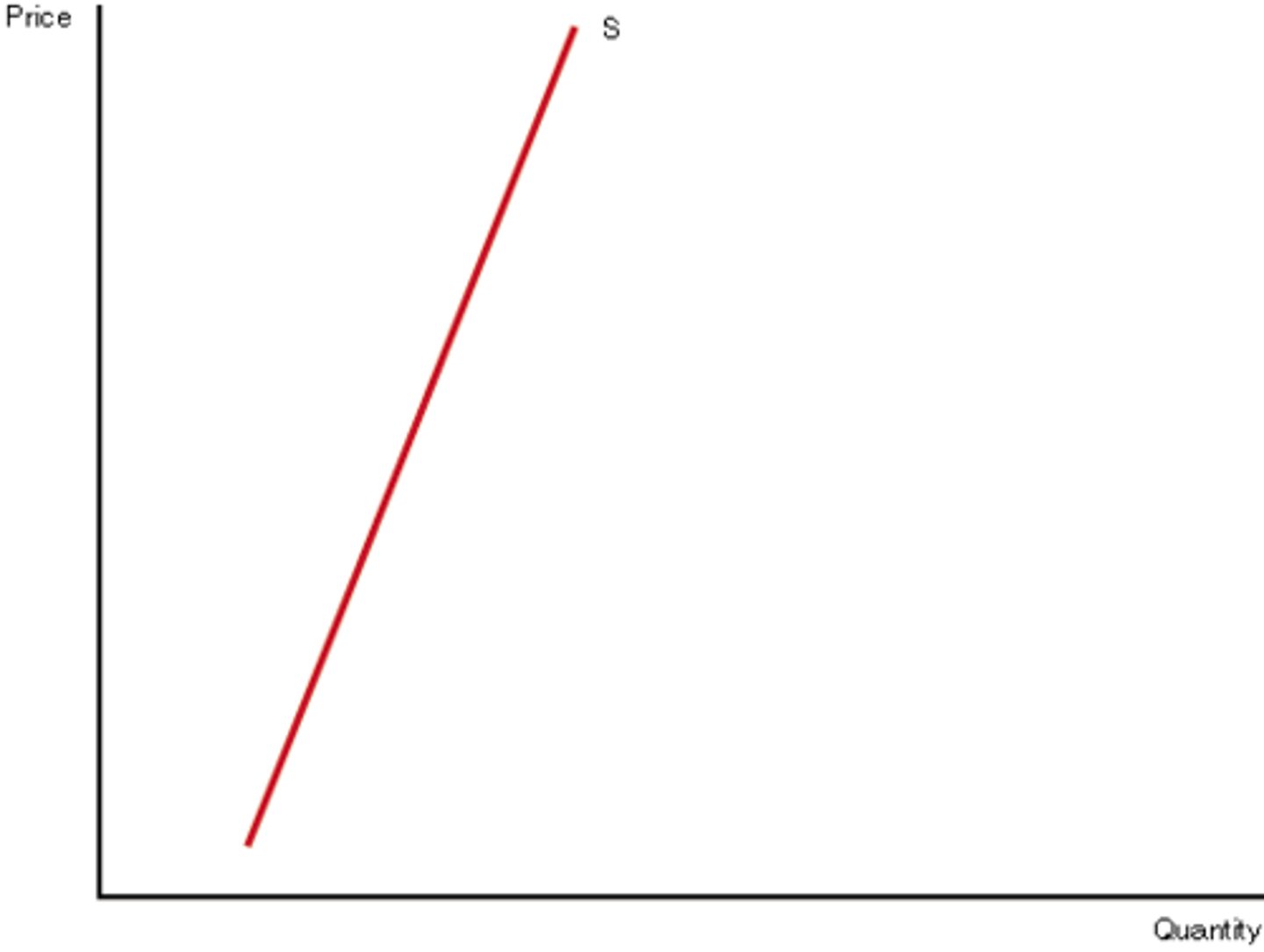
If supply is unit elastic then the value of price elasticity is _______ to 1
equal
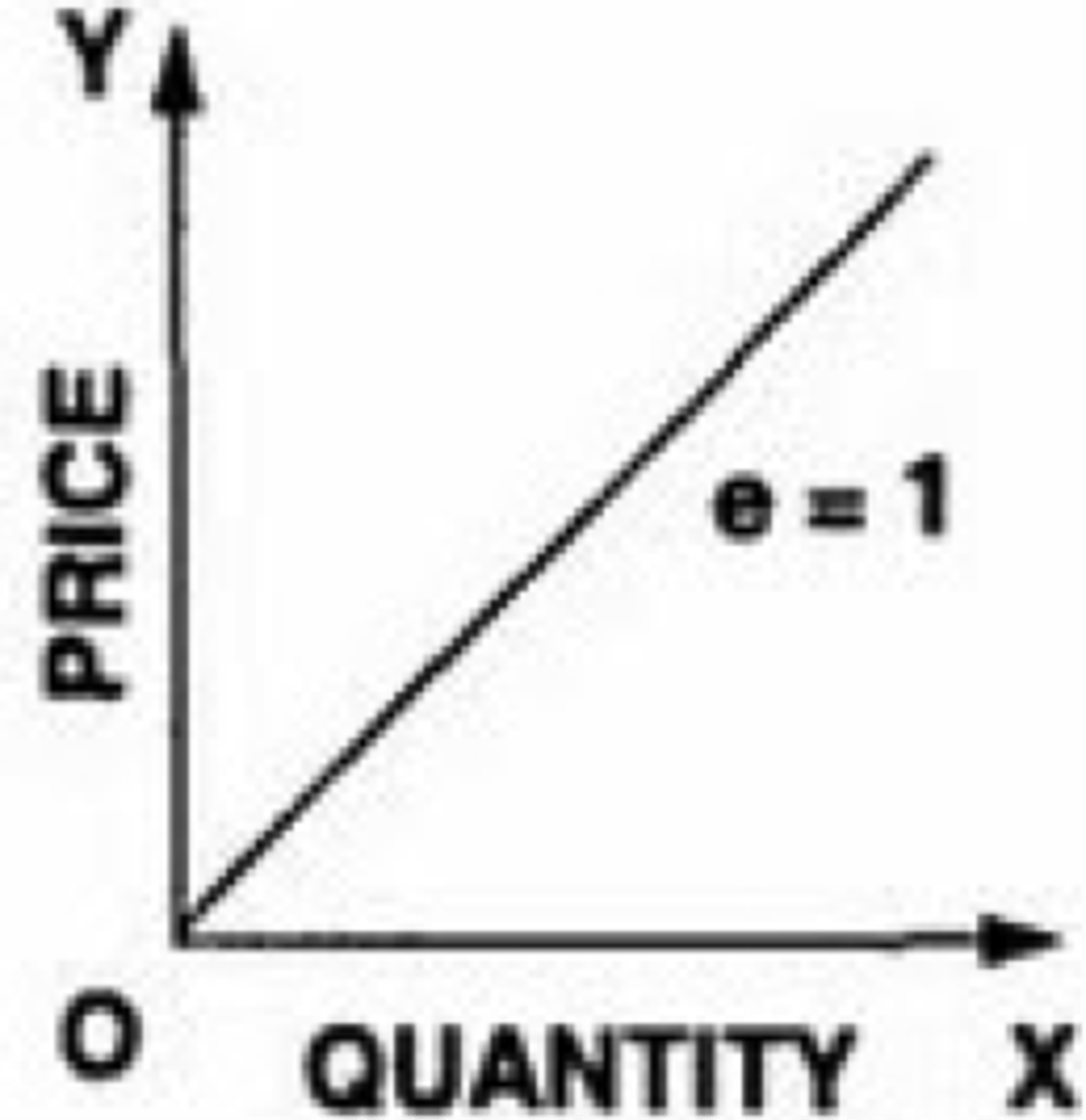
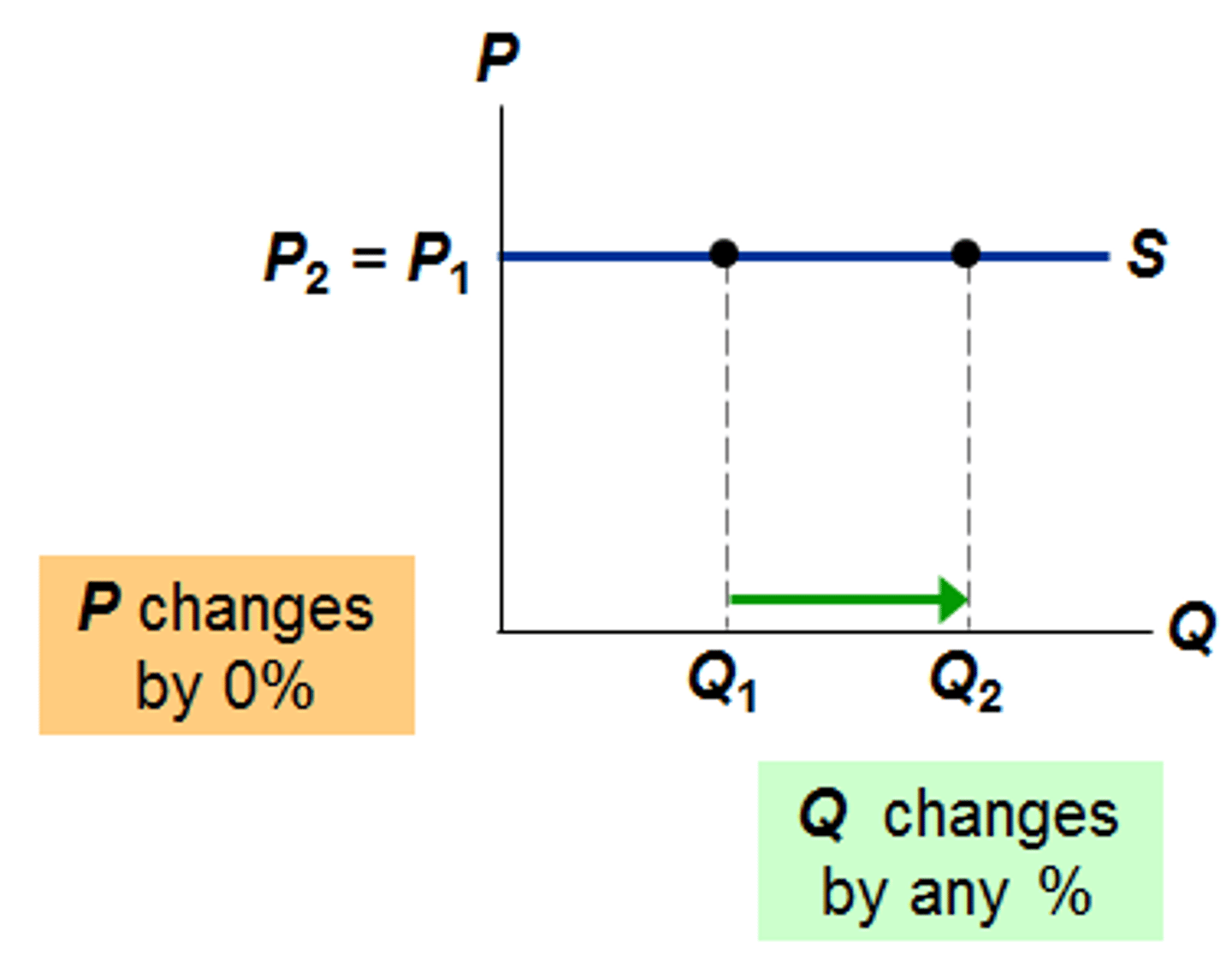
If supply is perfectly elastic then the value of price elasticity is
equal to infinity
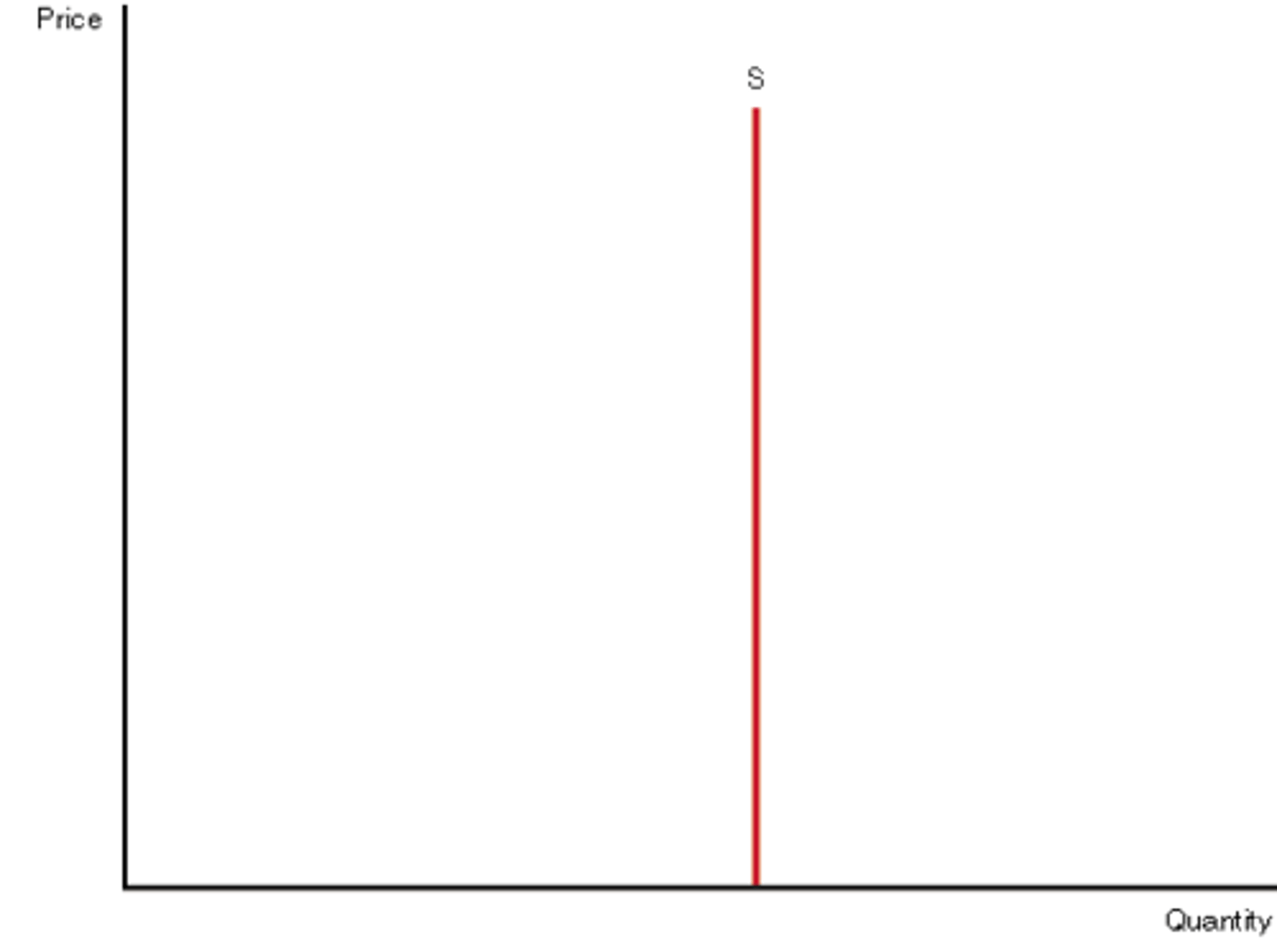
If supply is perfectly inelastic then the value of price elasticity is
equal to 0
True or False: Price increases more when supply is inelastic
True

Price elasticity of demand is a
measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price

The key determinants of the price elasticity of demand for a good are
the availability of close substitutes, the passage of time, weather the good is luxury or a necessity, the definition of the market, and the share of the good in the consumer’s budget