Biology Exam 2
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Which of the following statements about a typical plasma membrane is correct?
The two sides of the plasma membrane have different lipid and protein composition.
Which of the following best describes the structure of a biological membrane?
two layers of phospholipids, with proteins either crossing the layers or on the surface of the layers
Which of the following statements about osmosis is correct?
The presence of aquaporins (proteins that form water channels in the membrane) speeds up the process of osmosis.
Which of the following statements describes the role of the transport protein in facilitated diffusion?
Transport proteins allow solutes to move passively down their concentration gradients across the membrane.
The movement of glucose into a cell against its concentration gradient is most likely to be accomplished by which of the following?
cotransport of the glucose with a proton or sodium ion that was pumped across the membrane using the energy of ATP hydrolysis
Active and passive transport of solutes across a membrane typically differ in which of the following ways?
active transport always involves the utilization of cellular energy, whereas passive transport does not require cellular energy
A white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is an example of
phagocytosis
Energy is observed in two basic forms: potential and kinetic. Which of the following correctly matches these forms with a source of energy?
potential energy with the covalent bonds of a sugar molecule
The process of cellular respiration, which converts simple sugars such as glucose into CO2 and water, is an example of __________.
a catabolic pathway
Which of the following statements about equilibrium of chemical reactions is correct?
A reaction that is at equilibrium is not capable of doing any work.
Which of the following statements best describes the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
A decrease in entropy is associated with which of the following types of reaction?
dehydration
In general, enzymes are what kinds of molecules?
proteins
An enzyme _____.
an organic catalyst
As a result of its involvement in a reaction, an enzyme _____.
Is unchanged
Which of the following is NOT a way in which an enzyme can speed up the reaction that it catalyzes?
the active site can provide heat from the environment that raises the energy content of the substrate
If an enzyme is added to a solution where its substrate and product are in equilibrium, what will occur?
Nothing; the reaction will stay at equilibrium.
Which of the following is true for all exergonic reactions?
The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy.
In the process of cellular respiration, what is consumed and what is produced?
glucose is consumed and carbon dioxide is produced
Which of the following statements describing the process of glycolysis is correct?
It represents the first stage in the chemical oxidation of glucose by a cell.
A dehydration reaction (or condensation reaction) is the process in which
water molecules are produced as a polymer formed from monomers
The four main categories of large biological molecules present in living systems are
proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids
The characteristic that all lipids have in common is
none of them dissolves in water
Some regions of a polypeptide may coil or fold back on themselves. This folding is called __________, and the coils or folds are held in place by __________.
secondary structure, hydrogen bonds
A hydrophobic amino acid R group (side group) would be found where in a properly folded protein?
On the inside of the folded chain, away from water molecules
The building blocks ( monomers) of nucleic acid molecules are called
Nucleotides
Depletion of which of the following molecules from the mitochondria will most directly inhibit the citric acid cycle?
NAD+
A glucose molecule is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, but together these two processes yield only a few molecules of ATP. What happens to most of the energy that the cell obtains from the oxidation of glucose?
it is stored in NADH and FADH2
Energy released from the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ ions into which location in eukaryotic cells?
mitochondrial intermembrane space
When a cell is deprived of oxygen, which of the following processes will be inhibited first?
the electron transport chain
In the absence of oxygen, what is the net gain of ATP for each glucose molecule that enters glycolysis?
two ATP
the shape of protein
determines its function
how many levels of protein structure are there?
four
primary structure
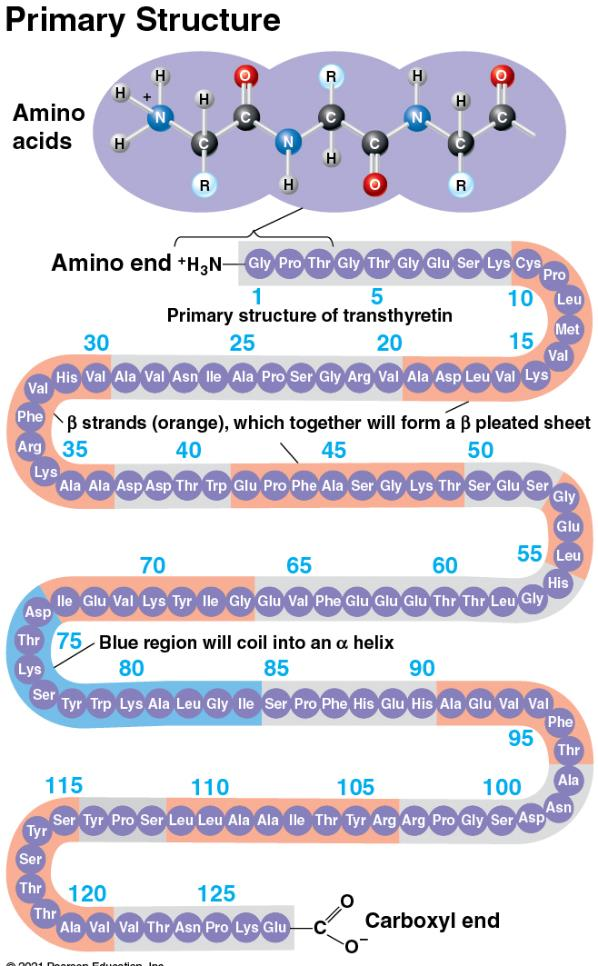
a peptide bond
secondary structure
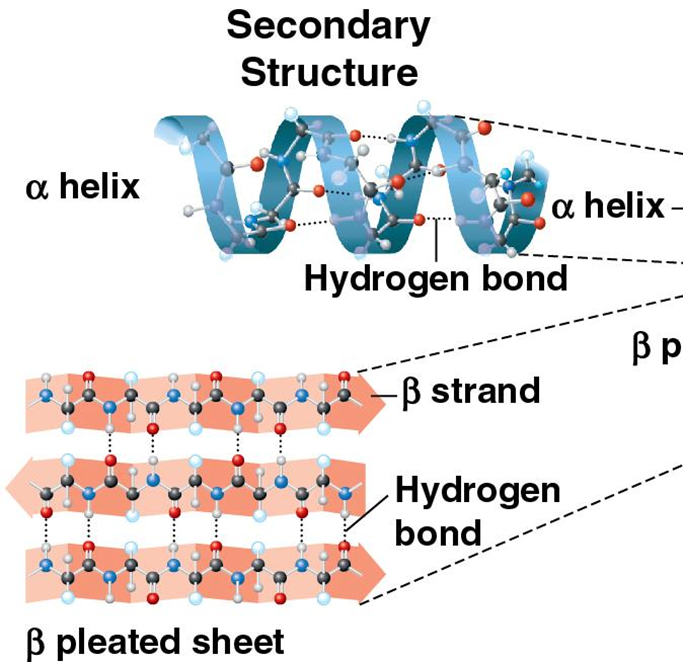
alpha helix, and beta sheet. there’s a hydrogen bond between the backbone as connecters
tertiary structure
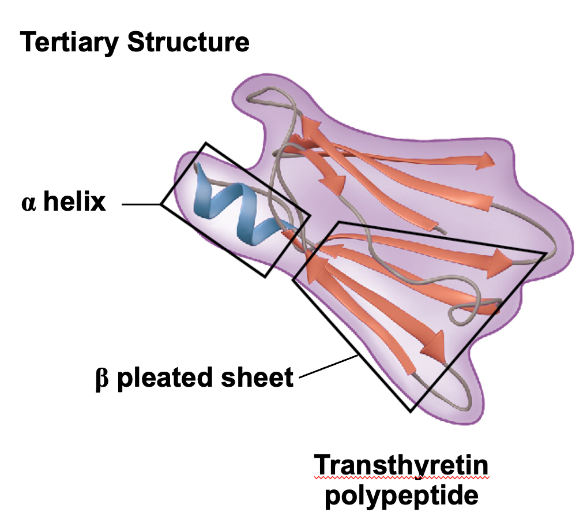
3D shape of polypeptide with interaction of side chains
Quaternary structure
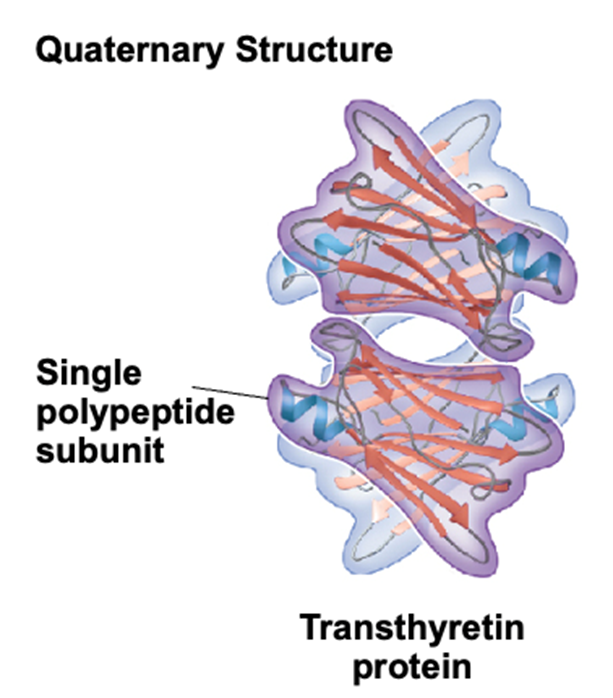
consists of multiple polypeptide chains
DNA
A G C T
RNA
A G C U
pyrimidines
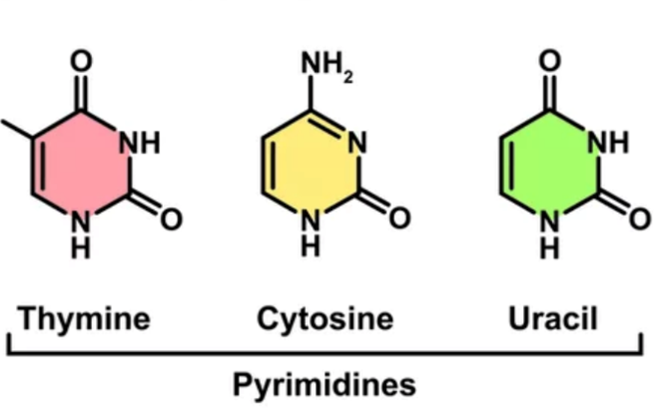
1 ring
purines
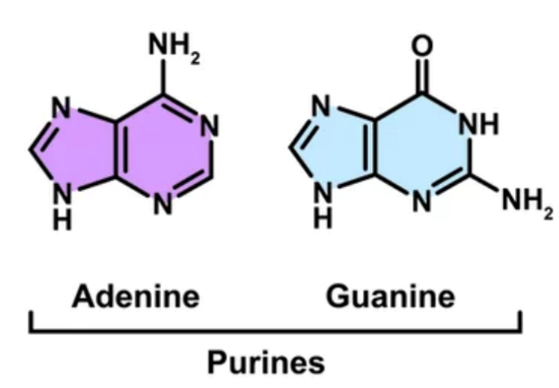
2 rings
Nucleotides are linked together by a linkage to build a polynucleotide
phosphodiester
membranes are held together by mainly
weak hydrophobic interactions
isotonic solution
the solute concentration is the same inside and outside of the cell
hypertonic solution
solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell, and as such the water leaves the cell.
hypotonic solution
solute concentration is less than that inside the cell, and as such the water enters the cell
facilitated transport
transport proteins speed up the passive movement of the molecules across the plasma membrane
active transport
the movement of substances against the concentration gradient. requires ATP.
passive transport
the movement of substances with the concentration gradient without energy
cations
are positive
anions
are negitive
catabolic pathways
release energy and break down complex molecules into simpler compounds
anabolic pathways
consume energy, and build complex molecules from simpler ones
spontaneous process
happens without energy input. Is nether slow or fast
delta G
is negative for all spontaneous reactions
exergonic reaction
proceeds with a net release of free energy
endergonic reaction
absorbs free energy from the surroundings
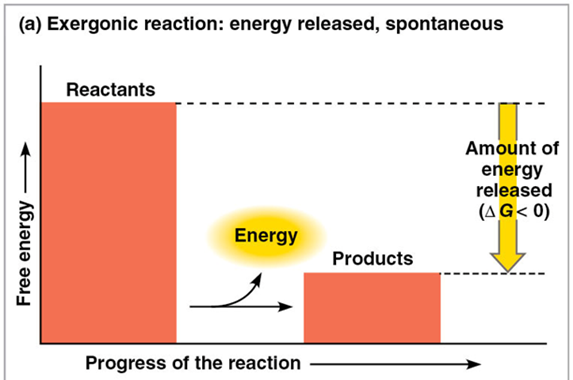
exergonic reaction
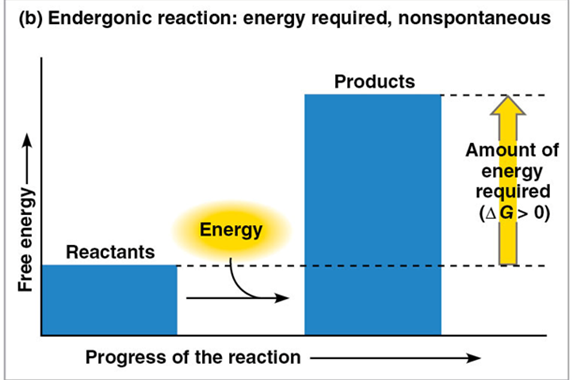
endergonic reaction
•Reactions in a , such as an isolated hydroelectric system, eventually and can then
closed system, reach equilibrium, do no work
oxidation
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
NAD+
is oxidized because loss of electrons
NADH
is reduced because the H gives electrons
The breakdown of organic molecules is
exergonic
Glycolysis
breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate